Qubit Adoption Method of a Quantum Computing-Based Metaheuristics Algorithm for Truss Structures Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
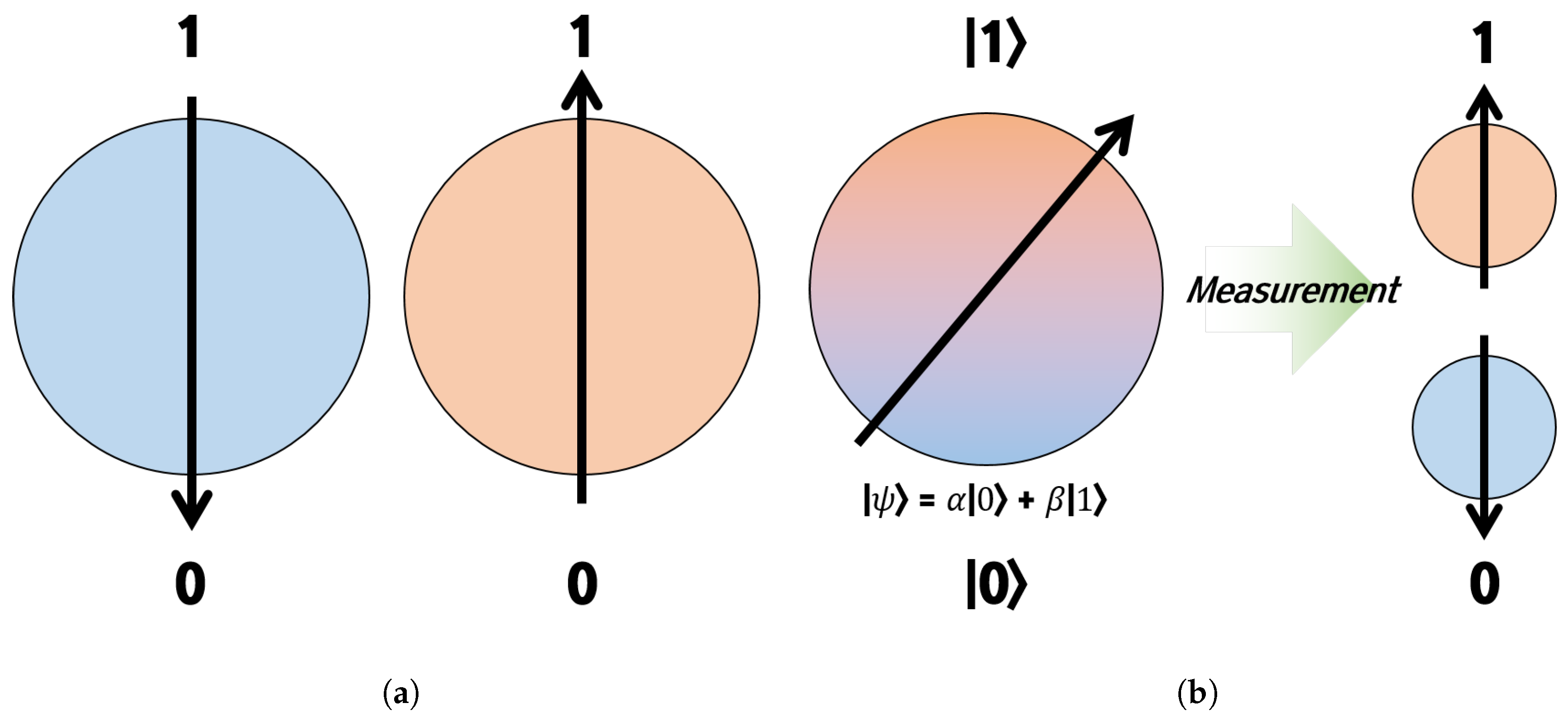
2. QbHS Algorithm
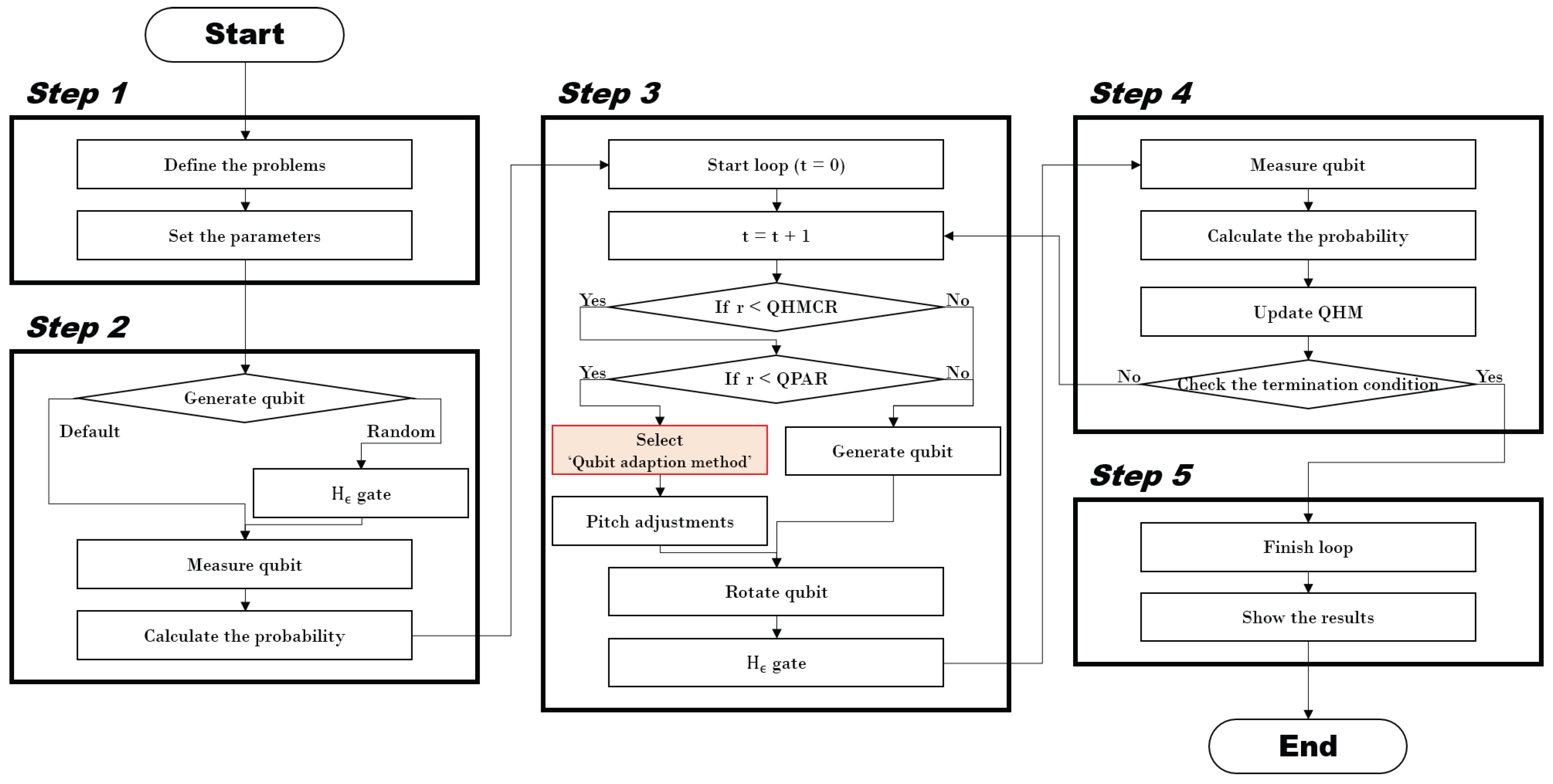
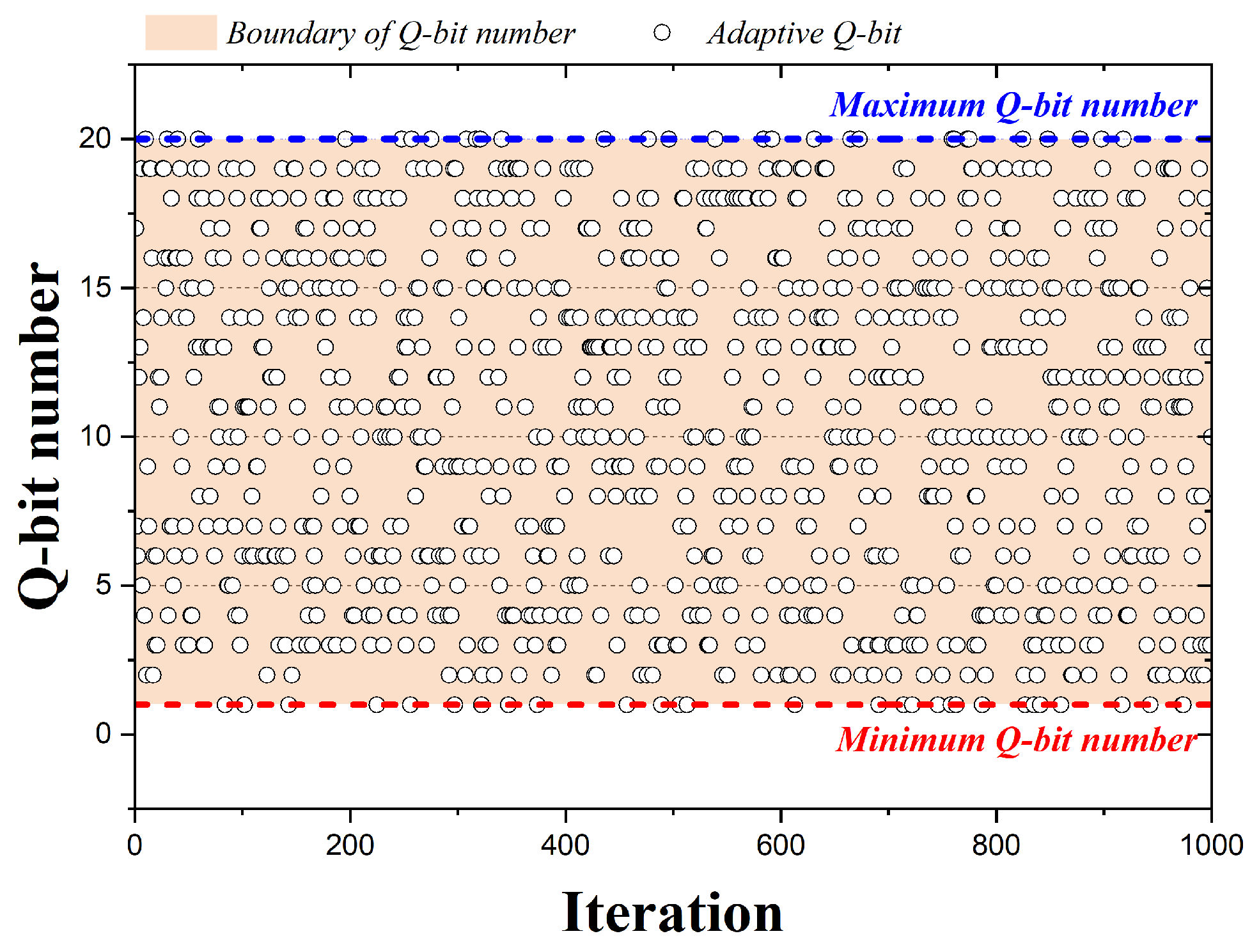
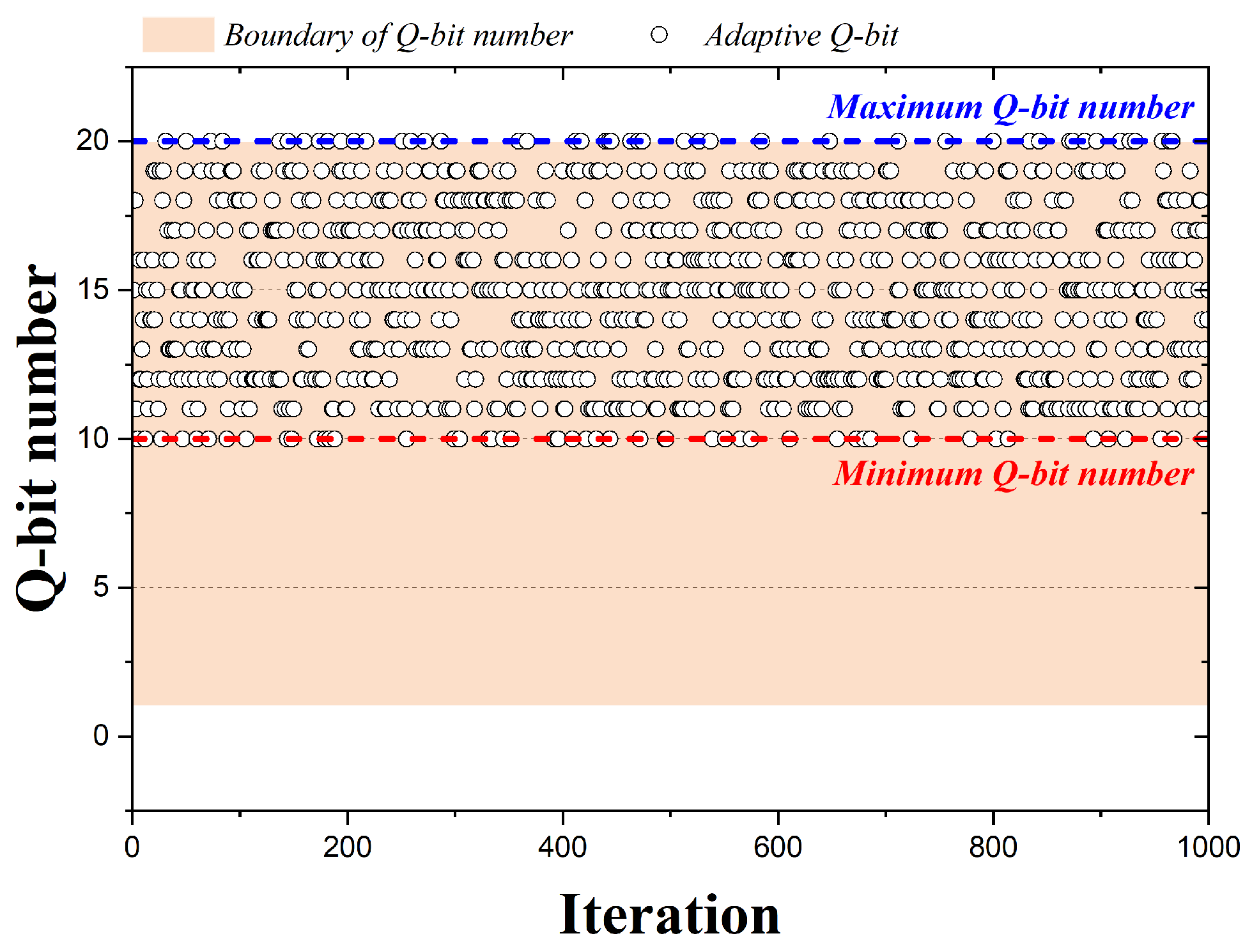
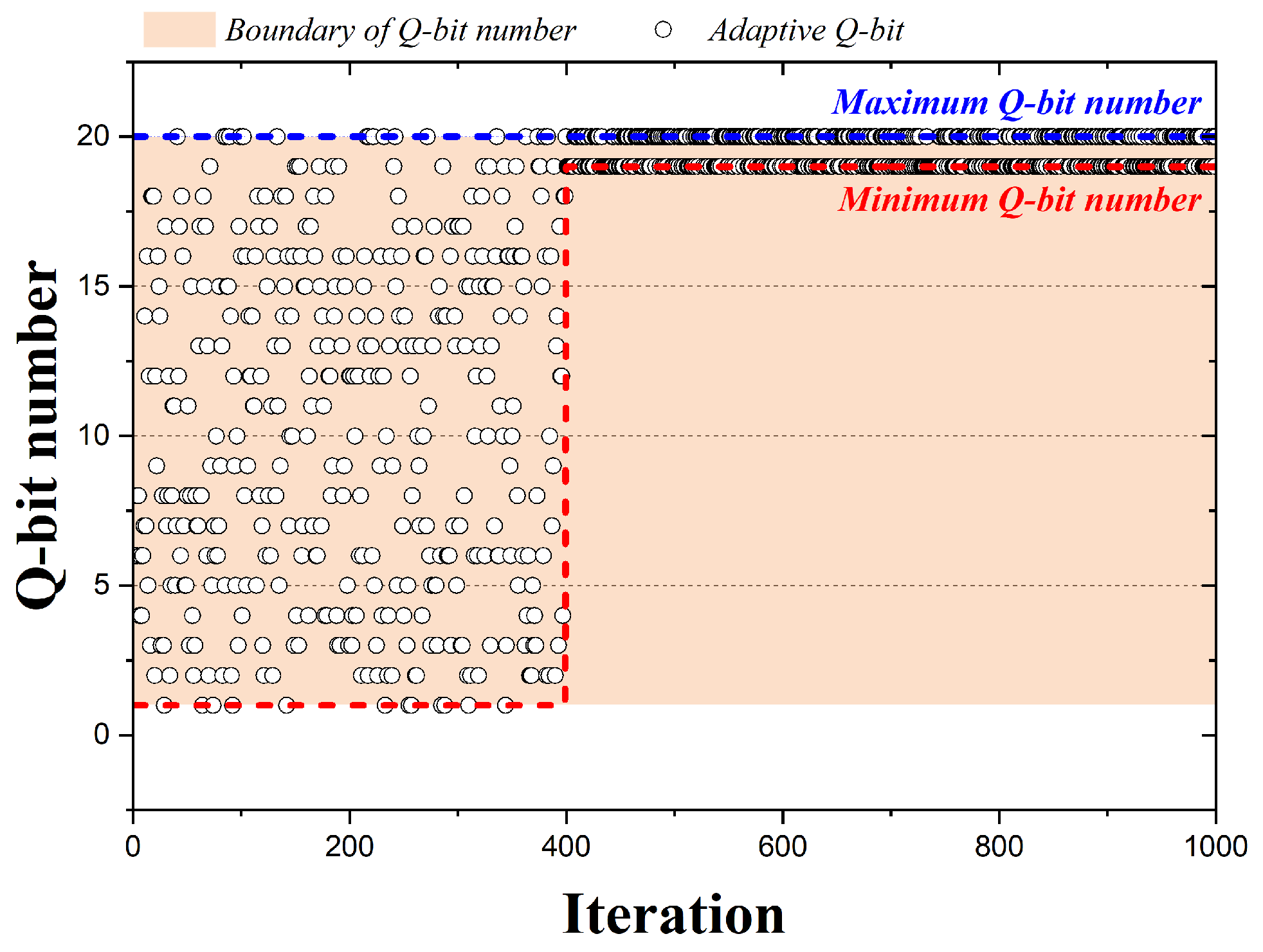
3. Qubit Adaption Method
3.1. Method I
3.2. Method II
3.3. Method III
3.4. Method IV
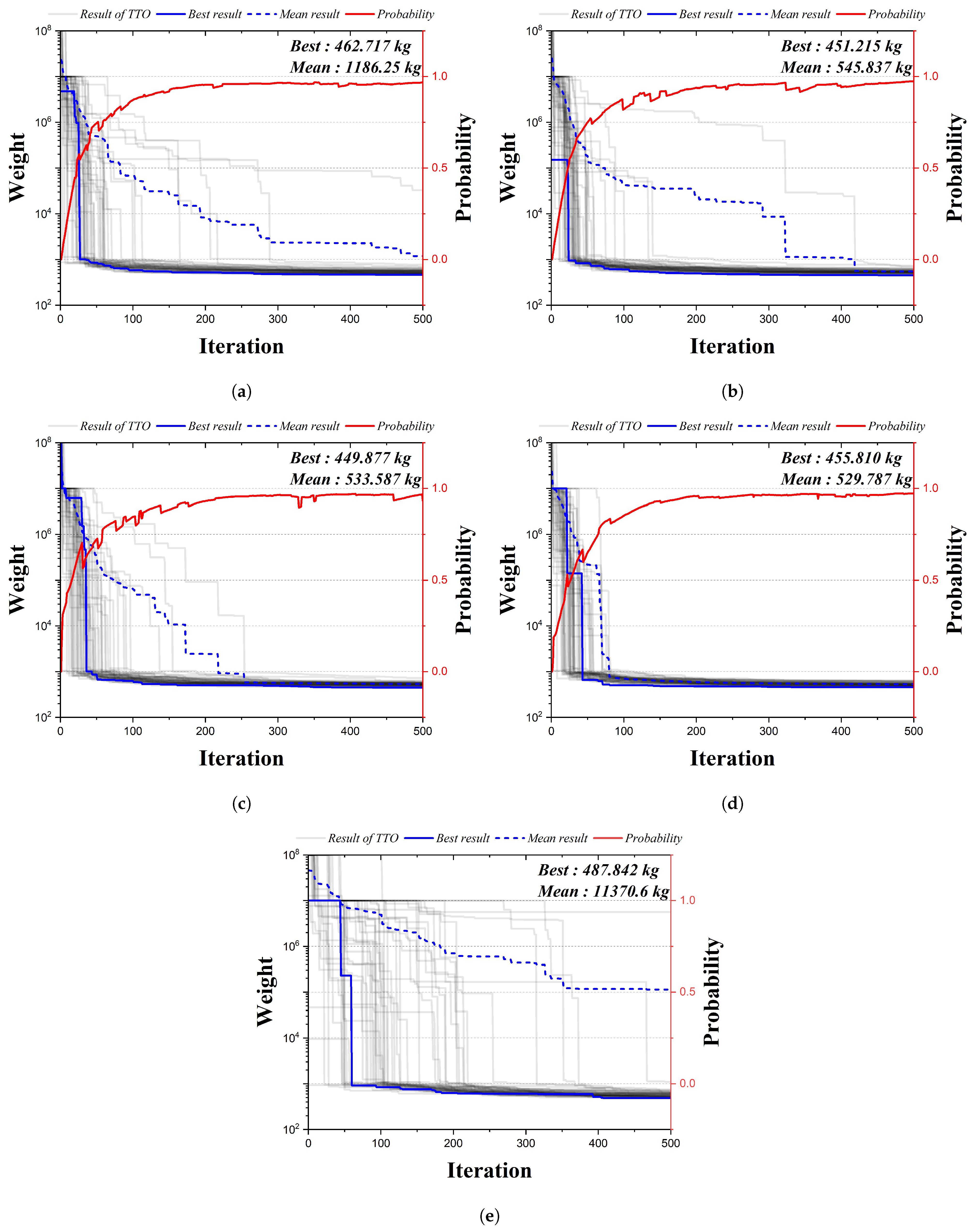
4. Numerical Example
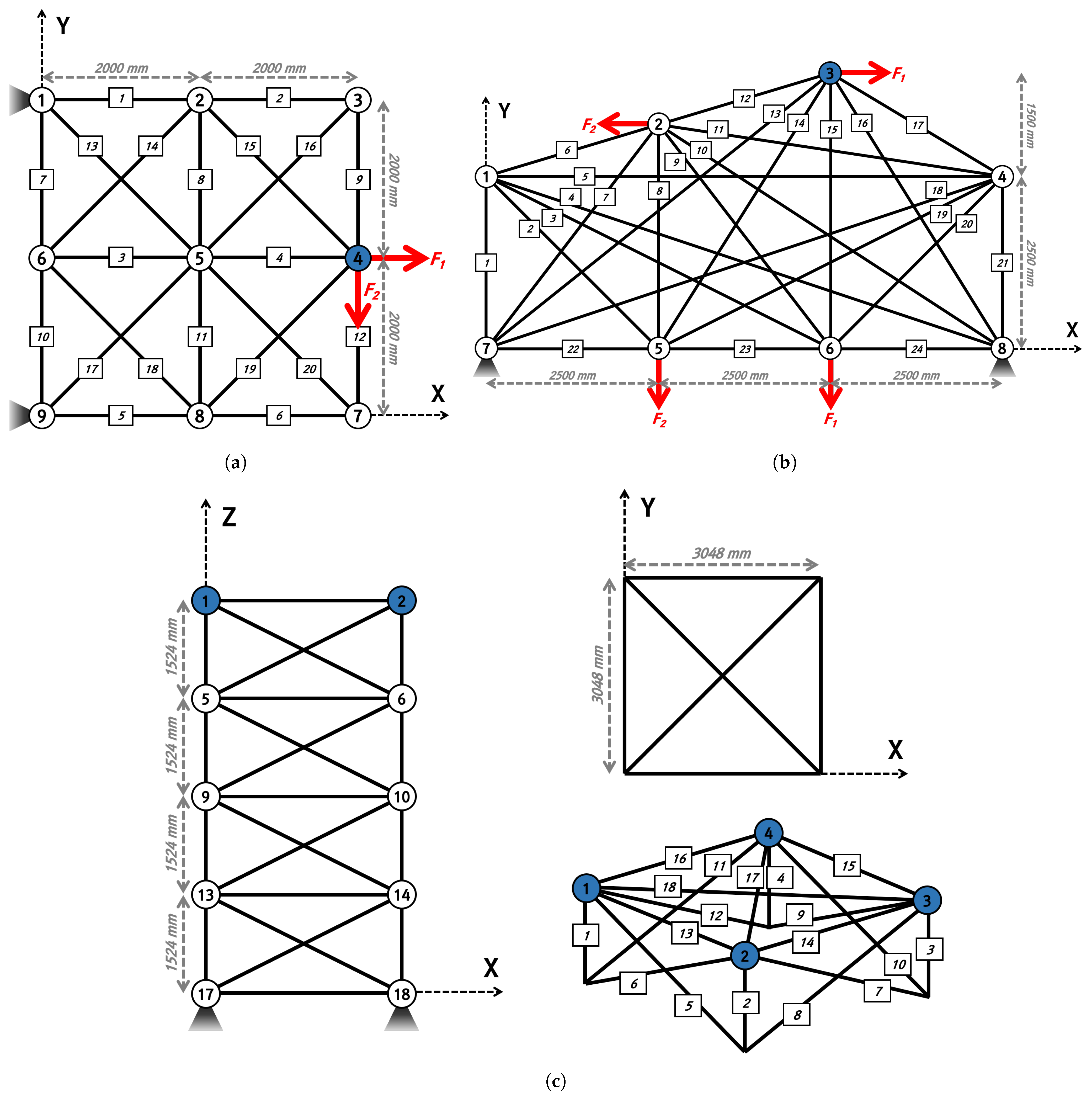
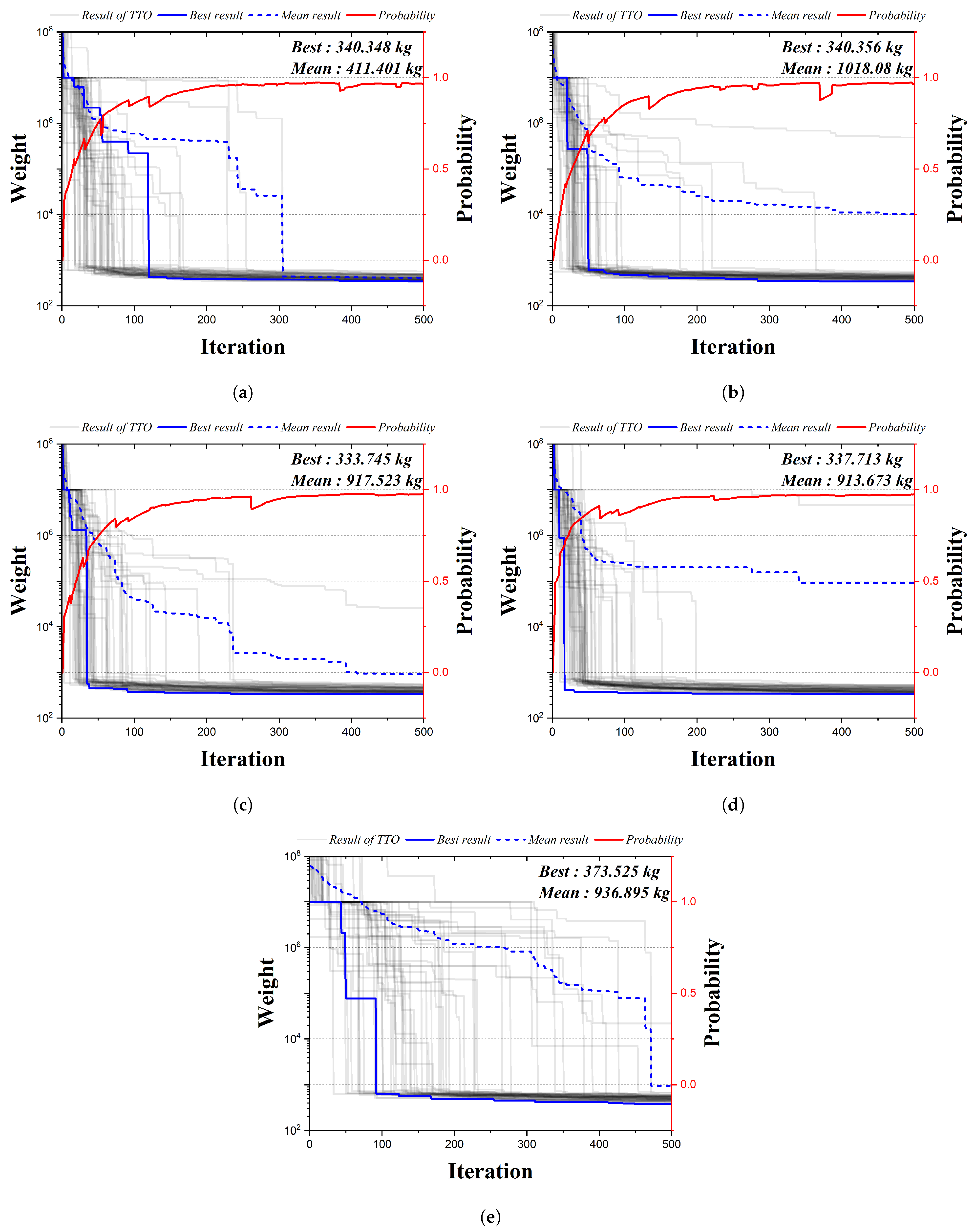
4.1. The 20-Bar Truss Structure
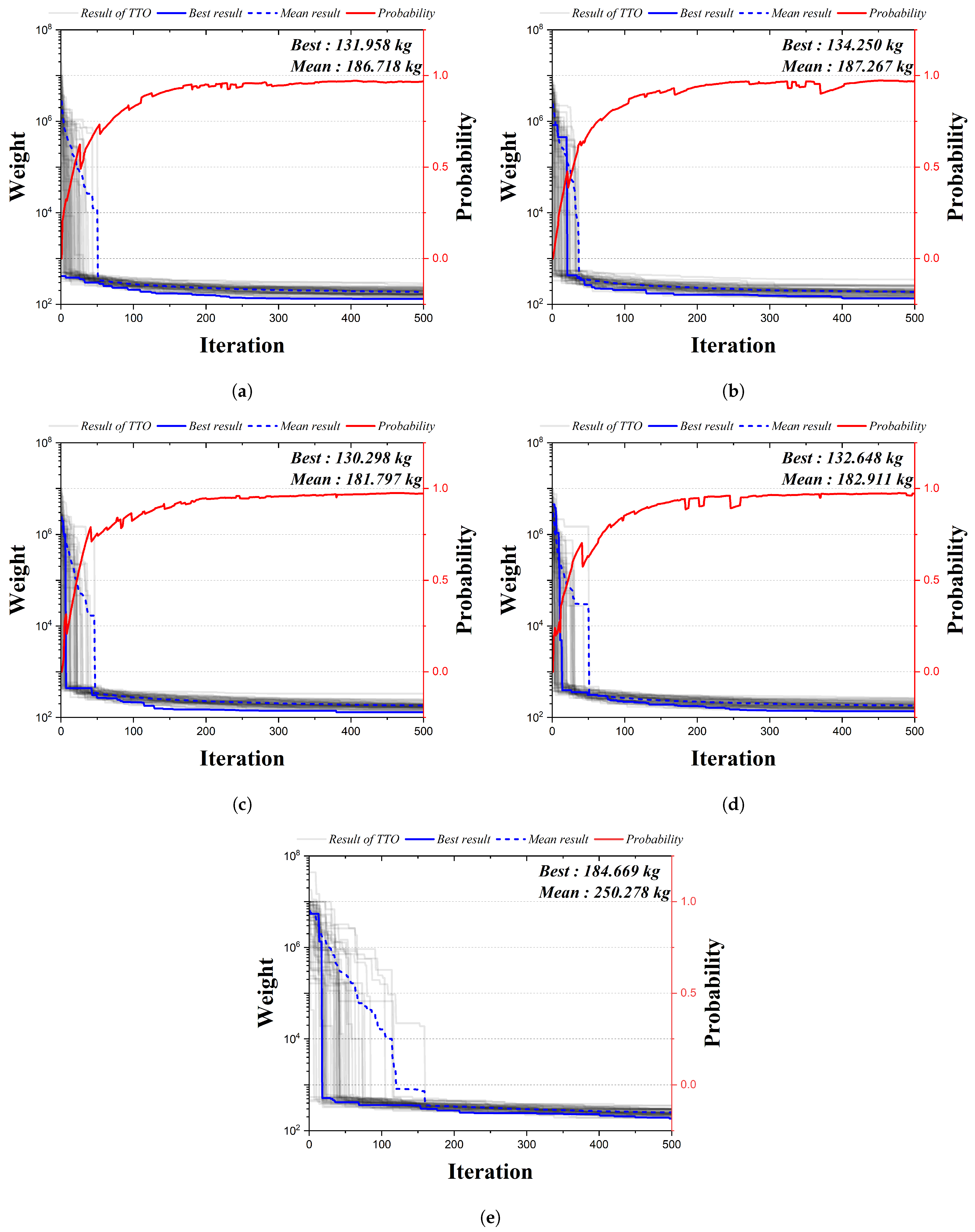
4.2. The 24-Bar Truss Structure
4.3. The 72-Bar Truss Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steane, A. Quantum computing. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1998, 61, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P. Simulating physics with computers. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2018, 21, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, D. Quantum theory, the Church–Turing principle and the universal quantum computer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1985, 400, 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gharehchopogh, F.S. Quantum-inspired metaheuristic algorithms: Comprehensive survey and classification. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 5479–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Grumbling, E.; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Quantum Computing: Progress and Prospects; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vedral, V.; Plenio, M.B. Basics of quantum computation. PRogress Quantum Electron. 1998, 22, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D. Quantum Computing Explained; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.S. A Quantum Computation Workbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hidary, J.D.; Hidary, J.D. Quantum Computing: An Applied Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Bawa, S. A comparative review of meta-heuristic approaches to optimize the SLA violation costs for dynamic execution of cloud services. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 3909–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Abutarboush, H.F.; Ganesh, T.; Mohamed, A.W. Metaheuristic algorithms on feature selection: A survey of one decade of research (2009–2019). IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26766–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Shon, S.; Lee, S. An Advanced Crow Search Algorithm for Solving Global Optimization Problem. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.H.; Kim, J.H. Genetic quantum algorithm and its application to combinatorial optimization problem. In Proceedings of the 2000 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC00 (Cat. No. 00TH8512), La Jolla, CA, USA, 16–19 July 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 1354–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.H.; Kim, J.H. Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for a class of combinatorial optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, M. A quantum particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2004 Congress on Evolutionary Computation (IEEE Cat. No. 04TH8753), Portland, OR, USA, 19–23 June 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Layeb, A. A hybrid quantum inspired harmony search algorithm for 0–1 optimization problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2013, 253, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamabadi-Pour, H. A quantum-inspired gravitational search algorithm for binary encoded optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 40, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Diao, M. Quantum-inspired teaching-learning-based optimization for linear array pattern synthesis. In Proceedings of the Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems, Harbin, China, 14–17 July 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 2106–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, K.; Mohd Salleh, M.N.; Cheng, S.; Shi, Y. Metaheuristic research: A comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2191–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakemi, S.; Houshmand, M.; KheirKhah, E.; Hosseini, S.A. A review of recent advances in quantum-inspired metaheuristics. Evol. Intell. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, O.H.M. A review of quantum-inspired metaheuristics: Going from classical computers to real quantum computers. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 814–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Elhefnawy, N.; El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Hadhoud, M.M. Quantum crossover based quantum genetic algorithm for solving non-linear programming. In Proceedings of the 2012 8th International Conference on Informatics and Systems (INFOS), Giza, Egypt, 14–16 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; p. BIO–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hakemi, S.; Houshmand, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Zhou, X. A Modified Quantum-Inspired Genetic Algorithm Using Lengthening Chromosome Size and an Adaptive Look-Up Table to Avoid Local Optima. Axioms 2023, 12, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J. A Quantum-Based Beetle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Numerical Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Ming, C.I. A review on metaheuristic algorithms: Recent trends, benchmarking and applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Smart Computing & Communications (ICSCC), Sarawak, Malaysia, 28–30 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Osaba, E.; Villar-Rodriguez, E.; Del Ser, J.; Nebro, A.J.; Molina, D.; LaTorre, A.; Suganthan, P.N.; Coello, C.A.C.; Herrera, F. A tutorial on the design, experimentation and application of metaheuristic algorithms to real-world optimization problems. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2021, 64, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alorf, A. A survey of recently developed metaheuristics and their comparative analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Shon, S.; Lee, S.; Ha, J. Size and Topology Optimization of Truss Structures Using Quantum-Based HS Algorithm. Buildings 2023, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ha, J.; Shon, S.; Lee, D. Weight Optimization of Discrete Truss Structures Using Quantum-Based HS Algorithm. Buildings 2023, 13, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geem, Z.W.; Kim, J.H.; Loganathan, G.V. A new heuristic optimization algorithm: Harmony search. Simulation 2001, 76, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.H.; Kim, J.H. Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithms with a new termination criterion, Hϵ gate, and two-phase scheme. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savsani, V.J.; Tejani, G.G.; Patel, V.K. Truss topology optimization with static and dynamic constraints using modified subpopulation teaching–learning-based optimization. Eng. Optim. 2016, 48, 1990–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savsani, V.J.; Tejani, G.G.; Patel, V.K.; Savsani, P. Modified meta-heuristics using random mutation for truss topology optimization with static and dynamic constraints. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2017, 4, 106–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | True | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | False | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | True | 1 | −1 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | False | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | True | 1 | −1 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 0 | False | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | True | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | False | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Algorithm | Parameters |
|---|---|
| QbHSA | QHMS = 10, Mea. = 2, QHMCR = 0.9, QPAR = 0.1, Qubit = 20, = 0.01, = 0.06, = 1.0, = 0.1, BWQ = 0.3, = 1.0, = 0.01, tolBW = 0.95 |
| HSA | HMS = 10, HMCR = 0.9, PAR = 0.1, bw = 0.03 |
| Lumped Mass | E | A | Load | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||||
| 200 kg | 69,000 MPa | 2740 kg/ | −100 ≤ x ≤ 100 | = 500 kN, = 0 kN | = 0 kN, = 500 kN |
| Design Variable | Method I | Method II | Method III | Method IV | HSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 31.259 | 50.001 | 51.575 | 68.115 | 39.252 |
| A2 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A4 | - | - | - | - | 5.017 |
| A5 | 75.043 | 33.328 | 51.319 | 39.845 | 77.294 |
| A6 | - | - | - | - | 13.740 |
| A7 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A8 | 31.630 | 53.155 | 52.735 | 66.725 | 54.288 |
| A9 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A10 | - | 4.212 | - | - | - |
| A11 | 53.137 | 65.924 | 33.804 | 42.621 | 90.668 |
| A12 | - | - | - | - | 2.100 |
| A13 | 49.327 | 56.260 | 68.946 | 81.251 | 56.214 |
| A14 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A15 | 53.520 | 83.315 | 63.546 | 59.729 | 55.469 |
| A16 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A17 | - | 3.259 | - | - | - |
| A18 | 87.500 | 51.661 | 50.025 | 42.311 | 72.267 |
| A19 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A20 | 75.002 | 53.415 | 75.468 | 60.104 | 53.204 |
| Lumped Mass | E | A | Load | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||||
| 500 kg | 69,000 MPa | 2740 kg/ | −40 ≤ x ≤ 40 | = 50 kN, = 0 kN | = 0 kN, = 50 kN |
| Design Variable | Method I | Method II | Method III | Method IV | HSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A2 | - | - | - | - | 4.938 |
| A3 | - | - | - | - | 5.383 |
| A4 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A5 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A6 | - | - | - | - | 14.560 |
| A7 | 20.039 | 22.523 | 20.625 | 20.080 | 26.305 |
| A8 | 5.025 | 3.145 | 4.064 | 5.078 | 10.875 |
| A9 | - | - | - | - | 1.402 |
| A10 | - | 0.113 | 0.060 | - | - |
| A11 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A12 | 0.236 | - | - | 0.0001 | - |
| A13 | 20.001 | 20.642 | 20.081 | 20.002 | 20.380 |
| A14 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A15 | 5.000 | 5.159 | 3.798 | 5.522 | 10.767 |
| A16 | 25.001 | 24.064 | 24.071 | 25.020 | 24.550 |
| A17 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A18 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A19 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A20 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A21 | - | - | - | - | - |
| A22 | - | 1.250 | 0.636 | 0.198 | - |
| A23 | 0.626 | - | - | 0.099 | - |
| A24 | 0.061 | 0.674 | 0.1 | - | 8.947 |
| Lumped Mass | E | A | Load | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | ||||
| 2270 kg | 68,950 MPa | 2767.99 kg/ | −30 ≤ x ≤ 30 | = = 22.25 kN, = −22.25 kN | = = = = −22.25 kN |
| Design Variable | Method I | Method II | Method III | Method IV | HSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 (A1–A4) | 4.880 | 5.655 | 7.985 | 4.776 | 6.574 |
| G2 (A5–A12) | 9.500 | 11.257 | 11.451 | 11.303 | 9.052 |
| G3 (A13–A16) | 5.651 | - | - | - | - |
| G4 (A17–A18) | - | - | - | - | 11.218 |
| G5 (A19–A22) | 15.002 | 7.500 | 6.573 | 9.264 | 18.603 |
| G6 (A23–A30) | 6.328 | 7.886 | 7.832 | 7.749 | 9.446 |
| G7 (A31–A34) | - | - | - | 2.873 | - |
| G8 (A35–A36) | 7.563 | 3.956 | 3.867 | 7.503 | - |
| G9 (A37–A40) | 11.549 | 15.074 | 15.485 | 9.864 | 12.434 |
| G10 (A41–A48) | 8.061 | 8.320 | 8.438 | 7.512 | 8.264 |
| G11 (A49–A52) | - | - | - | - | - |
| G12 (A53–A54) | - | - | - | - | - |
| G13 (A55–A58) | 14.581 | 15.032 | 14.063 | 18.199 | 14.989 |
| G14 (A59–A66) | 8.969 | 8.154 | 7.559 | 7.515 | 9.325 |
| G15 (A67–A70) | - | - | - | - | - |
| G16 (A71–A72) | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Shon, S. Qubit Adoption Method of a Quantum Computing-Based Metaheuristics Algorithm for Truss Structures Analysis. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9010011
Lee D, Lee S, Shon S. Qubit Adoption Method of a Quantum Computing-Based Metaheuristics Algorithm for Truss Structures Analysis. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Donwoo, Seungjae Lee, and Sudeok Shon. 2024. "Qubit Adoption Method of a Quantum Computing-Based Metaheuristics Algorithm for Truss Structures Analysis" Biomimetics 9, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9010011
APA StyleLee, D., Lee, S., & Shon, S. (2024). Qubit Adoption Method of a Quantum Computing-Based Metaheuristics Algorithm for Truss Structures Analysis. Biomimetics, 9(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9010011







