A Highly Sensitive Deep-Sea Hydrodynamic Pressure Sensor Inspired by Fish Lateral Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
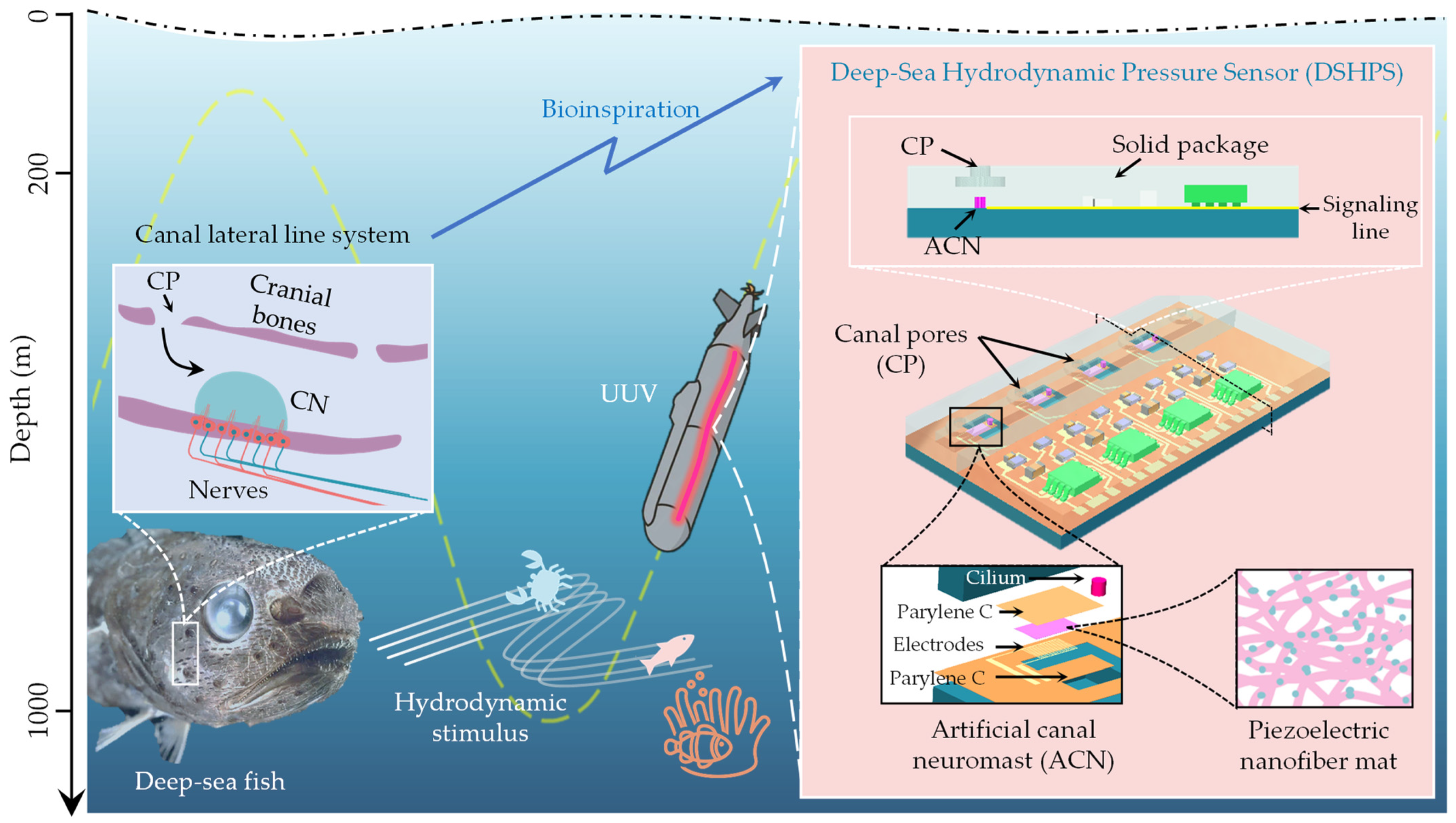
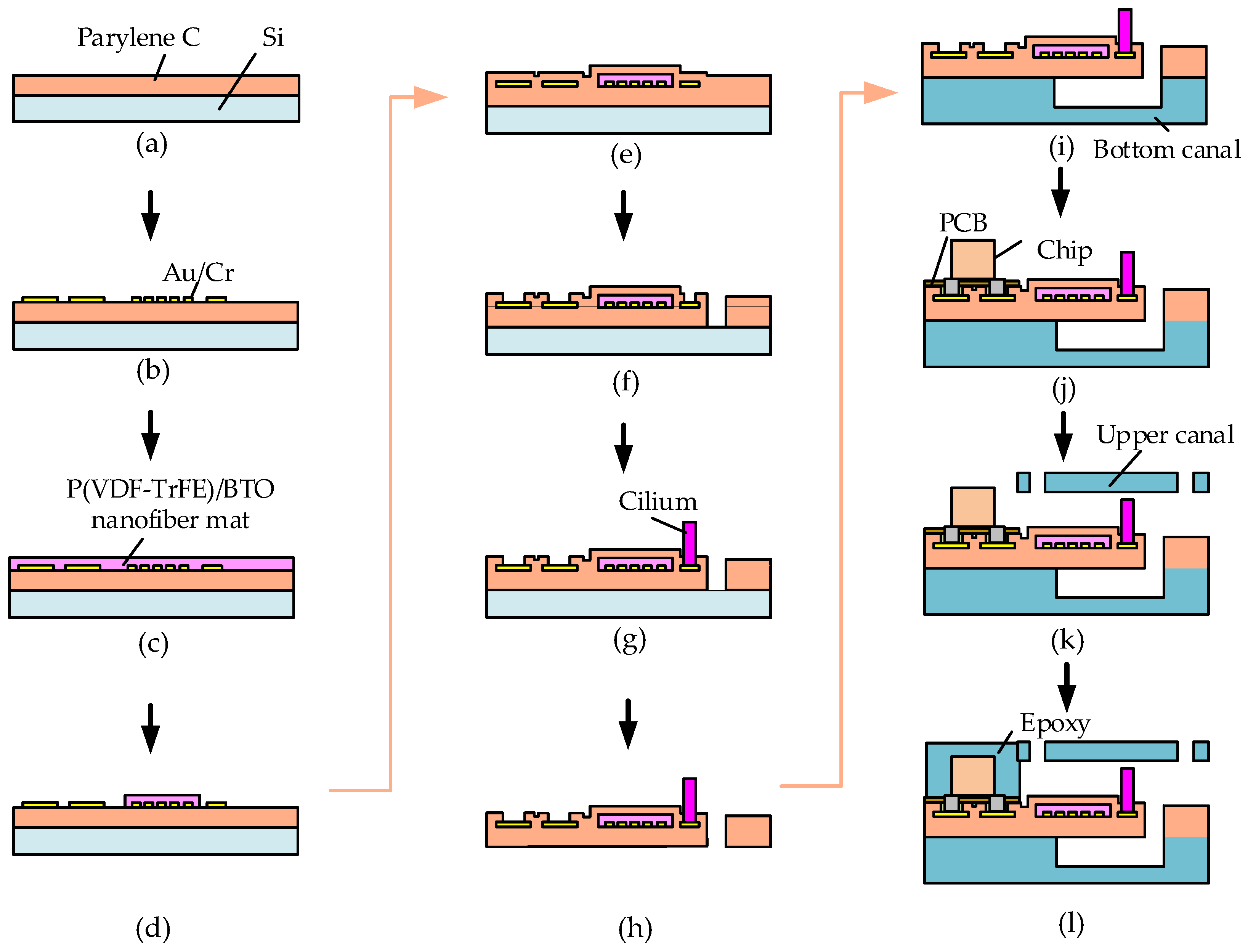
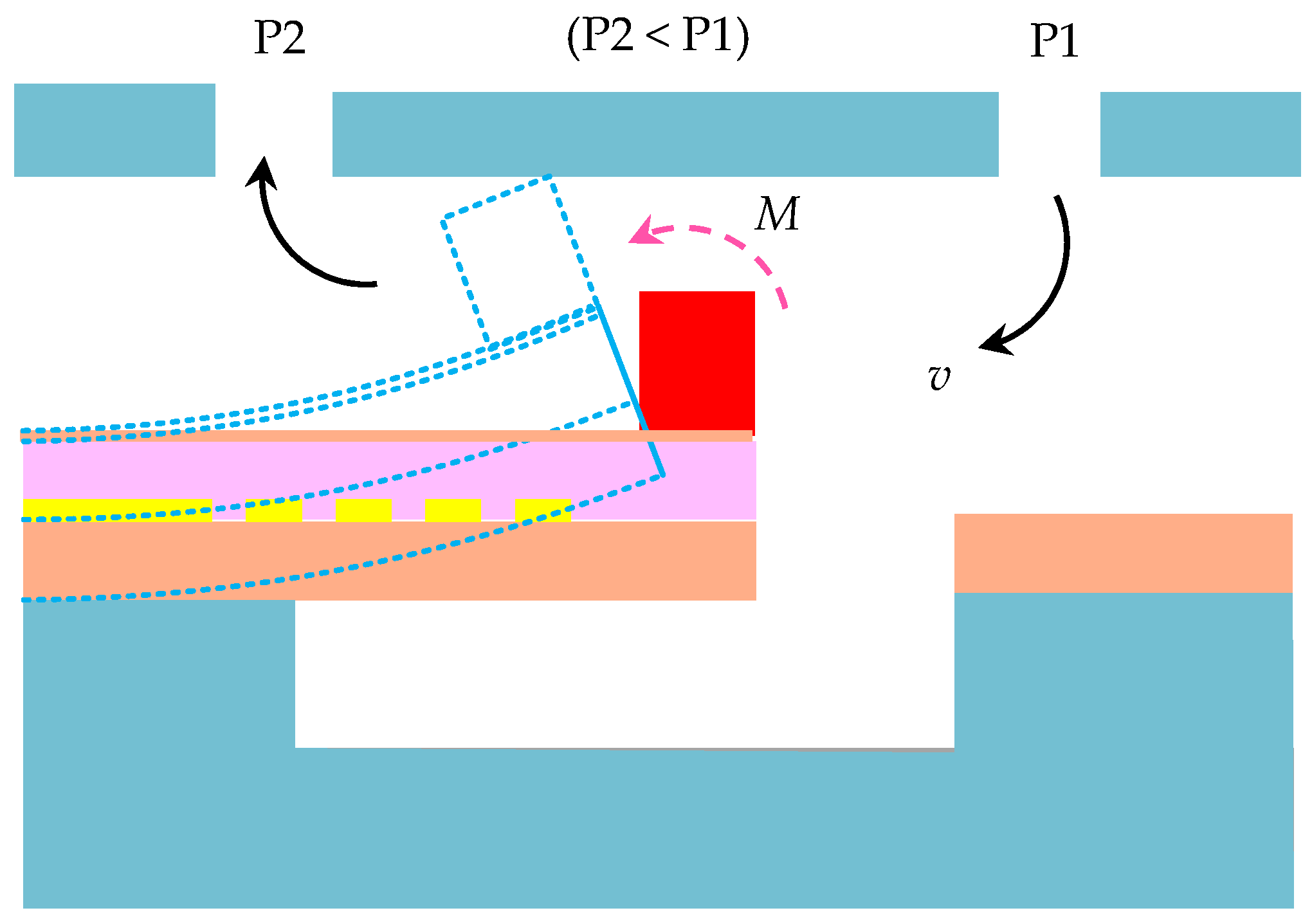
2.1. Design and Development of DSHPS
2.2. Characterization
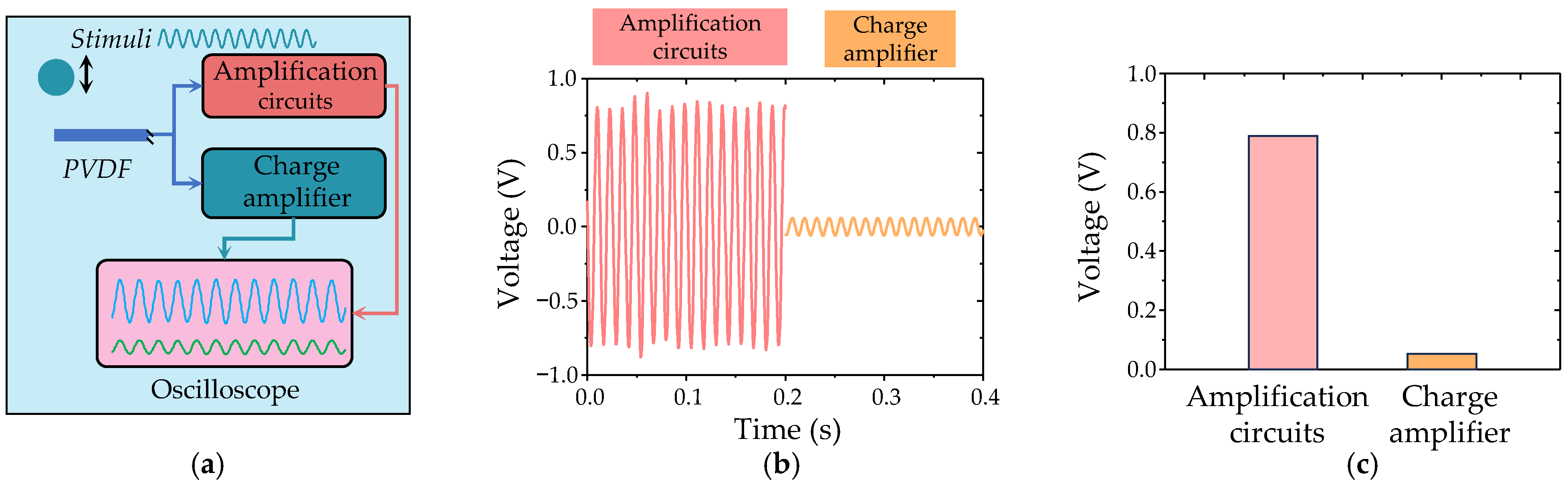
2.3. Pre-Amplification Circuit Evaluation
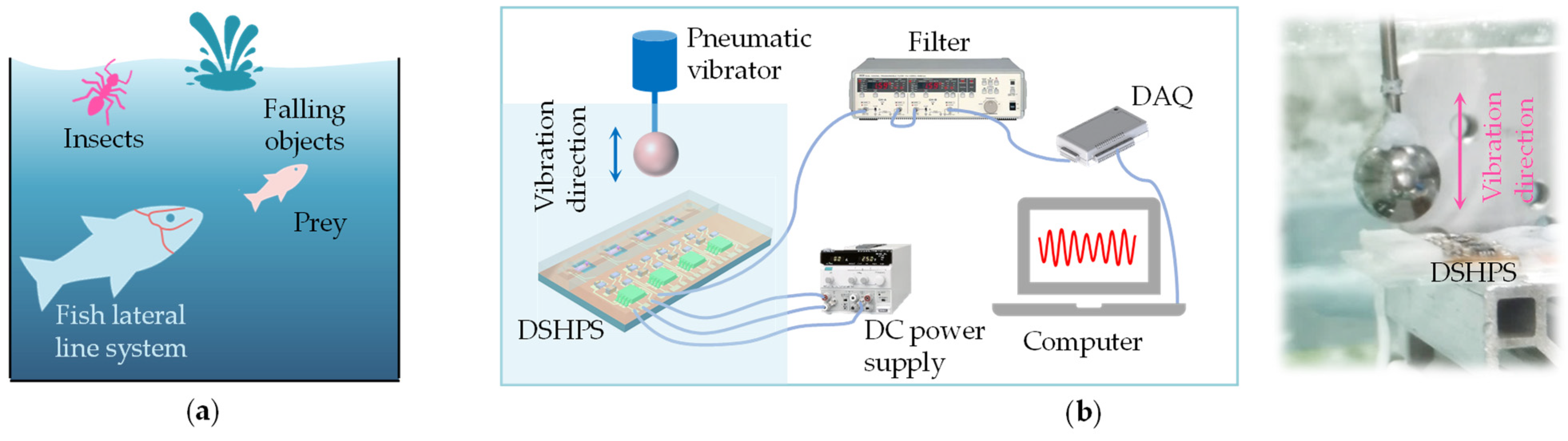
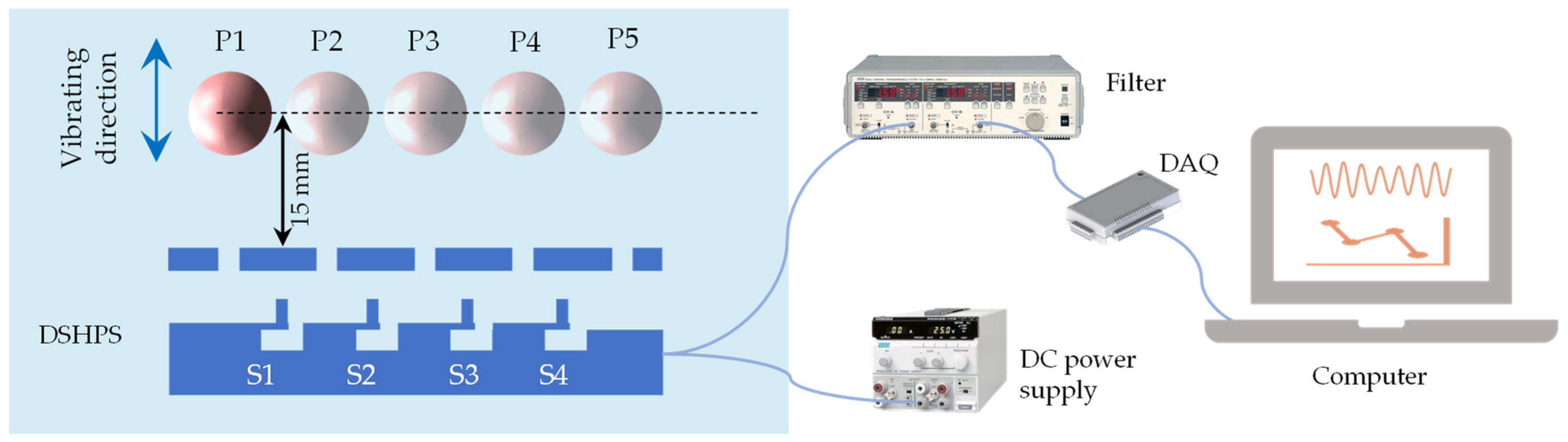
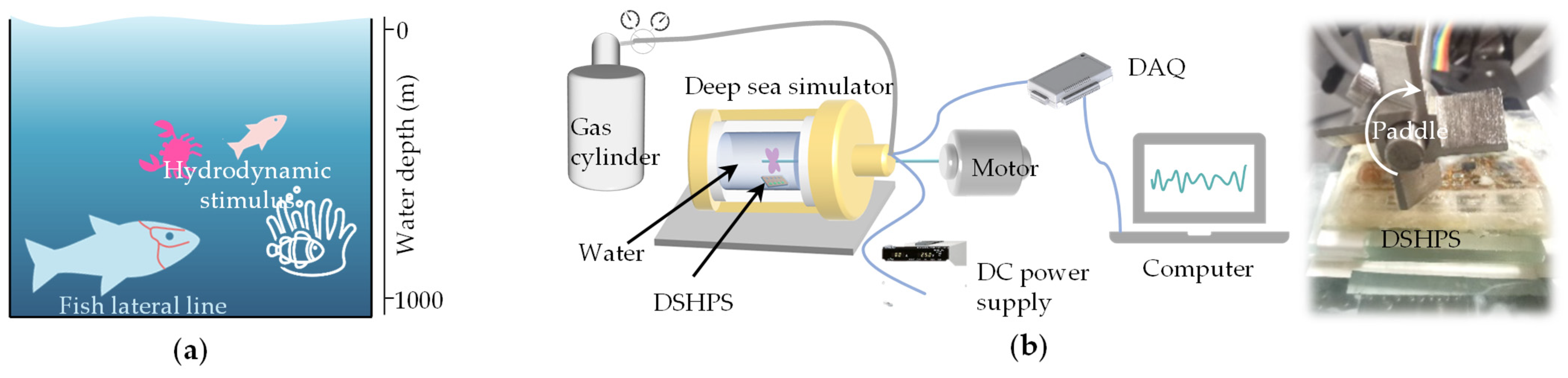
2.4. Dipole Source Experimental Platform Validation
2.5. Hydrodynamic Sensing Performance Evaluation of DSHPS
2.5.1. Shallow Water Experiment
2.5.2. Deep-Sea Environment Test
2.6. FEA of DSHPS
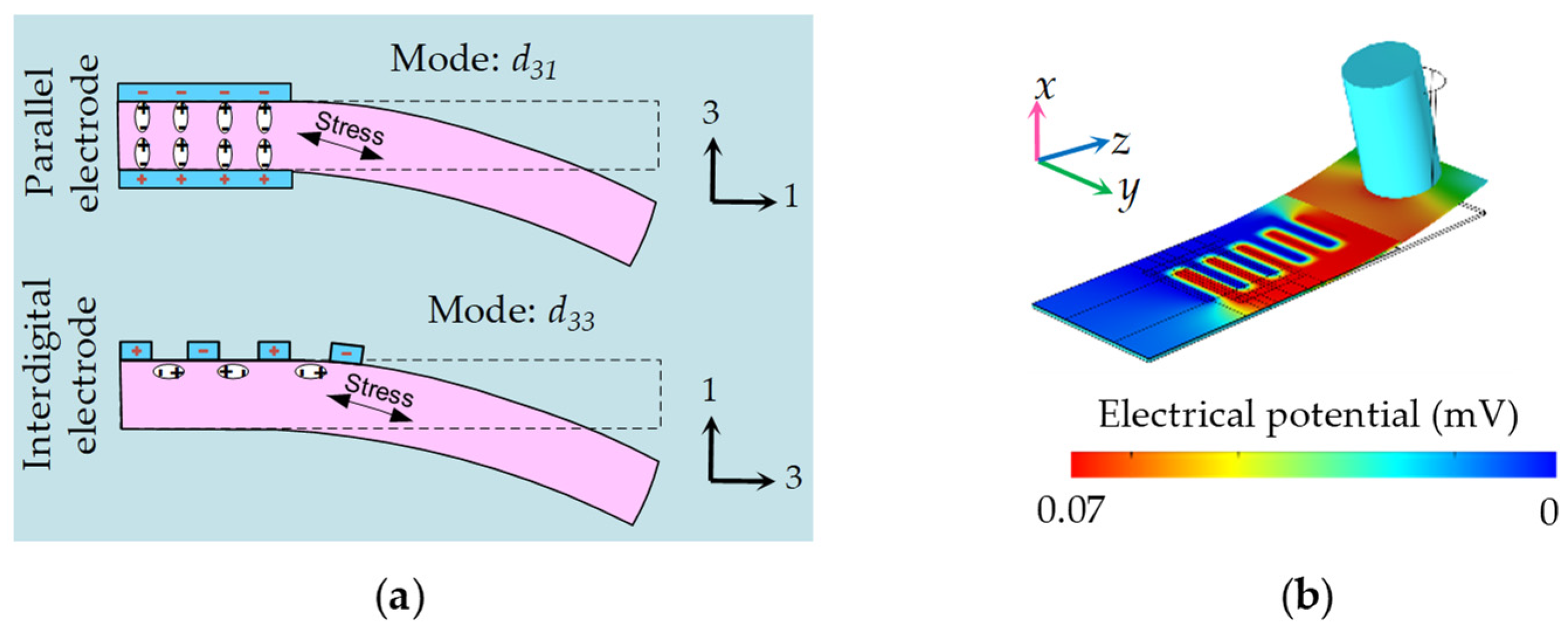
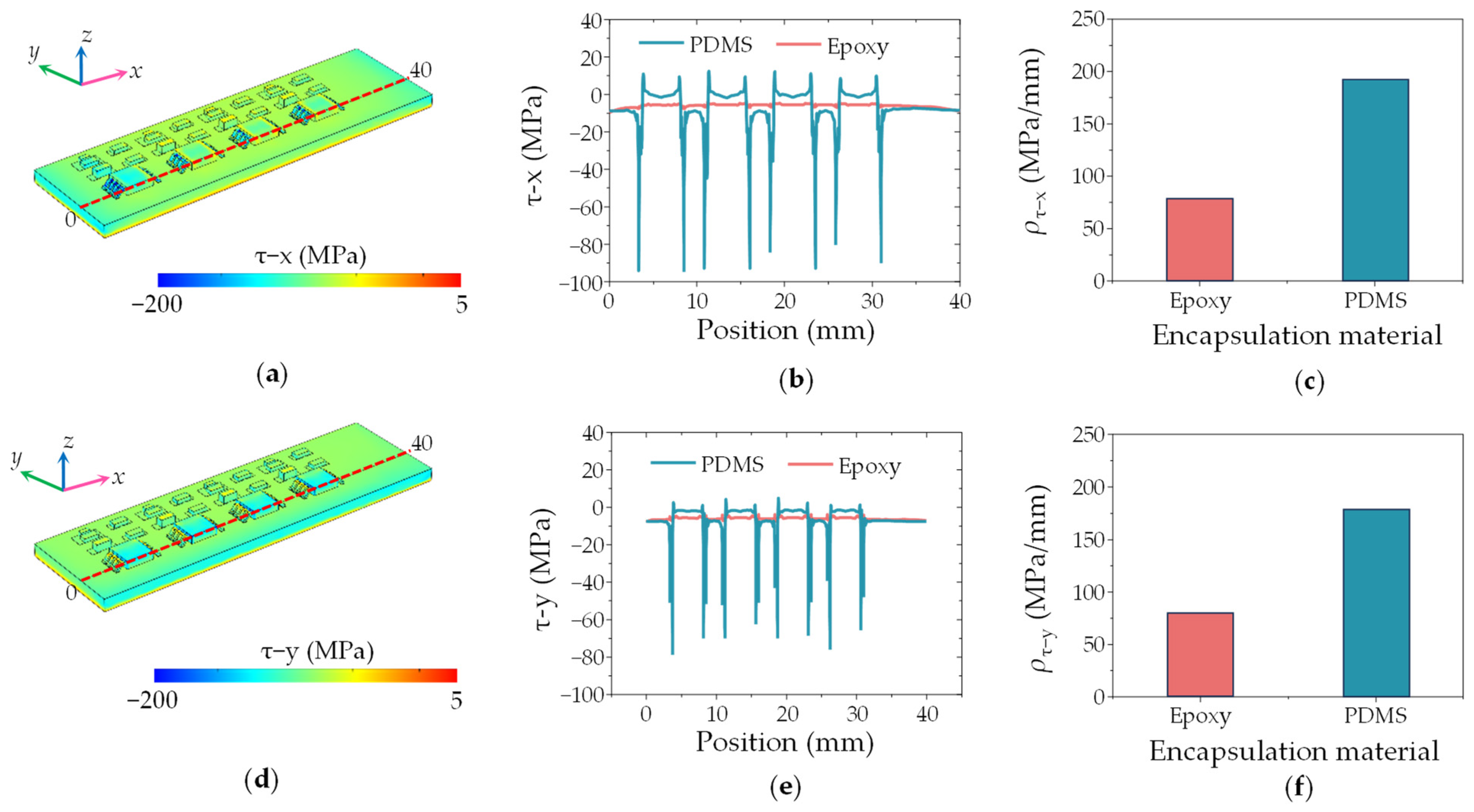
2.6.1. Three-Dimensional FEA Modeling of Interdigital Electrodes
2.6.2. Resonant Frequency Simulation of the Cantilever
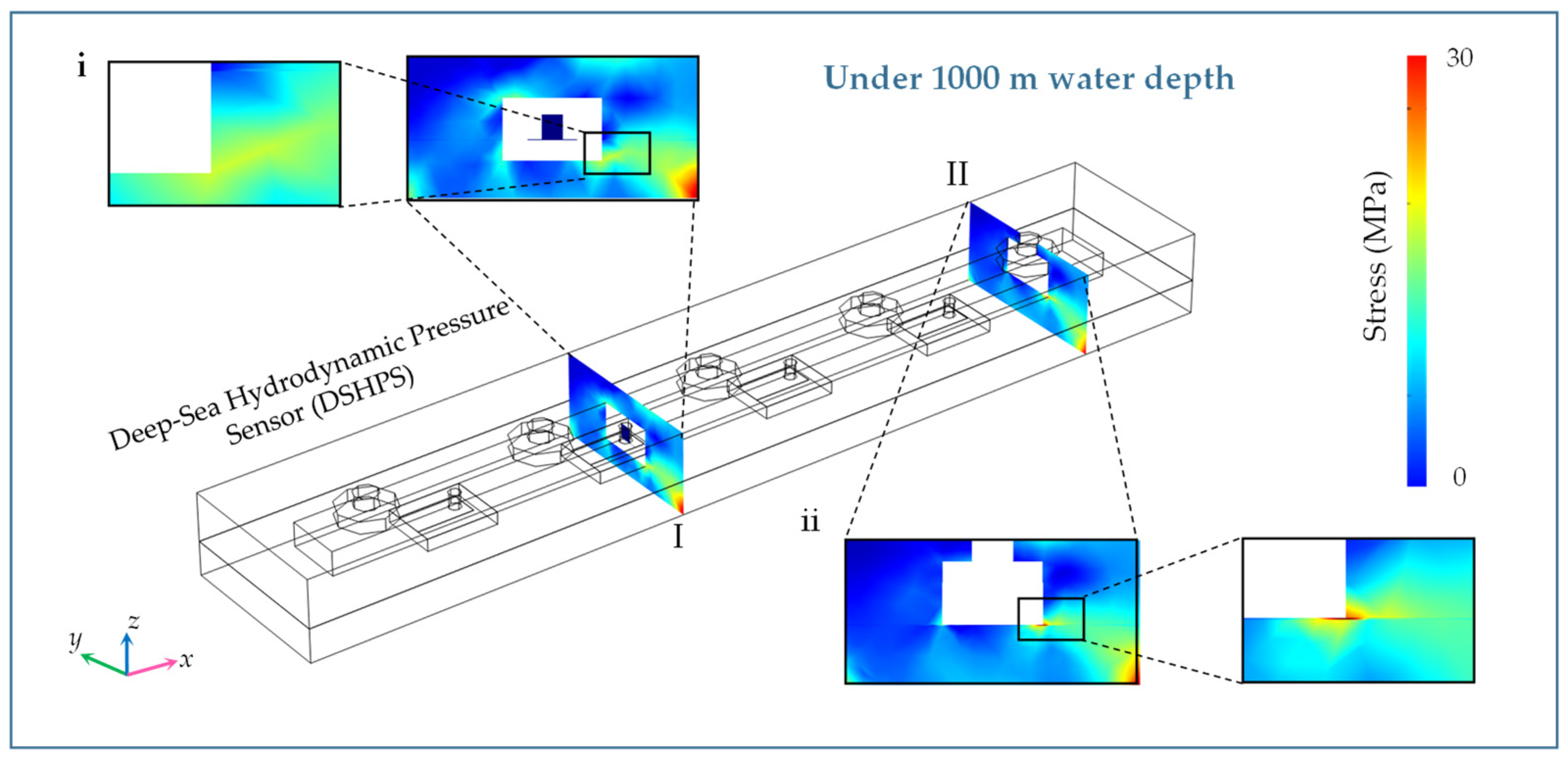
2.6.3. Deep-Sea High-Pressure Simulation
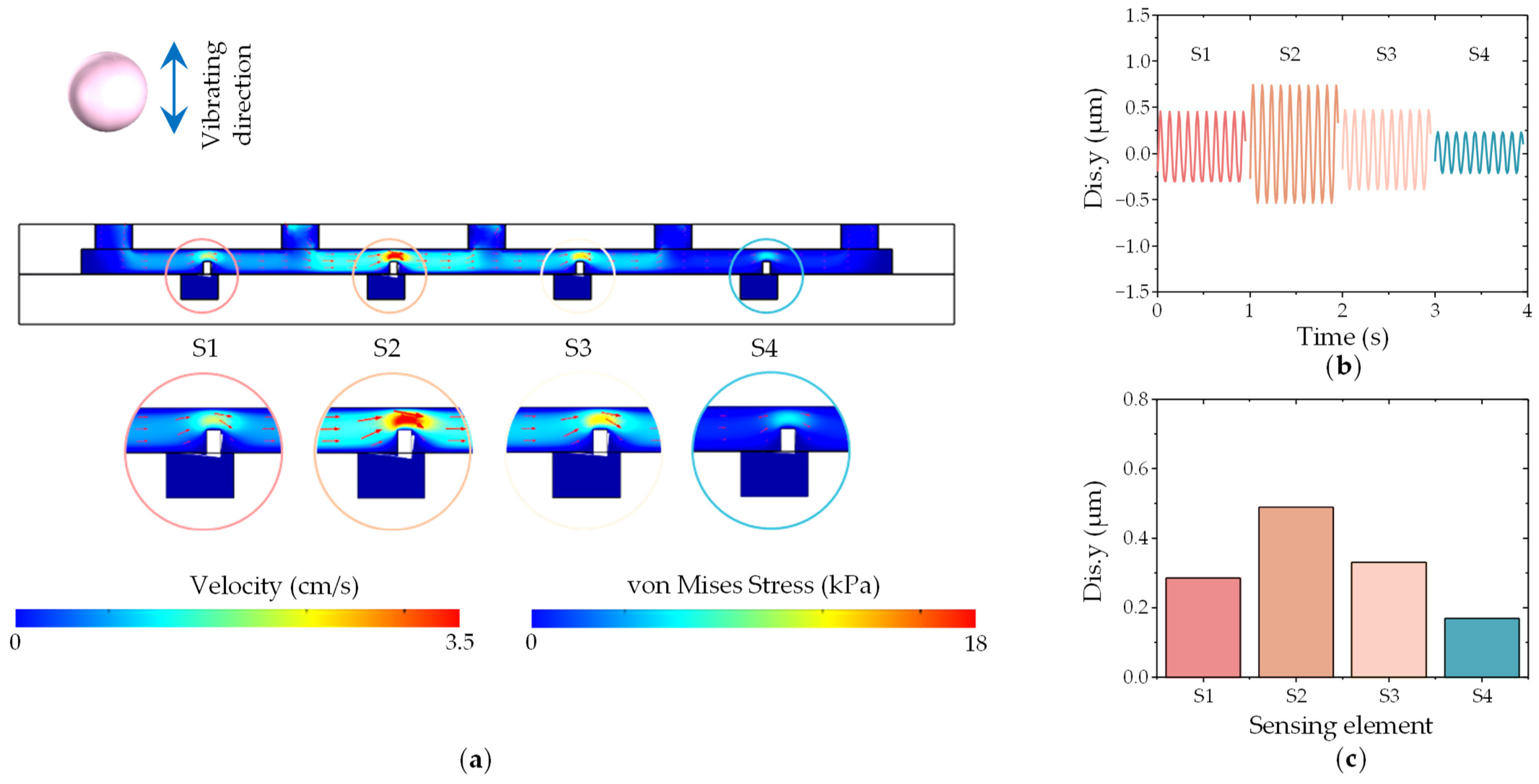
2.6.4. Vibrating Source Location Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
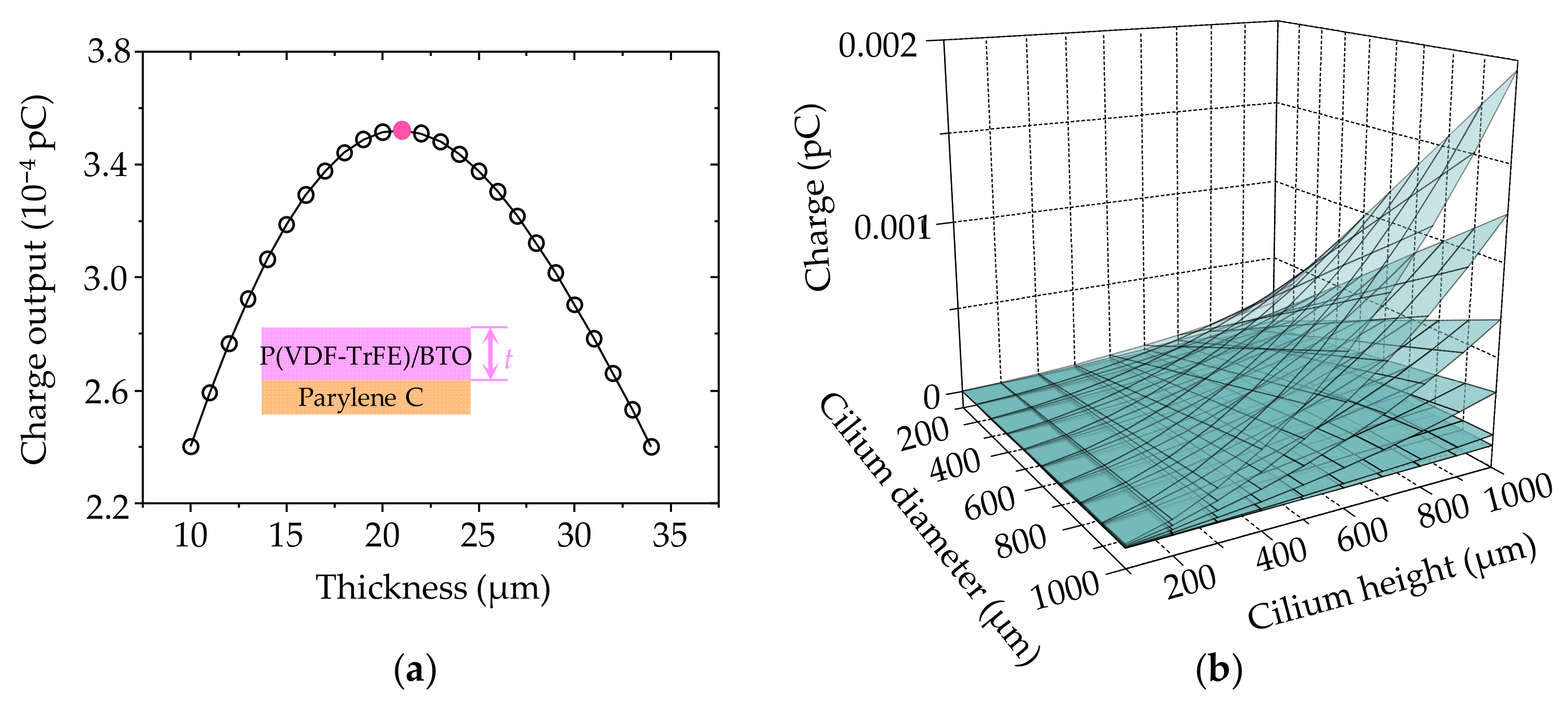
3.1. Material, Structural, Dimensional, and Package Optimization of DSHPS
3.2. Fabrication Results
3.3. Hydrodynamic Sensing Performance of DSHPS in Shallow Water Environment
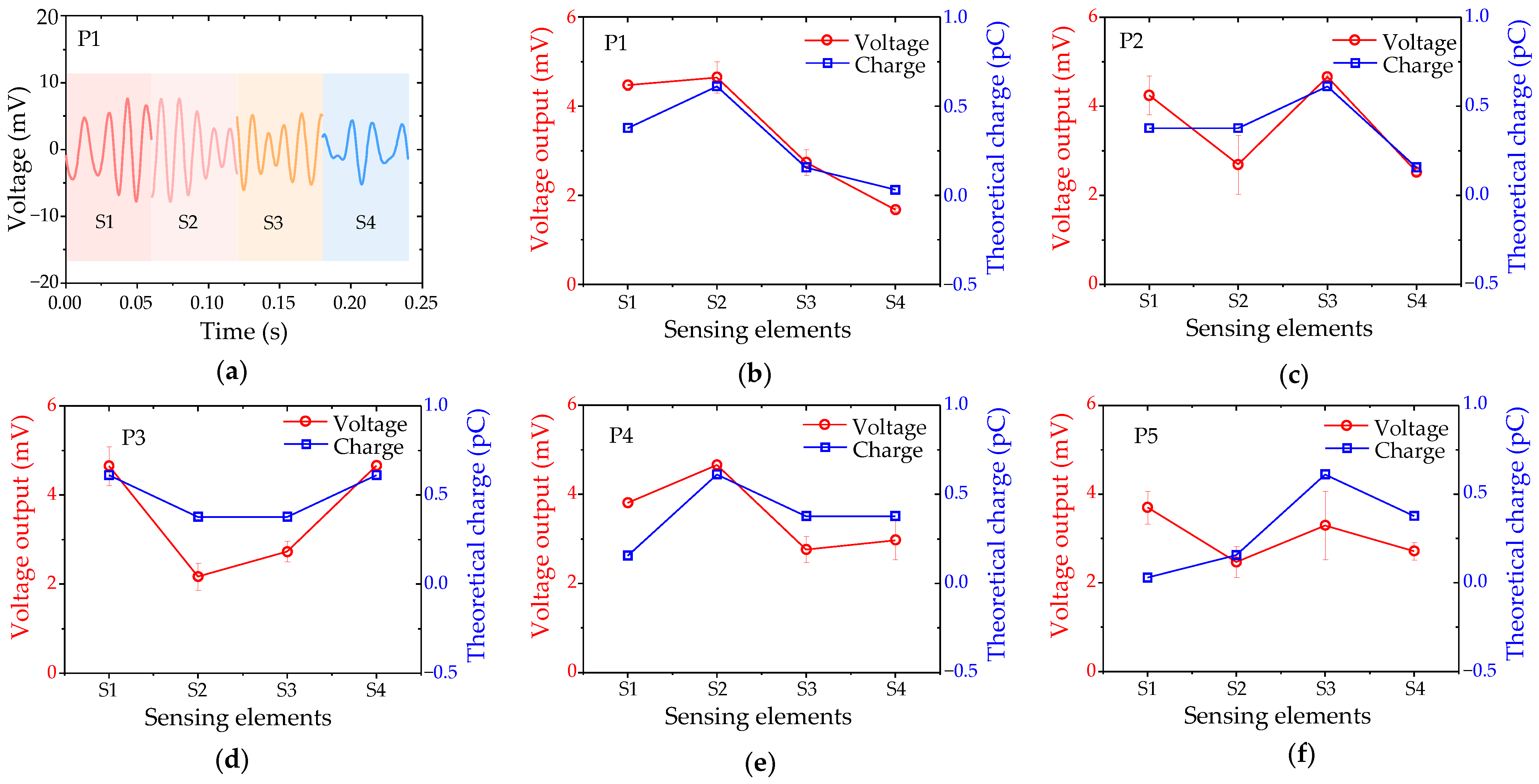
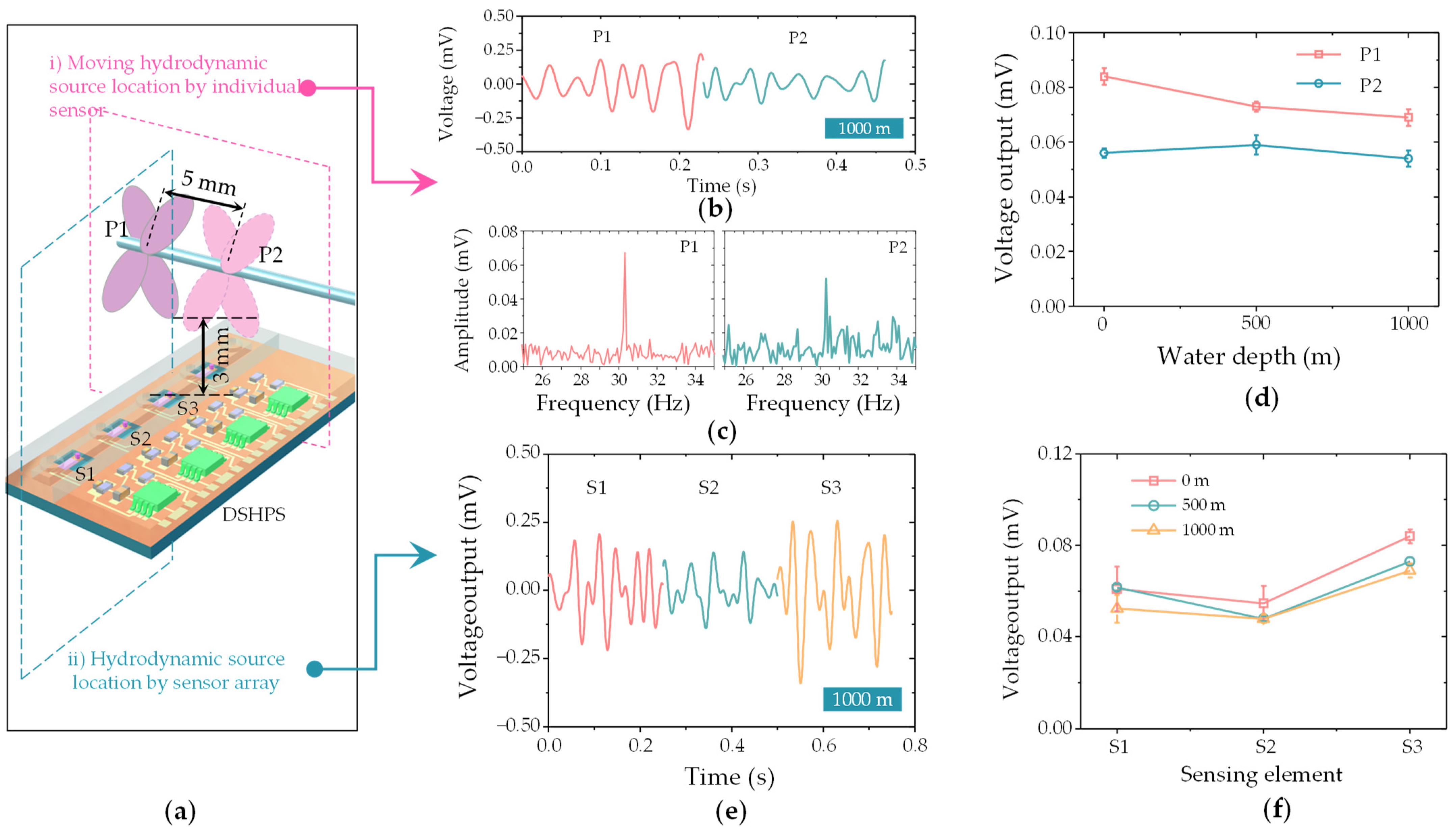
3.4. Object Localization Performance of DSHPS
3.5. Hydrodynamic Sensing Performance of DSHPS in Deep-Sea Environment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skålvik, A.M.; Saetre, C.; Frøysa, K.E.; Bjørk, R.N.; Tengberg, A. Challenges, Limitations, and Measurement Strategies to Ensure Data Quality in Deep-Sea Sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1152236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Multiphysics Co-Simulation and Experimental Study of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Energy Generation System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Panda, J.P.; Warrior, H.V. The Effects of Free Stream Turbulence on the Hydrodynamic Characteristics of an AUV Hull Form. Ocean Eng. 2019, 174, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Song, T.; Meng, Q. Development and Trials of a Novel Deep-Sea Multi-Joint Autonomous Underwater Vehicle. Ocean Eng. 2022, 265, 112558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponara, S. Sensing and Connection Systems for Assisted and Autonomous Driving and Unmanned Vehicles. Sensors 2018, 18, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Panda, J.P.; Warrior, H.V. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles over Sea-Beds with Complex Topography. Ocean Eng. 2020, 198, 106978. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Li, G.; Cao, X.; Li, T. Self-Powered Soft Robot in the Mariana Trench. Kexue Tongbao/Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2697–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelowska, G.; Kozaczka, E. Underwater Acoustic Imaging of the Sea. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 39, 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Rajapan, D.; Rajeshwari, P.M.; Zacharia, S. Importance of Underwater Acoustic Imaging Technologies for Oceanographic Applications—A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2022—Chennai, Chennai, India, 21–24 February 2022; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eren, F.; Pe’Eri, S.; Thein, M.W.; Rzhanov, Y.; Celikkol, B.; Swift, M.R. Position, Orientation and Velocity Detection of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) Using an Optical Detector Array. Sensors 2017, 17, 1741. [Google Scholar]
- Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Asadnia, M.; Miao, J.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Biomimetic Microsensors Inspired by Marine Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319475004. [Google Scholar]
- Peleshanko, S.; Julian, M.D.; Ornatska, M.; McConney, M.E.; LeMieux, M.C.; Chen, N.; Tucker, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Humphrey, J.A.C.; et al. Hydrogel-Encapsulated Microfabricated Haircells Mimicking Fish Cupula Neuromast. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2903–2909. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, J.C.; Baker, C.F.; Carton, A.G. The Lateral Line can Mediate Rheotaxis in Fish. Nature 1997, 389, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.M.; Zheng, X.; Bos, J.; Cao, M.; Triantafyllou, M.S.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Undulating Seal Whiskers Evolved Optimal Wavelength-to-Diameter Ratio for Efficient Reduction in Vortex-Induced Vibrations. Adv. Sci. 2023, 11, 2304304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.F.; Mazo-Mantilla, H.F.; Qaiser, N.; Khan, S.M.; Nassar, J.M.; Geraldi, N.R.; Duarte, C.M.; Hussain, M.M. Noninvasive Featherlight Wearable Compliant “Marine Skin”: Standalone Multisensory System for Deep-Sea Environmental Monitoring. Small 2019, 15, 1804385. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, T.; Gong, Z.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y. Flexible Conductivity-Temperature-Depth-Strain (CTDS) Sensor Based on a CNT/PDMS Bottom Electrode for Underwater Sensing. Flex. Print. Electron. 2022, 7, 045002. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, D. Flow Field Perception Based on the Fish Lateral Line System. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2019, 14, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Kamat, A.M.; Krushynska, A.O.; Cao, M.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. 3D Printed Graphene Piezoresistive Microelectromechanical System Sensors to Explain the Ultrasensitive Wake Tracking of Wavy Seal Whiskers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Liu, P. A Review of Artificial Lateral Line in Sensor Fabrication and Bionic Applications for Robot Fish. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2016, 2016, 4732703. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; Liu, C. A MEMS Flow Sensor Based on Fish Lateral Line Sensing System. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Song, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Niu, S.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L. Artificial Hair-Like Sensors Inspired from Nature: A Review. J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 409–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, G. Fish Lateral Line Inspired Flow Sensors and Flow-Aided Control: A Review. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 264–291. [Google Scholar]
- Asadnia, M.; Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Miao, J.; Warkiani, M.E.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Artificial Fish Skin of Self-Powered Micro-Electromechanical Systems Hair Cells for Sensing Hydrodynamic Flow Phenomena. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20150322. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.A.A.; Tan, X. A Pressure Gradient Sensor Inspired by the Canal Neuromasts of Fish. In Proceedings of the Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) XX, Denver, CO, USA, 4–8 March 2018; Volume 10594, p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhang, D. Development of a Flexible Artificial Lateral Line Canal System for Hydrodynamic Pressure Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Fu, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y. Canal-Type Artificial Lateral Line Sensor Array Based on Highly Aligned P(VDF-TrFE) Nanofibers. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 11th Annual International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Matsushima, Japan, 17–20 April 2016; pp. 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, D. BTO/P(VDF-TrFE) Nanofiber-Based Artificial Lateral Line Sensor with Drag Enhancement Structures. J. Bionic Eng. 2020, 17, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, N.J. The Lateral Line Systems of Three Deep-Sea Fish. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 49, 239–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lannoo, M.J.; Eastman, J.T.; Orr, J.W. Nervous and Sensory Systems in Sub-Arctic and Antarctic Snailfishes of the Genus Paraliparis (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes: Liparidae). Copeia 2009, 2009, 732–739. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, A.J.; Morris, J.P.; Linse, K.; Thatje, S. Plasticity in Shell Morphology and Growth among Deep-Sea Protobranch Bivalves of the Genus Yoldiella (Yoldiidae) from Contrasting Southern Ocean Regions. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 81, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Z.; Wang, S.; Wong, W.C.; Cai, X.; Feng, X.; Xiang, S.; Cai, Y.; Qian, P.Y.; Wang, N. An Insight into the Microstructures and Composition of 2,700 m-Depth Deep-Sea Limpet Shells. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 902815. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Yan, X.; Gong, L.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y. Improved Piezoelectric Sensing Performance of P(VDF-TrFE) Nanofibers by Utilizing BTO Nanoparticles and Penetrated Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7379–7386. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Lu, J.; Tan, C.W.; Miao, J.; Wang, Z. D33 Mode Piezoelectric Diaphragm Based Acoustic Transducer with High Sensitivity. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 189, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shan, X.; Xie, T.; Miao, J. A New Sensor Inspired by the Lateral-Line System of Fish Using the Self-Powered D33 Mode Piezoelectric Diaphragm for Hydrodynamic Sensing. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 141, 106476. [Google Scholar]
- Windsor, S.P.; Norris, S.E.; Cameron, S.M.; Mallinson, G.D.; Montgomery, J.C. The Flow Fields Involved in Hydrodynamic Imaging by Blind Mexican Cave Fish (Astyanax fasciatus). Part II: Gliding Parallel to a Wall. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3832–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiantzas, J.D. Explicit Power Formula for the Darcy–Weisbach Pipe Flow Equation: Application in Optimal Pipeline Design. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlapuk, M.; Bezusyak, O.; Volk, L.; Zhang, Z. Theoretical Research of Friction Factor in Hydraulically Smooth Pipes. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 280, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.I.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hwang, G.T.; Kang, S.J.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Lee, K.J. Piezoelectric BaTiO3 Thin Film Nanogenerator on Plastic Substrates. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4939–4943. [Google Scholar]
- Toprak, A.; Tigli, O. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting: State-of-the-Art and Challenges. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2014, 1, 031104. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.J.; Meng, E. Micromachining of Parylene C for BioMEMS. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 564–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.H.; Wong, C.K. Approximate Solutions for the Stresses in the Solder Joints of a Printed Circuit Board Subjected to Mechanical Bending. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2009, 51, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Micromachined Biomimetic Artificial Haircell Sensors. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2007, 2, S162. [Google Scholar]
- McConney, M.E.; Chen, N.; Lu, D.; Hu, H.A.; Coombs, S.; Liu, C.; Tsukruk, V.V. Biologically Inspired Design of Hydrogel-Capped Hair Sensors for Enhanced Underwater Flow Detection. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Klein, A.; Bleckmann, H.; Liu, C. Artificial Lateral Line Canal for Hydrodynamic Detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Goulet, J.; Engelmann, J.; Chagnaud, B.P.; Franosch, J.M.P.; Suttner, M.D.; Van Hemmen, J.L. Object Localization through the Lateral Line System of Fish: Theory and Experiment. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2008, 194, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D. PVDF Based Artificial Canal Lateral Line for Underwater Detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, Republic of Korea, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, P.; Xu, Y.; Hu, X.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, D. Constriction Canal Assisted Artificial Lateral Line System for Enhanced Hydrodynamic Pressure Sensing. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2019, 14, 066004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, V.I.; Hou, S.M.; Hover, F.S.; Lang, J.H.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Lateral-Line-Inspired Mems-Array Pressure Sensing for Passive Underwater Navigation; MIT Sea Grant Program; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, H.; Klein, A.; Bleckmann, H.; Holik, P.; Schmitz, S.; Siebke, G.; Tätzner, S.; Lacher, M.; Steltenkamp, S. μ-Biomimetic Flow-Sensors—Introducing Light-Guiding PDMS Structures into MEMS. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2015, 10, 36001. [Google Scholar]
- Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Asadnia, M.; Miao, J.M.; Barbastathis, G.; Triantafyllou, M.S. A Flexible Liquid Crystal Polymer MEMS Pressure Sensor Array for Fish-like Underwater Sensing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 115030. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Jiang, P. Synergistic Effect of Graphene Nanosheet and BaTiO3 Nanoparticles on Performance Enhancement of Electrospun PVDF Nanofiber Mat for Flexible Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, D.; Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Chen, S.H.; Miao, J.M.; Kwok, C.Y.; Triantafyllou, M.S.; Warkiani, M.E.; Asadnia, M. Characterization of Single Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Nanofiber for Flow Sensing Applications. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 105205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmijn, A.J. Hydrodynamic and Acoustic Field Detection. In Sensory Biology of Aquatic Animals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 83–130. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Ma, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, F.; Guo, S.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y. A Highly Sensitive Deep-Sea Hydrodynamic Pressure Sensor Inspired by Fish Lateral Line. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030190
Hu X, Ma Z, Gong Z, Zhao F, Guo S, Zhang D, Jiang Y. A Highly Sensitive Deep-Sea Hydrodynamic Pressure Sensor Inspired by Fish Lateral Line. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(3):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030190
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaohe, Zhiqiang Ma, Zheng Gong, Fuqun Zhao, Sheng Guo, Deyuan Zhang, and Yonggang Jiang. 2024. "A Highly Sensitive Deep-Sea Hydrodynamic Pressure Sensor Inspired by Fish Lateral Line" Biomimetics 9, no. 3: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030190
APA StyleHu, X., Ma, Z., Gong, Z., Zhao, F., Guo, S., Zhang, D., & Jiang, Y. (2024). A Highly Sensitive Deep-Sea Hydrodynamic Pressure Sensor Inspired by Fish Lateral Line. Biomimetics, 9(3), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9030190





