Hiding Full-Color Images into Audio with Visual Enhancement via Residual Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Planning
3. Numeric Watermark Embedding
3.1. Watermark Encryption
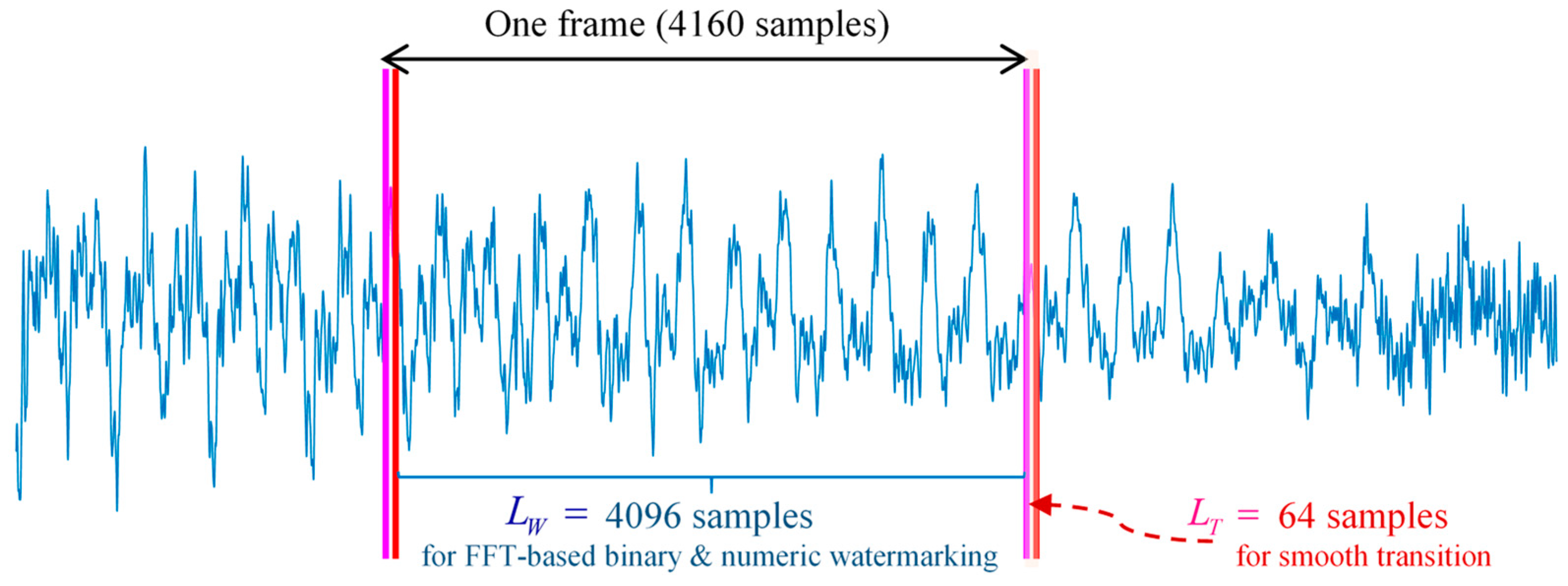
3.2. FFT-Based Phase Modulation
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Processing Time
4.2. Imperceptibility Test
4.3. Randomness Properties
4.4. Robustness Test
5. Watermark Enhancement
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charfeddine, M.; Mezghani, E.; Masmoudi, S.; Amar, C.B.; Alhumyani, H. Audio Watermarking for Security and Non-Security Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 12654–12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Huang, J.; Shi, Y.Q.; Goh, J.; Thing, V.L.L. Twenty years of digital audio watermarking—A comprehensive review. Signal Process. 2016, 128, 222–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-T.; Hsu, L.-Y. Robust, transparent and high-capacity audio watermarking in DCT domain. Signal Process. 2015, 109, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Zhao, H. A Novel Synchronization Invariant Audio Watermarking Scheme Based on DWT and DCT. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4835–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Natgunanathan, I.; Guo, S.; Zhou, W.; Nahavandi, S. Patchwork-Based Audio Watermarking Method Robust to De-synchronization Attacks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2014, 22, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-H.; Cheng, J.-S.; Yu, P.-T. Audio Watermarking Based on HAS and Neural Networks in DCT Domain. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2003, 2003, 764030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahpour, M.; Megias, D. High capacity robust audio watermarking scheme based on FFT and linear regression. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2012, 8, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar]
- Megías, D.; Serra-Ruiz, J.; Fallahpour, M. Efficient self-synchronised blind audio watermarking system based on time domain and FFT amplitude modification. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 3078–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, R.; Shimizu, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Nakamura, T. An audio watermarking method using a two-dimensional pseudo-random array. Signal Process. 2002, 82, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xue, X.; Lu, P. Localized audio watermarking technique robust against time-scale modification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2006, 8, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, P.; Xu, S.; Yang, H. A norm-space, adaptive, and blind audio watermarking algorithm by discrete wavelet transform. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-T.; Hsu, L.-Y. A DWT-Based Rational Dither Modulation Scheme for Effective Blind Audio Watermarking. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. A learning-based audio watermarking scheme using kernel Fisher discriminant analysis. Digit. Signal Process. 2013, 23, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-T.; Hsu, L.-Y.; Chou, H.-H. Variable-dimensional vector modulation for perceptual-based DWT blind audio watermarking with adjustable payload capacity. Digit. Signal Process. 2014, 31, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K.V.; Sengupta, I.; Das, A. An adaptive audio watermarking based on the singular value decomposition in the wavelet domain. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.Y.; Soon, I.Y.; Li, Z. Blind and robust audio watermarking scheme based on SVD–DCT. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-T.; Chou, H.-H.; Yu, C.; Hsu, L.-Y. Incorporation of perceptually adaptive QIM with singular value decomposition for blind audio watermarking. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2014, 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wornell, G.W. Quantization index modulation: A class of provably good methods for digital watermarking and information embedding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2001, 47, 1423–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, P.; Koetter, R. Data-Hiding Codes. Proc. IEEE 2005, 93, 2083–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, I.J.; Kilian, J.; Leighton, F.T.; Shamoon, T. Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassia, P.; Pitas, I.; Nikolaidis, N. Robust audio watermarking in the time domain. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2001, 3, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Natgunanathan, I.; Rong, Y.; Guo, S. Spread Spectrum-Based High Embedding Capacity Watermarking Method for Audio Signals. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Natgunanathan, I.; Peng, D.; Zhou, W.; Yu, S. A Dual-Channel Time-Spread Echo Method for Audio Watermarking. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Goh, J.; Thing, V.L.L. Time-Spread Echo-Based Audio Watermarking With Optimized Imperceptibility and Robustness. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, N.K.; Akhaee, M.A.; Ahadi, S.M.; Amindavar, H. Robust Multiplicative Patchwork Method for Audio Watermarking. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2009, 17, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, V.I.; Avez, A. Ergodic Problems of Classical Mechanics; Benjamin: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Hasler, M.; Maistrenko, Y.L. An introduction to the synchronization of chaotic systems: Coupled skew tent maps. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 1997, 44, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lee, T. High-Performance Self-Synchronous Blind Audio Watermarking in a Unified FFT Framework. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 19063–19076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, F.E. Sound Reproduction: The Acoustics and Psychoacoustics of Loudspeakers and Rooms, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CVG-UGR. (Computer Vision Group-University of Granada) Image Database. Available online: https://ccia.ugr.es/cvg/dbimagenes/ (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Kabal, P. An Examination and Interpretation of ITU-R BS.1387: Perceptual Evaluation of Audio Quality; TSP Lab Technical Report; Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, McGill University: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kabal, P. Matlab Implementation of the ITU-R BS 1387.1. 2004. Available online: http://www-mmsp.ece.mcgill.ca/Documents/Software/ (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Katzenbeisser, S.; Petitcolas, F.A.P. Information Hiding Techniques for Steganography and DIGITAL Watermarking; Katzenbeisser, S., Petitcolas, F.A.P., Eds.; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; p. xviii. 220p. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, W. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Barnes, N. A Deep Journey into Super-resolution: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, F.; Mei, K.; Zhang, G. Multi-scale Residual Network for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 527–542. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Wang, Y. A Note on Over-Smoothing for Graph Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13318. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.H.; Ye, J.C. Geometric GAN. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02894. [Google Scholar]
- Grubinger, M.; Clough, P.D.; Müller, H.; Deselaers, T. The IAPR TC-12 Benchmark: A New Evaluation Resource for Visual Information Systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Genoa, Italy, 24 May 2006; Available online: http://www-i6.informatik.rwth-aachen.de/imageclef/resources/iaprtc12.tgz (accessed on 15 August 2023).













| Embedding Scheme | FFT Index Range | Capacity [Bits/Numbers per Second] | SNR | ODG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVNM | [18, 37] | 169.62 bps | 25.004 [1.650] | 0.152 [0.014] |
| PM-(I) | [49, 96] | 508.85 nps | 18.954 [2.218] | −0.095 [0.049] |
| PM-(II) | [60, 107] | 508.85 nps | 20.218 [2.216] | −0.069 [0.055] |
| PM-(III) | [72, 119] | 508.85 nps | 21.260 [2.438] | −0.065 [0.082] |
| PM-(IV) | [85, 132] | 508.85 nps | 22.314 [2.593] | −0.052 [0.099] |
| AVNM + PM-(II) | [18, 37] & [60, 107] | 169.62 bps + 508.85 nps | 18.755 [1.326] | −0.094 [0.054] |
| Index Range | Entropy () | Correlation Coefficient () | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Watermarked | Original | Watermarked | |||
| PM-(I) | 15.041 [0.312] | 14.966 [0.256] | 0.105 [0.072] | 0.975 [0.019] | 0.975 [0.019] | 0.000 [4.9 × 10−6] |
| PM-(II) | 14.974 [0.255] | 0.096 [0.064] | 0.975 [0.019] | 0.000 [4.4 × 10−6] | ||
| PM-(III) | 14.987 [0.267] | 0.090 [0.066] | 0.975 [0.019] | 0.000 [4.2 × 10−6] | ||
| PM-(IV) | 14.984 [0.265] | 0.092 [0.067] | 0.975 [0.019] | 0.000 [4.6 × 10−6] | ||
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | Resampling | Conduct down-sampling to 22,050 Hz and then up-sampling back to 44,100 Hz. |
| B | Requantization | Quantize the watermarked signal to 8 bits/sample and then back to 16 bits/sample. |
| C | Zero thresholding | Zero out all samples below a threshold, which is set as 0.03 of the maximum dynamic range |
| D | Amplitude scaling | Scale the amplitude of the watermarked signal by 0.85. |
| E | Noise corruption (I) | Add zero-mean white Gaussian noise to the watermarked audio signal with SNR = 30 dB. |
| F | Noise corruption (II) | Add zero-mean white Gaussian noise to the watermarked audio signal with SNR = 20 dB. |
| G | Lowpass filtering | Apply a lowpass filter with a cutoff frequency of 4 kHz. |
| H | Lowpass filtering | Apply a lowpass filter with a cutoff frequency of 8 kHz. |
| I | DA/AD conversion | Convert the digital audio file to an analog signal and then resampling the analog signal at 44.1 kHz. The DA/AD conversion is performed through an onboard Realtek ALC892 audio codec, of which the line-out is linked with the line-in using a cable line during playback and recording. |
| J | Echo addition | Add an echo signal with a delay of 50 ms and a decay of 5% to the watermarked audio signal. |
| K | Jittering | Delete or add one sample randomly for every 100 samples. |
| L | MPEG-3 compression @ 128 kbps | Compress and decompress the watermarked audio signal with an MPEG layer III coder at a bit rate of 128 kbps. |
| M | MPEG-3 compression @ 64 kbps | Compress and decompress the watermarked audio signal with an MPEG layer III coder at a bit rate of 64 kbps. |
| Attack Type | FFT Index Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) [49, 96] | (II) [60, 107] | (III) [72, 119] | (IV) [85, 132] | |
| 0. None | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| A | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| B | 0.996 | 0.994 | 0.992 | 0.989 |
| C | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| D | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| E | 0.959 | 0.947 | 0.935 | 0.920 |
| F | 0.786 | 0.744 | 0.707 | 0.670 |
| G | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| H | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| I | 0.894 | 0.866 | 0.840 | 0.813 |
| J | 0.947 | 0.946 | 0.945 | 0.943 |
| K | 0.747 | 0.692 | 0.642 | 0.588 |
| L | 0.953 | 0.945 | 0.937 | 0.929 |
| M | 0.667 | 0.632 | 0.608 | 0.582 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.-T.; Lee, T.-T. Hiding Full-Color Images into Audio with Visual Enhancement via Residual Networks. Cryptography 2023, 7, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7040047
Hu H-T, Lee T-T. Hiding Full-Color Images into Audio with Visual Enhancement via Residual Networks. Cryptography. 2023; 7(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Hwai-Tsu, and Tung-Tsun Lee. 2023. "Hiding Full-Color Images into Audio with Visual Enhancement via Residual Networks" Cryptography 7, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7040047
APA StyleHu, H.-T., & Lee, T.-T. (2023). Hiding Full-Color Images into Audio with Visual Enhancement via Residual Networks. Cryptography, 7(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryptography7040047