Characterization of Raman Spectroscopy System Transfer Functions in Intensity, Wavelength, and Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Components in a Raman System
3. Transfer Function: Intensity
3.1. From the Excitation Source to the Sample
3.1.1. Laser
3.1.2. Steering Mirrors
3.1.3. Beam Splitter
3.1.4. Lenses
3.1.5. Filters
3.1.6. Optical Fibers
3.1.7. Inbound Summary
3.2. The Sample
3.2.1. Sample Interface
3.2.2. Raman Scattering
The Raman Cross Section
Scattering Collection
3.3. From the Sample to the Detector
3.3.1. 90° Collection Configuration
3.3.2. 180° Collection Configuration
3.3.3. Outbound Summary
3.4. Dispersive Device
3.5. Detectors
3.5.1. Photomultiplier Tubes (PMT)
3.5.2. Charge Coupled Device (CCD)
3.5.3. Avalanche Photodiode (APD)
3.6. Signal Transmission Cable
3.7. Amplifier
3.8. Data Acquisition Unit
3.9. Summary of the Intensity Transfer Function in a Raman System
4. Transfer Function: Wavelength
4.1. Laser
4.2. Sample
4.3. Filters
4.4. Optical Fiber
4.5. Dispersive Device
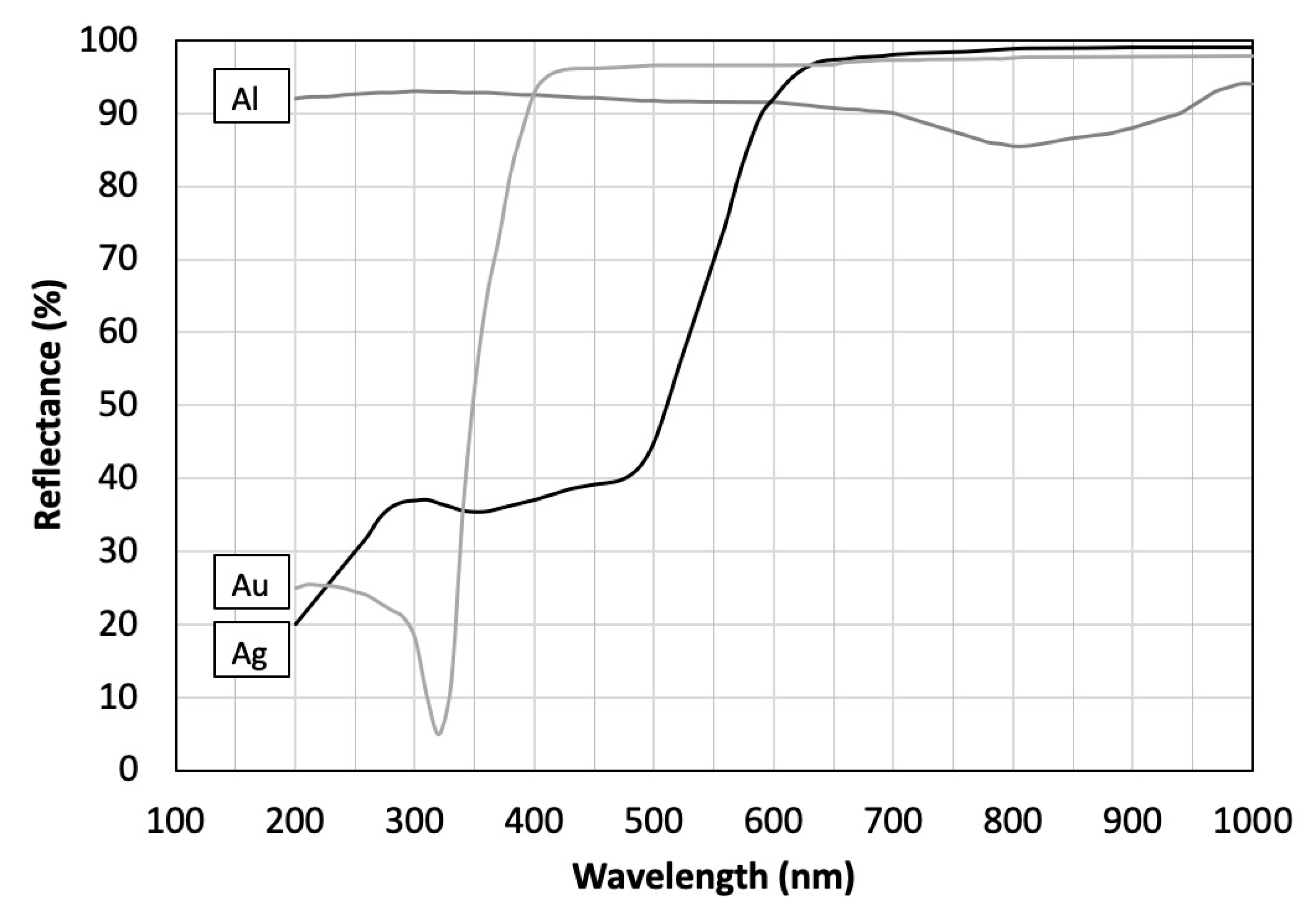
4.5.1. Mirrors
4.5.2. Grating
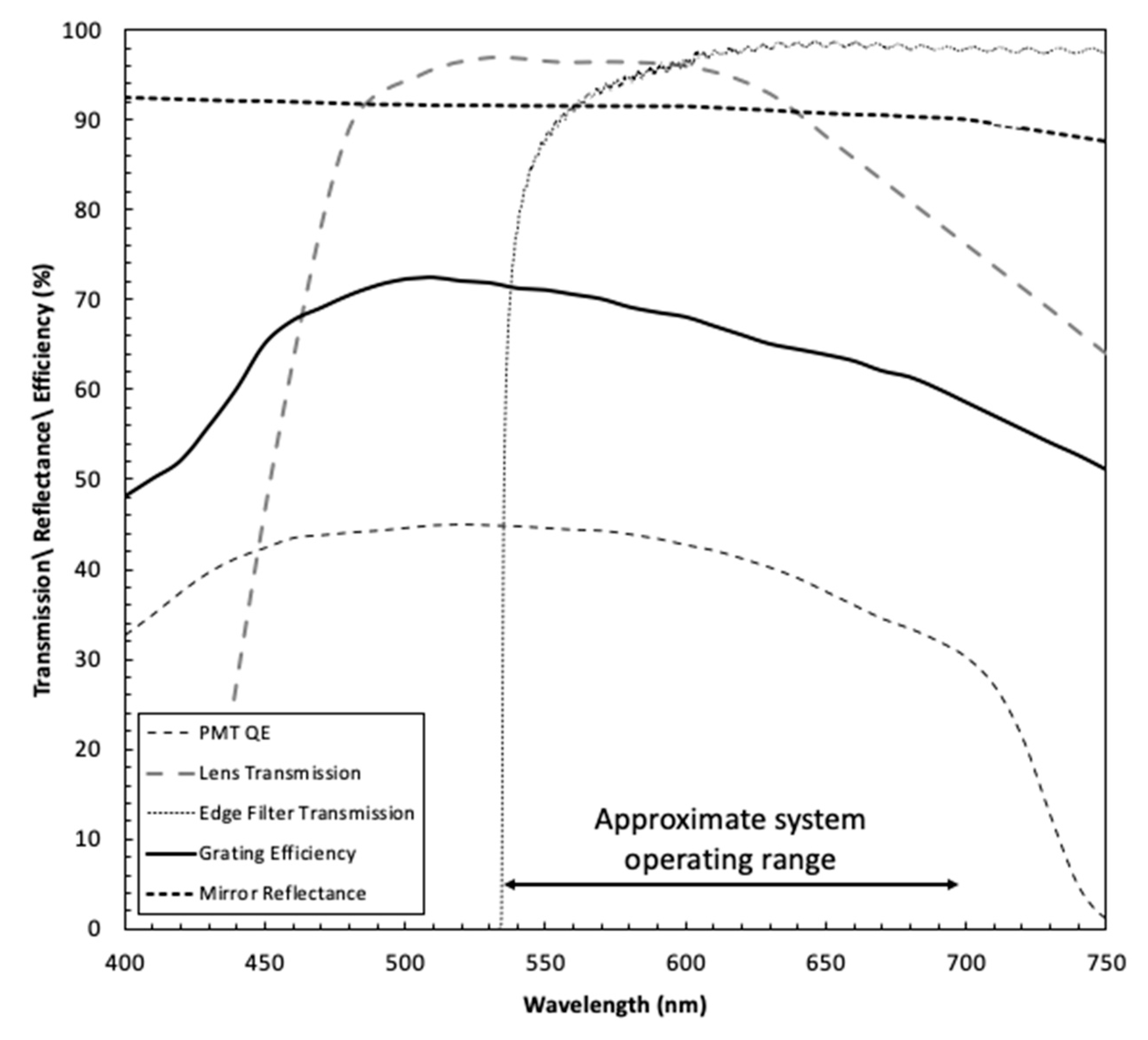
4.6. Detector
4.7. Effective Spectral Bandpass
4.8. Wavelength Resolving Power
4.9. Summary of the Wavelength Transfer Function in a Raman System
5. Transfer Function: Time
5.1. Optical Fibers
5.1.1. From Excitation Source to the Sample
5.1.2. From the Sample to the Dispersive Device
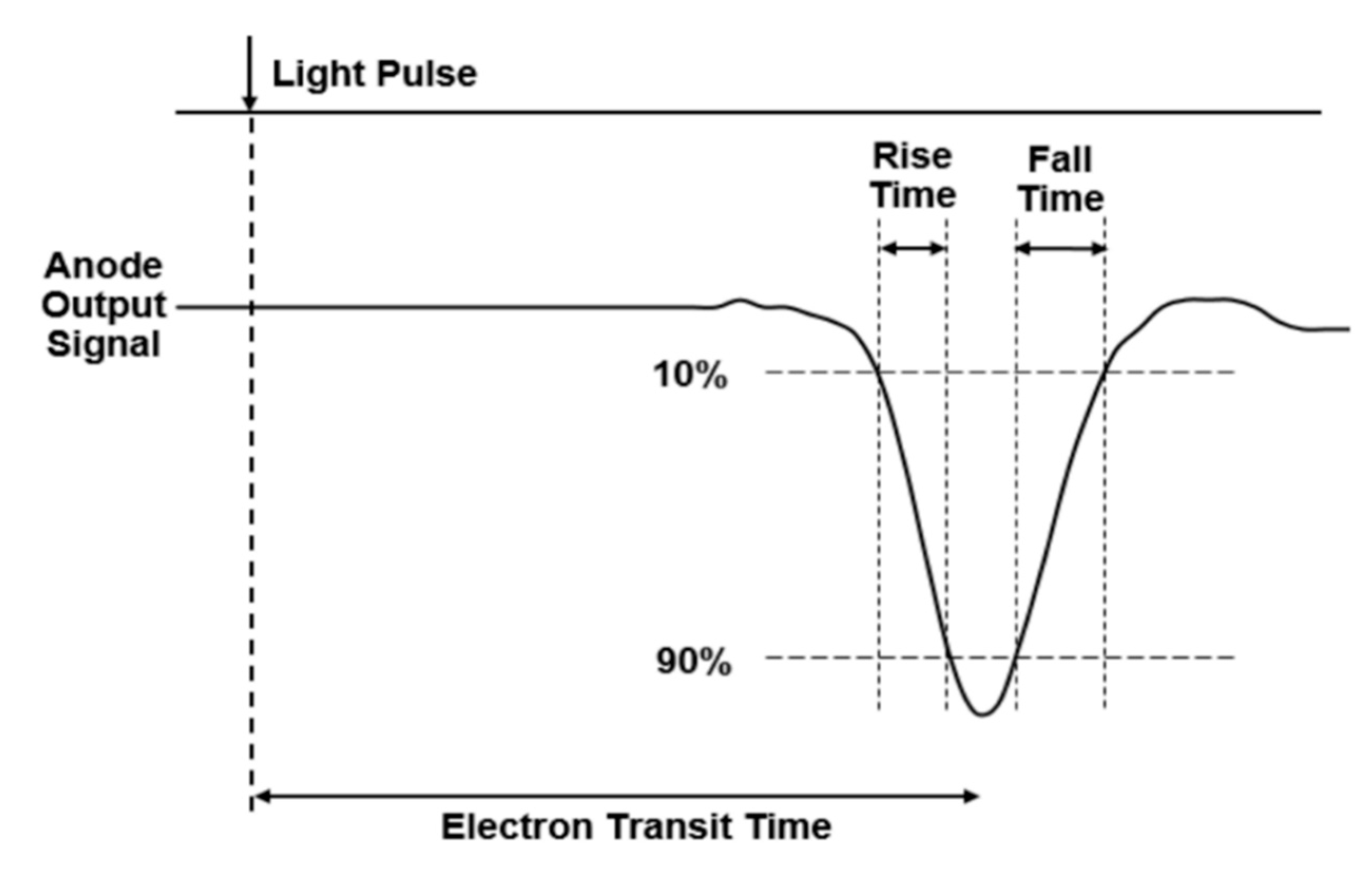
5.2. Detector Response Time
5.2.1. PMT
5.2.2. APD
5.2.3. CCD
5.3. Coaxial Cable Delay
5.4. Summary of the Time Transfer Function in a Raman System
6. Purdue CE Spectroscopy Lab 532 nm TRRS
6.1. System Description
6.1.1. Open-Path System
6.1.2. Closed-Path System
6.2. Open-Path Sample Calculation
- Equations in Table 2 have been employed to characterize the intensity of the laser source (Component {1} of the TRRS system) on a per pulse basis.
- Equations from Table 3 have been employed to define the intensity characteristics of the system on the inbound optical path to the sample, which contains one dichroic mirror {2} and one aspheric lens {3}.
- Due to the simplicity and open-path nature and careful optic selection of the Purdue TRRS system, no effects on time or wavelength are identified on the inbound path to the sample.
- The time characteristics of the system are defined by the inbound path length of 20 cm.
- Equations from Table 4 have been employed to characterize Raman scattering achieved in the sample cuvette {4}. As noted above, for the purpose of this example, the sample is defined as water and observations are focused on 649.98 nm with a Raman cross section equal to 7.29 × 10−29 cm2molecule−1 49].
- Equations from Table 5 have been employed to assess intensity effects on the outbound path which includes one aspheric lens {3}, the dichroic filter {2}, one achromat {5}, and one long-pass filter {7}.
- The wavelength transfer function is affected by the long-pass filter {7} in this stage of the system.
- The time characteristics of the system is defined by the outbound path length of 25 cm.
- Analysis of the intensity through the monochromator {8} in the system employs the equations in Section 3.4, which account for the mirrors and grating in the device.
- The wavelength transmission effects are directly linked to the mirror and grating characteristics of the system using equations articulated in Section 4.5.
- Transit time is estimated by the configuration of the monochromator.
- The output measures conveyed in the intensity analysis detailed in Table 7 are presented as a function of the total power at a given wavelength, λ, and then as a function of the number of photons at the wavelength λ. Power distribution cross the Raman spectrum is not specified.
- Equations detailed in Table 6 are employed to define the output intensity of the PMT {9}, and equations from Section 3.6, Section 3.7, and Section 3.8 are employed to define the intensity-related effects of the coaxial transmission cables, the amplifier {10}, and the data acquisition system {12}.
- The wavelength transfer function is most notably affected by the PMT {9} quantum efficiency curve in this stage of the system, as described in Section 4.6.
- Temporal effects in this stage of the system stem from transit delays in the PMT {9}, Amplifier {10}, and interconnecting cables as discussed in Section 5.3, as well as transit time spread in the PMT {9}.
6.3. Closed-Path System Sample Calculation
- As for the open-path system, the equations in Table 2 have been employed to characterize the intensity of the laser source (component {1} of the closed-path TRRS system) on a per pulse basis.
- The equations from Table 3 have been employed to define the intensity characteristics of the system on the inbound optical path to the sample, which contains one dichroic mirror {2}, one objective lens {13}, the in-bound fiber leg of the Raman probe, and the optical components built into the Raman probe {16}, which include an aspheric lens, bandpass filter, dichroic mirror, and focusing lens.
- Again, due to careful optic selection and use of low-OH fiber in the Raman probe {16}, no effects on wavelength are identified on the inbound path to the sample.
- The time characteristics of the system are defined by the inbound path length, including the in-bound fiber leg of the Raman probe.
- The calculation is similar to the open-path system discussion but with a different path length of the laser in the sample (dz) and notably different scattering collection (λ). Equations from Table 4 have been employed to characterize Raman scattering achieved in the sample cuvette {4}. As noted above, for the purpose of this example, the sample is again defined as water and observations are focused on 649.98 nm with a Raman cross section equal to 7.29 × 10−29 cm2molecule−1 [49].
- The equations from Table 5 have been employed to assess intensity effects on the outbound path which includes the outbound fiber leg of the Raman probe as well as its internal optics on the return path one micro aspheric lens, one dichroic mirror, one standard mirror, one long-pass filter, and a coupling optic {16}.
- The wavelength transfer function is affected by the long-pass filter in the probe in this stage in a manner identical to that in the open-path system.
- The time characteristics of the outbound path are defined by the outbound path length and fiber optic leg of the Raman probe {16}.
- Analysis of the intensity through the monochromator {15} in the system employs equations in Section 3.4, which account for the mirrors and grating in the device.
- The wavelength transmission effects are directly linked to the mirror and grating characteristics of the system using equations articulated in Section 4.5.
- Transit time is estimated by the configuration of the monochromator.
- As the components in this part of the system are identical to those in the open-path system, they will not be reanalyzed here and reference can be made to the previous discussion in Section 6.2.
6.4. Discussion of Transfer Function Analyses
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Symbols
| Radiated detector area | ||
| Area of the beam entering the optical train | ||
| Area of the beam entering the outbound optical train | ||
| Area of the beam on the coupling optic | ||
| Area of the beam exiting the optical train | ||
| Area of the beam on dispersive device coupling optic | ||
| Area of component immediately following dispersive device | ||
| APD | Avalanche photodiodes | |
| Capacitance in APD | ||
| Capacitance per meter length of the coaxial cable | ||
| CCD output in counts for a given pixel | ||
| CCD | Charge-coupled devices | |
| PMT collection efficiency | ||
| CCD device specific analog-to-digital conversion factor linking generated photoelectrons to reported counts | ||
| CCD device specific analog-to-digital conversion factor linking generated photoelectrons to a pixel intensity | ||
| CW | Continuous wave laser | |
| Speed of light | ||
| Density of scatters | ||
| Angular dispersion | ||
| DAQ | Data acquisition unit | |
| PMT detection efficiency | ||
| Linear dispersion | ||
| Material dispersion coefficient | ps/nm/km | |
| Diameter of the inbound beam at the pre-sample focusing optic | ||
| APD photon detection probability | ||
| Reciprocal linear dispersion | ||
| Waveguide dispersion coefficient | ps/nm/km | |
| Illuminated spot size in the sample | ||
| Diameter of the laser at the focal point | ||
| Path length of the laser in the sample | ||
| Change in the diffraction angle | ||
| Change in wavelength | ||
| Energy emitted by a CW laser | ||
| Charge of an electron | ||
| Energy emitted by a pulsed laser | ||
| Average pulse energy of a pulsed laser | ||
| Energy of a photon | ||
| Energy (in Joules) of photons of the dispersed band at wavelength λ | ||
| Energy of the laser excitation | ||
| Euler’s number | ||
| DAQ full scale range | ||
| The ratio of the lens’ focal length to the diameter of the aperture | ||
| Focal length of the focusing lens | ||
| Dispersive instrument focal length | ||
| Groove density of the grating | ||
| Amplifier gain | ||
| APD gain factor | ||
| CCD gain | ||
| PMT gain | ||
| Planck’s constant | ||
| Incident laser intensity on the sample | ||
| Intensity of a CW laser beam | ||
| Intensity of light ultimately reaching the dispersive device | ||
| The radiation coupled into the dispersive device that ultimately transits to the detector (at the exit of the dispersive device), at a given wavelength, λ | ||
| The intensity of light ultimately transmitted after traversing an optical train of components | ||
| Rounding down the number to the nearest integer | ||
| Intensity of collected Raman scattering immediately outside the sample container | ||
| Intensity of a pulsed laser beam | ||
| Raman intensity | ||
| Intensity of the laser beam | ||
| Angular wavenumber | ||
| Inductance per meter length of the coaxial cable | ||
| Coaxial cable loss per cable connector | ||
| Coaxial cable attenuation per unit length | ||
| Fiber optics connector loss | ||
| Fiber optics total loss | ||
| Fiber optics intrinsic loss/Fiber loss | ||
| Fiber optics splice loss | ||
| Length of the coaxial cable | ||
| Length of the fiber | ||
| MMF | Multi-mode fiber | |
| Diffraction order | ||
| DAQ bits | ||
| Number of grooves illuminated | ||
| Number of linked connector pairs | ||
| Number of fiber segments | ||
| Number of times the light interacts with gratings | ||
| Number of times the light interacts with mirrors | ||
| Number of splices | ||
| Effective refractive index | ||
| bulk fiber refractive index at the pulse center wavelength | ||
| . | Material refractive index | |
| P | Pulsed laser | |
| PMT | Photomultiplier tubes | |
| Average power of a CW laser | ||
| , | Light power incident on the detector for a given wavelength (band) λ | |
| Average power of a pulsed laser | ||
| Number of photon arrivals per unit time at the detector | ||
| Number of photons emitted from the laser over time | ||
| signal magnitude associated with a single photon | ||
| The efficiency (%) of the grating encountered at interaction | ||
| APD quantum efficiency | ||
| CCD quantum efficiency | ||
| PMT quantum efficiency | ||
| Reflectance | ||
| Number of quantization levels | ||
| Resistance in APD | ||
| Reflectance—air—container wall interface | ||
| Reflectance—container wall—air interface | ||
| Reflectance—container wall—sample interface | ||
| Grating chromatic resolving power | ||
| Reflectance of the fiber tip at the air-fiber interface | ||
| PMT circuit resistance load | ||
| Mirror reflectance | % | |
| Reflectance of the dispersive device mirrors | ||
| Reflectance of the lens | ||
| Reflectance—sample—container wall interface | ||
| Practical limit on wavelength resolution | ||
| APD photosensitivity | ||
| PMT photocathode radiant sensitivity | ||
| SAPD | Single-photon avalanche diodes | |
| SMF | Single-mode fiber | |
| Transmittance | ||
| Beam splitter transmittance | ||
| Percentage transmitted in a coaxial cable | ||
| The percentage of the excitation energy from the exterior of the sample interface that reaches the sample on the other side | ||
| Percentage transmitted of fiber optics | ||
| Transmittance of the filter | ||
| Transmittance of the lens | ||
| Signal transmission delay in a coaxial cable | ||
| Group delay | ||
| Transit time in fiber optics, highest order | ||
| Transit time in fiber optics, lowest order | ||
| Transit time in fiber optics | ||
| ton | Laser on time | s |
| Pulse width of a pulsed laser | s | |
| DAQ output voltage | ||
| APD output voltage | ||
| Electrical signal speed | ||
| CCD output voltage | ||
| Detector output voltage | ||
| Group velocity | ||
| Maximum values of the full-scale output | ||
| Minimum values of the full-scale output | ||
| Signal that ultimately reaches the data acquisition unit | ||
| Voltage threshold representative of a photon arrival | ||
| PMT voltage output | ||
| Illuminated width of the grating | ||
| Exit slit width | ||
| Diffraction angle | ||
| Repetition rate of a pulsed laser | ||
| Material chromatic dispersion | ||
| Pulse broadening | ||
| Total delay in a multi-mode optical fiber | ||
| Pulse broadening in a single-mode fiber | ||
| Waveguide dispersion broadening | ||
| Grating diffraction resolution limit | ||
| Raman shifts | ||
| CCD net integrative gain | ||
| APD net device gain in counting mode | ||
| PMT net device gain in counting mode | ||
| APD net integration mode gain | ||
| Net integration mode gain of the PMT | ||
| Collection cone angle | ||
| Incident angle relative to the fiber axis | ||
| Critical angle of acceptance in refraction | ||
| Wavelength | ||
| Emission band of a laser | ||
| Center peak laser line | ||
| Half-width at half maximum of the laser spectrum peak | ||
| Wavelength of the laser | ||
| Frequency of the laser source | ||
| Incident frequencies expressed in reciprocal centimeters | ||
| Scattered frequencies expressed in reciprocal centimeters | ||
| the compound product of the transmittances of all components in the inbound optical train | ||
| the compound product of the transmittances of all components in the return optical train | ||
| π | Mathematical constant that defines the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter | |
| Empirically determined Raman cross section | ||
| Pulse of spectral width | ||
| APD RC time constant | ||
| Collection optic diameter | ||
| Angle of critical ray incidence relative to the core-cladding normal | ||
| Projected area fraction of Raman scattering collected | ||
| Solid angle of Raman scattering collected by a lens | ||
| Light wave’s angular frequency |
References
- Raman, C.V.; Krishnan, K.S. A new type of secondary radiation. Nature 1928, 121, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowoidnich, K.; Schmidt, H.; Kronfeldt, H.-D.; Schwägele, F. A portable 671 nm Raman sensor system for rapid meat spoilage identification. Vib. Spectrosc. 2012, 62, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.S.; Lin, M. A portable Raman system for the identification of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. J. Rapid Methods Autom. Microbiol. 2008, 16, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waal, D. Micro-Raman and portable Raman spectroscopic investigation of blue pigments in selected Delft plates (17–20th Century). J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramendia, J.; Gomez-Nubla, L.; Castro, K.; Martinez-Arkarazo, I.; Vega, D.; Sanz López de Heredia, A.; García Ibáñez de Opakua, A.; Madariaga, J. Portable Raman study on the conservation state of four CorTen steel-based sculptures by Eduardo Chillida impacted by urban atmospheres. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arkarazo, I.; Sarmiento, A.; Maguregui, M.; Castro, K.; Madariaga, J. Portable Raman monitoring of modern cleaning and consolidation operations of artworks on mineral supports. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehlička, J.; Vítek, P.; Edwards, H.; Heagraves, M.; Čapoun, T. Application of portable Raman instruments for fast and non-destructive detection of minerals on outcrops. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Misra, A.K.; Sharma, B. Portable remote Raman system for monitoring hydrocarbon, gas hydrates and explosives in the environment. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Zou, M.; Wu, J. Rapid detection of gasoline by a portable Raman spectrometer and chemometrics. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceco, E.; Önnerud, H.; Menning, D.; Gilljam, J.L.; Bååth, P.; Östmark, H. Stand-off Imaging Raman Spectroscopy for Forensic Analysis of Post-Blast Scenes: Trace Detection of Ammonium Nitrate and 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene, Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and Explosives (CBRNE) Sensing XV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, B.R.; Heraud, P.; Stojkovic, S.; Morrison, D.; Beardall, J.; McNaughton, D. A portable Raman acoustic levitation spectroscopic system for the identification and environmental monitoring of algal cells. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 4955–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabuyele, M.B.; Martin, M.E.; Yan, F.; Stokes, D.L.; Mobley, J.; Cullum, B.M.; Wintenberg, A.L.; Lenarduzzi, R.; Vo-Dinh, T. Portable Raman Integrated Tunable Sensor (RAMiTs) for Environmental Field Monitoring, Advanced Environmental, Chemical, and Biological Sensing Technologies II.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Sinfield, J.V.; Monwuba, C.K. Assessment and correction of turbidity effects on Raman observations of chemicals in aqueous solutions. Appl. Spectrosc. 2014, 68, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCreery, R.L. Raman Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 225. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, G.; Fernández, J.; Tejeda, G.; Montero, S. The Raman spectra and cross-sections of H2O, D2O, and HDO in the OH/OD stretching regions. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 2004, 228, 38–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, G.W.; Copeland, R.A. Wavelength dependence of the Raman cross section for liquid water. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 2686–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenner, W.R.; Hyatt, H.A.; Kellam, J.M.; Porto, S. Raman cross section of some simple gases. JOSA 1973, 63, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penney, C.; Peters, R.S.; Lapp, M. Absolute rotational Raman cross sections for N2, O2, and CO2. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffey, A.H. Solid angle subtended by a circular aperture at point and spread sources: Formulas and some tables. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1954, 25, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy: Principles and Spectral Interpretation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Conners, T.E.; Banerjee, S. Surface Analysis of Paper; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, J. Introduction to Nonimaging Optics; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brennesholtz, M.S.; Stupp, E.H. Projection Displays; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Hass, G.; Schroeder, H.; Turner, A. Mirror coatings for low visible and high infrared reflectance. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1956, 46, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamatsu Photonics, K.K.; Editorial Committee. Photomultiplier Tubes, Basics and Applications, 4th ed.; Hamamatsu Photonics, K.K., Ed.; Electron Tube Division: Hamamatsu, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hamamatsu Photonics, K.K.; Editorial Committee. Opto-Semiconductor Handbook; Hamamatsu Photonics, K.K., Ed.; Solid State Division: Hamamatsu, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Durini, D. High Performance Silicon Imaging: Fundamentals and Applications of CMOS and CCD Sensors; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.; Dierker, S. Use of an unintensified charge-coupled device detector for low-light-level Raman spectroscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1986, 3, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillman, G.; Wolfe, C. Avalanche photodiodes. In Semiconductors and Semimetals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; Volume 12, pp. 291–393. [Google Scholar]
- Cova, S.; Ghioni, M.; Lacaita, A.; Samori, C.; Zappa, F. Avalanche photodiodes and quenching circuits for single-photon detection. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 1956–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renker, D. Geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes, history, properties and problems. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2006, 567, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, E.W. Coaxial Connector. U.S. Patent 4,035,054, 12 July 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Keithley Instruments Inc. Data Acquisition and Control Handbook; Keithley Instruments: Solon, Ohio, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Measurement Computing Corporation. Data Acquisition Handbook—A Reference for DAQ and Analog Digital Signal Conditioning; Measurement Computing Corporation: Norton, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, G. Optical Fiber Communications, 4th ed.; Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, J.M.; Jamro, M.Y. Optical Fiber Communications: Principles and Practice; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, C. Diffraction Grating Handbook, 7th ed.; Richardson Gratings, Newport Corporation: Rochester, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Office of the CTO, MKS Instruments, Inc. MKS Instruments Handbook-Principles & Applications in Photonics Technologies; MKS Instruments, Inc.: Andover, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L. Comparison of single-mode fiber dispersion measurement techniques. J. Lightwave Technol. 1985, 3, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillouin, L. Wave Propagation and Group Velocity; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Bogatyrev, V.A.; Bubnov, M.M.; Dianov, E.M.; Kurkov, A.; Mamyshev, P.V.; Prokhorov, A.; Rumyantsev, S.D.; Semenov, V.; Semenov, S.L.; Sysoliatin, A.A. A single-mode fiber with chromatic dispersion varying along the length. J. Lightwave Technol. 1991, 9, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hecht, J. Understanding Fiber Optics, 5th ed.; Laser Light Press: Auburndale, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Halme, L.; Kytonen, R. Background and introduction to EM screening (shielding) behaviours and measurements of coaxial and symmetrical cables, cable assemblies and connectors. In Proceedings of the IEE Colloquium on Screening Effectiveness Measurements, London, UK, 6 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- The ARRL UHF. Microwave Experimenter’s Handbook: Antennas, Components and Design; American Radio Relay League: Newington, CT, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Popovic, Z.; Kuester, E.F. Principles of RF and Microwave Measurements; University of Colorado, Electromagnetics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Campus Box: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005; Volume 425, pp. 80309–80425. [Google Scholar]
- Sinfield, J.V.; Colic, O.; Fagerman, D.; Monwuba, C. A low cost time-resolved Raman spectroscopic sensing system enabling fluorescence rejection. Appl. Spectrosc. 2010, 64, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinfield, J.V.; Colic, O. Time Resolved Raman Spectroscopy. US Patent 8,325,337, 4 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Monwuba, C.K. Geoenvironmental Influences on Raman Spectroscopic Monitoring of Chlorinated Solvents Natural Attenuation; Purdue University: Lafayette, IN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Plakhotnik, T.; Reichardt, J. Accurate absolute measurements of the Raman backscattering differential cross-section of water and ice and its dependence on the temperature and excitation wavelength. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 194, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
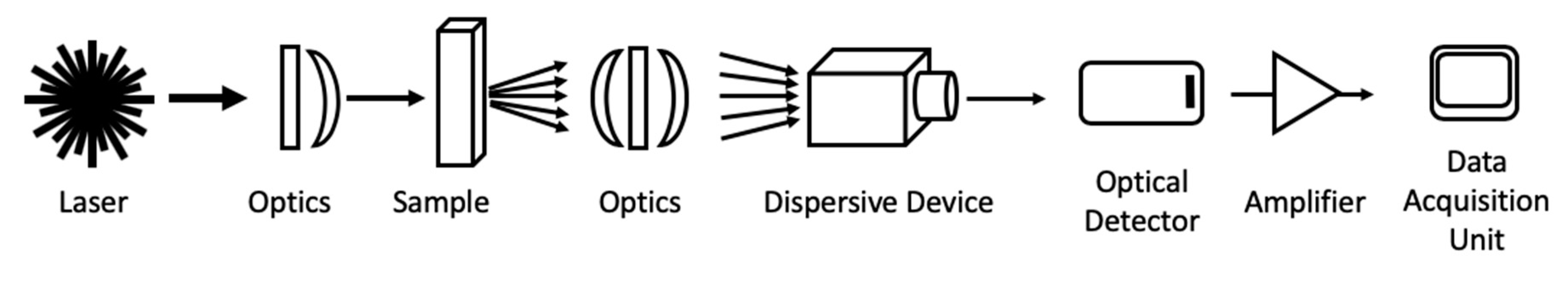




| Device/Object | Function | |
|---|---|---|
| Excitation source | Laser | A device that emits light of a narrow bandwidth through optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation; may be continuous wave (CW) (characterized by average power) or pulsed (characterized by average pulse power, pulse duration, and repetition rate) |
| Sample | Sample container | Typically, a cuvette or other container made of optical grade material (e.g., quartz) or having a window made of such material (e.g., sapphire) |
| Wavelength selector | Spectrograph | A device that disperses light into its component wavelengths; typically contains collimators (mirrors) and one or more gratings that diffract light |
| Monochromator | A device that disperses light into its component wavelengths and transmits a selected narrow subset of incident wavelengths; typically contains collimators (mirrors) and one or more gratings that diffract light | |
| Detector * | Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) | A device that converts inbound photons into electrons; photons impact a photocathode resulting in proportional ejection of electrons; electrons are accelerated and amplified in the device yielding a gain on the order of 106, enabling single photon counting |
| Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) | A device that converts light into an electrical signal by employing a silicon chip constructed of an array of photosensitive capacitors. The capacitors accumulate an electric charge proportional to incident light intensity; the array structure facilitates examination of multiple wavelength bands simultaneously; typically requires external cooling | |
| Avalanche Photodiode (APD) | A semiconductor device that takes advantage of the photoelectric effect to convert light into electricity, in which application of a high reverse bias voltage causes an avalanche effect yielding a significant gain | |
| Optics | Lens | An optic that focuses or disperses an optical beam. Sometimes, the surface is coated with different materials (typically metals) to eliminate reflections and/or to enhance transmission. |
| Mirror | An optic that reflects light; the reflected light usually has the same range of wavelengths as the incident light. | |
| Filter | An optical component that transmits or rejects a specific range of wavelengths | |
| Beam splitter | An optical component that divides the incident beam into two or more beams of different flux | |
| Amplifier | An electronic device that increases electrical signal power | |
| Data Acquisition Unit (DAQ) | A device that measures, digitizes, and records an electrical signal | |
| Optical fibers | A flexible dielectric waveguide consisting of a high refractive index core surrounded by cladding of a lower refractive index, which takes advantage of total internal reflection to transmit optical radiation over distance | |
| Coaxial Cable | A structured electrical cable consisting of an inner electrically insulated conductor surrounded by a conducting shield used to transmit electrical signals |
| Excitation Source (Inbound) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Laser Type | Continuous Wave (CW) | Pulsed (P) |
| Repetition rate | - | |
| Wavelength (nm) | ||
| Power (average) (Watts) | (2) | |
| Intensity (Watts/cm2) | ||
| Energy (Joules) | (1) | (3) |
| Number of photons | (hc/) (7) | |
| Section/Equation | 3.1.1 (1)–(3), (7) | |
| Inbound (Excitation Source—Optical Path—Outside Container Wall) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Mirror | Beam Splitter | Lens | Objective | Filter | Fiber Optics * | |||
| Fiber | Connector | Splice | Interface | ||||||
| Component quantity (number of units) | |||||||||
| (m) | |||||||||
| Reflectance (%) (per surface) | ⯍ | - | - | - | - | - | - | ⯍ | |
| Transmittance (%) | - | ▴ | - | - | - | - | |||
| Section/Equation | 3.1.2 | 3.1.3 | 3.1.4 (8) | 3.1.4 | 3.1.5 | 3.1.6 (9) (10) | 3.1.6 | ||
| % Loss (per component) | 1 − | (dB/m) | (dB) | (dB) | |||||
| ◈ | |||||||||
| % Passing (per component) | ★ | ||||||||
| % Passing ⯎ (total for component type) | |||||||||
| % Passing 🟀 (cumulative) | (12) | ||||||||
| From Inbound—Container Wall—Sample—Container Wall—to Outbound | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interface | Inbound Outside Container Wall | Container Wall—In | Scattering at Sample | Container Wall—Out | Outbound Outside Container Wall |
Reflectance (%)  | - | - | - | ||
| Transmittance (%) | - | - | - | ||
| Section/Equation | 3.1.7 (11), (14) | 3.2.1; 3.2.2 (13), (16) | 3.2.2 (17)–(19), (20) | 3.2.2 (21) | 3.2.2 (22) |
| % Passing | - | - | - | ||
| Intensity passing (Watts/cm2) | (Watts) | - | |||
| Outbound (Outside Container Wall—Optical Path—Entry to Dispersive Device) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Lens | Objective | Dichroic Mirror | Mirror | Filter | Fiber Optics * | |||
| Fiber | Connector | Splice | Interface | ||||||
| Component quantity (number of units) | |||||||||
| (m) | |||||||||
| Reflectance (%) (per surface) | - | - | ⯍ | - | - | - | - | ⯍ | |
| Transmittance (%) | - | ▴ | - | - | - | - | |||
| Section (for theory) | 3.1.4 | 3.1.4 | 3.1.3 | 3.1.2 | 3.1.5 | 3.1.6 | 3.1.6 | ||
| % Loss (per component) | 1- | (dB/m) | (dB) | (dB) | |||||
| ◈ | |||||||||
| % Passing (per component) | ★ | ||||||||
| % Passing ⯎ (total for component type) | |||||||||
| % Passing 🟀 (cumulative) | |||||||||
| From Dispersive Device—Detector—To Amplifier | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | PMT | CCD | APD |
| Input Power (W) @ λ | |||
| Input Photons/sec @ λ | |||
| Section/Equation | 3.5.1 (30)–(32) | 3.5.1 (33), (34) | 3.5.1 (35), (36) |
| Net Integration Gain | |||
| Integrated Output (Volts) | |||
| Net Counting Gain | |||
| Counting Output (Volts) | - | ||
| Counting Output (Counts) | - | - | |
| Path | Intensity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (component #) | Equation Source | Section/Equation | Parameters | % Passing Component | Cumulative % Passing | Power (Watts) | Intensity (Watts/cm2) (per pulse) | Related Parameter | ||
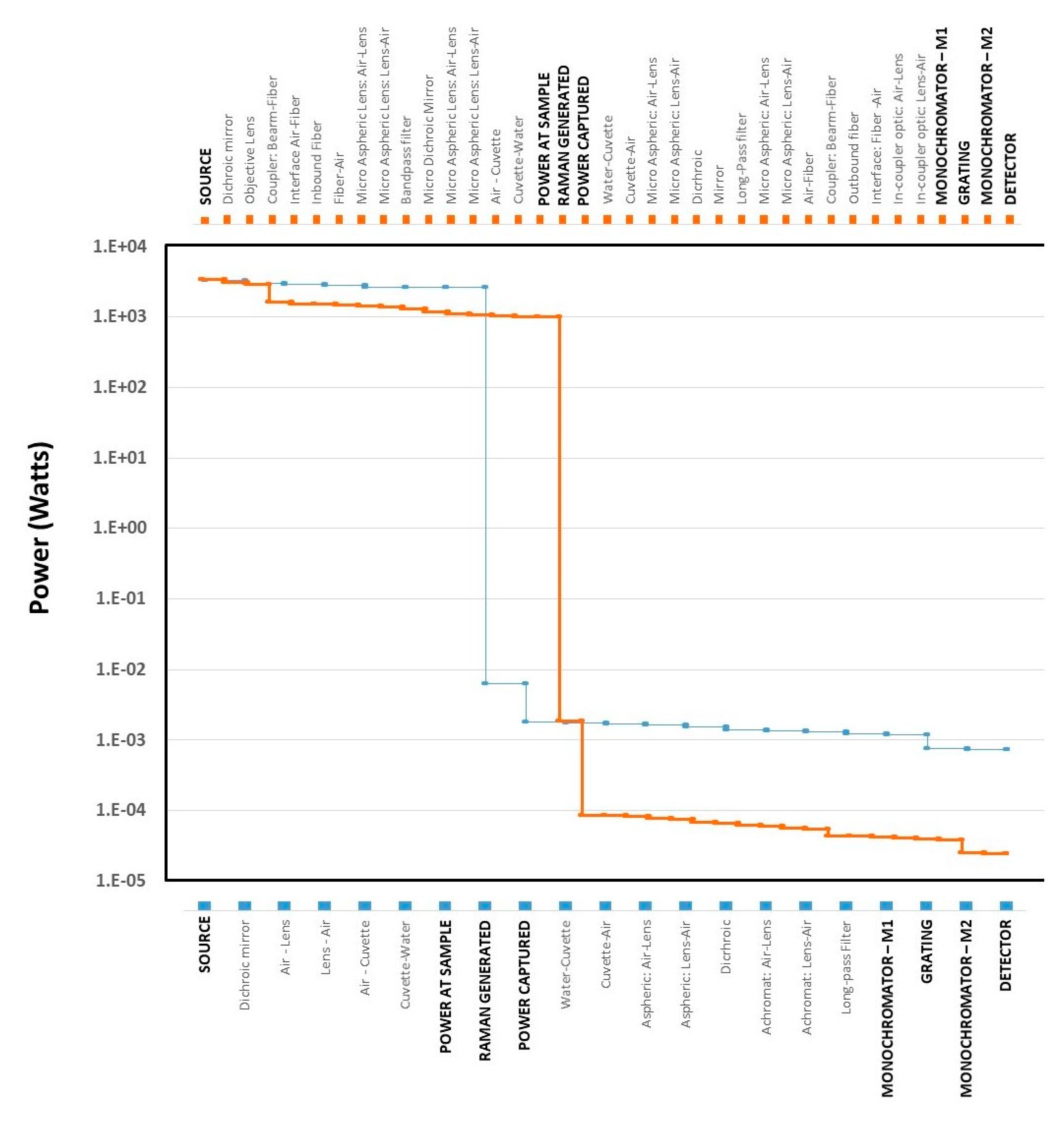
| Excitation | Laser Source {1} | Table 2 | 3.1.1/(3) | 3 μJ/pulse ps kHz | - | - | 3.33E + 03 | 2.52E + 05 | ||
| Dichroic mirror {2} | Table 3 | 3.1.3 | = 90% | 90.0% | 90.0% | 3.00E + 03 | 2.27E + 05 | |||
| Aspheric lens {3} | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 1.50 | 96.0% | 86.4% | 2.88E + 03 | 2.18E + 05 | |||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 82.9% | 2.76E + 03 | 2.09E + 05 | |||||
| Sample cuvette {4} | Table 4 | 3.2.1/(13) | Air-Cuvette | 96.5% | 80.0% | 2.67E + 03 | 2.02E + 05 | |||
| 3.2.1/(13) | Cuvette-Water | 97.8% | 78.2% | 2.61E + 03 | 1.97E + 05 | |||||
| 3.2.1/(14–16) | At sample (focal point) | - | - | 2.61E + 03 | 7.62E + 08 | |||||
| Raman | 3.2.2.1/(17) | cm2molecule−149]. molecules/cm3 cm cm2 | 2.44E − 04 | 1.91E − 02% | 6.73E − 03 | - | ||||
| 3.2.2.2/(18–20) | 28.1% | 5.37E − 03% | 1.79E − 03 | 9.12E − 05 | ||||||
| 3.2.2.2/(21) | Water—Cuvette | 97.8% | 5.23E − 03% | 1.75E − 03 | 8.92E − 05 | |||||
| 3.2.2.2/(21) | Cuvette—Air | 96.5% | 5.07E − 03% | 1.69E − 03 | 8.60E − 05 | |||||
| Aspheric lens {3} | Table 5 | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 96.0% | 4.87E − 03% | 1.62E − 03 | 8.26E − 05 | |||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 4.67E − 03% | 1.56E − 03 | 7.93E − 05 | |||||
| Dichroic mirror {2} | 3.1.3 | = 90% | 90.0% | 4.20E − 03% | 1.40E − 03 | 7.14E − 05 | ||||
| Achromat {5} | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 96.0% | 4.04E − 03% | 1.35E − 03 | 6.85E − 05 | ||||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 3.87E − 03% | 1.29E − 03 | 6.58E − 05 | |||||
| Long-pass Filter {7} | 3.1.5 | = 95% | 95.0% | 3.68E − 03% | 1.23E − 03 | 6.25E − 05 | ||||
| Monochromator {8} | 3.4 (25) | Collimator1: air→ mirror→ air | 97.5% | 3.59E − 03% | 1.20E − 03 | - | ||||
| 3.4 (26) | Grating Efficiency | 63.8% | 2.29E − 03% | 7.63E − 04 | - | |||||
| 3.4 (25) | Collimator 2: air→ mirror→ air | 97.5% | 2.23E − 03% | 7.44E − 04 | - | |||||
| PMT {9} | 3.4 (27) | cm2 | - | 2.23E −03% | 7.44E − 04 | 3.72E − 03 | ||||
| Intensity reaching detector will be dispersed across the Raman spectrum based on sample composition. All subsequent calculations illustrate the relative effects of detection, amplification, and DAQ electronics on measured outputs. | ||||||||||
| Component effect | Cumulative Effect | Units | ||||||||
| Electrons | PMT {9} | 3.5/(28) | = 0.20 cm2 | Watts @ λ | ||||||
| 3.5/(29) | J | (3.27E + 18) | Photons/s | |||||||
| 3.5.1/(32) | = 106 37.5 % = 80% Ω | (2.40E − 12) | Volts | |||||||
| Coaxial Cable | 3.6/(37)–(38) | = 1.3 dB/100m (RG-58 cable) cm dB loss | 91.2% | (2.19E − 11) | Volts | |||||
| Amplifier {10} | 3.7/(39) | 20× | (4.38E − 11) | Volts | ||||||
| Coaxial Cable | 3.6/(37)–(38) | = 1.3 dB/100m (RG-58 cable) cm dB loss | 91.0% | (3.98E − 11) | Volts | |||||
| DAQ {12} | 3.8/(40) | V Voltage Resolution V | If mV, one photon count is recorded | Photons | ||||||
| Path (Component #) | Section/Equation | Parameters | Wavelength at Component | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation | Laser Source {1} | 4.1 (41) | nm nm nm | nm |
| Dichroic mirror {2} | - | - | nm | |
| Aspheric lens {3} | - | - | nm | |
| Sample cuvette {4} | - | - | nm | |
| Raman | Sample cuvette {4} | 4.2 (42), (43) | cm−1 Sample: Water (peak) nm + Other minor Raman lines | nm+ Other minor Raman lines |
| Aspheric lens {3} | - | - | nm+ Other minor Raman lines | |
| Dichroic mirror {2} | - | - | nm+ Other minor Raman lines | |
| Achromat {5} | - | - | nm+ Other minor Raman lines | |
| Long-pass Filter {7} | 4.3 | Keep wavelength > nm | nm+ Other minor Raman lines (Range from 534 nm to 690 nm) | |
| Monochromator {8} | 4.5.1 | Collimator 1 | nm+ Other minor Raman lines (Range from 534 nm to 690 nm) | |
| 4.5.2 (44), (45), (47), (49) | Grating nm mm nm/mm mm 0.013 nm | nm+ Other minor Raman lines (Range from 534 nm to 690 nm) | ||
| 4.5.1 | Collimator 2 | nm+ Other minor Raman lines (Range from 534 nm to 690 nm) | ||
| Electron | PMT {9} | - | - | nm (Range from 534 nm (70 cm−1) to 690 nm (4300 cm−1)) |
| Coaxial Cable | - | - | - | |
| Amplifier {10} | - | - | - | |
| Coaxial Cable | - | - | - | |
| DAQ {12} | - | - | - |
| Path (Component #) | Section/Equation | Parameters | Time Delay at Component | Cumulative Time Delay | Time Spread | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation | Laser Source {1} | - | Inbound path length cm | - | - | - |
| Dichroic mirror {2} | - | - | - | - | ||
| Aspheric lens {3} | - | - | - | - | ||
| Sample cuvette {4} | - | ns | ns | - | ||
| Raman | Sample cuvette {4} | - | Outbound path length cm | - | - | - |
| Aspheric lens {3} | - | - | - | - | ||
| Dichroic mirror {2} | - | - | - | - | ||
| Achromat {5} | - | - | - | - | ||
| Long-pass Filter {7} | - | ns | ns | - | ||
| Monochromator {8} | - | Monochromator Configuration total path length cm | ns | ns | - | |
| Electron | PMT {9} | 5.2 | Electron transit time ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Coaxial Cable | 5.3 (60), (61) | (RG-58 cable) cm m/s ns | ns | ns | - | |
| Amplifier {10} | 5.3 | ns | ns (max) | ns (max) | - | |
| Coaxial Cable | 5.3 (60), (61) | (RG-58 cable) cm m/s ns | ns | ns (max) | - | |
| DAQ {12} | - | - | - | - | - |
| Path | Intensity | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (component #) | Equation Source | Section/Equation | Parameters | % passing Component | Cumulative % Passing | Power (Watts) | Intensity (Watts/cm2) (per pulse) | Related Parameter | |||
| Excitation | Laser Source {1} | Table 2 | 3.1.1/(3) | 3 μJ/pulse ps kHz | - | - | 3.33E + 03 | 2.52E + 05 | |||
| Dichroic mirror {2} | Table 3 | 3.1.3 | = 90% | 90.0% | 90.0% | 3.00E + 03 | 2.27E + 05 | ||||
| Fiber coupler—Objective lens {13} | 3.1.4/(8) | . | 93.0% | 83.7% | 2.79E + 03 | 2.11E + 05 | |||||
| - | Coupling Efficiency = 0.56 | 56.0% | 46.9% | 1.56E + 03 | 1.18E + 05 | ||||||
| - | Air-Fiber | 96.0% | 45.2% | 1.51E + 03 | - | ||||||
| Raman Probe {16} | Inbound fiber | ||||||||||
| 3.1.6 | m dB/km | 99% | 45.0% | 1.50E + 03 | 1.73E + 07 | ||||||
| - | Fiber-Air | 96.0% | 43.3% | 1.44E + 03 | - | ||||||
| Micro aspheric | |||||||||||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 96.0% | 41.6% | 1.39E + 03 | 1.62E + 04 | ||||||
| Lens—Air | 96.0% | 39.9% | 1.33E + 03 | 1.56E + 04 | |||||||
| Bandpass filter | 3.1.5 | = 95% | 95% | 37.9% | 1.26E + 03 | 1.48E + 04 | |||||
| Micro dichroic mirror | 3.1.3 | = 90% | 90% | 34.2% | 1.14E + 03 | 1.33E + 04 | |||||
| Micro aspheric lens | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 96.0% | 32.8% | 1.09E + 03 | 1.28E + 04 | |||||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 31.5% | 1.05E + 3 | 1.23E + 04 | ||||||
| Sample cuvette {4} | Table 4 | 3.2.1/(13) | Air-Cuvette | 96.5% | 30.4% | 1.01E + 03 | - | ||||
| 3.2.1/(13) | Cuvette-Water | 97.8% | 29.7% | 9.90E + 02 | - | ||||||
| 3.2.1/(14)–(16) | At sample (focal point) | - | - | 9.90E + 02 | 5.58E + 10 | . | |||||
| Raman | 3.2.2.1/(17) | cm2molecule−1 [49]. molecules/cm3 cm cm2 | 1.83E − 04% | 5.44E – 05% | 1.81E − 03 | - | |||||
| 3.2.2.2/(18)–(20) | 4.6% | 2.51E – 06% | 8.37E − 05 | 9.79E − 04 | |||||||
| 3.2.2.2/(21) | Water—Cuvette | 97.8% | 2.46E – 06% | 8.19E − 05 | 9.57E − 04 | ||||||
| 3.2.2.2/(21) | Cuvette—Air | 96.5% | 2.37E – 06% | 7.90E − 05 | 9.24E − 04 | ||||||
| Raman Probe {16} | Micro aspheric lens | Table 5 | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 1.50 | 96.0% | 2.28E – 06% | 7.59E − 05 | 8.87E − 04 | ||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 2.18E − 06% | 7.28E − 05 | 8.51E − 04 | ||||||
| Micro Dichroic mirror (as a mirror) | 3.1.3 | air→ mirror→ air | 90.0% | 1.97E − 06% | 6.55E − 05 | 7.66E − 04 | |||||
| Mirror | 3.1.2 | air→ mirror→ air | 96.0% | 1.89E − 06% | 6.29E − 05 | 7.36E − 04 | |||||
| Long-pass Filter | 3.1.5 | = 96% | 96.0% | 1.79E − 06% | 5.98E − 05 | 6.99E − 04 | |||||
| Micro aspheric lens | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 1.50 | 96.0% | 1.72E − 06% | 5.74E − 05 | 6.71E − 04 | ||||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 1.65E − 06% | 5.51E − 05 | 6.44E − 04 | ||||||
| - | Air-Fiber | 96.0% | 1.59E − 06% | 5.31E − 05 | - | ||||||
| Outbound fiber | - | Coupling Efficiency = 0.8 | 80% | 1.27E − 06% | 4.25E − 05 | - | |||||
| 3.1.6 | m dB/km | 99.6% | 1.27E − 06% | 4.23E − 05 | 1.35E − 01 | ||||||
| - | Air-Fiber | 96.0% | 1.22E − 06% | 4.08E − 05 | - | ||||||
| Fiber coupler w/f-matching lens | 3.1.4/(8) | Air—Lens | 1.50 | 96.0% | 1.17E − 06% | 3.91E − 05 | - | ||||
| 3.1.4/(8) | Lens—Air | 96.0% | 1.13E − 06% | 3.76E − 05 | - | ||||||
| Monochromator {8} | 3.4 (25) | Collimator1: air→ mirror→ air | 97.5% | 1.10E − 06% | 3.66E − 05 | - | |||||
| 3.4 (26) | Grating Efficiency | 67% | 7.36E − 07% | 2.45E − 05 | - | ||||||
| 3.4 (25) | Collimator 2: air→ mirror→ air | 97.5% | 7.18E − 07% | 2.39E − 05 | - | ||||||
| PMT {9} | 3.4 (27) | cm2 | - | 7.18E − 07% | 2.39E − 05 | 1.2E − 04 | |||||
| Path (Component #) | Section/Equation | Parameters | Time Delay at Component | Cumulative Time Delay | Time Spread | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation | Excitation source to coupler {13} | - | Path length = 15 cm | ns | ns | - |
| Raman Probe {16} Inbound fiber optics | 5.1.1/(50–53) | Inbound fiber optics length cm m/s ns ps/nm/km ps/nm/km nm m ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Raman | Raman Probe {16} Outbound fiber optics | 5.1.2/(54–59) | Outbound fiber optics length cm ns ns ns ps/nm/km ps/nm/km nm m ns | ns (min) ns (max) | ns (min) ns (max) | ns |
| Monochromator {15} | Monochromator Configuration total path length cm | ns | ns (min) ns (max) | - | ||
| Electron | PMT {9} | 5.2 | Electron transit time ns | ns | ns (min) ns (max) | ns |
| Coaxial Cable | 5.3 (60, 61) | (RG-58 cable) cm m/s ns | ns | . ns(min). ns (max) | - | |
| Amplifier {10} | 5.3 | ns | ns (max) | ns(min) ns (max) | - | |
| Coaxial Cable | 5.3 (60, 61) | (RG-58 cable) cm m/s ns | ns | ns (min) ns (max) | - | |
| DAQ {12} | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-C.; Sinfield, J.V. Characterization of Raman Spectroscopy System Transfer Functions in Intensity, Wavelength, and Time. Instruments 2020, 4, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments4030022
Lin Y-C, Sinfield JV. Characterization of Raman Spectroscopy System Transfer Functions in Intensity, Wavelength, and Time. Instruments. 2020; 4(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments4030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yu-Chung, and Joseph V. Sinfield. 2020. "Characterization of Raman Spectroscopy System Transfer Functions in Intensity, Wavelength, and Time" Instruments 4, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments4030022
APA StyleLin, Y.-C., & Sinfield, J. V. (2020). Characterization of Raman Spectroscopy System Transfer Functions in Intensity, Wavelength, and Time. Instruments, 4(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments4030022




