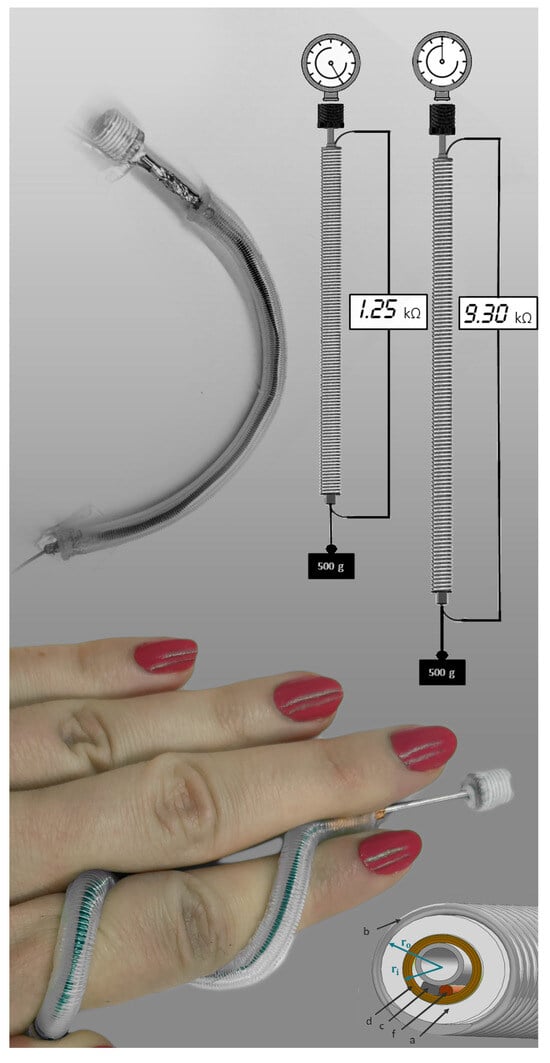
How to Easily Make Self-Sensing Pneumatic Inverse Artificial Muscles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Elastomeric Tube
2.2. Elastomeric Piezoresistive Sensor
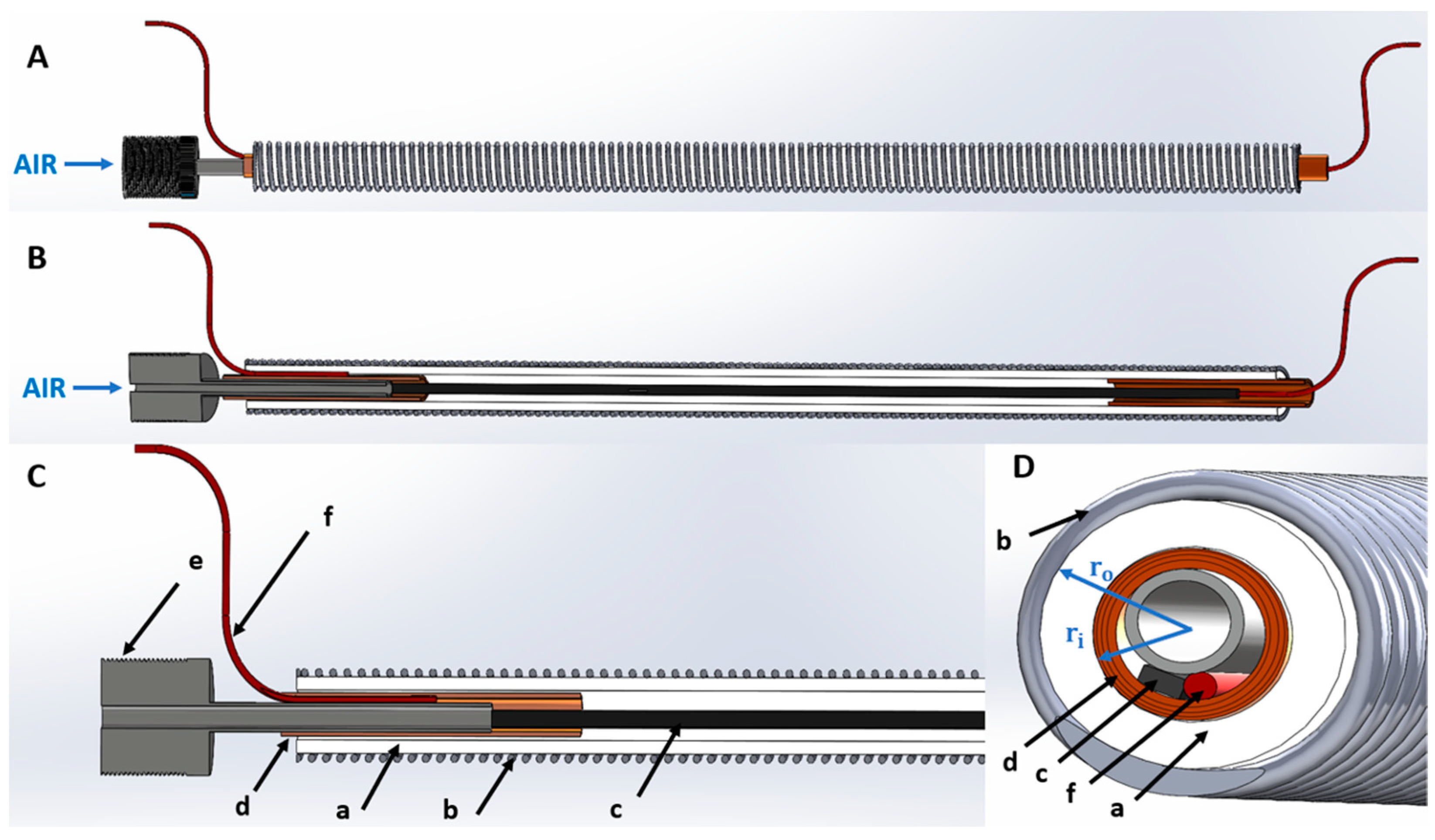
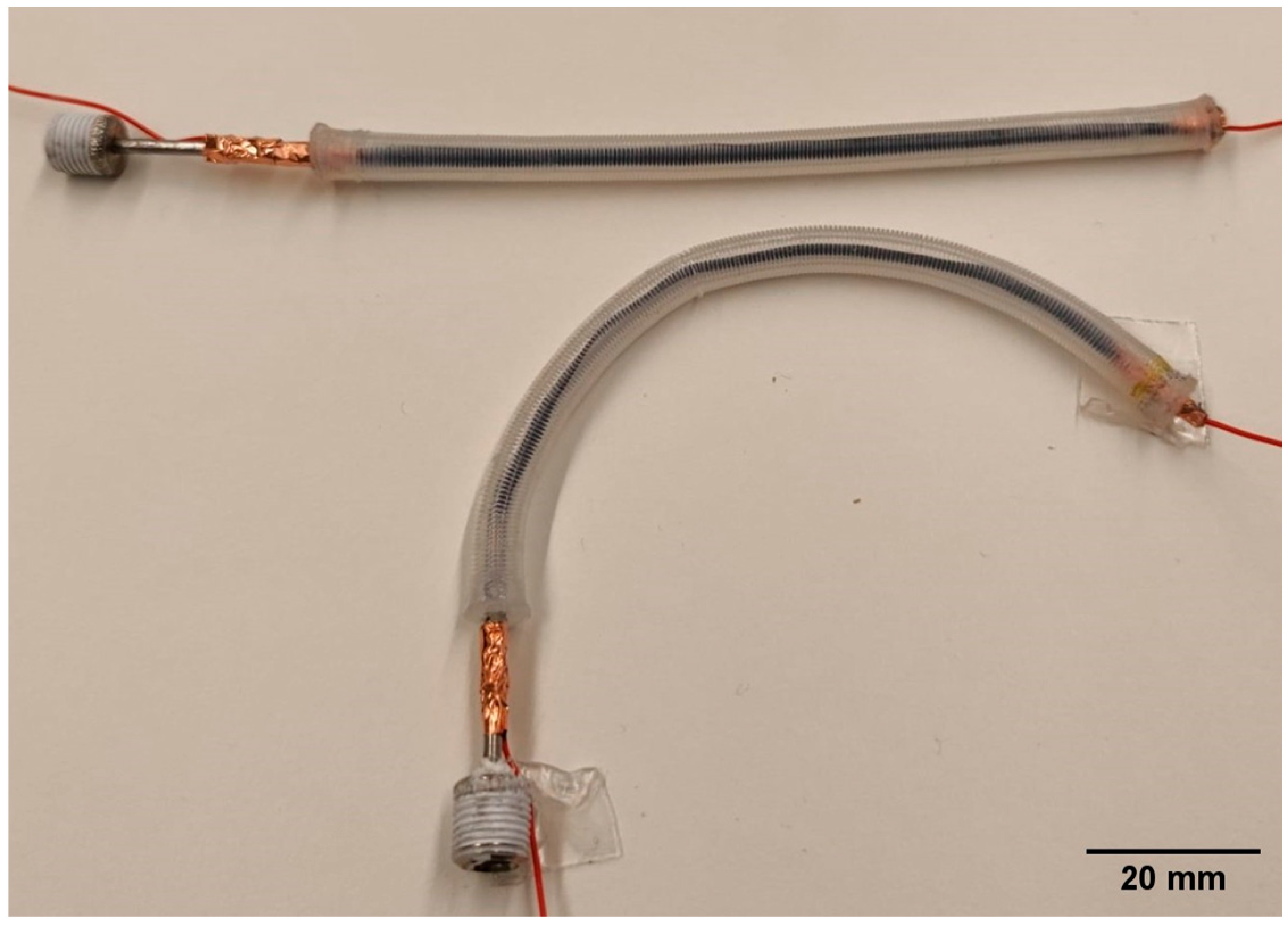
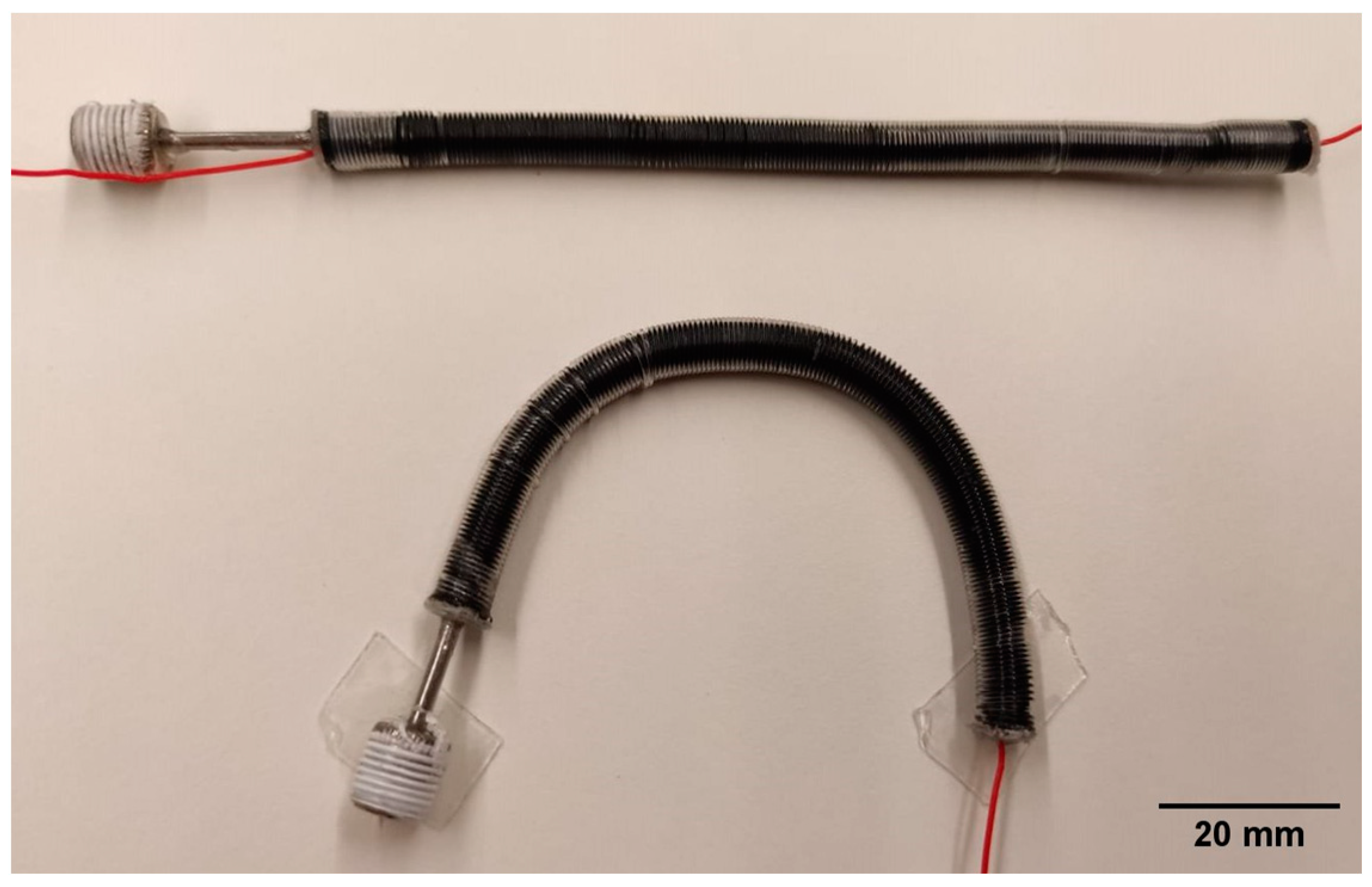
2.3. Fabrication of the Self-Sensing Pneumatic Inverse Artificial Muscle
2.3.1. Step 1: Preparation of the Restriction Coil
2.3.2. Step 2: Application of the Restriction Coil
2.3.3. Step 3: Creation of the Sensor and Its Electrical Contacts
2.3.4. Step 4: Combination of the Actuator and Sensor and Sealing of the Structure
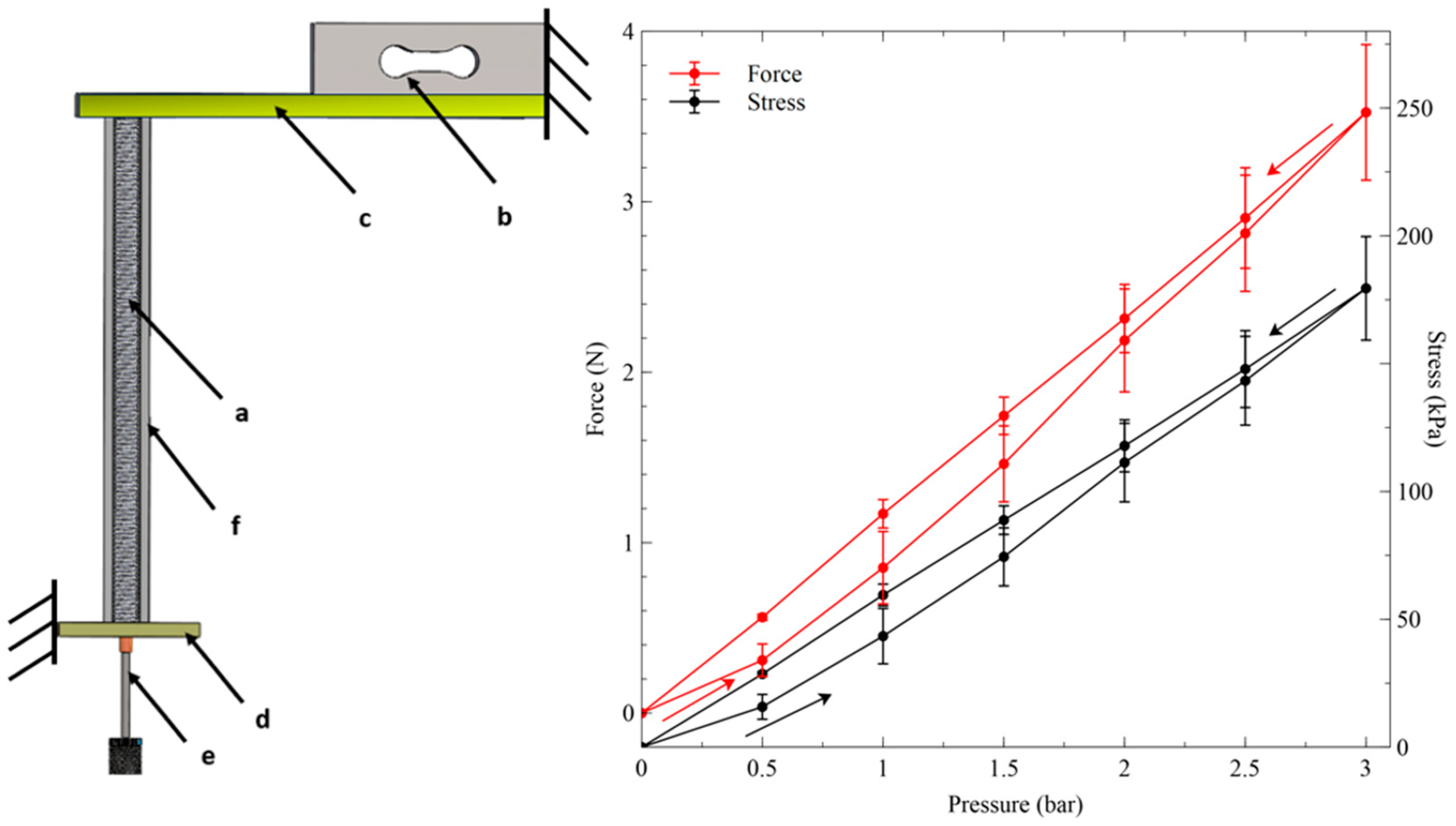
2.4. Measurement of the Actuation Free Stroke
2.5. Measurement of the Actuation Blocking Force
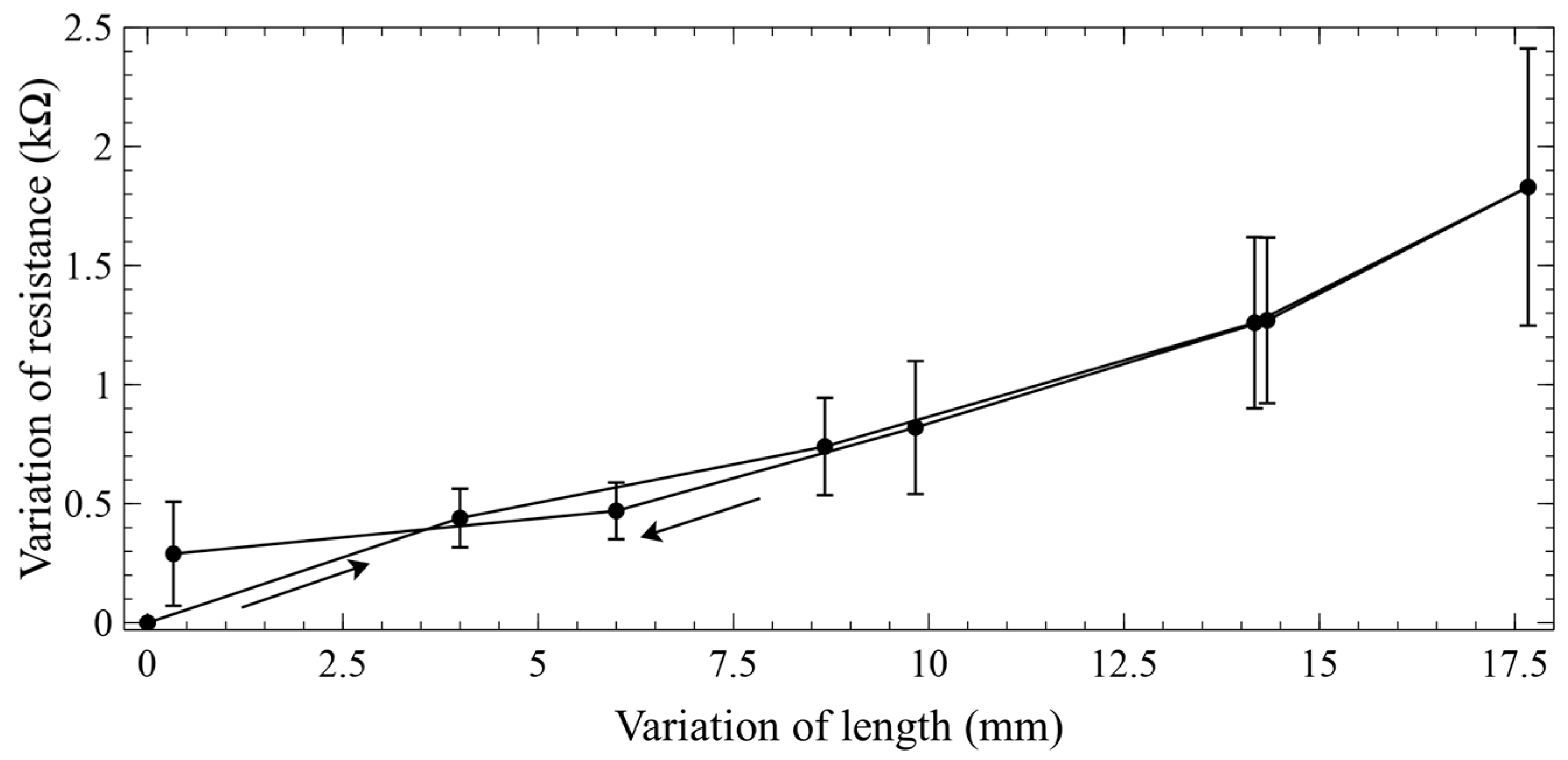
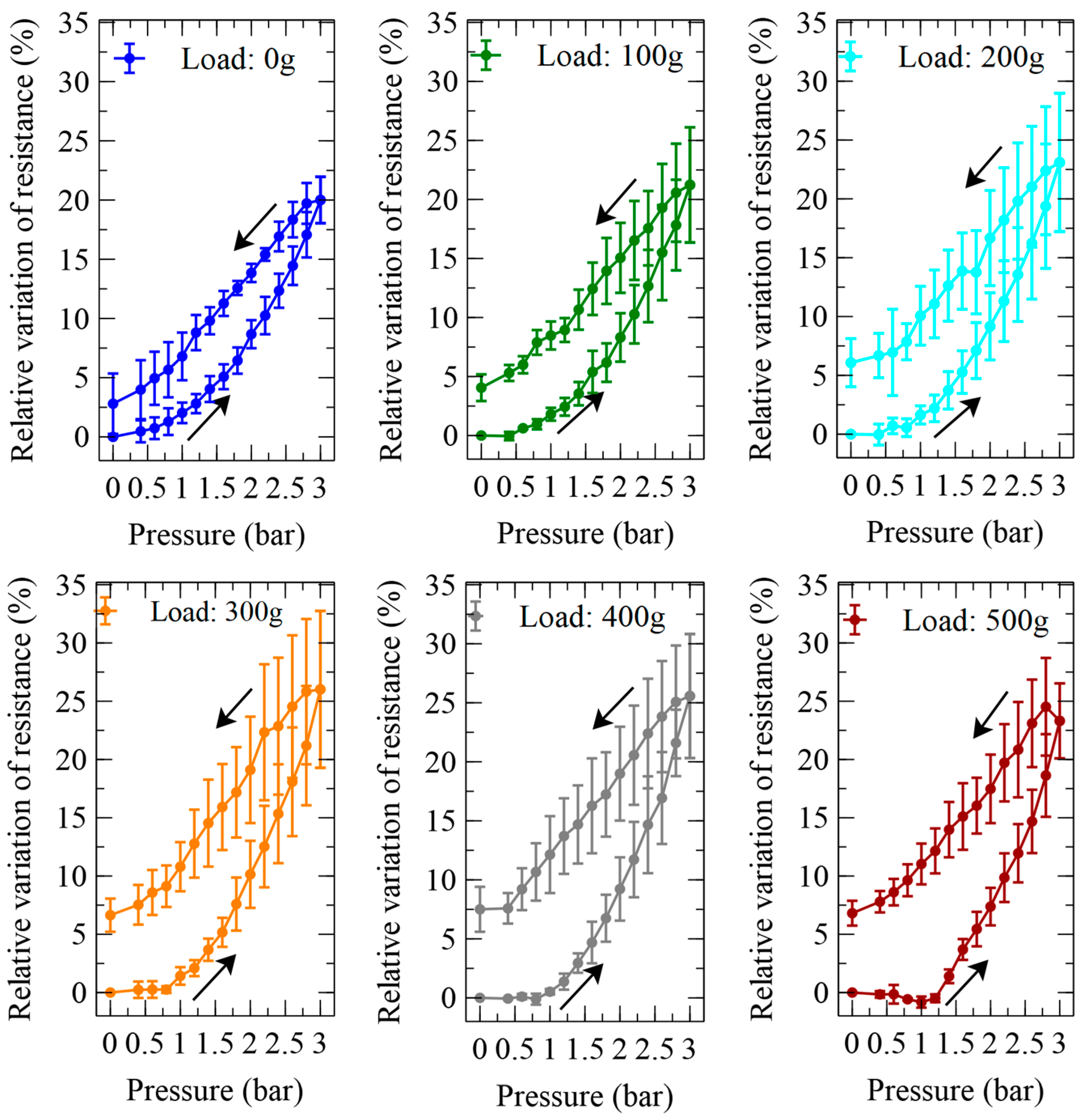
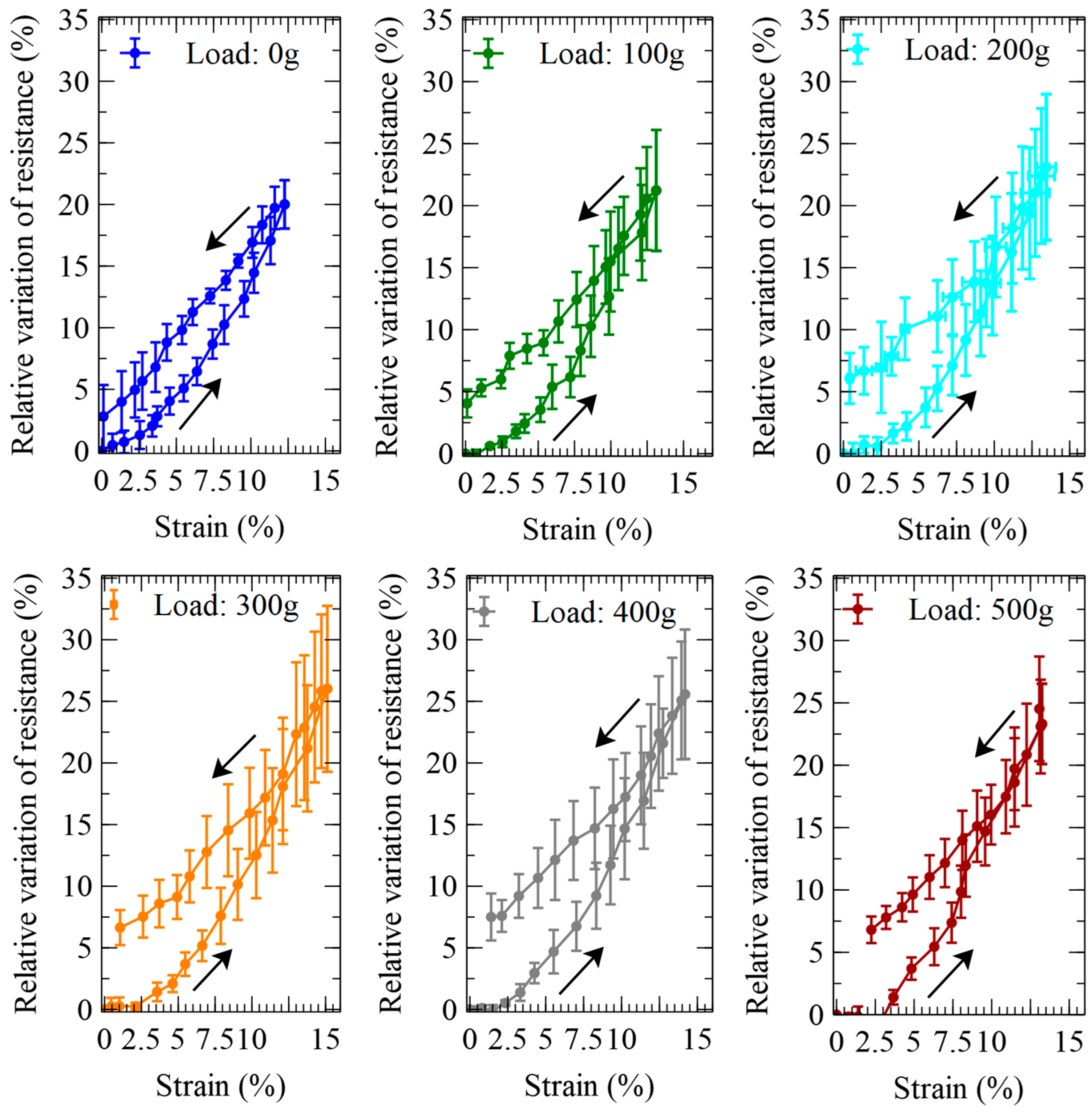
2.6. Measurement of the Actuator’s Self-Sensing Performance
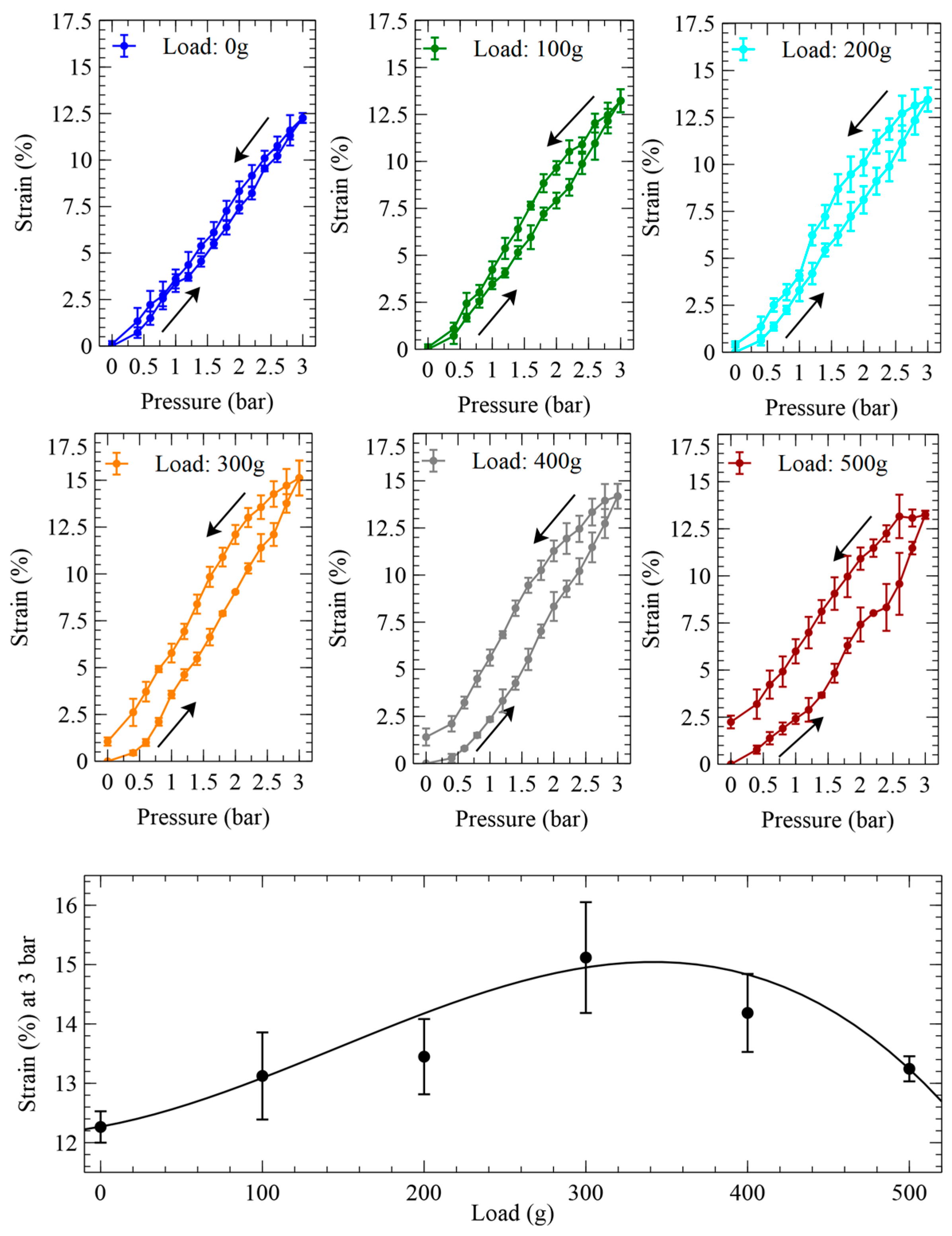
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vertongen, J.; Kamper, D.G.; Smit, G.; Vallery, H. Mechanical aspects of robot hands, active hand orthoses, and prostheses: A comparative review. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 26, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.B.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.J. Exo-glove poly II: A polymer-based soft wearable robot for the hand with a tendon-driven actuation system. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, M.; Quinlivan, B.; Aubin, P.M.; Martinez-Villalpando, E.; Baumann, M.; Stirling, L.; Holt, K.; Wood, R.; Walsh, C. A lightweight soft exosuit for gait assistance. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 3362–3369. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, H.; Takemoto, N.; Yakami, R.; Wakimoto, S.; Oshikawa, T.; Morinaga, K.; Kanda, T. Realistic and highly functional pediatric externally powered prosthetic hand using pneumatic soft actuators. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2020, 32, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Tsujiuchi, N.; Koizumi, T.; Kan, H.; Hirano, M.; Nakamura, Y. Development of prosthetic arm with pneumatic prosthetic hand and tendon-driven wrist. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 5048–5051. [Google Scholar]
- Polygerinos, P.; Correll, N.; Morin, S.A.; Mosadegh, B.; Onal, C.D.; Petersen, K.; Cianchetti, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F. Soft Robotics: Review of Fluid-Driven Intrinsically Soft Devices; Manufacturing, Sensing, Control, and Applications in Human-Robot Interaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F. (Ed.) Electromechanically Active Polymers: A Concise Reference; Springer: Zurich, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carpi, F.; Smela, E. (Eds.) Biomedical Applications of Electroactive Polymer Actuators; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carpi, F.; Kornbluh, R.; Sommer-Larsen, P.; Alici, G. Electroactive polymer actuators as artificial muscles: Are they ready for bioinspired applications? Bioinspiration Biomim. 2011, 6, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Coppola, M.; Di Franco, R.; Rosi, E.; Vizzarro, V. Bioinspired Electromechanically Active Polymer-Based Robotics. In Encyclopedia of Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Review of dielectric elastomer actuators and their applications in soft robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Hwang, G.; Kim, H.; Hyeon, K.; Park, J.; Kyung, K.U. Dielectric elastomer actuator for soft robotics applications and challenges. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochu, P.; Pei, Q. Advances in dielectric elastomers for actuators and artificial muscles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 10–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisti, M.; Giorelli, M.; Levy, G.; Mazzolai, B.; Hochner, B.; Laschi, C.; Dario, P. An octopus-bioinspired solution to movement and manipulation for soft robots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2011, 6, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicea, R.; Xiloyannis, M.; Chiaradia, D.; Barsotti, M.; Frisoli, A.; Masia, L. A soft, synergy-based robotic glove for grasping assistance. Wearable Technol. 2021, 2, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, L.; Chen, J.; Liarokapis, M. On the development of adaptive, tendon-driven, wearable exo-gloves for grasping capabilities enhancement. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Dong, E.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Alici, G.; Jie, Y. Soft and smart modular structures actuated by shape memory alloy (SMA) wires as tentacles of soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, J. A general soft robot module driven by twisted and coiled actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 035019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Qian, C.; Liang, Y. A review of shape memory alloy artificial muscles in bionic applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, C.S.; Lima, M.D.; Li, N.; Spinks, G.M.; Foroughi, J.; Madden, J.D.; Kim, S.H.; Fang, S.; Jung de Andrade, M.; Göktepe, F.; et al. Artificial muscles from fishing line and sewing thread. Science 2014, 343, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.S.; Tawk, C.D.; Zolfagharian, A.; Pinskier, J.; Howard, D.; Young, T.; Lai, J.; Harrison, S.M.; Yong, Y.K.; Bodaghi, M.; et al. Soft pneumatic actuators: A review of design, fabrication, modeling, sensing, control and applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59442–59485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, B.; Oh, N.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, H.; Rodrigue, H. A review and comparison of linear pneumatic artificial muscles. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2023, 11, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Zidek, T.; Harbel, C.; Yoon, S.; Strickland, F.S.; Kumar, S.; Shin, M. Soft robotics: A review of recent developments of pneumatic soft actuators. Actuators 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, B.; Leonessa, A.; Dwivedy, S.K. A review on the development of pneumatic artificial muscle actuators: Force model and application. Actuators 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurumaya, S.; Nabae, H.; Endo, G.; Suzumori, K. Design of thin McKibben muscle and multifilament structure. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 261, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felt, W.; Chin, K.Y.; Remy, C.D. Contraction sensing with smart braid McKibben muscles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 21, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.L.; Wood, R.J. Smart pneumatic artificial muscle actuator with embedded microfluidic sensing. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2013 IEEE, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Christensen, D.L.; Okamura, A.M. Design and implementation of a 300% strain soft artificial muscle. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 4022–4029. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzon, L.; Zrinscak, D.; Maselli, M.; Cianchetti, M. Modelling and characterization of a soft inverse pneumatic artificial muscle. In Proceedings of the ACTUATOR; International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuator Systems and Applications 2021, Online, 17–19 February 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic Afsar, O.; Shtarbanov, A.; Mor, H.; Nakagaki, K.; Forman, J.; Modrei, K.; Jeong, S.H.; Hjort, K.; Höök, K.; Ishii, H. OmniFiber: Integrated fluidic fiber actuators for weaving movement based interactions into the ‘fabric of everyday life’. In Proceedings of the UIST’21: The 34th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Monterey, CA, USA, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 1010–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Realmuto, J.; Sanger, T. A robotic forearm orthosis using soft fabric-based helical actuators. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 591–596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Do, T.N.; Hawkes, E.; Visell, Y. Fluidic fabric muscle sheets for wearable and soft robotics. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzon, L.; Beccali, G.; Maselli, M.; Cianchetti, M. A self-sensing inverse pneumatic artificial muscle. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Edinburgh, UK, 4–8 April 2022; pp. 817–822. [Google Scholar]
- Euro Technologies. Available online: https://www.euro-technologies.eu/en/product/electrically-conductive-elastomers (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Phan, P.T.; Thai, M.T.; Hoang, T.T.; Lovell, N.H.; Do, T.N. HFAM: Soft hydraulic filament artificial muscles for flexible robotic applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 226637–226652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potnik, V.; Frediani, G.; Carpi, F. How to Easily Make Self-Sensing Pneumatic Inverse Artificial Muscles. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030177
Potnik V, Frediani G, Carpi F. How to Easily Make Self-Sensing Pneumatic Inverse Artificial Muscles. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(3):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030177
Chicago/Turabian StylePotnik, Valentina, Gabriele Frediani, and Federico Carpi. 2024. "How to Easily Make Self-Sensing Pneumatic Inverse Artificial Muscles" Biomimetics 9, no. 3: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030177
APA StylePotnik, V., Frediani, G., & Carpi, F. (2024). How to Easily Make Self-Sensing Pneumatic Inverse Artificial Muscles. Biomimetics, 9(3), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030177