Design and Initial Testing of an Affordable and Accessible Smart Compression Garment to Measure Physical Activity Using Conductive Paint Stretch Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication and Integration of the Conductive Paint Sensors
2.2. Garment Testing
2.3. Testing Protocol
2.3.1. Calibration
2.3.2. Static 1 Phase
2.3.3. Dynamic Phase
2.3.4. Functional Phase
2.3.5. Static 2 Phase
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valevicius, A.M.; Jun, P.Y.; Hebert, J.S.; Vette, A.H. Use of optical motion capture for the analysis of normative upper body kinematics during functional upper limb tasks: A systematic review. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kruk, E.; Reijne, M.M. Accuracy of human motion capture systems for sport applications; state-of-the-art review. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 6, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, E.; Osei-Kuffour, D.; Chen, Y.-M.A.; McGregor, A.H. Use of wearable technology for performance assessment: A validation study. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 7, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, A.; Ye, M.; Shapiro, R.; Yang, R.; Noehren, B. Accuracy and repeatability of joint angles measured using a single camera markerless motion capture system. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, D. Accessible Motion Capture Set to Revolutionize Medical Device Development. Available online: http://www.mdtmag.com/blog/2015/11/accessible-motion-capture-set-revolutionize-medical-device-development (accessed on 2 February 2017).
- Pfister, A.; West, A.M.; Bronner, S.; Noah, J.A. Comparative abilities of microsoft kinect and vicon 3d motion capture for gait analysis. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2014, 38, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.B.; Babik, I.; Harbourne, R.; Cochran, N.J.; Stankus, J.; Szucs, K.; Lobo, M.A. Assessing the validity and reliability of a new video goniometer app for measuring joint angles in adults and children. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, D.T.P.; Chan, Y.Y. The use of wearable inertial motion sensors in human lower limb biomechanics studies: A systematic review. Sensors 2010, 10, 11556–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Huosheng, H.; Tao, Y. Inertial measurements of upper limb motion. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, M.; Estève, D.; Fourniols, J.-Y.; Escriba, C.; Campo, E. Smart wearable systems: Current status and future challenges. Artif. Intell. Med. 2012, 56, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, L.E.; Ashdown, S.P.; Smyth, B. Expanding garment functionality through embedded electronic technology. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2005, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W. Flexible fabric strain sensors. In Handbook of Smart Textiles; Tao, X., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2015; pp. 293–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gioberto, G.; Dunne, L. Theory and characterization of a top-thread coverstitched stretch sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Seoul, Korea, 14–17 October 2012; Volume 3, pp. 275–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Gioberto, G.; Dunne, L. Overlock-stitched stretch sensors: Characterization and effect of fabric property. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2013, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, B.; Hall, M.L.; Cao, H.; Lobo, M.A. Development and testing of a stitched stretch sensor with the potential to measure human movement. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, A.; Sanchez, V.; Atalay, O.; Vogt, D.M.; Haufe, F.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Batch Fabrication of Customizable Silicone-Textile Composite Capacitive Strain Sensors for Human Motion Tracking. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doshi, S.M.; Thostenson, E.T. Thin and Flexible Carbon Nanotube-Based Pressure Sensors with Ultrawide Sensing Range. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, B.; Gisby, T.; Anderson, I.A. Stretch sensors for human body motion. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices, EAPAD 2014; International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; p. 9056. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Glover, C.M.; Cho, H.; Araromi, O.A.; Graule, M.A.; Li, N.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Soft Sensing Shirt for Shoulder Kinematics Estimation. Available online: https://biodesign.seas.harvard.edu/files/biodesignlab/files/2020_jin_icra_soft_sensing_shirt_for_shoulder_kinematics_estimation.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Ma, S.; Ye, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Wei, L. Highly Oriented Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) Fibers via Mechanical Stretching for Wearable Motion Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, S.; Alessandro, C. Wearable electronics and smart textiles: A critical review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessandro, T.; Federico, L.; Gabriele, D.M.; Nicola, C.; Maria, P.; Rita, P.; Danilo, D.R. New generation of wearable goniometers for motion capture systems. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandro, T.; Federico, L.; Nicola, C.; De Danilo, R. Wearable goniometer and accelerometer sensory fusion for knee joint angle measurement in daily life. Sensors 2015, 15, 28435–28455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korshøj, M.; Skotte, J.H.; Christiansen, C.S.; Mortensen, P.; Kristiansen, J.; Hanisch, C.; Ingebrigtsen, J.; Holtermann, A. Validity of the Acti4 software using ActiGraph GT3X+accelerometer for recording of arm and upper body inclination in simulated work tasks. Ergonomics 2014, 57, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Gravunder, A.; Park, H.S. Commercial motion sensor based low-cost and convenient interactive treadmill. Sensors 2015, 15, 23667–23683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curtis, C.; Stephens, D.; Clarke, H.M.; Andrews, D. The active movement scale: An evaluative tool for infants with obstetrical brachial plexus palsy. J. Hand Surg. Am. Vol. 2002, 27, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bare Conductive – Electric Paint Safety Data Sheet English. Available online: https://www.bareconductive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/2020.05.ElectricPaint-MSDS.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Bare Conductive—Electric Paint Application Notes. 2016. Available online: https://www.bareconductive.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/ElectricPaint_ApplicationNotes.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Atalay, O.; Kennon, W.R.; Husain, D.M. Textile-based weft knitted sensors: Effect of fabric parameters on sensor properties. Sensors 2013, 13, 11114–11127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimpel, S.; Mohring, U.; Muller, H.; Neudeck, A.; Scheibner, W. Textile-based electronic substrate technology. J. Ind. Text. 2004, 33, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, J.; Hussain, T.; Maqsood, M. Modeling the mechanical and compression properties of polyamide/elastane knitted fabrics used in compression sportswear. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, J. Comparison of Stretch and Recovery Properties of Polyester and Polyamide Knitted Fabrics for Compression Sportswear. In Proceedings of the Fiber Society 2016 Fall Meeting and Technical Conference, Ithaca, New York, NY, USA, 10–12 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Move to Learn Innovation Lab – Conductive Paint Stretch Sensor DIY Manual. Available online: https://cpb-us-w2.wpmucdn.com/sites.udel.edu/dist/a/3635/files/2015/07/Stretch-Sensor-DIY-Manual.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).

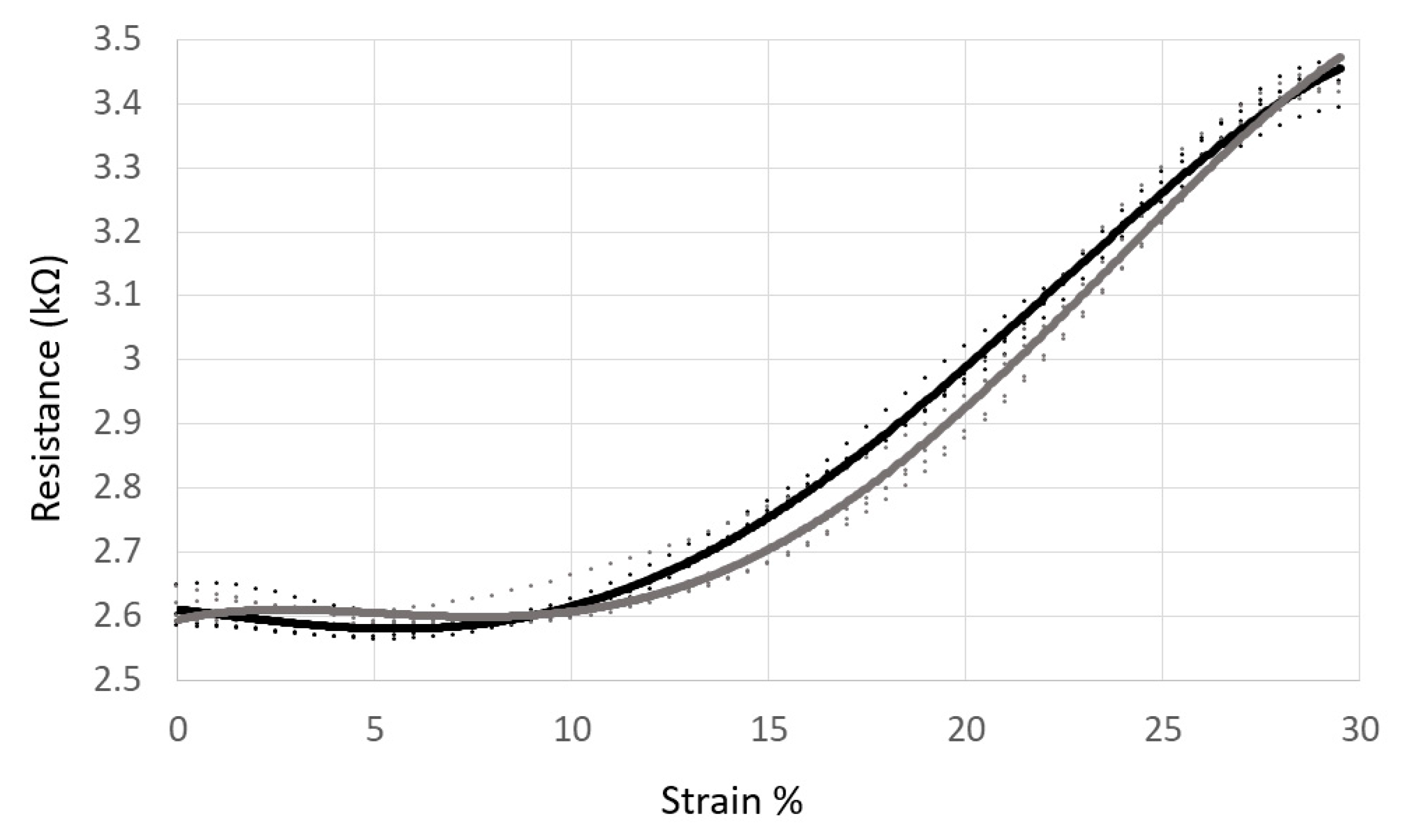
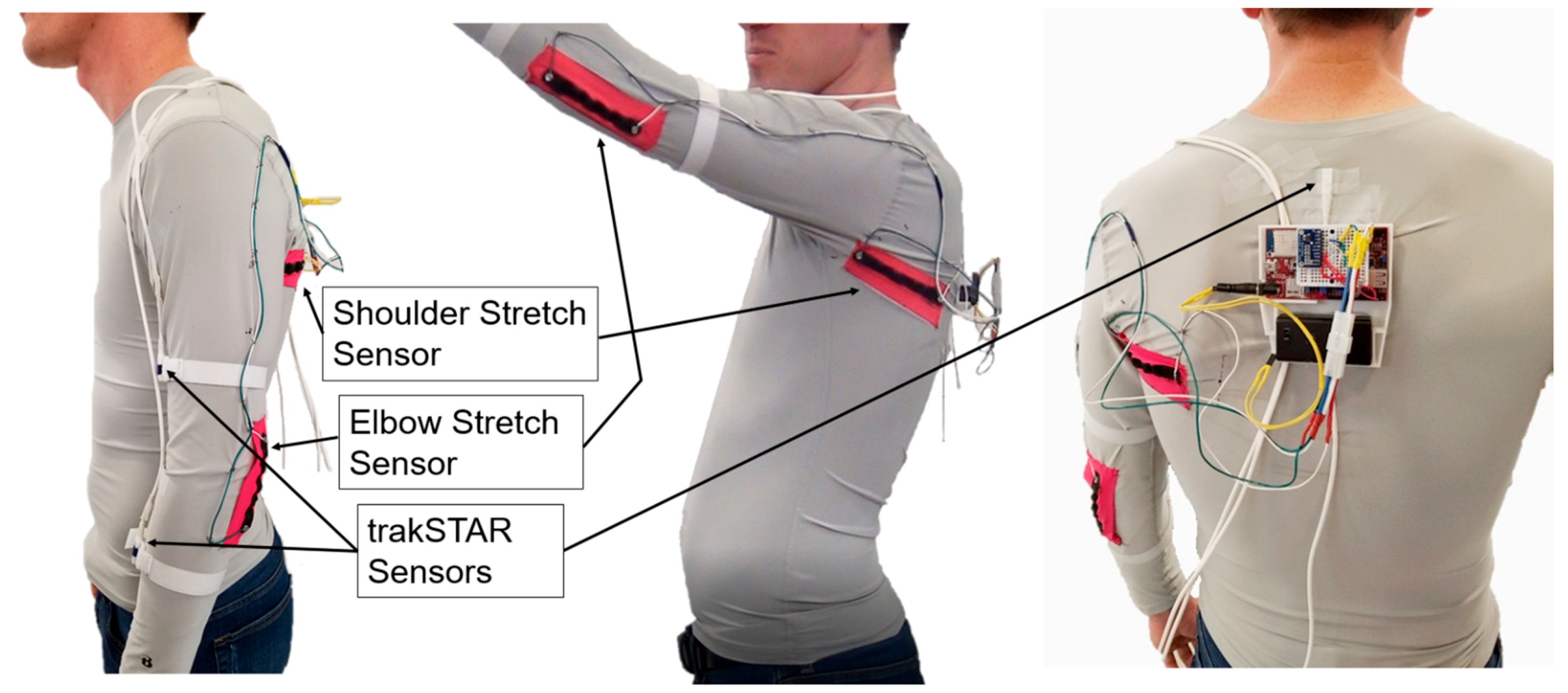
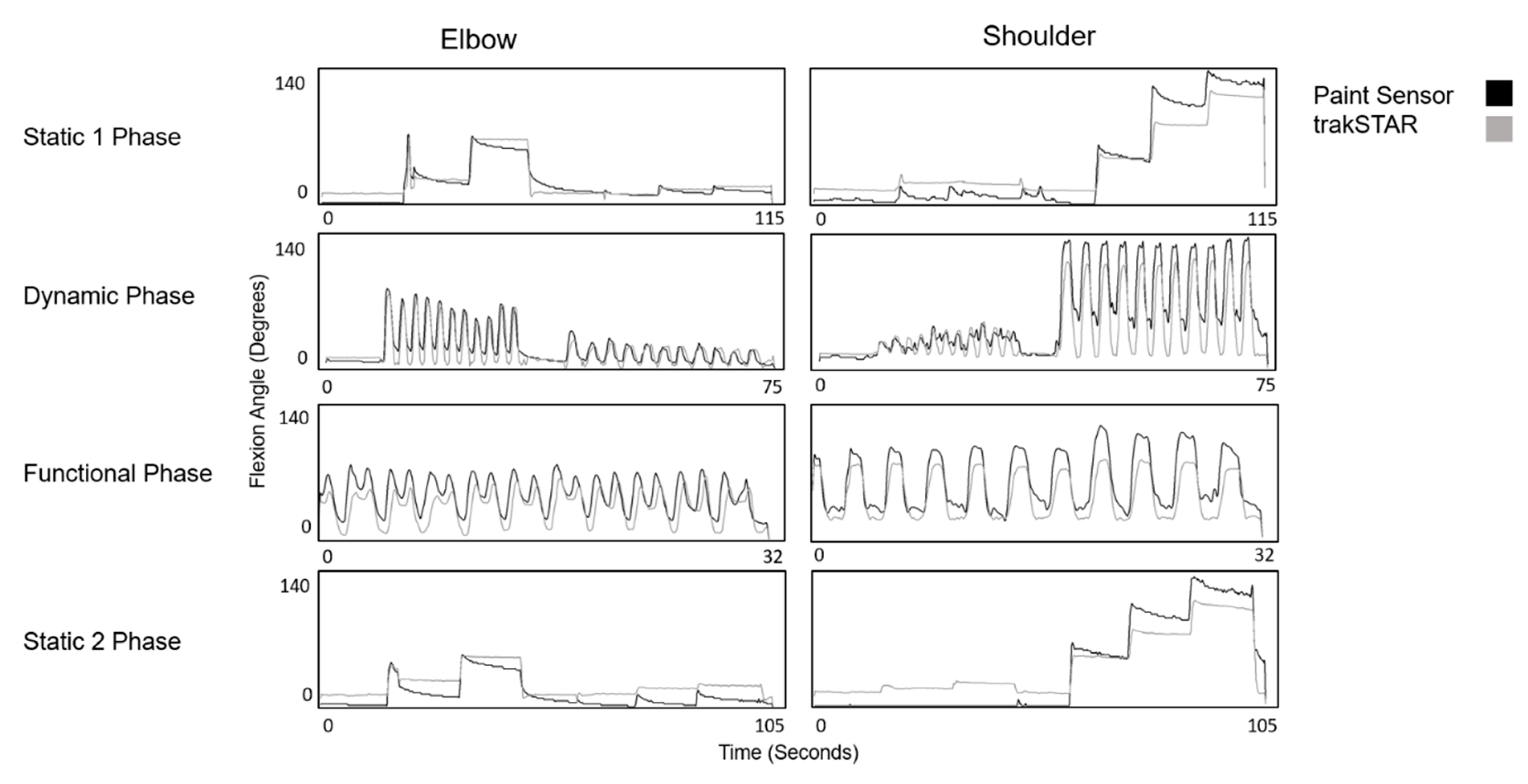
| A | Average Absolute Error | Static 1 | Dynamic | Functional | Static 2 | ||||
| Elbow | Shoulder | Elbow | Shoulder | Elbow | Shoulder | Elbow | Shoulder | ||
| Participant 1 | 10.85 | 13.12 | 15.16 | 31.98 | 29.68 | 24.11 | 17.14 | 16.62 | |
| Participant 2 | 6.69 | 9.26 | 18.75 | 22.94 | 9.73 | 36.54 | 17.83 | 14.36 | |
| Participant Average | 8.77 | 11.19 | 16.96 | 27.46 | 19.71 | 30.33 | 17.49 | 15.49 | |
| Total Average | 9.98 | 22.21 | 25.02 | 16.49 | |||||
| B | Average Absolute Error | Trial 1 | Trial 2 | Trial 3 |
| Participant 1 | 12.63 | 14.80 | 23.21 | |
| Participant 2 | 10.45 | 12.46 | 19.76 | |
| Total Average | 11.54 | 13.63 | 21.49 |
| C | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient | Dynamic | Functional | ||
| Elbow | Shoulder | Elbow | Shoulder | ||
| Participant 1 | 0.949 | 0.960 | 0.800 | 0.933 | |
| Participant 2 | 0.847 | 0.892 | 0.749 | 0.901 | |
| Participant Average | 0.898 | 0.926 | 0.775 | 0.917 | |
| Total Average | 0.912 | 0.846 | |||
| D | Activity Counts | Dynamic | Functional | ||
| Elbow | Shoulder | Elbow | Shoulder | ||
| Participant 1 | 96.97 | 81.08 | 87.10 | 75.00 | |
| Participant 2 | 98.42 | 69.57 | 61.29 | 77.78 | |
| Participant Average | 97.70 | 75.33 | 74.20 | 76.39 | |
| Total Average | 79.39 | 75.00 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greenspan, B.; Lobo, M.A. Design and Initial Testing of an Affordable and Accessible Smart Compression Garment to Measure Physical Activity Using Conductive Paint Stretch Sensors. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2020, 4, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti4030045
Greenspan B, Lobo MA. Design and Initial Testing of an Affordable and Accessible Smart Compression Garment to Measure Physical Activity Using Conductive Paint Stretch Sensors. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2020; 4(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti4030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreenspan, Ben, and Michele A. Lobo. 2020. "Design and Initial Testing of an Affordable and Accessible Smart Compression Garment to Measure Physical Activity Using Conductive Paint Stretch Sensors" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 4, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti4030045
APA StyleGreenspan, B., & Lobo, M. A. (2020). Design and Initial Testing of an Affordable and Accessible Smart Compression Garment to Measure Physical Activity Using Conductive Paint Stretch Sensors. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 4(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti4030045






