Experience of the NPC Brazil Network with a Comprehensive Program for the Screening and Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Sample Analyses
2.3.1. Quantification of LysoSM509
2.3.2. Chitotriosidase Enzyme Activity
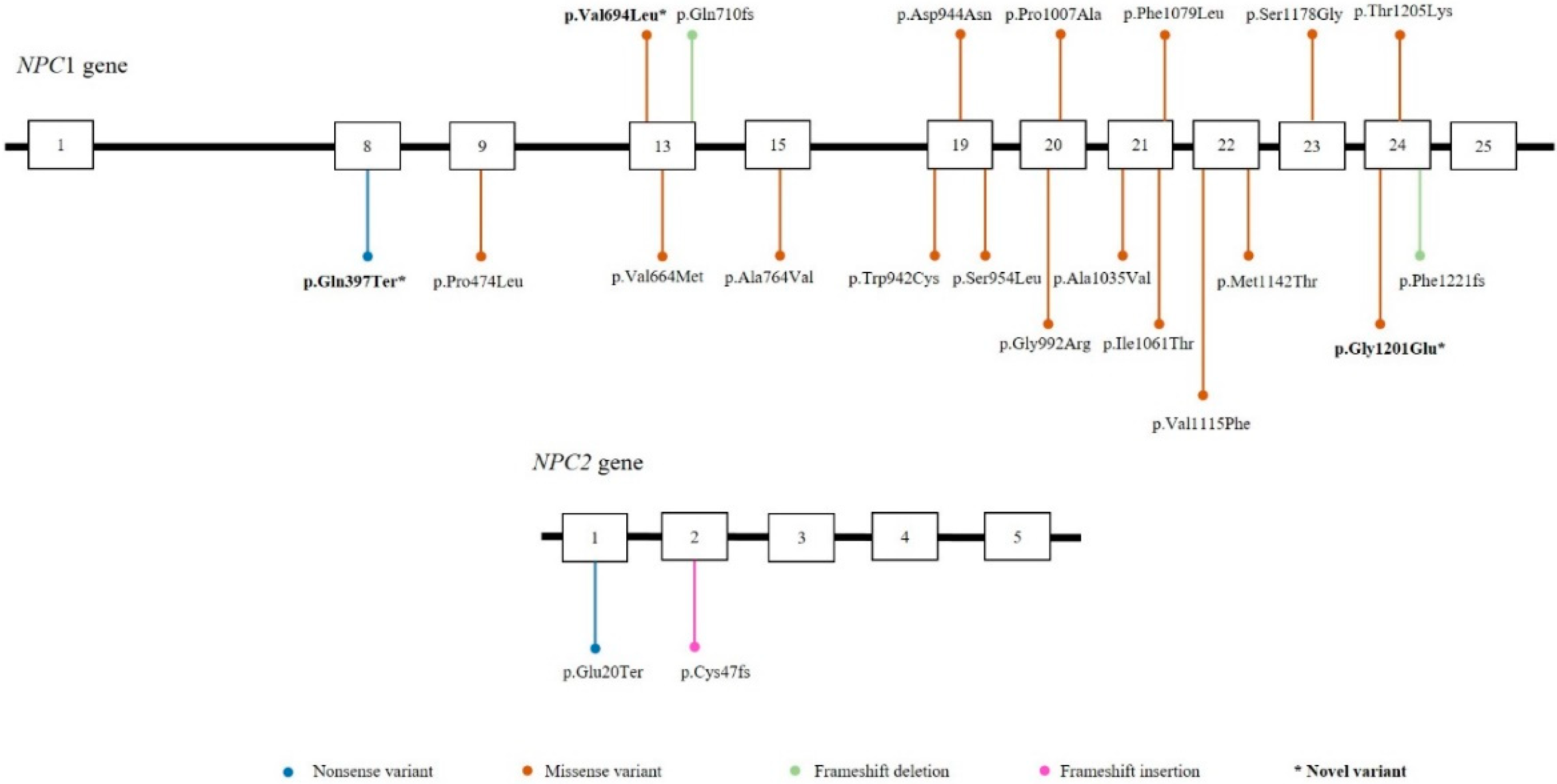
2.3.3. Molecular Analysis
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burlina, A. Niemann–Pick disease type C: Introduction and main clinical features. J. Neurol. 2014, 261 (Suppl. 2), 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patterson, M.C.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Walterfang, M.; Sedel, F.; Vanier, M.T.; Wijburg, F. Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Niemann–Pick disease type C: An update. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 106, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, M.C.; Mengel, E.; Wijburg, F.A.; Muller, A.; Schwierin, B.; Drevon, H.; Vanier, M.T.; Pineda, M. Disease and patient characteristics in NP-C patients: Findings from an international disease registry. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, M.T. Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardo, A.; De Nuccio, C.; Visentin, S.; Martire, A.; Minghetti, L.; Popoli, P.; Ferrante, A. Myelin Defects in Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Mechanisms and Possible Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitarska, D.; Ługowska, A. Laboratory diagnosis of the Niemann-Pick type C disease: An inherited neurodegenerative disorder of cholesterol metabolism. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pallottini, V.; Pfrieger, F.W. Understanding and Treating Niemann–Pick Type C Disease: Models Matter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Lieberman, A.P. Npc1 Acting in Neurons and Glia Is Essential for the Formation and Maintenance of CNS Myelin. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, B.E.; LeBlanc, V.G.; Mailman, T.M.; Fice, D.; Burton, I.; Karakach, T.K.; Karten, B. Pre-Symptomatic Activation of Antioxidant Responses and Alterations in Glucose and Pyruvate Metabolism in Niemann-Pick Type C1-Deficient Murine Brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, W.R.H.; Hendriksz, C. Niemann-Pick type C disease—The tip of the iceberg? A review of neuropsychiatric presentation, diagnosis and treatment. BJPsych Bull. 2017, 41, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGovern, M.M.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Giugliani, R.; Hwu, P.; Lidove, O.; Lukacs, Z.; Mengel, K.E.; Mistry, P.K.; Schuchman, E.H.; Wasserstein, M.P. Consensus recommendation for a diagnostic guideline for acid sphingomyelinase deficiency. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, R.; Raas-Rothschild, A.; Reish, O.; Regev, M.; Meiner, V.; Bargal, R.; Sury, V.; Meir, K.; Nadjari, M.; Hermann, G.; et al. The clinical spectrum of fetal Niemann-Pick type C. Am. J. Med Genet. Part A 2009, 149A, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentchev, P.G.; Comly, M.E.; Kruth, H.S.; Vanier, M.T.; Wenger, D.A.; Patel, S.; Brady, R.O. A defect in cholesterol esterification in Niemann-Pick disease (type C) patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 8247–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ries, M.; Schaefer, E.; Lührs, T.; Mani, L.; Kuhn, J.; Vanier, M.T.; Krummenauer, F.; Gal, A.; Beck, M.; Mengel, E. Critical assessment of chitotriosidase analysis in the rational laboratory diagnosis of children with Gaucher disease and Niemann–Pick disease type A/B and C. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, F.D.; Scherrer, D.E.; Lanier, M.H.; Langmade, S.J.; Molugu, V.; Gale, S.E.; Olzeski, D.; Sidhu, R.; Dietzen, D.J.; Fu, R.; et al. Cholesterol Oxidation Products Are Sensitive and Specific Blood-Based Biomarkers for Niemann-Pick C1 Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 56ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Sidhu, R.; Porter, F.D.; Yanjanin, N.M.; Speak, A.O.; te Vruchte, D.T.T.; Platt, F.M.; Fujiwara, H.; Scherrer, D.E.; Zhang, J.; et al. A sensitive and specific LC-MS/MS method for rapid diagnosis of Niemann-Pick C1 disease from human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stampfer, M.; Theiss, S.; Amraoui, Y.; Jiang, X.; Keller, S.; Ory, D.S.; Mengel, E.; Fischer, C.; Runz, H. Niemann-Pick disease type C clinical database: Cognitive and coordination deficits are early disease indicators. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reunert, J.; Fobker, M.; Kannenberg, F.; Du Chesne, I.; Plate, M.; Wellhausen, J.; Rust, S.; Marquardt, T. Rapid Diagnosis of 83 Patients with Niemann Pick Type C Disease and Related Cholesterol Transport Disorders by Cholestantriol Screening. eBioMedicine 2016, 4, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klinke, G.; Rohrbach, M.; Giugliani, R.; Burda, P.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Tran, C.; Gautschi, M.; Mathis, D.; Hersberger, M. LC-MS/MS based assay and reference intervals in children and adolescents for oxysterols elevated in Niemann–Pick diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanello, M.; Zampieri, S.; Bortolotti, N.; Deroma, L.; Sechi, A.; Fiumara, A.; Parini, R.; Borroni, B.; Brancati, F.; Bruni, A.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Plasma 7-Ketocholesterol and Cholestan-3β,5α,6β-Triol in an Italian Cohort of Patients Affected by Niemann-Pick Disease due to NPC1 and SMPD1 Mutations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 455, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, A.-K.; Mascher, H.; Grittner, U.; Eichler, S.; Kramp, G.J.; Lukas, J.; Vruchte, D.T.; Al Eisa, N.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Porter, F.D.; et al. A novel, highly sensitive and specific biomarker for Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettazzoni, M.; Froissart, R.; Pagan, C.; Vanier, M.T.; Ruet, S.; Latour, P.; Guffon, N.; Fouilhoux, A.; Germain, D.P.; Levade, T.; et al. LC-MS/MS multiplex analysis of lysosphingolipids in plasma and amniotic fluid: A novel tool for the screening of sphingolipidoses and Niemann-Pick type C disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.-K.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, T.-J.; Tsai, C.-C.; Liu, H.-L.; Lin, S.-P. A modified liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for predominant disaccharide units of urinary glycosaminoglycans in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welford, R.W.D.; Garzotti, M.; Lourenço, C.M.; Mengel, E.; Marquardt, T.; Reunert, J.; Amraoui, Y.; Kolb, S.A.; Morand, O.; Groenen, P. Plasma Lysosphingomyelin Demonstrates Great Potential as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C in a Retrospective Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, G.; Burlina, A.P.; Kolamunnage, T.B.; Zampieri, M.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Strisciuglio, P.; Zaninotto, M.; Plebani, M.; Burlina, A.B. Diagnosis of sphingolipidoses: A new simultaneous measurement of lysosphingolipids by LC-MS/MS. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2017, 55, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, G.; Burlina, A.P.; Ranieri, E.; Colucci, F.; Rubert, L.; Pascarella, A.; Duro, G.; Tummolo, A.; Padoan, A.; Plebani, M.; et al. Plasma and dried blood spot lysosphingolipids for the diagnosis of different sphingolipidoses: A comparative study. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollak, C.E.; Van Weely, S.; Van Oers, M.H.; Aerts, J. Marked elevation of plasma chitotriosidase activity. A novel hallmark of Gaucher disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitarska, D.; Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Ługowska, A. Treatment trials in Niemann-Pick type C disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounford, K.M.; Gissen, P. Genetic and laboratory diagnostic approach in Niemann Pick disease type C. J. Neurol. 2014, 261 (Suppl. 2), 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, W.-L.; Pacheco, J.; Cooper, S.; McGovern, M.M.; Cox, G.F.; Keutzer, J.; Zhang, X.K. Lyso-sphingomyelin is elevated in dried blood spots of Niemann–Pick B patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 111, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, H.; Patócs, A. Brief Summary of the Most Important Molecular Genetic Methods (PCR, qPCR, Microarray, Next-Generation Sequencing, etc.). Exp. Suppl. 2019, 111, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HGMD® Home Page. Available online: http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php (accessed on 24 February 2022).
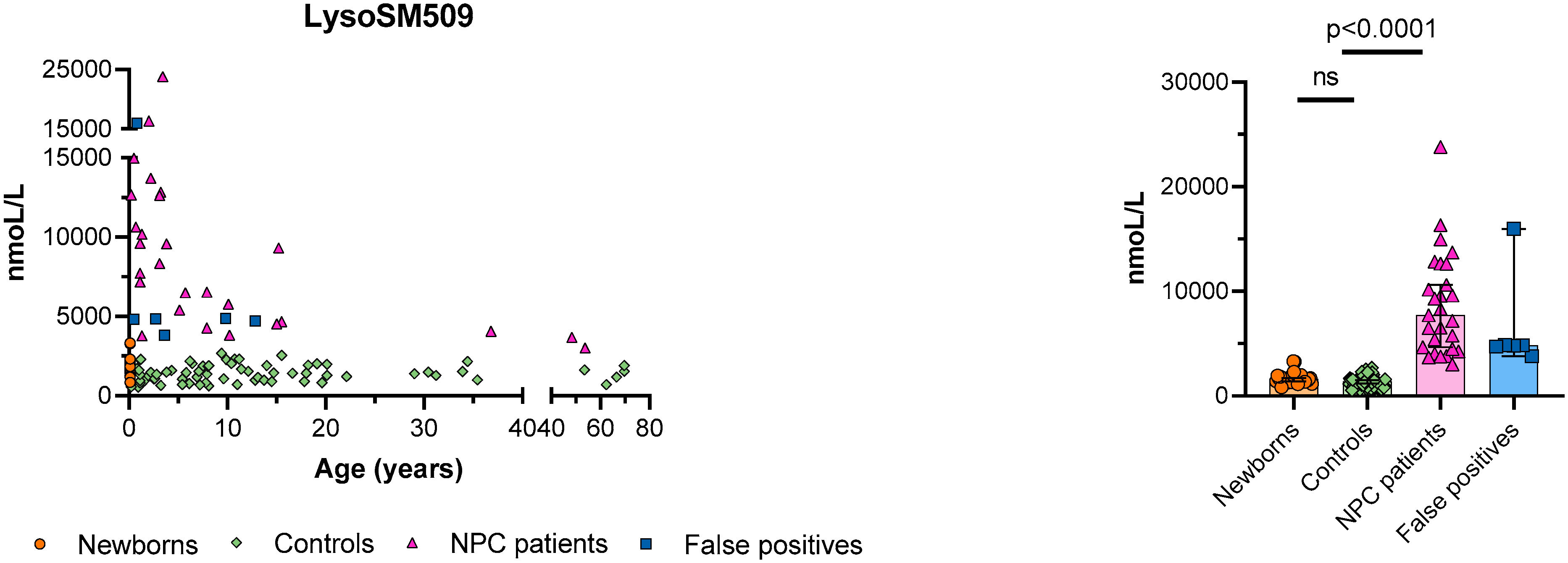


| ID | Gender | Age at Sample Collection † | Country | LysoSM509 (nmoL/L) 1 | Chitotriosidase Activity (nmoL/h/mL) 2 | Genotype | Gene with Variant(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 3.11 | Brazil | 8328 | 100 | p.A1035V/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 2 | Female | 1.11 | Brazil | 7722 | 0.8 | p.Q710fs/p.Q710fs | NPC1 |
| 3 | Female | 1.1 | Brazil | 9609 | 95 | p.A1035V/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 4 | Female | 10.2 | Brazil | 3819 | 9.7 | p.A1035V/p.V694L | NPC1 |
| 5 | Male | 1.4 | Brazil | 10,169 | 80 | p.F1221fs/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 6 | Male | 10.10 | Brazil | 5773 | 18 | p.C47fs/- | NPC2 |
| 7 | Female | 36.8 | Brazil | 4049 | 69 | p.A1035V/p.G992R | NPC1 |
| 8 | Male | 3.6 | Brazil | 3814 | 7.6 | -/- | ? |
| 9 | Male | 5.11 | Brazil | 5401 | 56 | p.A764V/p.A764V | NPC1 |
| 10 * | Male | 8.9 | Brazil | 4271 | # | p.T1205K/p.P1007A | NPC1 |
| 11 * | Male | 8.9 | Brazil | 6521 | # | p.T1205K/p.P1007A | NPC1 |
| 12 | Male | 5.7 | Brazil | 6495 | 33 | p.A1035V/- | NPC1 |
| 13 | Female | 2 | Brazil | 16,323 | 161 | p.W942C/p.W942C | NPC1 |
| 14 | Male | 2.7 | Brazil | 4839 | 5 | -/- | ? |
| 15 | Female | 0.7 | Brazil | 10,632 | 309 | p.A1035V/p.Q397 * | NPC1 |
| 16 | Male | 0.8 | Brazil | 15,958 | 26 | -/- | ? |
| 17 | Female | 3.8 | Brazil | 9571 | 23 | p.F1221fs/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 18 | Male | 0.5 | Brazil | 4820 | # | -/- | ? |
| 19 | Female | 2.2 | Brazil | 13,706 | 86 | p.W942C/p.W942C | NPC1 |
| 20 | Female | 1.3 | Brazil | 3785 | 78 | p.F1079L/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 21 | Female | 3.4 | Brazil | 23,812 | 32 | p.F1221fs/p.I1061T | NPC1 |
| 22 | Female | 3.2 | Brazil | 12,834 | 40 | p.A1035V/p.G1201E | NPC1 |
| 23 | Female | 0.2 | Brazil | 12,662 | n/a | p.A1035V/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 24 | Female | 53.8 | Brazil | 3003 | 11 | p.S954L/p.P474L | NPC1 |
| 25 | Female | 1.11 | Brazil | 7180 | n/a | p.A1035V/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 26 | Male | 15.5 | Brazil | 4669 | # | p.A1035V/p.A1035V | NPC1 |
| 27 | Male | 48.4 | Brazil | 3672 | 15 | p.P1007A/p.P1007A | NPC1 |
| 28 | Male | 3.1 | Colombia | 12,628 | 40 | p.D944N/p.D944N | NPC1 |
| 29 | Female | 0.5 | Colombia | 14,980 | 105 | p.E20 */p.E20 * | NPC2 |
| 30 | Male | 15 | Bolivia | 4525 | 17 | p.S1178G/p.V1115F | NPC1 |
| 31 | Female | 15.2 | Colombia | 9310 | 58 | p.M1142T/p.V1664M | NPC1 |
| 32 | Female | 9.8 | Colombia | 4881 | 7 | -/- | ? |
| 33 | Female | 12.8 | Colombia | 4726 | 56 | -/- | ? |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubaski, F.; Burlina, A.; Polo, G.; Pereira, D.; Herbst, Z.M.; Silva, C.; Trapp, F.B.; Michelin-Tirelli, K.; Lopes, F.F.; Burin, M.G.; et al. Experience of the NPC Brazil Network with a Comprehensive Program for the Screening and Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns8030039
Kubaski F, Burlina A, Polo G, Pereira D, Herbst ZM, Silva C, Trapp FB, Michelin-Tirelli K, Lopes FF, Burin MG, et al. Experience of the NPC Brazil Network with a Comprehensive Program for the Screening and Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2022; 8(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns8030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubaski, Francyne, Alberto Burlina, Giulia Polo, Danilo Pereira, Zackary M. Herbst, Camilo Silva, Franciele B. Trapp, Kristiane Michelin-Tirelli, Franciele F. Lopes, Maira G. Burin, and et al. 2022. "Experience of the NPC Brazil Network with a Comprehensive Program for the Screening and Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 8, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns8030039
APA StyleKubaski, F., Burlina, A., Polo, G., Pereira, D., Herbst, Z. M., Silva, C., Trapp, F. B., Michelin-Tirelli, K., Lopes, F. F., Burin, M. G., Brusius-Facchin, A. C., Netto, A. B. O., Faqueti, L., Iop, G. D., Poletto, E., & Giugliani, R. (2022). Experience of the NPC Brazil Network with a Comprehensive Program for the Screening and Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 8(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns8030039










