Molecular Surveillance for Vector-Borne Bacteria in Rodents and Tree Shrews of Peninsular Malaysia Oil Palm Plantations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. To Identify the Rodent and Tree Shrew Species Available at Oil Palm Plantations
2.2. To Detect the Presence of Vector-Borne Bacteria in the Rodents and Tree Shrews Captured in Oil Palm Plantations
| Organism | Target | Primer | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rodents | COI | BatL5310 a,c | ACTTCTGGGTGTCCAAAGAATCA | 726 | [23] |
| R6036R b,c | CCTACTCRGCCATTTTACCTATG | ||||
| Orientia tsutsugamushi | TSA47 | Ot-145F a | ACAGGCCAAGATATTGGAAG | 871 | [24] |
| Ot-1780R b | AATCGCCTTTAAACTAGATTTACTTATTA | ||||
| Ot-263F a,c | GTGCTAAGAAARGATGATACTTC | 821 | |||
| Ot-1133R b,c | ACATTTAACATACCACGACGAAT | ||||
| Bartonella spp. | gltA | BhCS.781p a,c | GGGGACCAGCTCATGGTGG | 379 | [28] |
| BhCS.1137n b,c | AATGCAAAAAGAACAGTAAACA | ||||
| Borrelia spp. | flaB | BflaPAD a | GATCARGCWCAAYATAACCAWATGCA | 800 | [25] |
| BflaPDU b | AGATTCAAGTCTGTTTTGGAAAGC | ||||
| BflaPBU a,c | GCTGAAGAGCTTGGAATGCAACC | 345 | |||
| BflaPCR b,c | TGATCAGTTATCATTCTAATAGCA | ||||
| Rickettsia spp. | gltA | CS1d a,c | ATGACTAATGGCAATAATAA | 889 | [26] |
| CS890r b,c | GCTTTIAGCTACATATTTAGG | ||||
| CS-239 a,c | GCTCTTCTCATCCTATGGCTATTAT | 830 | [27] | ||
| CS-1069 b,c | CAGGGTCTTCGTGCATTTCTT |
2.3. To Determine the Genetic Relatedness of the Detected Bacteria to Well-Characterized Counterparts
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Small Mammal Species
3.2. PCR Detection of Bacteria in Small Mammals
3.3. Sequence Analyses of the Detected Bacteria
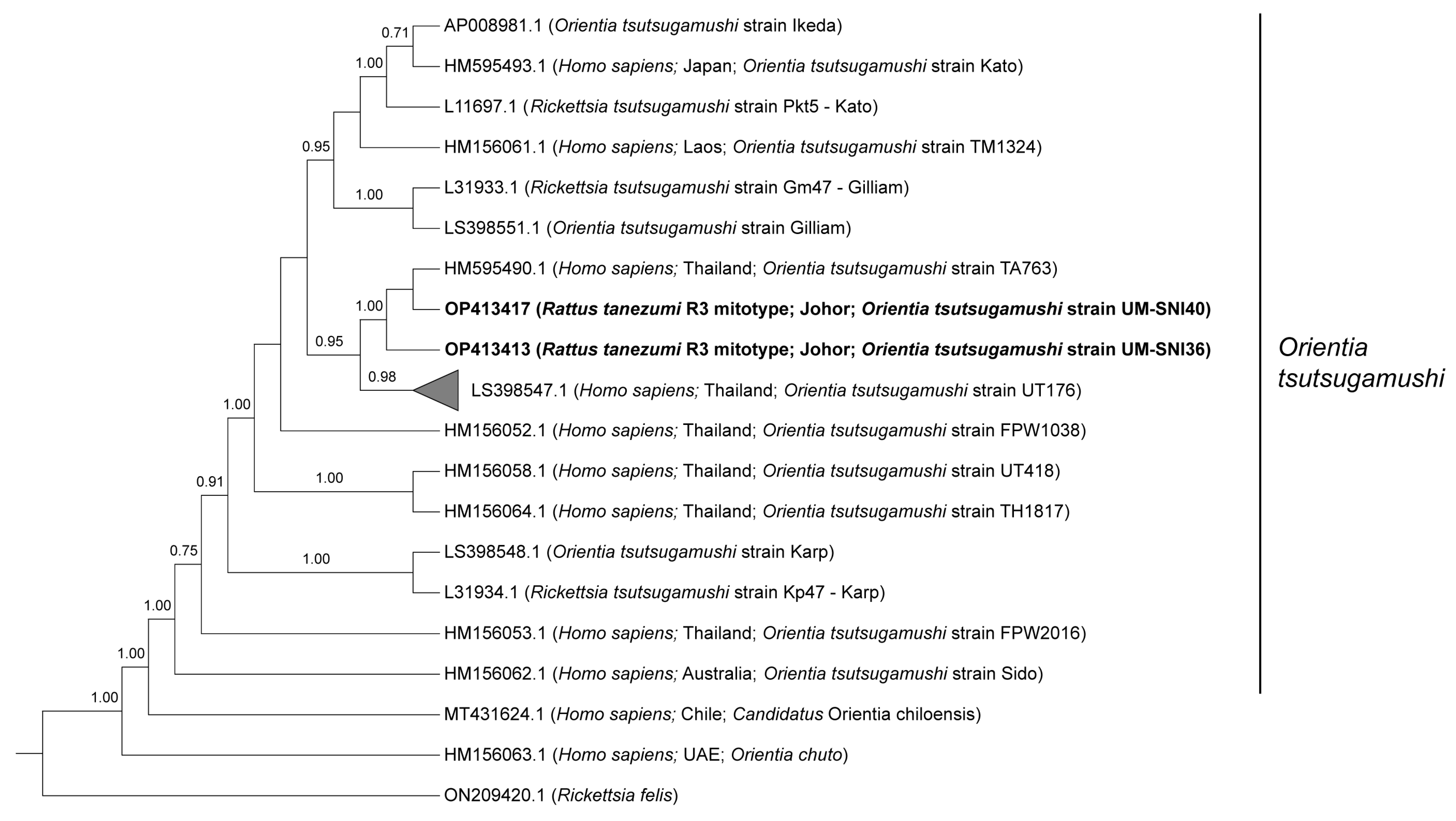
3.3.1. Orientia tsutsugamushi
3.3.2. Borrelia spp.
3.3.3. Bartonella spp.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muul, I.; Lim, B.L.; Walker, J.S. Scrub typhus infection in rats in four habitats in Peninsular Malaysia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1977, 71, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, S.; Blasdell, K.; Bordes, F.; Buchy, P.; Carcy, B.; Chaisiri, K.; Chaval, Y.; Claude, J.; Cosson, J.F.; Desquesnes, M.; et al. Changing landscapes of Southeast Asia and rodent-borne diseases: Decreased diversity but increased transmission risks. Ecol. Appl. 2019, 29, e01886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.A.; Huxley, P.; Elmes, J.; Murray, K.A. Agricultural land-uses consistently exacerbate infectious disease risks in Southeast Asia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karski, J.; Okoński, M.; Pietrzyk, D.; Karska, K.; Zaluski, M. Cat scratch disease in a 1.5-year-old girl-case report. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luce-Fedrow, A.; Lehman, M.L.; Kelly, D.J.; Mullins, K.; Maina, A.N.; Stewart, R.L.; Ge, H.; John, H.S.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L. A review of scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi and related organisms): Then, now, and tomorrow. J. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pun, S.B.; Agrawal, S.; Jha, S.; Bhandari, L.N.; Chalise, B.S.; Mishra, A.; Shah, R. First report of Lyme disease in Nepal. JMM Case Rep. 2018, 5, e005128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A. Louse-borne relapsing fever (Borrelia recurrentis infection). Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khor, C.S.; Hassan, H.; Mohdrahim, N.; Chandren, J.; Nore, S.S.; Johari, J.; Loong, S.K.; Abd-Jamil, J.; Khoo, J.J.; Lee, H.; et al. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi among the indigenous people (Orang Asli) of Peninsular Malaysia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loong, S.K.; Abd-Majid, M.A.; Teoh, B.T.; Cheh, M.J.; Khor, C.S.; Chao, C.C.; Khoo, J.J.; AbuBakar, S. Leptospirosis among dengue-negative febrile patients in Selangor, Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.N.; Shimizu, K.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Yunianto, A.; Salwati, E.; Yasuda, S.; Koma, T.; Rika, E.; Arikawa, J. Epidemiology of hantavirus infection in Thousand Islands regency of Jakarta, Indonesia. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leibler, J.H.; Zakhour, C.M.; Gadhoke, P.; Gaeta, J.M. Zoonotic and vector-borne infections among urban homeless and marginalized people in the United States and Europe, 1990-2014. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthawong, A.; Grieco, J.P.; Ngoen-klan, R.; Chao, C.C.; Chareonviriyaphap, T. Detection of Anaplasma spp. and Bartonella spp. from wild-caught rodents and their ectoparasites in Nakhon Ratchasima Province, Thailand. J. Vector Ecol. 2020, 45, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, S.T.; Mohamed Zan, H.A.; Lim, Y.A.; Ngui, R. Antibody prevalence and factors associated with exposure to Orientia tsutsugamushi in different aboriginal subgroups in West Malaysia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, W.T. Gender and livelihoods: A case study of the Mah Meri and the oil palm plantations of Carey Island. Asian J. Women’s Stud. 2011, 17, 66–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinniah, B.; Sabaridah, I.; Soe, M.; Sabitha, P.; Awang, I.; Ong, G.; Hassan, A. Determining the prevalence of intestinal parasites in three Orang Asli (Aborigines) communities in Perak, Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 29, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Loong, S.K.; Chen, H.; Ling, I.; Nellis, S.; Khor, C.; Mohd Rahim, N.; Hassan, H.; Chao, C.C.; Abu Bakar, S. Serological evidence of high Leptospira exposure among indigenous people (Orang Asli) in Peninsular Malaysia using a recombinant antigen-based ELISA. Trop. Biomed. 2018, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheela, A.; Ghermandi, A.; Vineetha, P.; Sheeja, R.; Justus, J.; Ajayakrishna, K. Assessment of relation of land use characteristics with vector-borne diseases in tropical areas. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkkey, H.; Tyson, A.; Choiruzzad, S.A.B. Palm oil intensification and expansion in Indonesia and Malaysia: Environmental and socio-political factors influencing policy. For. Policy Econ. 2018, 92, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Jongsakul, K.; Chouriyagune, C.; Paris, R. Differentiating dengue virus infection from scrub typhus in Thai adults with fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohd-Azami SN, I.; Loong, S.K.; Khoo, J.J.; Sahimin, N.; Lim, F.S.; Husin, N.A.; Mahfodz, N.H.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Ishak, S.N.; Makepeace, B.L.; et al. Molecular evidence of rat bocavirus among rodents in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruedas, L. A guide to the mammals of Southeast Asia. Q. Rev. Biol. 2008, 83, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbreteau, V.; Jittapalapong, S.; Rerkamnuaychoke, W.; Chaval, Y.; Cosson, J.F.; Morand, S. Protocols for Field and Laboratory Rodent Studies. 2011. Available online: http://www.ceropath.org/FichiersComplementaires/Herbreteau_Rodents_protocols_2011.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- Masakhwe, C.; Linsuwanon, P.; Kimita, G.; Mutai, B.; Leepitakrat, S.; Yalwala, S.; Abuom, D.; Auysawasi, N.; Gilbreath, T.; Wanja, E. Identification and characterization of Orientia chuto in Trombiculid chigger mites collected from wild rodents in Kenya. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01124-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, A.C.; Qiu, Y.; Moustafa MA, M.; Nakao, R.; Shimozuru, M.; Onuma, M.; Mohd-Azlan, J.; Tsubota, T. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and relapsing fever Borrelia in feeding Ixodes ticks and rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New geographical records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi. J. Pathogens 2020, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, V.; Rydkina, E.; Eremeeva, M.; Raoult, D. Citrate synthase gene comparison, a new tool for phylogenetic analysis, and its application for the rickettsiae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1997, 47, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labruna, M.B.; Whitworth, T.; Horta, M.C.; Bouyer, D.H.; McBride, J.W.; Pinter, A.; Popov, V.; Gennari, S.M.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsia species infecting Amblyomma cooperi ticks from an area in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, where Brazilian spotted fever is endemic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, K.; Maruyama, S.; Kabeya, H.; Yamada, N.; Ohashi, N.; Sato, Y.; Yukawa, M.; Masuzawa, T.; Kawamori, F.; Kadosaka, T. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella species isolated from wild rodents in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5086–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margos, G.; Gatewood, A.G.; Aanensen, D.M.; Hanincová, K.; Terekhova, D.; Vollmer, S.A.; Cornet, M.; Piesman, J.; Donaghy, M.; Bormane, A.; et al. MLST of housekeeping genes captures geographic population structure and suggests a European origin of Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8730–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonthayanon, P.; Peacock, S.J.; Chierakul, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Blacksell, S.D.; Holden MT, G.; Bentley, S.D.; Feil, E.J.; Day, N.P.J. High rates of homologous recombination in the mite endosymbiont and opportunistic human pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. J Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with Beauti and the Beast 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoo, J.J.; Lim, F.S.; Tan, K.K.; Chen, F.S.; Phoon, W.H.; Khor, C.S.; Pike, B.L.; Chang, L.Y.; AbuBakar, S. Detection in Malaysia of a Borrelia sp. from Haemaphysalis hystricis (Ixodida: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J.J.; Ishak, S.N.; Lim, F.S.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Khor, C.S.; Loong, S.K.; AbuBakar, S. Detection of a Borrelia sp. from Ixodes granulatus ticks collected from rodents in Malaysia. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binetruy, F.; Garnier, S.; Boulanger, N.; Talagrand-Reboul, É.; Loire, E.; Faivre, B.; Noël, V.; Buysse, M.; Duron, O. A novel Borrelia species, intermediate between Lyme disease and relapsing fever groups, in neotropical passerine-associated ticks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, G.S.; Kramer, M.; Göbel, U.B.; Wallich, R. Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, E.J.; Koh, S.E.; Park, T.K.; Jang, W.J.; Park, K.H.; Kim, B.J.; Kook, Y.H.; Lee, S.H. Evaluation of groEL gene analysis for identification of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1270–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elliott, I.; Pearson, I.; Dahal, P.; Thomas, N.V.; Roberts, T.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus ecology: A systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tay, S.T.; Kaewanee, S.; Ho, T.M.; Rohani, M.Y.; Devi, S. Serological evidence of natural infection of wild rodents (Rattus spp. and Tupaia glis) with rickettsiae in Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1998, 29, 560–562. [Google Scholar]
- Frances, S.P.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Tanskul, P. Occurrence of Orientia tsutsugamushi in chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) and small animals in an orchard near Bangkok, Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 1999, 36, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frances, S.P.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Tanskul, P. Investigation of the role of Blankaartia acuscutellaris (Acari: Trombiculidae) as a vector of scrub typhus in central Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2001, 32, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodkvamtook, W.; Ruang-Areerate, T.; Gaywee, J.; Richards, A.L.; Jeamwattanalert, P.; Bodhidatta, D.; Sangjun, N.; Prasartvit, A.; Jatisatienr, A.; Jatisatienr, C. Isolation and characterization of Orientia tsutsugamushi from rodents captured following a scrub typhus outbreak at a military training base, Bothong district, Chonburi province, central Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chareonviriyaphap, T.; Leepitakrat, W.; Lerdthusnee, K.; Chao, C.C.; Ching, W.M. Dual exposure of Rickettsia typhi and Orientia tsutsugamushi in the field-collected Rattus rodents from Thailand. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsuwanon, P.; Krairojananan, P.; Rodkvamtook, W.; Leepitakrat, S.; Davidson, S.; Wanja, E. Surveillance for scrub typhus, rickettsial diseases, and leptospirosis in US and multinational military training exercise Cobra Gold sites in Thailand. US Army Med. Dep. J. 2018, 18, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rodkvamtook, W.; Kuttasingkee, N.; Linsuwanon, P.; Sudsawat, Y.; Richards, A.L.; Somsri, M.; Sangjun, N.; Chao, C.C.; Davidson, S.; Wanja, E.; et al. Scrub typhus outbreak in Chonburi Province, Central Thailand, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elders, P.N.D.; Swe, M.M.M.; Phyo, A.P.; McLean, A.R.D.; Lin, H.N.; Soe, K.; Htay, W.Y.A.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Hla, T.K.; Tun, N.N.; et al. Serological evidence indicates widespread distribution of rickettsioses in Myanmar. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Luksameetanasan, R.; Kalambaheti, T.; Aukkanit, N.; Paris, D.H.; McGready, R.; Nosten, F.; Peacock, S.J.; Day, N.P.J. Genetic typing of the 56-kDa type-specific antigen gene of contemporary Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates causing human scrub typhus at two sites in north-eastern and western Thailand. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanifah, A. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi in chiggers and tissues of small mammals using polymerase chain reactions. Experiment 2013, 11, 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Wongprompitak, P.; Anukool, W.; Wongsawat, E.; Silpasakorn, S.; Duong, V.; Buchy, P.; Morand, S.; Frutos, R.; Ekpo, P.; Suputtamongkol, Y. Broad-coverage molecular epidemiology of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Thailand. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, I.; Thangnimitchok, N.; Chaisiri, K.; Wangrangsimakul, T.; Jaiboon, P.; Day, N.P.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N.; Morand, S. Orientia tsutsugamushi dynamics in vectors and hosts: Ecology and risk factors for foci of scrub typhus transmission in northern Thailand. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, S.; Rohani, M.; Devi, S. Isolation and PCR detection of rickettsiae from clinical and rodent samples in Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2002, 33, 772–779. [Google Scholar]
- Chaisiri, K.; Cosson, J.-F.; Morand, S. Infection of rodents by Orientia tsutsugamushi, the agent of scrub typhus in relation to land use in Thailand. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takhampunya, R.; Korkusol, A.; Promsathaporn, S.; Tippayachai, B.; Leepitakrat, S.; Richards, A.L.; Davidson, S.A. Heterogeneity of Orientia tsutsugamushi genotypes in field-collected trombiculid mites from wild-caught small mammals in Thailand. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takhampunya, R.; Korkusol, A.; Pongpichit, C.; Yodin, K.; Rungrojn, A.; Chanarat, N.; Promsathaporn, S.; Monkanna, T.; Thaloengsok, S.; Tippayachai, B.; et al. Metagenomic approach to characterizing disease epidemiology in a disease-endemic environment in northern Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.C.; Ghersi, B.M.; Alda, F.; Firth, C.; Frye, M.J.; Bai, Y.; Osikowicz, L.M.; Riegel, C.; Lipkin, I.; Kosoy, M.Y.; et al. Rodent-borne Bartonella infection varies according to host species within and among cities. EcoHealth 2017, 14, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisberg, B.; Campbell, J.; Bozeman, F. Antigenic diversity of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: Epidemiologic and ecologic significance. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1968, 12, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shirai, A.; Tanskul, P.; Andre, R.; Dohany, A.; Huxsoll, D. Rickettsia tsutsugamushi strains found in chiggers collected in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1981, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, V.; Mai TT, X.; Blasdell, K.; Lo, L.V.; Morvan, C.; Lay, S.; Anukool, W.; Wongprompitak, P.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Laurent, D.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Cambodia and Central Vietnam reveals a broad region-wide genetic diversity. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 15, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan Anh, L.T.; Viet Cuong, V.; Van Toan, T.; Thi Hong Nhung, H.; Van Anh, L.T.; Thi Thu Thuy, C.; Thi Ha Giang, P.; Thi Thanh Nga, B.; Thi Lan Anh, B.; Van Chau, N. Detection of DNA of Rickettsia and Orientia tsutsugamushi in rodents and ectoparasites in Ha Giang Province. Vietnam J. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Pham HT, T.; Hoang, H.T.; Trang, T.C.; Vu, T.N.; Ung TT, H.; Shimizu, K.; Arikawa, J.; Yamada, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; et al. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi in small mammals in Hanoi, Vietnam. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernieenor FC, L.; NorJaiza, M.J.; Fadillah, A.; Canedy, J.; Mariana, A. Screening and genotyping of Orientia tsutsugamushi from field-collected on-host chiggers (Acari: Prostigmata) recovered from a positive scrub typhus locality in Kelantan, Malaysia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 84, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkathiry, H.; Al-Rofaai, A.; Ya’cob, Z.; Cutmore, T.S.; Mohd-Azami SN, I.; Husin, N.A.; Lim, F.S.; Koosakulnirand, S.; Mahfodz, N.H.; Ishak, S.N.; et al. Habitat and season drive chigger mite diversity and abundance on small mammals in Peninsular Malaysia. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M.H.; Mispan, M.S.; Bhassu, S.; Khoo, J.J.; Abubakar, S.; Mohd-Azami, S.N.I.; Ishak, S.N.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Omar, H. Spatial distribution of Rattus species (Rodentia: Muridae) in oil palm plantations of Peninsular Malaysia with species verification using Cytochrome Oxidase I (COI) gene. J. Oil Palm Res. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, F.; Blasdell, K.; Morand, S. Transmission ecology of rodent-borne diseases: New frontiers. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Khlyap, L.; Cosson, J.F.; Morand, S. Aboriginal and invasive rats of genus Rattus as hosts of infectious agents. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S.; Bordes, F.; Blasdell, K.; Pilosof, S.; Cornu, J.-F.; Chaisiri, K.; Chaval, Y.; Cosson, J.-F.; Claude, J.; Feyfant, T.; et al. Assessing the distribution of disease-bearing rodents in human-modified tropical landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.H.; Aukkanit, N.; Jenjaroen, K.; Blacksell, S.D.; Day, N.P. A highly sensitive quantitative real-time PCR assay based on the groEL gene of contemporary Thai strains of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Paris, D.H.; Blacksell, S.D.; Aukkanit, N.; Newton, P.N.; Phetsouvanh, R.; Izzard, L.; Stenos, J.; Graves, S.R.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Diversity of the 47-kDa HtrA nucleic acid and translated amino acid sequences from 17 recent human isolates of Orientia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tay, S.T.; Kamalanathan, M.; Suan, K.A.; Chun, S.; Ming, H.; Md Yasin, R.; Sekaran, S. Seroepidemiologic survey of Orientia tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia typhi, and TT118 spotted fever group rickettsiae in rubber estate workers in Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tay, S.T.; Ho, T.M.; Rohani, M.Y.; Devi, S. Antibodies to Orientia tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia typhi and spotted fever group rickettsiae among febrile patients in rural areas of Malaysia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 94, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagin, D.D.; Ismail, G.; Nasian, L.M.; Jok, J.J.; Pang, E.K. Rickettsial infection in five remote Orang Ulu villages in upper Rejang River, Sarawak, Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2000, 31, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furuno, K.; Lee, K.; Itoh, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Yonemitsu, K.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Watarai, M.; Maeda, K.; Takano, A. Epidemiological study of relapsing fever borreliae detected in Haemaphysalis ticks and wild animals in the western part of Japan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumagai, Y.; Sato, K.; Taylor, K.R.; Zamoto-Niikura, A.; Imaoka, K.; Morikawa, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Kawabata, H. A relapsing fever group Borrelia sp. is widely distributed among wild deer in Japan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakamura, A.; Yoshitomi, H.; Song, Y.; Ashizuka, Y. Detection of Borrelia DNA in tick species collected from vegetation and wild animals in Fukuoka, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 73, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoo, J.J.; Husin, N.A.; Lim, F.S.; Oslan SN, H.; Mohd Azami SN, I.; To, S.W.; Abd Majid, M.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Loong, S.K.; Khor, C.S.; et al. Molecular detection of pathogens from ectoparasites recovered from peri-domestic animals, and the first description of a Candidatus Midichloria sp. from Haemaphysalis wellingtoni from rural communities in Malaysia. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 80, 102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhampunya, R.; Thaloengsok, S.; Tippayachai, B.; Promsathaporn, S.; Leepitakrat, S.; Gross, K.; Davidson, S.A. Retrospective survey of Borrelia spp. from rodents and ticks in Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, T.G.; Anderson, J.M.; Lopez, J.E.; Fischer, R.J.; Raffel, S.J.; McCoy, B.N.; Safronetz, D.; Sogoba, N.; Maïga, O.; Traoré, S.F. Endemic foci of the tick-borne relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia crocidurae in Mali, West Africa, and the potential for human infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye EH, I.; Diouf, F.S.; Ndiaye, M.; Bassene, H.; Raoult, D.; Sokhna, C.; Parola, P.; Diatta, G. Tick-borne relapsing fever borreliosis, a major public health problem overlooked in Senegal. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.R.; Takano, A.; Konnai, S.; Shimozuru, M.; Kawabata, H.; Tsubota, T. Borrelia miyamotoi infections among wild rodents show age and month independence and correlation with Ixodes persulcatus larval attachment in Hokkaido, Japan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siński, E.; Welc-Falęciak, R.; Zajkowska, J. Borrelia miyamotoi: A human tick-borne relapsing fever spirochete in Europe and its potential impact on public health. Adv. Med. Sci. 2016, 61, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platonov, A.E.; Karan, L.S.; Kolyasnikova, N.M.; Makhneva, N.A.; Toporkova, M.G.; Maleev, V.V.; Fish, D.; Krause, P.J. Humans infected with relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi, Russia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sthitmatee, N.; Jinawan, W.; Jaisan, N.; Tangjitjaroen, W.; Chailangkarn, S.; Sodarat, C.; Ekgatat, M.; Padungtod, P. Genetic and immunological evidences of Borrelia burgdorferi in dog in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2016, 47, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata, H.; Takano, A.; Kadosaka, T.; Fujita, H.; Nitta, Y.; Gokuden, M.; Honda, T.; Tomida, J.; Kawamura, Y.; Masuzawa, T.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing and DNA similarity analysis implicates that a Borrelia valaisiana-related sp. isolated in Japan is distinguishable from European B. Valaisiana. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loong, S.K.; Ishak, S.N.; Lim, F.S.; Khoo, J.J.; Tan, S.N.; Freddy-Jalin, E.J.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; AbuBakar, S. Paenibacillus lautus, an opportunistic bacterial pathogen, isolated from Ixodes granulatus Supino (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from a Müller’s giant Sunda rat (Sundamys muelleri). Syst. Appl. Acarol 2018, 23, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Chu, C.Y.; Takano, A.; Jiang, B.G.; Liu, W.; Kurtenbach, K.; Masuzawa, T.; Fingerle, V.; Cao, W.C.; Kawabata, H. Borrelia yangtzensis sp. nov., a rodent-associated species in Asia, is related to Borrelia valaisiana. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3836–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Yun, N.R.; Kim, D.M. Case report: The first Borrelia yangtzensis infection in a human in Korea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 106, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasdell, K.R.; Perera, D.; Firth, C. High prevalence of rodent-borne Bartonella spp. in urbanizing environments in Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, V.; Tan, T.; Ibrahim, J.; AbuBakar, S.; Lim, Y. First evidence of Bartonella phoceensis and Candidatus Mycoplasma haemomuris subsp. ratti in synanthropic rodents in Malaysia. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 13, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asyikha, R.; Sulaiman, N.; Mohd-Taib, F.S. Detection of Bartonella sp. in ticks and their small mammal hosts in mangrove forests of Peninsular Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2020, 37, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangthong, K.; Promsthaporn, S.; Leepitakrat, S.; Schuster, A.L.; McCardle, P.W.; Kosoy, M.; Takhampunya, R. The distribution and diversity of Bartonella species in rodents and their ectoparasites across Thailand. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No. | Species | Trapping Site | Total Number of Individuals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perak (n) | Johor (n) | |||||
| Residential Areas | Paddy Field | Oil Palm Plantation | Oil Palm Plantation | |||
| 1. | Rattus tanezumi R3 mitotype | 14 | 2 | 45 | 52 | 113 |
| 2. | Rattus tiomanicus | 2 | 0 | 7 | 13 | 22 |
| 3. | Rattus exulans | 3 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 17 |
| 4. | Rattus tanezumi sensu stricto | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5. | Rattus argentiventer | 0 | 21 | 3 | 0 | 24 |
| 6. | Tupaia glis | 3 | 0 | 4 | 33 | 40 |
| Total number of individuals | 116 | 101 | 217 | |||
| Location | Host Species | Detected Vector-Borne Bacteria | Number of Positive Individuals (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perak | Rattus tanezumi R3 mitotype | Bartonella phoceensis | 8 |
| Orientia tsutsugamushi | 11 | ||
| Borrelia sp. (LD) | 1 | ||
| Borrelia sp. (RF) | 4 | ||
| Rattus exulans | Borrelia sp. (undetermined) | 1 | |
| Orientia tsutsugamushi | 2 | ||
| Rattus argentiventer | Bartonella phoceensis | 1 | |
| Orientia tsutsugamushi | 2 | ||
| Rattus tiomanicus | Borrelia sp. (RF) | 1 | |
| Tupaia glis | Borrelia sp. (RF) | 1 | |
| Johor | Rattus tanezumi R3 mitotype | Bartonella phoceensis | 1 |
| Orientia tsutsugamushi | 7 | ||
| Borrelia sp. (LD) | 3 | ||
| Rattus tiomanicus | Orientia tsutsugamushi | 1 | |
| Tupaia glis | Orientia tsutsugamushi | 2 | |
| Borrelia sp. (RF) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohd-Azami, S.N.I.; Loong, S.K.; Khoo, J.J.; Husin, N.A.; Lim, F.S.; Mahfodz, N.H.; Ishak, S.N.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Makepeace, B.L.; AbuBakar, S. Molecular Surveillance for Vector-Borne Bacteria in Rodents and Tree Shrews of Peninsular Malaysia Oil Palm Plantations. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8020074
Mohd-Azami SNI, Loong SK, Khoo JJ, Husin NA, Lim FS, Mahfodz NH, Ishak SN, Mohd-Taib FS, Makepeace BL, AbuBakar S. Molecular Surveillance for Vector-Borne Bacteria in Rodents and Tree Shrews of Peninsular Malaysia Oil Palm Plantations. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(2):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8020074
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohd-Azami, Siti Nurul Izzah, Shih Keng Loong, Jing Jing Khoo, Nurul Aini Husin, Fang Shiang Lim, Nur Hidayana Mahfodz, Siti Nabilah Ishak, Farah Shafawati Mohd-Taib, Benjamin L. Makepeace, and Sazaly AbuBakar. 2023. "Molecular Surveillance for Vector-Borne Bacteria in Rodents and Tree Shrews of Peninsular Malaysia Oil Palm Plantations" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 2: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8020074
APA StyleMohd-Azami, S. N. I., Loong, S. K., Khoo, J. J., Husin, N. A., Lim, F. S., Mahfodz, N. H., Ishak, S. N., Mohd-Taib, F. S., Makepeace, B. L., & AbuBakar, S. (2023). Molecular Surveillance for Vector-Borne Bacteria in Rodents and Tree Shrews of Peninsular Malaysia Oil Palm Plantations. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(2), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8020074






