Optical Rules to Mitigate the Parallax-Related Registration Error in See-Through Head-Mounted Displays for the Guidance of Manual Tasks
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Vergence-Accommodation Conflict (VAC) and Focal Rivalry (FR)
1.2. Depth Perception Issues
1.3. Spatial Perception Issues
1.4. The “Holy Grail” of Light Field Displays
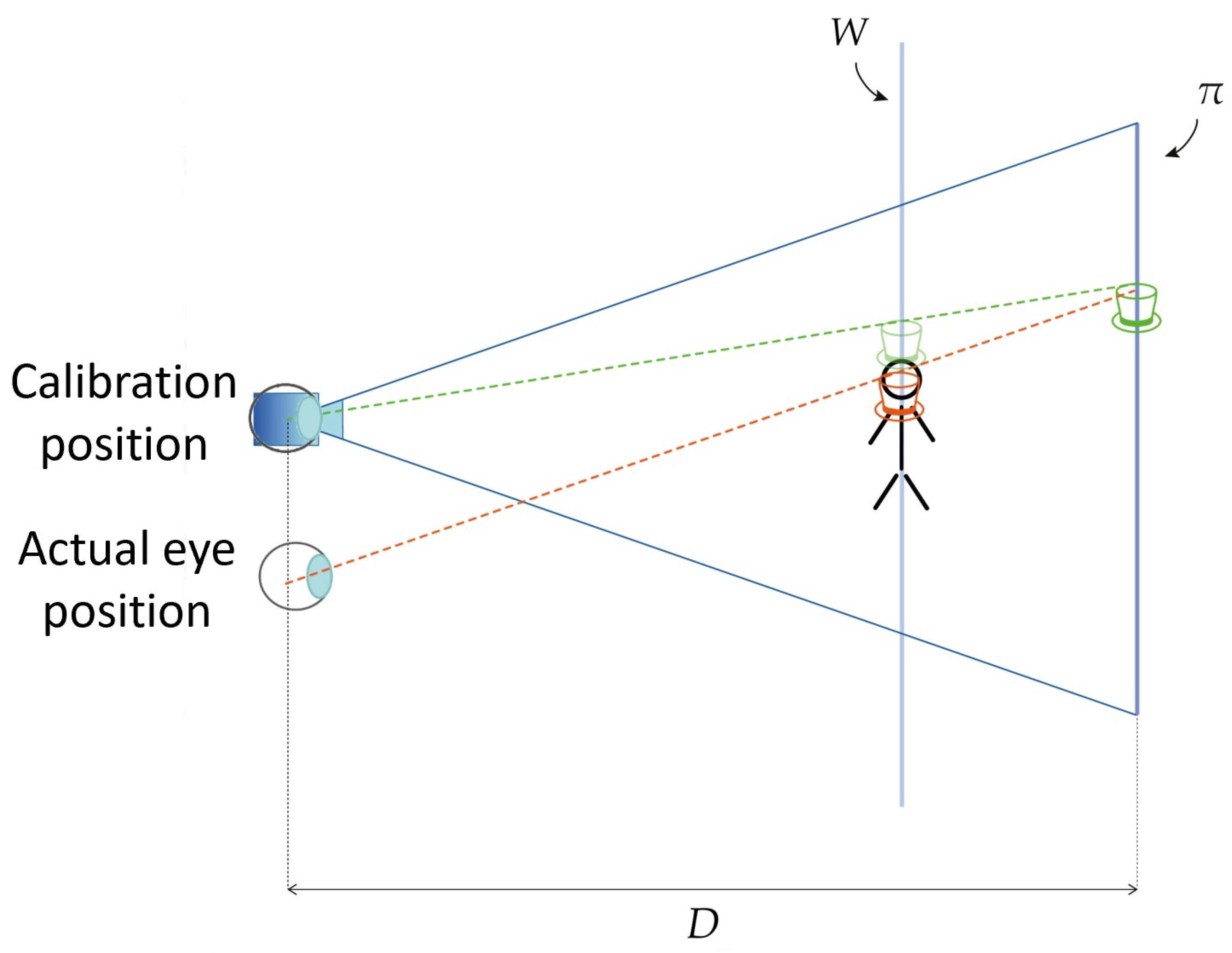
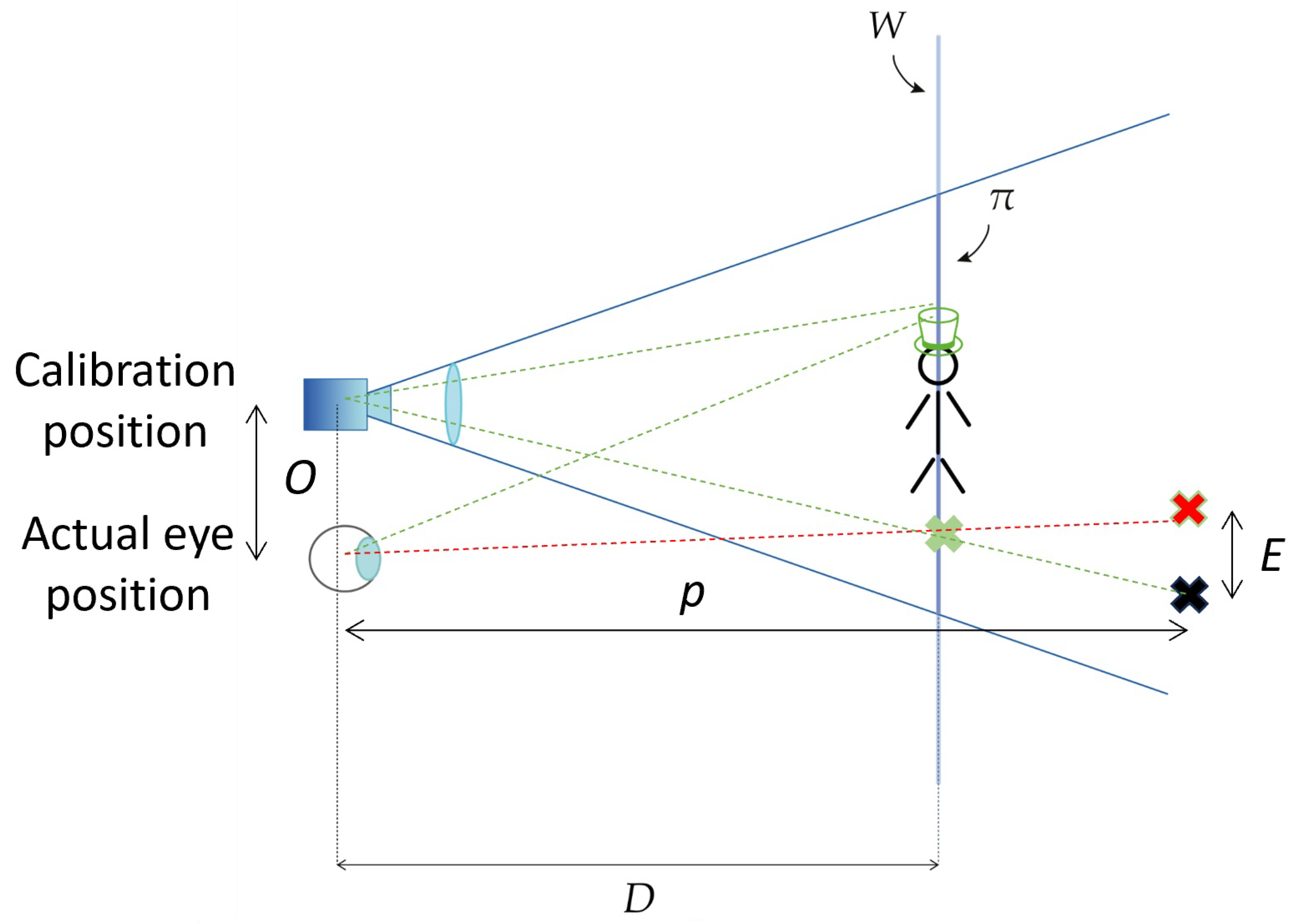
2. Appropriate Setting of the Display Focus Plane Distance
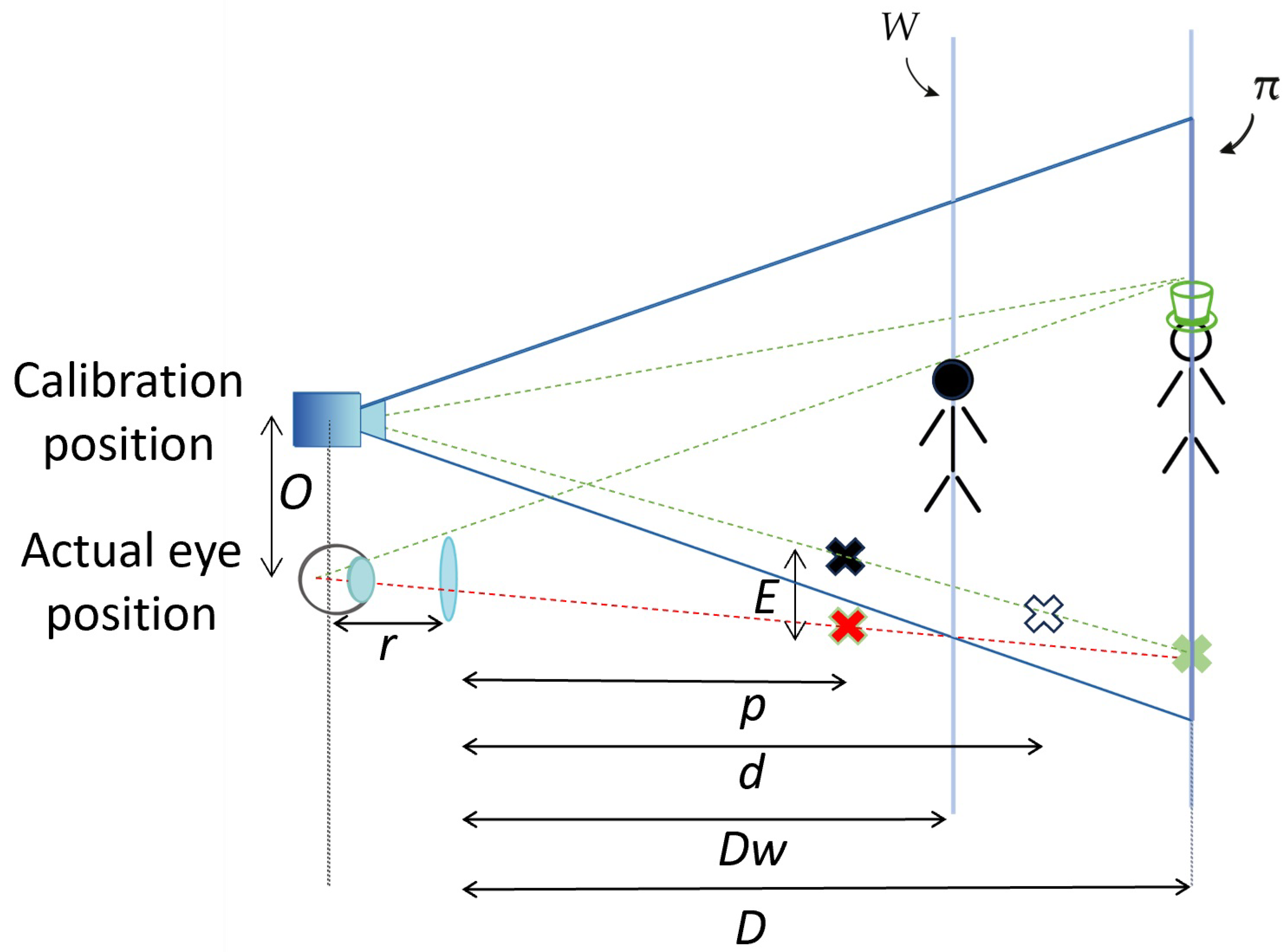
3. Additional Optics in Front of the OST Display
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| HMD | Head Mounted Display |
| OST | Optical See Through |
| VST | Video See Through |
References
- Abraham, M.; Annunziata, M. Augmented reality is already improving worker performance. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2017, 13, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khakurel, J.; Melkas, H.; Porras, J. Tapping into the wearable device revolution in the work environment: A systematic review. Inf. Technol. People 2018, 31, 791–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Owen, C.; Biocca, F.; Mou, W. Performance Evaluation of Augmented Reality for Directed Assembly. In Virtual and Augmented Reality Applications in Manufacturing; Ong, S.K., Nee, A.Y.C., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2004; pp. 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Ding, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Ling, Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, R. Designing a wearable navigation system for image-guided cancer resection surgery. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muensterer, O.J.; Lacher, M.; Zoeller, C.; Bronstein, M.; Kübler, J. Google Glass in pediatric surgery: An exploratory study. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Cutolo, F.; Condino, S.; Cercenelli, L.; D’Amato, R.; Badiali, G.; Ferrari, V. Architecture of a Hybrid Video/Optical See-through Head-Mounted Display-Based Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation Platform. Information 2022, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Ni, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, C.; Hou, Q.; Hou, W.; Luo, G.; et al. Design and manufacture AR head-mounted displays: A review and outlook. Light. Adv. Manuf. 2021, 2, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, J.P.; Cakmakci, O. The past, present, and future of head-mounted display designs. In Optical Design and Testing II; Wang, Y., Weng, Z., Ye, S., Sasian, J.M., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5638, pp. 368–377. [Google Scholar]
- Holliman, N.S.; Dodgson, N.A.; Favalora, G.E.; Lachlan, P. Three-Dimensional Displays: A Review and Applications Analysis. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2011, 57, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Duan, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Q.; Yang, T.; Hou, W.; Wang, D.; et al. Freeform OST-HMD system with large exit pupil diameter and vision correction capability. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlo, M.; Edwards, P.E.; Clarkson, M.; Stoyanov, D. Utility of optical see-through head mounted displays in augmented reality-assisted surgery: A systematic review. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 77, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, M.; Ghugre, N.R.; Wright, G.A. Augmenting performance: A systematic review of optical see-through head-mounted displays in surgery. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insight into vergence-accommodation mismatch. Proc. SPIE. 2013, 5, 8735.
- Kramida, G. Resolving the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict in Head-Mounted Displays. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016, 22, 1912–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condino, S.; Carbone, M.; Piazza, R.; Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V. Perceptual Limits of Optical See-Through Visors for Augmented Reality Guidance of Manual Tasks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, C. Information Visualization: Perception for Design; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sielhorst, T.; Feuerstein, M.; Navab, N. Advanced Medical Displays: A Literature Review of Augmented Reality. J. Disp. Technol. 2008, 4, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, S.J.; Akeley, K.; Ernst, M.O.; Banks, M.S. Focus cues affect perceived depth. J. Vis. 2005, 5, 834–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condino, S.; Turini, G.; Parchi, P.D.; Viglialoro, R.M.; Piolanti, N.; Gesi, M.; Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V. How to Build a Patient-Specific Hybrid Simulator for Orthopaedic Open Surgery: Benefits and Limits of Mixed-Reality Using the Microsoft HoloLens. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5435097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubert, J.; Itoh, Y.; Moser, K.; Swan, J.E. A Survey of Calibration Methods for Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Displays. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 24, 2649–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plopski, A.; Itoh, Y.; Nitschke, C.; Kiyokawa, K.; Klinker, G.; Takemura, H. Corneal-Imaging Calibration for Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Displays. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2015, 21, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Klinker, G. Performance and sensitivity analysis of INDICA: INteraction-Free DIsplay CAlibration for Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Displays. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Munich, Germany, 10–12 September 2014; pp. 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Klinker, G. Interaction-free calibration for optical see-through head-mounted displays based on 3D Eye localization. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces (3DUI), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 29–30 March 2014; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levoy, M. Light Fields and Computational Imaging. Computer 2006, 39, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hua, H. Systematic characterization and optimization of 3D light field displays. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 18508–18525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Javidi, B. A 3D integral imaging optical see-through head-mounted display. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 13484–13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, V.; Calabrò, E.M. Wearable light field optical see-through display to avoid user dependent calibrations: A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2016 SAI Computing Conference (SAI), London, UK, 13–15 July 2016; pp. 1211–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa, K.; Billinghurst, M.; Campbell, B.; Woods, E. An occlusion capable optical see-through head mount display for supporting co-located collaboration. In Proceedings of the Second IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Tokyo, Japan, 10 October 2003; pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Maimone, A.; Fuchs, H. Computational augmented reality eyeglasses. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Adelaide, Australia, 1–4 October 2013; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, T.; Xiong, J.; Zou, J.; Wu, S.T. Multifocal displays: Review and prospect. PhotoniX 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wann, J.P.; Rushton, S.; Mon-Williams, M. Natural problems for stereoscopic depth perception in virtual environments. Vis. Res. 1995, 35, 2731–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutolo, F.; Cattari, N.; Fontana, U.; Ferrari, V. Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Displays With Short Focal Distance: Conditions for Mitigating Parallax-Related Registration Error. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 572001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, M.; Seebacher, F.; Hoppe, H. High accuracy pixel-wise spatial calibration of optical see-through glasses. Comput. Graph. 2017, 64, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condino, S.; Cutolo, F.; Zari, G.; D’Amato, R.; Carbone, M.; Vincenzo, F. How to Mitigate Perceptual Limits of OST Display for Guiding Manual Tasks: A Proof of Concept Study with Microsoft HoloLens. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Metrology for Extended Reality, Artificial Intelligence and Neural Engineering (MetroXRAINE), Rome, Italy, 26–28 October 2022; pp. 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Depth-of-Focus of the Human Eye: Theory and Clinical Implications. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2006, 51, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.C. Optical Architectures for Augmented-, Virtual-, and Mixed-Reality Headsets; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, V.; Cattari, N.; Fontana, U.; Cutolo, F. Parallax Free Registration for Augmented Reality Optical See-Through Displays in the Peripersonal Space. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Display with an Appropriate Focus Plane Distance | Additional Optics in Front of the Display | |
|---|---|---|
| Parallax-related registration error | Avoided at the optimal design working distance, significantly mitigated in the surrounding area (Equation (1)) | Avoided at the optimal design working distance, significantly mitigated in the surrounding area (Equation (7)) |
| Focus rivalry | Avoided in a useful working distance range (Equations (2) and (3)) | Avoided in a useful working distance range |
| Vergence-accommodation conflict | Avoided in a useful working distance range (Equations (2) and (3)) | Can be an issue |
| Wave guide display with infinite focal plane | Not feasible | Feasible |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari, V.; Cattari, N.; Condino, S.; Cutolo, F. Optical Rules to Mitigate the Parallax-Related Registration Error in See-Through Head-Mounted Displays for the Guidance of Manual Tasks. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2024, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti8010004
Ferrari V, Cattari N, Condino S, Cutolo F. Optical Rules to Mitigate the Parallax-Related Registration Error in See-Through Head-Mounted Displays for the Guidance of Manual Tasks. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2024; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari, Vincenzo, Nadia Cattari, Sara Condino, and Fabrizio Cutolo. 2024. "Optical Rules to Mitigate the Parallax-Related Registration Error in See-Through Head-Mounted Displays for the Guidance of Manual Tasks" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti8010004
APA StyleFerrari, V., Cattari, N., Condino, S., & Cutolo, F. (2024). Optical Rules to Mitigate the Parallax-Related Registration Error in See-Through Head-Mounted Displays for the Guidance of Manual Tasks. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti8010004









