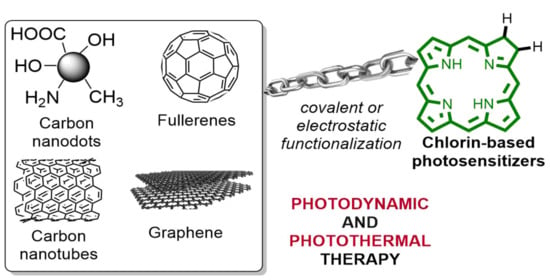
Learning from Nature: Bioinspired Chlorin-Based Photosensitizers Immobilized on Carbon Materials for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy
Abstract
Share and Cite
Dias, L.D.; Mfouo-Tynga, I.S. Learning from Nature: Bioinspired Chlorin-Based Photosensitizers Immobilized on Carbon Materials for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040053
Dias LD, Mfouo-Tynga IS. Learning from Nature: Bioinspired Chlorin-Based Photosensitizers Immobilized on Carbon Materials for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. Biomimetics. 2020; 5(4):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Lucas D., and Ivan S. Mfouo-Tynga. 2020. "Learning from Nature: Bioinspired Chlorin-Based Photosensitizers Immobilized on Carbon Materials for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy" Biomimetics 5, no. 4: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040053
APA StyleDias, L. D., & Mfouo-Tynga, I. S. (2020). Learning from Nature: Bioinspired Chlorin-Based Photosensitizers Immobilized on Carbon Materials for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. Biomimetics, 5(4), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040053