Study on the Perception Mechanism of Utricles Based on Bionic Models
Abstract
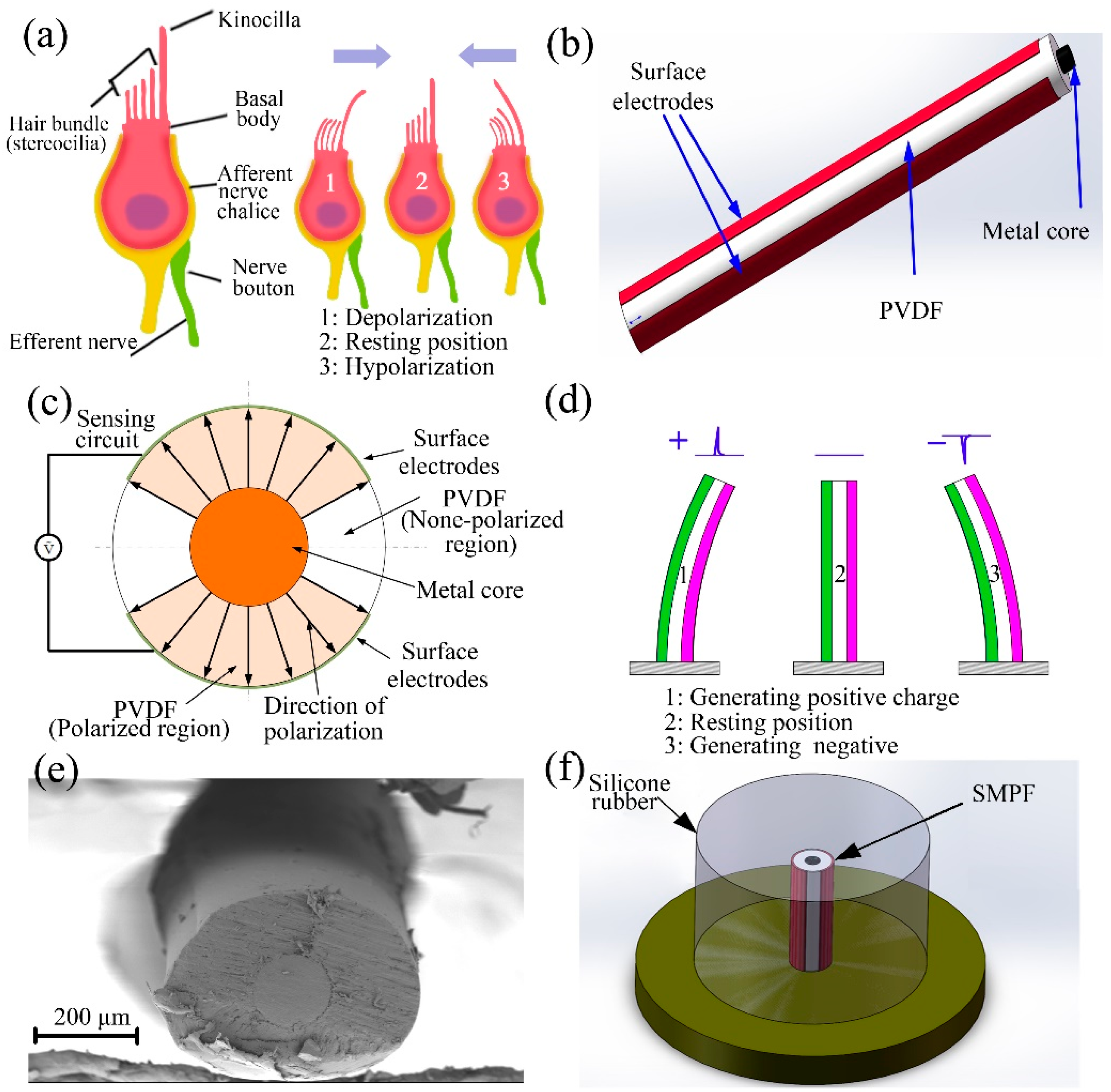
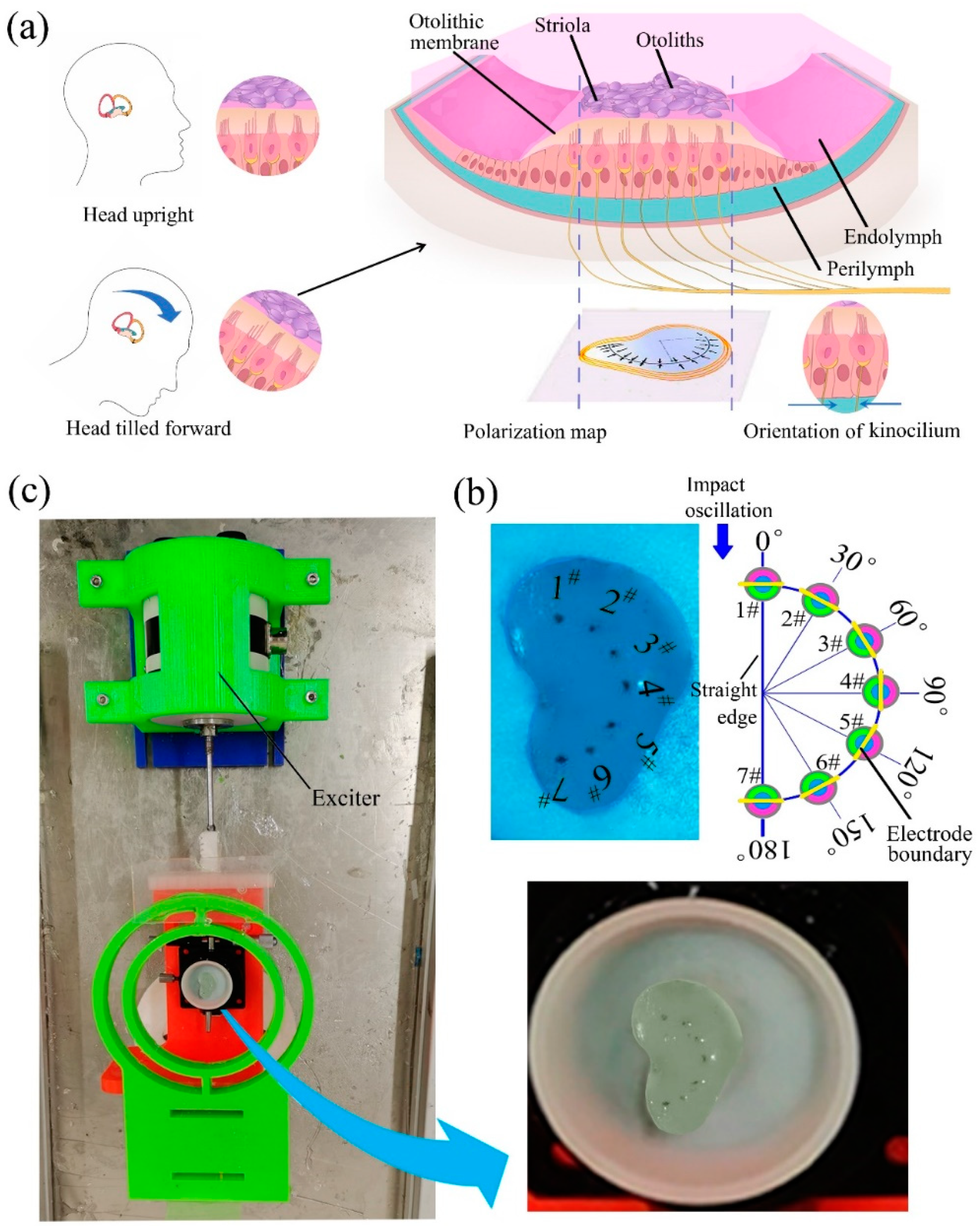
:1. Introduction
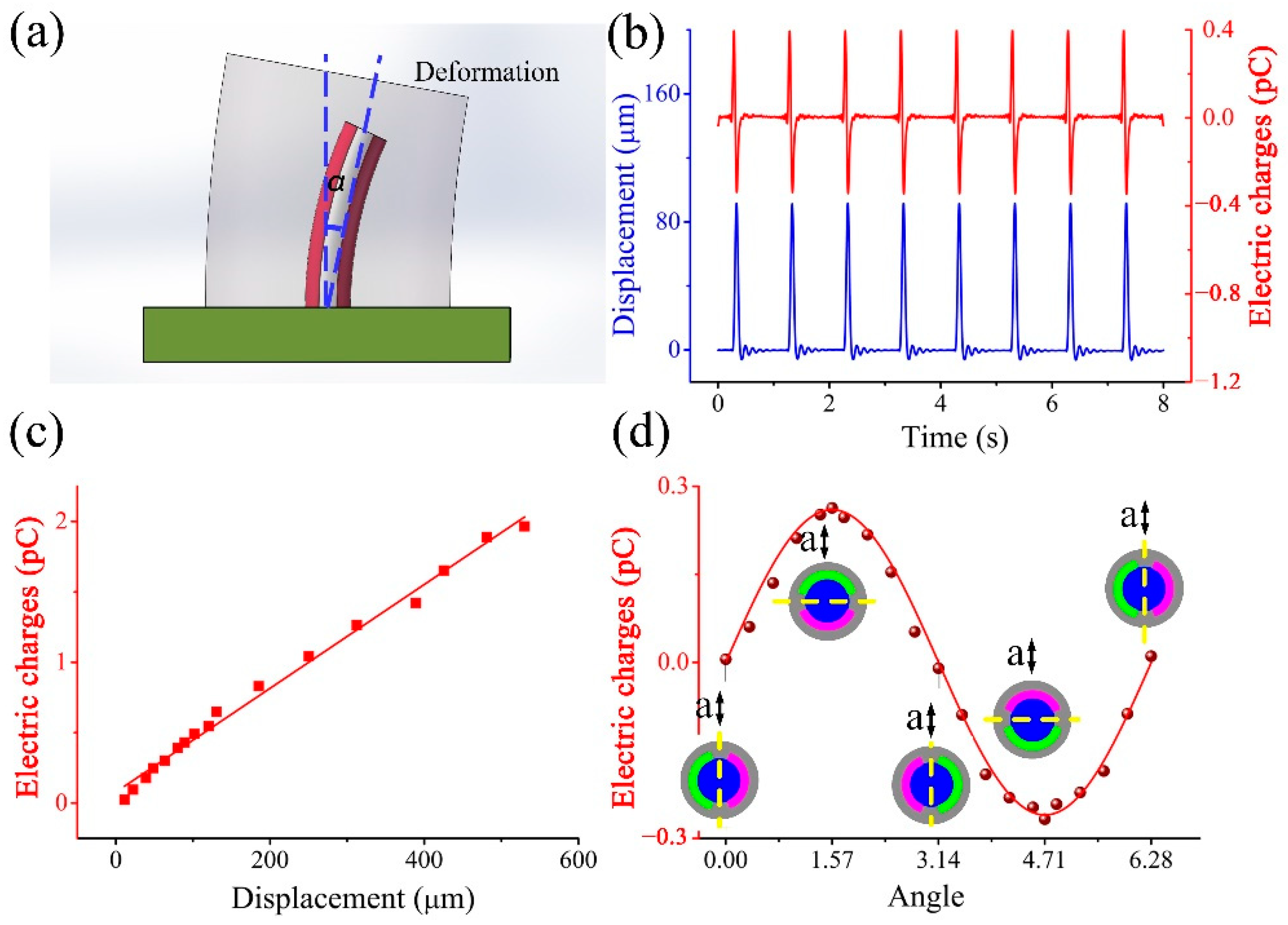
2. Fabrication of an SMPF Sensor
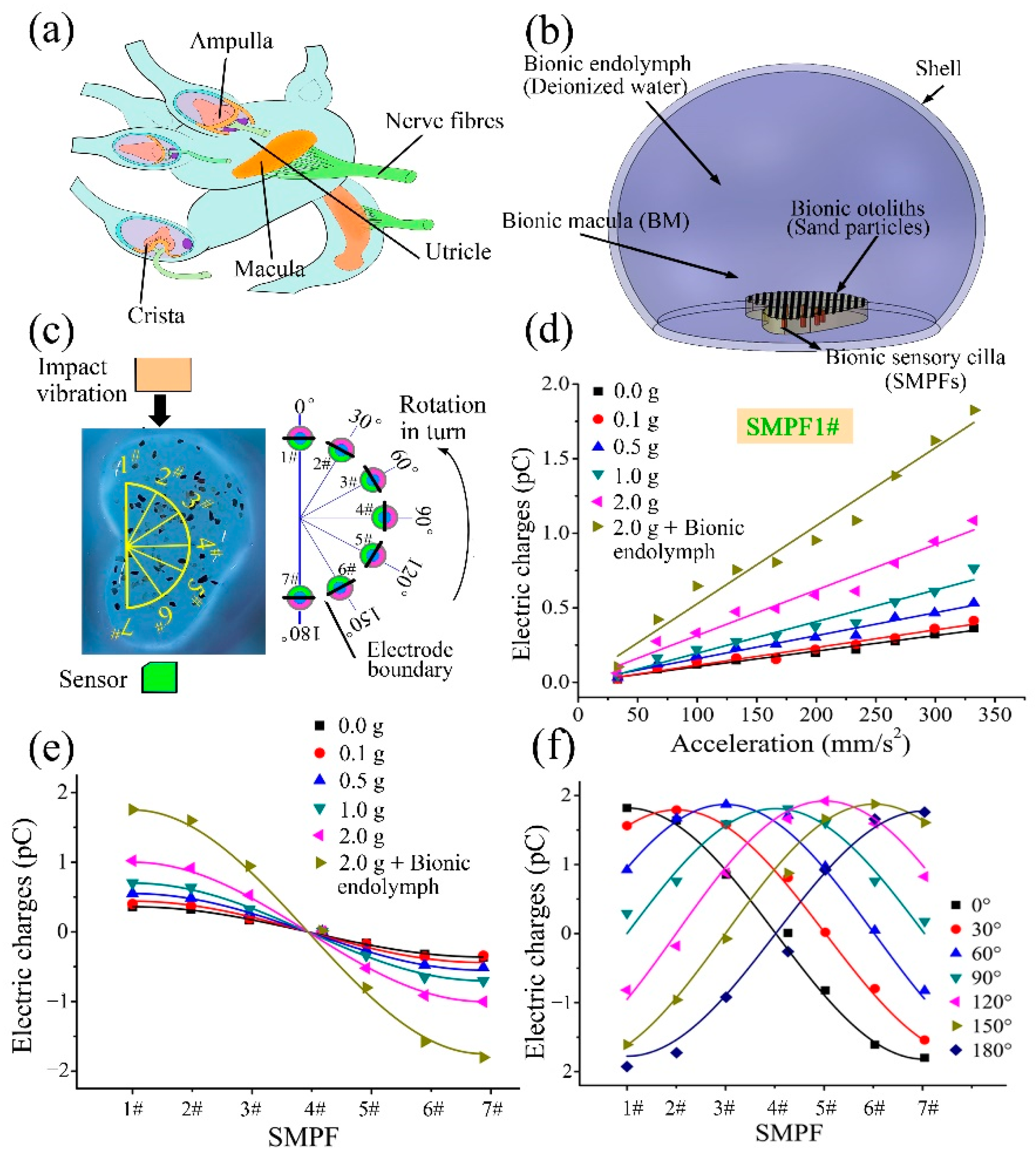
3. Fabrication of a BM and Its Sensing Ability
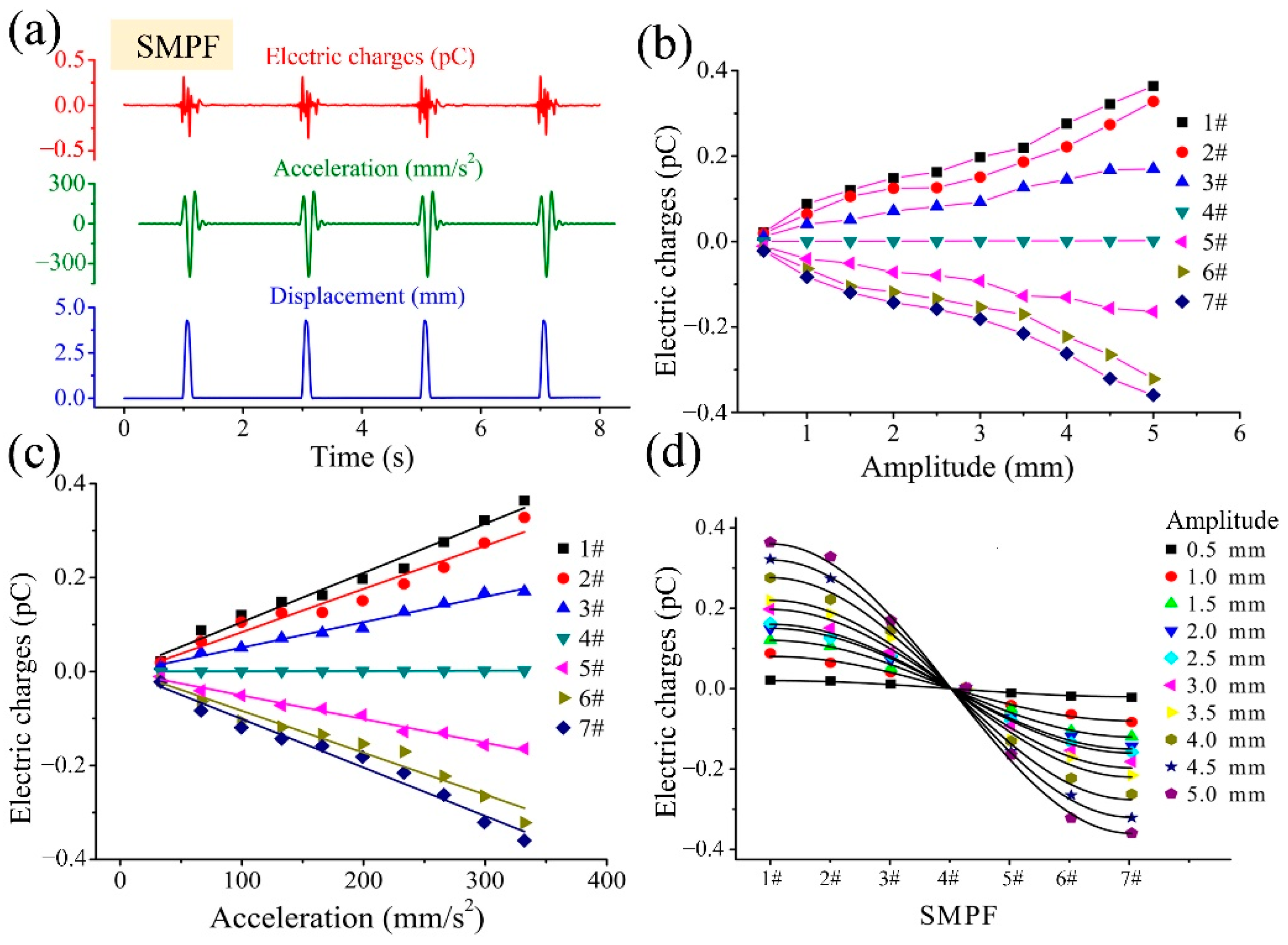
4. Development of a BU and Its Sensing Mechanism
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curthoys, I.S.; Wally Grant, J.; Pastras, C.J.; Brown, D.J.; Burgess, A.M.; Brichta, A.M.; Lim, R. A review of mechanical and synaptic processes in otolith transduction of sound and vibration for clinical VEMP testing. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 122, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pau, H.W.; Limberg, W. Fluid kinetics of endolymph during rotation. Acta Otolaryngol. 1990, 110, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highstein, S.M.; Holstein, G.R. The Anatomical and Physiological Framework for Vestibular Prostheses. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Miguel, A.R.; Zarowski, A.; Sluydts, M.; Ramos Macias, A.; Wuyts, F.L. The superiority of the otolith system. Audiol. Neurotol. 2020, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Santina, C.C.; Potyagaylo, V.; Migliaccio, A.A.; Minor, L.B.; Carey, J.P. Orientation of human semicircular canals measured by three-dimensional multiplanar CT reconstruction. JARO—J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2005, 6, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbitt, R.D. Directional coding of three-dimensional movements by the vestibular semicircular canals. Biol. Cybern. 1999, 80, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D. Flow Phenomena in the Inner Ear. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2019, 51, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Berg, R.; Ramos, A.; van Rompaey, V.; Bisdorff, A.; Perez-Fornos, A.; Rubinstein, J.T.; Phillips, J.O.; Strupp, M.; Della Santina, C.C.; Guinand, N. The vestibular implant: Opinion statement on implantation criteria for research. J. Vestib. Res. 2020, 30, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Grant, J.W.; Burgess, A.M.; Pastras, C.J.; Brown, D.J.; Manzari, L. Otolithic receptor mechanisms for vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials: A review. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeger, R.; Haslwanter, T. Otolith responses to dynamical stimuli: Results of a numerical investigation. Biol. Cybern. 2004, 90, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S. The Anatomical and Physiological Basis of Clinical Tests of Otolith Function. A Tribute to Yoshio Uchino. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalak, R.; Chien, S.; Mates, R.E. Handbook of Bioengineering. J. Biomech. Eng. 1987, 109, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, J.W.; Cotton, J.R. A model for otolith dynamic response with a viscoelastic gel layer. J. Vestib. Res. 1990, 1, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, J.M.; Cesar, F. The Vestibular System. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 16170–16176. [Google Scholar]
- Momani, A.; Cardullo, F. A review of the recent literature on the mathematical modeling of the vestibular system. In Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2018; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.M.; Mezey, L.E.; Manzari, L.; Macdougall, H.G.; McGarvie, L.A.; Curthoys, I.S. Effect of stimulus rise-time on the ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potential to bone-conducted vibration. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, W.; Curthoys, I. Otoliths—Accelerometer and seismometer; Implications in Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP). Hear. Res. 2017, 353, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrachuk, A.V. Modeling of mechanical stimulation of hair cells in otolithic organs. Adv. Sp. Res. 2006, 38, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S. Concepts and physiological aspects of the otolith organ in relation to electrical stimulation. Audiol. Neurotol. 2020, 25, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Merfeld, D.M. Prototype Neural Semicircular Canal Prosthesis using Patterned Electrical Stimulation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 28, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Nienhaus, A.; Zamaro, E.; Kalla, R.; Mantokoudis, G.; Strupp, M. Determinants for a successful sémont maneuver: An in vitro study with a semicircular canal model. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, W.; Merfeld, D.M. System Design and Performance of a Unilateral Horizontal Semicircular Canal Prosthesis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Santina, C.C.; Migliaccio, A.A.; Patel, A.H. Electrical stimulation to restore vestibular function development of a 3-d vestibular prosthesis. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 17–18 January 2006; pp. 7380–7385. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, B.; Fridman, G.Y.; Dai, C.; Rahman, M.A.; Della Santina, C.C. Design and performance of a multichannel vestibular prosthesis that restores semicircular canal sensation in rhesus monkey. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obrist, D.; Hegemann, S.; Kronenberg, D.; Häuselmann, O.; Rösgen, T. In vitro model of a semicircular canal: Design and validation of the model and its use for the study of canalithiasis. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Liu, C. Bioinspired water-enhanced acceleration sensing using artificial haircell sensor. In Proceedings of the 2010 Solid-State, Actuator and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 6–10 June 2010; pp. 382–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, M.A.; Moshizi, S.A.; Razmjou, A.; Wu, S.; Warkiani, M.E.; Asadnia, M. Development of a Biomimetic Semicircular Canal With MEMS Sensors to Restore Balance. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 11675–11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolpour Moshizi, S.; Azadi, S.; Belford, A.; Razmjou, A.; Wu, S.; Han, Z.J.; Asadnia, M. Development of an Ultra-Sensitive and Flexible Piezoresistive Flow Sensor Using Vertical Graphene Nanosheets. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Hong, J.; Huang, H.; Hui, S. Design and fabrication of a metal core PVDF fiber for an air flow sensor. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S.; MacDougall, H.G.; Vidal, P.P.; de Waele, C. Sustained and transient vestibular systems: A physiological basis for interpreting vestibular function. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Buskirk, W.C.; Watts, R.G.; Liu, Y.K. The fluid mechanics of the semicircular canals. J. Fluid Mech. 1976, 78, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telban, R.J.; Cardullo, F. Motion Cueing Algorithm Development: Human-Centered Linear and Nonlinear Approaches. In NASA TechReport; 2005; CR-2005-213747. Available online: http://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20050180246.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Qin, Y.; He, C.; Bian, Y. Study on the Perception Mechanism of Utricles Based on Bionic Models. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010028
Jiang Y, Wang X, Lu S, Qin Y, He C, Bian Y. Study on the Perception Mechanism of Utricles Based on Bionic Models. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yani, Xianjin Wang, Shien Lu, Yongbin Qin, Can He, and Yixiang Bian. 2022. "Study on the Perception Mechanism of Utricles Based on Bionic Models" Biomimetics 7, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010028
APA StyleJiang, Y., Wang, X., Lu, S., Qin, Y., He, C., & Bian, Y. (2022). Study on the Perception Mechanism of Utricles Based on Bionic Models. Biomimetics, 7(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7010028





