A Simplified Approach for the Determination of Penetrant Residual Velocity for Penetration Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Residual Velocity Determination
3. Non-Dimensional Study for Penetrant Residual Velocity
Buckingham Pi Theorem
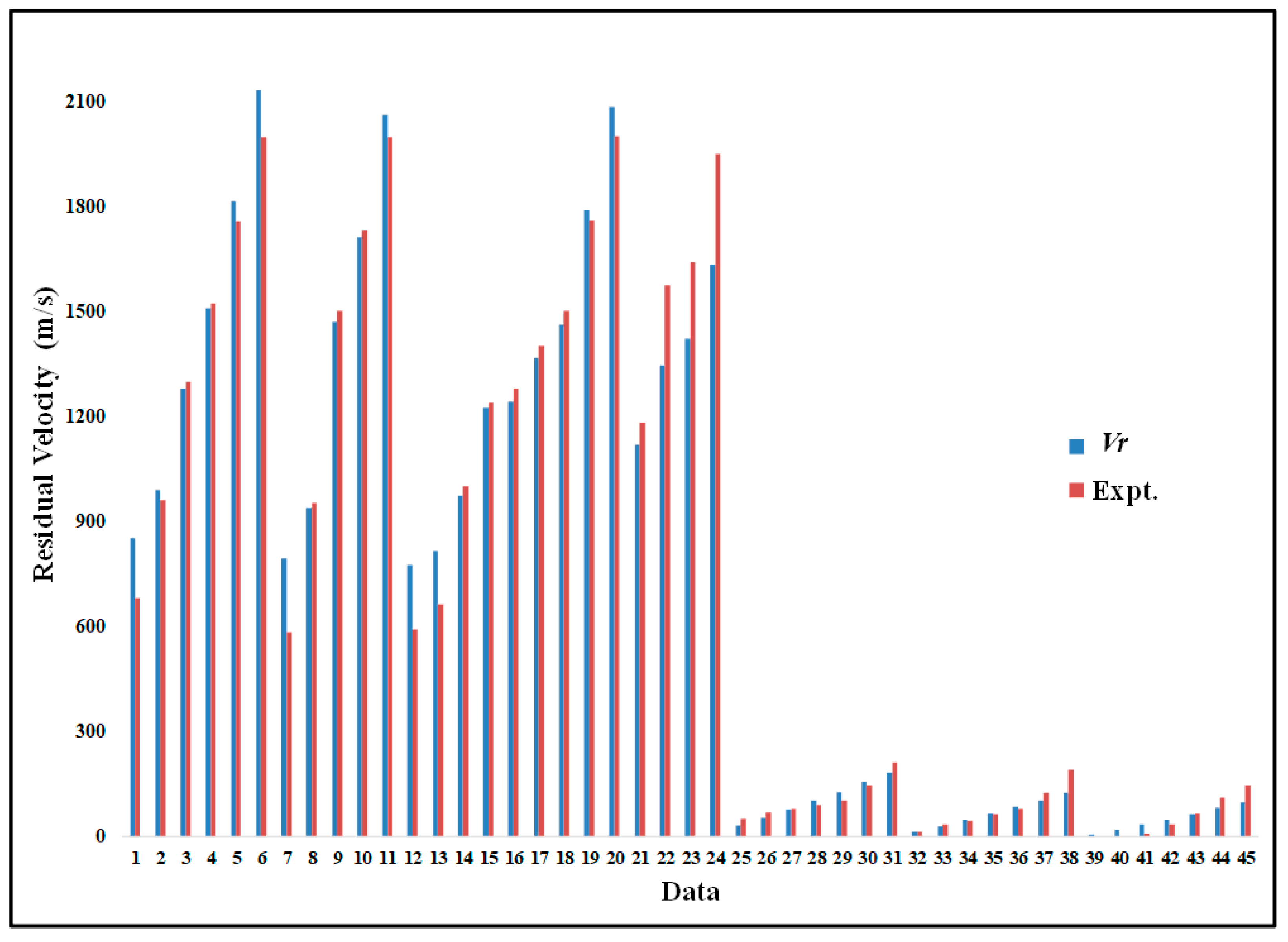
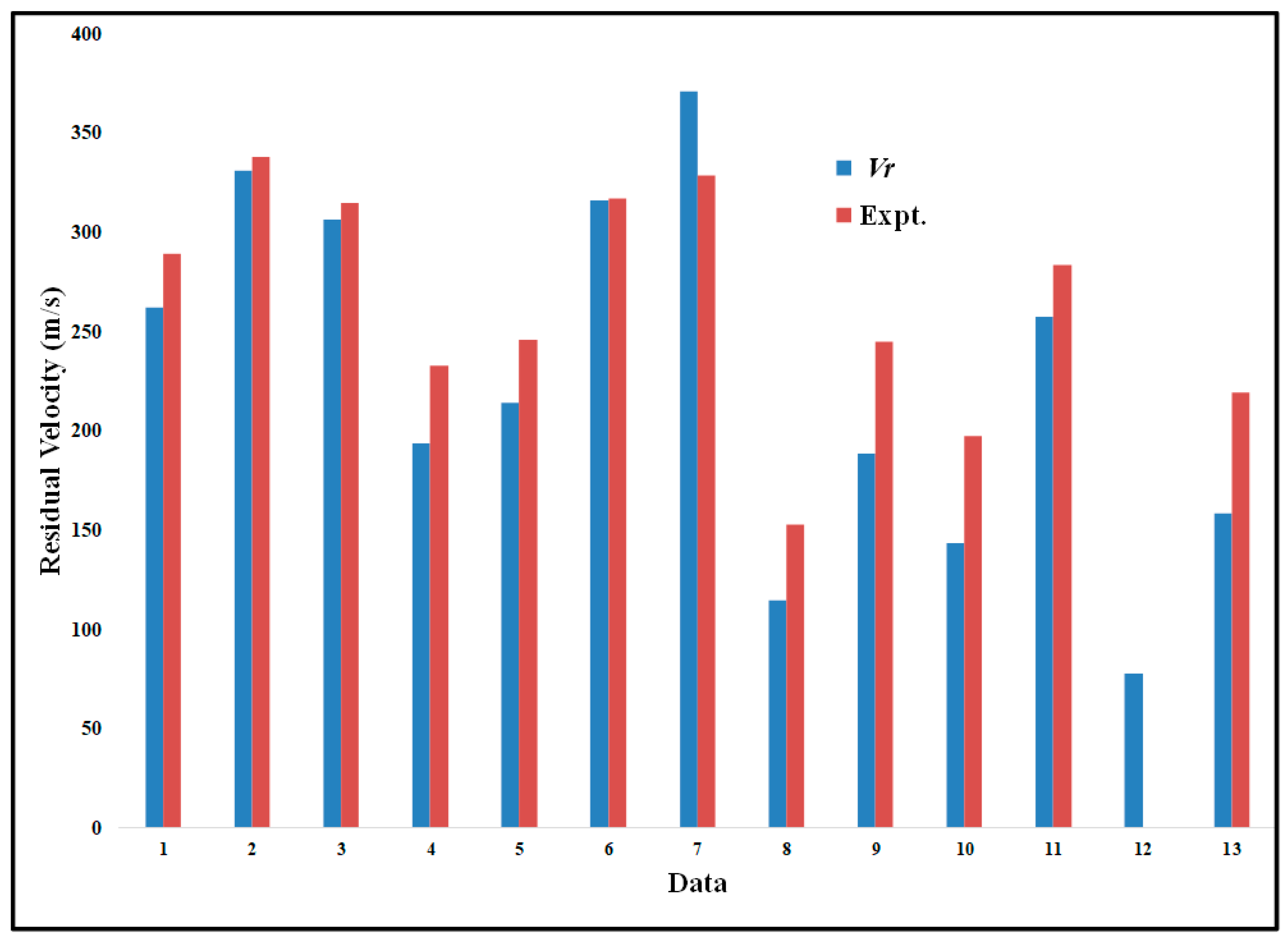
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papyrin, A.; Kosarev, V.; Klinkov, S.; Alkimov, A.; Fomin, V. Cold Spray Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, G.M.; Millward, H.R.; Potter, C.D.; Hewson, G.; Burkoth, T.L.; Bellhouse, B.J. Oral PowderJect: A novel system for administering local anaesthetic to the oral mucosa. Br. Dent. J. 1998, 185, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, V.K., Jr.; Helfritch, D.; Dinavahi, P.G.S.; Leyman, P. Theoretical and Experimental Particle Velocity in Cold Spray. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhulaifi, A.; Buck, G.; Arbegast, W. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Cold Spray Gas Dy-namic Effects for Polymer Coating. Therm. Spray Technol. 2012, 21, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinberg, D.; Simonnet, C.; Groisman, A. Pneumatic capillary gun for ballistic delivery of microparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.M.; Mark, A.F.K.; Brian, J.B. A ballistic study of micro-particle penetration to the oral mucosa. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2003, 28, 581–599. [Google Scholar]
- Birt, A.M.; Champagne, V.K.; Sisson, R.D.; Apelian, D. Microstructural analysis of Ti–6Al–4V powder for cold gas dynamic spray applications. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 28, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpenyigba, K.M.; Jankowiak, T.; Rusinek, A.; Pesci, R.; Wang, B. Effect of projectile nose shape on ballistic resistance of intersti-tial-free steel sheets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 79, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, M.L. Mechanics of penetration and perforation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1978, 16, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.K.; Iqbal, M.; Sekhon, G. Effect of projectile nose shape, impact velocity and target thickness on deformation behavior of aluminum plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 3411–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, Z.; Dekel, E. Revisiting the perforation of ductile plates by sharp-nosed rigid projectiles. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhu, V.; Bhat, T.B.; Gupta, N.K. Normal and Oblique Impacts of Hard Projectile on Single and Layered Plates-An Experimental Study. Def. Sci. J. 2003, 53, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunniff, P. Dimensionless Parameters for Optimization of Textile Based Body Armor Systems. In Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium on Ballistics, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–19 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.-W.; Wang, Y.-W.; An, R.; Cheng, H.-W.; Wang, F.-C. Investigation of the mechanical and ballistic properties of hybrid carbon/ aramid woven laminates. Def. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Dong, Y.; Cui, M.; Yu, B. A similarity method for predicting the residual velocity and deceleration of projectiles during impact with dissimilar materials. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, A.; Nazeer, F.; Wang, Y. A Prospective Way to Achieve Ballistic Impact Resistance of Lightweight Magnesium Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Wang, Y.; Huanwu, C.; Nazeer, F.; Khan, M.A. Post deformation analysis of the ballistic impacted magnesium alloys, a short-review. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2020, 9, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Nazeer, F.; Khan, M.A. Microstructure evolution of Mg-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy against soft steel core projectile. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 79, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoç, H.; Karabulut, Ş.; Çıtak, R. Study on mechanical and ballistic performances of boron carbide reinforced Al 6061 aluminum alloy produced by powder metallurgy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 148, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS. ABAQUS Standard User’s Manual; Version 6.14; Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc.: Pawtucket, RI, USA, 2014; Volume I–III. Available online: https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML0407/ML040760830.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Ghaseminia, A.; Vahedi, K. The Comparison Study of Long-Rod Penetration Models in Semi-Infinite Targets. Master’s Thesis, Emam Hossein University, Tehran, Iran, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- James, D. A unified theory of penetration. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1987, 15, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.; Rishworth, S.; Carter, F.; Mitchell, T. Effects of Relative Humidity and Ambient Temperature on the Ballistic Delivery of Micro-Particles to Excised Porcine Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, Y.; Riad, A. Perforation of Thick Plates by High-Speed Projectiles. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Aerospace Sciences & Aviation Technology, ASAT-13, Cairo, Egypt, 26–28 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadhan, A. High Velocity Impact Damage in Kevlar-29/Epoxy-AL2O3. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Res. 2012, 2, 138–154. [Google Scholar]
- Bridgman, P.W. Dimensional Analysis; Yale University Press: London, UK, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhu, X.; Hou, H.; Tian, X.; Shen, X. A new analytical model for the low-velocity perforation of thin steel plates by hemispherical-nosed projectiles. Def. Technol. 2017, 13, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhulaifi, A.S. A Simplified Approach for the Determination of Penetrant Residual Velocity for Penetration Processes. Designs 2022, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6010019
Alhulaifi AS. A Simplified Approach for the Determination of Penetrant Residual Velocity for Penetration Processes. Designs. 2022; 6(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhulaifi, Abdulaziz S. 2022. "A Simplified Approach for the Determination of Penetrant Residual Velocity for Penetration Processes" Designs 6, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6010019
APA StyleAlhulaifi, A. S. (2022). A Simplified Approach for the Determination of Penetrant Residual Velocity for Penetration Processes. Designs, 6(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6010019




