From SuperTIGER to TIGERISS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SuperTIGER
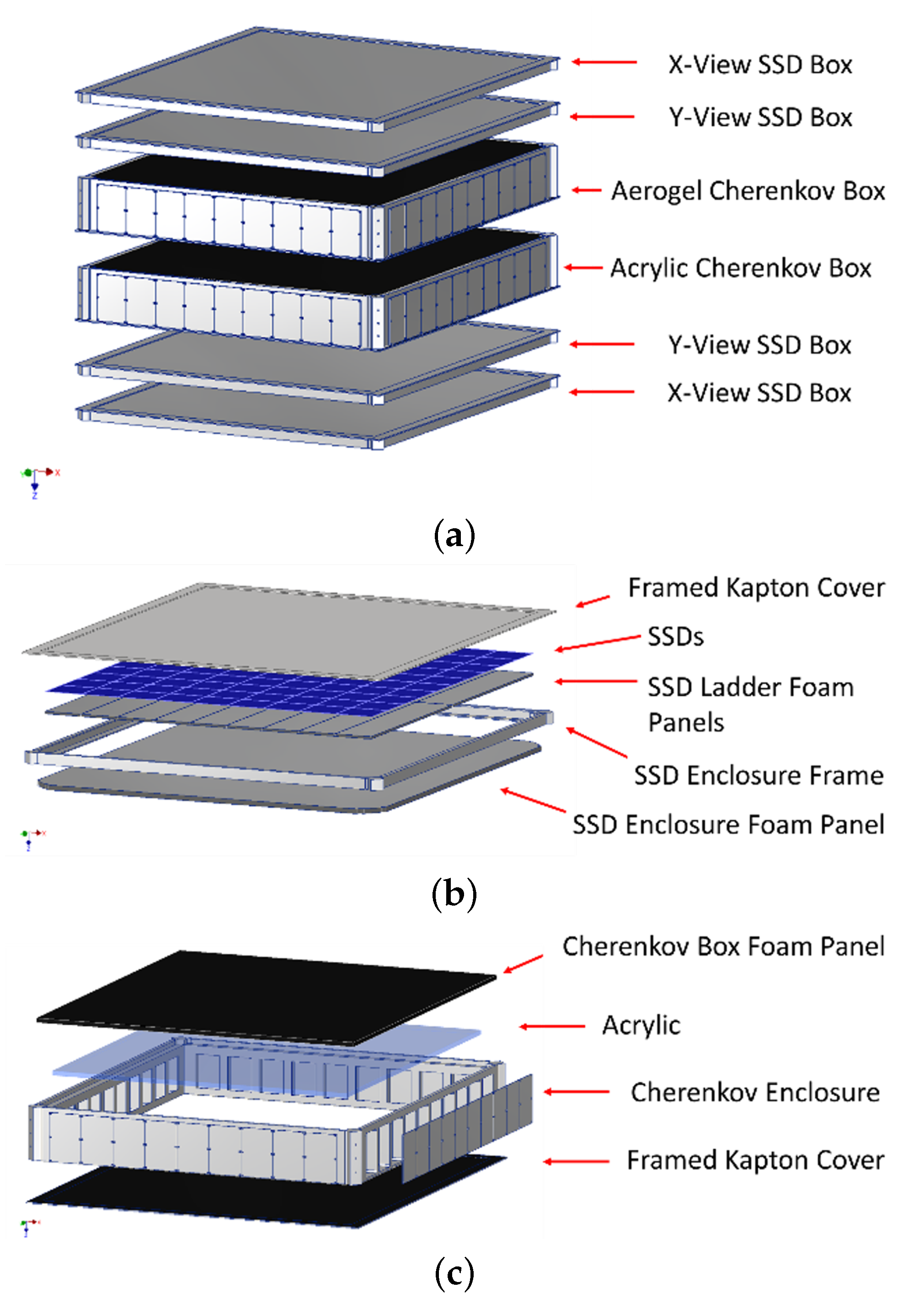
2.1. Instrument Design
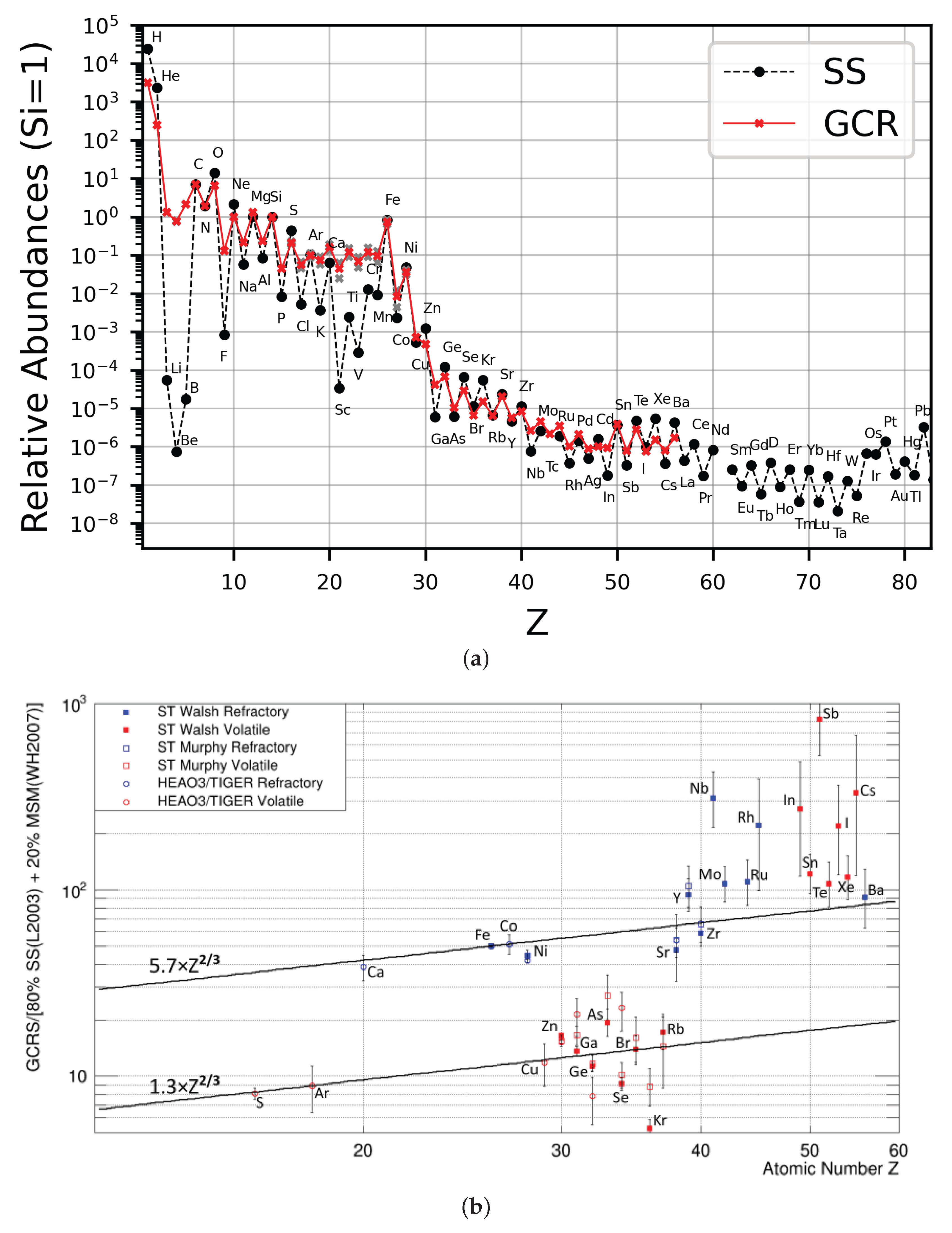
2.2. UHGCR Science
2.3. Future Prospects
3. TIGERISS
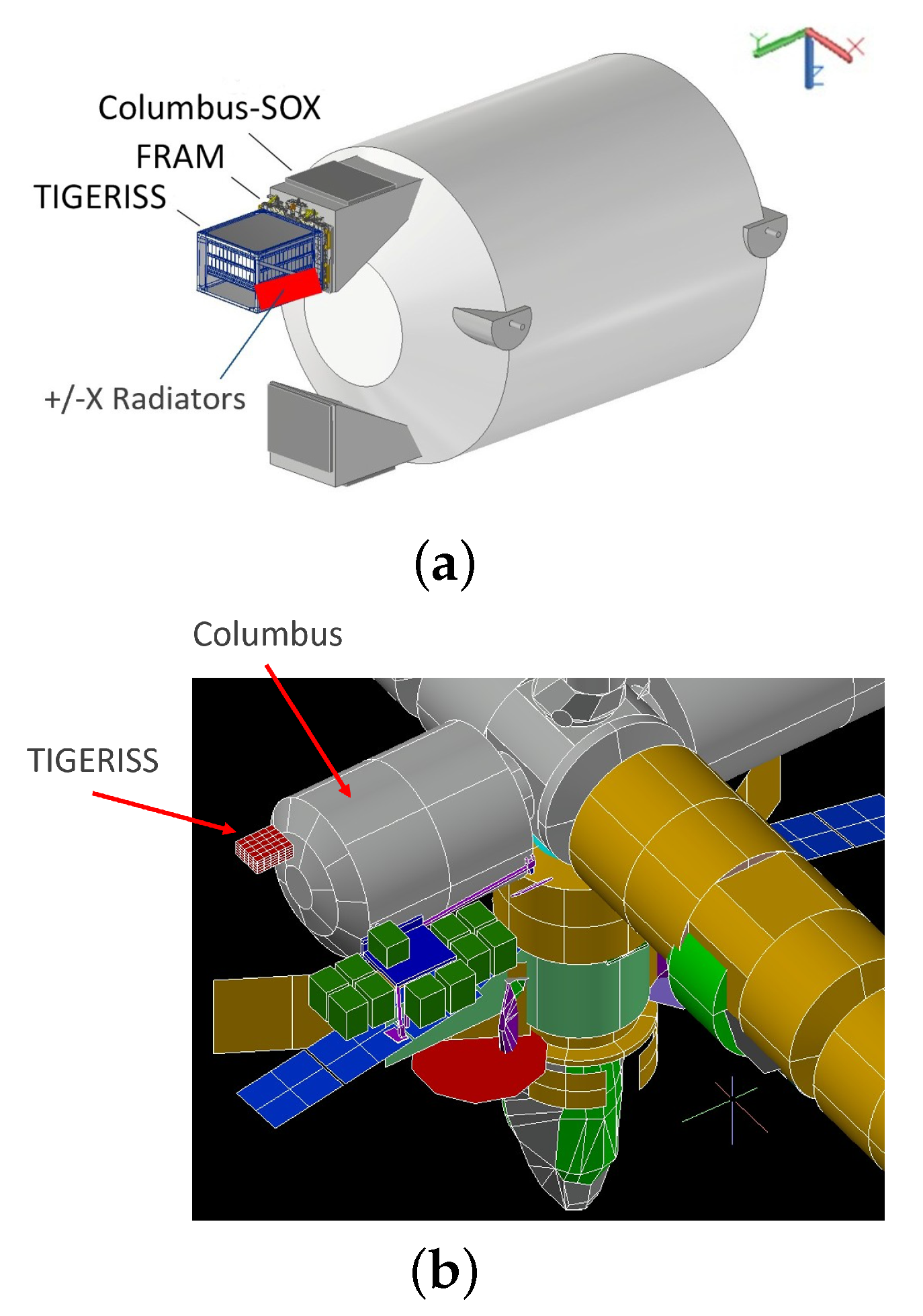
3.1. Instrument Concept
3.2. Payload Model Development
3.3. Thermal Analysis
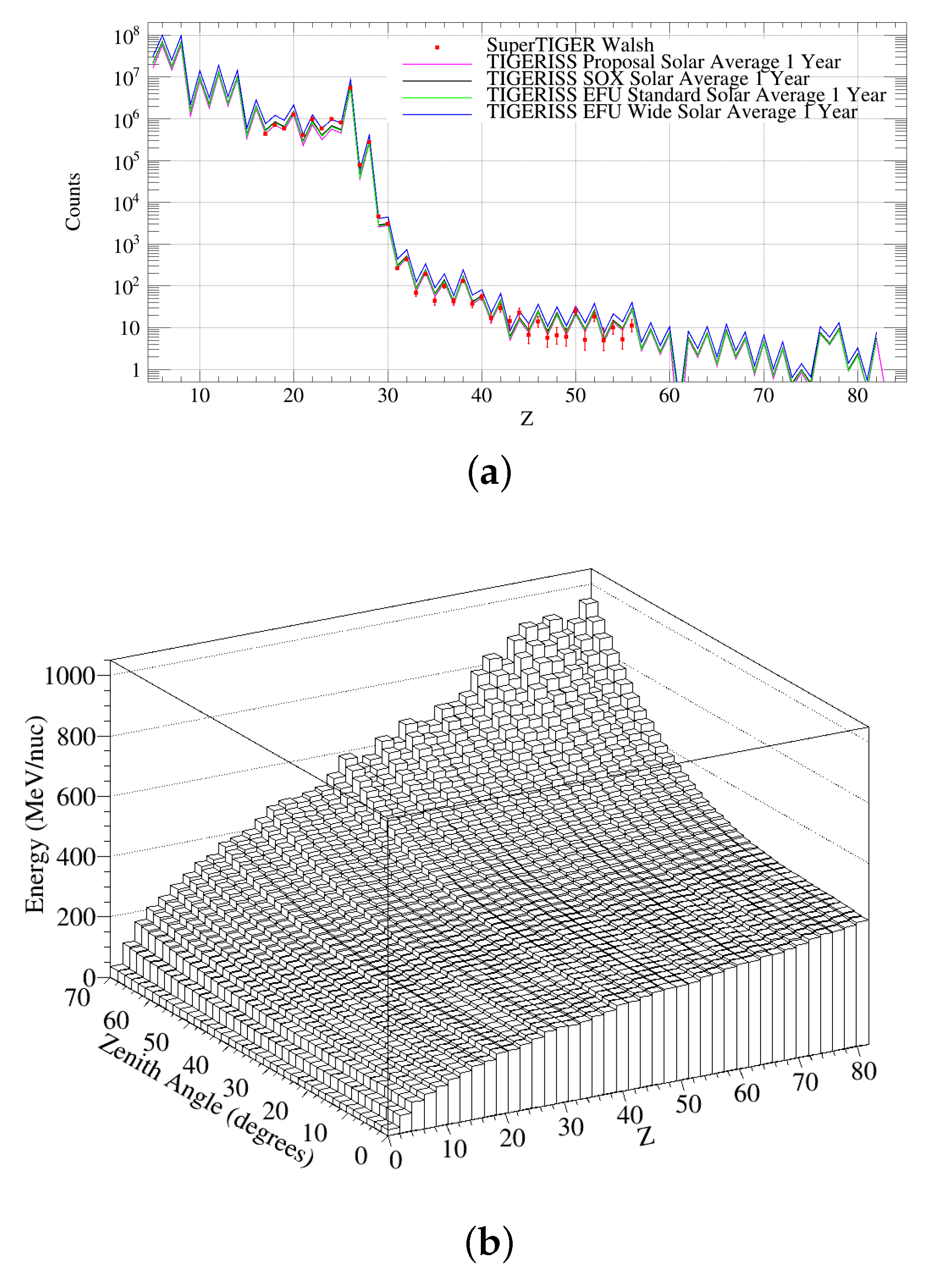
3.4. Predicted TIGERISS Measurements
3.4.1. Statistics from One Year
3.4.2. Statistics from Extended Observations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ACE | Advanced Composition Explorer |
| ADAPT | Antarctic Demonstrator for the Advanced Particle-astrophysics Telescope |
| AGILE | Light Imager for Gamma-ray Astrophysics |
| AMS | Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer |
| APT | Advanced Particle-astrophysics Telescope |
| BAS | Balloon Air Sampler |
| BNSM | binary neutron star merger |
| Caltech | California Institute of Technology |
| CALET | CALorimetric Electron Telescope |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CR | cosmic ray |
| CRIS | Cosmic Ray Isotope Spectrometer |
| DAMPE | Dark Matter Particle Explorer |
| DAQ | data acquisition |
| EAS | extensive air shower |
| ECOSTRESS | ECOsystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station |
| EFU | Exposed Facility Unit |
| ELC | ExPRESS Logistics Carrier |
| E-MIST | Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere |
| EPACT | Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition, and Transport investigation |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| ExPRESS | EXpedite the PRocessing of Experiments to the Space Station |
| FPGA | field-programmable gate array |
| GCR | galactic cosmic rays |
| GEDI | Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation |
| GGS | Global Geospace Science |
| HARP | HyperAngular Rainbow Polarimeter |
| HEAO | High-Energy Astronomy Observatory |
| HELIX | High-Energy Light Isotope eXperiment |
| HNE | Heavy Nuclei Experiment |
| INCA | Ionospheric Neutron Content Analyzer |
| ISM | interstellar media |
| ISS | International Space Station |
| JAXA | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency |
| JEM | Japanese Experiment Module |
| LAT | Large-Area Telescope |
| LDB | Long-Duration Balloon |
| LDEF | Long-Duration Exposure Facility |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| NKU | Northern Kentucky University |
| NSM | Neutron Star Merger |
| PACE | Plankton, Aerosol, Clouds, ocean Ecosystem |
| PAMELA | Payload for Antimatter Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics |
| PMC-Turbo | Polar Mesospheric Cloud Turbulence |
| PMT | photomultiplier tube |
| PSU | Pennsylvania State University |
| SiPM | silicon photomultiplier |
| SN | supernova |
| SNe | supernovae |
| SONTRAC | Solar Neutron TRACking |
| SOX | Starboard Overhead X-Direction |
| SS | Solar System |
| SSD | silicon strip detector |
| STEREO | Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| SuperTIGER | Super Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder |
| TIGER | Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder |
| TIGERISS | Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder for the International Space Station |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
| UHCRE | Ultra-Heavy Cosmic Ray Experiment |
| UHECR | ultra-high energy cosmic ray |
| UHGCR | ultra-heavy galactic cosmic ray |
| UMBC | University of Maryland Baltimore County |
| WUSTL | Washington University in St. Louis |
References
- Walsh, N.E. SuperTIGER Elemental Abundances for the Charge Range 41≤Z≤56. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, N.E.; Akaike, Y.; Binns, W.; Bose, R.; Brandt, T.; Braun, D.; Cannady, N.; Dowkontt, P.; Hams, T.; Israel, M.; et al. SuperTIGER Abundances of Galactic Cosmic Rays for the Atomic Number (Z) Interval 30 to 56. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2021), Berlin, Germany, 12–23 July 2021; Volume 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, N.E.; Akaike, Y.; Binns, W.R.; Bose, R.G.; Brandt, T.J.; Braun, D.L.; Cannady, N.W.; Dowkontt, P.F.; Hams, T.; Israel, M.H.; et al. SuperTIGER instrument abundances of galactic cosmic rays for the charge interval 41 ⩽ Z ⩽ 56. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, N.E. SuperTIGER Abundances of Galactic Cosmic Rays for the Atomic Number (Z) Interval 40 to 56. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2023), Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; Volume 444, p. 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, B.F.; Zober, W.V.; Borda, R.F.; Bose, R.G.; Braun, D.L.; Buckley, J.; Calderon, J.; Cannady, N.W.; Caputo, R.; Coutu, S.; et al. The Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder for the International Space Station (TIGERISS). In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2023), Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; Volume 444, p. 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, B.F.; Zober, W.V.; Borda, R.F.; Bose, R.G.; Braun, D.L.; Buckley, J.; Calderon, J.; Cannady, N.W.; Caputo, R.; Coutu, S.; et al. Modeling Expected TIGERISS Observations. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2023), Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; Volume 444, p. 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zober, W.V.; Rauch, B.F.; Borda, R.F.; Bose, R.G.; Braun, D.L.; Buckley, J.; Calderon, J.; Cannady, N.W.; Caputo, R.; Coutu, S.; et al. Science Objectives and Goals of the TIGERISS mission. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2023), Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; Volume 444, p. 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocchesi, P. CALET: A calorimeter-based orbital observatory for High Energy Astroparticle Physics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2012, 692, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Alemanno, F.; Altomare, C.; An, Q.; Azzarello, P.; Barbato, F.C.T.; Bernardini, P.; Bi, X.J.; Cagnoli, I.; Cai, M.S.; et al. Measurement of Heavy Nulei beyond Iron in Cosmic Rays with the DAMPE Experiment. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2023), Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; Volume 444, p. 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, M.H.; Lave, K.A.; Wiedenbeck, M.E.; Binns, W.R.; Christian, E.R.; Cummings, A.C.; Davis, A.J.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Leske, R.A.; Mewaldt, R.A.; et al. Elemental Composition at the Cosmic-Ray Source Derived from the ACE-CRIS Instrument. I. 6C to 28Ni. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, W.R.; Wiedenbeck, M.E.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Israel, M.H.; Christian, E.R.; Cummings, A.C.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Leske, R.A.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Stone, E.C. The Isotopic Abundances of Galactic Cosmic Rays with Atomic Number 29 ≤ Z ≤ 38. Astrophys. J. 2022, 936, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, W.R.; Garrard, T.L.; Gibner, P.S.; Israel, M.H.; Kertzman, M.P.; Klarmann, J.; Newport, B.J.; Stone, E.C.; Waddington, C.J. Abundances of Ultraheavy Elements in the Cosmic Radiation: Results from HEAO 3. Astrophys. J. 1989, 346, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, P.H.; Walker, R.N.F.; Masheder, M.R.W.; Moses, R.T.; Worley, A.; Gay, A.M. Ariel 6 Measurements of the Fluxes of Ultra-heavy Cosmic Rays. Astrophys. J. 1987, 314, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, P.B.; Lowder, D.M.; Westphal, A.J.; Wilkes, R.D.; Brennen, R.A.; Afanasyev, V.G.; Akimov, V.V.; Rodin, V.G.; Baryshinikov, G.K.; Gorshkov, L.A.; et al. Trek-a Cosmic-Ray Experiment on the Russian Space Station MIR. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1992, 197, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, A.J.; Price, P.B.; Weaver, B.A.; Afanasiev, V.G. Evidence against stellar chromospheric origin of Galactic cosmic rays. Nature 1998, 396, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.; Thompson, A.; O’Sullivan, D.; Daly, J.; Drury, L.; Domingo, V.; Wenzel, K.P. Actinide and Ultra-Heavy Abundances in the Local Galactic Cosmic Rays: An Analysis of the Results from the LDEF Ultra-Heavy Cosmic-Ray Experiment. Astrophys. J. 2012, 747, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.P. Identifying the Origin of Galactic Cosmic Rays with the SuperTIGER Instrument. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, R.P.; Sasaki, M.; Binns, W.R.; Brandt, T.J.; Hams, T.; Israel, M.H.; Labrador, A.W.; Link, J.T.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Mitchell, J.W.; et al. Galactic Cosmic Ray Origins and OB Associations: Evidence from SuperTIGER Observations of Elements 26Fe through 40Zr. Astrophys. J. 2016, 831, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, B.F.; Walsh, N.E.; Zober, W.V. SuperTIGER Ultra-Heavy Galactic Cosmic Ray Atmospheric Propagation Corrections and Uncertainty Analysis. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2021), Berlin, Germany, 12–23 July 2021; Volume 395, p. 089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, B.F.; Bose, R.G.; West, A.T.; Lisalda, L.; Abarr, Q.; Akaike, Y.; Binns, W.; Brandt, T.; Braun, D.L.; Dowkontt, P.; et al. SuperTIGER-2 2018 Flight Payload Recovery and Preliminary Instrument Assessment. In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2019), Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019; Volume 358, p. 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, J.T. Measurements of Ultra-Heavy Galactic Cosmic Rays with the TIGER Instrument. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Link, J.T.; Barbier, L.M.; Binns, W.R.; Christian, E.R.; Cummings, J.R.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Geier, S.; Israel, M.H.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Mitchell, J.W.; et al. Measurements of the Ultra-Heavy Galactic Cosmic-Ray Abundances between Z = 30 and Z = 40 with the TIGER Instrument. In Proceedings of the 28th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Tsukuba, Japan, 31 July–7 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, B.F. Measurement of the Relative Abundances of the Ultra-Heavy Galactic Cosmic Rays (30≤Z≤40) with the Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder (TIGER) Instrument. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, B.F.; Link, J.T.; Lodders, K.; Israel, M.H.; Barbier, L.M.; Binns, W.R.; Christian, E.R.; Cummings, J.R.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Geier, S.; et al. Cosmic Ray origin in OB Associations and Preferential Acceleration of Refractory Elements: Evidence from Abundances of Elements 26Fe through 34Se. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.J. The trans-iron galactic element recorder: A detector that will measure the elemental abundances of the ultra-heavy cosmic rays. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sposato, S.H. The 1997 balloon flight of the trans-iron galactic element recorder. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D.J.; Barbier, L.M.; Beatty, J.J.; Binns, W.R.; Christian, E.R.; Crary, D.J.; Ficenec, D.J.; Hink, P.L.; Klarmann, J.; Krombel, K.E.; et al. Large-area scintillating-fiber time-of-flight/hodoscope detectors for particle astrophysics experiments. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 1999, 420, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Z.; Buckley, J.; Bergström, L.; Binns, W.; Buhler, J.; Chen, W.; Cherry, M.; Funk, S.; Hooper, D.; Mitchell, J.; et al. Report of 2019 APTlite balloon flight. In Proceedings of the 236th American Astronomical Society Meeting, online, 1–3 June 2020; Volume 236, p. 142.04. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, Z.D. Toward an Understanding of High-Mass Gamma-Ray Binaries: An Investigation Using Current Observatories and the Development of a Future GeV Instrument. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meshik, A.; Kehm, K.; Pravdivtseva, O.; Rauch, B. Measurements of Atmospheric Noble Gases in Antarctica Captured by Autonomous Balloon Sampling. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 December 2022; Volume 2022, p. P54A–02. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.J.; Thakrar, P.J.; Bharrat, A.E.; Dokos, A.G.; Kinney, T.L.; James, L.M.; Lane, M.A.; Khodadad, C.L.; Maguire, F.; Maloney, P.R.; et al. A Balloon-Based Payload for Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere (E-MIST). Gravit. Space Res. 2022, 2, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.P.; Kjellstrand, B.; Jones, G.; Reimuller, J.D.; Fritts, D.C.; Miller, A.; Geach, C.; Limon, M.; Hanany, S.; Kaifler, B.; et al. The PMC-Turbo Balloon Mission to Study Gravity Waves and Turbulence through High-Resolution Imaging of Polar Mesospheric Clouds. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–15 December 2017; Volume 2017, p. SA24A–08. [Google Scholar]
- Binns, W.R.; Bose, R.G.; Braun, D.L.; Brandt, T.J.; Daniels, W.M.; Dowkontt, P.F.; Fitzsimmons, S.P.; Hahne, D.J.; Hams, T.; Israel, M.H.; et al. The SUPERTIGER Instrument: Measurement of Elemental Abundances of Ultra-Heavy Galactic Cosmic Rays. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanuki, T.; Motoki, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Seo, E.S.; Wang, J.Z.; Abe, K.; Anraku, K.; Asaoka, Y.; Fujikawa, M.; Imori, M.; et al. Precise Measurement of Cosmic-Ray Proton and Helium Spectra with the BESS Spectrometer. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Alcaraz, J.; Allaby, J.; Alpat, B.; Ambrosi, G.; Anderhub, H.; Ao, L.; Arefiev, A.; Arruda, L.; Azzarello, P.; et al. Isotopic Composition of Light Nuclei in Cosmic Rays: Results from AMS-01. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, J.J.; Ferrando, P.; Soutoul, A.; Goret, P.; Juliusson, E.; Koch-Miramond, L.; Lund, N.; Masse, P.; Peters, B.; Petrou, N.; et al. Charge composition and energy spectra of cosmic-ray nuclei for elements from Be to Ni - Results from HEAO-3-C2. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 233, 96–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lodders, K. Solar System Abundances and Condensation Temperatures of the Elements. Astrophys. J. 2003, 591, 1220–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Heger, A. Nucleosynthesis and remnants in massive stars of solar metallicity. Phys. Rep. 2007, 442, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingenfelter, R.E. The Origin of Cosmic Rays: How Their Composition Defines Their Sources and Sites and the Processes of Their Mixing, Injection, and Acceleration. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2019, 245, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.C.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Cook, W.R.; Cummings, A.C.; Gauld, B.; Kecman, B.; Leske, R.A.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Thayer, M.R.; Dougherty, B.L.; et al. The Cosmic-Ray Isotope Spectrometer for the Advanced Composition Explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 1998, 86, 285–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prest, M.; Barbiellini, G.; Bordignon, G.; Fedel, G.; Liello, F.; Longo, F.; Pontoni, C.; Vallazza, E. The AGILE silicon tracker: An innovative γ-ray instrument for space. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2003, 501, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, D.; AMS-Tracker Collaboration. The AMS-02 silicon tracker: First year on ISS in space. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2013, 718, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Barbier, L.M.; Karsch, J.; Liberman, R.; Madden, M.P.; Nolan, T.; Reames, D.V.; Ryan, L.; Singh, S.; Trexel, H.; et al. The Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition, and Transport (EPACT) investigation on the WIND spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 1995, 71, 155–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, W.B.; Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Althouse, W.; Anderson, B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Band, D.L.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. The Large Area Telescope on the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 1071–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straulino, S.; Adriani, O.; Bonechi, L.; Bongi, M.; Castellini, G.; D’Alessandro, R.; Gabbanini, A.; Grandi, M.; Papini, P.; Ricciarini, S.; et al. The PAMELA silicon tracker. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2004, 530, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.E.; Burnham, J.A.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Cook, W.R.; Crabill, R.M.; Cummings, A.C.; Davis, A.J.; Kecman, B.; Labrador, A.W.; Leske, R.A.; et al. Thin silicon solid-state detectors for energetic particle measurements-Development, characterization, and application on NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 650, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewaldt, R.A.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Cook, W.R.; Cummings, A.C.; Davis, A.J.; Geier, S.; Kecman, B.; Klemic, J.; Labrador, A.W.; Leske, R.A.; et al. The Low-Energy Telescope (LET) and SEP Central Electronics for the STEREO Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 136, 285–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.G.; Bruno, A. Performance Characteristics of the Ionospheric Neutron Content Analyzer (INCA). In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2019), Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019; Volume 36, p. 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, J.S.; Brewer, I.; Briggs, M.S.; Bruno, A.; Burns, E.; Caputo, R.; Cenko, B.; Cucchiara, A.; De Nolfo, G.; Dumonthier, J.; et al. BurstCube: A CubeSat for gravitational wave counterparts. Proc. SPIE 2020, 11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.; Alnussirat, S.; Altomare, C.; Bose, R.G.; Braun, D.L.; Buckley, J.H.; Buhler, J.; Burns, E.; Chamberlain, R.D.; Chen, W.; et al. The Advanced Particle-astrophysics Telescope (APT) Project Status. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2021), Berlin, Germany, 12–23 July 2021; Volume 395, p. 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nolfo, G.A.; Mitchell, J.G.; Suarez, G.; Ryan, J.M.; Bruno, A.; Dumonthier, J.; Legere, J.; Messner, R.; Tatoli, T.; Williams, L. Next-generation SOlar Neutron TRACking (SONTRAC) instrument. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2023, 1054, 168352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H. The Design and Status of the HELIX Ring Imaging Cherenkov Detector and Hodoscope Systems. In Proceedings of the 38th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2023), Nagoya, Japan, 26 July–3 August 2023; Volume 444, p. 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.V.; Fernandez-Borda, R.; McBride, B.; Remer, L.; Barbosa, H.M.J. The Harp Hype Ran Gular Imaging Polarimeter and the Need for Small Satellite Payloads with High Science Payoff for Earth Science Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2018), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 6304–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Knobelspiesse, K.; Zhai, P.W.; Xu, F.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Chowdhary, J.; Hasekamp, O.; Dubovik, O.; Wu, L.; Ahmad, Z.; et al. Retrieving Aerosol Characteristics From the PACE Mission, Part 2: Multi-Angle and Polarimetry. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.; Hook, S.; Fisher, J.; Lee, C. ECOSTRESS, A NASA Earth-Ventures Instrument for studying links between the water cycle and plant health over the diurnal cycle. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5494–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubayah, R.; Blair, J.B.; Goetz, S.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Hansen, M.; Healey, S.; Hofton, M.; Hurtt, G.; Kellner, J.; Luthcke, S.; et al. The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation: High-resolution laser ranging of the Earth’s forests and topography. Sci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. F. Rauch for the CALET Collaboration. Predicted CALET measurements of ultra-heavy cosmic ray relative abundances. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.S.; Lave, K.A.; Wiedenbeck, M.E.; Binns, W.R.; Cummings, A.C.; Davis, A.J.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Hink, P.L.; Israel, M.H.; Leske, R.A.; et al. Elemental Composition and Energy Spectra of Galactic Cosmic Rays During Solar Cycle 23. Astrophys. J. 2009, 698, 1666–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, B.F.; Walsh, N.E.; Zober, W.V. Determination of Expected TIGERISS Observations. In Proceedings of the 37th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2021), Berlin, Germany, 12–23 July 2021; Volume 395, p. 088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ISS Attachment | Length | Width | Height | Area | Geometry Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JEM-EF proposal | 1.67 m | 0.67 m | 0.40 m | 1.12 m2 | 1.66 m2sr |
| Columbus SOX | 1.00 m | 0.90 m | 0.42 m | 0.90 m2 | 1.28 m2sr |
| JEM-EF standard | 1.50 m | 0.60 m | 0.42 m | 0.90 m2 | 1.19 m2sr |
| JEM-EF wide | 1.50 m | 0.80 m | 0.42 m | 1.20 m2 | 1.83 m2sr |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rauch, B.F.; Zober, W.V.; Abarr, Q.; Akaike, Y.; Binns, W.R.; Borda, R.F.; Bose, R.G.; Brandt, T.J.; Braun, D.L.; Buckley, J.H.; et al. From SuperTIGER to TIGERISS. Instruments 2024, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments8010004
Rauch BF, Zober WV, Abarr Q, Akaike Y, Binns WR, Borda RF, Bose RG, Brandt TJ, Braun DL, Buckley JH, et al. From SuperTIGER to TIGERISS. Instruments. 2024; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleRauch, B. F., W. V. Zober, Q. Abarr, Y. Akaike, W. R. Binns, R. F. Borda, R. G. Bose, T. J. Brandt, D. L. Braun, J. H. Buckley, and et al. 2024. "From SuperTIGER to TIGERISS" Instruments 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments8010004
APA StyleRauch, B. F., Zober, W. V., Abarr, Q., Akaike, Y., Binns, W. R., Borda, R. F., Bose, R. G., Brandt, T. J., Braun, D. L., Buckley, J. H., Cannady, N. W., Coutu, S., Crabill, R. M., Dowkontt, P. F., Israel, M. H., Kandula, M., Krizmanic, J. F., Labrador, A. W., Labrador, W., ... Williams, L. P. (2024). From SuperTIGER to TIGERISS. Instruments, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments8010004








