Non-Invasive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Saliva versus Nasopharyngeal Swabs Using Nanobodies Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using RT-qPCR
2.3. Conjugation of SARS-CoV-2 S1-RBD Nanobodies (RBD-Nbs) with Colloidal Gold NANOPARTICLES (AuNPs)
2.4. Testing the Reactivity of AuNPs-Nbs Probes and Free Nbs against SARS-CoV-2 S1 Antigen
2.5. Development and Optimization of Sandwich ELISA
2.6. Evaluation Using Clinical Samples
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Samples Characterization
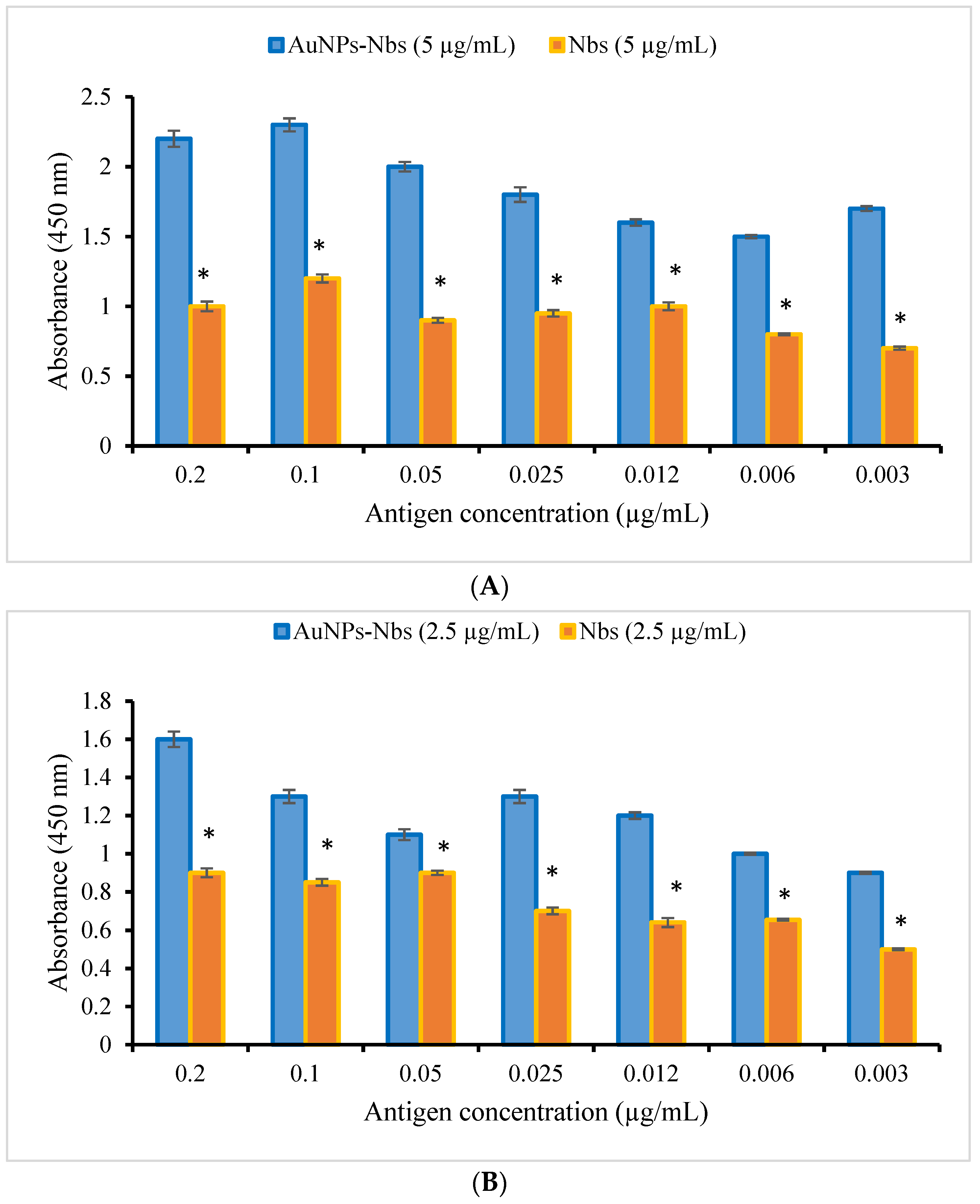
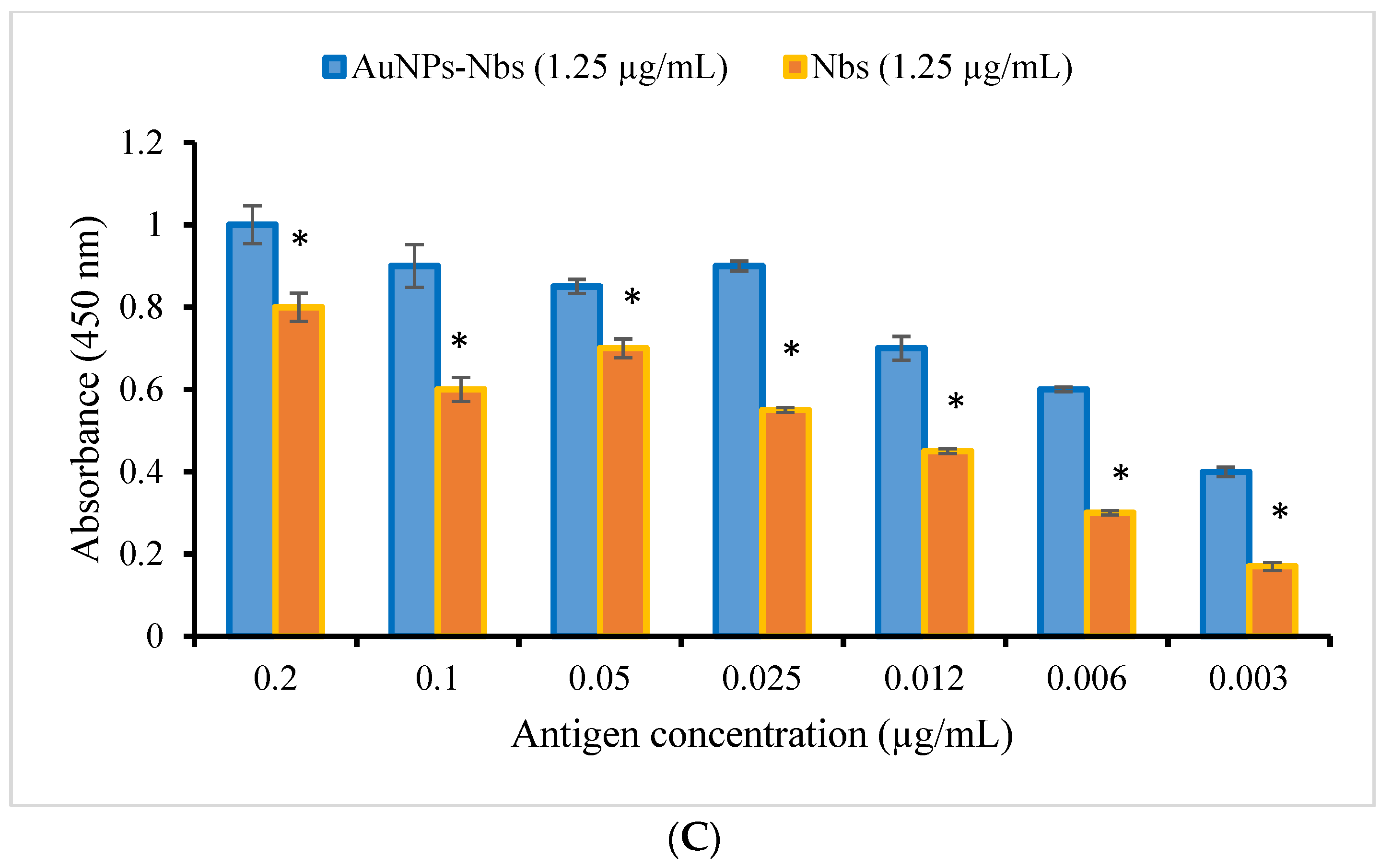
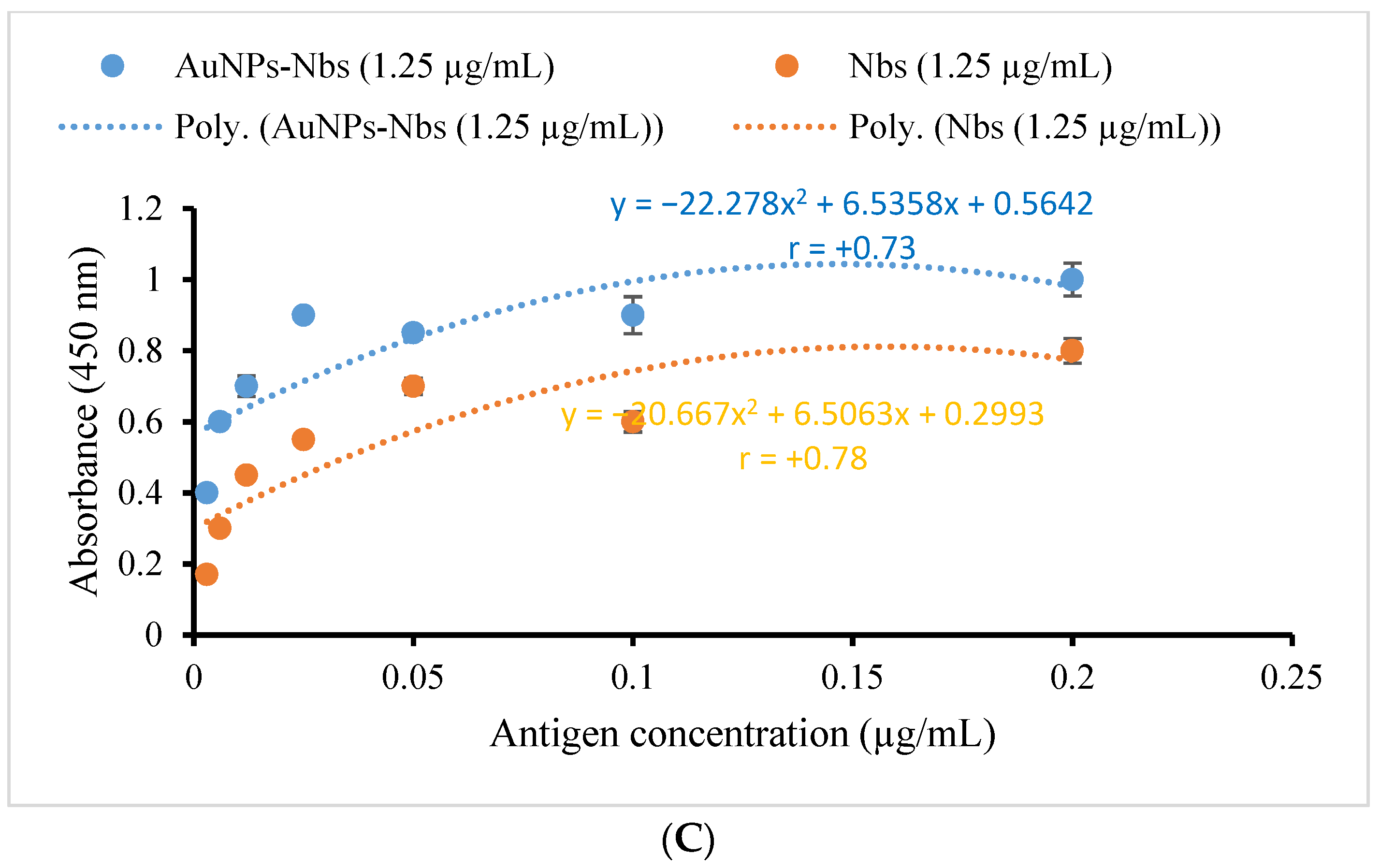
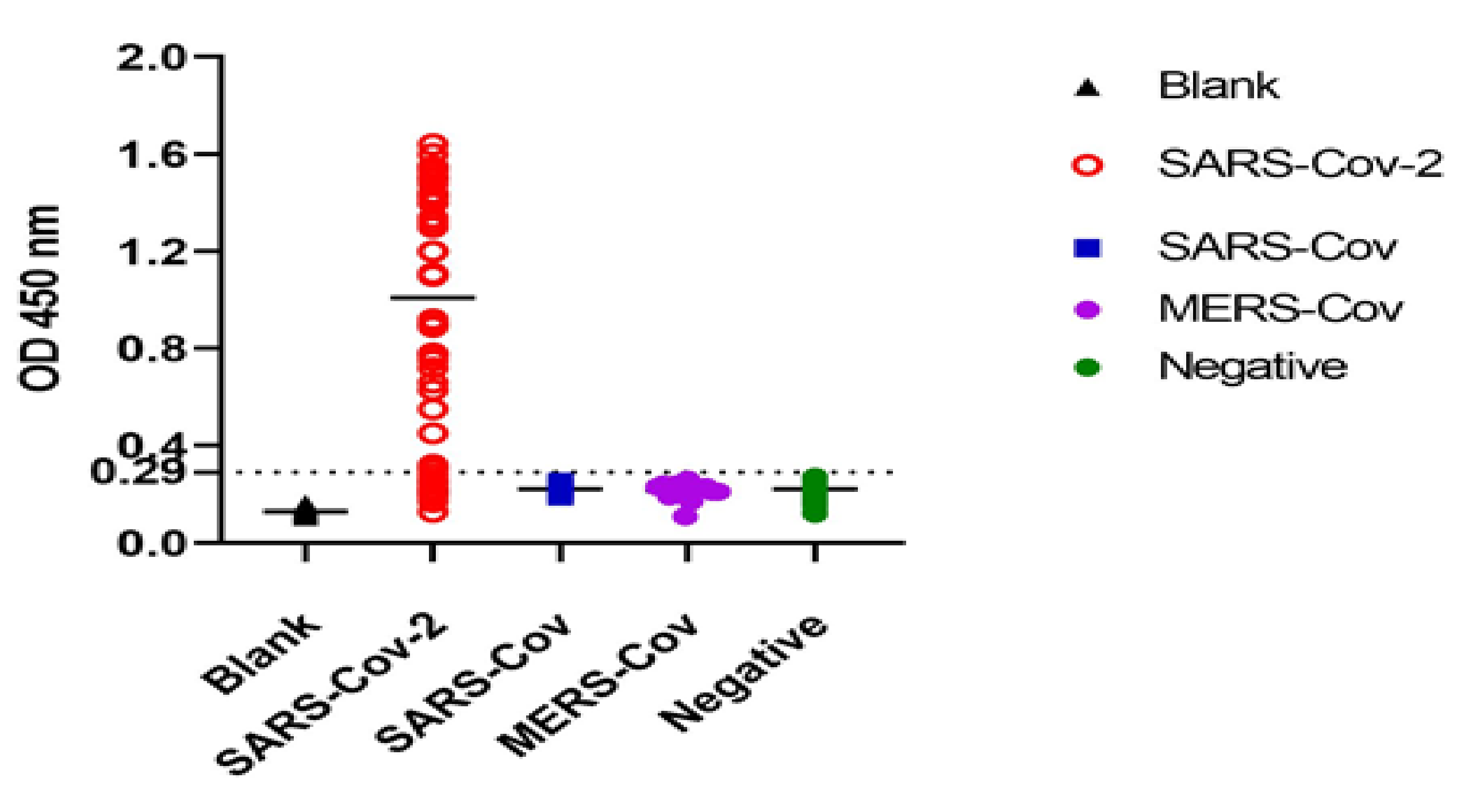
3.2. Characterization and Testing of Reactivity of AuNPs-Nbs as Well as Free Nbs against SARS-CoV-2 S1 Recombinant Antigen
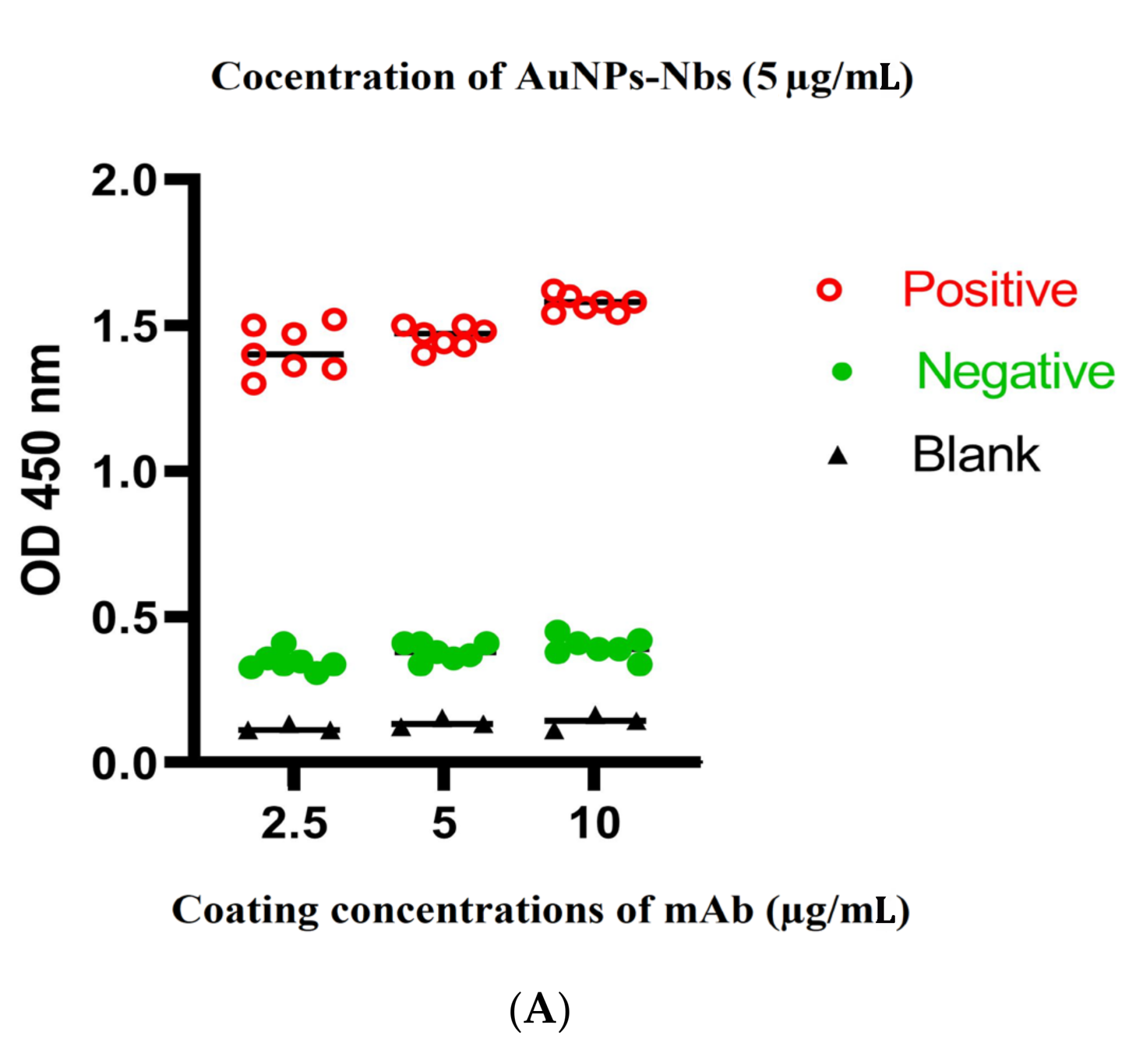
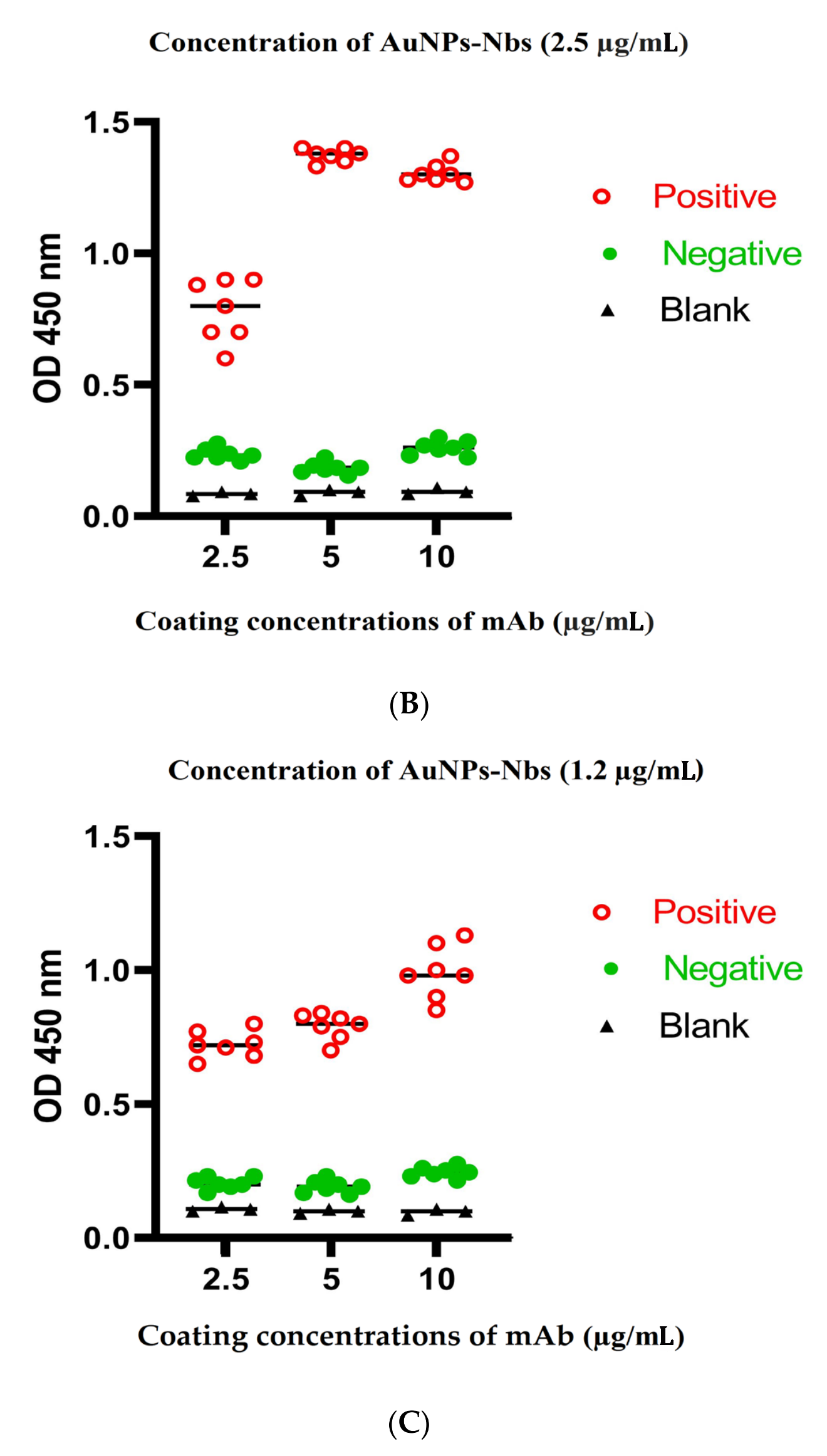
3.3. Optimization of Sandwich ELISA
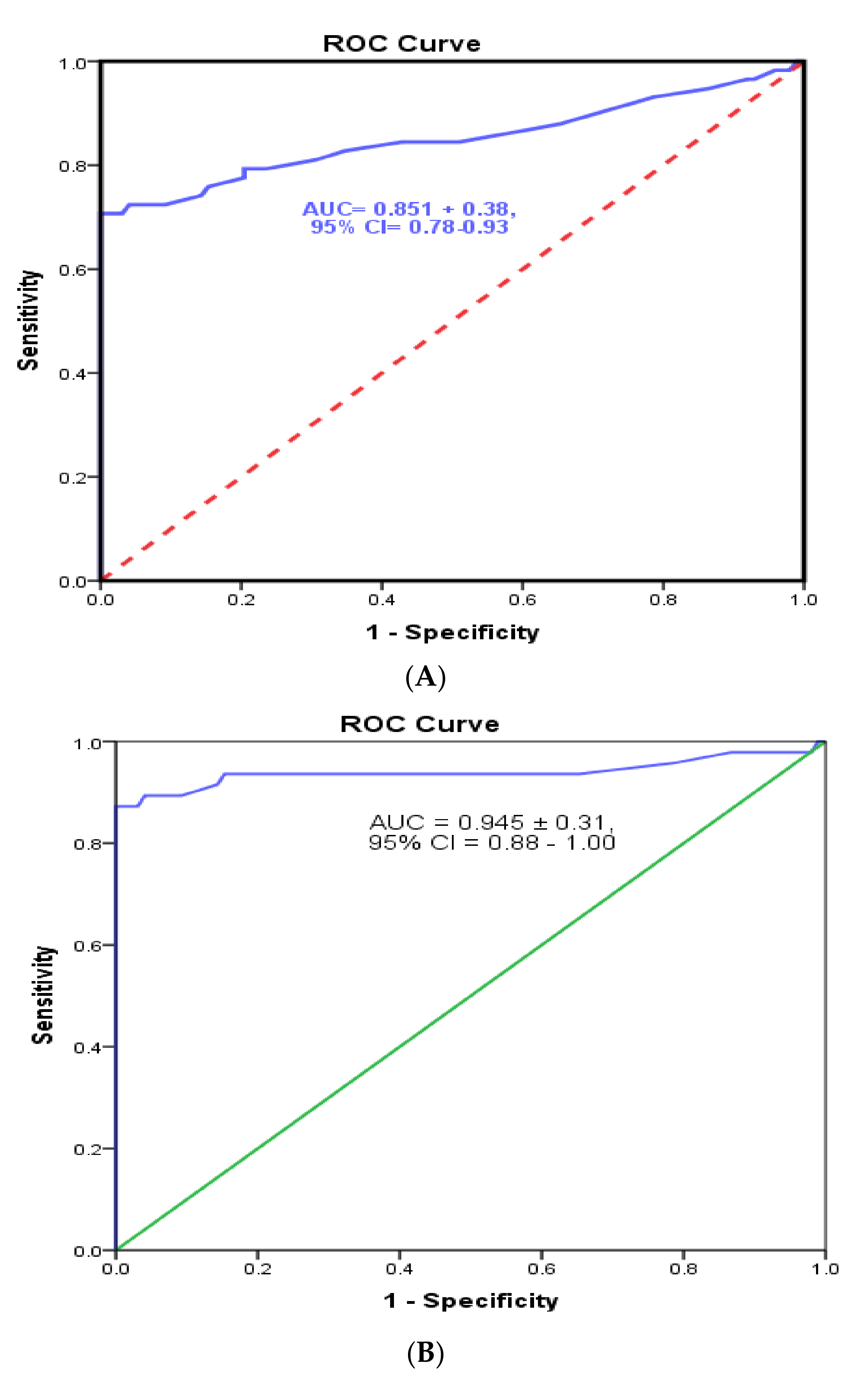
3.4. Cutoff Value and Evaluation of the Developed Sandwich ELISA System
4. Discussion
Limitation of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. Atenei Parm. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.W.; Wong, V.T.; Tang, S.C.W. COVID-19: An Update on the Epidemiological, Clinical, Preventive and Therapeutic Evidence and Guidelines of Integrative Chinese-Western Medicine for the Management of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 737–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peto, J. COVID-19 mass testing facilities could end the epidemic rapidly. BMJ 2020, 368, m1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, L.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qin, C.; et al. Development of an automatic integrated gene detection system for novel severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV2). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.T.; Ko, J.H.; Shin, H.; Sung, M.; Kim, J.Y. Drive-Through Screening Center for COVID-19: A Safe and Efficient Screening System against Massive Community Outbreak. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliger, P.; Hudson, P.J. Engineered antibody fragments and the rise of single domains. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh, G.; Devoogdt, N.; De Pauw, P.; Vincke, C.; Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies and their potential applications. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goode, J.; Dillon, G.; Millner, P.A. The development and optimization of nanobody based electrochemical immunosensors for IgG. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 234, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador, J.P.; Vilaplana, L.; Marco, M.P. Nanobody: Outstanding features for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Le Bas, A.; Ruza, R.R.; Duyvesteyn, H.; Mikolajek, H.; Malinauskas, T.; Tan, T.K.; Rijal, P.; Dumoux, M.; Ward, P.N.; et al. Neutralizing nanobodies bind SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD and block interaction with ACE2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girt, G.C.; Lakshminarayanan, A.; Huo, J.; Dormon, J.; Norman, C.; Afrough, B.; Harding, A.; James, W.; Owens, R.J.; Naismith, J.H. The use of nanobodies in a sensitive ELISA test for SARS-CoV-2 Spike 1 protein. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 211016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altawalah, H.; AlHuraish, F.; Alkandari, W.A.; Ezzikouri, S. Saliva specimens for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Kuwait: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 132, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, J.J.; Lamy, E.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Lopez-Jornet, P.; Capela E Silva, F.; Eckersall, P.D.; Tvarijonaviciute, A. Use of Saliva for Diagnosis and Monitoring the SARS-CoV-2: A General Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingsley, M.M.; Riley, R.S.; Day, E.S. Antibody-nanoparticle conjugates to enhance the sensitivity of ELISA-based detection methods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, M.; Wang, T.; Liang, M.; Wang, Z. Enzyme-Antibody-Modified Gold Nanoparticle Probes for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Nucleocapsid Protein in SFTSV. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, B.; Guedens, W.J.; Keene, C.; Kubiak-Ossowska, K.; Mulheran, P.; Kotowska, A.M.; Scurr, D.J.; Alexander, M.R.; Broisat, A.; Johnson, S.; et al. Direct Immobilization of Engineered Nanobodies on Gold Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 17353–17360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ju, C.; Han, C.; Shi, R.; Chen, X.; Duan, D.; Yan, J.; Yan, X. Nanozyme chemiluminescence paper test for rapid and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 173, 112817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.; Pt, U.; Kaduskar, O.; Vijay, N.; Rakhe, A.; Vidhate, S.; Khutwad, K.; Deshpande, G.R.; Tilekar, B.; Saka, S.; et al. Performance assessment of seven SARS-CoV-2 IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6696–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, I.; Poujois, S.; Albert, E.; Colomina, J.; Navarro, D. Evaluation of a rapid antigen test (Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag rapid test device) for SARS-CoV-2 detection in asymptomatic close contacts of COVID-19 patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 636.e1–636.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scohy, A.; Anantharajah, A.; Bodéus, M.; Kabamba-Mukadi, B.; Verroken, A.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H. Low performance of rapid antigen detection test as frontline testing for COVID-19 diagnosis. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strömer, A.; Rose, R.; Schäfer, M.; Schön, F.; Vollersen, A.; Lorentz, T.; Fickenscher, H.; Krumbholz, A. Performance of a Point-of-Care Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, N.; Khandker, S.S.; Haq, A.; Chaity, M.A.; Khalek, A.; Nazim, A.Q.; Kaitsuka, T.; Tomizawa, K.; Mie, M.; Kobatake, E.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by antigen ELISA test is highly swayed by viral load and sample storage condition. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.; El-Baz, H.; Demerdah, Z.; El-Karaksy, S.; El-Gendy, N.; Hassan, S.; Salah, F.; El-Moneem, E.; Hendawy, M.; Aly, I. Nano-immunoassay for diagnosis of active schistosomal infection. World J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Wu, W.B.; Yang, X.X.; Huang, C.Z. Gold Nanoparticle-based Enhanced ELISA for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 2935–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Rong, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Lu, J. Gold nanoparticle-based enzyme-linked antibody-aptamer sandwich assay for detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16974–16981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Total Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ct ≤ 30 | |||||
| In saliva | 93.30% | 100% | 100% | 98% | 98.4 |
| In nasopharyngeal swabs | 90% | 100% | 100% | 97% | 97.6 |
| Ct > 30- ≤ 35 | |||||
| In saliva | 87.50% | 100% | 100% | 95% | 96.2 |
| In nasopharyngeal swabs | 80% | 100% | 100% | 92% | 93.9 |
| Ct > 35- ≤ 40 | |||||
| In saliva | 86% | 100% | 100% | 93% | 95.1 |
| In nasopharyngeal swabs | 88% | 100% | 100% | 94% | 95.8 |
| Ct Value | RT-qPCR | Kappa Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | N | ||||
| Ct ≤ 30 | ELISA | P | 28 | 0 | 0.955 * |
| 21.9% | 0.0% | ||||
| N | 2 | 98 | |||
| 1.6% | 76.6% | ||||
| Ct > 30- ≤ 35 | ELISA | P | 35 | 0 | 0.908 * |
| 25.9% | 0.0% | ||||
| N | 5 | 95 | |||
| 3.7% | 70.4% | ||||
| Ct > 35- ≤40 | ELISA | P | 43 | 0 | 0.889 * |
| 30.1% | 0.0% | ||||
| N | 7 | 93 | |||
| 4.9% | 65.0% | ||||
| Ct Value | RT-qPCR | Kappa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | N | ||||
| Ct ≤ 30 | ELISA | P | 27 | 0 | 0.932 * |
| 21.3% | 0.0% | ||||
| N | 3 | 97 | |||
| 2.4% | 76.4% | ||||
| Ct > 30- ≤ 35 | ELISA | P | 32 | 0 | 0.848 * |
| 24.2% | 0.0% | ||||
| N | 8 | 92 | |||
| 6.1% | 69.7% | ||||
| Ct > 35- ≤ 40 | ELISA | P | 44 | 0 | 0.905 * |
| 30.6% | 0.0% | ||||
| N | 6 | 94 | |||
| 4.2% | 65.3% | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamel, M.; Maher, S.; El-Baz, H.; Salah, F.; Sayyouh, O.; Demerdash, Z. Non-Invasive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Saliva versus Nasopharyngeal Swabs Using Nanobodies Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7060102
Kamel M, Maher S, El-Baz H, Salah F, Sayyouh O, Demerdash Z. Non-Invasive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Saliva versus Nasopharyngeal Swabs Using Nanobodies Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(6):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7060102
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamel, Manal, Sara Maher, Hanan El-Baz, Faten Salah, Omar Sayyouh, and Zeinab Demerdash. 2022. "Non-Invasive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Saliva versus Nasopharyngeal Swabs Using Nanobodies Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 6: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7060102
APA StyleKamel, M., Maher, S., El-Baz, H., Salah, F., Sayyouh, O., & Demerdash, Z. (2022). Non-Invasive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Saliva versus Nasopharyngeal Swabs Using Nanobodies Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(6), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7060102





