Chair Size Design Based on User Height
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- How properly to link the functional dimensions of a chair with the human body’s sizes;
- How to deal with the lack of some data in the anthropometric database used.
2. Chair Dimensioning
3. Methodology: A Proposal for Linking the Functional Dimensions of a Chair to the Anthropometric Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. A Novel Finding of This Study
4.2. Study Limitations
- Children and adolescents under 20, who have specific ages’ body proportions;
- The results also do not apply to people whose body proportions significantly differ from the average due to other causes, e.g., due to genetic conditions, physical activity, specific lifestyle, or disability.
5. Summary and Concluding Remarks
- The database used to calculate the body proportions limits the calculation results presented in this article to people with standard body proportions characteristic of adults.
- These limitations can be effectively eliminated by using a more specialized database; for example, the anthropometric database of obese people whose body proportions differ. It is then possible to modify the proportionality coefficients given in Equations (1)–(7) and, as a result, obtain formulas for designing chairs for obese people.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISO 18458:2015; Biomimetics—Terminology, Concepts and Methodology. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Sydor, M.; Zabłocki, M. Wybrane problemy doboru i konfiguracji wózka inwalidzkiego z napędem ręcznym / Chosen problems of manual wheelchair selection and configuration. Fizjoterapia Pol. 2006, 2, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Openshaw, S.; Taylor, E. Ergonomics and Design: A Reference Guide; Allsteel Inc.: Muscatine, IA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gedliczka, A.; Pochopień, P. Atlas Miar Człowieka: Dane Do Projektowania i Oceny Ergonomicznej: Antropometria, Biomechanika, Przestrzeń Pracy, Wymiary Bezpieczeństwa/Atlas of Human Measures: Data for Ergonomic Design and Assessment: Anthropometry, Biomechanics, Work Space, Safety Dimensions; Centralny Instytut Ochrony Pracy: Warszawa, Poland, 2001; ISBN 978-83-88703-38-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, A.R.; Dreyfuss, H. (Eds.) The Measure of Man and Woman: Human Factors in Design; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-471-09955-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fryar, C.D.; Gu, Q.; Ogden, C.L. Anthropometric Reference Data for Children and Adults: United States, 2007–2010; Vital and Health Statistics, Series 11; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–48.
- Salvendy, G. (Ed.) Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-470-52838-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tillman, B.; Woodson, W.E. (Eds.) Human Factors and Ergonomics Design Handbook, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-07-170287-4. [Google Scholar]
- Seid, A.; Trieb, R.; Rissiek, A. Heiner Bubb Standards in Anthropometry. In Handbook of Standards and Guidelines in Human Factors and Ergonomics; Karwowski, W., Szopa, A., Marcelo Soares, Eds.; Human Factors and Ergonomics; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 229–269. ISBN 978-0-429-16924-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y. Applications and Research Trends of Digital Human Models in the Manufacturing Industry. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2019, 1, 558–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Miehling, J.; Wartzack, S. Challenges in Interaction Modelling with Digital Human Models—A Systematic Literature Review of Interaction Modelling Approaches. Ergonomics 2020, 63, 1442–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branowski, B.; Zabłocki, M.; Kurczewski, P.; Sydor, M. A Method for Modeling the Individual Convenient Zone of a Human. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, M.; Crannell, A. Viewpoints: Mathematical Perspective and Fractal Geometry in Art; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-691-12592-3. [Google Scholar]
- Massen, M. Figure Drawing in Proportion: Easy to Remember, Accurate Anatomy for Artists; North Light Books: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4403-3762-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hitka, M.; Sedmák, R.; Joščák, P.; Ližbetinová, L. Positive Secular Trend in Slovak Population Urges on Updates of Functional Dimensions of Furniture. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W. A Plea for Uniformity in the Delimitation of the Regions of the Abdomen. J. Anat Physiol 1892, 26, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EN 1729:2015; Furniture—Chairs and Tables for Educational Institutions—Part 1: Functional Dimensions. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- Goonetilleke, R.S.; Feizhou, S. A Methodology to Determine the Optimum Seat Depth. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2001, 27, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, S.L.; Jürgens, H.W.; Helbig, K. Designing A Chair: A Scientific Perspective. Indian Anthropol. 1984, 14, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Stoudt, H.W.; Damon, A.; McFarland, R.; Roberts, J. Weight, Height, and Selected Body Dimensions of Adults United States—1960–1962; National Center for Health Services Research and Development: Rockville, MD, USA, 1965.
- Floyd, W.F.; Roberts, D.F. Anatomical and Physiological Principles in Chair and Table Design. Ergonomics 1958, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitka, M.; Štarchoň, P.; Simanová, Ľ.; Čuta, M.; Sydor, M. Dimensional Solution of Wooden Chairs for the Adult Bariatric Population of Slovakia: Observational Study. Forests 2022, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/BIFMA X5.41-2021; Large Occupant Public and Lounge Seating. BIFMA: Grand Rapids, MI, USA, 2021.
- Åkerblom, B. Standing and Sitting Posture: With Special Reference to the Construction of Chairs; Nordiska Bokhandeln: Stockholm, Sweden, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, B.J.; Ortengren, R.; Nachemson, A.; Elfström, G. Lumbar Disc Pressure and Myoelectric Back Muscle Activity during Sitting. I. Studies on an Experimental Chair. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1974, 6, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helander, M.G.; Zhang, L. Field Studies of Comfort and Discomfort in Sitting. Ergonomics 1997, 40, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouvali, M.K.; Boudolos, K. Match between School Furniture Dimensions and Children’s Anthropometry. Appl. Ergon. 2006, 37, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci, H.I.; Arezes, P.M.; Molenbroek, J.F.M. Equations for Defining the Mismatch between Students and School Furniture: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2015, 48, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langová, N.; Blašková, S.; Gáborík, J.; Lizoňová, D.; Jurek, A. Mismatch Between the Anthropometric Parameters and Classroom Furniture in The Slovak Primary Schools. Acta Fac. Xylologiae Zvolen 2021, 63, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, E.; Pisent, C.; Sergi, G.; Grigoletto, F.; Enzi, G. ILSA Working Group Anthropometric Measurements in the Elderly: Age and Gender Differences. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 87, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowgill, L.W.; Eleazer, C.D.; Auerbach, B.M.; Temple, D.H.; Okazaki, K. Developmental Variation in Ecogeographic Body Proportions. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2012, 148, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, V.; Rajagopalan, A. Worldwide Variation in Human Growth and the World Health Organization Growth Standards: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e003735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wells, J.C.K. Sexual Dimorphism of Body Composition. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoudt, H.W.; Damon, A.; McFarland, R.A.; Roberts, J. Skinfolds, Body Girths, Biacromial Diameter, and Selected Anthropometric Indices of Adults. United States, 1960–1962; Vital and Health Statistics, Series 11; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1970; pp. 1–63.
- Abraham, S.; Johnson, C.L.; Najjar, M.F. Weight by Height and Age for Adults, 18-74 Years, United States, 1971–1974; Vital and Health Statistics, Series 11; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1979; pp. 1–63.
- Johnson, C.L. Basic Data on Anthropometric Measurements and Angular Measurements of the Hip and Knee Joints for Selected Age Groups 1–74 Years of Age, United States, 1971–1975; Vital and Health Statistics; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1981.
- Najjar, M.F.; Rowland, M. 1945-Anthropometric Reference Data and Prevalence of Overweight, United States, 1976–1980; Vital and Health Statistics; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1987.
- Panero, J.; Zelinik, M. Human Dimension & Interior Space: A Source Book of Design Reference Standards; Whitney Library of Design, an imprint of Watson-Guptill Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1979; ISBN 978-0-8230-7271-2. [Google Scholar]

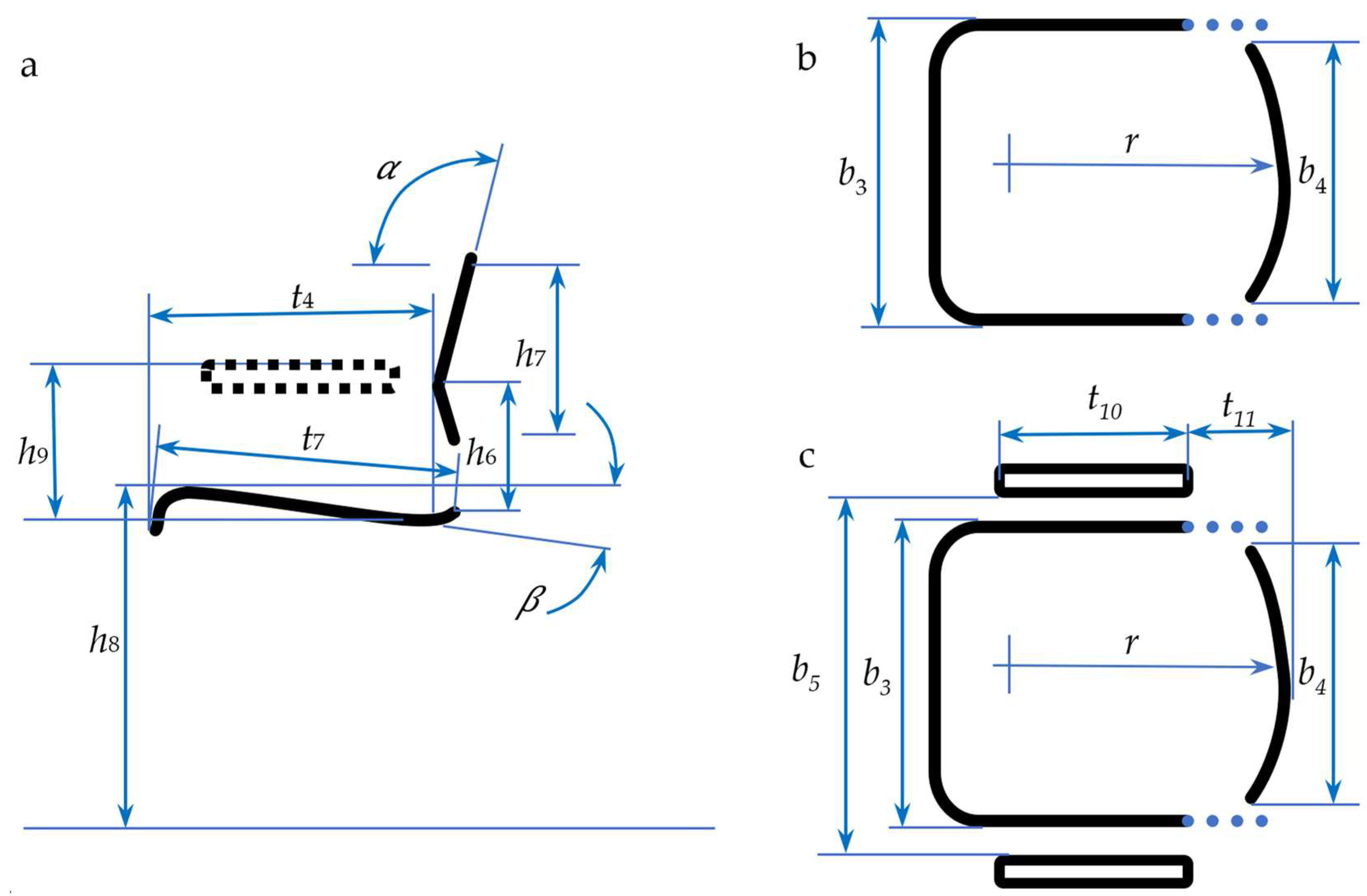










| Measurements of a Human | Measurements of a Chair (According to Figure 1) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| A—Buttock-popliteal length | t7, t4 (indirectly) | t7 should be less than A |
| B—Popliteal height | h8 | h8 should be equal to B |
| C—Bi-trochanteric breath or trochanteric width (hip breath) | b3 | b3 should be greater than C |
| D—Elbow-to-elbow breath | b5 | b5 should be equal to D |
| E—Elbow rest height | h9 | h9 should be equal to E |
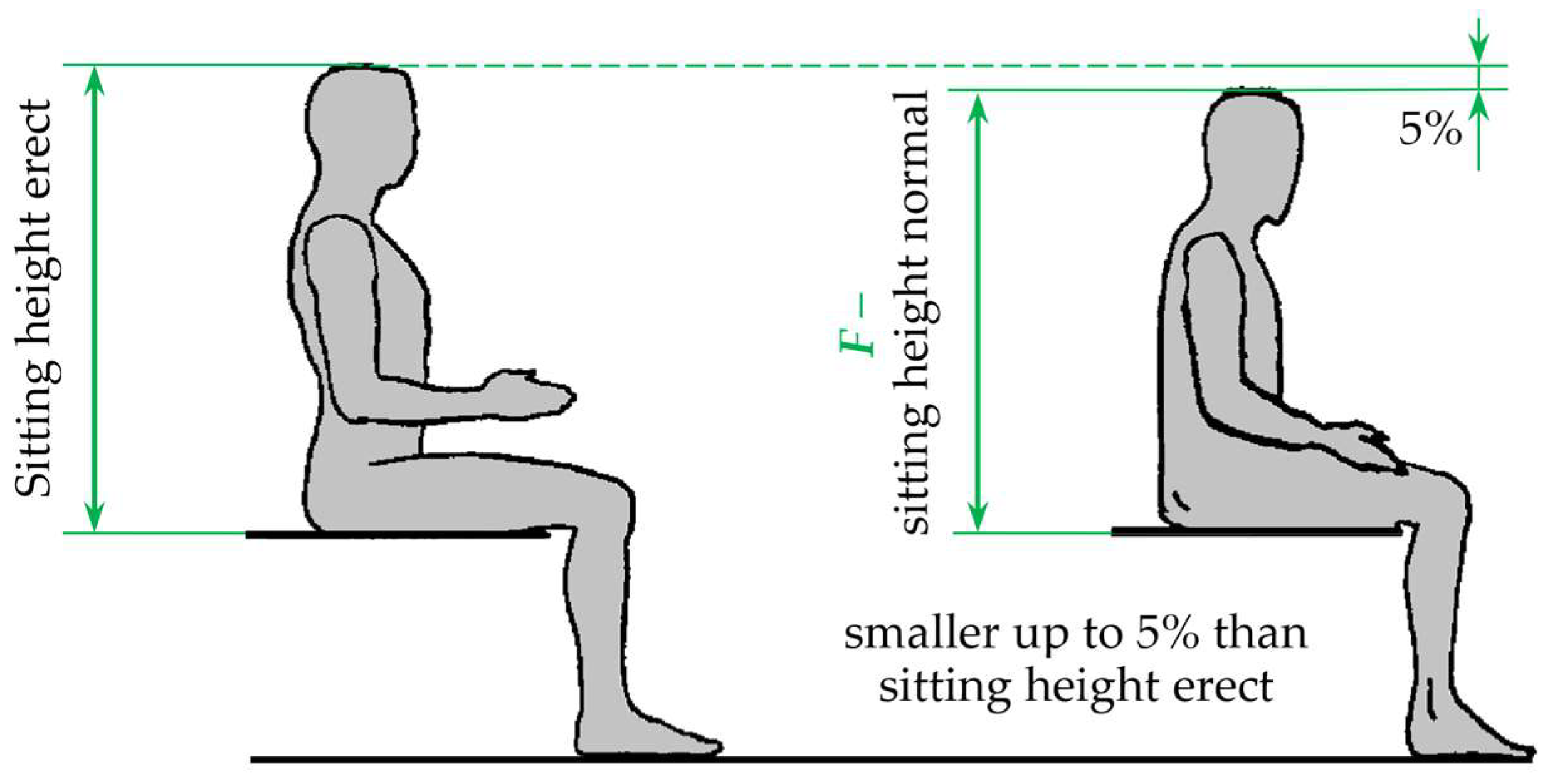
| F—Sitting height, normal | h7 | h7 should be less than F |
| G—Shoulder breath (bi-acromial breadth) | b4 | b4 should be equal to G or wider |
| L.H.—Lumbar height | h6 | h6 should be equal to H |
| Reference Measurement of a Human | Example Literature Data | Chair Measurement | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A—buttock-popliteal length | [20,34] | t7—seat depth | Height of the smallest expected user, e.g., 5th-percentile woman | |
| B—popliteal height | [20,34] | h8—seat height | Height of the average user, with average popliteal height | |
| C—bi-trochanteric breadth or trochanteric width (hip breath) | [35,36,37] | b3—seat width | Height of the user with the broadest bi-trochanteric breadth and spacing | |
| D—elbow-to-elbow breath | [20,34] | b5—armrest spacing | Height of the user with the broadest elbow-to-elbow breath and spacing | |
| E—elbow rest height | [20,34] | h9—armrest height | Height of the average user, with average elbow rest height | |
| F—sitting height | [20] | h7—backrest height | Height of the average user, with average sitting height | |
| G—shoulder breath (bi-acromial breadth) | [6] | b4—backrest breath | Height of the biggest user, with the broadest shoulder breath | |
| L.H.—lumbar height | [17,38] | h6—lumbar support height | 20–22 cm | EN 1729-1 |
| Chair Measurement | User Height 150–185 (Proposed in Figure 12) | User Height 133–159 (EN 1729-1:2015) | User Height 174–207 (EN 1729-1:2015) |
|---|---|---|---|
| t7—seat depth | 43.6 | 31 | 43 |
| h8—seat height | 44.2 | 38 | 51 |
| b3—seat width | 47.3 | 34 | 40 |
| b5—armrest spacing | 66.7 | 39–44 | 51–57 |
| h9—armrest height | 23.5 | 19 | 25 |
| h7—backrest height | 63.2 | min. 10 | min. 10 |
| b4—backrest breath | 43.2 | 27 | 36 |
| h6—lumbar support height | 20–22 | 19 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sydor, M.; Hitka, M. Chair Size Design Based on User Height. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010057
Sydor M, Hitka M. Chair Size Design Based on User Height. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleSydor, Maciej, and Miloš Hitka. 2023. "Chair Size Design Based on User Height" Biomimetics 8, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010057
APA StyleSydor, M., & Hitka, M. (2023). Chair Size Design Based on User Height. Biomimetics, 8(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010057






