Artificial Pain May Induce Empathy, Morality, and Ethics in the Conscious Mind of Robots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A pain nervous system is embedded into robots so they can feel pain.
- Through the development of MNS, robots may feel pain in others.
- That is, emotional contagion, emotional empathy, cognitive empathy, and sympathy/compassion can be developed inside robots.
- Proto-morality emerges.
- Robots could be agents who could be moral beings, and at the same time, subjects to moral consideration.
2. A Nervous System for Pain Sensation
3. From an Artificial Pain System to a Moral Being
3.1. Artificial Pain
3.2. Artificial Empathy
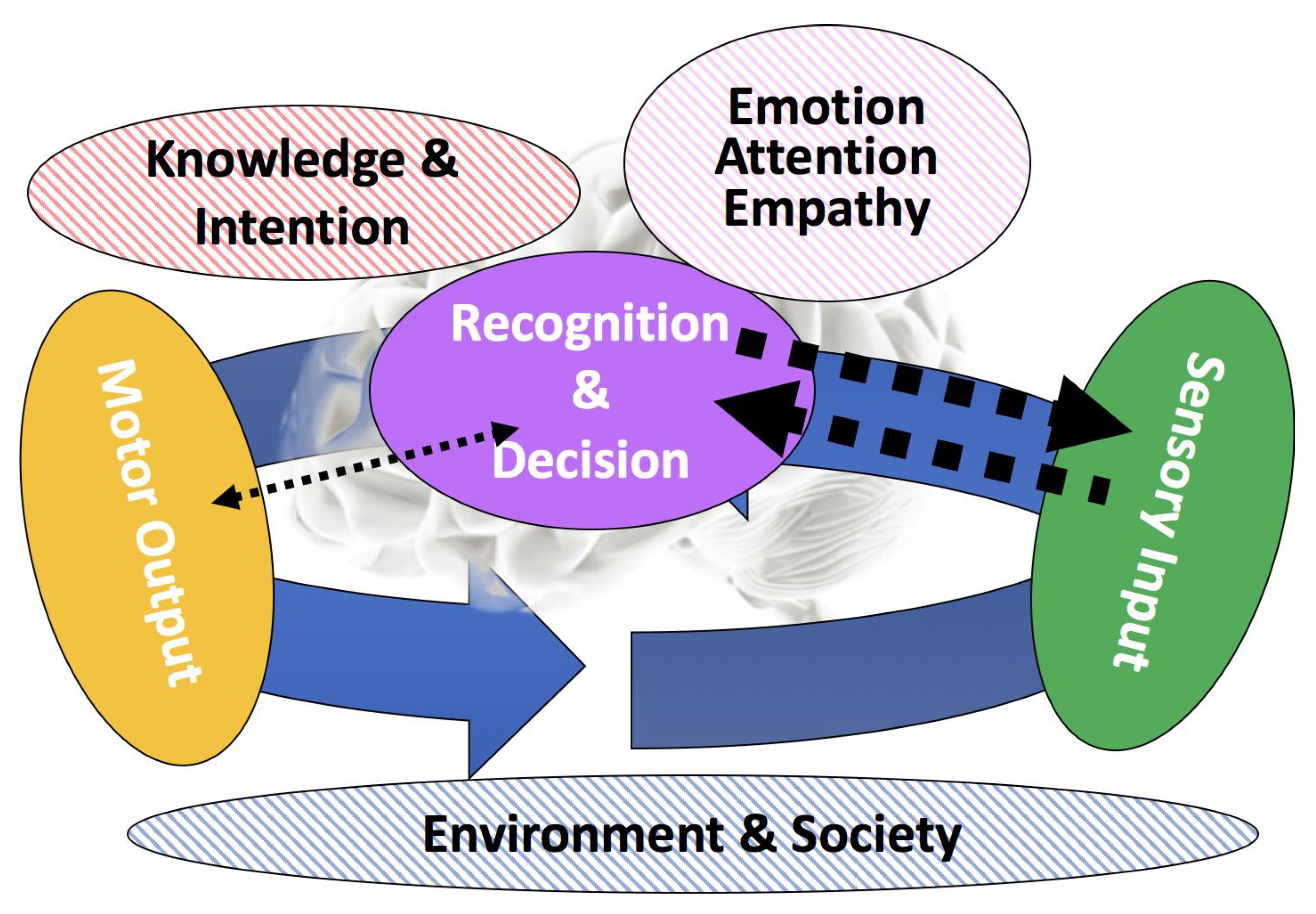
and those terms are organized in order from the evolutionary and developmental perspectives. The bottom-right of Figure 8 shows a conceptual model of empathy development ([9]), and the rest of the figure indicates the related studies, which are briefly introduced in the following sections. According to the evolutionary process of empathy proposed by de Waal [11], upper rectangles of empathy-related terms, such as emotional contagion, emotional empathy, and cognitive empathy, and lower ones related to imitation are positioned in parallel with the developmental process for self/other discrimination. The vertical ellipses indicate mental functions needed for empathy to emerge. In the case of emotional contagion, “MNS” is an assumption and “self-awareness” is an acquired mental function, and another assumption for “emotional empathy” to emerge. The numbers indicate the internal stage of the developmental process of empathy as follows:The narrow definition of empathy is simply the ability to form an embodied representation of another’s emotional state while, at the same time, being aware of the causal mechanism that induced that emotional state [10]. This suggests that the empathizer has interoceptive awareness of his or her own bodily states and is able to distinguish between the self and other, which is a key aspect of the definitions of empathy-related terms from an evolutionary perspective,
- No discrimination of self/others
- Self/non-self discrimination
- Self-awareness
- Complete self/others discrimination
- Metacognition of self as others
- Emotion regulation of self as others
- In-group/out-group emotion control
3.2.1. Dynamic Coupling Between Body and Brain with Neural Oscillator Networks
- Two kinds of motions and network structures behind may correspond to very primitive levels of unconscious (stable motion) and conscious (unstable motion) states, respectively. More plausibly, stable motions could be attractors, and unstable motions appear to transit between the attractors in the phase space.
- The separation of two kinds of subnetworks can be regarded as functional differentiation that is a basic mechanism for the emergence of new functions [13].
3.2.2. Emergence of MNS and Emotion Sharing
3.2.3. Sharing Painful Situations Induces Sympathetic Behavior
- The information for sensory discrimination of pain (location, intensity, and quality) is transmitted to the central nervous system from the sensory system.
- If the above experience is new, the related information, such as cause and/or reason, is also transmitted with the information above.
- Else, the memory of this experience is enhanced in the memory storage.
- When the painful situations of others are observed, emotion sharing of pain happens, and also the memory of the similar experience is recalled.
- Take actions to reduce the pain of others based on the recalled experience.
4. Discussion
- Associate the sensory discrimination of pain with the affective and motivational responses to pain (the construction of the pain matrix and memory dynamics).
- Recall the experience when a painful situation of others is observed.
- Generate appropriate behavior to reduce the pain.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Available online: http://www.deeplearningbook.org (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Asada, M.; Hosoda, K.; Kuniyoshi, Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Inui, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Ogino, M.; Yoshida, C. Cognitive developmental robotics: A survey. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2009, 1, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, J. Exploring Robotic Minds: Actions, Symbols, and Consciousness as Self-Organizing Dynamic Phenomena; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.A.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Hall, W.C.; LaMantia, A.S.; McNamara, J.O.; White, L.E. (Eds.) Neuroscience, 5th ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Melzack, R.; Wall, P.D. Pain Mechanisms: A New Theory. Science 1965, 150, 971–979. Available online: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/150/3699/971.full.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, J.; Haddadin, S. An Artificial Robot Nervous System to Teach Robots How to Feel Pain and Reflexively React to Potentially Damaging Contacts. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasetsu, T.; Horii, T.; Ishihara, H.; Asada, M. Flexible Tri-axis Tactile Sensor Using Spiral Inductor and Magnetorheological Elastomer. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 5834–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, T.; Seymour, B.; O’Doherty, J.; Kaube, H.; Dolan, R.J.; Frith, C.D. Empathy for pain involves the affective but not sensory components of pain. Science 2004, 303, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, M. Towards Artificial Empathy. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2015, 7, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Liencresa, C.; Shamay-Tsooryc, S.G.; Brünea, M. Towards a neuroscience of empathy: Ontogeny, phylogeny, brain mechanisms, context and psychopathology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waal, F.B. Putting the Altruism Back into Altruism: The Evolution of Empathy. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Mori, H.; Okuyama, Y.; Asada, M. Chaotic itinerancy within the coupled dynamics between a physical body and neural oscillator networks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguti, Y.; Tsuda, I. Mathematical modeling for evolution of heterogeneous modules in the brain. Neural Netw. 2015, 62, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, Y.; Kawai, Y.; Asada, M. Emergence of Mirror Neuron System: Immature vision leads to self-other correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning, and Epigenetic Robotics (ICDL-EpiRob 2011), Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 24–27 August 2011. (CD–ROM). [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, A.; Ogino, M.; Asada, M. Mapping Facial Expression to Internal States Based on Intuitive Parenting. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2007, 19, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horii, T.; Nagai, Y.; Asada, M. Imitation of human expressions based on emotion estimation by mental simulation. Paladyn J. Behav. Robot. 2016, 7, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, M.; Nishikawa, A.; Asada, M. A motivation model for interaction between parent and child based on the need for relatedness. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1 | |
| 2 |








© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asada, M. Artificial Pain May Induce Empathy, Morality, and Ethics in the Conscious Mind of Robots. Philosophies 2019, 4, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/philosophies4030038
Asada M. Artificial Pain May Induce Empathy, Morality, and Ethics in the Conscious Mind of Robots. Philosophies. 2019; 4(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/philosophies4030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsada, Minoru. 2019. "Artificial Pain May Induce Empathy, Morality, and Ethics in the Conscious Mind of Robots" Philosophies 4, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/philosophies4030038
APA StyleAsada, M. (2019). Artificial Pain May Induce Empathy, Morality, and Ethics in the Conscious Mind of Robots. Philosophies, 4(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/philosophies4030038