A Case Report of Secondary Syphilis Co-Infected with Measles: A Diagnostic Dilemma with Fever and Rash
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
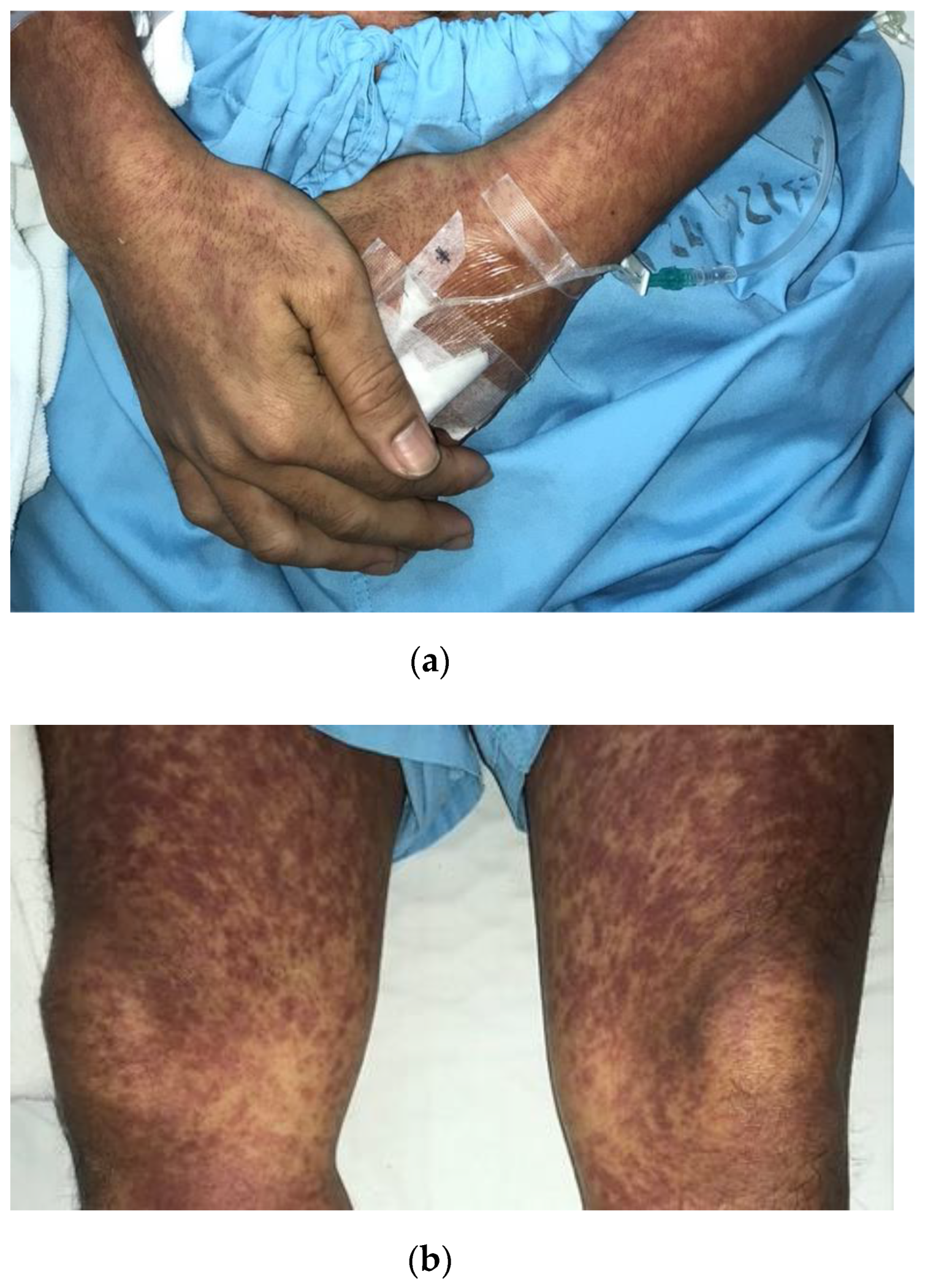
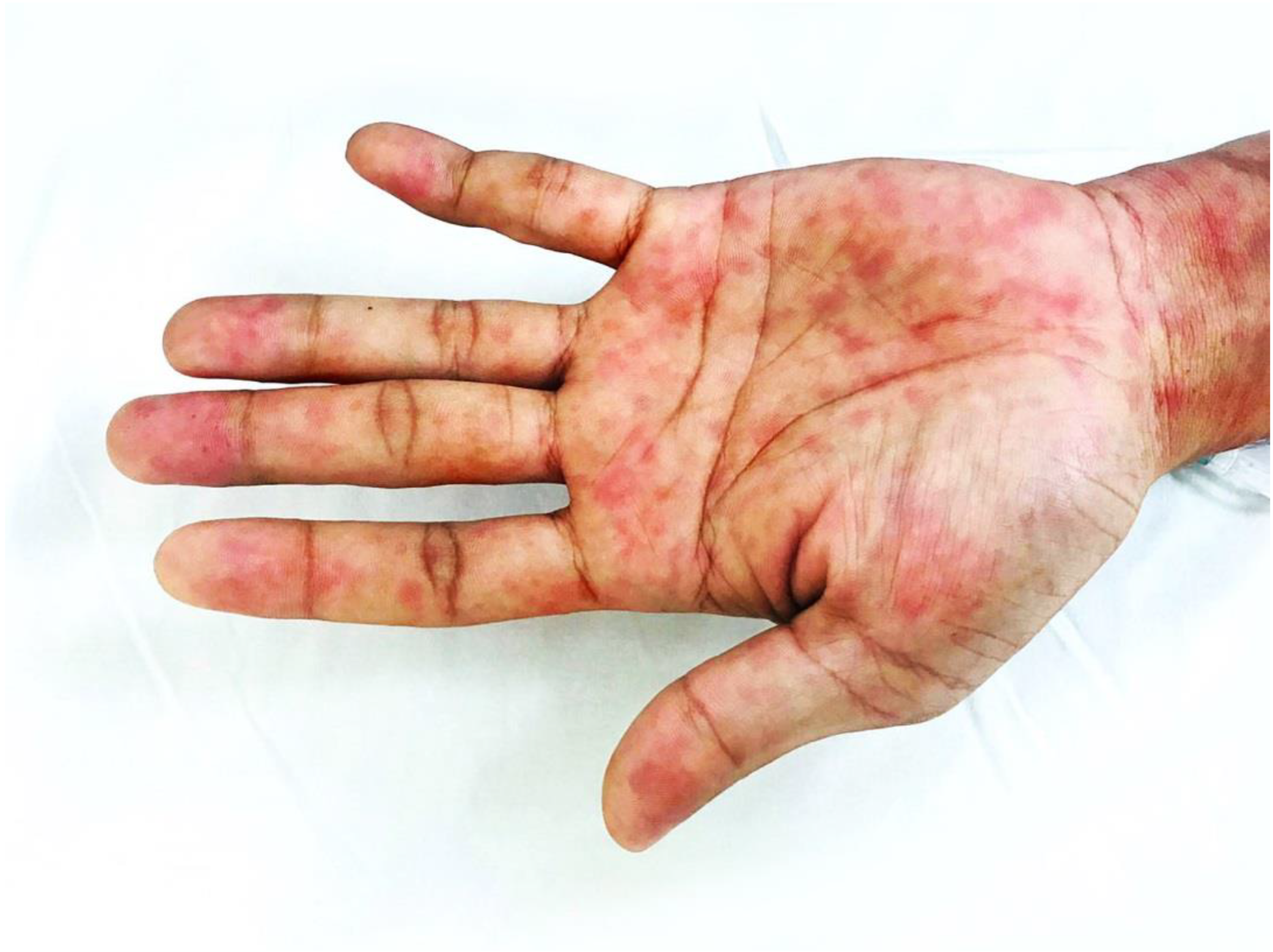
3. Case Report
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKinnon, H.D., Jr.; Howard, T. Evaluating the febrile patient with a rash. Am. Fam. Physician 2000, 62, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H. Febrile Illness with Skin Rashes. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 47, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Gasparini, G.; Cogorno, L.; Javor, S.; Toniolo, A.; Broccolo, F. Contemporary infectious exanthems: An update. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabak, F.; Murtezaoglu, A.; Tabak, O.; Ozaras, R.; Mete, B.; Kutlubay, Z.; Mert, A.; Öztürk, R. Clinical Features and Etiology of Adult Patients with Fever and Rash. Ann. Dermatol. 2012, 24, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanlapakorn, N.; Wasitthankasem, R.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Auphimai, C.; Yoocharoen, P.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Antibodies against measles and rubella virus among different age groups in Thailand: A population-based serological survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV and syphilis infection among men who have sex with men--Bangkok, Thailand, 2005–2011. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 60, 518–520. [Google Scholar]
- Parsian, Z.; Ghafouri, R.R.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Targhi, S.T.; Varshochi, M.; Yarani, R.; Golzari, S.E.J. First report of a disease by rhazes 10 centuries ago. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, T.L.; Durrheim, D.N.; Merritt, T.D.; Birch, C.; Tran, T. Measles with a possible 23 day incubation period. Commun. Dis. Intell. Q. Rep. 2012, 36, E277–E280. [Google Scholar]
- Laksono, B.M.; De Vries, R.D.; McQuaid, S.; Duprex, W.P.; De Swart, R.L. Measles Virus Host Invasion and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2016, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, R.T.; Halsey, N.A. The Clinical Significance of Measles: A Review. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189 (Suppl. 1), S4–S16. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Harada, T. Koplik spots in measles. Postgrad. Med J. 2019, 95, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brem, J. Koplik spots for the record: An illustrated historical note. Clin. Pediatr. 1972, 11, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.; Hon, K.L.; Leong, K.F.; Sergi, C.M. Measles: A disease often forgotten but not gone. Hong Kong Med. J. 2018, 24, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales, G.B.; Muñoz, M.A. Immune amnesia induced by measles and its effects on concurrent epidemics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2021, 18, 20210153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, M.J.; Metcalf, C.J.E.; De Swart, R.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Grenfell, B.T. Long-term measles-induced immunomodulation increases overall childhood infectious disease mortality. Science 2015, 348, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchanan, R.; Bonthius, D.J. Measles Virus and Associated Central Nervous System Sequelae. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 19, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Afzal, S.; Ahmad, J.; Alghamdi, S.; Khurram, M. The Resurgence of Measles Infection and its Associated Complications in Early Childhood at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Peshawar, Pakistan. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.C. Neurological Complications of Measles (Rubeola). Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, P.S.; Rajendran, T.; Tilakaratne, S. Neurological complications of measles. Ceylon Med. J. 2014, 46, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, J. Complications and Sequelae of Measles. Calif. State J. Med. 1904, 2, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Anis-ur-Rehman, S.T.; Idris, M. Clinical outcome in measles patients hospitalized with complications. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2008, 20, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fragkou, P.C.; Thomas, K.; Sympardi, S.; Liatsos, G.D.; Pirounaki, M.; Sambatakou, H.; Marantos, T.; Karofylakis, E.; Dourakis, S.P.; Tsiodras, S.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of measles outbreak in adults: A multicenter retrospective observational study of 93 hospitalized adults in Greece. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 131, 104608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Band, I.C.; Reichel, M. Al Rhazes and the Beginning of the End of Smallpox. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltey, J.E.; Cohen, S.E. Syphilis transmission: A review of the current evidence. Sex. Health 2015, 12, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, G.P.; Aral, S.O.; Hoyle, D.V.; Cates, W., Jr.; Anderson, R.M. The natural history of syphilis. Implications for the transmission dynamics and control of infection. Sex. Transm. Dis. 1997, 24, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, E.; Marks, R.; Jones, E. Secondary syphilis: A clinico-pathological review. Br. J. Dermatol. 1975, 93, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarraga-Cañas, C.; Ayerdi-Aguirrebengoa, O.; Menéndez-Prieto, B.; Tello-Romero, E.; Rodríguez-Martín, C.; del Romero-Guerrero, J. Is dark-field microscopy still useful for the primary syphilis diagnosis in the 21ST century? Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. 2022, 40, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.A.; Steiner, B.M.; Rudolph, A.H. Laboratory diagnosis and interpretation of tests for syphilis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfin, A.A.; Liu, H.; Sutton, M.Y.; Steiner, B.; Pillay, A.; Markowitz, L.E. Amplification of the DNA polymerase I gene of Treponema pallidum from whole blood of persons with syphilis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2001, 40, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhai, L.; Jianzhong, Z.; Cao, Y. Detection of Treponema pallidum in skin lesions of secondary syphilis and characterization of the inflammatory infiltrate. Dermatology 2004, 208, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psevdos, G.; Mahapatra, R.; Clarke, G.; Lobo, Z. Cervical syphilitic lymphadenitis causing fever of unknown origin followed by rash of secondary syphilis. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2019, 62, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dylewski, J.; Duong, M. The rash of secondary syphilis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2006, 176, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baughn, R.E.; Musher, D.M. Secondary Syphilitic Lesions. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapel, T.A. The Signs and Symptoms of Secondary Syphilis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 1980, 7, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanne, J.H. Measles cases and deaths are increasing worldwide, warn health agencies. BMJ 2020, 371, m4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Carson, P.J.; Jansen, R.J. Resurgence of Syphilis in the United States: An Assessment of Contributing Factors. Infect. Dis. Res. Treat. 2019, 12, 1178633719883282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimala, C.A.; Kadia, B.M.; Nji, M.A.M.; Bechem, N.N. Factors associated with measles resurgence in the United States in the post-elimination era. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abara, W.E.; Hess, K.L.; Neblett Fanfair, R.; Bernstein, K.T.; Paz-Bailey, G. Syphilis Trends among Men Who Have Sex with Men in the United States and Western Europe: A Systematic Review of Trend Studies Published between 2004 and 2015. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyrer, C.; Kawichai, S.; Hyder, J.A.; Borwornsin, S.; Srirak, N.; Natpratan, C.; Celentano, D.D.; Khamboonruang, C. Patterns of HIV and syphilis infection in Northern Thailand 1998–2001. Int. J. STD AIDS 2007, 18, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonett, S.; Tam, V.; Singapur, A.; Min, J.; Koenig, H.C.; Wood, S.M. Incidence of syphilis infection and syphilis-related care utilization among adolescents and young adults living with HIV. Int. J. STD AIDS 2021, 33, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, E.; Girault, P.; Gultom, M.; Sukartini, N.; Kumalawati, J.; Jazan, S.; Donegan, E. HIV, syphilis infection, and sexual practices among transgenders, male sex workers, and other men who have sex with men in Jakarta, Indonesia. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2004, 80, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kassutto, S.; Sax, P.E. HIV and syphilis coinfection: Trends and interactions. AIDS Clin. Care 2003, 15, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luvira, V.; Silachamroon, U.; Piyaphanee, W.; Lawpoolsri, S.; Chierakul, W.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Thawornkuno, C.; Wattanagoon, Y. Etiologies of Acute Undifferentiated Febrile Illness in Bangkok, Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imad, H.; Matsee, W.; Kludkleeb, S.; Asawapaithulsert, P.; Phadungsombat, J.; Nakayama, E.; Suzuki, K.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Piyaphanee, W.; Phumratanaprapin, W.; et al. Post–Chikungunya Virus Infection Musculoskeletal Disorders: Syndromic Sequelae after an Outbreak. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imad, H.A.; Atsawawaranunt, K.; Sharma, C.; Poonam, T.; Piyaphanee, W. Fever, rash, and red eyes in Thailand: A diagnostic challenge. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenigl, M.; Green, N.; Camacho, M.; Gianella, S.; Mehta, S.R.; Smith, D.M.; Little, S.J. Signs or Symptoms of Acute HIV Infection in a Cohort Undergoing Community-Based Screening. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moylett, E.H.; Shearer, W.T. HIV: Clinical manifestations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posuwan, N.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Sa-Nguanmoo, P.; Wasitthankasem, R.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Klinfueng, S.; Poovorawan, Y. The success of a universal hepatitis B immunization program as part of Thailand’s EPI after 22 years’ implementation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Signore, C. Rubella. Prim. Care Update Ob/Gyns 2001, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, A.D.; Campion, G.V.; Chishick, A.; Wise, S.; Cohen, B.J.; Klouda, P.T.; Caul, O.; Dieppe, P.A. Clinical manifestations of human parvovirus B19 in adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 1989, 149, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Petty, R.E.; Tingle, A.J. Rubella virus and arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1987, 13, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, I. Rubella (German measles)--still a major infectious disease. Med. Mon. Fur Pharm. 2012, 35, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Imad, H.; Phadungsombat, J.; Nakayama, E.; Kludkleeb, S.; Matsee, W.; Ponam, T.; Suzuki, K.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Piyaphanee, W.; Phumratanaprapin, W.; et al. Chikungunya Manifestations and Viremia in Patients WhoPresented to the Fever Clinic at Bangkok Hospital for Tropical Diseases during the 2019 Outbreak in Thailand. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.M.; Grossman, M.E.; Gregory, N. Koplik spots and a purpuric eruption associated with parvovirus B19 infection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 27, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Shirabe, K.; Takeda, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Okayama, K.; Kozawa, K. The Association Between Documentation of Koplik Spots and Laboratory Diagnosis of Measles and Other Rash Diseases in a National Measles Surveillance Program in Japan. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, J.; Lüthy, R.; Oelz, O. Severe Measles Pneumonitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 1060–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goetz, M.; Mathisen, G.E. Clinical Course and Treatment of Adults with Severe Measles Pneumonitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slifka, M.K.; Homann, D.; Tishon, A.; Pagarigan, R.; Oldstone, M.B. Measles virus infection results in suppression of both innate and adaptive immune responses to secondary bacterial infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Kellett, J.G.; Hallas, P.; Brabrand, M. Fever increases heart rate and respiratory rate; a prospective observational study of acutely admitted medical patients. Acute Med. 2019, 18, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Chetrit, E.; Oster, Y.; Jarjou’I, A.; Megged, O.; Lachish, T.; Cohen, M.J.; Stein-Zamir, C.; Ivgi, H.; Rivkin, M.; Milgrom, Y.; et al. Measles-related hospitalizations and associated complications in Jerusalem, 2018–2019. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 26, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, E.U. The Visceral Lesions in Measles: With a Report of Koplik Spots in the Colon. Am. J. Pathol. 1945, 21, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pancharoen, C.; Ruttanamongkol, P.; Suwangool, P.; Likitnukul, S.; Thisyakorn, U. Measles-associated appendicitis: Two case reports and literature review. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karaşahin, E.F.; Karaşahin, O. Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis after Measles. Arch. Iran. Med. 2021, 24, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.; Anderson, M. Cross-reactions in rubella and parvovirus specific IgM tests. Lancet 1985, 326, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurman, O.H.; Ziola, B.R. IgM-class rheumatoid factor interference in the solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella-specific IgM antibodies. J. Clin. Pathol. 1978, 31, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, N.; Strebel, P.; Orenstein, W.; Icenogle, J.; Poland, G.A. Rubella. Lancet 2015, 385, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miqdhaadh, A.; Imad, H.A.; Fazeena, A.; Ngamprasertchai, T.; Nguitragool, W.; Nakayama, E.E.; Shioda, T. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in an Adult: A Case Report from the Maldives. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitukweerakul, S.; Sinyagovskiy, P.; Aung, P.P. Purpura Fulminans in Acute Meningococcemia. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Inoue, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Hadano, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Morino, K.; Shimizu, T. Meningococcemia in Adults: A Review of the Literature. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pancharoen, C.; Hongsiriwon, S.; Swasdichai, K.; Puthanakit, T.; Tangsathapornpong, A.; Lolekha, S.; Punpanich, W.; Tarunotai, U.; Warachit, B.; Mekmullica, J.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive meningococcal disease in 13 government hospitals in Thailand, 1994–1999. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2000, 31, 708–711. [Google Scholar]
- Kollars, T.M.; Tippayachai, B.; Bodhidatta, D. Short report: Thai tick typhus, Rickettsia honei, and a unique rickettsia detected in Ixodes granulatus (Ixodidae: Acari) from Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 65, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parola, P.; Miller, R.S.; McDaniel, P.; Telford, S.R., III; Rolain, J.M.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Raoult, D. Emerging rickettsioses of the Thai-Myanmar border. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparling, P.F. Diagnosis and treatment of syphilis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 284, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.L.; Lin, L.R.; Tong, M.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Huang, S.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Guo, X.J.; Xi, Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for the Prozone Phenomenon in Serologic Testing for Syphilis in a Large Cohort. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, J.; Fang, H. Moth-eaten alopecia: A sign of secondary syphilis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 185, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pourang, A.; Fung, M.A.; Tartar, D.; Brassard, A. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 10, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuddenham, S.; Hamill, M.M.; Ghanem, K.G. Diagnosis and Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuddenham, S.; Ghanem, K.G. Management of Adult Syphilis: Key Questions to Inform the 2021 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, S127–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eça Júnior, A.; Rodrigues, L.D.S.; Costa, L.C. Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in a patient with syphilis and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Rev. Da Soc. Bras. De Med. Trop. 2018, 51, 877–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T. The Jarisch–Herxheimer Reaction After Antibiotic Treatment of Spirochetal Infections: A Review of Recent Cases and Our Understanding of Pathogenesis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 96, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Day of Illness | Third Day | Fourth Day |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin g/dL (14.0–18.0) | 16.8 | 16.7 |
| Hematocrit % (40.0–54.0) | 49.2 | 49.6 |
| Leukocytes/µL (5000–1000) | 5800 | 5100 |
| Neutrophils/µL (2500–6000) | 4408 | 3723 |
| Lymphocytes/µL (1000–4800) | 406 | 561 |
| Monocytes/µL (200–800) | 0 | 102 |
| Eosinophils/µL (30–350) | 0 | 0 |
| Basophils/µL (0–300) | 0 | 0 |
| Band form/µL (0–4) | 928 | 510 |
| Atypical lymphocytes/µL (0–600) | 58 | 204 |
| Platelets/µL (150,000–450,000) | 155,000 | 136,000 |
| Direct bilirubin mg/dL (0.0–0.3) | 0.1 | |
| Total bilirubin mg/dL (0.0–1.2) | 0.3 | |
| Total protein g/dL (6.6–8.7) | 7.1 | |
| Albumin g/dL (3.5–5.2) | 3.9 | |
| Globulin g/dL (2.5–3.5) | 3.2 | |
| Alkaline phosphatase IU/L (40–129) | 80 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase IU/L (0–40) | 44 | |
| Alanine transferase IU/L (0–41) | 42 | |
| Creatinine mg/dL (0.67–1.17) | 1.05 | |
| Blood urea nitrogen mg/dL (6–20) | 15.4 | |
| Sodium mmol/L (136–145) | 130 | |
| Potassium mmol/L (3.5–5.1) | 3.6 | |
| Chloride mmol/L (98–107) | 96 | |
| Dengue NS1 | Negative | |
| Measles IgM | Positive | |
| Measles IgG | Positive | |
| Rubella IgM | Positive | |
| Rubella IgG | Positive | |
| Hepatitis B surface Ag | Negative | |
| Anti-hepatitis B surface Ab | Positive | |
| Anti-hepatitis C Ab | Negative | |
| Anti-HIV Ag/Ab | Negative | |
| RPR | Reactive | |
| TPHA | Reactive | |
| Blood culture | No growth | |
| Stool culture | No growth |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imad, H.A.; Lakanavisid, P.; Pisutsan, P.; Trerattanavong, K.; Ngamprasertchai, T.; Matsee, W.; Piyaphanee, W.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Nguitragool, W.; Nakayama, E.E.; et al. A Case Report of Secondary Syphilis Co-Infected with Measles: A Diagnostic Dilemma with Fever and Rash. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050070
Imad HA, Lakanavisid P, Pisutsan P, Trerattanavong K, Ngamprasertchai T, Matsee W, Piyaphanee W, Leaungwutiwong P, Nguitragool W, Nakayama EE, et al. A Case Report of Secondary Syphilis Co-Infected with Measles: A Diagnostic Dilemma with Fever and Rash. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(5):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050070
Chicago/Turabian StyleImad, Hisham Ahmed, Ploi Lakanavisid, Phimphan Pisutsan, Kentaro Trerattanavong, Thundon Ngamprasertchai, Wasin Matsee, Watcharapong Piyaphanee, Pornsawan Leaungwutiwong, Wang Nguitragool, Emi E. Nakayama, and et al. 2022. "A Case Report of Secondary Syphilis Co-Infected with Measles: A Diagnostic Dilemma with Fever and Rash" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 5: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050070
APA StyleImad, H. A., Lakanavisid, P., Pisutsan, P., Trerattanavong, K., Ngamprasertchai, T., Matsee, W., Piyaphanee, W., Leaungwutiwong, P., Nguitragool, W., Nakayama, E. E., & Shioda, T. (2022). A Case Report of Secondary Syphilis Co-Infected with Measles: A Diagnostic Dilemma with Fever and Rash. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(5), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7050070








