Comparative Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Adhesion to a Poly-(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine)-Modified Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Materials
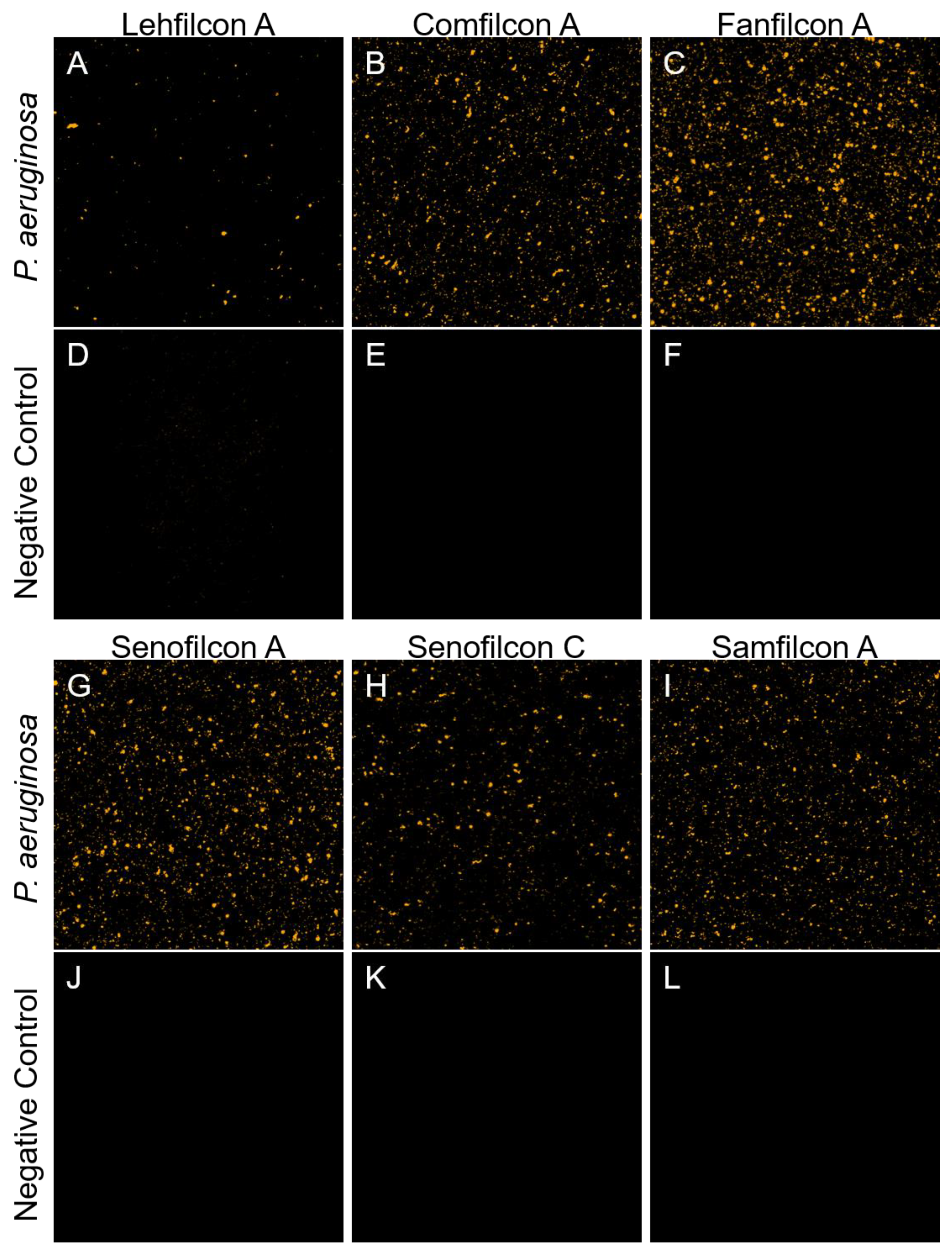
2.2. Confocal Microscopy
2.3. Adhesion Assays
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuller, M.E.; Streger, S.H.; Rothmel, R.K.; Mailloux, B.J.; Hall, J.A.; Onstott, T.C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Balkwill, D.L.; DeFlaun, M.F. Development of a vital fluorescent staining method for monitoring bacterial transport in subsurface environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4486–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorente Pascua, J.; Garcia Bernal, A.; Garcia Sanchez, E.; Almeida Gonzalez, C.V. Microorganisms and antibiotic resistance of bacterial keratitis at a rural county hospital in seville. Eye Contact Lens 2022, 48, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavuoto, K.; Zutshi, D.; Karp, C.L.; Miller, D.; Feuer, W. Update on bacterial conjunctivitis in south florida. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.L.C.; Cote, E.; Saldanha, M.; Lichtinger, A.; Slomovic, A.R. Bacterial keratitis in toronto: A 16-year review of the microorganisms isolated and the resistance patterns observed. Cornea 2017, 36, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.H.; Sun, C.C.; Yeh, L.K.; Ma, D.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Tan, H.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, Y.C. Shifting trends in bacterial keratitis in taiwan: A 10-year review in a tertiary-care hospital. Cornea 2016, 35, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirani, J.; Wurity, S.; Ali, M.H. Multidrug-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis: Risk factors, clinical characteristics, and outcomes. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2110–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mela, E.K.; Giannelou, I.P.; Koliopoulos, J.X.; Gartaganis, S.P. Ulcerative keratitis in contact lens wearers. Eye Contact Lens 2003, 29, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, G.S.; Vijay, A.K.; Stapleton, F.; Henriquez, F.L.; Carnt, N. Understanding clinical and immunological features associated with pseudomonas and staphylococcus keratitis. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, S.; Atta, S.; Durrani, A.; Perera, C.; Kowalski, R.; Jhanji, V. Microbiological evaluation of corneal and contact lens cultures in contact lens-associated bacterial keratitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Alfonso, E.C.; Miller, D. Shifting trends in bacterial keratitis in south florida and emerging resistance to fluoroquinolones. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, B.J.; Weissman, B.A.; Farb, M.D.; Pettit, T.H. Corneal ulcers associated with daily-wear and extended-wear contact lenses. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 102, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, F.; Keay, L.; Edwards, K.; Naduvilath, T.; Dart, J.K.; Brian, G.; Holden, B.A. The incidence of contact lens-related microbial keratitis in australia. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P.B.; Efron, N.; Hill, E.A.; Raynor, M.K.; Whiting, M.A.; Tullo, A.B. Incidence of keratitis of varying severity among contact lens wearers. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dart, J.K.; Radford, C.F.; Minassian, D.; Verma, S.; Stapleton, F. Risk factors for microbial keratitis with contemporary contact lenses: A case-control study. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzman, T.; Kutija, M.B.; Juri, J.; Jandrokovic, S.; Skegro, I.; Olujic, S.M.; Kordic, R.; Cerovski, B. Lens wearers non-compliance—Is there an association with lens case contamination? Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2014, 37, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, F.; Edwards, K.; Keay, L.; Naduvilath, T.; Dart, J.K.; Brian, G.; Holden, B. Risk factors for moderate and severe microbial keratitis in daily wear contact lens users. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, J.R.; Collier, S.A.; Rao, M.M.; Chalmers, R.; Mitchell, G.L.; Richdale, K.; Wagner, H.; Kinoshita, B.T.; Lam, D.Y.; Sorbara, L.; et al. Contact lens wearer demographics and risk behaviors for contact lens-related eye infections--united states, 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, D.C.; Grant, G.B.; O’Donnell, K.; Wannemuehler, K.A.; Noble-Wang, J.; Rao, C.Y.; Jacobson, L.M.; Crowell, C.S.; Sneed, R.S.; Lewis, F.M.; et al. Multistate outbreak of fusarium keratitis associated with use of a contact lens solution. JAMA 2006, 296, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, B.; Heiler, D.; Norton, S. Report on testing from an investigation of fusarium keratitis in contact lens wearers. Eye Contact Lens 2006, 32, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verani, J.R.; Lorick, S.A.; Yoder, J.S.; Beach, M.J.; Braden, C.R.; Roberts, J.M.; Conover, C.S.; Chen, S.; McConnell, K.A.; Chang, D.C.; et al. National outbreak of acanthamoeba keratitis associated with use of a contact lens solution, united states. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, D.; Kovacs, C.; Lynch, S.; Rah, M. Biocidal efficacy of multipurpose solutions against gram-negative organisms associated with corneal infiltrative events. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2017, 100, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAnally, C.; Walters, R.; Campolo, A.; Harris, V.; King, J.; Thomas, M.; Gabriel, M.M.; Shannon, P.; Crary, M. Antimicrobial efficacy of contact lens solutions assessed by iso standards. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, R.; Campolo, A.; Miller, E.; McAnally, C.; Gabriel, M.; Shannon, P.; Crary, M. Differential antimicrobial efficacy of preservative-free contact lens disinfection systems against common ocular pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0213821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, M.M.; McAnally, C.; Bartell, J. Antimicrobial efficacy of multipurpose disinfecting solutions in the presence of contact lenses and lens cases. Eye Contact Lens 2018, 44, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walters, R.; Campolo, A.; Miller, E.; Gabriel, M.M.; Crary, M.; McAnally, C.; Shannon, P. Reduction of disinfection efficacy of contact lens care products on the global market in the presence of contact lenses and cases. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022, 7, e000955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliam, Y.; Kaye, S.; Winstanley, C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and microbial keratitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subedi, D.; Vijay, A.K.; Willcox, M. Study of disinfectant resistance genes in ocular isolates of pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Stapleton, F.; Willcox, M.D.P. Susceptibility of contact lens-related pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis isolates to multipurpose disinfecting solutions, disinfectants, and antibiotics. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczotka-Flynn, L.B.; Imamura, Y.; Chandra, J.; Yu, C.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Pearlman, E.; Ghannoum, M.A. Increased resistance of contact lens-related bacterial biofilms to antimicrobial activity of soft contact lens care solutions. Cornea 2009, 28, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.T.; Zhu, H.; Willcox, M.; Stapleton, F. The effectiveness of various cleaning regimens and current guidelines in contact lens case biofilm removal. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5287–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, F.; Dart, J.K.; Seal, D.V.; Matheson, M. Epidemiology of pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis in contact lens wearers. Epidemiol. Infect. 1995, 114, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogushi, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Kuwahara, T.; Hayabuchi, N.; Kawabata, M. Molecular genetic investigations of contaminated contact lens storage cases as reservoirs of pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis. Jpn J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 54, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, I.; Kwan, L.; Yu, C.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M. Role of the corneal epithelial basement membrane in ocular defense against pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3264–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcon, I.; Tam, C.; Mun, J.J.; LeDue, J.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M. Factors impacting corneal epithelial barrier function against pseudomonas aeruginosa traversal. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustin, D.K.; Heimer, S.R.; Tam, C.; Li, W.Y.; Le Due, J.M.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M. Role of defensins in corneal epithelial barrier function against pseudomonas aeruginosa traversal. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mun, J.J.; Tam, C.; Kowbel, D.; Hawgood, S.; Barnett, M.J.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M. Clearance of pseudomonas aeruginosa from a healthy ocular surface involves surfactant protein d and is compromised by bacterial elastase in a murine null-infection model. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wirostko, B.; Rafii, M.; Sullivan, D.A.; Morelli, J.; Ding, J. Novel therapy to treat corneal epithelial defects: A hypothesis with growth hormone. Ocul. Surf. 2015, 13, 204–212.e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Callaghan, R.J.; Engel, L.S.; Hobden, J.A.; Callegan, M.C.; Green, L.C.; Hill, J.M. Pseudomonas keratitis. The role of an uncharacterized exoprotein, protease iv, in corneal virulence. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 534–543. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Karmakar, M.; Taylor, P.R.; Rietsch, A.; Pearlman, E. Exos and exot adp ribosyltransferase activities mediate pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis by promoting neutrophil apoptosis and bacterial survival. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleiszig, S.M.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P.; Miyazaki, H.; Vallas, V.; Mostov, K.E.; Kanada, D.; Sawa, T.; Yen, T.S.; Frank, D.W. Pseudomonas aeruginosa-mediated cytotoxicity and invasion correlate with distinct genotypes at the loci encoding exoenzymes. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zolfaghar, I.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M. Twitching motility contributes to the role of pili in corneal infection caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 5389–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, N.; Suzuki, T.; Ishikawa, E.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hayashi, N.; Gotoh, N.; Ohashi, Y. Relationship of virulence factors and clinical features in keratitis caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 6892–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zegans, M.E.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Ray, K.; Naimie, A.; Keller, A.E.; Stover, C.K.; Lalitha, P.; Srinivasan, M.; Acharya, N.R.; Lietman, T.M. Association of biofilm formation, psl exopolysaccharide expression, and clinical outcomes in pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis: Analysis of isolates in the steroids for corneal ulcers trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brennan, N.A.; Coles, M.L.; Comstock, T.L.; Levy, B. A 1-year prospective clinical trial of balafilcon a (purevision) silicone-hydrogel contact lenses used on a 30-day continuous wear schedule. Ophthalmology 2002, 109, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.; Sousa, C.; Lira, M.; Elisabete, M.; Oliveira, R.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. Adhesion of pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphylococcus epidermidis to silicone-hydrogel contact lenses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2005, 82, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Cantu-Crouch, D.; Sharma, V.; Pruitt, J.; Yao, G.; Fukazawa, K.; Wu, J.Y.; Ishihara, K. Surface characterization of a silicone hydrogel contact lens having bioinspired 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymer layer in hydrated state. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Fukazawa, K.; Sharma, V.; Liang, S.; Shows, A.; Dunbar, D.C.; Zheng, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhang, S.; Hong, Y.; et al. Antifouling silicone hydrogel contact lenses with a bioinspired 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymer surface. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7058–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.D.; Yao, K.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.J.; Xu, Z.K. Surface modification of silicone intraocular lens by 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphoryl-choline binding to reduce staphylococcus epidermidis adherence. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2007, 35, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Matsumoto, H.N.; Koyama, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Ishihara, K.; Takakuda, K. Prevention of biofilm formation with a coating of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymer. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2008, 70, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunimatsu, R.; Tsuka, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Sumi, K.; Yoshimi, Y.; Kado, I.; Inada, A.; Kiritoshi, Y.; Tanimoto, K. The influence of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymer materials on orthodontic friction and attachment of oral bacteria. Materials 2022, 15, 5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Murakami, K.; Yoshida, K.; Sakurai, S.; Kudo, Y.; Ozaki, K.; Hirota, K.; Fujii, H.; Suzuki, M.; Miyake, Y.; et al. Suppressive effects of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (mpc)-polymer on the adherence of candida species and mrsa to acrylic denture resin. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Yoo, K.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Park, S.B.; Choi, Y.K.; Kim, Y.I. Enhanced antimicrobial and remineralizing properties of self-adhesive orthodontic resin containing mesoporous bioactive glass and zwitterionic material. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajunaid, S.O.; Baras, B.H.; Weir, M.D.; Xu, H.H.K. Denture acrylic resin material with antibacterial and protein-repelling properties for the prevention of denture stomatitis. Polymers 2022, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, T.; Saito, T.; Shobuike, T.; Miyamoto, H.; Matsuda, J.; Fukazawa, K.; Ishihara, K.; Tanaka, S.; Moro, T. 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymer coating inhibits bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on a suture: An in vitro and in vivo study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5639651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pifer, R.; Harris, V.; Sanders, D.; Crary, M.; Shannon, P. Evaluation of serratia marcescens adherence to contact lens materials. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkis, C.; Fleiszig, S.M. Resistance of pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates to hydrogel contact lens disinfection correlates with cytotoxic activity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.J.; Wilson, L.A.; Ahearn, D.G. Adherence of pseudomonas aeruginosa to rigid gas-permeable contact lenses. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 1447–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luensmann, D.; Omali, N.B.; Suko, A.; Drolle, E.; Heynen, M.; Subbaraman, L.N.; Scales, C.; Fadli, Z.; Jones, L. Kinetic deposition of polar and non-polar lipids on silicone hydrogel contact lenses. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.B.; Efron, N. Quarter of a century of contact lens prescribing trends in the united kingdom (1996–2020). Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2022, 45, 101446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, C.W.; Cilimberg, K.C.; Moore, A. Contact lens care tips for patients: An optometrist’s perspective. Clin. Optom. 2017, 9, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Zimmerman, A.B.; Lam, D.; Kinoshita, B.; Rosner, B.; Mitchell, G.L.; Richdale, K. Defining daily disposable contact lens wear in a clinical study. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2023, 100, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Richdale, K.; Jalbert, I.; Doung, K.; Gokhale, M. Non-invasive objective and contemporary methods for measuring ocular surface inflammation in soft contact lens wearers—A review. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2017, 40, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczotka-Flynn, L.; Lass, J.H.; Sethi, A.; Debanne, S.; Benetz, B.A.; Albright, M.; Gillespie, B.; Kuo, J.; Jacobs, M.R.; Rimm, A. Risk factors for corneal infiltrative events during continuous wear of silicone hydrogel contact lenses. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5421–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steele, K.R.; Szczotka-Flynn, L. Epidemiology of contact lens-induced infiltrates: An updated review. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2017, 100, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holden, B.A.; La Hood, D.; Grant, T.; Newton-Howes, J.; Baleriola-Lucas, C.; Willcox, M.D.; Sweeney, D.F. Gram-negative bacteria can induce contact lens related acute red eye (clare) responses. CLAO J. 1996, 22, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sankaridurg, P.R.; Willcox, M.D.; Sharma, S.; Gopinathan, U.; Janakiraman, D.; Hickson, S.; Vuppala, N.; Sweeney, D.F.; Rao, G.N.; Holden, B.A. Haemophilus influenzae adherent to contact lenses associated with production of acute ocular inflammation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willcox, M.; Sharma, S.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Sankaridurg, P.R.; Gopinathan, U.; Holden, B.A. External ocular surface and lens microbiota in contact lens wearers with corneal infiltrates during extended wear of hydrogel lenses. Eye Contact Lens 2011, 37, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.; Lass, J.H.; Heinzel, F.P.; Petroll, W.M.; Gomez, J.; Diaconu, E.; Kalsow, C.M.; Pearlman, E. Regulation of endotoxin-induced keratitis by pecam-1, mip-2, and toll-like receptor 4. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 2278–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, B.A.; Reddy, M.K.; Sankaridurg, P.R.; Buddi, R.; Sharma, S.; Willcox, M.D.; Sweeney, D.F.; Rao, G.N. Contact lens-induced peripheral ulcers with extended wear of disposable hydrogel lenses: Histopathologic observations on the nature and type of corneal infiltrate. Cornea 1999, 18, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasuri, M.K.; Venkata, N.; Kumar, V.M. Differential diagnosis of microbial keratitis and contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer. Eye Contact Lens 2003, 29, S60–S62, discussion S83–S64, S192–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donshik, P.C.; Suchecki, J.K.; Ehlers, W.H. Peripheral corneal infiltrates associated with contact lens wear. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1995, 93, 49–60, discussion 60–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.Z.; Zhu, H.; Stapleton, F.; Hume, E.; Aliwarga, Y.; Thakur, A.; Willcox, M.D. Effects of alpha-toxin-deficient staphylococcus aureus on the production of peripheral corneal ulceration in an animal model. Curr. Eye Res. 2005, 30, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, M.D.; Hume, E.B.; Aliwarga, Y.; Kumar, N.; Cole, N. A novel cationic-peptide coating for the prevention of microbial colonization on contact lenses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, N.; Hume, E.B.; Vijay, A.K.; Sankaridurg, P.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D. In vivo performance of melimine as an antimicrobial coating for contact lenses in models of clare and clpu. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalaiselvan, P.; Konda, N.; Pampi, N.; Vaddavalli, P.K.; Sharma, S.; Stapleton, F.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Dutta, D. Effect of antimicrobial contact lenses on corneal infiltrative events: A randomized clinical trial. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, M.D.P.; Hume, E.B.H.; Vijay, A.K.; Petcavich, R. Ability of silver-impregnated contact lenses to control microbial growth and colonisation. J. Optom. 2010, 3, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantam, J.; Zhu, H.; Willcox, M.; Ozkan, J.; Naduvilath, T.; Thomas, V.; Stapleton, F. In vivo assessment of antimicrobial efficacy of silver-impregnated contact lens storage cases. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, A.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Stapleton, F. In vivo efficacy of silver-impregnated barrel contact lens storage cases. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Montanaro, L.; Caramazza, R.; Sassoli, V.; Cavedagna, D. Inhibition of bacterial adherence to a high-water-content polymer by a water-soluble, nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory drug. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danion, A.; Arsenault, I.; Vermette, P. Antibacterial activity of contact lenses bearing surface-immobilized layers of intact liposomes loaded with levofloxacin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2350–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvan, P.; Dutta, D.; Bhombal, F.; Konda, N.; Vaddavalli, P.K.; Sharma, S.; Stapleton, F.; Willcox, M.D.P. Ocular microbiota and lens contamination following mel4 peptide-coated antimicrobial contact lens (macl) extended wear. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2022, 45, 101431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Cole, N.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D. Broad spectrum antimicrobial activity of melimine covalently bound to contact lenses. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, J.C.; Liao, C.J.; Lewis, K.; Klibanov, A.M. Designing surfaces that kill bacteria on contact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Gu, H.; Smith, C.; Ren, D. Microtopographic patterns affect escherichia coli biofilm formation on poly(dimethylsiloxane) surfaces. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2686–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, M.N.; Liang, E.I.; Rodriguez, L.A.; Vollereaux, N.; Yee, A.F. Nanopatterned polymer surfaces with bactericidal properties. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, A.K.; Wong, T.S.; Belisle, R.A.; Boggs, E.M.; Aizenberg, J. Liquid-infused structured surfaces with exceptional anti-biofouling performance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13182–13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacCallum, N.; Howell, C.; Kim, P.; Sun, D.; Friedlander, R.; Ranisau, J.; Ahanotu, O.; Lin, J.J.; Vena, A.; Hatton, B.; et al. Liquid-infused silicone as a biofouling-free medical material. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, D.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, E.H.; Suh, H.; Choi, K.S. Bacterial adhesion on peg modified polyurethane surfaces. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Mu, M.; Konno, T.; Inoue, Y.; Fukazawa, K. The unique hydration state of poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 884–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vales, T.P.; Jee, J.P.; Lee, W.Y.; Cho, S.; Lee, G.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Development of poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine)-functionalized hydrogels for reducing protein and bacterial adsorption. Materials 2020, 13, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, Y.; Onodera, Y.; Ishihara, K. Preparation of a thick polymer brush layer composed of poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization and analysis of protein adsorption resistance. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, C.; Melo, M.A.; Bai, Y.X.; Cheng, L.; Xu, H.H. A novel protein-repellent dental composite containing 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2015, 7, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goda, T.; Matsuno, R.; Konno, T.; Takai, M.; Ishihara, K. Photografting of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine from polydimethylsiloxane: Tunable protein repellency and lubrication property. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 63, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibarani, J.; Takai, M.; Ishihara, K. Surface modification on microfluidic devices with 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymers for reducing unfavorable protein adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 54, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, K.; Nomura, H.; Mihara, T.; Kurita, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Nakabayashi, N. Why do phospholipid polymers reduce protein adsorption? J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 39, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, A.L.; Chang, C.Y.; Yang, J.; Luckett, J.; Cockayne, A.; Atkinson, S.; Mei, Y.; Bayston, R.; Irvine, D.J.; Langer, R.; et al. Combinatorial discovery of polymers resistant to bacterial attachment. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epa, V.C.; Hook, A.L.; Chang, C.; Yang, J.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G.; Williams, P.; Davies, M.C.; Alexander, M.R.; Winkler, D.A. Modelling and prediction of bacterial attachment to polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundas, A.A.; Sanni, O.; Dubern, J.F.; Dimitrakis, G.; Hook, A.L.; Irvine, D.J.; Williams, P.; Alexander, M.R. Validating a predictive structure-property relationship by discovery of novel polymers which reduce bacterial biofilm formation. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1903513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanni, O.; Chang, C.Y.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R.; Davies, M.C.; Williams, P.M.; Williams, P.; Alexander, M.R.; Hook, A.L. Bacterial attachment to polymeric materials correlates with molecular flexibility and hydrophilicity. Adv. Health Mater. 2015, 4, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magennis, E.P.; Hook, A.L.; Davies, M.C.; Alexander, C.; Williams, P.; Alexander, M.R. Engineering serendipity: High-throughput discovery of materials that resist bacterial attachment. Acta Biomater. 2016, 34, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.T.; Fang, P.C.; Chen, J.L.; Hsu, S.L.; Chao, T.L.; Yu, H.J.; Lai, Y.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Kuo, M.T. Molecular bioburden of the lens storage case for contact lens-related keratitis. Cornea 2018, 37, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodjikian, L.; Casoli-Bergeron, E.; Malet, F.; Janin-Manificat, H.; Freney, J.; Burillon, C.; Colin, J.; Steghens, J.P. Bacterial adhesion to conventional hydrogel and new silicone-hydrogel contact lens materials. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaraman, L.N.; Borazjani, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Jones, L.; Willcox, M.D. Influence of protein deposition on bacterial adhesion to contact lenses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Cole, N.; Willcox, M. Factors influencing bacterial adhesion to contact lenses. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 14–21. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harris, V.; Pifer, R.; Shannon, P.; Crary, M. Comparative Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Adhesion to a Poly-(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine)-Modified Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens. Vision 2023, 7, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010027
Harris V, Pifer R, Shannon P, Crary M. Comparative Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Adhesion to a Poly-(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine)-Modified Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens. Vision. 2023; 7(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarris, Valerie, Reed Pifer, Paul Shannon, and Monica Crary. 2023. "Comparative Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Adhesion to a Poly-(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine)-Modified Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens" Vision 7, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010027
APA StyleHarris, V., Pifer, R., Shannon, P., & Crary, M. (2023). Comparative Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Adhesion to a Poly-(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine)-Modified Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens. Vision, 7(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010027





