Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Patients with Mild Hyperphenylalaninemia Identified by Newborn Screening Program in Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Statistical Analysis
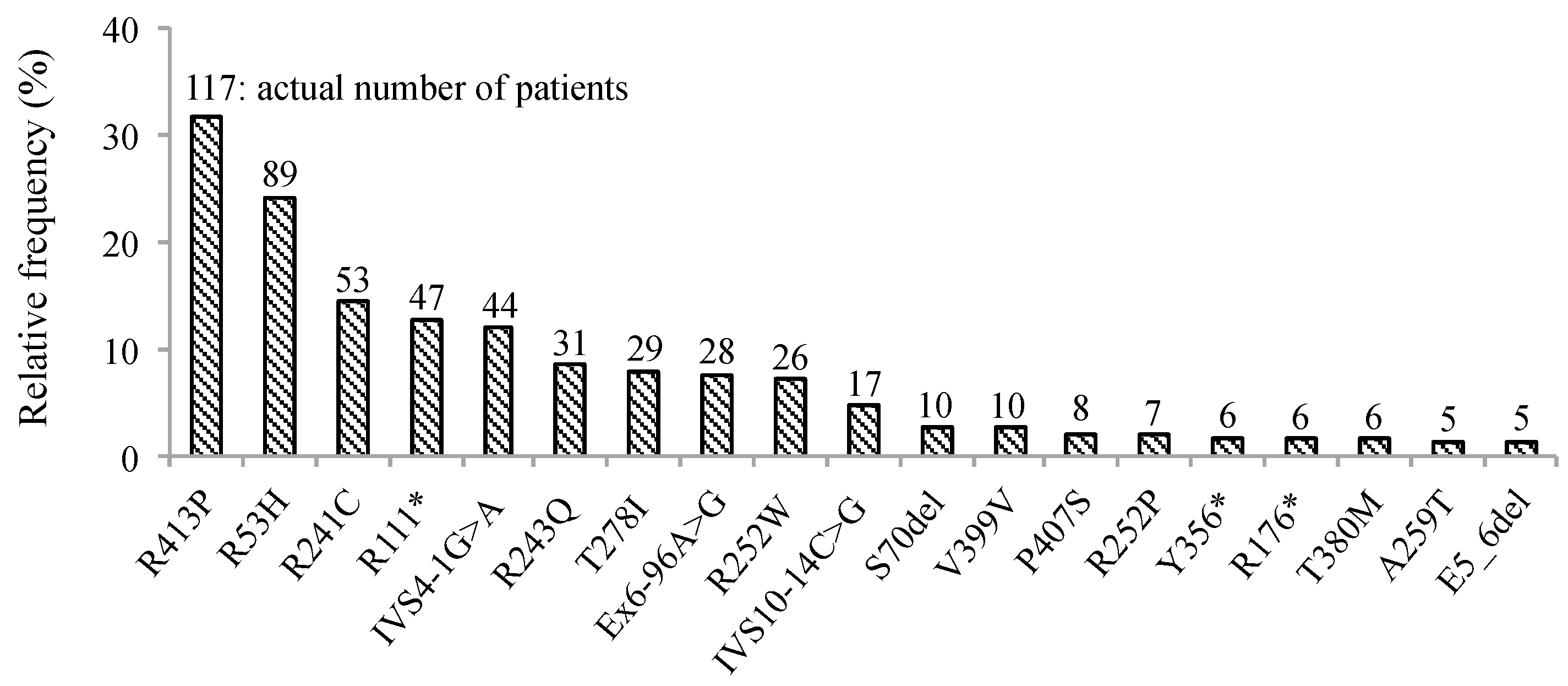
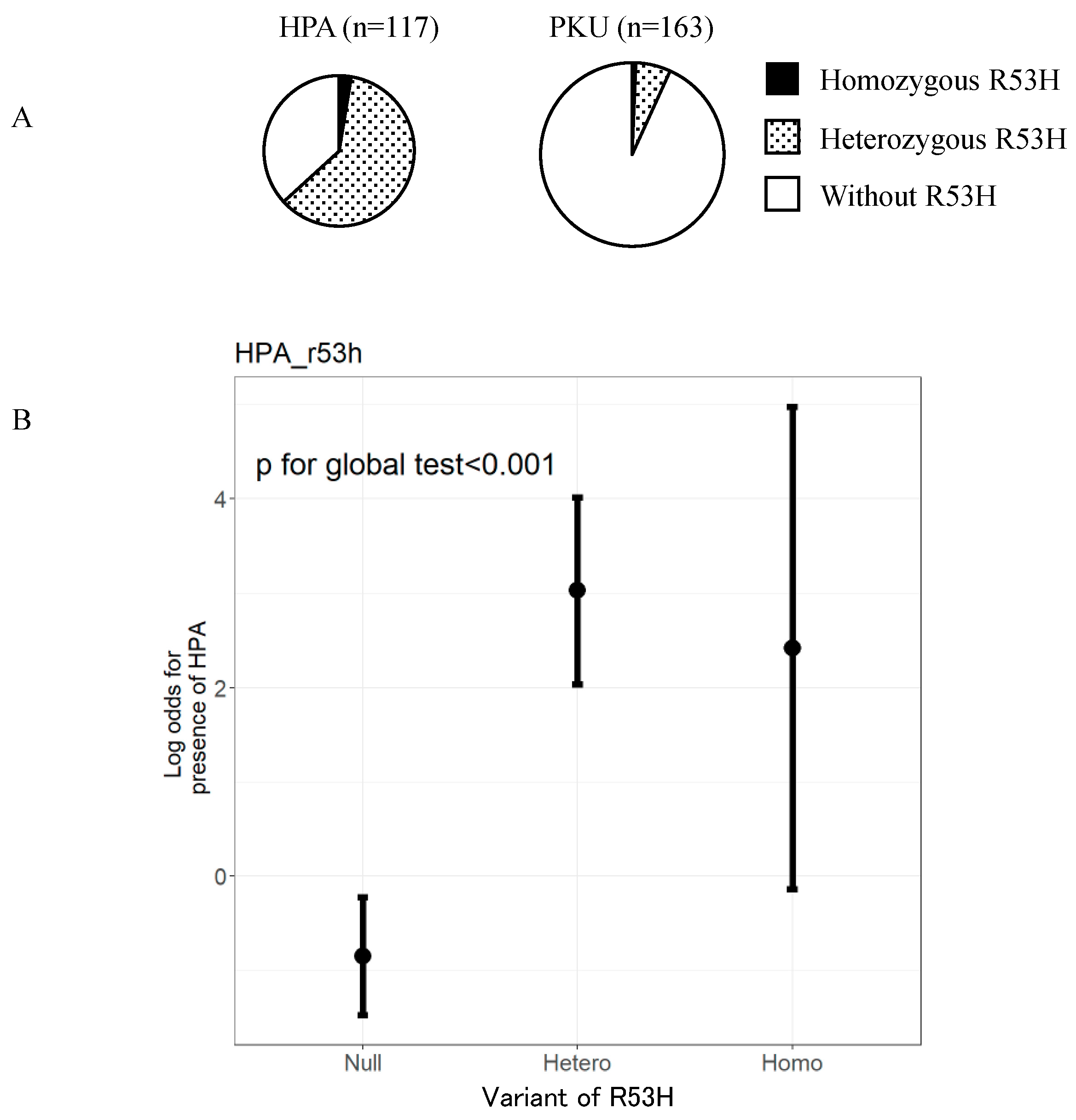
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blau, N.; van Spronsen, F.J.; Levy, H.L. Phenylketonuria. Lancet 2010, 376, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, Y.; Eisensmith, R.C.; Güttler, F.; Lichter-Konecki, U.; Konecki, D.S.; Trefz, F.K.; Dasovich, M.; Wang, T.; Henriksen, K.; Lou, H.; et al. Molecular Basis of Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Phenylketonuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldberg, P.; Rey, F.; Zschocke, J.; Romano, V.; François, B.; Michiels, L.; Ullrich, K.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Burgard, P.; Schmidt, H.; et al. A European Multicenter Study of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Deficiency: Classification of 105 Mutations and a General System for Genotype-Based Prediction of Metabolic Phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 63, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Wegberg, A.M.J.; Macdonald, A.; Ahring, K.; BéLanger-Quintana, A.; Blau, N.; Bosch, A.M.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camp, K.M.; Parisi, M.A.; Acosta, P.B.; Berry, G.T.; Bilder, D.A.; Blau, N.; Bodamer, O.A.; Brosco, J.P.; Brown, C.S.; Burlina, A.B.; et al. Phenylketonuria Scientific Review Conference: State of the science and future research needs. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 112, 87–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasaki, M.; Yasuda, J.; Katsuoka, F.; Nariai, N.; Kojima, K.; Kawai, Y.; Yamaguchi-Kabata, Y.; Yokozawa, J.; Danjoh, I.; Saito, S.; et al. Rare variant discovery by deep whole-genome sequencing of 1,070 Japanese individuals. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dateki, S.; Watanabe, S.; Nakatomi, A.; Kinoshita, E.; Matsumoto, T.; Yoshiura, K.I.; Moriuchi, H. Genetic background of hyperphenylalaninemia in Nagasaki, Japan. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Koo, S.K.; Lee, K.-S.; Yeon, Y.-J.; Oh, H.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, S.-S.; Lee, J.-E.; Jo, I.; et al. The molecular basis of phenylketonuria in Koreans. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 49, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; He, C.; Li, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, J.; Deng, Y.; et al. Analysis of the genotype-phenotype correlation in patients with phenylketonuria in mainland China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Seoung, C.S.; Lee, S.W.; Oh, K.H.; Lee, D.H.; Yim, J. Identification of three novel mutations in Korean phenylketonuria patients: R53H, N207D, and Y325X. Hum. Mutat. 1998, 11, S121–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, Y.; Kudo, S.; Nishi, Y.; Sakaguchi, T.; Aso, K. Molecular characterization of phenylketonuria and tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in Japan. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 56, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, M.-Z.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chao, H.-K.; Fwu, V.T.; Chiang, S.-H.; Hsiao, K.-J.; Niu, D.-M.; Su, T.-S. The mutation spectrum of the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene and associated haplotypes reveal ethnic heterogeneity in the Taiwanese population. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 59, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Li, N.; Jia, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Deng, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, J. Correlation between genotype and the tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenotype in Chinese patients with phenylketonuria. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisensmith, R.C.; Woo, S.L.C. Molecular basis of phenylketonuria and related hyperphenylalaninemias: Mutations and polymorphisms in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Hum. Mutat. 1992, 1, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingsen, S.; Knappskog, P.M.; Eiken, H.G. Phenylketonuria splice mutation (EXON6nt-96Ag) masquerading as missense mutation (Y204C). Hum. Mutat. 1997, 9, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.L.; Castro-Magalhães, M.; Fonseca, C.G.; Starling, A.L.P.; Januário, J.N.; Aguiar, M.J.B.; Carvalho, M.R.S. PKU in Minas Gerais State, Brazil: Mutation analysis. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2008, 72, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jia, H.; Liu, Z.; Tao, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Jin, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Molecular characterisation of phenylketonuria in a Chinese mainland population using next-generation sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 15769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hennermann, J.B.; Vetter, B.; Wolf, C.; Windt, E.; Bührdel, P.; Seidel, J.; Mönch, E.; Kulozik, A.E. Phenylketonuria and hyperphenylalaninemia in eastern Germany: A characteristic molecular profile and 15 novel mutations. Hum Mutat. 2000, 15, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, Y.; Asada, M.; Kang, Y.; Nishi, Y.; Hase, Y.; Oura, T.; Isshiki, G. Molecular characterization of phenylketonuria in Japanese patients. Hum Genet. 1998, 103, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, Y.; Hase, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Furuyama, J.I.; Shintaku, H.; Oura, T.; Isshiki, G. Frequency and distribution of phenylketonuric mutations in orientals. Hum. Mutat. 1992, 1, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiba, S.; Motoike, I.; Kojima, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Shirota, M.; Saito, T.; Saigusa, D.; Danjoh, I.; Katsuoka, F.; Ogishima, S.; et al. The structural origin of metabolic quantitative diversity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, R.; Lee, J.; Park, H.D.; Park, J.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Ki, C.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, D.H. Reassessing the significance of the PAH c.158G>A (p.Arg53His) mutation in patients with hyperphenylalaninemia. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillert, A.; Anikster, Y.; Belanger-Quintana, A.; Burlina, A.; Burton, B.K.; Carducci, C.; Chiesa, A.E.; Christodoulou, J.; Đorđević, M.; Blau, N.; et al. The Genetic Landscape and Epidemiology of Phenylketonuria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, N.; Ichinose, H.; Nagatsu, T.; Heizmann, C.W.; Zacchello, F.; Burlina, A.B. A missense mutation in a patient with guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I deficiency missed in the newborn screening program. J. Pediatr. 1995, 126, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, N.; Martinez, A.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Thöny, B. DNAJC12 deficiency: A new strategy in the diagnosis of hyperphenylalaninemias. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Society for Inherited Metabolic Disease. Newborn Screening Clinical Guideline; Shindan to Chiryo Sha: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; pp. 11–24. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Evinç, S.G.; Pektaş, E.; Foto-Özdemir, D.; Yıldız, Y.; Karaboncuk, Y.; Bilginer-Gürbüz, B.; Dursun, A.; Tokatlı, A.; Coskun, T.; Öktem, F.; et al. Cognitive and behavioral impairment in mild hyperphenylalaninemia. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2018, 60, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Variants with R53H (n = 74) | Variants without R53H (n = 43) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted HPA phenotype | Predicted PKU phenotype or unknown phenotype | ||||
| Genotype | n | Genotype | n | Genotype | n |
| R53H/R413P | 15 | R71H/T278I | 1 | R241C/R241C | 3 |
| R53H/R243Q | 6 | A132V/R413P | 1 | R241C/S70del | 2 |
| R53H/T278I | 6 | A132V/ | 1 | R241C/P407S | 1 |
| R53H/Ex6-96A>G | 5 | R297C/ IVS4-1G>A | 1 | R241C/ IVS4-1G>A | 1 |
| R53H/IVS4-1G>A | 4 | A373T/R241C | 1 | R241C/Ex6-96A>G | 1 |
| R53H/R252W | 4 | A373T/T380M | 1 | R241C/R243Q | 1 |
| R53H/E5_6del | 3 | A373T/R413P | 1 | R241C/R252P | 1 |
| R53H/E3del4bp | 3 | Q375E/delS70 | 1 | R241C/T278I | 3 |
| R53H/R111* | 3 | Q375E/ IVS4-1G>A | 1 | R241C/R413P | 2 |
| R53H/R241C | 3 | V379A/R111* | 1 | R241C/P281A | 1 |
| R53H/E6del | 2 | V379A/R252W | 1 | R241C/ | 2 |
| R53H/V399V | 2 | T380M/IVS10-14C>G | 3 | R413P/ | 2 |
| R53H/A259T | 1 | T380M/R111* | 1 | F55L/Y154D | 1 |
| R53H/S70del | 1 | T380M/ IVS4-1G>A | 1 | R243Q/ | 1 |
| R53H/F402I | 1 | F402I/R252W | 1 | K431N/ | 1 |
| R53H/IVS10-14C>G | 1 | A403V/S16* | 1 | S67C/ | 1 |
| R53H/IVS10-1C>G | 1 | D415N/R353W | 1 | ||
| R53H/L421T | 1 | ||||
| R53H/P281L | 1 | ||||
| R53H/R176X | 1 | ||||
| R53H/R243* | 1 | ||||
| R53H/R408W | 1 | ||||
| R53H/R413C | 1 | ||||
| R53H/V412P | 1 | ||||
| R53H/A132V/R413P | 1 | ||||
| R53H/ | 5 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Odagiri, S.; Kabata, D.; Tomita, S.; Kudo, S.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nakano, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Shintaku, H.; Hamazaki, T. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Patients with Mild Hyperphenylalaninemia Identified by Newborn Screening Program in Japan. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010017
Odagiri S, Kabata D, Tomita S, Kudo S, Sakaguchi T, Nakano N, Yamamoto K, Shintaku H, Hamazaki T. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Patients with Mild Hyperphenylalaninemia Identified by Newborn Screening Program in Japan. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2021; 7(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleOdagiri, Shino, Daijiro Kabata, Shogo Tomita, Satoshi Kudo, Tomoko Sakaguchi, Noriko Nakano, Kouji Yamamoto, Haruo Shintaku, and Takashi Hamazaki. 2021. "Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Patients with Mild Hyperphenylalaninemia Identified by Newborn Screening Program in Japan" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 7, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010017




