The Effect of Corneal Thickness, Densitometry and Curvature on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Applanation, Rebound and Dynamic Contour Tonometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Corneal Measurements
2.2. Intraocular Pressure Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Corneal Thickness and Densitometry
3.2. Refraction and Astigmatism
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quigley, H.A.; Broman, A.T. The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, M.; Li, L.; Yu, A.; Wang, Q.; Elsheikh, A. Clinical Evaluation of Methods to Correct Intraocular Pressure Measurements by the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer, Ocular Response Analyzer, and Corvis ST Tonometer for the Effects of Corneal Stiffness Parameters. J. Glaucoma 2016, 25, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabasia, P.L.; Lawrenson, J.G.; Murdoch, I.E. Evaluation of a new rebound tonometer for self-measurement of intraocular pressure. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaian, E.; Choe, J.E.; Lin, S.; Stamper, R.L. Central corneal thickness of Caucasians, Chinese, Hispanics, Filipinos, African Americans, and Japanese in a glaucoma clinic. Ophthalmology 2004, 111, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekeroglu, M.A.; Anayol, M.A.; Gulec, M.; Atalay, M.; Ozgul Yilmazoglu, M.; Yilmazbas, P. Corneal densitometry: A new technique for objective assessment of corneal clarity in Pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J. Glaucoma 2016, 25, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreanos, K.; Koutsandrea, C.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Diagourtas, A.; Kotoulas, A.; Dimitrakas, P.; Moschos, M.M. Comparison of Goldmann applanation tonometry and Pascal dynamic contour tonometry in relation to central corneal thickness and corneal curvature. Clin. Ophthalmol. (Auckl. N.Z.) 2016, 10, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, M.; Iaccarino, S.; Cennamo, M.; Irregolare, C.; Romano, V.; Carnevale, U.A. Comparison between Corvis and other tonometers in healthy eyes. Contact Lens Anterior Eye J. Br. Contact Lens Assoc. 2015, 38, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.J.; Jain, S.P.; Kapadia, P.R.; Patel, N.V.; Patel, S.; Patel, V. Can higher end tonometers be used interchangeably in routine clinical practice? Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 64, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Frances, F.; Sanz-Pozo, C.; Borrego-Sanz, L.; Janez, L.; Morales-Fernandez, L.; Martinez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Garcia-Sanchez, J.; Garcia-Feijoo, J.; Santos-Bueso, E. Dependence of dynamic contour and Goldmann applanation tonometries on peripheral corneal thickness. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunvant, P.; Baskaran, M.; Vijaya, L.; Joseph, I.S.; Watkins, R.J.; Nallapothula, M.; Broadway, D.C.; O’Leary, D.J. Effect of corneal parameters on measurements using the pulsatile ocular blood flow tonograph and Goldmann applanation tonometer. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes, C.G.V.; Prata, T.S.; Liebmann, J.; Ritch, R. Modalities of Tonometry and their Accuracy with Respect to Corneal Thickness and Irregularities. J. Optom. 2008, 1, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Feijoo, J.; Martinez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Morales-Fernandez, L.; Saenz Frances, F.; Santos-Bueso, E.; Garcia-Saenz, S.; Mendez-Hernandez, C. New technologies for measuring intraocular pressure. In Progress in Brain Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 221, pp. 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.H.; Betinjane, A.J.; Quiroga, V.A. Correlations between different tonometries and ocular biometric parameters in patients with primary congenital glaucoma. Arq. Bras. De Oftalmol. 2013, 76, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Willekens, K.; Rocha, R.; Van Keer, K.; Vandewalle, E.; Abegao Pinto, L.; Stalmans, I.; Marques-Neves, C. Review on Dynamic Contour Tonometry and Ocular Pulse Amplitude. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 55, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanngiesser, H.E.; Kniestedt, C.; Robert, Y.C. Dynamic contour tonometry: Presentation of a new tonometer. J. Glaucoma 2005, 14, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achiron, A.; Blumenfeld, O.; Avizemer, H.; Karmona, L.; Leybowich, G.; Man, V.; Bartov, E.; Burgansky-Eliash, Z. Intraocular pressure measurement after DSAEK by iCare, Goldmann applanation and dynamic contour tonometry: A comparative study. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2016, 39, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arribas-Pardo, P.; Mendez-Hernandez, C.; Cuina-Sardina, R.; Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Garcia-Feijoo, J. Tonometry after Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments for Keratoconus. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2017, 94, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.; Lachkar, Y. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry with goldman applanation tonometry over a wide range of central corneal thickness. J. Glaucoma 2005, 14, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duba, I.; Wirthlin, A.C. Dynamic contour tonometry for post-LASIK intraocular pressure measurements. Klin. Mon. Augenheilkd. 2004, 221, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, C.; Bachmann, L.M.; Thiel, M.A. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry with goldmann applanation tonometry. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3118–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchaki, B.; Hashemi, H.; Yekta, A.; Khabazkhoob, M. Comparison of current tonometry techniques in measurement of intraocular pressure. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2017, 29, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Carnevale, U.A.G.; di Staso, S.; Sconocchia, M.B.; Costagliola, C. Analysis of differences in intraocular pressure evaluation performed with contact and non-contact devices. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcura, F.; Yildirim, N.; Sahin, A.; Colak, E. Comparison of Goldmann applanation tonometry, rebound tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 8, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlitzsch, M.; Gonnermann, J.; Maier, A.K.; Schwenteck, T.; Torun, N.; Bertelmann, E.; Klamann, M.K. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry versus Goldmann applanation tonometry according to the International Ocular Tonometer Standards ISO 8612 in glaucoma patients. Klin. Mon. Augenheilkd. 2014, 231, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales-Sanz, M.; Arranz-Marquez, E.; Pinero, D.P.; Arruabarrena, C.; Mikropoulos, D.G.; Teus, M.A. Effect of Laser in Situ Keratomileusis on Schiotz, Goldmann, and Dynamic Contour Tonometric Measurements. J. Glaucoma 2016, 25, e419–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siganos, D.S.; Papastergiou, G.I.; Moedas, C. Assessment of the Pascal dynamic contour tonometer in monitoring intraocular pressure in unoperated eyes and eyes after LASIK. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2004, 30, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejwani, S.; Dinakaran, S.; Joshi, A.; Shetty, R.; Sinha Roy, A. A cross-sectional study to compare intraocular pressure measurement by sequential use of Goldman applanation tonometry, dynamic contour tonometry, ocular response analyzer, and Corvis ST. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 63, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umurhan Akkan, J.C.; Akkan, F.; Sezgin Akcay, B.I.; Ayintap, E.; Tuncer, K. Dynamic Contour Tonometry and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry: Difference of Intraocular Pressure Values Between Eyes with and without Glaucomatous Damage in Thin Corneas. Klin. Mon. Augenheilkd. 2015, 232, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Nakakura, S.; Matsuo, N.; Yoshitomi, K.; Handa, M.; Tabuchi, H.; Kiuchi, Y. Agreement among Goldmann applanation tonometer, iCare, and Icare PRO rebound tonometers; non-contact tonometer; and Tonopen XL in healthy elderly subjects. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 38, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontzos, G.; Agiorgiotakis, M.; Kapsala, Z.; Detorakis, E. Limbal rebound tonometry: Clinical comparisons and applications. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, Y. Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1912–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcura, F.; Yildirim, N. Reply to comment by De Bernardo and Rosa on “Evaluation of Goldmann applanation tonometry, rebound tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry in keratoconus“. J. Optom. 2018, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniestedt, C.; Kanngiesser, H.; Stamper, R.L. Assessment of Pascal dynamic contour tonometer in monitoring IOP after LASIK. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2005, 31, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, J.D. Stop “adjusting” intraocular pressure measurements. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughty, M.J.; Zaman, M.L. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: A review and meta-analysis approach. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2000, 44, 367–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, D.; Sawada, A.; Yamamoto, T. Evaluation of a New Rebound Self-tonometer, Icare HOME: Comparison With Goldmann Applanation Tonometer. J. Glaucoma 2017, 26, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamcelik, N.; Atalay, E.; Cicik, E.; Ozkok, A. Comparability of Icare Pro Rebound Tonometer with Goldmann Applanation and Noncontact Tonometer in a Wide Range of Intraocular Pressure and Central Corneal Thickness. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 54, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas-Pardo, P.; Mendez-Hernandez, C.; Cuina-Sardina, R.; Fernandez-Perez, C.; Diaz-Valle, D.; Garcia-Feijoo, J. Measuring intraocular pressure after intrastromal corneal ring segment implantation with rebound tonometry and Goldmann applanation tonometry. Cornea 2015, 34, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Foulsham, W.; Pronin, S.; Tatham, A.J. The Influence of Corneal Biomechanical Properties on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Using a Rebound Self-tonometer. J. Glaucoma 2018, 27, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bernardo, M.; Rosa, N. Evaluation of Goldmann applanation tonometry, rebound tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry in keratoconus. J. Optom. 2018, 11, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.S.; Jin, K.W.; Yi, K.; Choi, D.G. Comparison of Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Rebound, Noncontact, and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry in Children. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorian, F.; Grigorian, A.P.; Li, A.; Sattar, A.; Krishna, R.; Olitsky, S.E. Comparison of the Icare rebound tonometry with the Goldmann applanation tonometry in a pediatric population. J. AAPOS 2015, 19, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodencarevic, A.N.; Jusufovic, V.; Terzic, S.; Halilbasic, M. Comparison of Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Rebound, Noncontact, and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry in Children. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 163, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulze-Pankert, M.; Dariel, R.; Hoffart, L. Corneal Scheimpflug Densitometry Following Photorefractive Keratectomy in Myopic Eyes. J. Refract. Surg. (Thorofare N.J. 1995) 2016, 32, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Corneal densitometry in high myopia. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni Dhubhghaill, S.; Rozema, J.J.; Jongenelen, S.; Ruiz Hidalgo, I.; Zakaria, N.; Tassignon, M.J. Normative values for corneal densitometry analysis by Scheimpflug optical assessment. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, T.; Marten, L.; Wang, M. Measuring the cornea: The latest developments in corneal topography. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2007, 18, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, A.; Laser-Junga, H. Photography of the anterior eye segment according to Scheimpflug’s principle: Options and limitations—A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anayol, M.A.; Sekeroglu, M.A.; Ceran, B.B.; Dogan, M.; Gunaydin, S.; Yilmazbas, P. Quantitative assessment of corneal clarity in keratoconus: A case control study of corneal densitometry. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 26, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.; Ramos, I.; Ambrosio, R., Jr. Corneal densitometry in keratoconus. Cornea 2014, 33, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, N.; Poyales, F.; Illarramendi, I.; Mendicute, J.; Janez, O.; Caro, P.; Lopez, A.; Argueso, F. Corneal densitometry and its correlation with age, pachymetry, corneal curvature, and refraction. Int. Ophthalmol. 2017, 37, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Grading of corneal transparency. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2004, 27, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otri, A.M.; Fares, U.; Al-Aqaba, M.A.; Dua, H.S. Corneal densitometry as an indicator of corneal health. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Palanca-Sanfrancisco, J.M.; García-Lázaro, S.; Madrid-Costa, D.; Cerviño, A. The Effect of Anesthetic Eye Drop Instillation on the Distribution of Corneal Thickness. Cornea 2013, 32, e102–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.; De Bernardo, M.; Borrelli, M.; Filosa, M.L.; Lanza, M. Effect of Oxybuprocaine Eye Drops on Corneal Volume and Thickness Measurements. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
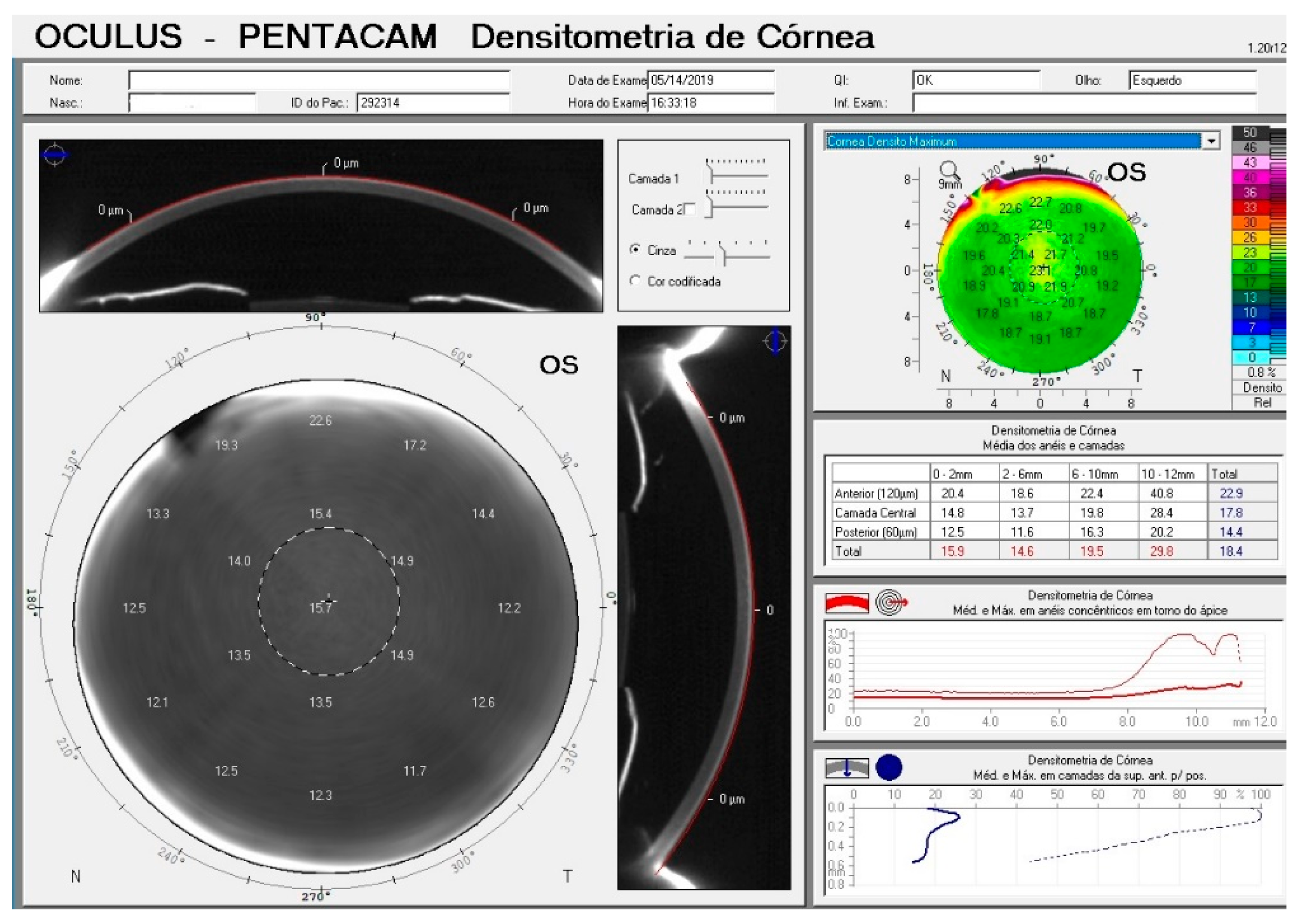

| Median | Interquartile Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 39.0 | 32.0 to 49.0 |
| Race | ||
| White | 36 (90%) | |
| Black | 1 (2.5%) | |
| Asian | 3 (7.5%) | |
| Spherical Equivalent (D) | −0.75 | −2.25 to 0.75 |
| K1 (D) | 42.9 | 41.8 to 44.0 |
| K2 (D) | 44.5 | 43.2 to 46.1 |
| Corneal astigmatism (D) | 1.0 | 0.60 to 1.70 (range 0.1 to 4.8) |
| Corneal Measurements | ||
| CCT (µm) | 531 | 510 to 549 |
| Pachymetry 4 mm (µm) | 542 | 518 to 558 |
| Pachymetry 6 mm (µm) | 575 | 547 to 589 |
| Densitometry 0–2 mm (GSU) | 16.1 | 15.7 to 16.6 |
| Densitometry 2–6 mm (GSU) | 14.8 | 14.2 to 15.3 |
| Densitometry 6–10 mm (GSU) | 17.4 | 15.1 to 21.4 |
| Densitometry 10–12 mm (GSU) | 22.7 | 20.3 to 24.9 |
| IOP Measurements | ||
| GAT 180 (mm Hg) | 13 | 11 to 15 |
| GAT 90 (mm Hg) | 13 | 12 to 15 |
| DCT (mm Hg) | 12.1 | 10.5 to 13.6 |
| RT (mm Hg) | 15.2 | 12.8 to 16.9 |
| NCT (mm Hg) | 16.0 | 14.4 to 18.5 |
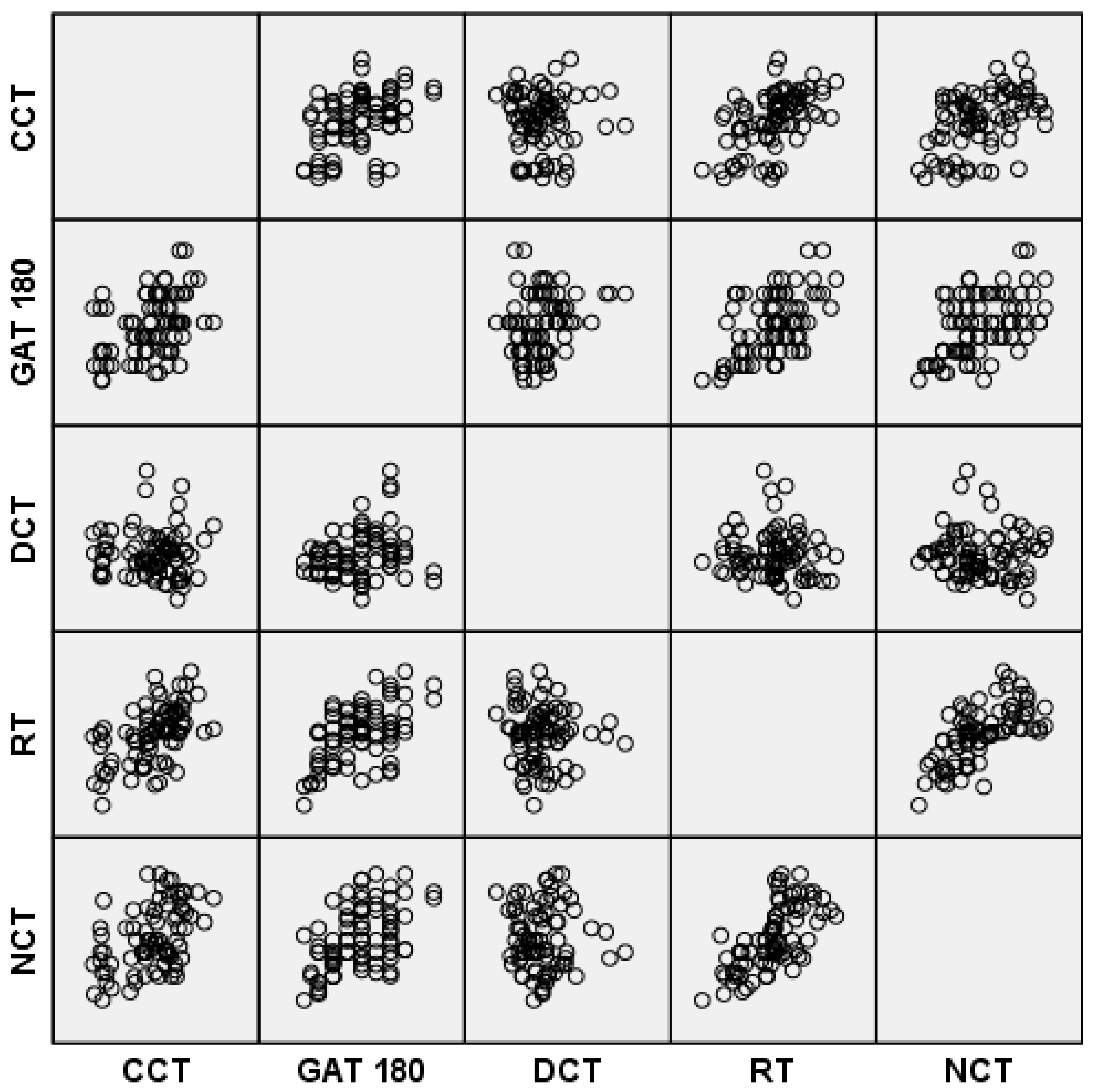
| GAT180 | GAT90 | NCT | RT | DCT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAT180 | −0.9 | −3.4 | −2.2 | 0.5 | |
| (−4.1 to 2.4) | (−8.2 to 1.4) | (−6.8 to 2.4) | (−5.0 to 6.1) | ||
| GAT90 | −2.5 | −1.3 | 1.4 | ||
| (−7.1 to 2.0) | (−6.5 to 3.8) | (−4.1 to 6.8) | |||
| NCT | −1.2 | −3.9 | |||
| (−5.5 to 3.1) | (−11.1 to 3.2) | ||||
| RT | 2.7 | ||||
| (−4.6 to 10.1) | |||||
| DCT |
| Age | CCT | Pach 4 mm | Pach 6 mm | SE | Astigmatism | GAT 180 | GAT 90 | DCT | RT | NCT | Dens 0–2 mm | Dens 2–6 mm | Dens 6–10 mm | Dens 10–12 mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Coefficient | 0.064 | 0.067 | 0.069 | 0.716 | −0.447 | 0.359 | 0.248 | −0.161 | 0.236 | 0.329 | 0.125 | 0.387 | 0.642 | 0.394 | |
| P-value | 0.285 | 0.277 | 0.273 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.076 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.135 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| CCT | Coefficient | 0.064 | 1. | 0.990 | 0.963 | −0.122 | 0.048 | 0.418 | 0.442 | −0.036 | 0.580 | 0.460 | −0.064 | −0.053 | −0.076 | 0.017 |
| P-value | 0.285 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.284 | 0.673 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.377 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.286 | 0.321 | 0.251 | 0.442 | ||
| Pach4 mm | Coefficient | 0.067 | 0.990 | 1.000 | 0.982 | 0.170 | −0.134 | 0.439 | 0.469 | −0.002 | 0.568 | 0.448 | −0.051 | −0.041 | −0.072 | 0.019 |
| P-value | 0.277 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.066 | 0.240 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.494 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.326 | 0.358 | 0.263 | 0.435 | ||
| Pach6 mm | Coefficient | 0.069 | 0.963 | 0.982 | 1.000 | 0.161 | −0.141 | 0.440 | 0.451 | −0.017 | 0.552 | 0.436 | −0.122 | −0.092 | −0.067 | 0.034 |
| P-value | 0.273 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.076 | 0.216 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.441 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.140 | 0.208 | 0.276 | 0.382 | ||
| SE | Coefficient | 0.716 | 0.201 | 0.170 | 0.161 | 1.000 | −0.381 | 0.226 | 0.161 | −0.268 | 0.259 | 0.272 | 0.013 | 0.169 | 0.371 | 0.110 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.037 | 0.066 | 0.076 | <0.001 | 0.022 | 0.077 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.453 | 0.067 | <0.001 | 0.166 | ||
| Astigmatism | Coefficient | −0.447 | 0.048 | −0.134 | −0.141 | −0.381 | 1,000 | −0.184 | −0.153 | −0.044 | −0.168 | −0.133 | 0.026 | 0.000 | −0.179 | −0.157 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.673 | 0.240 | 0.216 | <0.001 | 0.105 | 0.179 | 0.704 | 0.138 | 0.241 | 0.821 | 1.000 | 0.114 | 0.167 | ||
| GAT 180 | Coefficient | 0.359 | 0.418 | 0.439 | 0.440 | 0.226 | −0.184 | 1.000 | 0.703 | 0.243 | 0.500 | 0.492 | −0.028 | −0.002 | 0.240 | 0.279 |
| P-value | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.022 | 0.105 | <0.001 | 0.015 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.404 | 0.492 | 0.016 | 0.006 | ||
| GAT 90 | Coefficient | 0.248 | 0.442 | 0.469 | 0.451 | 0.161 | −0.153 | 0.703 | 1.000 | 0.240 | 0.456 | 0.589 | −0.116 | −0.008 | 0.255 | 0.287 |
| P-value | 0.013 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.077 | 0.179 | <0.001 | 0.016 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.153 | 0.470 | 0.011 | 0.005 | ||
| DCT | Coefficient | −0.161 | −0.036 | −0.002 | −0.017 | −0.268 | −0.044 | 0.243 | 0.240 | 1.000 | −0.086 | −0.024 | 0.044 | −0.061 | −0.136 | 0.079 |
| P-value | 0.076 | 0.377 | 0.494 | 0.441 | 0.008 | 0.704 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.224 | 0.417 | 0.351 | 0.295 | 0.114 | 0.244 | ||
| RT | Coefficient | 0.236 | 0.580 | 0.568 | 0.552 | 0.259 | −0.168 | 0.500 | 0.456 | −0.086 | 1.000 | 0.690 | 0.111 | 0.183 | 0.125 | 0.086 |
| P-value | 0.017 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.138 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.224 | <0.001 | 0.163 | 0.052 | 0.134 | 0.223 | ||
| NCT | Coefficient | 0.329 | 0.460 | 0.448 | 0.436 | 0.272 | −0.133 | 0.492 | 0.589 | −0.024 | 0.690 | 1.000 | −0.069 | 0.040 | 0.236 | 0.142 |
| P-value | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.241 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.417 | <0.001 | 0.271 | 0.362 | 0.018 | 0.104 | ||
| Dens 0–2 mm | Coefficient | 0.125 | −0.064 | −0.051 | −0.122 | 0.013 | 0.026 | −0.028 | −0.116 | 0.044 | 0.111 | −0.069 | 1.000 | 0.759 | −0.009 | −0.052 |
| P-value | 0.135 | 0.286 | 0.326 | 0.140 | 0.453 | 0.821 | 0.404 | 0.153 | 0.351 | 0.163 | 0.271 | <0.001 | 0.469 | 0.322 | ||
| Dens 2–6 mm | Coefficient | 0.387 | −0.053 | −0.041 | −0.092 | 0.169 | 0.000 | −0.002 | −0.008 | −0.061 | 0.183 | 0.040 | 0.759 | 1.000 | 0.434 | 0.164 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.321 | 0.358 | 0.208 | 0.067 | 1.000 | 0.492 | 0.470 | 0.295 | 0.052 | 0.362 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.073 | ||
| Dens 6–10 mm | Coefficient | 0.642 | −0.076 | −0.072 | −0.067 | 0.371 | −0.179 | 0.240 | 0.255 | −0.136 | 0.125 | 0.236 | −0.009 | 0.434 | 1.000 | 0.602 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.251 | 0.263 | 0.276 | <0.001 | 0.114 | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.114 | 0.134 | 0.018 | 0.469 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Dens 10–12 mm | Coefficient | 0.394 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.034 | 0.110 | −0.157 | 0.279 | 0.287 | 0.079 | 0.086 | 0.142 | −0.052 | 0.164 | 0.602 | 1.000 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.442 | 0.435 | 0.382 | 0.166 | 0.167 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.244 | 0.223 | 0.104 | 0.322 | 0.073 | <0.001 |
| Coefficient | 95% CI | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAT180 | |||
| Age (years) | −0.27 | −0.734 to 0.202 | 0.261 |
| Dens 0–2 mm | 0.08 | 0.042 to 0.115 | <0.001 |
| GAT180 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.08 | 0.045 to 0.125 | <0.001 |
| Dens 2–6 mm | −0.22 | −0.606 to 0.127 | 0.244 |
| GAT180 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.07 | 0.035 to 0.108 | <0.001 |
| Dens 6–10 mm | 0.002 | −0.026 to 0.029 | 0.904 |
| GAT180 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.06 | 0.022 to 0.105 | 0.003 |
| Dens 10–12 mm | 0.03 | −0.051 to 0.109 | 0.476 |
| GAT90 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.05 | 0.007 to 0.089 | 0.023 |
| Dens 0–2 mm | −0.36 | −0.889 to 0.177 | 0.187 |
| GAT90 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.05 | 0.002 to 0.094 | 0.039 |
| Dens 2–6 mm | −0.17 | −0.606 to 0.271 | 0.449 |
| GAT90 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.04 | −0.003 to 0.080 | 0.068 |
| Dens 6–10 mm | 0.002 | −0.029 to 0.033 | 0.911 |
| GAT90 | |||
| Age (years) | 0.028 | −0.020 to 0.075 | 0.250 |
| Dens 10–12 mm | 0.04 | −0.052 to 0.121 | 0.395 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olyntho Junior, M.A.d.C.; Augusto, L.B.; Gracitelli, C.P.B.; Tatham, A.J. The Effect of Corneal Thickness, Densitometry and Curvature on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Applanation, Rebound and Dynamic Contour Tonometry. Vision 2020, 4, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision4040045
Olyntho Junior MAdC, Augusto LB, Gracitelli CPB, Tatham AJ. The Effect of Corneal Thickness, Densitometry and Curvature on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Applanation, Rebound and Dynamic Contour Tonometry. Vision. 2020; 4(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision4040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlyntho Junior, Marco Antonio de Castro, Lucas Bertazzi Augusto, Carolina P. B. Gracitelli, and Andrew J. Tatham. 2020. "The Effect of Corneal Thickness, Densitometry and Curvature on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Applanation, Rebound and Dynamic Contour Tonometry" Vision 4, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision4040045
APA StyleOlyntho Junior, M. A. d. C., Augusto, L. B., Gracitelli, C. P. B., & Tatham, A. J. (2020). The Effect of Corneal Thickness, Densitometry and Curvature on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Obtained by Applanation, Rebound and Dynamic Contour Tonometry. Vision, 4(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision4040045





