Burden and Epidemiology of Human Intestinal Giardia duodenalis Infection in Colombia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Selection of Studies
2.4. Data Extraction and Analysis
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
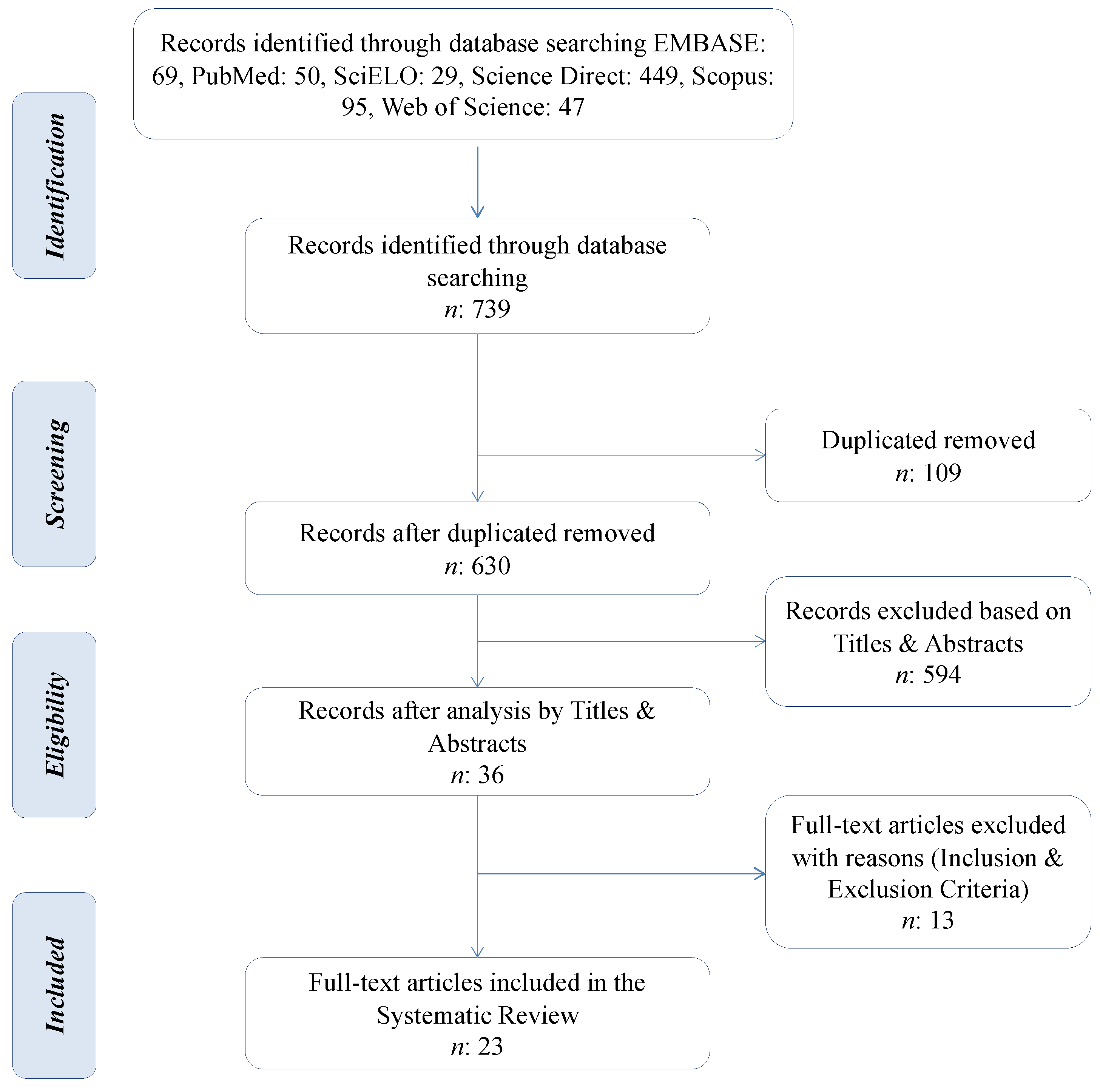
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Molecular Characteristics of the Selected Studies
3.4. Reported Prevalence of Giardiasis
4. Discussion
4.1. Epidemiology of Giardia in Colombia
4.2. Microscopic vs Molecular Methods
4.3. Burden and Perspective to Colombia
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morrison, H.G.; McArthur, A.G.; Gillin, F.D.; Aley, S.B.; Adam, R.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Best, A.A.; Cande, W.Z.; Chen, F.; Cipriano, M.J.; et al. Genomic minimalism in the early diverging intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia. Science 2007, 317, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Einarsson, E.; Ma’ayeh, S.; Svärd, S.G. An up-date on Giardia and giardiasis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muadica, A.S.; Balasegaram, S.; Beebeejaun, K.; Köster, P.C.; Bailo, B.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; Dashti, A.; Dacal, E.; Saugar, J.M.; Fuentes, I.; et al. Risk associations for intestinal parasites in symptomatic and asymptomatic schoolchildren in central Mozambique. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Hopkins, R.M.; Homan, W.L. Nomenclature and genetic groupings of Giardia infecting mammals. Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Ash, A. Molecular epidemiology of Giardia and Cryptosporidium infections. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 40, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Ash, A. Molecular epidemiology of Giardia and Cryptosporidium infections—What’s new? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.D. Giardia duodenalis: Biology and Pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0002419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muadica, A.S.; Köster, P.C.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; Reh, L.; Balasegaram, S.; Verlander, N.Q.; Ruiz Chércoles, E.; Carmena, D. Molecular diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in asymptomatic school children in Leganés, Madrid (Spain). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dacal, E.; Saugar, J.M.; de Lucio, A.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; Robinson, E.; Köster, P.C.; Aznar-Ruiz-de-Alegría, M.L.; Espasa, M.; Ninda, A.; Gandasegui, J.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Strongyloides stercoralis, Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis spp. isolates in school children in Cubal, Western Angola. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniels, M.E.; Shrivastava, A.; Smith, W.A.; Sahu, P.; Odagiri, M.; Misra, P.R.; Panigrahi, P.; Suar, M.; Clasen, T.; Jenkins, M.W. Cryptosporidium and Giardia in humans, domestic animals, and village water sources in rural India. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. Giardia duodenalis infections in humans and other animals in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zahedi, A.; Field, D.; Ryan, U. Molecular typing of Giardia duodenalis in humans in Queensland—First report of assemblage E. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipiková, J.; Papajová, I.; Majláthová, V.; Šoltys, J.; Bystrianska, J.; Schusterová, I.; Vargová, V. First report on Giardia duodenalis assemblage F in Slovakian children living in poor environmental conditions. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Certad, G.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabé, M.; Cacciò, S.M. Pathogenic mechanisms of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buret, A.G.; Cacciò, S.M.; Favennec, L.; Svärd, S. Update on Giardia: Highlights from the seventh International Giardia and Cryptosporidium Conference. Parasite 2020, 27, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Zoonotic potential and molecular epidemiology of Giardia species and giardiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 110–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savioli, L.; Smith, H.; Thompson, A. Giardia and Cryptosporidium join the ‘Neglected Diseases Initiative’. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Muñoz, N.F.; Vásquez-Arteaga, L.R.; González-Fernández, D.; Marín-Agudelo, N.D.; González-Cuellar, F.E.; Montero-Carvajal, J.B.; Palechor-García, M.E. Situation of intestinal parasitism in preschools of a state child’s home in Popayan, Colombia. Med. Lab. 2017, 23, 573–584. Available online: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/medlab/myl-2017/myl1711-12e.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Merchán Garzón, M.C.; Ordóñez Vásquez, A.; Bernal Villegas, J.; Suárez Obando, F. Estimación de la frecuencia de infección por Giardia intestinalis en comunidades indígenas y afros de Colombia: Estudio de corte trasversal. Medicina 2016, 38, 10–24. Available online: https://revistamedicina.net/ojsanm/index.php/Medicina/article/view/112-2 (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Gaviria, A.; Davila, C.; Ruiz, F.; Burgos, G. Informe al Congreso de la República 2015-2016: Sector administrativo de salud y protección social. Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social 2016, 1–208. Available online: https://www.minsalud.gov.co/sites/rid/Lists/BibliotecaDigital/RIDE/DE/PES/informe-congreso-2016-2017.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Arrivillaga, M. Assesing Health Services in Colombia: Development of a Conceptual Framework and Measurement tools based on primary data. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 21582440211016844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.; Zambrano, A.; Vélez, M.; Ramírez Gómez, M. Health insurance as a strategy for access: Streamlined facts of the Colombian Health Care Reform. Universidad del Rosario 2007, 1–25. Available online: https://repository.urosario.edu.co/bitstream/handle/10336/11016/2783.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Tovar-Cuevas, L.M.; Arrivillaga-Quintero, M. State of the art in access to health services research in Colombia, 2000–2013: A systematic review. Rev. Gerencia y Politicas de Salud 2014, 12–27. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A451311732/IFME?u=anon~6efa8475&sid=googleScholar&xid=e4597b51 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Rodríguez-Morales, A.J.; Granados-Álvarez, S.; Escudero-Quintero, H.; Vera-Polania, F.; Mondragon-Cardona, A.; Díaz-Quijano, F.A.; Sosa-Valencia, L.; Lozada-Riascos, C.O.; Escobedo, A.A.; Liseth, O.; et al. Estimating and mapping the incidence of giardiasis in Colombia, 2009–2013. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 49, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bedoya-Arias, H.A.; Cortés-Puentes, P.A.; Ramírez-Echeverri, M.; Montenegro-Jurado, H.S.; Hernández-Vanegas, N.; Zapata-Orozco, J.M.; Cardona-Ospina, J.A.; Escobedo, A.A.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. Estimating the burden of disease and the economic costs attributable to giardiasis in Colombia, 2009–2016. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 73, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.R.; Sultana, M.; Mahumud, R.A.; Ali, N.; Huda, T.M.; Salim Uzzaman, M.; Haider, S.; Rahman, H.; Islam, Z.; Khan, J.; et al. Economic costs of hospitalized diarrheal disease in Bangladesh: A societal perspective. Glob. Health Res. Policy. 2018, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, C.; Ashton, J.J.; Borca, F.; Cullen, M.; Walker, D.M.; Beattie, R.M. Children and young people with inflammatory bowel disease attend less school than their healthy Peers. Arch. Dis. Child. 2020, 105, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topal, F.; Camyar, H.; Saritas Yuksel, E.; Gunay, S.; Topal, F.; Gür, E.Ö. Work productivity loss in inflammatory bowel disease patients in Turkey. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 6979720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, S.J.; Nery, S.V.; D’Este, C.A.; Gray, D.J.; McCarthy, J.S.; Traub, R.J.; Andrews, R.M.; Llewellyn, S.; Vallely, A.J.; Williams, G.M.; et al. Water, sanitation and hygiene related risk factors for soil-transmitted helminth and Giardia duodenalis infections in rural communities in Timor-Leste. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, H.; Sharafi, S.M.; Yousefi, H.; Hadipur, M.; Sepahvand, A.; Darani, H.Y. Diagnosis of Giardia duodenalis infection using dot blot in comparison with microscopy. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets. 2016, 16, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourabi, M.; Boughattas, S.; Abdallah, A.M.; Ismail, A.; Behnke, J.M.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Abu-Madi, M. Genetic Diversity and Prevalence of Giardia duodenalis in Qatar. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 652946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzosa, M.; Graham, J.P.; Salinas, L.; Trueba, G. Potential zoonotic transmission of Giardia duodenalis in semi-rural communities near Quito, Ecuador. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2018, 16, 1–6. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/0ch002dz (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Hooshyar, H.; Rostamkhani, P.; Arbabi, M.; Delavari, M. Giardia lamblia infection: Review of current diagnostic strategies. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed. Bench. 2019, 12, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duque, S.; Arévalo, A.; Nicholls, R.S. La Parasitología en Colombia: Una visión panorámica. Biomedica 2021, 41, 5–7. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0120-41572021000500005 (accessed on 20 September 2022). [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munn, Z.; Moola, S.; Lisy, K.; Riitano, D.; Tufanaru, C. Methodological guidance for systematic reviews of observational epidemiological studies reporting prevalence and cumulative incidence data. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.A.; Guzmán, G.E.; Lora-Suárez, F.M.; Torres, E.; Gómez, J.E. Prevalencia de protozoos intestinales en 79 niños de 2 a 5 años de edad de un hogar infantil estatal en Circasia, Quindío. Infectio 2010, 14, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeke, C.E.; Mora-Plazas, M.; Forero, Y.; Villamor, E. Intestinal protozoan infections in relation to nutritional status and gastrointestinal morbidity in Colombian school children. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2010, 56, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Londoño Alvarez, J.C.; Hernández, A.P.; Vergara Sánchez, C. Parasitismo intestinal en hogares comunitarios de dos municipios del departamento del Atlántico, norte de Colombia. Bol. Malariol. Salud Ambient. 2010, 50, 251–260. Available online: http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1690-46482010000200009&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Arroyo-Salgado, B.; Buelvas-Montes, Y.; Villalba-Vizcaíno, V.; Salomón-Arzuza, O. Caracterización genética por reacción en cadena de la polimerasa de Giardia intestinalis en muestras de humanos y perros del Caribe colombiano. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2014, 32, 424–427. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=6147153 (accessed on 29 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, V.; Espinosa, O.; Carranza, J.C.; Duque, S.; Arévalo, A.; Clavijo, J.A.; Urrea, D.A.; Vallejo, G.A. Genotipos de Giardia duodenalis en muestras de niños de las guarderías del Instituto Colombiano de Bienestar Familiar y de perros en Ibagué, Colombia. Biomedica 2014, 34, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Muñoz, D.Y.; Gómez-Gómez, N.E.; Polanco, L.C.; Cardona- Osorio, J.A.C.; Ríos-Arias, L. Prevalencia de parasitismo intestinal en la comunidad Seminke del resguardo indígena Wiwa de la Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, 2014. Arch. de medicina 2015, 11, 6. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=5139237 (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Fillot, M.; Guzman, J.; Cantillo, L.; Gómez, L.; Sánchez Majana, L.; Acosta, B.M.; Sarmiento-Rubiano, L.A. Prevalencia de parásitos intestinales en niños del Área Metropolitana de Barranquilla, Colombia. Rev. Cubana Med. Trop. 2015, 67. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0375-07602015000300002&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Ramírez, J.D.; Heredia, R.D.; Hernández, C.; León, C.M.; Moncada, L.I.; Reyes, P.; Pinilla, A.E.; Lopez, M.C. Molecular diagnosis and genotype analysis of Giardia duodenalis in asymptomatic children from a rural area in central Colombia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 32, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafañe-Ferrer, L.M.; Pinilla-Pérez, M. Intestinal parasites in children and soil from Turbaco, Colombia and associated risk factors. Rev, Salud Publica (Bogota) 2016, 18, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, A.; Munoz, M.; Gómez, N.; Tabares, J.; Segura, L.; Salazar, Á.; Restrepo, C.; Ruíz, M.; Reyes, P.; Qian, Y.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Giardia, Blastocystis and Cryptosporidium among Indigenous Children from the Colombian Amazon Basin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa Aranzales, A.F.; Radon, K.; Froeschl, G.; Pinzon Rondon, A.M.; Delius, M. Prevalence and risk factors for intestinal parasitic infections in pregnant women residing in three districts of Bogotá, Colombia. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo-Ospina, B.; Fontal-Vargas, P.A.; López-Muñoz, D.F.; Beltrán-Angarita, L.; Morales-Jiménez, V.; Gómez, M.N. Prevalence of intestinal parasites in children of an invasion community in a municipality of Colombia. Int. J. Biol. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 12, 208–214. Available online: https://copei.acofaen.org.co/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Parasitos-intestinales.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Villalba-Vizcaíno, V.; Buelvas, Y.; Arroyo-Salgado, B.; Castro, L.R. Molecular identification of Giardia intestinalis in two cities of the Colombian Caribbean Coast. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 189, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avendaño, C.; Ramo, A.; Vergara-Castiblanco, C.; Bayona, M.; Velasco-Benitez, C.A.; Sánchez-Acedo, C.; Quílez, J. Occurrence and molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis in child population from Colombia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 76, 104034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Restrepo, H.; Orrego-Morales, C.; Vega-Orrego, T.; Arango-Arango, S.; Buitrago-Agudelo, D.; Maya-Betancourt, M.C.; Maya-Betancourt, V.; Restrepo-Álvarez, L.; Silva-Cáceres, N.; Suarez-Urquijo, S.; et al. Screening for intestinal parasites in adults from three different regions of Colombia. Infectio 2019, 23, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P.C.; Morales, L.; Chaparro-Olaya, J.; Sarmiento, D.; Jaramillo, J.F.; Ordoñez, G.A.; Cortés, F.; Sánchez, L.K. Intestinal parasitic infections and associated factors in children of three rural schools in Colombia. A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedraza, B.; Suarez, H.; De-la-Hoz, I.; Fragoso, P. Prevalencia de parásitos intestinales en niños de 2-5 años en hogares comunitarios de Cartagena de Indias, Colombia. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2019, 46, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villamizar, X.; Higuera, A.; Herrera, G.; Vasquez-A, L.R.; Buitron, L.; Muñoz, L.M.; Gonzalez-C, F.E.; Lopez, M.C.; Giraldo, J.C.; Ramírez, J.D. Molecular and descriptive epidemiology of intestinal protozoan parasites of children and their pets in Cauca, Colombia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higuera, A.; Villamizar, X.; Herrera, G.; Giraldo, J.C.; Vasquez-A, L.R.; Urbano, P.; Villalobos, O.; Tovar, C.; Ramírez, J.D. Molecular detection and genotyping of intestinal protozoa from different biogeographical regions of Colombia. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peña-Quistial, M.G.; Benavides-Montaño, J.A.; Duque, N.J.R.; Benavides-Montaño, G.A. Prevalence and associated risk factors of Intestinal parasites in rural high-mountain communities of the Valle del Cauca-Colombia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, S.; Hartmann, M.; Alker, J.; Hansen, J.; Dib, J.C.; Aristizabal, A.; Concha, G.; Schotte, U.; Kreienbrock, L.; Frickmann, H. Seasonal patterns of enteric pathogens in Colombian Indigenous People–A more pronounced effect on bacteria than on parasites. Pathogens 2022, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz Salas, K.; Barrios, A.P.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Macias, J.R.; Zapata, C.V. Giardia duodenalis genotyping not linked to clinical symptomatology and nutritional status of school-aged children of Soledad and Galapa municipality schools, Atlántico, Colombia. J. Parasitol. 2022, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, D.; Drews-Elger, K.; Saldarriaga-Muñoz, P.J.; Correa-Sierra, S.; Gaviria-Gallego, D.A.; Atehortúa-Salazar, S.; Valencia, N.; Cardona-Castro, M.C. Intestinal parasitosis in children from a rural Caribbean area in Colombia. Infectio 2022, 26, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-Gómez, J.M.; Lora, F.; Henao, L.H.; Mejía, S.; Gómez-Marín, J.E. Prevalencia de giardiasis y parásitos intestinales en preescolares de hogares atendidos en un programa estatal en Armenia, Colombia [Prevalence of giardiasis and intestinal parasites in pre-school children from homes being attended as part of a state programme in Armenia, Colombia]. Rev. Salud Publica (Bogota) 2005, 7, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornace, K.M.; Senyonjo, L.; Martin, D.L.; Gwyn, S.; Schmidt, E.; Agyemang, D.; Marfo, B.; Addy, J.; Mensah, E.; Solomon, A.W.; et al. Characterising spatial patterns of neglected tropical disease transmission using integrated sero-surveillance in Northern Ghana. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samie, A.; Tanih, N.F.; Seisa, I.; Seheri, M.; Mphahlele, J.; ElBakri, A.; Mbati, P. Prevalence and genetic characterization of Giardia lamblia in relation to diarrhea in Limpopo and Gauteng provinces, South Africa. Parasite Epidemiol. Control. 2020, 9, e00140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eligio-García, L.; Cortes-Campos, A.; Cota-Guajardo, S.; Gaxiola, S.; Jiménez-Cardoso, E. Frequency of Giardia intestinalis assemblages isolated from dogs and humans in a community from Culiacan, Sinaloa, Mexico using beta-giardin restriction gene. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 156, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cervantes, P.C.; Báez-Flores, M.E.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; Ponce-Macotela, M.; Nawa, Y.; De-la-Cruz-Otero, M.D.; Martínez-Gordillo, M.N.; Díaz-Camacho, S.P. Giardia duodenalis genotypes among schoolchildren and their families and pets in urban and rural areas of Sinaloa, Mexico. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebbad, M.; Ankarklev, J.; Tellez, A.; Leiva, B.; Andersson, J.O.; Svärd, S. Dominance of Giardia assemblage B in León, Nicaragua. Acta Trop. 2008, 106, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minvielle, M.C.; Molina, N.B.; Polverino, D.; Basualdo, J.A. First genotyping of Giardia lamblia from human and animal feces in Argentina, South America. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2008, 103, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez Puebla, L.E.; Núñez, F.A.; Santos, L.P.; Rivero, L.R.; Silva, I.M.; Valdés, L.A.; Millán, I.A.; Müller, N. Molecular analysis of Giardia duodenalis isolates from symptomatic and asymptomatic children from La Habana, Cuba. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2017, 2, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez Puebla, L.E.; Núñez, F.A.; García, A.B.; Rivero, L.R.; Millán, I.A.; Prado, R.C. Prevalence of Giardia duodenalis among children from a central region of Cuba: Molecular characterization and associated risk factors. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez Puebla, L.E.; Núñez-Fernández, F.A.; Fraga Nodarse, J.; Atencio Millán, I.; Cruz Rodríguez, I.; Martínez Silva, I.; Ayllón Valdés, L.; Robertson, L.J. Diagnosis of intestinal protozoan infections in patients in Cuba by microscopy and molecular methods: Advantages and disadvantages. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 179, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez Puebla, L.E.; Núñez Fernández, F.A.; Fraga, J.; Rivero, L.R.; Millán, I.A.; Valdés, L.A.; Silva, I.M.; Müller, N.; Robertson, L.J. Concordance of Giardia duodenalis assemblages determined by different PCR methodologies in three observational studies in Cuba. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 209, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ramírez, R.; Berumen-Rodríguez, A.A.; Martínez-Castillo, M.A.; Alcántara-Quintana, L.E.; Díaz-Barriga, F.; Díaz de León-Martínez, L. A review of Environmental risks and vulnerability factors of indigenous populations from Latin America and the Caribbean in the face of the COVID-19. Glob. Public Health 2021, 16, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria-Guzmán, Y.; Chávez-Romero, Y.; Bernal, J.E.; González-Jiménez, F.E.; Serrano-Silva, N.; Fusaro, C. Molecular identification of Giardia spp. in Latin America: An updated systematic review on reports from 2017 to 2021. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.H.; Durigan, M.; Leal, D.A.G.; Schneider, A.B.; Franco, R.M.B.; Singer, S.M. Giardiasis as a neglected disease in Brazil: Systematic review of 20 years of publications. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Köster, P.C.; Malheiros, A.F.; Shaw, J.J.; Balasegaram, S.; Prendergast, A.; Lucaccioni, H.; Moreira, L.M.; Lemos, L.M.S.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; et al. Multilocus Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis in Mostly Asymptomatic Indigenous People from the Tapirapé Tribe, Brazilian Amazon. Pathogens 2021, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsafi, S.H.; Al-Maqati, T.N.; Hussein, M.I.; Adam, A.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Al Zahrani, E.M. Comparison of microscopy, rapid immunoassay, and molecular techniques for the detection of Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium parvum. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyhan, Y.E.; Taş Cengiz, Z. Comparison of microscopy, ELISA, and real-time PCR for detection of Giardia intestinalis in human stool specimens. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 47, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incani, R.N.; Ferrer, E.; Hoek, D.; Ramak, R.; Roelfsema, J.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Kortbeek, T.; Pinelli, E. Diagnosis of intestinal parasites in a rural community of Venezuela: Advantages and disadvantages of using microscopy or RT-PCR. Acta Trop. 2017, 167, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijjawi, N.; Yang, R.; Hatmal, M.; Yassin, Y.; Mharib, T.; Mukbel, R.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Al-Shudifat, A.E.; Ryan, U. Comparison of ELISA, nested PCR and sequencing and a novel qPCR for detection of Giardia isolates from Jordan. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 185, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emisiko, J.; Shaviya, N.; Shiluli, C.; Kiboi, N.; Wamalwa, R.; Jumba, B.; Zablon, J.; Mambo, F.; Barasa, M. Comparison of Microscopy and PCR for Detection of Giardia Lamblia and Entamoeba Histolytica in Human Stool Specimens in a Resource Limited Setting in Western Kenya. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2020, 30, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, A.; Köster, P.C.; Carmena, D. Giardia duodenalis: Detection by Quantitative Real-Time PCR and Molecular Diversity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2369, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreich, F.; Hahn, A.; Eberhardt, K.A.; Kann, S.; Feldt, T.; Sarfo, F.S.; Di Cristanziano, V.; Frickmann, H.; Loderstädt, U. Comparative Evaluation of Real-Time Screening PCR Assays for Giardia duodenalis and of Assays Discriminating the Assemblages A and B. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Betancourt, W.; Gennaccaro, A.L.; Scott, T.M.; Rose, J.B. Assessment of methods for detection of infectious Cryptosporidium oocysts and Giardia cysts in reclaimed effluents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5380–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, R.; Tasca, T. Giardiasis: An update review on sensitivity and specificity of methods for laboratorial diagnosis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 129, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koontz, F.; Weinstock, J.V. The approach to stool examination for parasites. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 1996, 25, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nahas, H.A.; Salem, D.A.; El-Henawy, A.A.; El-Nimr, H.I.; Abdel-Ghaffar, H.A.; El-Meadawy, A.M. Giardia diagnostic methods in human fecal samples: A comparative study. Cytometry B. Clin. Cytom. 2013, 84, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mank, T.G.; Zaat, J.O.; Deelder, A.M.; van Eijk, J.T.; Polderman, A.M. Sensitivity of microscopy versus enzyme immunoassay in the laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1997, 16, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, F.D.; Kuştimur, S.; Ozekinci, T.; Balaban, N.; Ilhan, M.N. The use of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) methods for diagnosis of Giardia intestinalis. Turkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2006, 30, 275–278. Available online: https://tparazitolderg.org/pdf/pdf_TPD_205.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2022). [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.H.B.; Han, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Nugraha, A.B.; Recuenco, F.; Murakoshi, F.; Xuan, X.; Kato, K. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium species in poultry in Bangladesh. One Health 2020, 9, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, F.E.; Singh, G.; Reddy, P.; Stenström, T.A. Methods for the detection of Cryptosporidium and Giardia: From microscopy to nucleic acid based tools in clinical and environmental regimes. Acta Trop. 2018, 184, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.A.; Payment, P.; Krull, U.J.; Horgen, P.A. Real-time PCR for quantification of Giardia and Cryptosporidium in environmental water samples and sewage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5178–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Hermida, J.A.; González-Warleta, M.; Mezo, M. Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis as pathogenic contaminants of water in Galicia, Spain: The need for safe drinking water. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Traub, R.; Pham, P.D.; Nguyen, H.V.; Nguyen, K.C.; Phung, C.D.; Dalsgaard, A. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidum spp. and Giardia spp. in environmental samples in Hanam province, Vietnam. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2016, 3, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vohra, P.; Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, U. A comprehensive review of diagnostic techniques for detection of Cryptosporidium parvum in stool samples. J. Pharm. 2012, 2, 15–26. Available online: http://www.iosrphr.org/papers/v2i5/Part_7/D0251526.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.R.; Sorour, S.S.G. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Giardia duodenalis Assemblage D of Dogs in Egypt, and Its Zoonotic Implication. Microbes Infect. Chemother. 2021, 1, e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.V.; Mank, T.G. Diagnosis of human Giardiasis. In Giardia a Model Organism; Lujan, H.D., Svard, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 353–374. [Google Scholar]
- Monis, P.T.; Saint, C.P. Development of a nested-PCR assay for the detection of Cryptosporidium parvum in finished water. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, S.C.; Soccol, V.T.; Costa, A.O.; Oliveira-Silva, M.B.; Pereira, J.T.; Procópio, A.E. Polymerase chain reaction and nested-PCR approaches for detecting Cryptosporidium in water catchments of water treatment plants in Curitiba, State of Paraná, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2013, 46, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystajecky, N.; Huck, P.M.; Schreier, H.; Isaac-Renton, J.L. Assessment of Giardia and Cryptosporidium spp. as a microbial source tracking tool for surface water: Application in a mixed-use watershed. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2328–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulloa-Stanojlović, F.M.; Aguiar, B.; Jara, L.M.; Sato, M.I.; Guerrero, J.A.; Hachich, E.; Matté, G.R.; Dropa, M.; Matté, M.H.; de Araújo, R.S. Occurrence of Giardia intestinalis and Cryptosporidium sp. in wastewater samples from São Paulo State, Brazil, and Lima, Peru. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 22197–22205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaeen, M.; Mesdaghinia, A.R.; Jeddi, T.M.; Rezaeian, M.; Makimura, K. A nested-PCR assay for detection of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts in water samples. Iran. J. Public Health 2005, 34, 13–18. Available online: https://ijph.tums.ac.ir/index.php/ijph/article/view/1873 (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Coupe, S.; Delabre, K.; Pouillot, R.; Houdart, S.; Santillana-Hayat, M.; Derouin, F. Detection of Cryptosporidium, Giardia and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in surface water, including recreational areas: A one-year prospective study. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, A.; Moreira, M.J.; Soares, S.; Delgado, M.; Figueiredo, J.; Silva, E.; Castro, A.; Cosa, J.M. Presence of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in drinking water samples in the North of Portugal. Korean J. Parasitol. 2010, 48, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Vajpayee, P.; Ram, S.; Shanker, R. Environmental reservoirs for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in south Asian Gangetic riverine system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6475–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanabara, Y.; Ueda, Y. A rapid and simple real-time PCR assay for detecting foodborne pathogenic bacteria in human feces. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 69, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Vajpayee, P.; Rani, N.; Amoah, I.D.; Stenström, T.A.; Shanker, R. Exploring the potential reservoirs of nonspecific TEM beta lactamase (bla(TEM)) gene in the Indo-Gangetic region: A risk assessment approach to predict health hazards. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 314, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothikumar, N.; Murphy, J.L.; Hill, V.R. Detection and identification of Giardia species using real-time PCR and sequencing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 189, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, C.; Radam, E.; Rausch, S.; Gosten-Heinrich, P.; Aebischer, T. Real-Time PCR for molecular detection of zoonotic and non-zoonotic Giardia spp. in wild rodents. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squire, S.A.; Yang, R.; Robertson, I.; Ayi, I.; Ryan, U. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in farmers and their ruminant livestock from the Coastal Savannah zone of Ghana. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uiterwijk, M.; Nijsse, R.; Kooyman, F.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Koop, G.; Ploeger, H.W. Comparing four diagnostic tests for Giardia duodenalis in dogs using latent class analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legido-Quigley, H.; Camacho Lopez, P.A.; Balabanova, D.; Perel, P.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Schwalm, J.D.; McCready, T.; Yusuf, S.; McKee, M. Patients’ knowledge, attitudes, behaviour and health care experiences on the prevention, detection, management and control of hypertension in Colombia: A qualitative study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rentería-Ramos, R.; Hurtado-Heredia, R.; Urdinola, B.P. Morbi-Mortality of the Victims of Internal Conflict and Poor Population in the Risaralda Province, Colombia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamprea, E.; García, J. Closing the Gap between Formal and Material Health Care Coverage in Colombia. Health Hum. Rights. 2016, 18, 49–65. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5394995/ (accessed on 20 September 2022). [PubMed]



| Reference | Quartile SJR | Location | Rural/Urban | Collection Period | Target Population | Age (years) | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arias et al., 2010 [37] | Q4 | Quindío | Rural | 2008 | Children | 2–5 | Moderate |
| Boeke et al., 2010 [38] | Q2 | Bogotá | Urban | 2006 | School Children | 5–12 | High |
| Londoño Alvarez et al., 2010 [39] | Q4 | Atlántico | Urban | 2004 | Children | 2–6 | Moderate |
| Arroyo-Salgado et al., 2014 [40] | Q4 | Bolívar Sucre | Urban | 2009 | Children | <7 | Moderate |
| Rodriguez et al., 2014 [41] | Q3 | Tolima | Urban | 2009 | Children | 1–5 | Moderate |
| Espinosa-Muñoz et al., 2015 [42] | Q4 | Magdalena | Rural | 2014 | Indigenous | 1–93 | Moderate |
| Fillot et al., 2015 [43] | Q4 | Atlántico | Urban | 2014 | Children | 1–10 | Moderate |
| Ramírez et al., 2015 [44] | Q2 | Cundinamarca | Rural | NR | Children | Under 16 | High |
| Villafañe-Ferrer and Pinilla-Pérez, 2016 [45] | Q4 | Bolívar | Rural | NR | Children | 2–12 | Moderate |
| Sánchez et al., 2017 [46] | Q1 | Amazonas | Rural | NR | Children | Under 15 | High |
| Espinosa Aranzales et al., 2018 [47] | Q1 | Bogotá | Urban | 2015–2016 | Pregnant Women | 14–43 | High |
| Giraldo-Ospina et al., 2018 [48] | Q3 | Valle del Cauca | Rural | 2015–2017 | Children | 1–10 | Moderate |
| Villalba-Vizcaíno et al., 2018 [49] | Q3 | Bolívar Magdalena | Urban | NR | Children Adults | 0–80 | Moderate |
| Avendaño et al., 2019 [50] | Q2 | Bogotá Valle del Cauca Nariño | Rural Urban | 2014 | Children Teenagers | 1–19 | High |
| Carvajal-Restrepo et al., 2019 [51] | Q3 | Antioquia Cauca Chocó | Rural | 2009–2010 | Adults | >18 | Moderate |
| Hernández et al., 2019 [52] | Q1 | Cundinamarca | Rural | 2017 | School Children | 1–15 | High |
| Pedraza et al., 2019 [53] | Q4 | Bolívar | Urban | NR | Children | 2–5 | Moderate |
| Villamizar et al., 2019 [54] | Q1 | Cauca | Rural Urban | NR | School Children | 1–5 | High |
| Higuera et al., 2020 [55] | Q1 | Amazonas Antioquia Bolívar Boyacá Caldas Casanare Cauca Córdoba Cundinamarca Guainía Quindío Risaralda Tolima | Rural Urban | NR | Children Adults | 1–70 | High |
| Peña-Quistial et al., 2020 [56] | Q1 | Valle del Cauca | Rural | 2019 | Children | 1–12 | High |
| Kann et al., 2022 [57] | Q2 | Cesar Guajira | Rural | 2014–2018 | Indigenous | 1–20 | High |
| Muñoz Salas et al., 2022 [58] | Q3 | Atlántico | Rural | 2017 | School Children | 2–10 | Moderate |
| Vásquez et al., 2022 [59] | Q4 | Córdoba | Rural | 2017–2018 | Children | 1–10 | Moderate |
| Reference | Samples Analyzed | Replica Number (Mx) | Concentration Method | DNA Extraction Method | Detection Method | Genes Investigated | Assemblages/Subassemblages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arias et al., 2010 [37] | SS | 3 | Ritchie concentration technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Boeke et al., 2010 [38] | SS | 1 | Formol-ether technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Londoño Alvarez et al., 2010 [39] | SS | NR | Ritchie concentration technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Arroyo-Salgado et al., 2014 [40] | SS | NR | NR | Organic solvents | Microscopy Semi-nested PCR | tpi | A, B |
| Rodriguez et al., 2014 [41] | SS | NR | Faust float | QIAmp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) | Microscopy PCR-RFLP | gdh bg | AIII, BIII, BIV |
| Espinosa-Muñoz et al., 2015 [42] | SS | 1 | Mini Parasep SF fecal parasite concentrator | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Fillot et al., 2015 [43] | SS | NR | Ritchie concentration technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Ramírez et al., 2015 [44] | SS | NR | Ritchie concentration technique Kato-katz Richie-Frick | QIAmp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) | Microscopy Nested and semi-nested PCR | tpi gdh SSU rDNA | A, B, A + B, AI, AII, BIII, BIV |
| Villafañe-Ferrer and Pinilla-Pérez, 2016 [45] | SS | 3 | Formol-ether technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Sánchez et al., 2017 [46] | SS | NR | NR | Norgen Stool DNA isolation kit (Norgen Biotek Corporation, Thorold, Canada) | Microscopy qPCR | tpi gdh | AI, AII, BIII, BIV |
| Espinosa Aranzales et al., 2018 [47] | SS | 1–2 | Formol-ether technique | Norgen Stool DNA isolation kit (Norgen Biotek Corporation, Thorold, Canada) | Microscopy qPCR | 16S rRNA | NR |
| Giraldo-Ospina et al., 2018 [48] | SS | NR | Ritchie concentration technique Formol-ether technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Villalba-Vizcaíno et al., 2018 [49] | SS | NR | Diethyl-ether method | ISOLATE II Genomic DNA Kit Cat.: 137 BIO-52066 (Bioline) | MicroscopyPCR | tpi gdh bg | A |
| Avendaño et al., 2019 [50] | SS | 1 | Biphasic sedimentation | QIAmp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) | MicroscopyNested PCR | tpi bg SSUrRNA | A, AII, B |
| Carvajal-Restrepo et al., 2019 [51] | SS | NR | Formalin-ethyl acetate technique | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Hernández et al., 2019 [52] | SS | 1 | Mini Parasep SF fecal parasite concentrator | QIAamp® Fast DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) | Microscopy, Nested and Semi-nested PCR | tpi gdh bg | AI, AII, BIII, BIV, AII + BIII |
| Pedraza et al., 2019 [53] | SS | NR | NR | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Villamizar et al., 2019 [54] | SS | NR | Ritchie concentration technique Kato-katz technique | Norgen Stool DNA isolation kit (Norgen Biotek Corporation, Thorold, Canada) | Microscopy qPCR | tpi gdh | AII, BIII, BIV, D |
| Higuera et al., 2020 [55] | SS | NR | Ritchie concentration technique | Norgen Stool DNA isolation kit (Norgen Biotek Corporation, Thorold, Canada) | Microscopy PCR | tpi gdh | AII, BIII, BIV, D, G |
| Peña-Quistial et al., 2020 [56] | SS | NR | Sheather technique Kato-katz | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
| Kann et al., 2022 [57] | SS | NR | NR | QIAmp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) | PCR | SSUrRNA | NR |
| Muñoz Salas et al., 2022 [58] | SS | 3 | Ritchie concentration technique | AccuPrept Stool Genomic DNA kit (BioNeer Corp., Munpyeong-seo, Republic of Korea) | Microscopy PCR | bg | A, B, A + B |
| Vásquez et al., 2022 [59] | SS | NR | NR | NR | Microscopy | NR | NR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusaro, C.; Chávez-Romero, Y.A.; Prada, S.L.G.; Serrano-Silva, N.; Bernal, J.E.; González-Jiménez, F.E.; Sarria-Guzmán, Y. Burden and Epidemiology of Human Intestinal Giardia duodenalis Infection in Colombia: A Systematic Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7100325
Fusaro C, Chávez-Romero YA, Prada SLG, Serrano-Silva N, Bernal JE, González-Jiménez FE, Sarria-Guzmán Y. Burden and Epidemiology of Human Intestinal Giardia duodenalis Infection in Colombia: A Systematic Review. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(10):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7100325
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusaro, Carmine, Yosef A. Chávez-Romero, Sonia Liliana Gómez Prada, Nancy Serrano-Silva, Jaime E. Bernal, Francisco Erik González-Jiménez, and Yohanna Sarria-Guzmán. 2022. "Burden and Epidemiology of Human Intestinal Giardia duodenalis Infection in Colombia: A Systematic Review" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 10: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7100325
APA StyleFusaro, C., Chávez-Romero, Y. A., Prada, S. L. G., Serrano-Silva, N., Bernal, J. E., González-Jiménez, F. E., & Sarria-Guzmán, Y. (2022). Burden and Epidemiology of Human Intestinal Giardia duodenalis Infection in Colombia: A Systematic Review. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(10), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7100325







