Using NLP for Fact Checking: A Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review Studies on Using NLP for Fact Checking
2.1. Background
NLP Methods
2.2. Claim Identification and Extraction
2.2.1. Searching for Claims
2.2.2. Claim Extraction
2.2.3. Mathematical Method for Statistical Properties
2.3. Sources of Evidence
2.3.1. Fact Databases
2.3.2. The Internet
2.3.3. Other External Sources
2.3.4. Originator and Language
2.4. Claim Verification
2.4.1. Language Analysis
2.4.2. Comparing to Fact Databases
2.4.3. Comparing to Pre-Checked Claims
2.4.4. Comparing to External Sources
2.5. Aggregate Method: Claim Buster
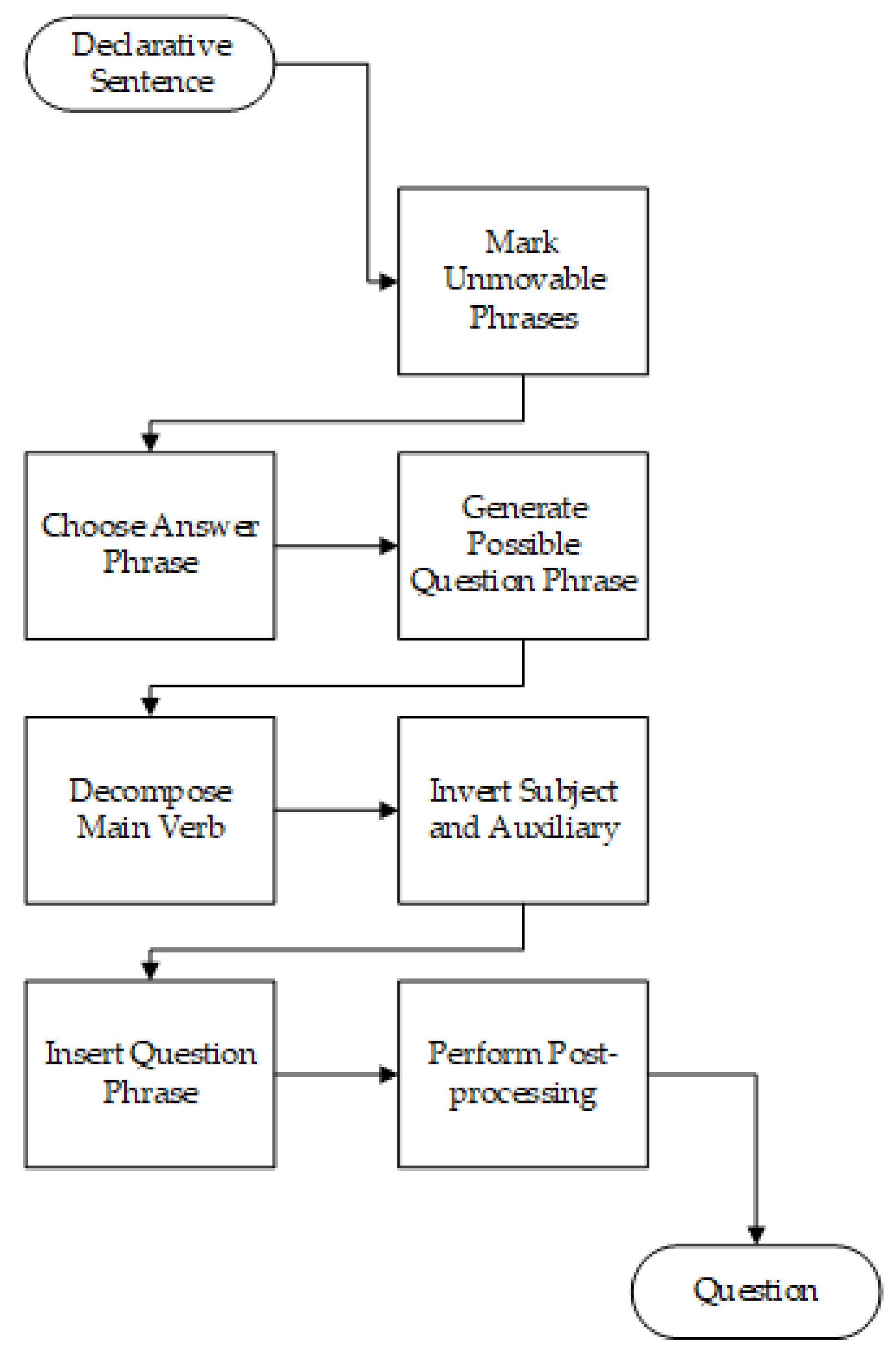
2.5.1. Question Generation
2.5.2. Question Answering
2.5.3. Database Searching
2.5.4. External Support Retrieval & Comparison
3. Related Task: Speaker & Source Analysis for Fact Checking
3.1. User Profile
3.2. Answer Context and Language
3.3. External Evidence
3.4. Intra-Forum Evidence
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graves, L.; Cherubini, F. The Rise of Fact-Checking Sites in Europe; Reuters Institute: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vargo, C.J.; Guo, L.; Amazeen, M.A. The agenda-setting power of fake news: A big data analysis of the online media landscape from 2014 to 2016. N. Media Soc. 2017, 20, 2028–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinovskiy, L.; Price, O.; Babakar, M.; Zubiaga, A. Towards Automated Factchecking: Developing an Annotation Schema and Benchmark for Consistent Automated Claim Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1809.08193. [Google Scholar]
- Claim Buster. Available online: https://idir.uta.edu/claimbuster/ (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- Shin, J.; Thorson, K. Partisan Selective Sharing: The Biased Diffusion of Fact-Checking Messages on Social Media. J. Commun. 2017, 67, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadzhov, G.; Nakov, P.; Marquez, L.; Barron-Cedeno, A.; Koychev, I. Fully Automated Fact Checking Using External Sources. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.00341. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.; Zhang, G.; Arslan, F.; Caraballo, J.; Jimenez, D.; Gawsane, S.; Hasan, S.; Joseph, M.; Kulkarni, A.; Nayak, A.K.; et al. ClaimBuster: The first end-to-end fact-checking system. In Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Munich, Germany, 28 August 2017; Volume 10, pp. 1945–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.; Vlachos, A.; Christodoulopoulos, C.; Mittal, A. FEVER: A Large-Scale Dataset for Fact Extrac-tion and VERification. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, D.; Dali, L.; Fortuna, B.; Grobelnik, M.; Mladeni, D. Triplet Extraction from Sentences. In Proceedings of the 10th International Multiconference, Information Society-IS, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 8–12 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, A.; Riedel, S. Identification and Verification of Simple Claims about Statistical Properties. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 2596–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, J.; Vlachos, A. An Extensible Framework for Verification of Numerical Claims. In Proceedings of the Software Demonstrations of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Riedel, B.; Augenstein, I.; Spithourakis, G.P.; Riedel, S. A Simple but Tough-to-Beat Baseline for the Fake News Challenge Stance Detection Task. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1707.03264. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, W.; Vlachos, A. Emergent: A novel data-set for stance classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1163–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Vrandečić, D.; Krötzsch, M.W. Wikidata: A free collaborative knowledgebase. Commun. ACM 2014, 57, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y. “Liar, Liar Pants on Fire”: A New Benchmark Dataset for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rashkin, H.; Choi, E.; Jang, J.Y.; Volkova, S.; Choi, Y. Truth of Varying Shades: Analyzing Language in Fake News and Political Fact-Checking. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–11 September 2017; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 2931–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashole, N.; Mitchell, T.M. Language-Aware Truth Assessment of Fact Candidates. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 1009–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, A.; Riedel, S. Fact Checking: Task definition and dataset construction. In Proceedings of the ACL 2014 Workshop on Language Technologies and Computational Social Science, Baltimore, MD, USA, 26 June 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Agirre, E.; Cer, D.; Diab, M.; Gonzalez-Agirre, A.; Guo, W. SEM 2013 Shared Task: Semantic Textual Similarity. In Second Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics (*SEM), Proceedings of the Main Conference and the Shared Task: Semantic Textual Similarity, Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–14 June 2013; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaraman, A.; Leskovec, J.; Ullman, J. Mining of Massive Datasets. 2014. Available online: http://www.mmds.org (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, D.; Christopher, D. GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation. 2014. Available online: https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/ (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- Hassan, N.; Arslan, F.; Li, C.; Tremayne, M. Toward Automated Fact-Checking. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1803–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Heilman, M.; Smith, N.A. Question Generation via Overgenerating Transformations and Ranking; Defense Technical Information Center (DTIC): Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2009.
- Zheng, Z. AnswerBus question answering system. In Proceedings of the Human Language Technology Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–27 March 2002; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaylova, T.; Karadzhov, G.; Atanasova, P.; Baly, R.; Mohtarami, M.; Nakov, P. SemEval-2019 Task 8: Fact Checking in Community Question Answering Forums. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–7 June 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 860–869. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Bari, M.S.; Mohuiddin, T.; Joty, S. MultiMix: A Robust Data Augmentation Framework for Cross-Lingual NLP. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13240. [Google Scholar]







| Main Category | Subcategory | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Not a claim | “Give it all to them, I really don’t mind.” | |
| Other | Other | “Molly gives so much of who she is away throughout the film.” |
| Support/policy | “He has advocated for a junk food tax.” | |
| Quote | “The Brexit secretary said he would guarantee free movement of bankers.” | |
| Trivial claim | “It was a close call.” | |
| Voting record | “She just lost a parliamentary vote.” | |
| Public opinion | “A poll showed that most people who voted Brexit were concerned with immigration.” | |
| Definition | “The unemployed are only those actively looking for work.” | |
| Quantity | Current Value | “1 in 4 people wait longer than 6 weeks to see a doctor.” |
| Changing quantity | ||
| Comparison | ||
| Ranking | ||
| Prediction | Hypothetical statements | “The IFS says that school funding will have fallen by 5% by 2019.” |
| Claims about the future | ||
| Personal experience | Uncheckable | “I can’t save for a deposit” |
| Correlation/causation | Correlation | “Tetanus vaccine causes infertility” |
| Causation | ||
| Absence of a link | ||
| Laws/rules | Public Institutional procedures | “The UK allows a single adult to care for fewer children than other European countries.” |
| Rules/rule changes |
| Claim | Not a Claim |
|---|---|
| Quantity | Personal experience |
| Correlation/causation | Other |
| Laws/rules | Not a claim |
| Prediction |
| Sentence Category | Example |
|---|---|
| NFS | But I think it’s time to talk about the future. You remember the last time you said that? |
| UFS | Next Tuesday is Election day. Two days ago we ate lunch at a restaurant. |
| CFS | He voted against the first Gulf War. Over a million and a quarter Americans are HIV-positive. |
| Pattern | Data |
|---|---|
| The population of X is y | France: 66,000,000 Russia: 140,000,000 Iceland: 325,000 |
| X’s population is estimated at y | France: 66,030,000 Russia: 140,000,000 |
| X has y inhabitants | Russia: 140,000,000 Iceland: 300,000 |
| True/False | 6 Classes of Truthfulness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text | Text + TF-IDF | Text | Text + IDF | |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.44 | 0.58 | 0.16 | 0.21 |
| Maximum Entropy | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.20 | 0.21 |
| LSTM | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
| Similarity Rating | Sentences |
|---|---|
| 5 | The bird is bathing in the sink. Birdie is washing itself in the water basin. |
| 4 | In May 2010, the troops attempted to invade Kabul. The US army invaded Kabul on 7 May last year, 2010. |
| 3 | John said he is considered a witness but not a suspect. “I am not a suspect anymore,” John said. |
| 2 | They flew out of the nest in groups. They flew into the nest together |
| 1 | The woman is playing the violin. The young lady enjoys listening to the guitar. |
| 0 | John went horseback riding at dawn with a whole group of friends. Sunrise at dawn is a magnificent view to take in if you wake up early enough for it. |
| Claim | Generated Query |
|---|---|
| Texas teenager Ahmed Mohamed was arrested and accused of creating a “hoax bomb” after bringing a home-assembled clock to school | ‘Texas’—‘Ahmed Mohamed’—hoax—bomb—clock—arrested—accused |
| Is the popular casual dining chain Chipotle closing all locations soon? | ‘Chipotle’—dining—locations—popular—closed |
| Deficiency | Description |
|---|---|
| Ungrammatical | The question does not appear to be a valid English sentence. |
| Does not make sense | The question is indecipherable (e.g., Who was the investment?). |
| Vague | The question is too vague to know what it is talking about (e.g., What did Lincoln do?). |
| Obvious answer | The correct answer is obvious or clearly yes. |
| Missing answer | The answer to the question is not in the original input sentence. |
| Wrong question word | The question would be acceptable if the correct question word were used (e.g., What is the Eiffel Tower located?). |
| Formatting | Minor formatting errors with capitalization, punctuation, etc. |
| Other | Other reasons that a question may be unacceptable. |
| Answer Category | Explanation | Example Question | Example Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| FACTUAL—TRUE | The answer is true, and this can be manually verified using a trusted external resource. | I wanted to know if there were any specific shots and vaccinations I should get before coming over [to Doha] | Yes, there are; though it varies depending on which country you come from. In the UK, the doctor has a list of all countries and the vaccinations needed for each. |
| FACTUAL—FALSE | The answer gives a factual response, but it is false. | Can I bring my pit bulls to Qatar? | Yes, you can bring it but be careful this kind of dog is very dangerous. |
| FACTUAL—PARTIALLY TRUE | Only part of the answer could be verified. | I will be relocating from the UK to Qatar […] is there a league or TT clubs/nights in Doha? | Visit Qatar Bowling Center during Thursday and Friday and you’ll find people playing TT there. |
| FACTUAL—CONDITIONALLY TRUE | The answer is true in some cases and false in others, depending on some conditions that the answer does not mention. | My wife does not have NOC from Qatar Airways; but we are married now so can I bring her legally on my family visa as her husband? | Yes, you can. |
| FACTUAL—RESPONDER UNSURE | The person giving the answer is not sure about the veracity of their statement. | Will there actually be a raid on Area 51? | I heard that this was going to happen, not sure if anyone will show up though. |
| NONFACTUAL | The answer is not factual but is rather an opinion, advice, etc. that cannot be verified. | Should I buy this motorcycle? | I made the mistake of buying one like that and I am still paying for that mistake 3 years later, so I do not recommend it. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazarski, E.; Al-Khassaweneh, M.; Howard, C. Using NLP for Fact Checking: A Survey. Designs 2021, 5, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5030042
Lazarski E, Al-Khassaweneh M, Howard C. Using NLP for Fact Checking: A Survey. Designs. 2021; 5(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazarski, Eric, Mahmood Al-Khassaweneh, and Cynthia Howard. 2021. "Using NLP for Fact Checking: A Survey" Designs 5, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5030042
APA StyleLazarski, E., Al-Khassaweneh, M., & Howard, C. (2021). Using NLP for Fact Checking: A Survey. Designs, 5(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs5030042





