Investigating Spatial Patterns of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Main Related Factors in Bandar Lampung, Indonesia Using Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
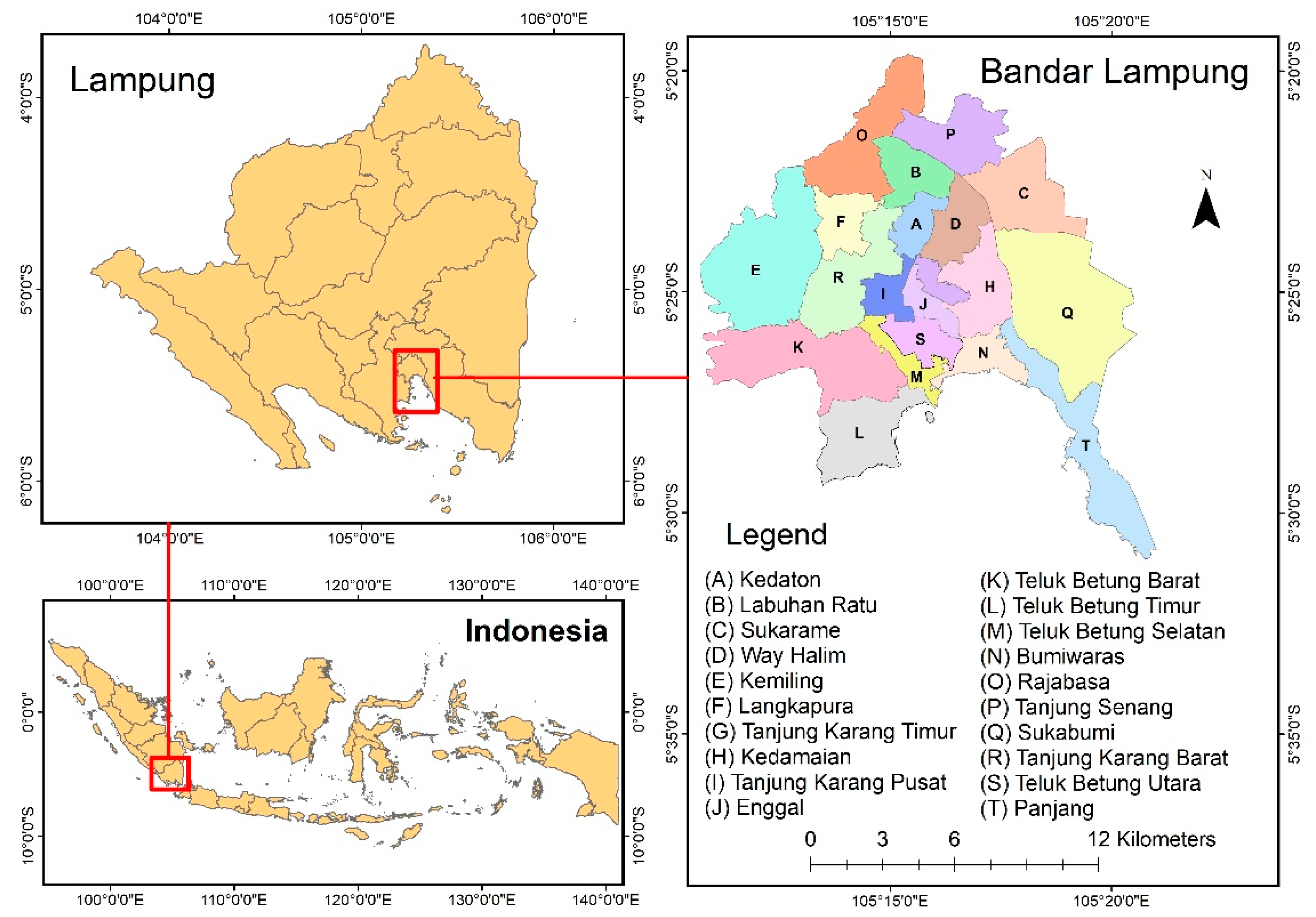
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Spatial Data Used in This Study
2.2.1. Socio-Demographic Data
2.2.2. Land Use Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Scatter Plot and Correlation Analysis
2.3.2. Ordinary Least Square (OLS)
2.3.3. Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression (GWPR)
2.3.4. Model Assessment
2.3.5. Investigating Spatial Patterns of Incidence Rate and Main Variables
3. Results
3.1. Correlation and OLS of AFB Smear-Positive Pulmonary TB
3.2. Estimation of Pulmonary TB Cases Based on GWPR Method
3.3. Statistical Analysis of GWPR Model
3.4. Spatial Pattern of Pulmonary TB Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021 [Homepage on the Internet]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Ahmed, A.; Mekonnen, D.; Shiferaw, A.M.; Belayneh, F.; Yenit, M.K. Incidence and determinants of tuberculosis infection among adult patients with HIV attending HIV care in north-east Ethiopia: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e016961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Hong, J.Y.; Yuan, M.K.; Chang, S.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Chang, S.C.; Hsu, L.C.; Chen, S.L. Risk factors in patients with AFB smear-positive sputum who receive inappropriate antituberculous treatment. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2013, 7, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acid-Fast Bacillus (AFB) Tests: MedlinePlus Medical Test. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/acid-fast-bacillus-afb-tests/ (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- Tanrikulu, A.C.; Acemoglu, H.; Palanci, Y.; Eren Dagli, C. Tuberculosis in Turkey: High altitude and other socio-economic risk factors. Public Health 2008, 122, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, S.W.; Fang, Q.; Chen, J.X.; Zhou, X.N. Spatial variations of pulmonary tuberculosis prevalence co-impacted by socio-economic and geographic factors in People’s Republic of China, 2010. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Ren, Z.P.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, S.W.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, J.F.; Zhou, X.N. Co-endemicity of pulmonary tuberculosis and intestinal helminth infection in the People’s Republic of China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.M.; Shah, S.A.; Mahmood, M.I. Geographical Information System (GIS) application in tuberculosis spatial clustering studies: A systematic review. Malays. J. Public Health Med. 2018, 18, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, S.; Enqueselassie, F.; Hagos, S. Spatial and space-time clustering of tuberculosis in Gurage Zone, Southern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masabarakiza, P.; Adel Hassaan, M. Spatial-temporal analysis of tuberculosis incidence in Burundi using GIS. Cent. Afr. J. Public Health 2019, 5, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchincloss, A.H.; Gebreab, S.Y.; Mair, C.; Diez Roux, A.V. A review of spatial methods in epidemiology, 2000–2010. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2012, 33, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahara, G.; Yang, K.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Guo, X. Socio-economic predictors and distribution of tuberculosis incidence in Beijing, China: A study using a combination of spatial statistics and GIS technology. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollalo, A.; Mao, L.; Rashidi, P.; Glass, G.E. A gis-based artificial neural network model for spatial distribution of tuberculosis across the continental united states. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alene, K.A.; Viney, K.; Moore, H.C.; Wagaw, M.; Clements, A.C.A. Spatial patterns of tuberculosis and HIV coinfection in Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.S.; Dos Santos, D.T.; Arcoverde, M.A.M.; Berra, T.Z.; Arroyo, L.H.; Ramos, A.C.V.; De Assis, I.S.; De Queiroz, A.A.R.; Alonso, J.B.; Alves, J.D.; et al. Detection of risk clusters for deaths due to tuberculosis specifically in areas of southern Brazil where the disease was supposedly a non-problem. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Amsalu, E.; Tao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. The spatio-temporal analysis of the incidence of tuberculosis and the associated factors in mainland China, 2009–2015. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rasam, A.R.; Mohd Shariff, N.; Dony, J.F. Geospatial-Based Model for Diagnosing Potential High-Risk Areas of Tuberculosis Disease in Malaysia. MATEC Web. Conf. 2019, 266, 02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yuan-Yuan, J.; Ci, Y.; Ahan, A.; Ming-Qin, C. Local spatial variations analysis of smear-positive tuberculosis in Xinjiang using Geographically Weighted Regression model. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J. Spatial distribution of tuberculosis and its socioeconomic influencing factors in mainland China 2013–2016. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2019, 24, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangisso, M.H.; Datiko, D.G.; Lindtjørn, B. Identifying geographical heterogeneity of pulmonary tuberculosis in southern Ethiopia: A method to identify clustering for targeted interventions. Glob. Health Action 2020, 13, 1785737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9789240013131. [Google Scholar]
- Rood, E.; Khan, A.H.; Modak, P.K.; Mergenthaler, C.; Van Gurp, M.; Blok, L.; Bakker, M. A spatial analysis framework to monitor and accelerate progress towards SDG 3 to end TB in Bangladesh. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemerintah Provinsi Lampung Dinkes. Riskesdas Profil Kesehatan Provinsi Lampung Tahun 2019; Pemerintah Provinsi Lampung Dinkes: Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 2019; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Badan Pusat Statistik Kota Bandar Lampung. Bandar Lampung in Figure 2021 [Homepage on the Internet]; Badan Pusat Statistik Kota Bandar Lampung: Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 2021; Available online: https://bandarlampungkota.bps.go.id/publication/2021/02/26/89c1b3d0038567aff884ca04/kota-bandar-lampung-dalam-angka-2021.html (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Badan Pusat Statistik Kota Bandar Lampung. Bandar Lampung in Figure 2022 [Homepage on the Internet]; Badan Pusat Statistik Kota Bandar Lampung: Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 2022; Available online: https://bandarlampungkota.bps.go.id/publication/2022/02/25/0890a0fd32082cf574db32af/kota-bandar-lampung-dalam-angka-2022.html (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Profil Perumahan Dan Kawasan Permukiman Kota Bandar Lampung—Perkim.Id. Available online: https://perkim.id/pofil-pkp/profil-kabupaten-kota/profil-perumahan-dan-kawasan-permukiman-kota-bandar-lampung/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Rencana Strategis Dinkes Provinsi Lampung Tahun 2015–2019; Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Lampung: Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 2019; Volume 58.
- Lestari, A. Pengaruh Terapi Psikoedukasi Keluarga Terhadap Pengetahuan dan Tingkat Ansietas Keluarga Dalam Merawat Anggota Keluarga yang Mengalami Tuberculosis Paru di Kota Bandar Lampung. J. Ilmiah Kesehatan 2011, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinas Kesehatan Kota Bandar Lampung. Bandar Lampung Health Profile 2015-2020 [Homepage on the Internet]. Dinas Kesehatan Kota Bandar Lampung: Bandar Lampung, Indonesia. 2020. Available online: https://dinkeskotabalam.com/laporan (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- BAPPEDA|Kota Bandar Lampung. Available online: https://bappeda.bandarlampungkota.go.id/ (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Singh, P.K.; Rai, R.K. Under-five mortality in high focus states in india: A district level geospatial analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0037515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, J. Exploring spatially varying and scale-dependent relationships between soil contamination and landscape patterns using geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 82, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, T.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically weighted poisson regression for disease association mapping. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 2695–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Soewarno. Hidrologi Aplikasi Metode Statistik untuk Analisa Data, 1st ed.; NOVA: Bandung, Indonesian, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Helland, I.S. On the interpretation and use of R2 in regression analysis. Biometrics 1987, 43, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorcintanami, S.; Widyaningsih, Y.; Abdullah, S. Geographically weighted models for modelling the prevalence of tuberculosis in Java. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2021, 1722, 012089. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, L.V.; Mor, Z.; Chemtob, D.; Ha, S.T.; Levine, H. Use of geographically weighted poisson regression to examine the effect of distance on tuberculosis incidence: A case study in Nam Dinh, Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Gong, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, J.; Ibrahim, A.N.; Zhou, Y. A spatial, social and environmental study of tuberculosis in China using statistical and GIS technology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 1425–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.A.P.S.; Albuquerque, M.F.P.M.; Ximenes, R.A.A.; Lucena-Silva, N.L.C.L.; Braga, C.; Campelo, A.R.L.; Dantas, O.M.S.; Montarroyos, U.R.; Souza, W.V.; Kawasaki, A.M.; et al. Risk factors for treatment delay in pulmonary tuberculosis in Recife, Brazil. BMC Public Health 2005, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelson, P.J.; Phypers, M. TB transmission on public transportation: A review of published studies and recommendations for contact tracing. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2011, 9, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbudebe, C.L.; Chukwu, J.N.; Nwafor, C.C.; Meka, A.O.; Ekeke, N.; Madichie, N.O.; Anyim, M.C.; Osakwe, C.; Onyeonoro, U.; Ukwaja, K.N.; et al. Reaching the underserved: Active tuberculosis case finding in urban slums in southeastern Nigeria. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2015, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bam, K.; Bhatt, L.P.; Thapa, R.; Dossajee, H.K.; Angdembe, M.R. Illness perception of tuberculosis (TB) and health seeking practice among urban slum residents of Bangladesh: A qualitative study. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, S.; Rahman, M.T.; Uddin, M.K.M.; Khatun, R.; Ahmed, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Husain, M.A.; van Leth, F. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in an urban slum of Dhaka City, Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0077721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerubo, G.; Amukoye, E.; Niemann, S.; Kariuki, S. Drug susceptibility profiles of pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from patients in informal urban settlements in Nairobi, Kenya. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, J.R.; Mayer, J.; Oren, E. The global health threat of African urban slums: The example of urban tuberculosis. Afr. Geogr. Rev. 2015, 34, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.R.; Boccia, D.; Evans, C.A.; Adato, M.; Petticrew, M.; Porter, J.D.H. The social determinants of tuberculosis: From evidence to action. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.; Lönnroth, K.; Carvalho, C.; Lima, F.; Carvalho, A.C.C.; Muñoz-Torrico, M.; Centis, R. Tuberculosis, social determinants and co-morbidities (including HIV). Pulmonology 2018, 24, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Rachow, A.; Ivanova, O.; Wallis, R.; Charalambous, S.; Jani, I.; Bhatt, N.; Kampmann, B.; Sutherland, J.; Ntinginya, N.E.; Evans, D.; et al. TB sequel: Incidence, pathogenesis and risk factors of long-term medical and social sequelae of pulmonary TB—A study protocol. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goschin, Z.; Druica, E. Regional factors hindering tuberculosis spread in Romania: Evidence from a semiparimetric GWR model. J. Soc. Sci. Econ. 2017, 6, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, R.; Thiruvengadam, K.; Jayabal, L.; Selvaraju, S.; Watson, B.; Malaisamy, M.; Nagarajan, K.; Tripathy, S.P.; Chinnaiyan, P.; Chandrasekaran, P. An influence of dew point temperature on the occurrence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis disease in Chennai, India. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, R.; Sheng, L.; Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Hou, J.; Yuan, L.; Ke, L.; et al. Temperature and humidity associated with increases in tuberculosis notifications: A time-series study in Hong Kong. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 149, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.M.d.C.; Martins, E.d.S.; Pedrosa, D.M.A.S.; Evangelista, M.d.S.N. Relationship between climatic factors and air quality with tuberculosis in the Federal District, Brazil, 2003–2012. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Lin, H.C.; Yang, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Ling, M.P.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, W.Y.; You, S.H.; Lu, T.H.; Liao, C.M. Association between ambient air pollution and elevated risk of tuberculosis development. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3835–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.C.; Chiang, C.Y.; Wu, C.F.; Yang, S.L.; Liu, D.P.; Chan, C.C.; Lin, H.H. Ambient air pollution and risk of tuberculosis: A cohort study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 73, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Xiang, H.; Yang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, L.; Deng, S.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, X.; et al. Short-term effect of air pollution on tuberculosis based on kriged data: A time-series analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dye, C.; Lönnroth, K.; Jaramillo, E.; Williams, B.G.; Raviglione, M. Trends in tuberculosis incidence and their determinants in 134 countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2009, 87, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaliq, A.; Khan, I.H.; Akhtar, M.W.; Chaudhry, M.N. Environmental risk factors andsocial determinants of pulmonary tuberculosis in Pakistan. Epidemiol. Open Access 2015, 5, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, L.M.; Bhatt, L.D.; Karmacharya, I.; Yadav, D.K. Dietary practice and nutritional status of tuberculosis patients in Pokhara: A cross sectional study. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heunis, J.C.; Kigozi, N.G.; Chikobvu, P.; Botha, S.; Van Rensburg, H.D. Risk factors for mortality in TB patients: A 10-year electronic record review in a South African province. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimeles, E.; Enquselassie, F.; Aseffa, A.; Tilahun, M.; Mekonen, A.; Wondimagegn, G.; Hailu, T. Risk factors for tuberculosis: A case–control study in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lu, W.; Li, X.; Shen, H. Specific urban units identified in tuberculosis epidemic using a geographical detector in Guangzhou, China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemahagn, M.A.; Alene, G.D.; Yimer, S.A. Spatial-temporal clustering of notified pulmonary tuberculosis and its predictors in East Gojjam Zone, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Ju, K.; Gao, Y.M.; Pan, J. The association between internal migration and pulmonary tuberculosis in China, 2005-2015: A spatial analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwitira, I.; Karumazondo, N.; Shekede, M.D.; Sandy, C.; Siziba, N.; Chirenda, J. Spatial patterns of pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) cases in Zimbabwe from 2015 to 2018. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, C.; Kim, Y. Spatial pattern of tuberculosis (TB) and related socio-environmental factors in South Korea, 2008–2016. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, W.; Cai, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Epidemiological characteristics of tuberculosis and effects of meteorological factors and air pollutants on tuberculosis in Shijiazhuang, China: A distribution lag non-linear analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaweno, D.; Karmakar, M.; Alene, K.A.; Ragonnet, R.; Clements, A.C.; Trauer, J.M.; Denholm, J.T.; McBryde, E.S. Methods used in the spatial analysis of tuberculosis epidemiology: A systematic review. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Kesehatan, R.I. Indonesia Health Profile 2020 [Homepage on the Internet]; Kementerian Kesehatan RI: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2020; Available online: https://pusdatin.kemkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin/profil-kesehatan-indonesia/Profil-Kesehatan-Indonesia-Tahun-2020.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Lampung. Lampung Health Profile 2020 [Homepage on the Internet]; Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Lampung: Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 2020; Available online: https://dinkes.lampungprov.go.id/wpfd_file/profil-kesehatan-provinsi-lampung-tahun-2020/ (accessed on 15 August 2022).






| No. | Data | Data Class | Timespan | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Number of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Cases | Socio-demographic | 2020 | [29] |
| 2 | Pulmonary Tuberculosis Growth Rate | Socio-demographic | 2015–2020 | [29] |
| 3 | Population | Socio-demographic | 2020 | [24] |
| 4 | Distance to the Urban Center | Land Use | 2020 | [24] |
| 5 | Industrial Area | Land Use | 2020 | [30] |
| 6 | Green Open Space Area | Land Use | 2020 | [30] |
| 7 | Slums Area | Land Use | 2020 | [30] |
| 8 | Built Area (GAIA) | Land Use | 1985–2018 | [31] |
| Variable | Coefficient | StdError | t-Statistics | Probability | Robust_SE | Robust_t | Robust_Pr | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −7.420 | 25.487 | −0.291 | 0.078 | 19.944 | −0.372 | 0.716 | - |
| Population | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.320 | 0.006 * | 0.001 | 5.773 | 0.000 * | 2.631 |
| Distance to the Urban Center | −3.416 | 1.975 | −1.730 | 0.109 | 1.336 | −2.556 | 0.025 * | 1.828 |
| Industrial Area | 0.167 | 3.763 | 0.044 | 0.965 | 2.568 | 0.065 | 0.949 | 3.678 |
| Green Open Space | −40.034 | 56.106 | −0.714 | 0.489 | 37.453 | −1.069 | 0.306 | 1.931 |
| Built Area | −8.995 | 6.864 | −1.311 | 0.215 | 5.318 | −1.691 | 0.117 | 2.591 |
| 5 Years Average Pulmonary TB Growth Rate | 5.615 | 1.157 | 4.581 | 0.000 * | 1.195 | 4.697 | 0.001 * | 1.352 |
| Slums | 0.249 | 0.143 | 1.735 | 0.108 | 0.078 | 3.190 | 0.008 * | 2.633 |
| Diagnostics of OLS | ||||||||
| Number of Observations | 20 | Akaike’s Information Criterion (AICc) | 205.284 | |||||
| Multiple R-Squared | 0.83 | Adjusted R-Squared | 0.73 | |||||
| Joint F-Statistics | 8.288 | Prob (>F), (7,12) degrees of freedom | 0.001 * | |||||
| Joint Wald Statistics | 177.349 | Prob (>chi-squared), (7) degrees of freedom | 0.000 * | |||||
| Koenker (BP) Statistics | 9.603 | Prob (>chi-squared), (7) degrees of freedom | 0.212 * | |||||
| Jarque–Bera Statistics | 0.896 | Prob (>chi-squared), (2) degrees of freedom | 0.639 * | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Helmy, H.; Kamaluddin, M.T.; Iskandar, I.; Suheryanto. Investigating Spatial Patterns of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Main Related Factors in Bandar Lampung, Indonesia Using Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090212
Helmy H, Kamaluddin MT, Iskandar I, Suheryanto. Investigating Spatial Patterns of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Main Related Factors in Bandar Lampung, Indonesia Using Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(9):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090212
Chicago/Turabian StyleHelmy, Helina, Muhammad Totong Kamaluddin, Iskhaq Iskandar, and Suheryanto. 2022. "Investigating Spatial Patterns of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Main Related Factors in Bandar Lampung, Indonesia Using Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 9: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090212
APA StyleHelmy, H., Kamaluddin, M. T., Iskandar, I., & Suheryanto. (2022). Investigating Spatial Patterns of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Main Related Factors in Bandar Lampung, Indonesia Using Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(9), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090212







