A Practical Approach to Screening for Strongyloides stercoralis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Techniques and Diagnostic Challenges
3. Strongyloidiasis and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Reason for the Increase in Awareness
4. Screening Algorithm for Strongyloidiasis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buonfrate, D.; Bisanzio, D.; Giorli, G.; Odermatt, P.; Fürst, T.; Greenaway, C.; French, M.; Reithinger, R.; Gobbi, F.; Montresor, A.; et al. The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, G.V.; Welch, E.; Bailey, J.W.; Bell, D.R.; Beeching, N.J. Chronic Strongyloides stercoralis infection in former British Far East prisoners of war. QJM 2004, 97, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gétaz, L.; Castro, R.; Zamora, P.; Kramer, M.; Gareca, N.; Torrico-Espinoza, M.D.C.; Macias, J.; Lisarazu-Velásquez, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Valencia-Rivero, C.; et al. Epidemiology of Strongyloides stercoralis infection in Bolivian patients at high risk of complications. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chankongsin, S.; Wampfler, R.; Ruf, M.-T.; Odermatt, P.; Marti, H.; Nickel, B.; Keoluangkhot, V.; Neumayr, A. Strongyloides stercoralis prevalence and diagnostics in Vientiane. Lao People’s Democr. Republic. Infect Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.L.; Piraisoody, N.; Kramme, S.; Marti, H.; Silué, K.D.; Panning, M.; Nickel, B.; Kern, W.V.; Herrmann, M.; Hatz, C.F.; et al. Real-time PCR for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in human stool samples from Côte d’Ivoire: Diagnostic accuracy, inter-laboratory comparison and patterns of hookworm co-infection. Acta Trop. 2015, 150, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnino, L.; Schwob, J.-M.; Neofytos, D.; Lazo-Porras, M.; Chappuis, F.; Eperon, G. Screening for Parasitic Infection and Tuberculosis in Immunosuppressed and Pre-Immunosuppressed Patients: An Observational Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, J.; Gomez-Junyent, J.; Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Zammarchi, L.; Requena-Méndez, A. Evidence-Based Guidelines for Screening and Management of Strongyloidiasis in Non-Endemic Countries. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 645–652. [Google Scholar]
- Lier, A.J.; Tuan, J.J.; Davis, M.W.; Paulson, N.; McManus, D.; Campbell, S.; Peaper, D.R.; Topal, J.E. Case Report: Disseminated Strongyloidiasis in a Patient with COVID-19. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1590–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, V.; Crosato, V.; Gulletta, M.; Castelnuovo, F.; Cristini, G.; Matteelli, A.; Castelli, F. Strongyloides infection manifested during immunosuppressive therapy for SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. Infection 2021, 49, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wilton, A.; Nabarro, L.E.; Godbole, G.S.; Chiodini, P.L.; Boyd, A.; Woods, K. Risk of Strongyloides Hyperinfection Syndrome when prescribing dexamethasone in severe COVID-19. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggild, A.; Libman, M.; Greenaway, C.; McCarthy, A. CATMAT statement on disseminated strongyloidiasis: Prevention, assessment and management guidelines. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2016, 42, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, W.M.; Alpern, J.D.; Walker, P.F. COVID-19 and Dexamethasone: A Potential Strategy to Avoid Steroid-Related Strongyloides Hyperinfection. JAMA 2020, 324, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkati, S.; Greenaway, C.; Libman, M.D. Strongyloidiasis in immunocompromised migrants to non-endemic countries in the era of COVID-19: What is the role for presumptive ivermectin? J. Travel Med. 2021, taab155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohareb, A.M.; Rosenberg, J.M.; Bhattacharyya, R.P.; Kotton, C.N.; Chu, J.T.; Jilg, N.; Hysell, K.M.; Albin, J.S.; Sen, P.; Bloom, S.M.; et al. Preventing Infectious Complications of Immunomodulation in COVID-19 in Foreign-Born Patients. J. Immigr. Minor Health 2021, 23, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.L.S.; Inês, E.d.J.; Souza, A.B.d.S.; Dias, V.M.d.S.; Guimarães, C.M.; Menezes, E.R.; Barbosa, L.G.; Del Carmen, M.M.A.; Teixeira, M.C.A.; Soares, N.M. Association between Strongyloides stercoralis infection and cortisol secretion in alcoholic patients. Acta Trop. 2016, 154, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eperon, G.; Bühler, S.; Enriquez, N.; Vaudaux, B. The immunosuppressed traveler : Vaccination guidelines. Rev. Med. Suisse 2018, 14, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luvira, V.; Trakulhun, K.; Mungthin, M.; Naaglor, T.; Chantawat, N.; Pakdee, W.; Phiboonbanakit, D.; Dekumyoy, P. Comparative Diagnosis of Strongyloidiasis in Immunocompromised Patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bon, B.; Houze, S.; Talabani, H.; Magne, D.; Belkadi, G.; Develoux, M.; Senghor, Y.; Chandenier, J.; Ancelle, T.; Hennequin, C. Evaluation of a Rapid Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Diagnosis of Strongyloidiasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1716–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buonfrate, D.; Salas-Coronas, J.; Muñoz, J.; Maruri, B.T.; Rodari, P.; Castelli, F.; Zammarchi, L.; Bianchi, L.; Gobbi, F.; Cabezas-Fernández, T.; et al. Multiple-dose versus single-dose ivermectin for Strongyloides stercoralis infection (Strong Treat 1 to 4): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled superiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. A Parasitic Infection That Can Turn Fatal with Administration of Corticosteroids. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/17-12-2020-a-parasitic-infection-that-can-turn-fatal-with-administration-of-corticosteroids (accessed on 28 September 2021).
 Strongyloidiasis prevalence: high-endemic countries > 5%, low-endemic countries > 0.1% and ≤5%, very low-endemic countries ≤ 0.1% (modified from Buonfrate et al., The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection, Pathogens 2020). * Italy, southern Spain, Australian Aboriginal communities, Southern USA and Japan. Consider a lower cutoff in the case of immunosuppression.
Strongyloidiasis prevalence: high-endemic countries > 5%, low-endemic countries > 0.1% and ≤5%, very low-endemic countries ≤ 0.1% (modified from Buonfrate et al., The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection, Pathogens 2020). * Italy, southern Spain, Australian Aboriginal communities, Southern USA and Japan. Consider a lower cutoff in the case of immunosuppression.
 Strongyloidiasis prevalence: high-endemic countries > 5%, low-endemic countries > 0.1% and ≤5%, very low-endemic countries ≤ 0.1% (modified from Buonfrate et al., The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection, Pathogens 2020). * Italy, southern Spain, Australian Aboriginal communities, Southern USA and Japan. Consider a lower cutoff in the case of immunosuppression.
Strongyloidiasis prevalence: high-endemic countries > 5%, low-endemic countries > 0.1% and ≤5%, very low-endemic countries ≤ 0.1% (modified from Buonfrate et al., The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection, Pathogens 2020). * Italy, southern Spain, Australian Aboriginal communities, Southern USA and Japan. Consider a lower cutoff in the case of immunosuppression.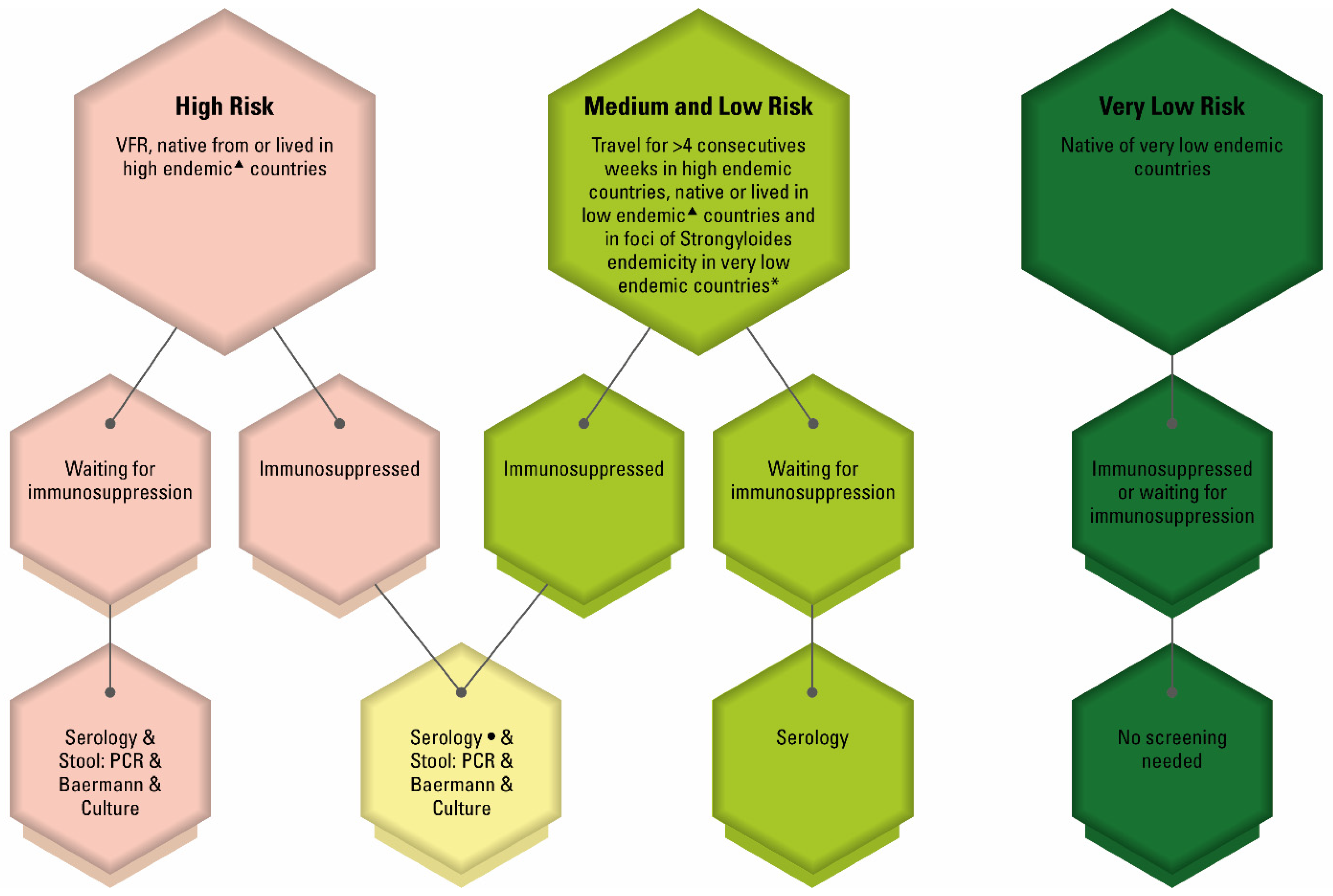

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carnino, L.; Schwob, J.-M.; Gétaz, L.; Nickel, B.; Neumayr, A.; Eperon, G. A Practical Approach to Screening for Strongyloides stercoralis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040203
Carnino L, Schwob J-M, Gétaz L, Nickel B, Neumayr A, Eperon G. A Practical Approach to Screening for Strongyloides stercoralis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2021; 6(4):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040203
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarnino, Luisa, Jean-Marc Schwob, Laurent Gétaz, Beatrice Nickel, Andreas Neumayr, and Gilles Eperon. 2021. "A Practical Approach to Screening for Strongyloides stercoralis" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 6, no. 4: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040203
APA StyleCarnino, L., Schwob, J. -M., Gétaz, L., Nickel, B., Neumayr, A., & Eperon, G. (2021). A Practical Approach to Screening for Strongyloides stercoralis. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 6(4), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6040203






