Bioinspired Synthesis and Characterization of Dual-Function Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Saccharopolyspora hirsuta: Exploring Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
2.4. Determination of ZnO-NP Cytotoxic Activity
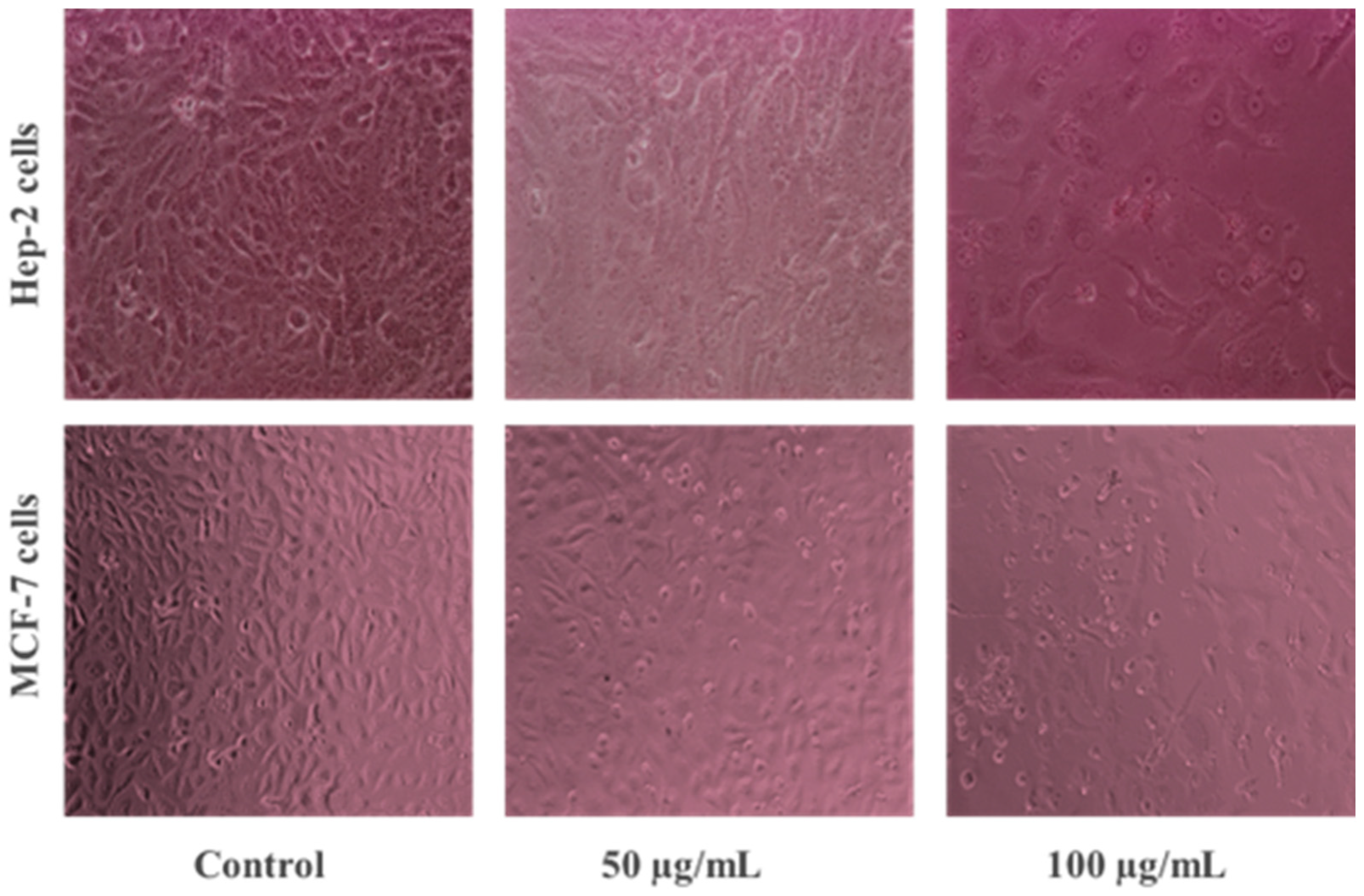
2.5. Morphological Analysis of ZnO-NP-Treated Cancer Cells
2.6. Antibacterial Activity and Minimum Inhibitory/Bactericidal Concentrations (MIC/MBC) of ZnO-NPs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
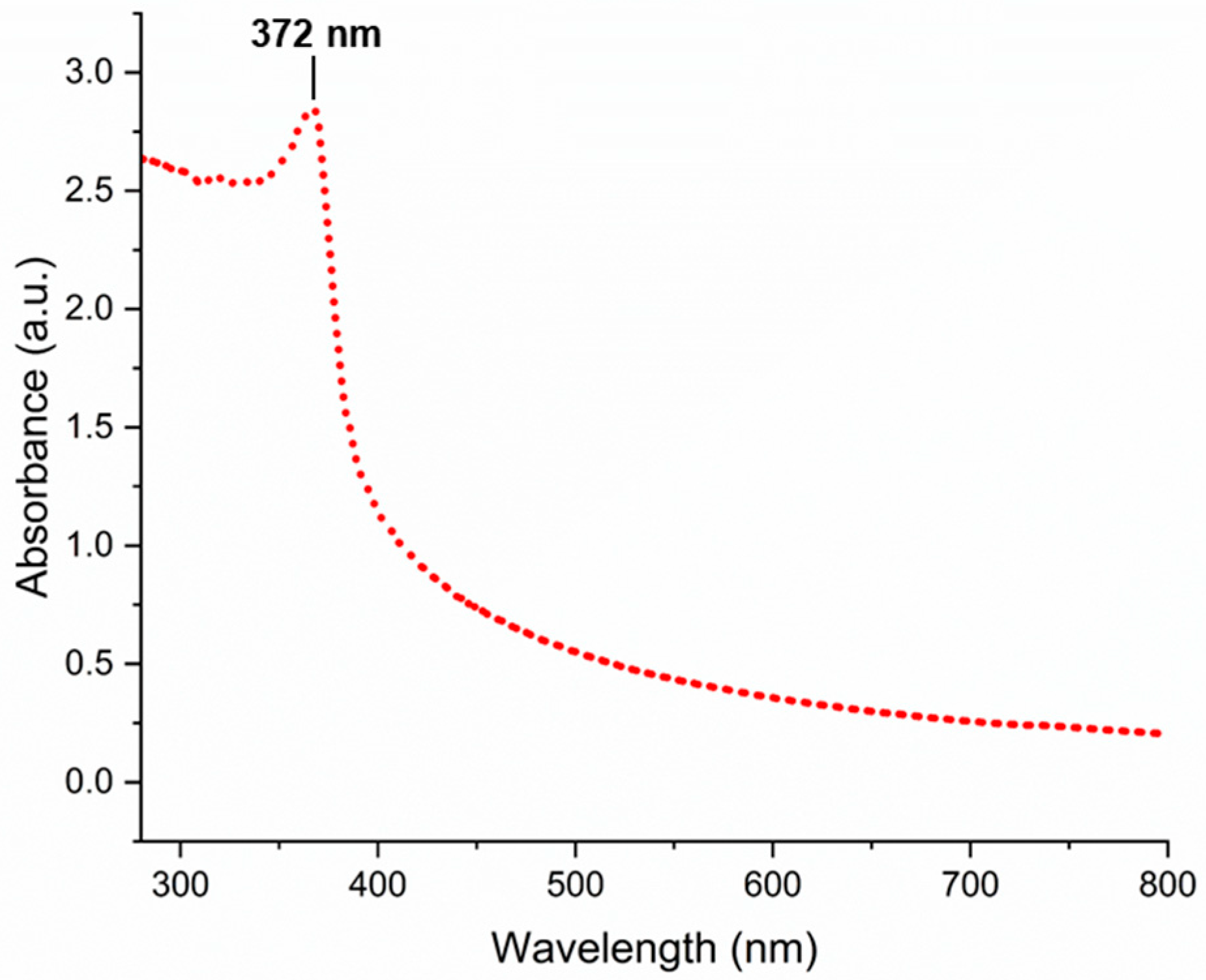
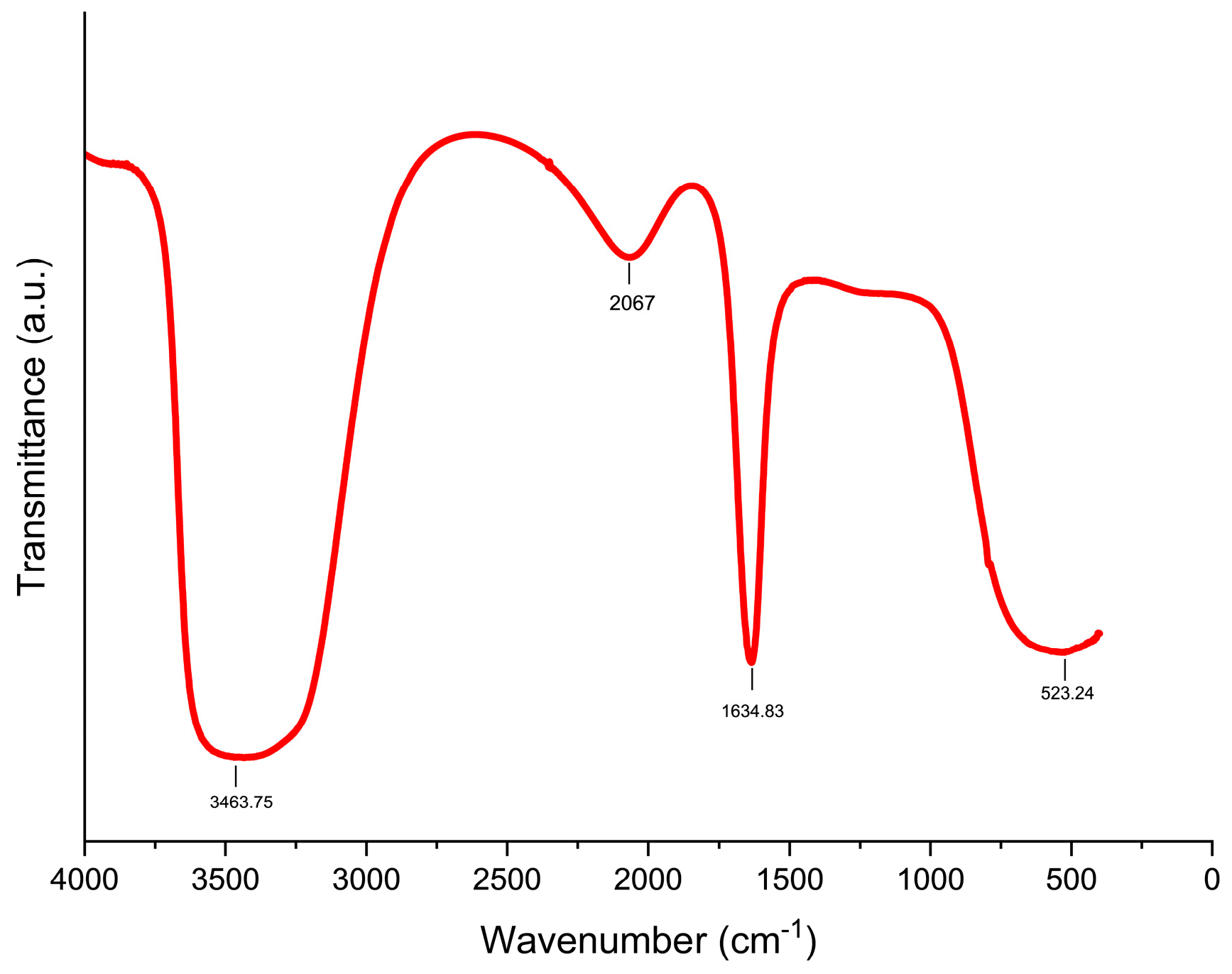
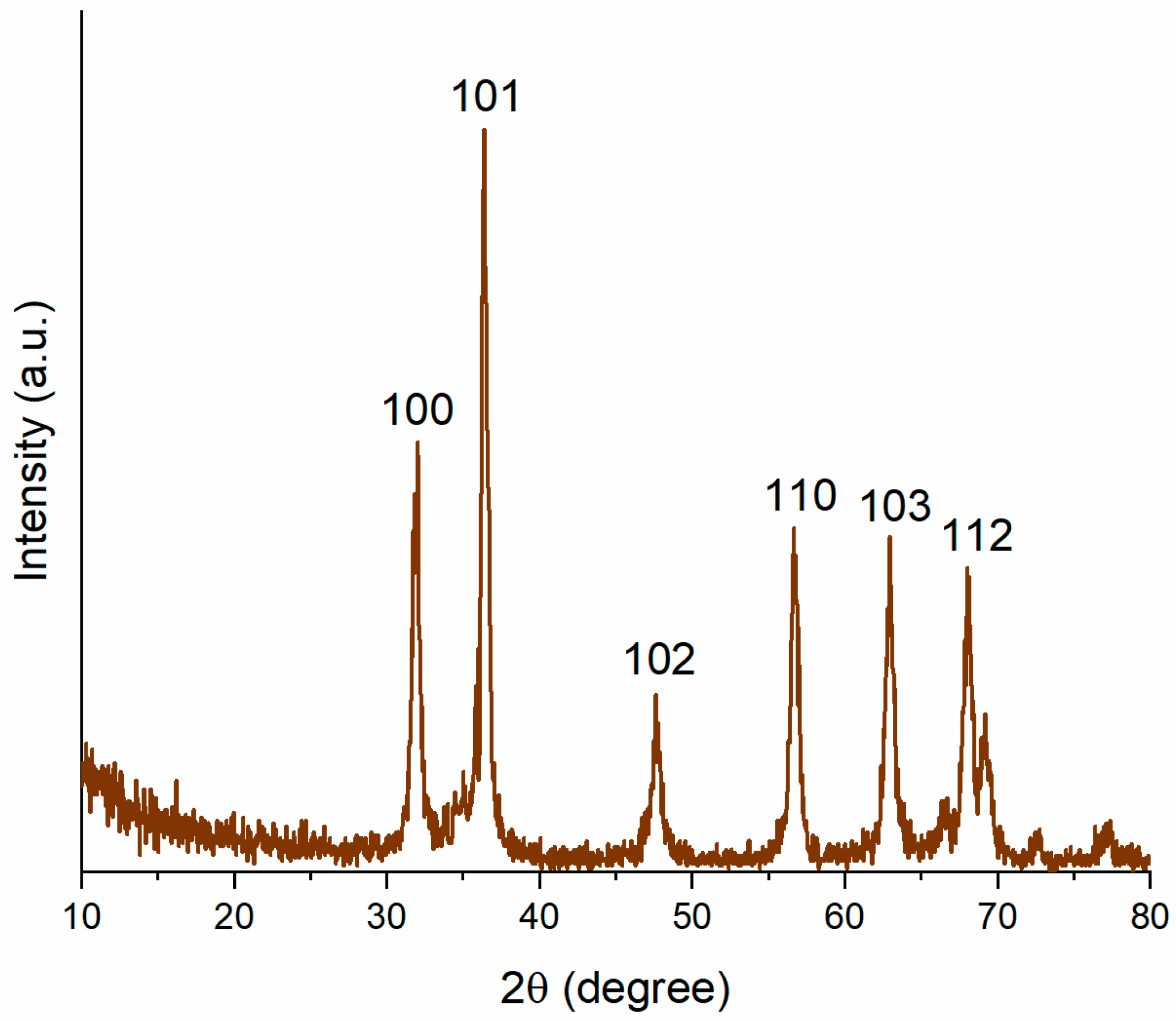
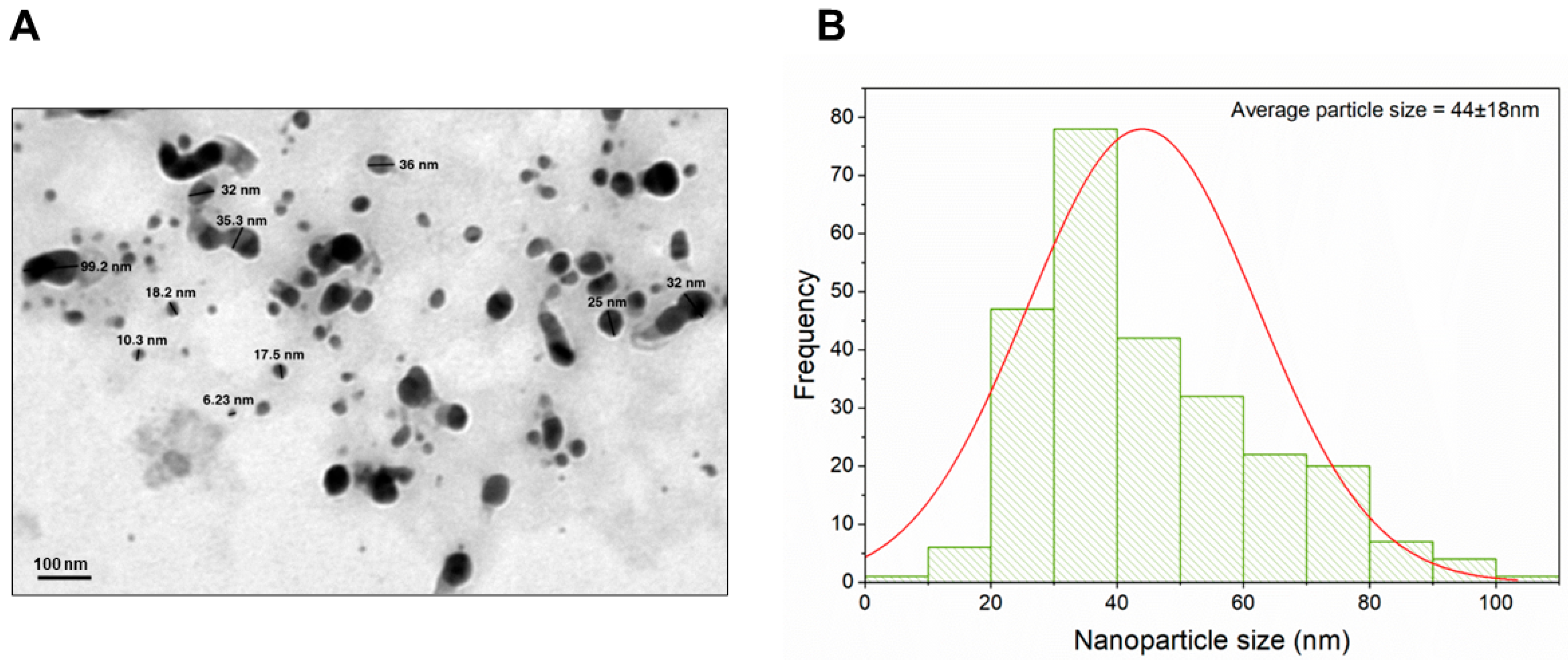
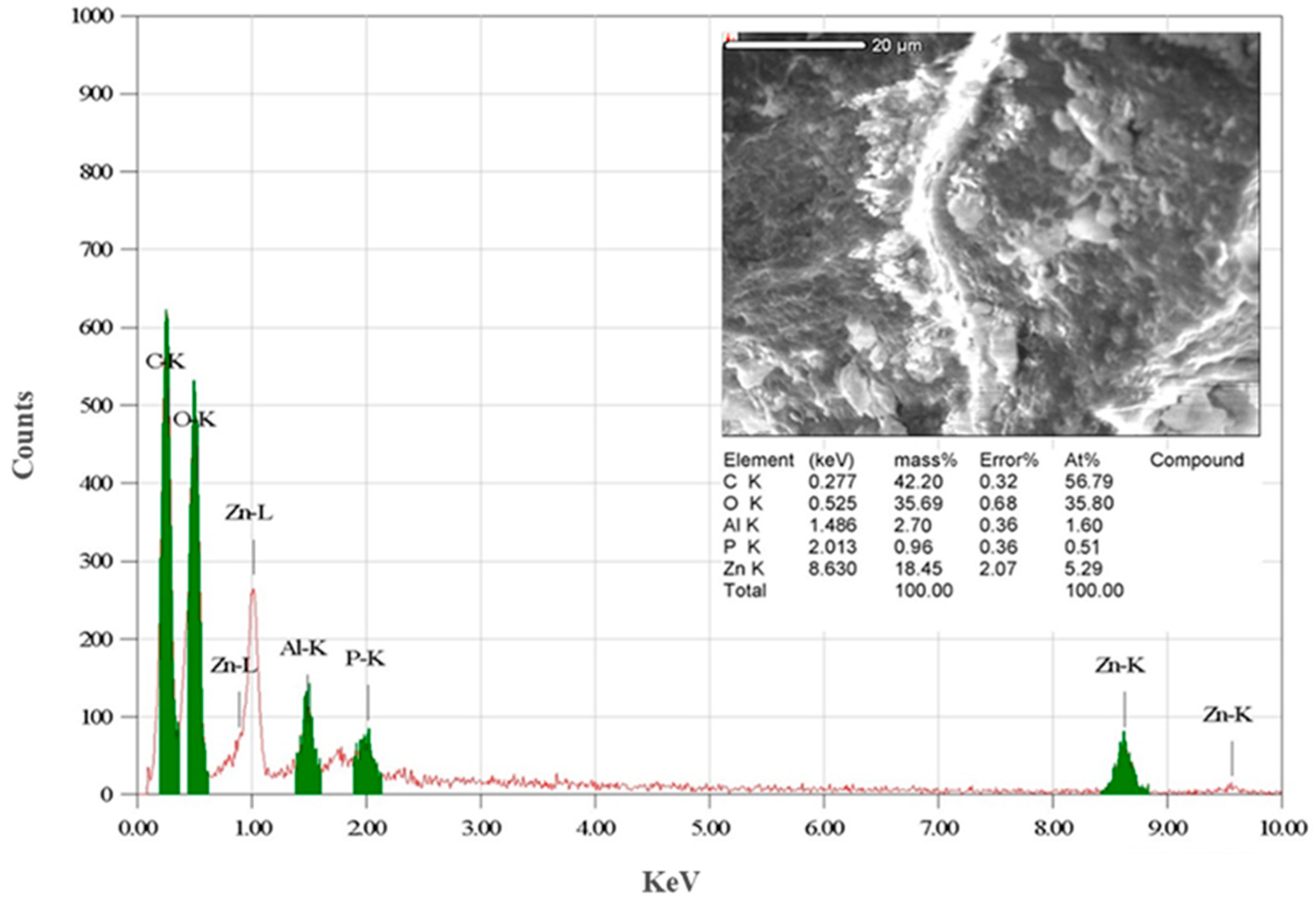
3.1. Characterization of Biogenically Synthesized ZnO-NPs Using S. hirsute
3.2. Evaluation of Biomedical Potential of S. hirsuta-Mediated ZnO-NPs
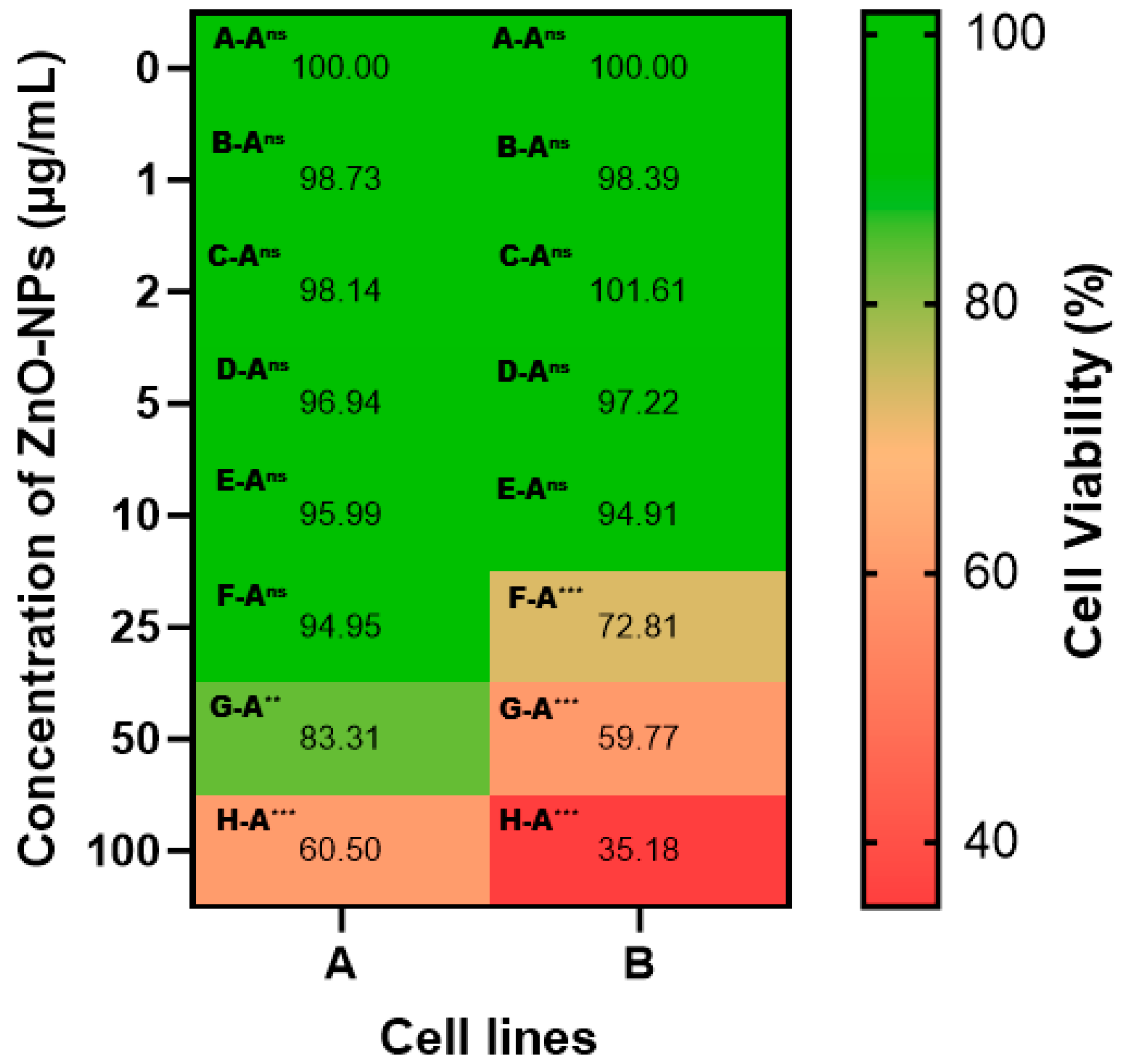
3.2.1. Anticancer Potential
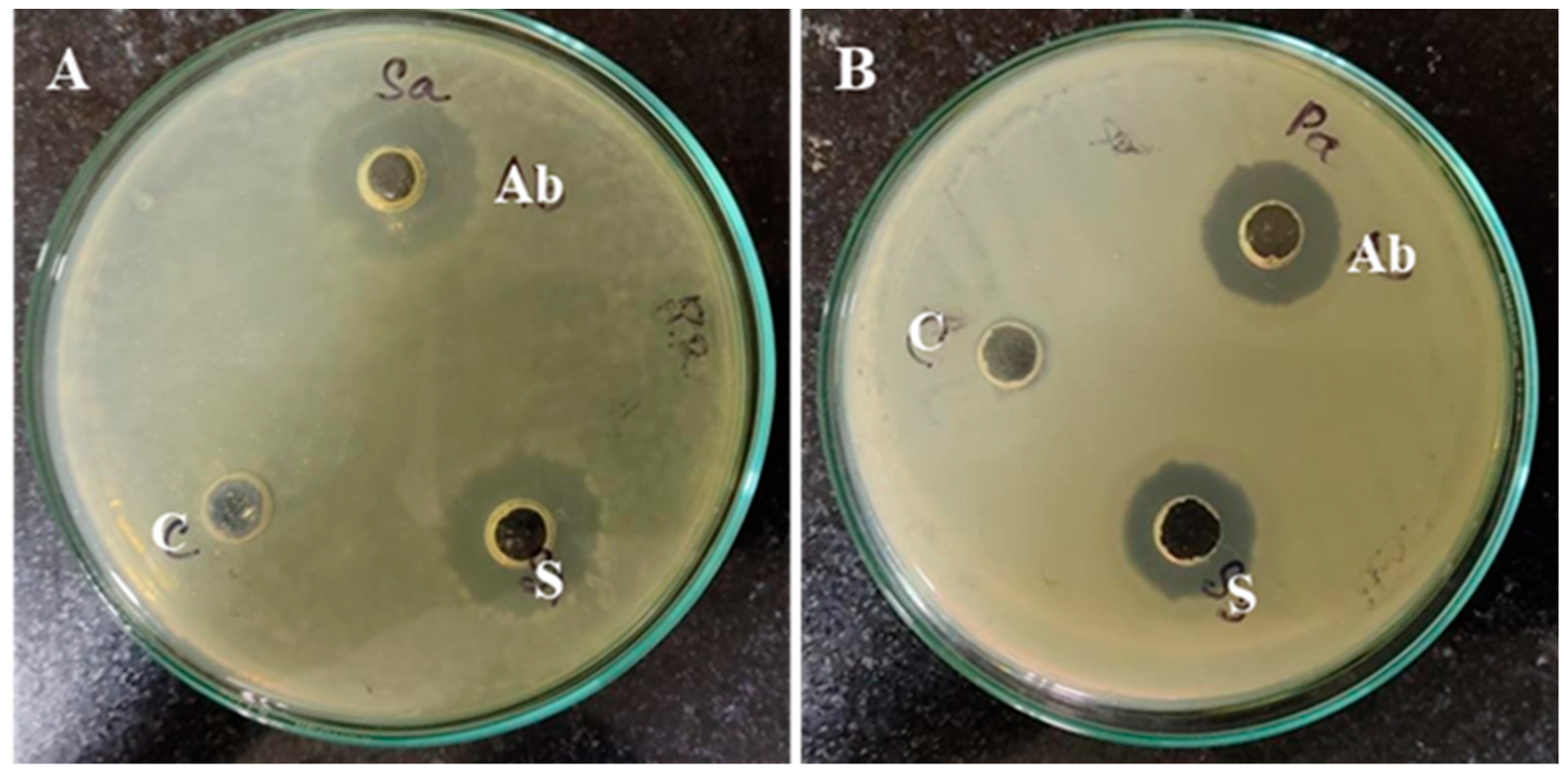
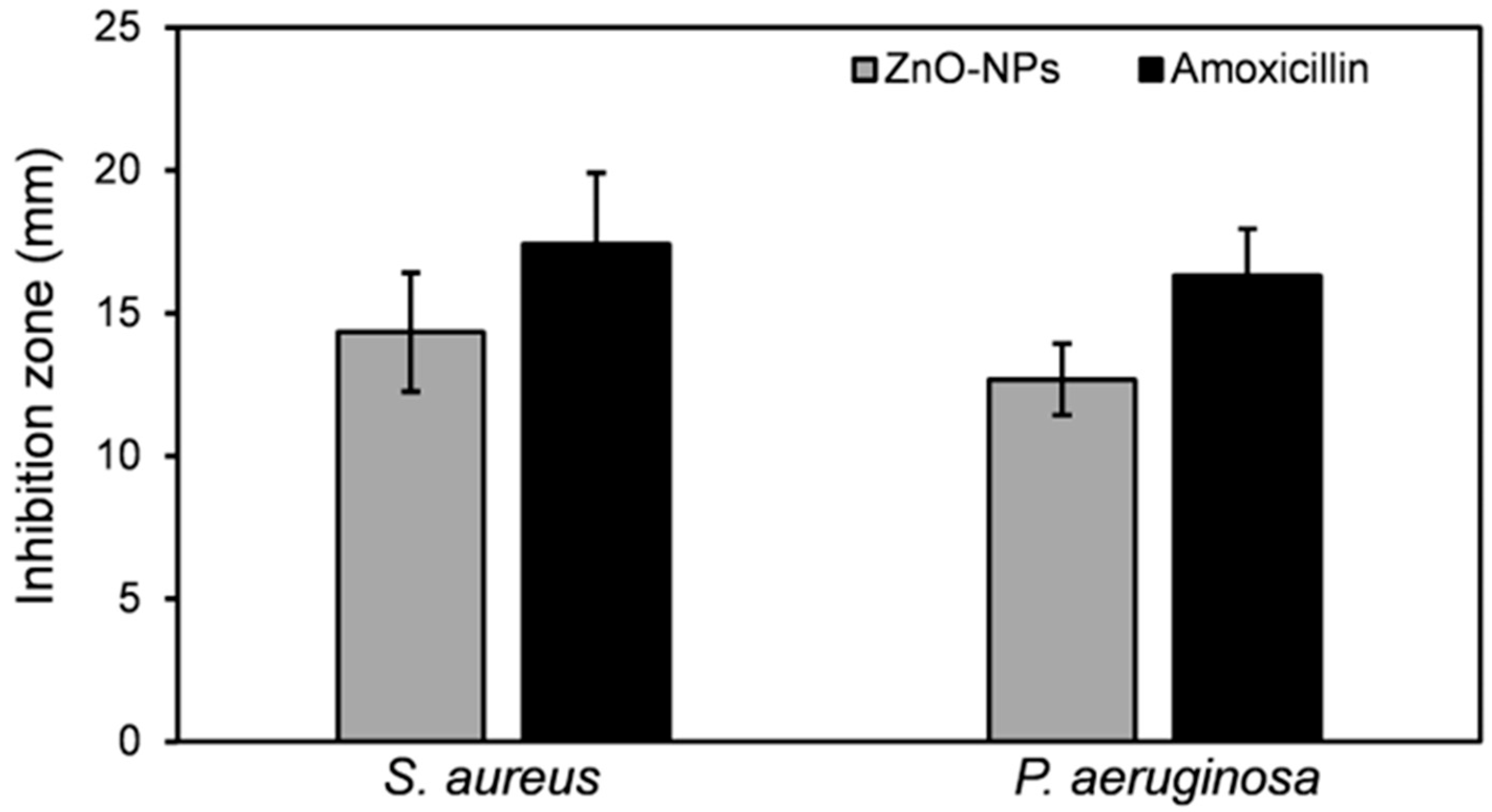
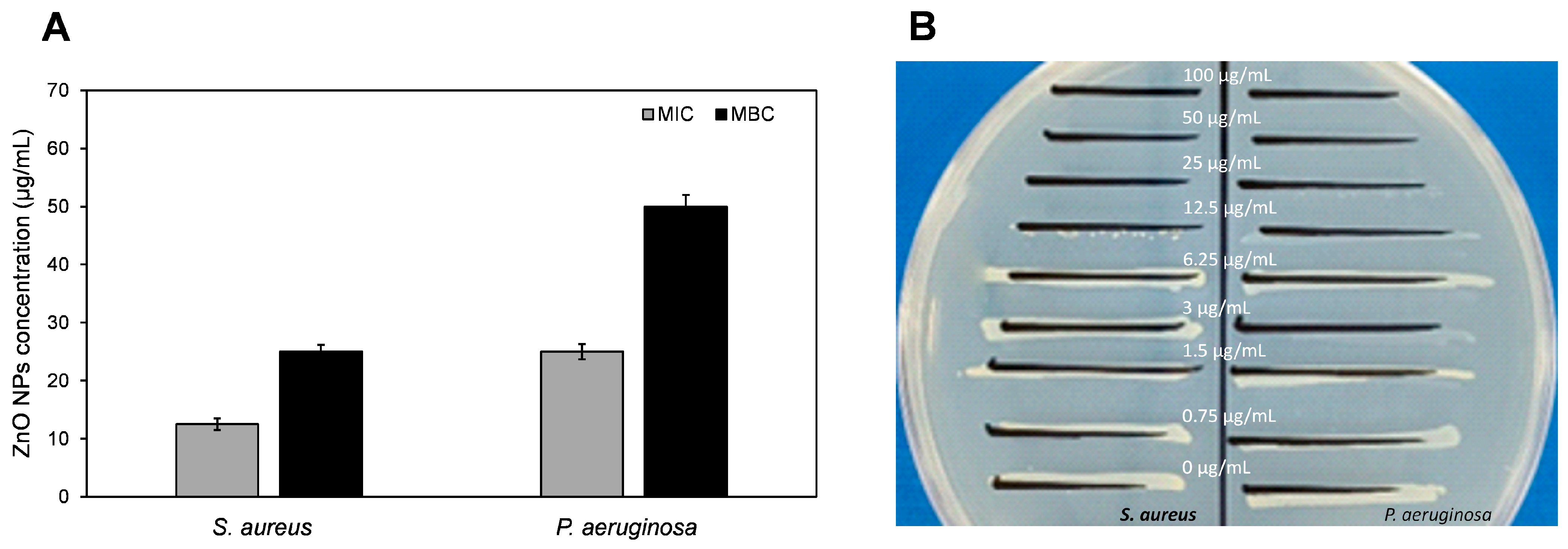
3.2.2. Antimicrobial Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rana, A.; Pathak, S.; Lim, D.-K.; Kim, S.-K.; Srivastava, R.; Sharma, S.N.; Verma, R. Recent advancements in plant-and microbe-mediated synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanomaterials and their emerging antimicrobial applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 8106–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkan, K.; Rumjit, N.P.; Ngangbam, A.K.; Vijayanand, S.; Nedumpillil, N.K. Novel advancements in the sustainable green synthesis approach of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) for antibacterial therapeutic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 499, 215528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.N.M.; Abu, R.; Mohamad, S.F.S.; Hipeni, A.R.H. Microorganism-Based Synthesis of Nanomaterials and Their Applications. Green. Synth. Nanomater. Biol. Environ. Appl. 2024, 2024, 46–70. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.H.; Shin, J.W.; Ki, M.-R.; Pack, S.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles on biosilica diatomite: Well-dispersed particle formation and reusability. Process Biochem. 2023, 125, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical-Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2020, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, J. Microbial synthesized nanoparticles in environment management. In Microbiome-Based Decontamination of Environmental Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 381–401. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, A.; Musheer, N.; Ashraf, S.; Saeed, S. Microbe-mediated nanoparticles: Potential nanobiofungicides. In Nanofungicides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Rathnakumar, S.S.; Noluthando, K.; Kulandaiswamy, A.J.; Rayappan, J.B.B.; Kasinathan, K.; Kennedy, J.; Maaza, M. Stalling behaviour of chloride ions: A non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of α-Endosulfan using CuO interface. Sens. Actuat B-Chem. 2019, 293, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.V.; Manemann, E.M.; Rowe, S.E.; Callender, M.C.; Soto, W. Marine actinomycetes, new sources of biotechnological products. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, S.N.; Thakur, D. Actinobacteria. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 443–476. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Lakshmi, S.; Amala, T.; Akula, D.; Rao, M.; Mohapatra, P.; Thekkangil, A. Actinomycetes as Nanofactories: Synthesis and Therapeutic Applications. In Concepts in Pharmaceutical Biotechnology and Drug Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 139–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kaari, M.; Manikkam, R.; Annamalai, K.K.; Joseph, J. Actinobacteria as a source of biofertilizer/biocontrol agents for bio-organic agriculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, A.; Nigam, A.; Saxena, A.; Dhingra, G.G.; Kumar, R. Microbial Bioproduction of Antiaging Molecules. Microb. Bioreact. Ind. Mol. 2023, 2023, 465–485. [Google Scholar]
- Subathra Devi, C.; Merlyn Keziah, S.; Jemimah Naine, S.; Mohanasrinivasan, V. Actinomycetes: Microbiology to systems biology. In Actinobacteria: Microbiology to Synthetic Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenpoth, M.; Engl, T. Defensive microbial symbionts in H ymenoptera. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaradoddi, J.S.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Kontro, M.H.; Ganachari, S.V.; Hallad, S.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Ramaswamy, V. Recent trends of actinomycetes in nanotechnology. In Actinobacteria: Ecology, Diversity, Classification and Extensive Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Koul, B.; Poonia, A.K.; Yadav, D.; Jin, J.O. Microbe-Mediated Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles: Applications and Future Prospects. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, S.; Inbaneson, S.J.; Uthiraselvam, M.; Priya, S.R.; Ramu, A.; Banerjee, M.B. Diversity of Endophytic Actinomycetes from Karangkadu Mangrove Ecosystem and Its Antibacterial Potential against Bacterial Pathogens. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 4, 294–296. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeswaran, S.; Veeraiyan, B.; Saravanan, V.; Manickam, E.; Danaraj, J. Biogenic facile green synthesis of actinobacterium exopolysaccharide-fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles for the diverse biomedical applications. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabairavi, N.; Raju, C.S.; Karthikeyan, C.; Varutharaju, K.; Nethaji, S.; Hameed, A.S.H.; Shajahan, A. Biosynthesis of novel zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using endophytic bacteria Sphingobacterium thalpophilum. In Recent Trends in Materials Science and Applications; Ebenezar, J., Ed.; Springer Proceedings in Physics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 4 May 2017; Volume 189, pp. 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Golinska, P.; Wypij, M.; Ingle, A.; Gupta, I.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. Biogenic synthesis of metal nanoparticles from actinomycetes: Biomedical applications and cytotoxicity. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 8083–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.; Rai, P.; Pandey, A. Chapter 1—Green synthesis of nanoparticles: A greener approach for a cleaner future. In Green Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Nanoparticles; Shukla, A.K., Iravani, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, S.S. A mini review on green nanotechnology and its development in biological effects. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Sivakumar, K.; Kim, S.-K. Actinobacteria mediated synthesis of nanoparticles and their biological properties: A review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, B.; Yu, L.; Tong, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhang, R.; Han, W.; Hao, Y.; Shangguan, L.; Zhang, S. Research progresses in preparation methods and applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 2023, 170316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.P.; Sapkota, D.R.; Jamarkattel, M.K.; Stillion, Q.; Collins, R.W. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles—Solution-Based Synthesis and Characterizations. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, J.; Revathi, D.; Dhanraj, G.; Ramasubburayan, R. Bioinspired Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles by marine-derived Streptomyces plicatus and its multifaceted biomedicinal properties. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 193, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajivgandhi, G.N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Kanisha, C.C.; Ramachandran, G.; Manoharan, N.; Alanzi, K.F. Identification of carbapenems resistant genes on biofilm forming K. Pneumoniae from urinary tract infection. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajivgandhi, G.; Gnanamangai, B.M.; Prabha, T.H.; Poornima, S.; Maruthupandy, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Li, W.-J. Biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using actinomycetes enhance the anti-bacterial efficacy against K. Pneumoniae. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjivkumar, M.; Silambarasan, T.; Ananthi, S.; ThangaTharani, K. Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles from an estuarine-associated actinobacterium Streptomyces spp. and its biotherapeutic applications. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameshbabu, D.; Sarojini, K.; Sanjivkumar, M.; Ramasubburayan, R.; Prakash, S.; Punitha, M.J.; Immanuel, G. Investigation on characterization, antifouling and cytotoxic properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles biosynthesized by a mangrove-associated actinobacterium Streptomyces olivaceus (MSU3). Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, A.B.; Moawad, R.; Abdallah, Y.; Abdel-Rasheed, M.; Zaher, A.M.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles promise anticancer and antibacterial activity in ovarian cancer. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholkamy, E.N.; Ahamd, M.S.; Yasser, M.M.; Eslam, N. Anti-microbiological activities of bio-synthesized silver Nano-stars by Saccharopolyspora hirsuta. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Mahadevan, S.; Arulmozhi, P.; Sriram, S.; Praseetha, P.K. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Atalantia monophylla leaf extracts: Characterization and antimicrobial analysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 82, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, H.K.; Banerjee, S.; Chaudhuri, U.; Lahiri, P.; Dasgupta, A.K. Cell selective response to gold nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar SR, S.; Rao, K.V.B. In-vitro antimicrobial activity of marine actinobacteria against multidrug resistance Staphylococcus aureus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, M.; Paliwal, J.S.; Singh, S.K.; Selvarajan, E.; Subathradevi, C.; Mohanasrinivasan, V. Studies on the inhibitory activity of biologically synthesized and characterized zinc oxide nanoparticles using lactobacillus sporogens against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 7, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Shivani; Bhojiya, A.A.; Singh, H.; Daima, H.K.; Singh, M.; Mohanty, S.R.; Stephen, B.J.; Singh, A. Microbial Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Photocatalytic Properties. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachaiappan, R.; Rajendran, S.; Ramalingam, G.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Priya, P.M.; Soto-Moscoso, M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Justicia adhatoda leaves and their antimicrobial activity. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2021, 44, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Rajput, J.; Kaith, B.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, S. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and study of their antibacterial and antifungal properties. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 519, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, N.; Patil, S.M.; Tandon, R.; Kumar, P. Magnetically recyclable silica-coated ferrite magnetite-K 10 montmorillonite nanocatalyst and its applications in O, N, and S-acylation reaction under solvent-free conditions. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21291–21300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Basri, M.S.; Mustapha, F.; Mazlan, N.; Ishak, M.R. Rice husk ash-based geopolymer binder: Compressive strength, optimize composition, FTIR spectroscopy, microstructural, and potential as fire-retardant material. Polymers 2021, 13, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.J.; Asokan, C.; Gadinas, N.; Kravchenko, P.; Getsoian, A.B.; Christopher, P.; Hibbitts, D. Theoretical and experimental characterization of adsorbed CO and NO on γ-Al2O3-supported Rh nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 19733–19755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dappula, S.S.; Kandrakonda, Y.R.; Shaik, J.B.; Mothukuru, S.L.; Lebaka, V.R.; Mannarapu, M.; Amooru, G.D. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Andrographis alata: Characterization, optimization and assessment of their antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic and anti-Alzheimer’s properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1273, 134264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Xie, F.; Ma, X.; Niu, B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Long, D. General synthesis of ultrafine metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for ultrahigh-flux nanofiltration membrane. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalithamba, H.S.; Raghavendra, M.; Uma, K.; Yatish, K.V.; Mousumi, D.; Nagendra, G. Capsicum annuum Fruit Extract: A Novel Reducing Agent for the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Multifunctional Applications. Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Oves, M.; Alajmi, M.F.; Hussain, I.; Amir, S.; Ahmed, J.; Rehman, M.T.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Ali, I. Biogenesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pandanus odorifer leaf extract: Anticancer and antimicrobial activities. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15357–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Chimal, R.; García-Pérez, V.I.; Álvarez-Pérez, M.A.; Tavera-Hernández, R.; Reyes-Carmona, L.; Martínez-Hernández, M.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.Á. Influence of the particle size on the antibacterial activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using Dysphania ambrosioides extract, supported by molecular docking analysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.T.; Mostafa, A.A.-F.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Al-Otibi, F.O. Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles with potential synergistic activity with common antifungal agents against multidrug-resistant candidal strains. Crystals 2022, 12, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, J.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Mohan, S.K.; Wang, C.; Yu, X. Synthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles from Marsdenia tenacissima inhibits the cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in laryngeal cancer cells (Hep-2). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 201, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, R.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Saquib, Q.; Dwivedi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Shin, H.-S. ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumari, D.; Deepa, R.; Mahalakshmi, V.; Subhashini, P.; Lakshminarayan, N. Anti cancer activity of ZnO nanoparticles on MCF7 (breast cancer cell) and A549 (lung cancer cell). ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 5418–5421. [Google Scholar]
- Boroumand Moghaddam, A.; Moniri, M.; Azizi, S.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Bin Ariff, A.; Navaderi, M.; Mohamad, R. Eco-friendly formulated zinc oxide nanoparticles: Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in the MCF-7 cancer cell line. Genes 2017, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.; Hashim, M.; Malik, S.A.; Khan, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hano, C. Recent advances in zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for cancer diagnosis, target drug delivery, and treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.K.; Sharma, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.; Sultana, S.; Dhawan, A. ROS-mediated genotoxicity induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, T.J.; Wick, P.; Manser, P.; Spohn, P.; Grass, R.N.; Limbach, L.K.; Bruinink, A.; Stark, W.J. In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: Comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Env. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, V.; Bamane, S. PEG-beta-cyclodextrin functionalized zinc oxide nanoparticles show cell imaging with high drug payload and sustained pH responsive delivery of curcumin in to MCF-7 cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Anderson, D.; Dhawan, A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2). Apoptosis 2012, 17, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagamani, K.; Muthukrishnan, P.; Saravanakumar, K.; Shankar, K.; Kathiresan, A. Photocatalytic degradation of environmental perilous gentian violet dye using leucaena-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticle and its anticancer activity. Rare Met. 2019, 38, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Murali, M.; Prasad, D.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alomary, M.N.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Singh, S.B.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Ashwini, B.S. Cinnamomum verum bark extract mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their antibacterial potentiality. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, M.-R.; Kim, S.H.; Park, T.I.; Pack, S.P. Self-Entrapment of Antimicrobial Peptides in Silica Particles for Stable and Effective Antimicrobial Peptide Delivery System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Mahendra, C.; Rajashekar, N.; Sudarshana, M.; Raveesha, K.; Amruthesh, K. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles from Ceropegia candelabrum L.—An endemic species. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 179, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Wahab, S.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; Nisar, N.; Alraey, Y.; Alqahtani, A.; Mir, M.A.; Irfan, S.; Saeed, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticle: An effective antibacterial agent against pathogenic bacterial isolates. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Daskalakis, N.; Jeuken, L.; Povey, M.; O’neill, A.J.; York, D.W. Mechanistic investigation into antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles against E. coli. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010, 12, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Gul, A.; Jehan, S.; Khan, Z.; Saeed, J.; Shirazi, R.R.; Raziq, A.; Waseem Khan, M.; Ullah, H. Biodiversity of Actinomycetes and Their Secondary Metabolites: A Comprehensive Review. J. Adv. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 6, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebbah, F.Z.; Belyagoubi, L.; Abdelouahid, D.E.; Kherbouche, F.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V.; Ravindran, B. Isolation and characterization of novel Streptomyces strain from Algeria and its in-vitro antimicrobial properties against microbial pathogens. J. Infect. Public. Health 2021, 14, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sholkamy, E.N.; Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Khalifa, H.O.; Ki, M.-R.; Pack, S.P. Bioinspired Synthesis and Characterization of Dual-Function Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Saccharopolyspora hirsuta: Exploring Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080456
Sholkamy EN, Abdelhamid MAA, Khalifa HO, Ki M-R, Pack SP. Bioinspired Synthesis and Characterization of Dual-Function Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Saccharopolyspora hirsuta: Exploring Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(8):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080456
Chicago/Turabian StyleSholkamy, Essam N., Mohamed A. A. Abdelhamid, Hazim O. Khalifa, Mi-Ran Ki, and Seung Pil Pack. 2024. "Bioinspired Synthesis and Characterization of Dual-Function Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Saccharopolyspora hirsuta: Exploring Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities" Biomimetics 9, no. 8: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080456
APA StyleSholkamy, E. N., Abdelhamid, M. A. A., Khalifa, H. O., Ki, M.-R., & Pack, S. P. (2024). Bioinspired Synthesis and Characterization of Dual-Function Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Saccharopolyspora hirsuta: Exploring Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Biomimetics, 9(8), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080456







