Geometric Parameter Control of Infill Patterns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
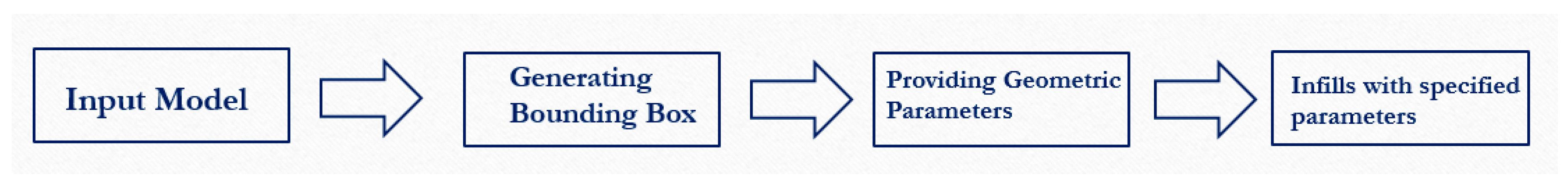
- We have developed a new method for controlling the geometric parameters of infill patterns. Our approach reduces the amount of printing materials consumed and results in a more lightweight interior for 3D printed fabrications.
- The method enables the user to specify the geometric parameters for infill patterns.
- Our method can create variations of infill patterns derived from a single pattern type. It also is applicable for different polygonal and linear type infill patterns.
2. Related Work
2.1. Subdivision
2.2. Infill Patterns
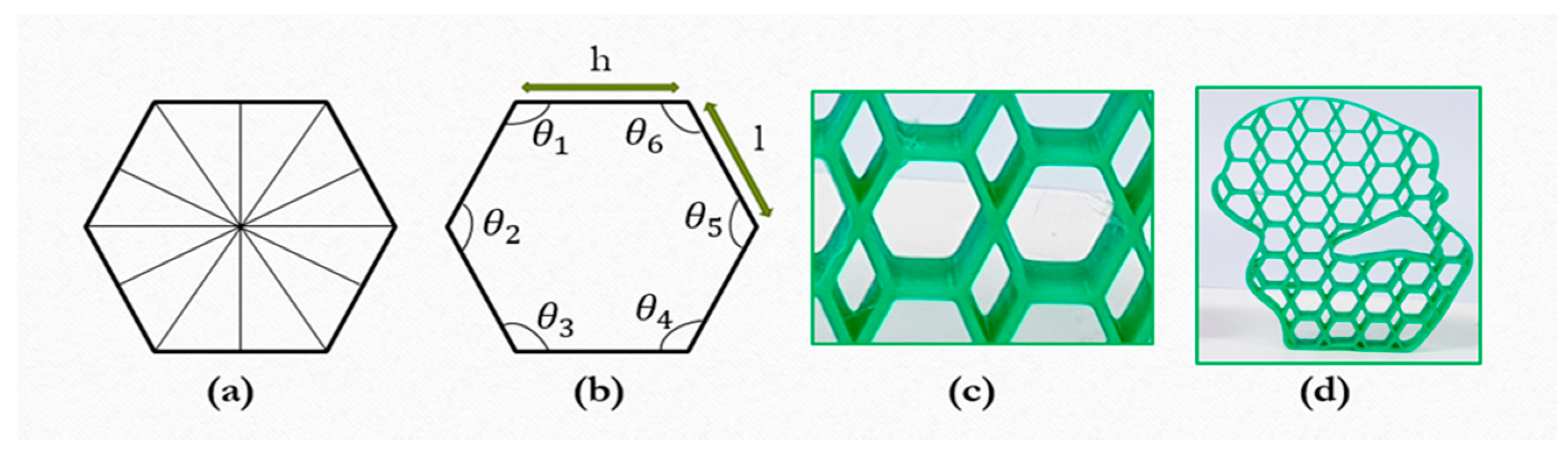
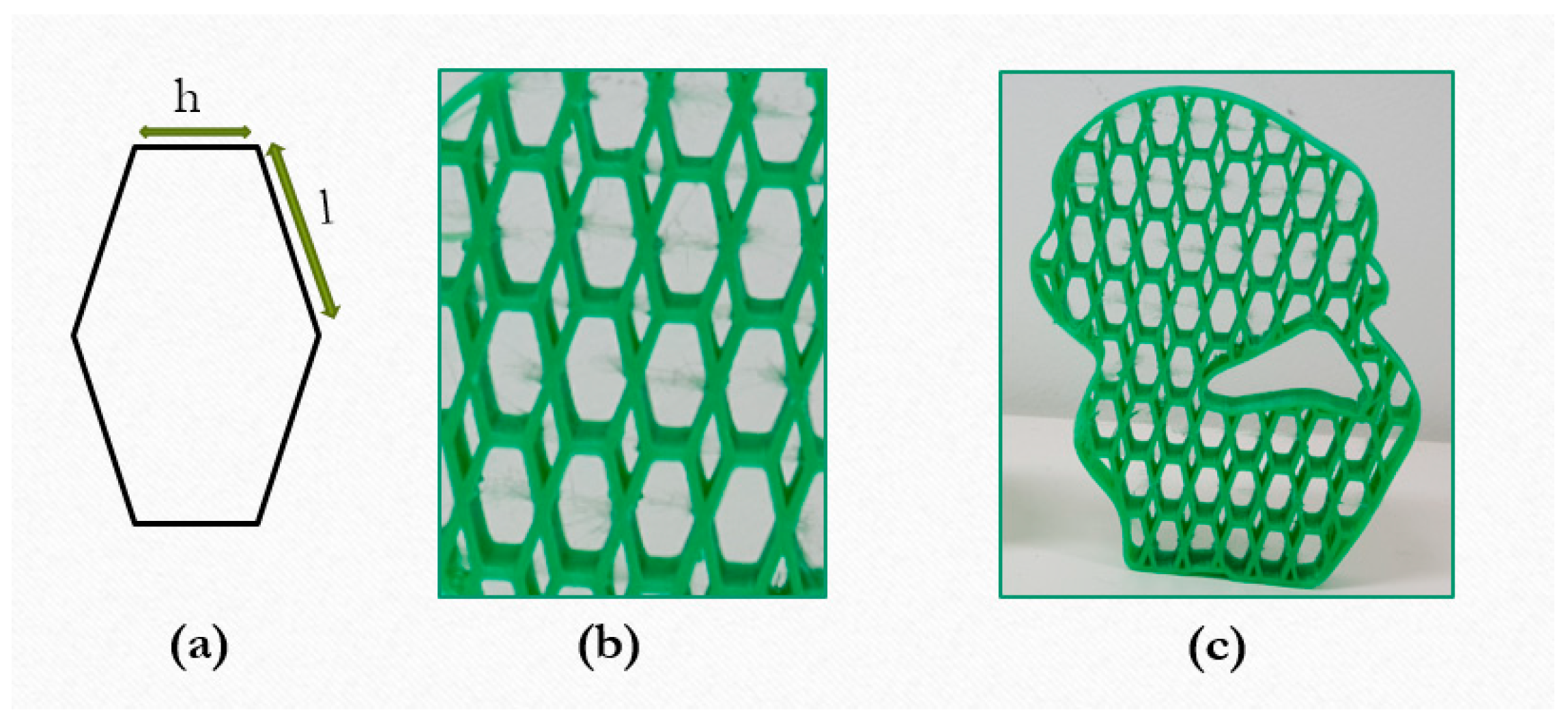
3. Pattern Size Controlling Method
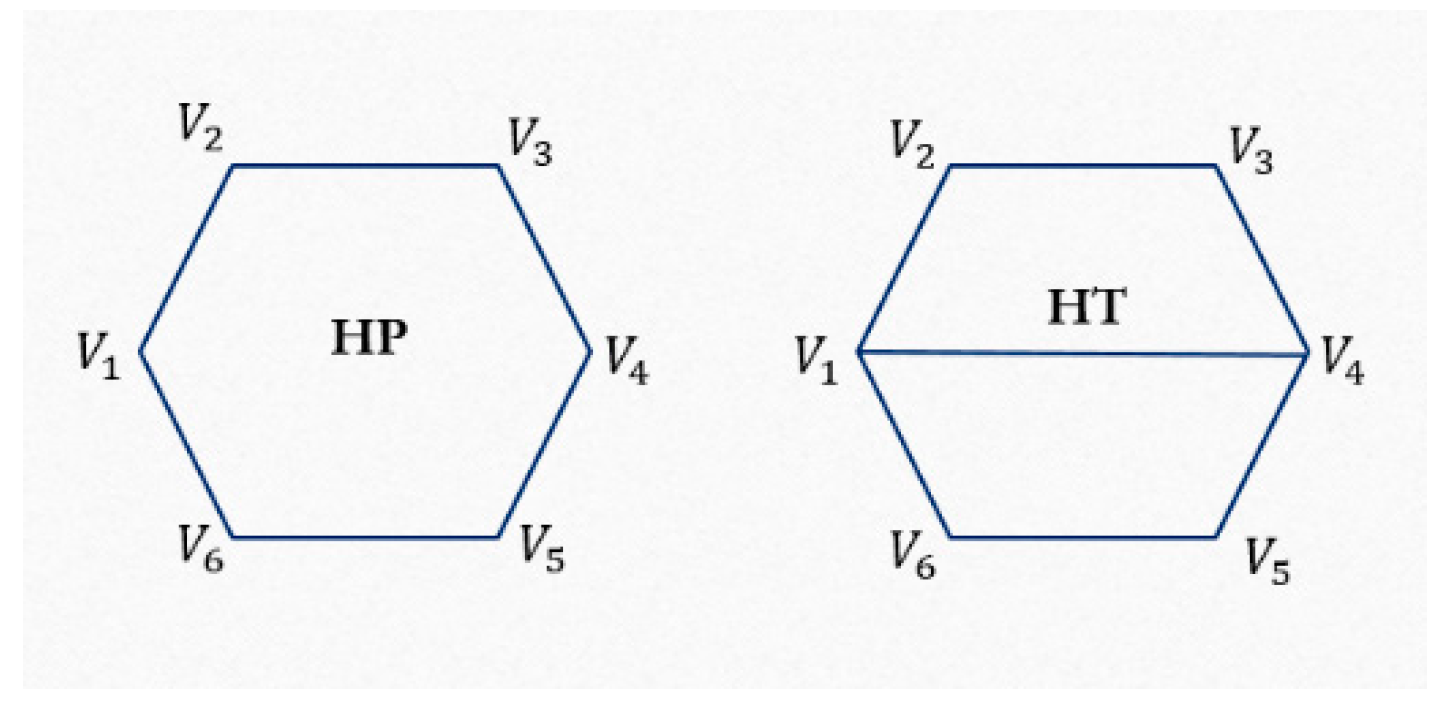
3.1. Infill Patterns
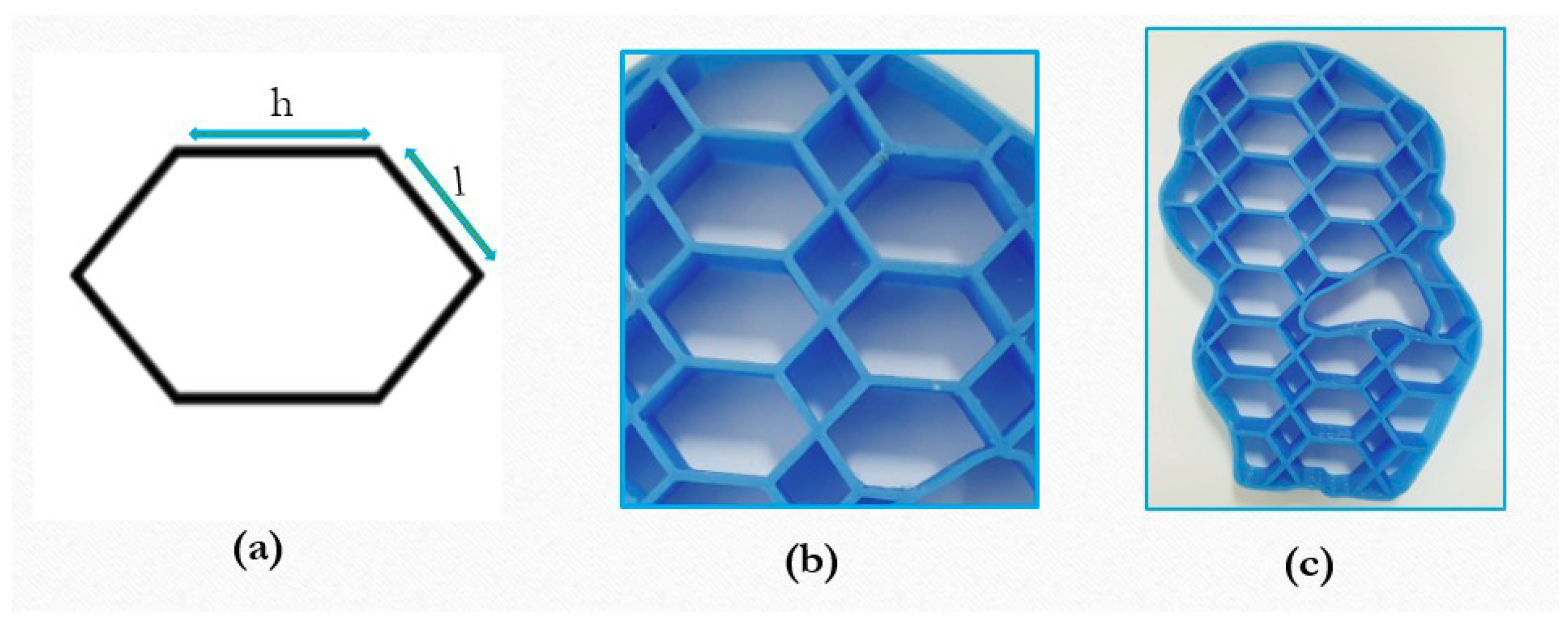
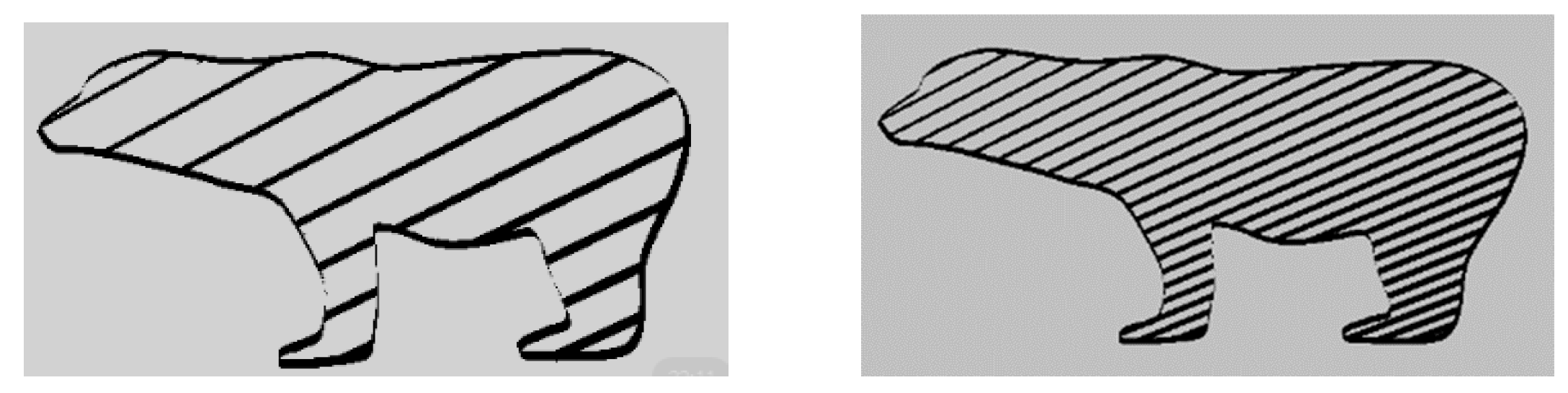
3.2. Linear Infill Pattern
3.3. Pattern Size Regulation
4. Experiment Results
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steuben, J.; van Bossuyt, D.L.; Turner, C. Design for Fused Filament Fabrication Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 2–5 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultimaker Cura. Available online: https://ultimaker.com/en/products/ultimaker-cura-software (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- KISSlicer. Available online: http://www.kisslicer.com/ (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Slic3r. Available online: https://slic3r.org/ (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Chaikin, G.M. An Algorithm for High Speed Curve Generation. Comput. Gr. Image Process. 1974, 3, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catmull, E.; Clark, J. Recursively generated B-spline surfaces on arbitrary topological meshes. Comput. Aided Des. 1978, 10, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doo, D.; Sabin, M. Behaviour of recursive division surfaces near extraordinary points. Comput. Aided Des. 1978, 10, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Reif, U. The simplest subdivision scheme for smoothing polyhedral. ACM Trans. Graph. 1997, 16, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Warren, J. Edge and vertex insertion for a class of C1 subdivision surfaces. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 1999, 16, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyn, N.; Levin, D.; Gregory, J.A. A butterfly subdivision scheme for surface interpolation with tension control. ACM Trans. Graph. 1990, 9, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorin, D.; Schröder, P.; Sweldens, W. Interpolating subdivision for meshes with arbitrary topology. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Maya. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/maya/overview (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Rhinoceros. Available online: https://www.rhino3d.com/ (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- 3DS MAX. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/3ds-max/overview (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Blender. Available online: https://www.blender.org/ (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Stava, O.; Vanek, J.; Benes, B.; Carr, N.; Měch, R. Stress relief: Improving structural strength of 3D printable objects. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 48:1–48:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, T.Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Tong, X.; Tong, W. Cost-effective printing of 3D objects with skin-frame structures. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 13, 177:1–177:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sharf, A.; Zhao, H.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, X. Build-to-last: Strength to weight 3D printed objects. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 33, 97:1–97:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Tu, C.; Wang, W. Medial axis tree-an internal supporting structure for 3D printing. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2015, 5, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, A.M. Adaptive Voids Primal and Dual Adaptive Cellular Structures for Additive Manufacturing. Vis. Comp. 2015, 31, 799–808. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, J.; Dumas, J.; Lefebvre, S. Procedural voronoi foams for additive manufacturing. ACM Trans. Gr. 2016, 35, 1–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, A. Beautiful and Functional: A Review of Biomimetic Design in Additive Manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Dai, N.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X. Interior structural optimization based on the density-variable shape modeling of 3D printed objects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chynybekova, K.; Choi, S.M. Multilevel Design for the Interior of 3D Fabrications. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, A.N.; Schmidt, R.; Bærentzen, J.A. Automatic balancing of 3D models. Comput. Aided Des. 2015, 58, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, R.; Whiting, E.; Lefebvre, S.; Sorkine-Hornung, O. Make it stand: Balancing shapes for 3d fabrication. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32, 81:1–81:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, R. Balancing 3D models with movable masses. In Proceedings of the Vision Modeling and Visualization, Bonn, Germany, 25–27 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, C.C.L.; Zhang, X.T.; Westermann, R. Self-supporting rhombic infill structures for additive manufacturing. Comput. Aided Des. 2016, 80, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, K.M.; Suziki, H.; Gupinar, E. A generative sampling system for profile designs with shape constraints and user evaluation. Comput. Aided Des. 2019, 111, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Model | Weight of Models with Patterns | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kitten |  15 g |  12 g |  21 g | |
| 2 | Kitten |  24 g |  20 g |  28 g | |
| 3 | Bear |  14 g |  23 g | ||
 20 g | |||||
| NO. | Model | Stress-Sustainability of Models | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kitten |  1155 N |  559 N |  1617 N | |
| 2 | Bear |  263 N |  1048 N | ||
 167 N | |||||
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chynybekova, K. Geometric Parameter Control of Infill Patterns. Designs 2019, 3, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs3040049
Chynybekova K. Geometric Parameter Control of Infill Patterns. Designs. 2019; 3(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs3040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleChynybekova, Kanygul. 2019. "Geometric Parameter Control of Infill Patterns" Designs 3, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs3040049
APA StyleChynybekova, K. (2019). Geometric Parameter Control of Infill Patterns. Designs, 3(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs3040049




