Pulse Oximetry Values in Newborns with Critical Congenital Heart Disease upon ICU Admission at Altitude
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
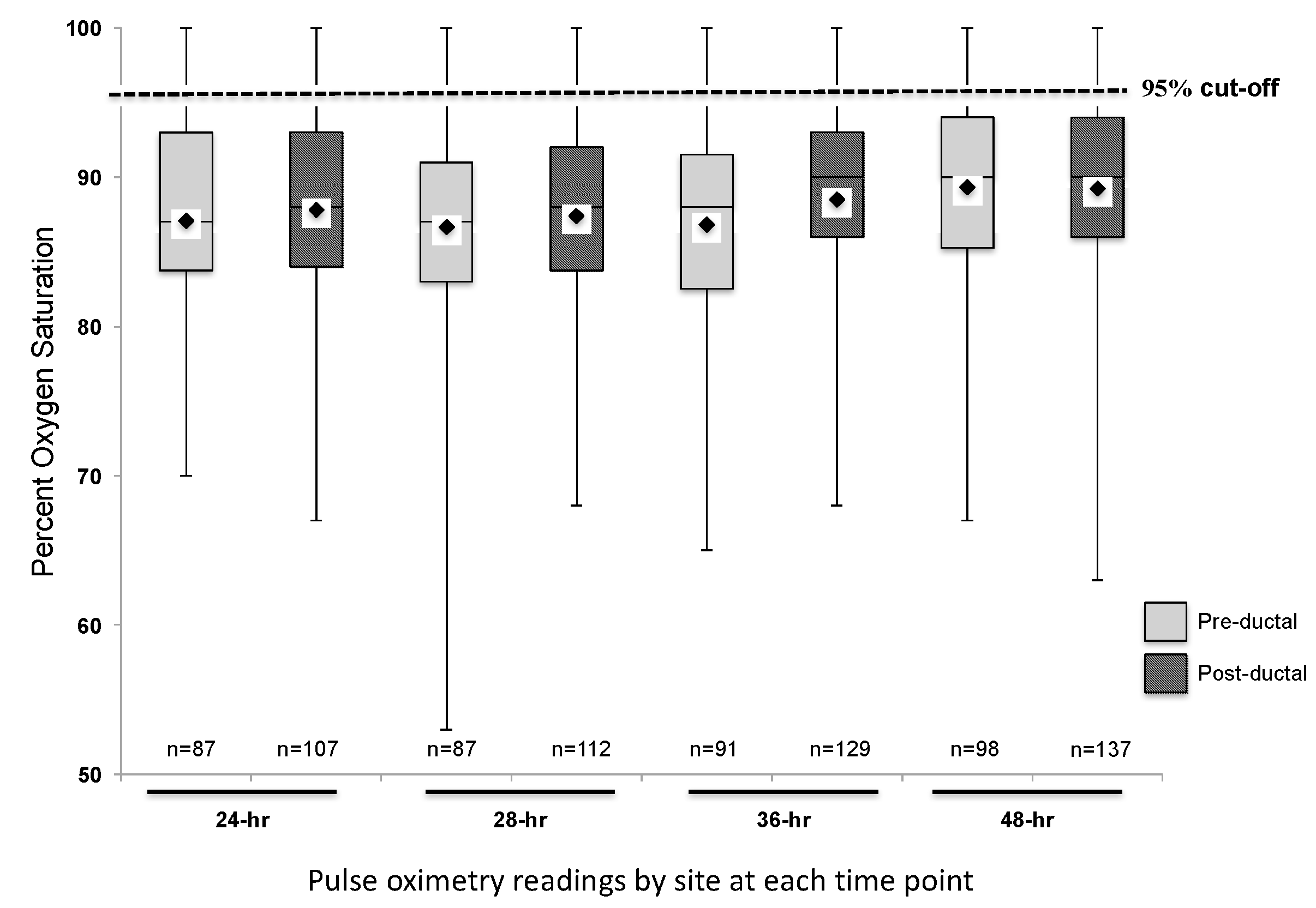
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of Study Cohort
3.2. Secondary Analysis: Hypothetical Screening of Study Cohort
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffman, J.I.E. It Is Time for Routine Neonatal Screening by Pulse Oximetry. Neonatology 2011, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, C.; Richmond, S.; Donaldson, L. Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in Infancy: Implications for Routine Examination. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999, 80, F49–F53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.; Kohn, M.; Niermeyer, S.; Rausch, C.M. Feasibility of Critical Congenital Heart Disease Newborn Screening at Moderate Altitude. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e561–e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, C.; Grosse, S.D.; Oster, M.E.; Olney, R.S.; Cassell, C.H. Cost-Effectiveness of Routine Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in US Newborns. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e595–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahle, W.T.; Newburger, J.W.; Matherne, G.P.; Smith, F.C.; Hoke, T.R.; Koppel, R.; Gidding, S.S.; Beekman, R.H.; Grosse, S.D. Role of Pulse Oximetry in Examining Newborns for Congenital Heart Disease: A Scientific Statement from the AHA and AAP. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahle, W.T.; Martin, G.R.; Beekman, R.H.; Morrow, W.R. Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Executive Committee. Endorsement of Health and Human Services Recommendation for Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.R.; Beekman, R.H.; Mikula, E.B.; Fasules, J.; Garg, L.F.; Kemper, A.R.; Morrow, W.R.; Pearson, G.D.; Mahle, W.T. Implementing Recommended Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e185–e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, A.R.; Mahle, W.T.; Martin, G.R.; Cooley, W.C.; Kumar, P.; Morrow, W.R.; Kelm, K.; Pearson, G.D.; Glidewell, J.; Grosse, S.D.; et al. Strategies for Implementing Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e1259–e1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plana, M.N.; Zamora, J.; Suresh, G.; Fernandez-Pineda, L.; Thangaratinam, S.; Ewer, A.K. Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Defects. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 3, CD011912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oster, M.E.; Aucott, S.W.; Glidewell, J.; Hackell, J.; Kochilas, L.; Martin, G.R.; Phillippi, J.; Pinto, N.M.; Saarinen, A.; Sontag, M.; et al. Lessons Learned from Newborn Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Defects. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20154573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueth, E.; Russell, L.; Wright, J.; Duster, M.; Kohn, M.; Miller, J.; Eller, C.; Sontag, M.; Rausch, C. A Novel Approach to Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) Screening at Moderate Altitude. IJNS 2016, 2, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilo, E.H.; Park-Moore, B.; Berman, E.R.; Carson, B.S. Oxygen Saturation by Pulse Oximetry in Healthy Infants at an Altitude of 1610 M (5280 Ft). What Is Normal? Am. J. Dis. Child. 1991, 145, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravert, P.; Detwiler, T.L.; Dickinson, J.K. Mean Oxygen Saturation in Well Neonates at Altitudes between 4498 and 8150 Feet. Adv. Neonatal Care 2011, 11, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, A.F.; Habib, H.S. Normal Values of Pulse Oximetry in Newborns at High Altitude. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2005, 51, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, T.Y.; Bromiker, R.; Mimouni, F.B.; Picard, E.; Lahav, S.; Mandel, D.; Goldberg, S. Newborn Oxygen Saturation at Mild Altitude Versus Sea Level: Implications for Neonatal Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap)—A Metadata-Driven Methodology and Workflow Process for Providing Translational Research Informatics Support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailes, E.C.; Gilboa, S.M.; Honein, M.A.; Oster, M.E. Estimated Number of Infants Detected and Missed by Critical Congenital Heart Defect Screening. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaratinam, S.; Brown, K.; Zamora, J.; Khan, K.S.; Ewer, A.K. Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Defects in Asymptomatic Newborn Babies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Wahl Granelli, A.; Wennergren, M.; Sandberg, K.; Mellander, M.; Bejlum, C.; Inganäs, L.; Eriksson, M.; Segerdahl, N.; Agren, A.; Ekman-Joelsson, B.-M.; et al. Impact of Pulse Oximetry Screening on the Detection of Duct Dependent Congenital Heart Disease: A Swedish Prospective Screening Study in 39,821 Newborns. BMJ 2009, 338, a3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewer, A.K.; Middleton, L.J.; Furmston, A.T.; Bhoyar, A.; Daniels, J.P.; Thangaratinam, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Khan, K.S. PulseOx Study Group. Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Defects in Newborn Infants (PulseOx): A Test Accuracy Study. Lancet 2011, 378, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manja, V.; Mathew, B.; Carrion, V.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Critical Congenital Heart Disease Screening by Pulse Oximetry in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.-J.; Zhao, Q.-M.; Ma, X.-J.; Yan, W.-L.; Ge, X.-L.; Jia, B.; Liu, F.; Wu, L.; Ye, M.; Huang, G.-Y. Pulse Oximetry Could Significantly Enhance the Early Detection of Critical Congenital Heart Disease in Neonatal Intensive Care Units. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, e499–e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, E.M.; Magnuson, K.M.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Porte, M.A.; Hokanson, J.S. Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Naarden Braun, K.; Grazel, R.; Koppel, R.; Lakshminrusimha, S.; Lohr, J.; Kumar, P.; Govindaswami, B.; Giuliano, M.; Cohen, M.; Spillane, N.; et al. Evaluation of Critical Congenital Heart Defects Screening Using Pulse Oximetry in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niermeyer, S.; Shaffer, E.M.; Thilo, E.; Corbin, C.; Moore, L.G. Arterial Oxygenation and Pulmonary Arterial Pressure in Healthy Neonates and Infants at High Altitude. J. Pediatr. 1993, 123, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Study Subjects (n = 158) | Excluded Subjects (n = 56) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age, weeks (range) | 38.2 ± 2.4 (29–45) | 38.3 ± 2.4 (30–41.3) | 0.379 |
| Birth weight, g (range) | 2988.7 ± 579.3 (1230–4165) | 3071.0 ± 671.7 (960–4780) | 0.277 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 101 (63.9) | 35 (62.5) | 0.849 |
| Race, n (%) | 0.470 | ||
| White/Caucasian | 111 (70.3) | 37 (66.1) | |
| Black/African American | 10 (6.3) | 3 (5.4) | |
| Hawaiian/Pacific Islander | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0) | |
| Asian | 1 (0.6) | 1 (1.8) | |
| American Indian/Alaskan Native | 3 (3.2) | 1 (1.8) | |
| Other | 26 (16.5) | 9 (16.1) | |
| Not specified | 4 (2.5) | 5 (8.9) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.088 | ||
| Hispanic/Latino | 54 (34.2) | 15 (26.8) | |
| Not Hispanic/Latino | 100 (63.3) | 36 (64.3) | |
| Not specified | 4 (2.5) | 5 (8.9) | |
| Apgar score, score (range) | |||
| 1 min | 7 ± 2 (0–9) | 7 ± 2 (2–8) | 0.409 |
| 5 min | 8 ± 1 (0–9) | 8 ± 1 (4–9) | 0.212 |
| Prenatal diagnosis of CCHD, n (%) | 84 (53.2) | 20 (35.7) | 0.152 |
| Family history of CCHD, n (%) | 18 (11.4) | 3 (5.4) | 0.361 |
| Genetic diagnosis, n (%) | 0.825 | ||
| Down syndrome | 2 (1.3) | 0 (0) | |
| 22q11 deletion | 6 (3.8) | 1 (1.8) | |
| None specified | 150 (94.9) | 50 (89.3) | |
| CCHD diagnosis, n (%) | 0.002 * | ||
| HLHS | 48 (30.4) | 17 (30.4) | |
| TOF | 34 (21.5) | 5 (8.9) | |
| TGA | 30 (19.0) | 26 (46.4) | |
| TA | 13 (8.2) | 2 (3.6) | |
| TAPVR | 10 (6.3) | 5 (8.9) | |
| TVA | 10 (6.3) | 0 (0) | |
| PA/IVS | 7 (4.4) | 1 (1.8) | |
| Combination of above | 6 (3.8) | 0 (0) | |
| Maternal age, years (range) | 28.1 ± 5.8 (15–42) | 26.5 ± 6.0 (15–41) | 0.089 |
| Maternal diabetes status, n (%) | 0.272 | ||
| Diabetes (Type I or Type II) | 7 (4.5) | 0 (0) | |
| Gestational diabetes | 6 (3.8) | 3 (5.4) | |
| Not diabetic | 144 (91.7) | 53 (94.6) |
| No Support | PGE | Oxygen | Both PGE and Oxygen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24-hours | Pre-ductal | 90.3 ± 7.7 (77–100) (n = 7) | 88.6 ± 7.3 (75–100) (n = 30) | 86.6 ± 4.3 (80–95) (n = 14) | 85.2 ± 7.6 (70–98) (n = 36) |
| Post-ductal | 89.4 ± 5.4 (80–97) (n = 14) | 87.8 ± 6.3 (73–99) (n = 33) | 88.9 ± 6.0 (78–97) (n = 18) | 86.8 ± 6.6 (67–100) (n = 42) | |
| 28-hours | Pre-ductal | 88.0 ± 5.0 (81–95) (n = 7) | 88.3 ± 6.8 (74–100) (n = 28) | 84.6 ± 7.1 (72–96) (n = 18) | 86.1 ± 7.8 (53–96) (n = 34) |
| Post-ductal | 90.3 ± 6.2 (78–100) (n = 14) | 88.5 ± 7.4 (70–100) (n = 35) | 85.7 ± 6.7 (72–95) (n = 20) | 86.2 ± 7.6 (68–100) (n = 43) | |
| 36-hours | Pre-ductal | 89.0 ± 9.2 (77–99) (n = 4) | 88.4 ± 5.0 (76–100) (n = 33) | 86.3 ± 8.0 (65–98) (n = 16) | 85.5 ± 8.9 (65–100) (n = 38) |
| Post-ductal | 90.0 ± 4.9 (82–100) (n = 15) | 90.2 ± 4.4 (79–98) (n = 46) | 88.9 ± 7.0 (72–100) (n = 22) | 86.1 ± 8.2 (68–99) (n = 46) | |
| 48-hours | Pre-ductal | 91.0 ± 5.3 (80–97) (n = 8) | 90.4 ± 6.4 (70–100) (n = 42) | 89.8 ± 4.5 (81–98) (n = 13) | 87.4 ± 7.3 * (67–100) (n = 35) |
| Post-ductal | 90.3 ± 6.4 (75–100) (n = 21) | 90.5 ± 5.2 (75–99) (n = 51) | 91.5 ± 4.8 (80–97) (n = 20) | 86.3 ± 7.0 * (63–100) (n = 45) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.S.; Ariefdjohan, M.W.; Sontag, M.K.; Rausch, C.M. Pulse Oximetry Values in Newborns with Critical Congenital Heart Disease upon ICU Admission at Altitude. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2018, 4, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040030
Kim JS, Ariefdjohan MW, Sontag MK, Rausch CM. Pulse Oximetry Values in Newborns with Critical Congenital Heart Disease upon ICU Admission at Altitude. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2018; 4(4):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, John S., Merlin W. Ariefdjohan, Marci K. Sontag, and Christopher M. Rausch. 2018. "Pulse Oximetry Values in Newborns with Critical Congenital Heart Disease upon ICU Admission at Altitude" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 4, no. 4: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040030
APA StyleKim, J. S., Ariefdjohan, M. W., Sontag, M. K., & Rausch, C. M. (2018). Pulse Oximetry Values in Newborns with Critical Congenital Heart Disease upon ICU Admission at Altitude. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 4(4), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns4040030





