Learning from Octopuses: Cutting-Edge Developments and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Octopus and Soft Robot Sensor Technology
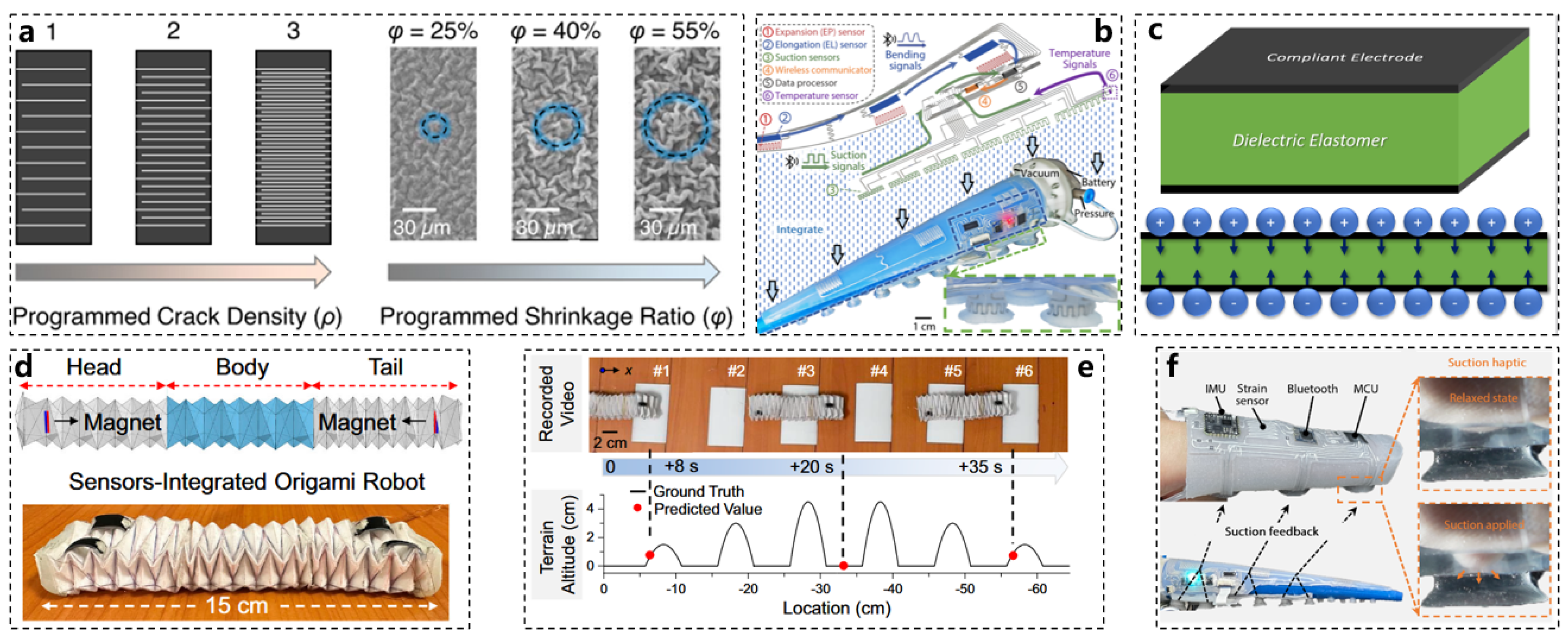
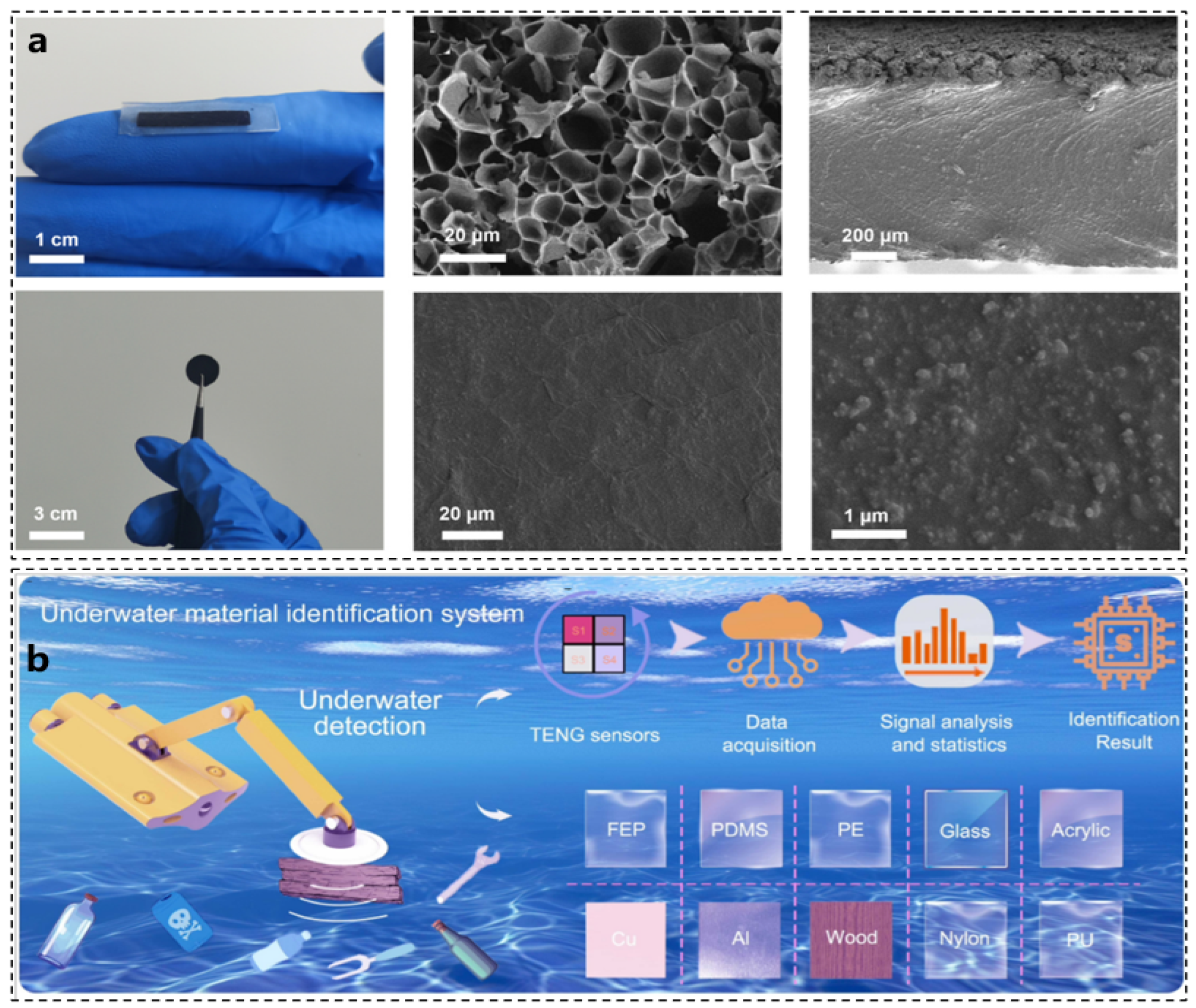
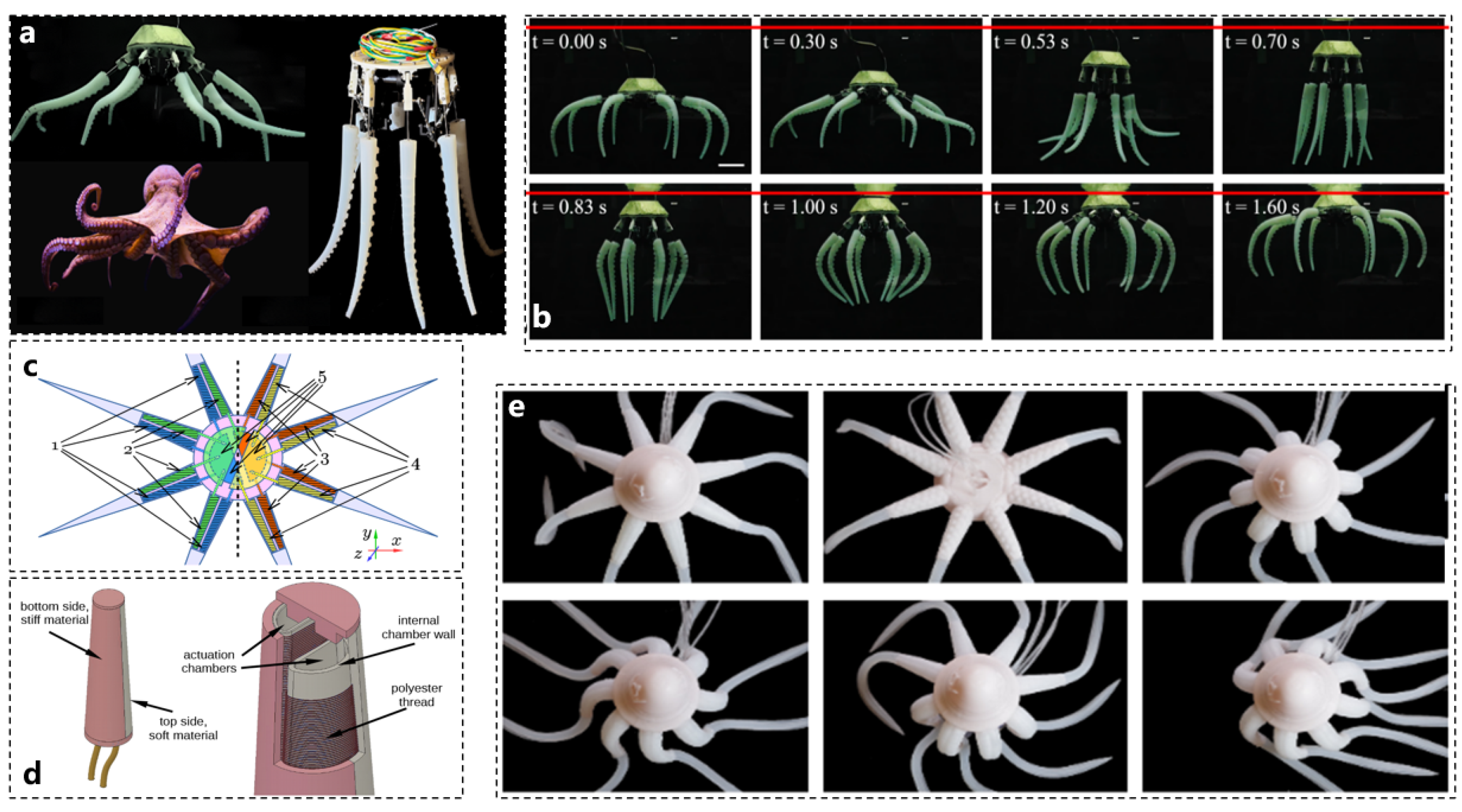
3. Octopus and Soft Robotic Actuators


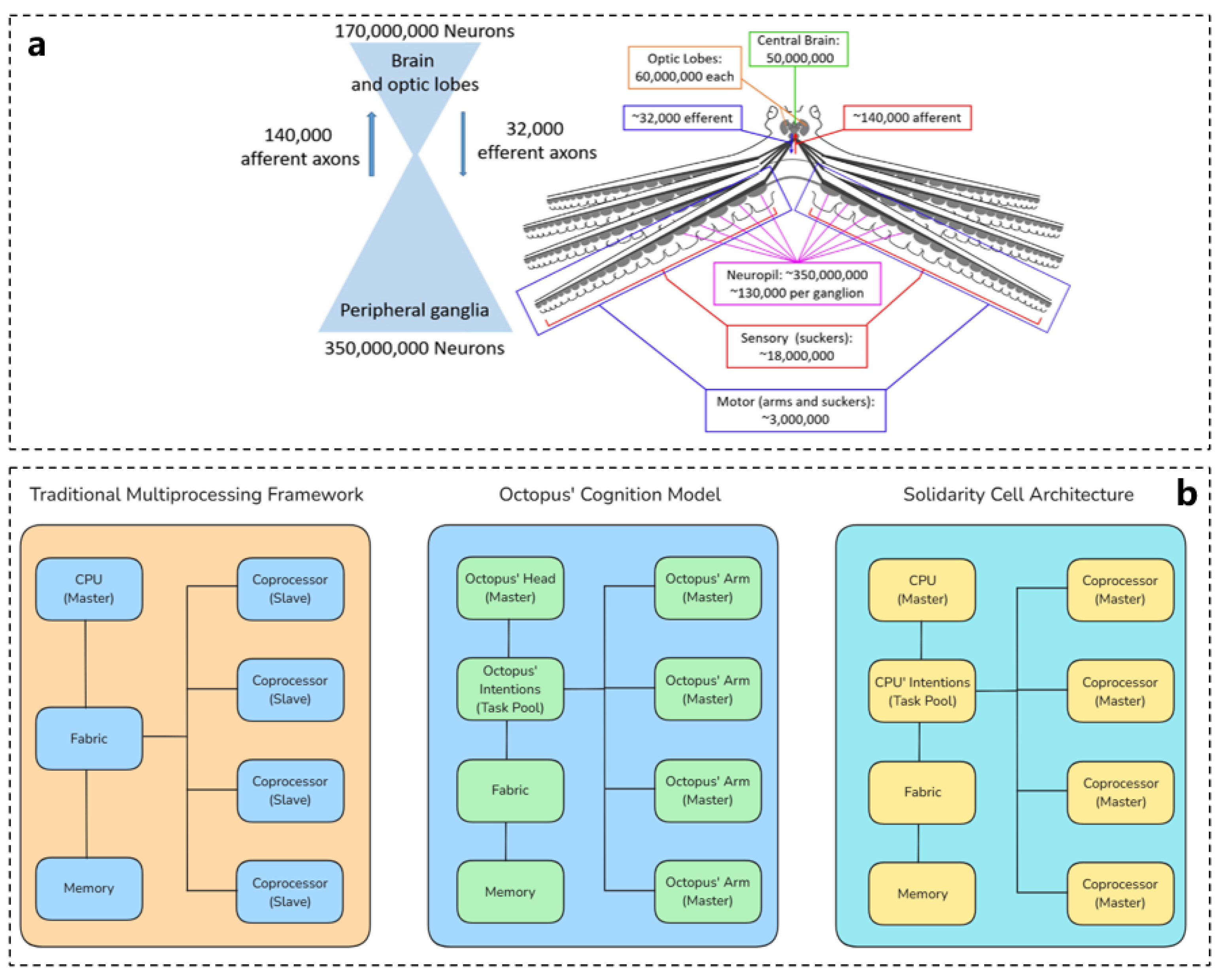
4. Octopus and Processor Architecture and Intelligent Optimization Algorithms
5. Octopus Inspires Other Aspects of Robotics
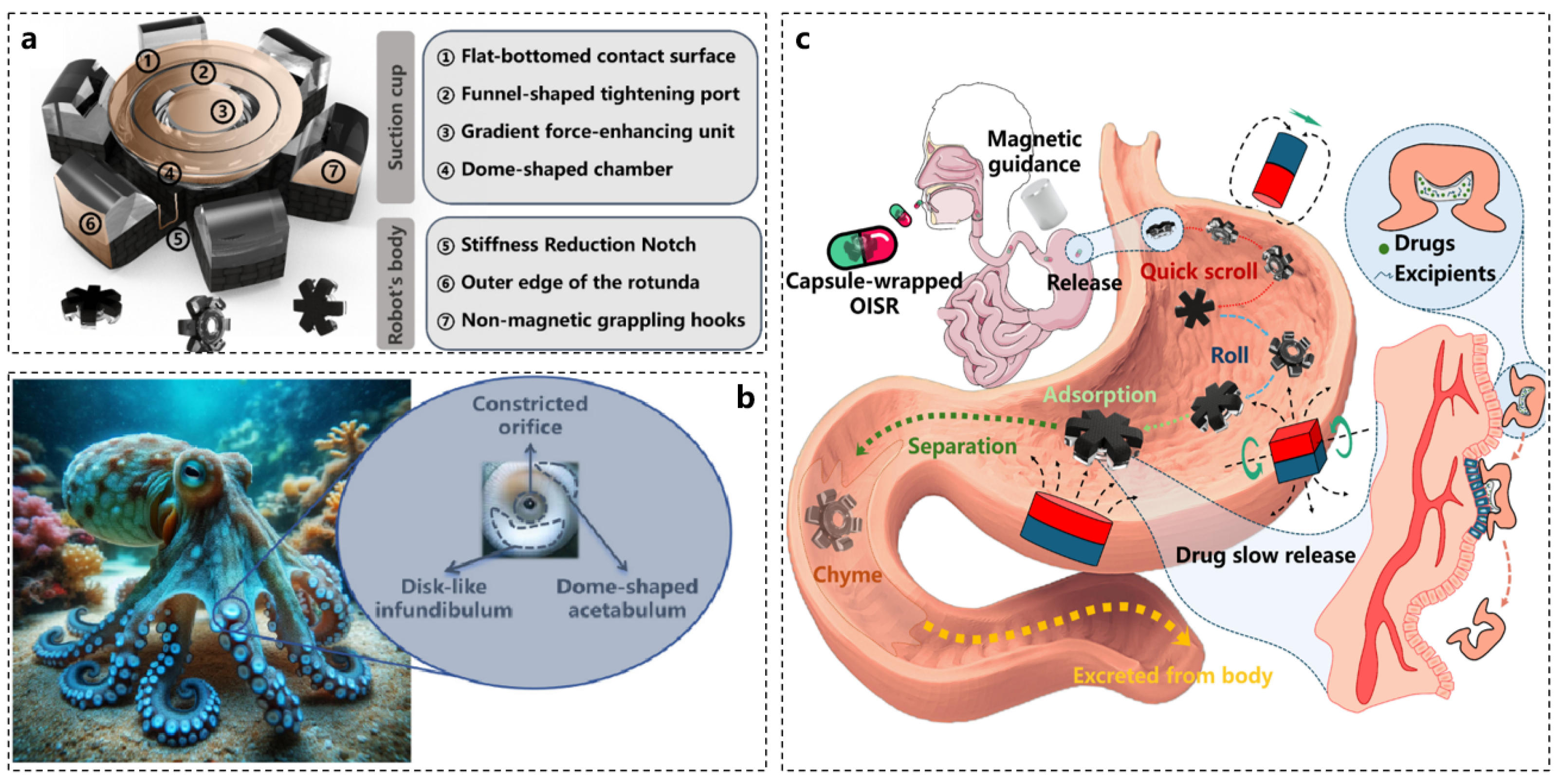

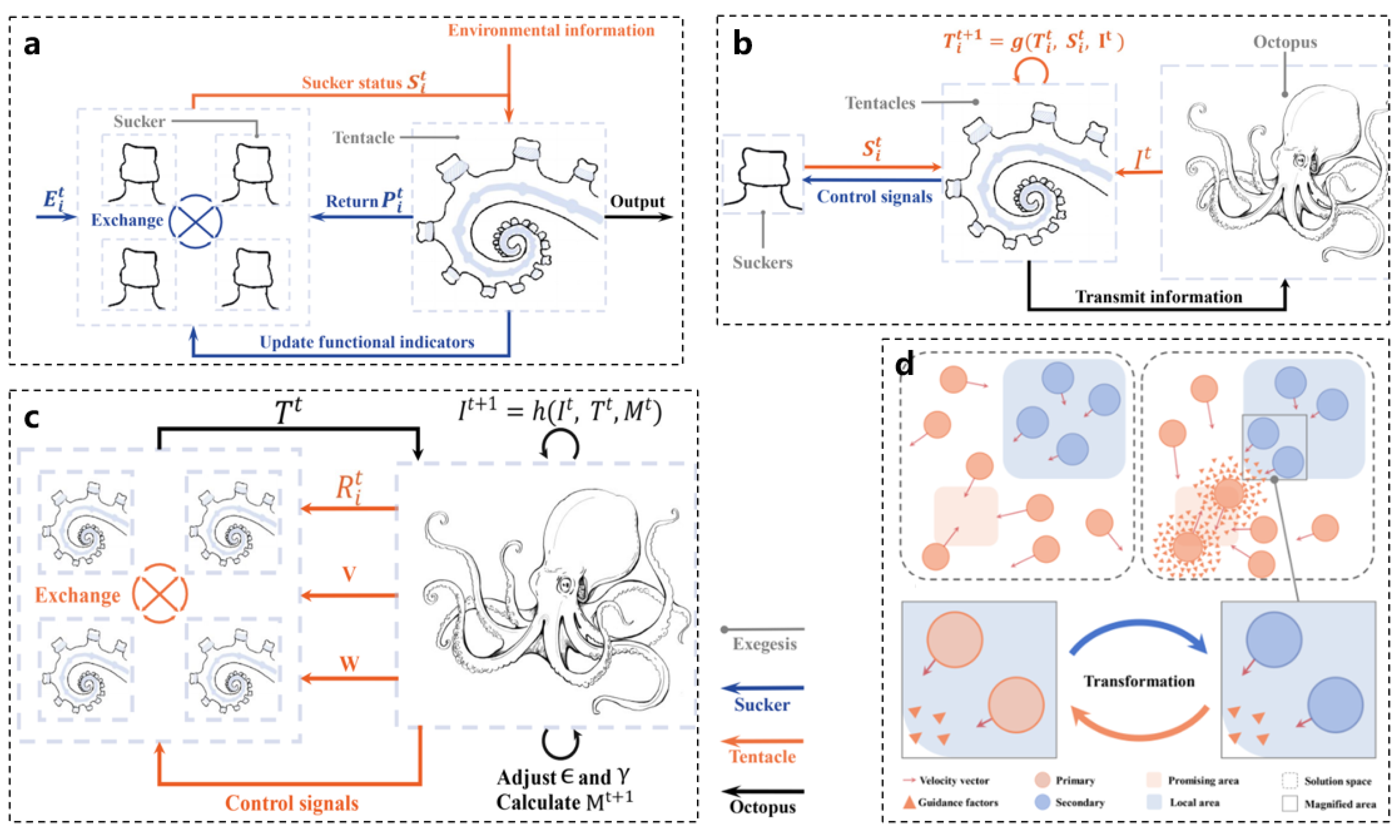
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Quan, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, D. Progress, Challenges, and Prospects of Soft Robotics for Space Applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, F.; Baumgartner, M.; Kaltenbrunner, M. Becoming sustainable, the new frontier in soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Kong, T.; Xu, J.; Qi, C. A Shift from Efficiency to Adaptability: Recent Progress in Biomimetic Interactive Soft Robotics in Wet Environments. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F.; He, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, B.; Niu, S.; Han, Z.; et al. Bioinspired hydrogel actuator for soft robotics: Opportunity and challenges. Nano Today 2023, 49, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Jiao, P.; Ren, H. Bioinspired soft robotics: How do we learn from creatures? IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 17, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, A.; Ul Islam, T.; Islam, M.R. A Review on Recent Trends of Bioinspired Soft Robotics: Actuators, Control Methods, Materials Selection, Sensors, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2025, 7, 2400414. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, W.; Zhong, G.; Cao, J.; Shi, Z.; Peng, B.; Jiang, L. Soft Robotic Manipulators: Designs, Actuation, Stiffness Tuning, and Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somero, G.N. Solutions: How adaptive changes in cellular fluids enable marine life to cope with abiotic stressors. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 389–413. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. A Numerical Study of Fin and Jet Propulsions Involving Fluid-Structure Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wong, T.W.; Shih, B.; Guo, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Wu, B.; et al. Bioinspired soft robots for deep-sea exploration. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.; Ahmad, S.; Liaf, A.F.; Karimi, M.; Ahmed, T.; Shawon, M. Oceanic Challenges to Technological Solutions: A Review of Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Path Technologies in Biomimicry, Control, Navigation and Sensing. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 46202–46231. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, J. Octopus consciousness: The role of perceptual richness. NeuroSci 2021, 2, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chao, X.; Hameed, I.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Jing, X. Biomimetic omnidirectional multi-tail underwater robot. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 173, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Tan, M.; Yu, J. A Survey on Reinforcement Learning Methods in Bionic Underwater Robots. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Xiao, H.; Ji, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Integrated and Intelligent Soft Robots. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 99862–99877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, G.; Carlotti, M.; Mazzolai, B. A perspective on cephalopods mimicry and bioinspired technologies toward proprioceptive autonomous soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cong, Q.; Chen, T.; Liu, C. Advanced Bionic Attachment Equipment Inspired by the Attachment Performance of Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tan, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W. Review on Research Progress of Hydraulic Powered Soft Actuators. Energies 2022, 15, 9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoli, A.; Chapelle, F.; Corrales-Ramon, J.A.; Mezouar, Y.; Lapusta, Y. Review of soft fluidic actuators: Classification and materials modeling analysis. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 31, 013001. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, W.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X.; Guo, J. Pneumatic Soft Robots: Challenges and Benefits. Actuators 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, K.; Han, L.; Guan, S. Modeling and Control of Robotic Manipulators Based on Artificial Neural Networks: A Review. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2023, 47, 1307–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Deng, J.; He, R. Octopus Inspired Optimization Algorithm: Multi-Level Structures and Parallel Computing Strategies. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.07968. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lim, K.M.; Yang, L.; Wang, N.; Peng, L. Research on control strategy of pneumatic soft bionic robot based on improved CPG. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmdas, A.; Patil, A.Y.; Baig, A.; Hosmani, O.Z.; Mathad, S.N.; Patil, M.B.; Kumar, R.; Kotturshettar, B.B.; Fattah, I.M.R. An Experimental and Simulation Study of the Active Camber Morphing Concept on Airfoils Using Bio-Inspired Structures. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Rab, S.; Suman, R. Significance of sensors for industry 4.0: Roles, capabilities, and applications. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, C.; Su, J.; Tan, J.M.R.; He, K.; Chen, X.; Magdassi, S. Sensing in soft robotics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15277–15307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ding, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Swaminathan, R.; Ng, S.W.L.; Pan, X.; Ho, G.W. Computational design of ultra-robust strain sensors for soft robot perception and autonomy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. A review on robotic fish enabled by ionic polymer–metal composite artificial muscles. Robot. Biomim. 2017, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, Z. Integrated Actuation and Sensing: Toward Intelligent Soft Robots. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2025, 6, 0105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nižetić, S.; Ong, H.C.; Tarelko, W.; Pham, V.V.; Le, T.H.; Chau, M.Q.; Nguyen, X.P. A review on application of artificial neural network (ANN) for performance and emission characteristics of diesel engine fueled with biodiesel-based fuels. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurani, A.; Doshi, P.; Vakharia, A.; Shah, M. A Comprehensive Comparative Study of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Support Vector Machines (SVM) on Stock Forecasting. Ann. Data Sci. 2023, 10, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Mishra, D.B.; Goldschmidtboeing, F.; Woias, P. Soft octopus-inspired suction cups using dielectric elastomer actuators with sensing capabilities. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2024, 19, 036009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Santina, C.; Duriez, C.; Rus, D. Model-based control of soft robots: A survey of the state of the art and open challenges. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2023, 43, 30–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mengaldo, G.; Renda, F.; Brunton, S.L.; Bächer, M.; Calisti, M.; Duriez, C.; Chirikjian, G.S.; Laschi, C. A concise guide to modelling the physics of embodied intelligence in soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2022, 4, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Renda, F.; Le Gall, A.; Mocellin, L.; Bernabei, M.; Dangel, T.; Ciuti, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Stefanini, C. Data-Driven Methods Applied to Soft Robot Modeling and Control: A Review. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 2241–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, J.; Jeffs, A.; Spreitzenbarth, S. The Effect of Prey Size and Prey Density on Paralarval Feeding Success of the Common Sydney Octopus, Octopus tetricus. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2024, 4, e70028. [Google Scholar]
- Awa, N.; Dan, S.; Nagatsuka, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shimba, A.; Anaguchi, Y.; Kamei, Y.; Hamasaki, K. Ontogeny of predatory capacity and prey choice during early life of the holobenthic octopus Amphioctopus fangsiao (d’Orbigny, 1841): Switching prey-choice strategy. Mar. Biol. 2024, 171, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yuan, F.; Liu, J.; Tian, L.; Chen, B.; Fu, Z.; Mao, S.; Jin, T.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; et al. Octopus-inspired sensorized soft arm for environmental interaction. Sci. Robot. 2023, 8, eadh7852. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, G.; Fan, X.; Xiao, P.; Zhu, L. Biomimetic Octopus Suction Cup with Attachment Force Self-Sensing Capability for Cardiac Adhesion. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Afridi, W.H.; Wu, J.; Afridi, R.H.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Xie, G. Octopus-Inspired Underwater Soft Robotic Gripper with Crawling and Swimming Capabilities. Research 2024, 7, 0456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, Q.; Lv, Y.; Yang, L. Liquid-Amplified Electrostatically Driven Octopus Sucker-Inspired Suction Cup. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2025, 7, 2400279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Cheng, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, A. Bionic octopus-like flexible three-dimensional force sensor for meticulous handwriting recognition in human-computer interactions. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Liu, A.; Ye, X.; Wang, J.; Fu, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Review of intelligent detection and health assessment of underwater structures. Eng. Struct. 2024, 308, 117958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Mazinani, A.; Othman, N.Q.H.; Amjad, H. Towards the internet of underwater things: A comprehensive survey. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 735–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wen, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Chen, B. Octopus-inspired multichannel tactile sensor for enhanced underwater material identification. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ashok, A.; Nguyen, C.C.; Yamauchi, Y.; Do, T.N.; Phan, H. Integrated Sensors for Soft Medical Robotics. Small 2024, 20, e2308805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jin, T.; Lin, W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H.; Yue, T.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, C. Multimodal sensors enabled autonomous soft robotic system with self-adaptive manipulation. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 9980–9996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, J. A Multi-Sensor Fusion Underwater Localization Method Based on Unscented Kalman Filter on Manifolds. Sensors 2024, 24, 6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; An, Y.; Zhao, H.; Miao, X.; Liu, R.; Fortino, G. Multi-sensor information fusion based on machine learning for real applications in human activity recognition: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 2022, 80, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusheef, A.S.; Shahbazi, M.; Hashemi, R. Deep Learning-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion for Process Monitoring: Application to Fused Deposition Modeling. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 10501–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Zhao, X. Magnetic soft materials and robots. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5317–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chortos, A. Control strategies for soft robot systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Waqas, M.; Shaikh, B.; Khan, U.; Soomro, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Ashraf, H.; Memon, F.H.; Choi, K.H. Multi-material Bio-inspired Soft Octopus Robot for Underwater Synchronous Swimming. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Clemente, A. Neural Control and Biomechanics of the Octopus Arm Muscular Hydrostat. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Genoa, Genova, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, R.K. EMG Analysis of Octopus Arms’ Muscles. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kier, W.; Stella, M. The arrangement and function of octopus arm musculature and connective tissue. J. Morphol. 2007, 268, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Domel, A.G.; An, N.; Green, C.; Gong, Z.; Wang, T.; Knubben, E.M.; Weaver, J.C.; Bertoldi, K.; Wen, L. Octopus Arm-Inspired Tapered Soft Actuators with Suckers for Improved Grasping. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.S.; Tawk, C.D.; Zolfagharian, A.; Pinskier, J.; Howard, D.; Young, T.; Lai, J.; Harrison, S.M.; Yong, Y.K.; Bodaghi, M.; et al. Soft pneumatic actuators: A review of design, fabrication, modeling, sensing, control and applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59442–59485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, E.; Tsakiris, D.P.; Sfakiotakis, M. An Octopus-Inspired Soft Pneumatic Robotic Arm. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flash, T.; Zullo, L. Biomechanics, motor control and dynamic models of the soft limbs of the octopus and other cephalopods. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226 (Suppl. S1), jeb245295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochner, B.; Zullo, L.; Shomrat, T.; Levy, G.; Nesher, N. Embodied mechanisms of motor control in the octopus. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R1119–R1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotak, P.; Maxson, S.; Weerakkody, T.; Cichella, V.; Lamuta, C. Octopus-Inspired Muscular Hydrostats Powered by Twisted and Coiled Artificial Muscles. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, J. Review of Recent Advances in the Drive Method of Hydraulic Control Valve. Processes 2023, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fras, J.; Noh, Y.; Macias, M.; Wurdemann, H.; Althoefer, K. Bio-Inspired Octopus Robot Based on Novel Soft Fluidic Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Sameoto, D. A review of electrically driven soft actuators for soft robotics. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albukhari, A.; Mescheder, U. Inchworm Motors and Beyond: A Review on Cooperative Electrostatic Actuator Systems. Actuators 2023, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, H.; Zhu, Z.H. Review of Machine Learning in Robotic Grasping Control in Space Application. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 220, 37–61. [Google Scholar]
- Febrer-Nafría, M.; Nasr, A.; Ezati, M.; Brown, P.; Font-Llagunes, J.M.; McPhee, J. Predictive multibody dynamic simulation of human neuromusculoskeletal systems: A review. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2023, 58, 299–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Li, Q.; Gu, F.; DU, X.; He, Y.; Deng, Y. Design, modeling, and control of morphing aircraft: A review. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xuan, S.; Ng, H.W.; Liufu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Laschi, C. Octopus-Swimming-Like Robot with Soft Asymmetric Arms. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.11764. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, D.; Li, X.; Yin, M.; Li, F. Dynamic modeling and fuzzy adaptive control strategy for space flexible robotic arm considering joint flexibility based on improved sliding mode controller. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 3520–3539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Cherubini, A.; Dune, C.; Navarro-Alarcon, D.; Alambeigi, F.; Berenson, D.; Ficuciello, F.; Harada, K.; Kober, J.; Li, X.; et al. Challenges and outlook in robotic manipulation of deformable objects. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2022, 29, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.M.; Kim, Y.; Shin, B.; Moghadam, M.H.; Mansour, N.A. Mansour Modeling and control analysis of an arc-shaped SMA actuator using PID, sliding and integral sliding mode controllers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 340, 113523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ni, L.; Wang, G.; Aphale, S.S.; Zhang, L. Q-Learning-Based Dumbo Octopus Algorithm for Parameter Tuning of Fractional-Order PID Controller for AVR Systems. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Modeling and motion control of an octopus-like flexible manipulator actuated by shape memory alloy wires. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 33, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, J.A. Ethics and invertebrates: The problem is us. Animals 2023, 13, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.H. Intelligence in Light of Perspectivalism: Lessons from Octopus Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence. J. Hum. Earth Future 2022, 3, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Carls-Diamante, S. Where is it like to be an octopus? Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 840022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivitilli, D.M. Reverse Engineering the Octopus Arm. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kuuspalu, A.; Cody, S.; Hale, M.E. Multiple nerve cords connect the arms of octopuses, providing alternative paths for inter-arm signaling. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 5415–5421.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Íñiguez, A. The Octopus as a Model for Artificial Intelligence-A Multi-Agent Robotic Case Study. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence: ICAART, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017; pp. 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivitilli, D.M.; Smith, J.R.; Gire, D.H. Lessons for robotics from the control architecture of the octopus. Front. Robot. AI 2022, 9, 862391. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Halder, U.; Gribkova, E.; Gillette, R.; Gazzola, M.; Mehta, P.G. Neural Models and Algorithms for Sensorimotor Control of an Octopus Arm. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01074. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, W.; Li, P. Neural Network-Based Shape Analysis and Control of Continuum Objects. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, S.; Gedikli, E.; Kahraman, H.T. A novel stochastic fractal search algorithm with fitness-distance balance for global numerical optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2021, 61, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Sangwan, O.P.; Abraham, A. Improved novel bat algorithm for test case prioritization and minimization. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 12393–12419. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, S.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Albeshri, A. Data Locality in High Performance Computing, Big Data, and Converged Systems: An Analysis of the Cutting Edge and a Future System Architecture. Electronics 2023, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Shi, F. A comparative survey of big data computing and HPC: From a parallel programming model to a cluster architecture. Int. J. Parallel Program. 2022, 50, 27–64. [Google Scholar]
- Andronie, M.; Lăzăroiu, G.; Karabolevski, O.L.; Ștefănescu, R.; Hurloiu, I.; Dijmărescu, A.; Dijmărescu, I. Remote Big Data Management Tools, Sensing and Computing Technologies, and Visual Perception and Environment Mapping Algorithms in the Internet of Robotic Things. Electronics 2023, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Radanovic, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Fang, Y.; Khoshelham, K.; Palaniswami, M.; Ngo, T. Real-time monitoring of construction sites: Sensors, methods, and applications. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, R.; Ouyang, Y.; Guan, Q.; Shen, Y.; Saiz, E.; Li, M.; Hou, X. Harnessing Biomimicry for Controlled Adhesion on Material Surfaces. Small 2024, 20, e2401859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wahab, M.A.; Will, G.; Karim, M.R.; Pan, T.; Gao, M.; Lai, D.; Lin, Y.; Miraz, M.H. Recent Advances in Stretchable and Wearable Capacitive Electrophysiological Sensors for Long-Term Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q.; Fan, X.; Yang, Z. Octopus-Inspired Soft Robot for Slow Drug Release. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21448:2022; Road Vehicles—Safety of the Intended Functionality, International Standard. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Sabelhaus, A.P.; Patterson, Z.J.; Wertz, A.T.; Majidi, C. Safe Supervisory Control of Soft Robot Actuators. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 561–572. [Google Scholar]
- Fattepur, G.; Patil, A.Y.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Hegde, C.; Siddhalingeshwar, I.G.; Kumar, R.; Khan, T.M.Y. Bio-inspired designs: Leveraging biological brilliance in mechanical engineering—An overview. 3 Biotech 2024, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V.; Cianchetti, M.; Dario, P. Design and Development of a Soft Actuator for a Robot Inspired by the Octopus Arm. In Experimental Robotics; Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Khatib, O., Kumar, V., Pappas, G.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, Z.; Meng, F.; Tan, B.; Hou, S. Octopus Predation-Inspired Underwater Robot Capable of Adsorption through Opening and Closing Claws. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.; Hellebrekers, T.; Majidi, C. Machine Learning for Soft Robotic Sensing and Control. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Teng, X.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, W.; Zou, B. Magnetically Driven Quadruped Soft Robot with Multimodal Motion for Targeted Drug Delivery. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Su, W.; Hong, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Y. Finite-Time Line-of-Sight Guidance-Based Path-Following Control for a Wire-Driven Robot Fish. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R.; Hou, N.; Afridi, W.H.; Afridi, R.H.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Xie, G. Glowing Sucker Octopus (Stauroteuthis syrtensis)-Inspired Soft Robotic Gripper for Underwater Self-Adaptive Grasping and Sensing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, G.; Chiandetti, C.; Edelman, D.B.; Imperadore, P.; Pieroni, E.M.; Fiorito, G. Cephalopod Behavior: From Neural Plasticity to Consciousness. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 787139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudithipudi, D.; Aguilar-Simon, M.; Babb, J.; Bazhenov, M.; Blackiston, D.; Bongard, J.; Brna, A.P.; Chakravarthi Raja, S.; Cheney, N.; Clune, J.; et al. Biological underpinnings for lifelong learning machines. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, G.; Zhu, K.; Liu, S.; Guo, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z. Materials, Devices, and Systems of On-Skin Electrodes for Electrophysiological Monitoring and Human–Machine Interfaces. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Yu, M.; Lei, M.; Jin, C.; Yin, R.; Zhao, W. An adaptive bionic sensor: Enhancing ankle joint tracking with high sensitivity and superior cushioning performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamilyan, O.; Kabin, I.; Dyka, Z.; Kuba, M.; Langendoerfer, P. Octopuses: Biological facts and technical solutions. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 7–11 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kalman | Real-time performance Efficient calculation Multidimensional data fusion | Dependent linear models Noise sensitivity | Soft tentacle pose estimation Dynamic environment position |
| CNN | Spatial feature extraction High-dimensional data processing End-to-end learning | Highly data-dependent Limited real-time performance | Object recognition (grasping) Tactile texture perception |
| RNN/LSTM | Temporal modeling capabilities Dynamic adaptation Multi-modal fusion | High training complexity Computational delay | Continuous motion planning Abnormal state detection |
| Bionic Objects | Design Features | Drive Mode | Application Scenarios | Technical Challenges and Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Octopus | (1) Highly flexible (2) Dynamic grasping (3) Stable attachment | Pneumatic/hydraulic drive SMA | Flexible gripping Underwater detection Medical endoscope | Nonlinear deformation control is complex |
| Elephant Trunk | (1) Flexible and rigid, can carry heavy objects (2) Layered muscle structure | Pneumatic/hydraulic drive | Industrial handling Rescue robots | Insufficient dynamic stability under high loads |
| Earthworm | (1) Segmented structure (2) Low energy consumption | Pneumatic Electroactive polymers | Underground exploration Pipeline inspection | Slower movement speed |
| Fish | (1) Streamlined body (2) Low noise | Motor Electroactive polymers | Marine ecological monitoring Underwater military reconnaissance | Limited steering flexibility |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, J.; Lei, Y.; Fang, J.; Qi, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Wu, Y. Learning from Octopuses: Cutting-Edge Developments and Future Directions. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040224
Duan J, Lei Y, Fang J, Qi Q, Zhan Z, Wu Y. Learning from Octopuses: Cutting-Edge Developments and Future Directions. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(4):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040224
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Jinjie, Yuning Lei, Jie Fang, Qi Qi, Zhiming Zhan, and Yuxiang Wu. 2025. "Learning from Octopuses: Cutting-Edge Developments and Future Directions" Biomimetics 10, no. 4: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040224
APA StyleDuan, J., Lei, Y., Fang, J., Qi, Q., Zhan, Z., & Wu, Y. (2025). Learning from Octopuses: Cutting-Edge Developments and Future Directions. Biomimetics, 10(4), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040224







