Bioinspired Self-Shaping Clay Composites for Sustainable Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Clay-Water Mixtures Preparation
2.3. Clay-Starch-Water Mixtures Preparation
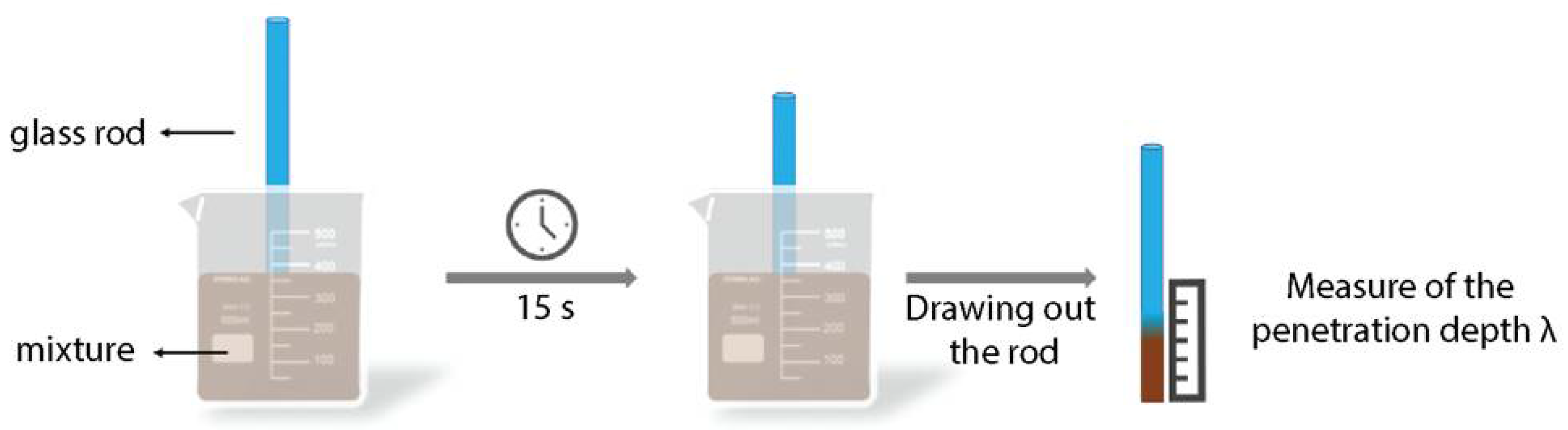
2.4. Measurement of the Penetration Depth λ
2.5. Measurement of the Shrinkage of the Matrix
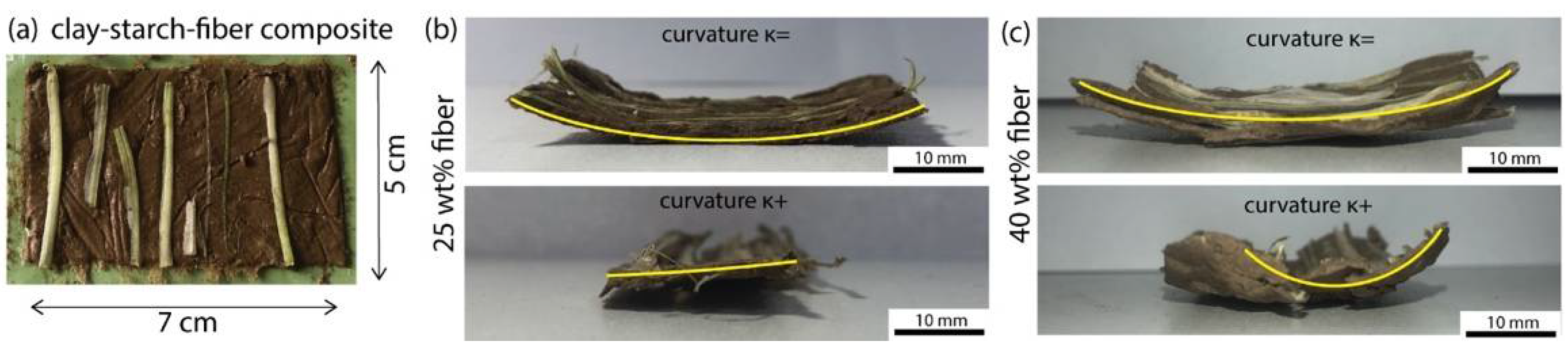
2.6. Fabrication of Clay-Starch-Fiber Anisotropic Composites
2.7. Characterization of the Change in Shape
3. Results
3.1. Approach
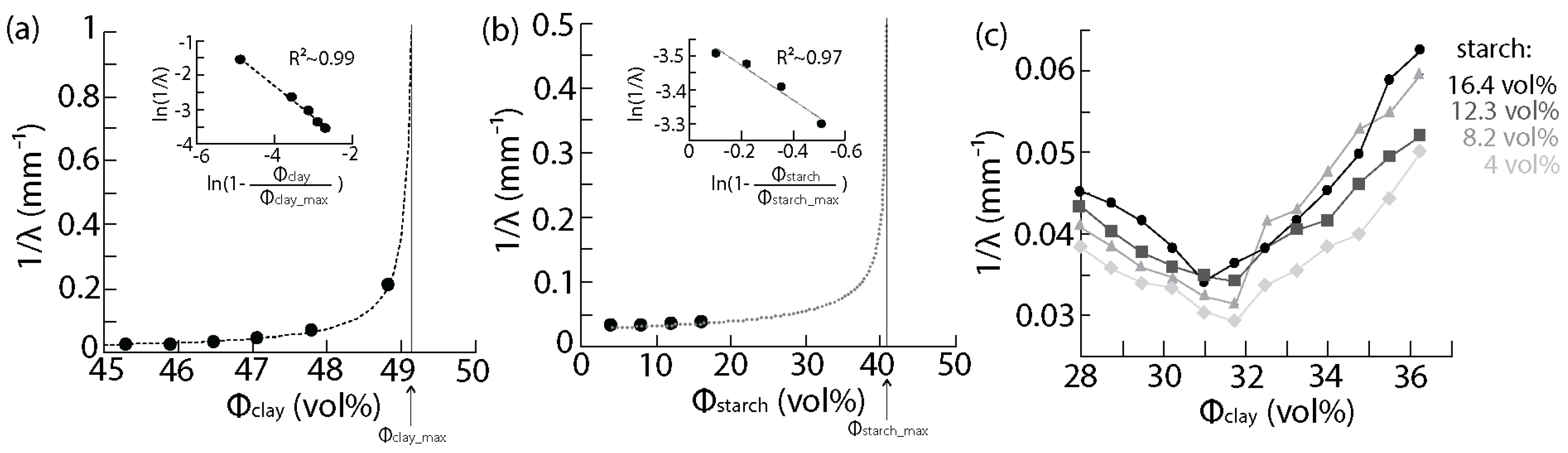
3.2. Processing of Homogeneous Clay-Based Matrices
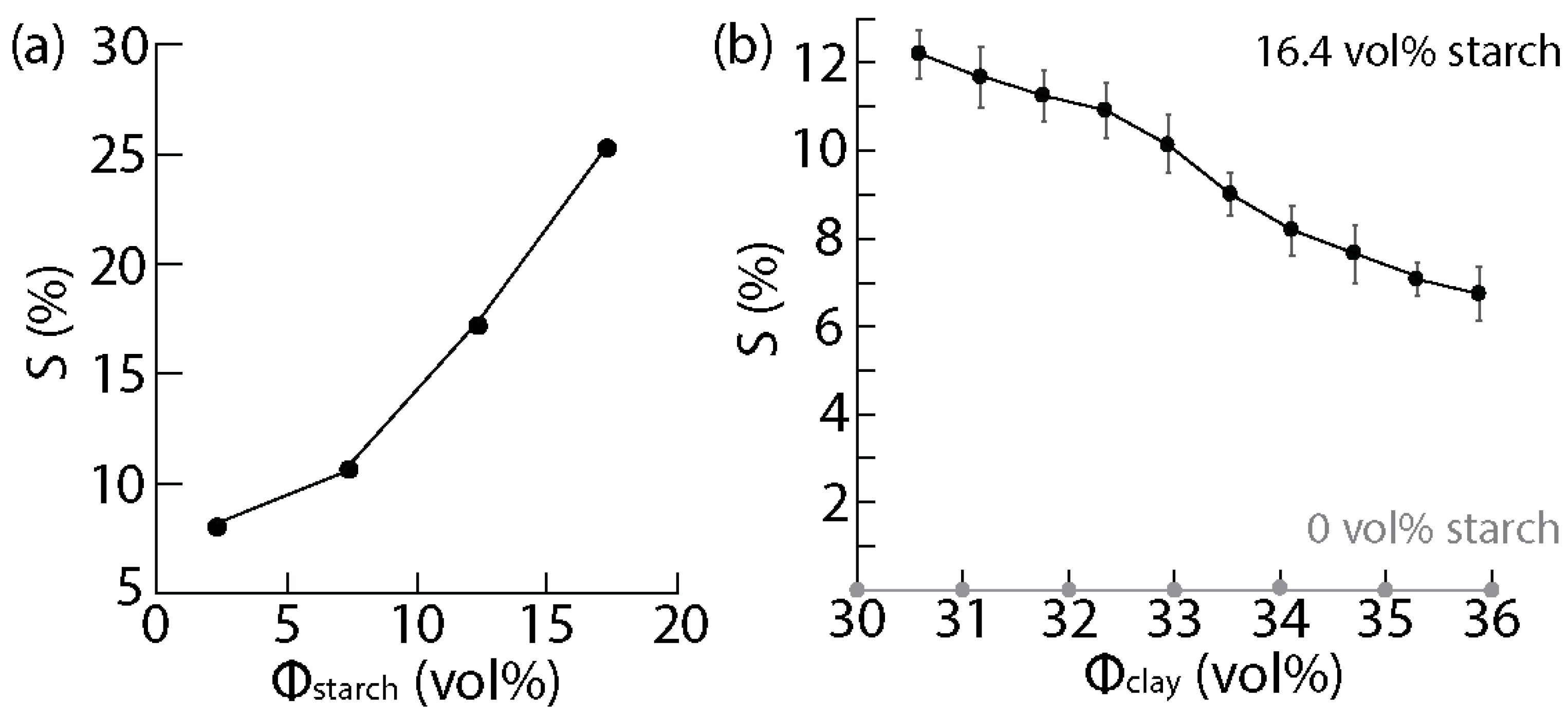
3.3. Shrinkage of the Clay-Based Matrices upon Drying
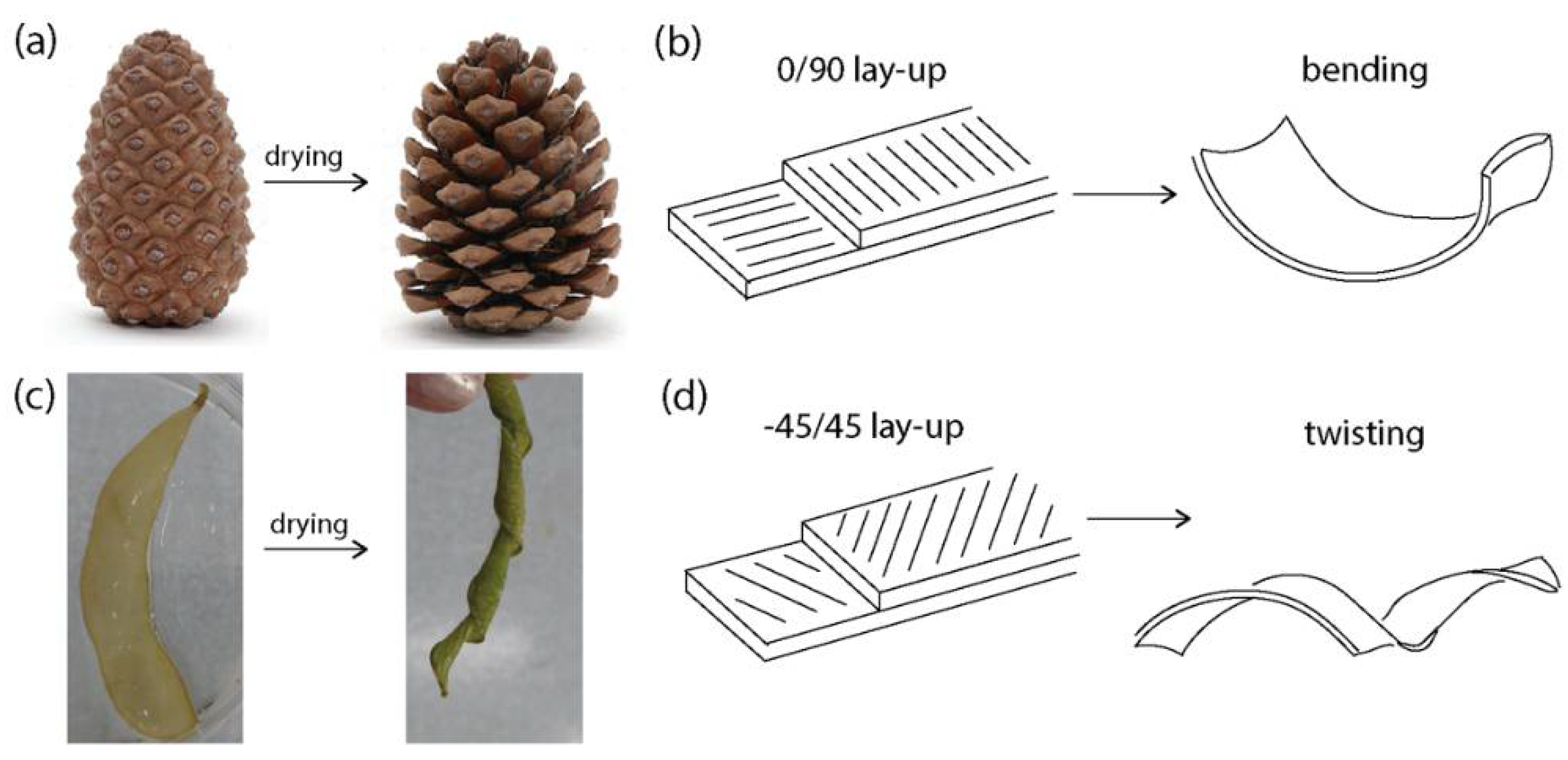
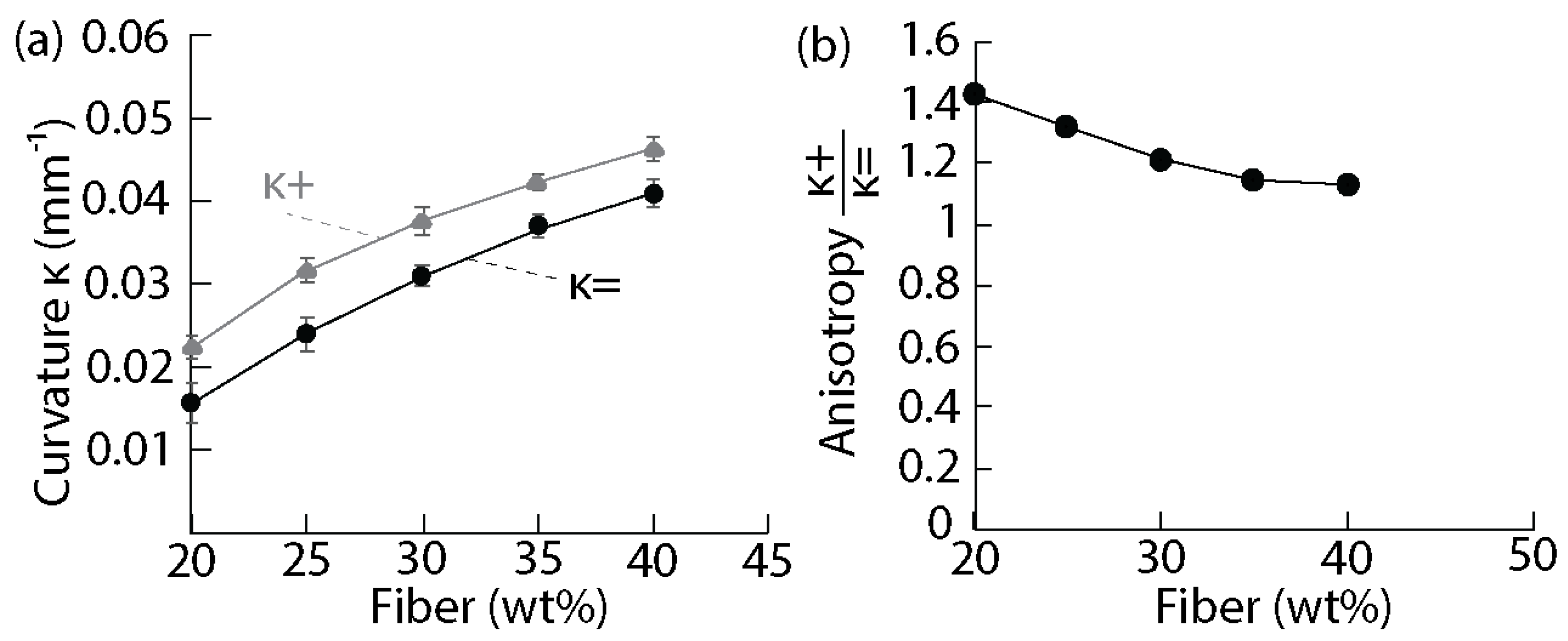
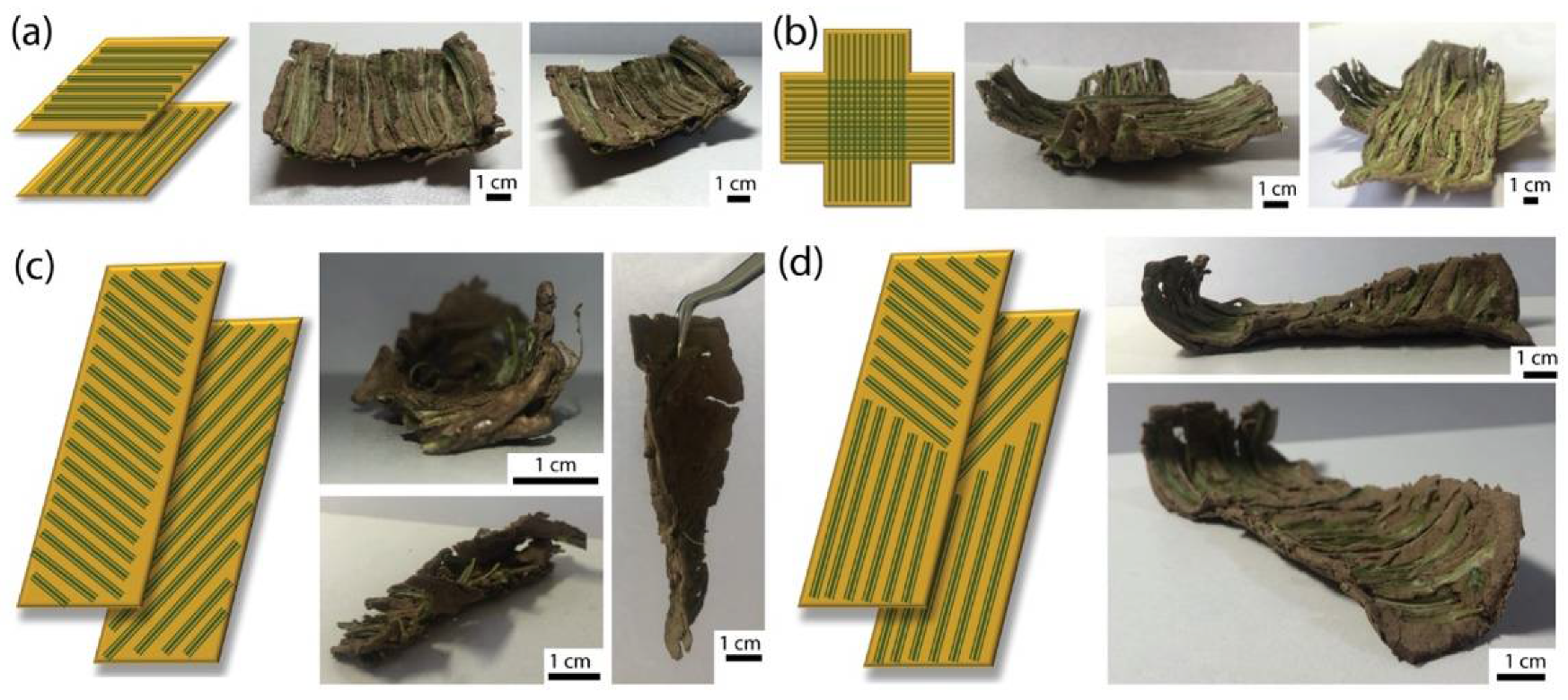
3.4. Building Anisotropy Using Fibers
3.5. Bending and Twisting Deformations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bargardi, F.L.; Le Ferrand, H.; Libanori, R.; Studart, A.R. Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydney Gladman, A.; Matsumoto, E.A.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Mahadevan, L.; Lewis, J.A. Biomimetic 4D printing. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Wood, D.; Kiesewetter, L.; Ozdemir, E.; Antorveza, K.; Menges, A. Programming material compliance and actuation: Hybrid additive fabrication of biocomposite structure for large-scale self-shaping. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 1, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ferrand, H.; Studart, A.R.; Arrieta, A.F. Filtered mechanosensing using snapping composites with embedded mechano-electrical transduction. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4752–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, K.; Seddon, A.; Trask, R.S. Morphing in nature and beyond: A review of natural and synthetic shape-changing materials and mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10663–10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Manen, T.; Janbaz, S.; Zadpoor, A.A. Programming the shape-shifting of flat soft matter. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulos, N.; Siakavellas, N.J. Programmable thermal emissivity structures based on bioinspired self-shape materials. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüggeberg, M.; Burgert, I. Bio-Inspired wooden actuators for large scale applications. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, B.; Song, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ren, L.; Zhou, X. 3D printing of structural gradient soft actuators by variation of bioinspired architectures. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6542–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liang, X.; Zhu, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L. Bilayer hydrogel actuators with tight interfacial adhesion fully constructed from natural polysaccharides. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Thielen, M.; Poppinga, S.; Tahouni, Y.; Wood, D.; Steinberg, T.; Menges, A.; Speck, T. Bio-inspired motion mechanisms: Computational design and material programming of self-adjusting 4D-printed wearable systems. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, C.; Wang, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Weijia Lu, W. Bioinspired multichannel nerve guidance conduit based on shape memory nanofibers for potential application in peripheral nerve repair. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12579–12595. [Google Scholar]
- Grönquist, P.; Wood, D.; Hassani, M.M.; Wittel, F.K.; Menges, A.; Rüggeberg, M. Analysis of hygroscopic self-shaping wood at large scale for curved mass timber structures. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grönquist, P.; Panchadcharam, P.; Wood, D.; Menges, A.; Rüggeberg, M.; Wittel, F.K. Computational analysis of hygromorphic self-shaping wood gridshell structures: Self-shaping wood gridshell structures. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 192210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, O.; Speck, D.; Horn, R.; Gantner, J.; Sedlbauer, K.P. Biomimetic bio-inspired biomorph sustainable? An attempt to classify and clarify biology-derived technical developments. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2017, 12, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z. Recent progress in 3D printing of bioinspired structures. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Fruleux, T.; Matsuzaki, R.; Chabaud, G.; Ueda, M.; Castro, M. 4D printing of continuous flax-fibre based shape-changing hygromorph biocomposites: Towards sustainable metamaterials. Mater. Des. 2021, 211, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Du, X. Bio-inspired sensing and actuating materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 6493–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Saleem, M.A.; Kazmi SM, S.; Munir, M.J. Production of sustainable clay bricks using waste fly ash: Mechanical and durability properties. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 14, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppinga, S.; Schenck, P.; Speck, O.; Speck, T.; Bruchmann, B.; Masselter, T. Self-actuated paper and wood models: Low-cost handcrafted biomimetic compliant systems for research and teaching. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppinga, S.; Metzger, A.; Speck, O.; Masselter, T.; Speck, T. Fallenbewegungen fleischfressender Pflanzen. Biol. Unserer Zeit 2013, 43, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganewatta, M.S.; Wang, Z.; Tang, C. Chemical syntheses of bioinspired and biomimetic polymers toward biobased materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studart, A.R.; Erb, R.M. Bioinspired materials that self-shape through programmed microstructures. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falin, P.; Horsanali, N.; Hansen, F.T.; Mäkelä, M. Practitioners’ experience in clay 3d printing: Metaphorical viewing for gaining embodied understanding. FormAkademisk 2021, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.L.; Pennings, R.M.; Edwards, L.; Franks, G.V. 3D printing of clay for decorative architectural applications: Effect of solids volume fraction on rheology and printability. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fgaier, F.; Lafhaj, Z.; Chapiseau, C.; Antczak, E. Effect of sorption capacity on thermo-mechanical properties of unfired clay bricks. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 6, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Marín, C.; Rivera-Gómez, C.; Petric, J. Clay-based composite stabilized with natural polymer and fibre. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, G.; Seshadri, S.A.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Nagaraja, K.C.A. Comprehensive review on natural fiber/nano-clay reinforced hybrid polymeric composites: Materials and technologies. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 3687–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabragh, A.R.; Bordbar, A.T.; Javadi, A.A. A study on the mechanical behavior of a fiber-clay composite with natural fiber. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2013, 31, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musielak, G.; Mierzwa, D. Permanent strains in clay-like material during drying. Dry. Technol. 2009, 27, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgiutti-Dauphiné, F.; Pauchard, L. Dynamic delamination of drying colloidal films: Warping and creep behavior. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, K.W. Plant-inspired adaptive structures and materials for morphing and actuation: A review. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2017, 12, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, B.; Sui, X.; Livanov, K.; Achrai, B.; Kalfon-Cohen, E.; Wiesel, E.; Daniel Wagner, H. Structural origins of morphing in plant tissues. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 033703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Requile, S.; Beaugrand, J. Natural fibres actuators for smart bio- inspired hygromorph biocomposites. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correa, D.; Poppinga, S.; Mylo, M.D.; Westermeier, A.S.; Bruchmann, B.; Menges, A.; Speck, T. 4D pine scale: Biomimetic 4D printed autonomous scale and flap structures capable of multi-phase movement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 4796292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthanveetil, S.; Liu, W.C.; Riley, K.S.; Arrieta, A.F.; Le Ferrand, H. Programmable multistability for 3D printed reinforced multifunctional composites with reversible shape change. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 217, 109097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, K.S.; Le Ferrand, H.; Arrieta, A.F. Modeling of snapping composite shells with magnetically aligned bio-inspired reinforcements. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opdenbosch, D.; Fritz-Popovski, G.; Wagermaier, W.; Paris, O.; Zollfrank, C. Moisture-driven ceramic bilayer actuators from a biotemplating approach. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5235–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, O.; Speck, T. Biomimetics and education in europe: Challenges, opportunities, and variety. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanieck, K.; Ritzinger, D.; Zollfrank, C.; Jacobs, S. Biomimetics: Teaching the tools of the trade. FEBS Open Bio. 2020, 10, 2250–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gutierrez, M.; Missana, T.; Mingarro, M.; Cormenzana, J. Diffusion coefficients and accessible porosity for HTO and chloride in compacted FEBEX bentonite. In Advances in Understanding Engineered Clay Barriers; Alonso, E.E., Ledesma, A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2005; pp. 515–523. [Google Scholar]
- Dengate, H.N.; Baruch, D.W.; Meredith, P. The Density of Wheat Starch Granules: A Tracer Dilution Procedure for Determining the Density of an Immiscible Dispersed Phase. Starch Stärke 1978, 30, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ferrand, H.; Bouville, F.; Niebel, T.P.; Studart, A.R. Magnetically assisted slip casting of bioinspired heterogeneous composites. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kicińska-Jakubowska, A.; Bogacz, E.; Zimniewska, M. Review of Natural Fibers. Part I-Vegetable Fibers. J. Nat. Fibers 2012, 9, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakri, B.; Eichhorn, S.J. Elastic coils: Deformation micromechanics of coir and celery fibres. Cellulose 2010, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridon, I.; Darie-Nita, R.N.; Hitruc, G.E.; Ludwiczak, J.; Cianga Spiridon, I.A.; Niculaua, M. New opportunities to valorize biomass wastes into green materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Llewellin, E.W.; Mader, H.M. The rheology of suspensions of solid particles. Proc. R. Soc. A 2010, 466, 1201–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmied, J.U.; Le Ferrand, H.; Ermanni, P.; Studart, A.R.; Arrieta, A.F. Programmable snapping composites with bio-inspired architecture. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 026012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.J.; Liu, D.M. Effect of processing variables on warping behaviours of injection-moulded ceramics. Ceram. Int. 1998, 24, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, I.; Cinar, K.; Ersoy, N.; Akkerman, R.; Hattel, J.H. A Review on the Mechanical Modeling of Composite Manufacturing Processes. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2017, 24, 365–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafa, N.Y.; Shaltout, A.A.; Abdel-Aal, M.S.; El-maghraby, A. Sintering mechanism of blast furnace slag-kaolin ceramics. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.L.; Dennis, R.G.; Mooney, D.J. The tensile properties of alginate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3187–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Su, Y.; Wang, D. Mechanical properties of PNIPAM based hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.; Ratri, M.C.; Kim, K.; Jung, Y.; Tae, G.; Shin, K. Formulation of Sugar/Hydrogel Inks for Rapid Thermal Response 4D Architectures with Sugar-derived Macropores. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chi, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yin, J. Shape-morphing materials and structures for energy-efficient building envelopes. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 22, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Jin, C.; Trase, I.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z. Helical structures mimicking chiral seedpod opening and tendril coiling. Sensors 2018, 18, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lendlein, A.; Gould, O.E.C. Reprogrammable recovery and actuation behaviour of shape-memory polymers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, X.J.; Peh, P.; Liao, S.; Sng, C.; Li, J. Controlled drug release from biodegradable thermoresponsive physical hydrogel nanofibers. J. Control. Release 2010, 143, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, T.; Farrington, J. What is sustainability? Sustainability 2010, 2, 3436–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manohar, D.E. Essential Alignment: Corporate Social Responsibility and Social Impact Assessment for Sustainable Development-an Empirical Study. J. Manag. 2019, 6, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İyigün, N.Ö. What could Entrepreneurship do for Sustainable Development? A Corporate Social Responsibility-Based Approach. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shubbar, A.A.; Sadique, M.; Kot, P.; Atherton, W. Future of clay-based construction materials—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumitha, G.; Fowsiya, J.; Mohana Roopan, S.; Thakur, V.K. Recent advances in starch–clay nanocomposites. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2018, 23, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.P.; Ralegaonkar, R.V.; Mandavgane, S.A. Development of sustainable construction material using industrial and agricultural solid waste: A review of waste-create bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 4037–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreola, F.; Borghi, A.; Pedrazzi, S.; Allesina, G.; Tartarini, P.; Lancellotti, I.; Barbieri, L. Spent coffee grounds in the production of lightweight clay ceramic aggregates in view of urban and agricultural sustainable development. Materials 2019, 12, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seco, A.; Urmeneta, P.; Prieto, E.; Marcelino, S.; García, B.; Miqueleiz, L. Estimated and real durability of unfired clay bricks: Determining factors and representativeness of the laboratory tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Le Ferrand, H. Bioinspired Self-Shaping Clay Composites for Sustainable Development. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010013
Zhang Y, Le Ferrand H. Bioinspired Self-Shaping Clay Composites for Sustainable Development. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuxiang, and Hortense Le Ferrand. 2022. "Bioinspired Self-Shaping Clay Composites for Sustainable Development" Biomimetics 7, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010013
APA StyleZhang, Y., & Le Ferrand, H. (2022). Bioinspired Self-Shaping Clay Composites for Sustainable Development. Biomimetics, 7(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010013





