Human Defensin 5 Inhibits Plasmodium yoelii Development in Anopheles stephensi by Promoting Innate Immune Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Rearing and Infection
2.2. HD5 Treatment
2.3. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative PCR
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. RNA Interference
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
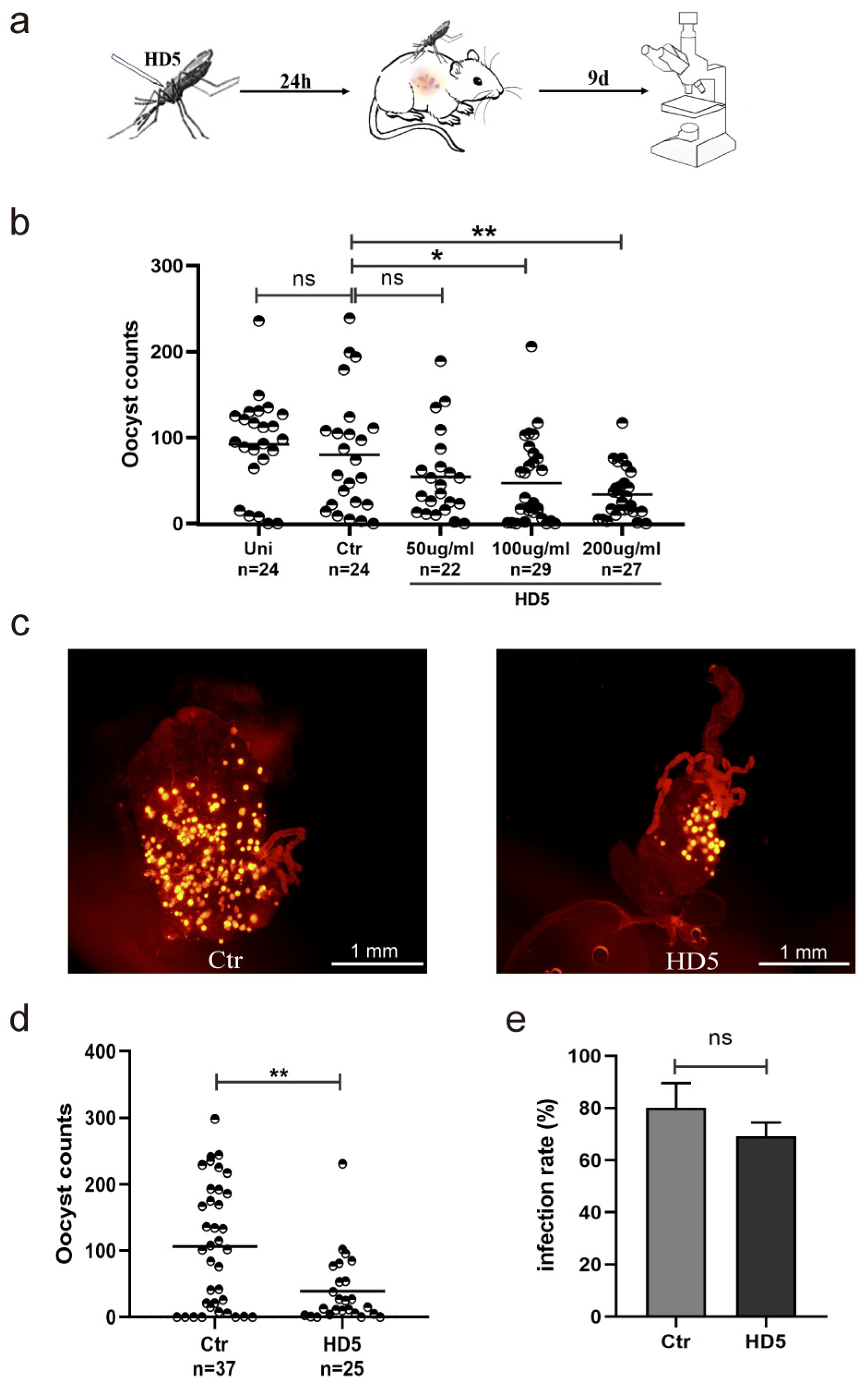
3.1. HD5 Injection Prior to Infection Reduced P. yoelii Infection Density in An. stephensi
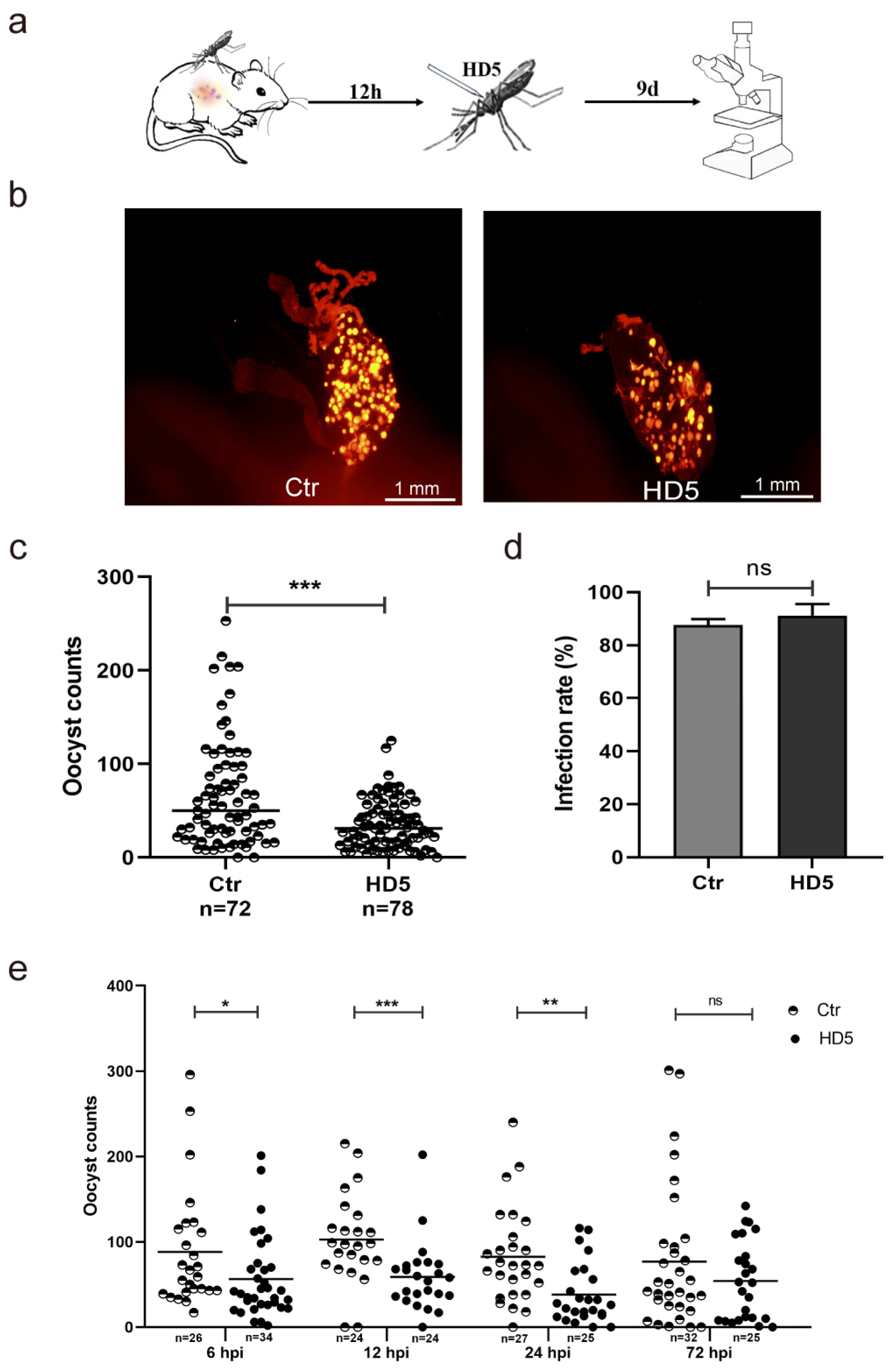
3.2. HD5 Treatment Post-Infection Inhibited P. yoelii Infection in An. stephensi
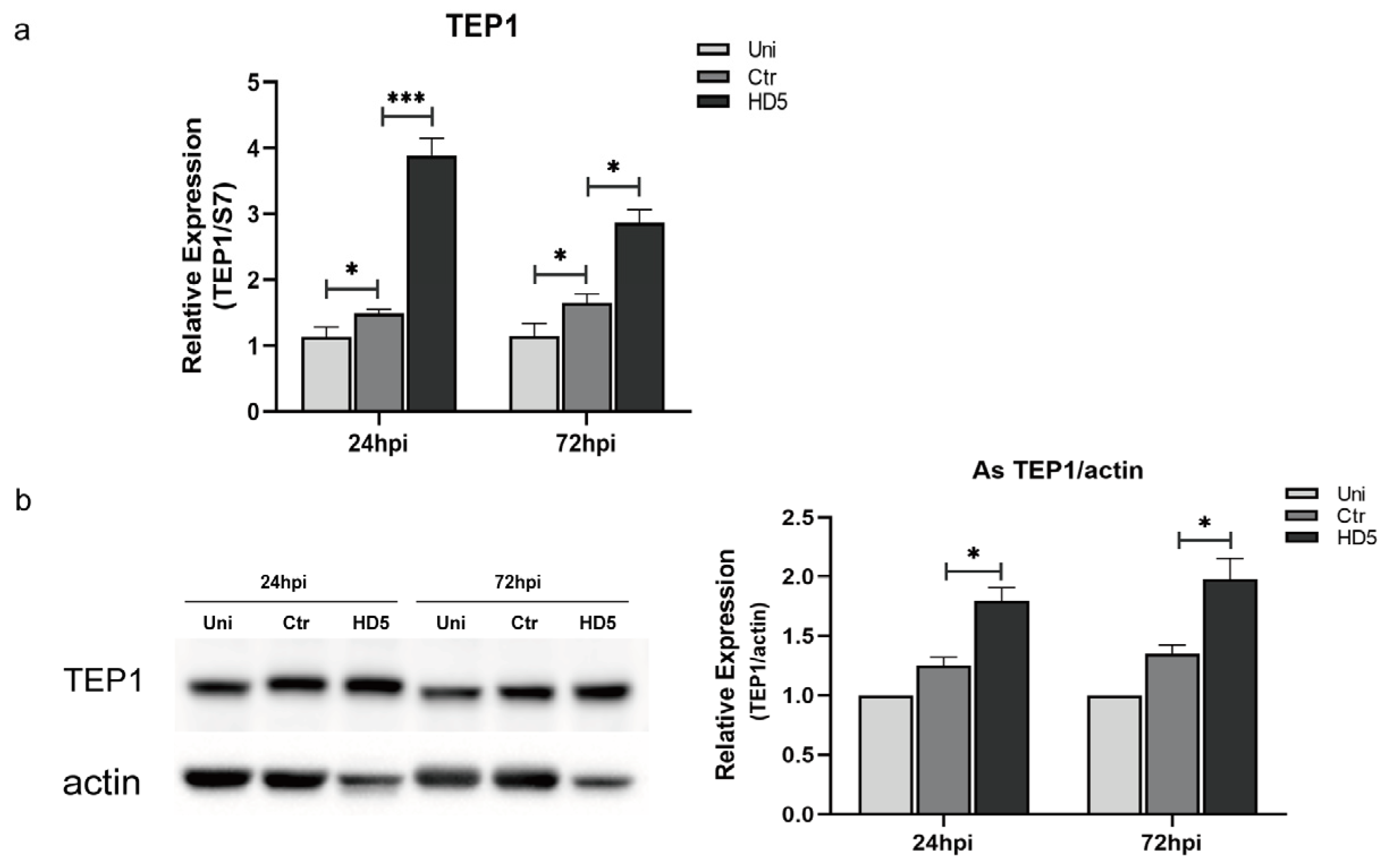
3.3. HD5 Treatment Upregulated TEP1 Expression in An. stephensi
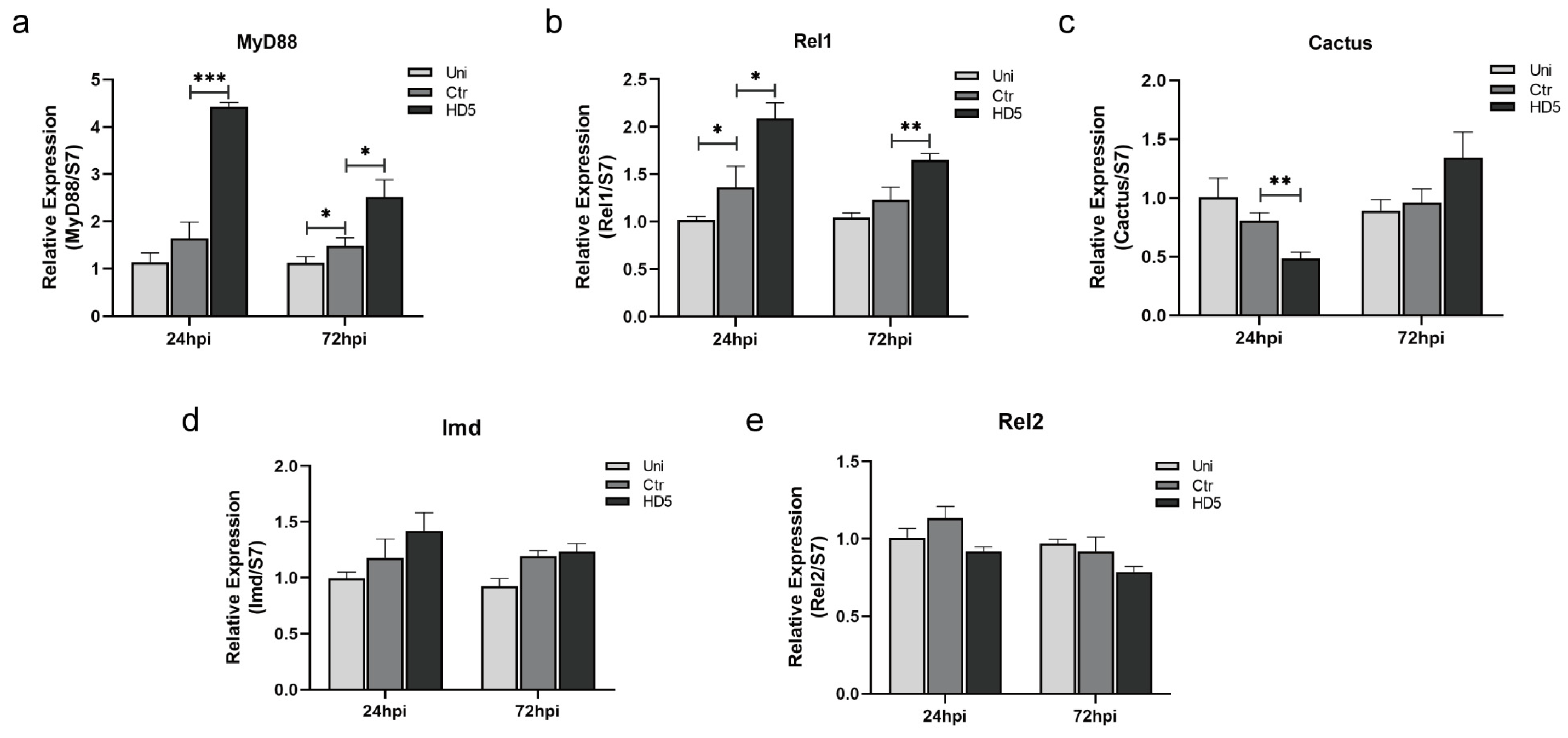
3.4. Toll Signaling Pathway Was Upregulated by Injection with HD5
3.5. Inhibition of Oocyst Development in An. stephensi by HD5 Could Be Reversed by Toll Signaling Pathway Interference
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2023; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Biabi, M.; Fogang, B.; Essangui, E.; Maloba, F.; Donkeu, C.; Keumoe, R.; Cheteug, G.; Magoudjou, N.; Slam, C.; Kemleu, S.; et al. High Prevalence of Polyclonal Plasmodium falciparum Infections and Association with Poor IgG Antibody Responses in a Hyper-Endemic Area in Cameroon. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, J. The role of vector control in stopping the transmission of malaria: Threats and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volohonsky, G.; Paul-Gilloteaux, P.; Stafkova, J.; Soichot, J.; Salamero, J.; Levashina, E.A. Kinetics of Plasmodium midgut invasion in Anopheles mosquitoes. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, A.M.; Dong, Y.; Dimopoulos, G. The Anopheles innate immune system in the defense against malaria infection. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Xia, Q. Research progress in anti-inflammatory activity of insect antimicrobial peptides and anti-inflammatory mechanism based on signal pathway. Tianjin Med. J. 2022, 50, 1002–1008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Ding, J.; Liao, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, W. Defensins: The natural peptide antibiotic. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlett, L.; Wu, M. Defensins in innate immunity. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheim, J.J.; Biragyn, A.; Kwak, L.W.; Yang, D. Roles of antimicrobial peptides such as defensins in innate and adaptive immunity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62 (Suppl. 2), ii17–ii21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovlev, A.Y.; Nesin, A.P.; Simonenko, N.P.; Gordya, N.A.; Tulin, D.V.; Kruglikova, A.A.; Chernysh, S.I. Fat body and hemocyte contribution to the antimicrobial peptide synthesis in Calliphora vicina R.-D. (Diptera: Calliphoridae) larvae. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2017, 53, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, M.; Fields, I.; Bulet, P.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Miller, L.H. Plasmodium gallinaceum: Differential killing of some mosquito stages of the parasite by insect defensin. Exp. Parasitol. 1998, 89, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandin, S.; Moita, L.F.; Kocher, T.; Wilm, M.; Kafatos, F.C.; Levashina, E.A. Reverse genetics in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae: Targeted disruption of the Defensin gene. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Alto, B.W.; Smartt, C.T.; Shin, D. Transcription Profiling for Defensins of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) during Development and in Response to Infection with Chikungunya and Zika Viruses. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cunliffe, R.N.; Rose, F.R.; Keyte, J.; Abberley, L.; Chan, W.C.; Mahida, Y.R. Human defensin 5 is stored in precursor form in normal Paneth cells and is expressed by some villous epithelial cells and by metaplastic Paneth cells in the colon in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2001, 48, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, D.; Liddell, S.; Mahida, Y.R. Impaired luminal processing of human defensin-5 in Crohn’s disease: Persistence in a complex with chymotrypsinogen and trypsin. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Battur, B.; Boldbaatar, D.; Liao, M.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. Parasiticidal activity of human alpha-defensin-5 against Toxoplasma gondii. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.M.; Yang, H.X. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 and human defensin 5 in primary endocervical epithelial cells. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaq, F.; Swain, S.; Kumar, S.S. Anopheles stephensi (Asian Malaria Mosquito). Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simwela, N.V.; Waters, A.P. Current status of experimental models for the study of malaria. Parasitology 2022, 149, 729–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conteh, S.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Anderson, C.; Hoffman, S.L. Plasmodium yoelii-infected A. stephensi inefficiently transmit malaria compared to intravenous route. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8947. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, J.; Fong, M.Y.; Lau, Y.L. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of Anopheles dirus TEP1 and NOS during Plasmodium berghei infection, using three reference genes. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, N.A.; Duduit, J.R.; Huang, D.; Zhao, F.; Ranney, T.G.; Liu, W. Stepwise Optimization of Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2653, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Wang, P.; Qin, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y. Bacillus sphaericus exposure reduced vector competence of Anopheles dirus to Plasmodium yoelii by upregulating the Imd signaling pathway. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volohonsky, G.; Hopp, A.K.; Saenger, M.; Soichot, J.; Scholze, H.; Boch, J.; Blandin, S.A.; Marois, E. Transgenic Expression of the Anti-parasitic Factor TEP1 in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, R.V.; Sousa, G.L.; Sneed, S.D.; Farrant, K.V.; Christophides, G.K.; Povelones, M. Stimulation of a protease targeting the LRIM1/APL1C complex reveals specificity in complement-like pathway activation in Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Contet, A.; Hou, C.D.; Levashina, E.A.; Baxter, R. Anopheles gambiae TEP1 forms a complex with the coiled-coil domain of LRIM1/APL1C following a conformational change in the thioester domain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Arends, B.R.; Smith, R.C. Late-phase immune responses limiting oocyst survival are independent of TEP1 function yet display strain specific differences in Anopheles gambiae. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirimotich, C.M.; Dong, Y.; Garver, L.S.; Sim, S.; Dimopoulos, G. Mosquito immune defenses against Plasmodium infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souvannaseng, L.; Hun, L.V.; Baker, H.; Klyver, J.M.; Wang, B.; Pakpour, N.; Bridgewater, J.M.; Napoli, E.; Giulivi, C.; Riehle, M.A.; et al. Inhibition of JNK signaling in the Asian malaria vector Anopheles stephensi extends mosquito longevity and improves resistance to Plasmodium falciparum infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandin, S.; Shiao, S.H.; Moita, L.F.; Janse, C.J.; Waters, A.P.; Kafatos, F.C.; Levashina, E.A. Complement-like protein TEP1 is a determinant of vectorial capacity in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Cell 2004, 116, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B.; Nicolas, E.; Michaut, L.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Pillars article: The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996. 86: 973-983. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5210–5220. [Google Scholar]
- Barletta, A.; Saha, B.; Trisnadi, N.; Talyuli, O.; Raddi, G.; Barillas-Mury, C. Hemocyte differentiation to the megacyte lineage enhances mosquito immunity against Plasmodium. eLife 2022, 11, e81116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassanayake, R.S.; Silva, G.Y.; Tobe, S.S. Evolutionary selective trends of insect/mosquito antimicrobial defensin peptides containing cysteine-stabilized alpha/beta motifs. Peptides 2007, 28, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.Y.; Chowdhury, M.; Huang, Y.D.; Yu, X.Q. Insect antimicrobial peptides and their applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5807–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, A.N.; Rocher, J.; D’Alencon, E.; Bouton, M.; Landais, I.; Quesada-Moraga, E.; Vey, A.; Fournier, P.; Mita, K.; Devauchelle, G. Characterization and transcriptional profiles of three Spodoptera frugiperda genes encoding cysteine-rich peptides. A new class of defensin-like genes from lepidopteran insects? Gene 2003, 319, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulet, P.; Cociancich, S.; Reuland, M.; Sauber, F.; Bischoff, R.; Hegy, G.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A. A novel insect defensin mediates the inducible antibacterial activity in larvae of the dragonfly Aeschna cyanea (Paleoptera, Odonata). Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 209, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, C.A.; Lima, A.C.; Jansen, A.M.; Galvao, C.; Jurberg, J.; Costa, J.; Azambuja, P.; Waniek, P.J. Genes encoding defensins of important Chagas disease vectors used for phylogenetic studies. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4503–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Garrido, P.; Cardenas-Guerra, R.E.; Martinez, I.; Poggio, S.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, K.; Rivera-Santiago, L.; Ortega-Lopez, J.; Sanchez-Esquivel, S.; Espinoza, B. Differential activity on trypanosomatid parasites of a novel recombinant defensin type 1 from the insect Triatoma (Meccus) pallidipennis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 139, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vomackova, K.B.; Sassu, F.; Volf, P.; Telleria, E.L. RNAi-mediated gene silencing of Phlebotomus papatasi defensins favors Leishmania major infection. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1182141. [Google Scholar]
- Kokoza, V.; Ahmed, A.; Cho, W.L.; Jasinskiene, N.; James, A.A.; Raikhel, A. Engineering blood meal-activated systemic immunity in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9144–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Koo, H.; Richman, A.M.; Seeley, D.; Vizioli, J.; Klocko, A.D.; O’Brochta, D.A. Ectopic expression of a cecropin transgene in the human malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae): Effects on susceptibility to Plasmodium. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoza, V.; Ahmed, A.; Woon, S.S.; Okafor, N.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Blocking of Plasmodium transmission by cooperative action of Cecropin A and Defensin A in transgenic Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8111–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Takano, R.; Furukawa, A.; Murakoshi, F.; Kato, K. Involvement of beta-defensin 130 (DEFB130) in the macrophage microbicidal mechanisms for killing Plasmodium falciparum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| As-TEP 1 | F: ACCGATTGTCCAAGTTCTCG |
| R: AGCGCATCTGGTTCTGGTAG | |
| As-MyD88 | F: TCGGCGGACAGTGACATTATTACG |
| R: TCACGATCCTTCAGACACAGTTGC | |
| As-Rel 1 | F: GAACTGGATTCGGTCACGCTAAGG |
| R: CGGCAGATAATCAGGTCGGACATG | |
| As-Cactus | F: CGCTTGCAGATGCTAGTGGTCAG |
| R: CCGCTGTTCGCTGGCTGTTC | |
| As-Imd | F: CGACCGGAATGCAGGTGTATCAG |
| R: CCGCAGAGCCACTCGTTGAAG | |
| As-Rel 2 | F: AATTACCCGCATTCTGATCG |
| R: CTCCAGCACGTAGTTCACGA | |
| As-S7 | F: CTAACGACACGAAGACCACAAGA |
| R: CAACCTGCAACGACAGCAAAA |
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| T7-dsGFP | F: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGTCAAGTTCAACGTGTCCGGCG |
| R: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGGACCATTTGATCGCGCTT | |
| T7-dsTEP1 | F: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGTCGGGCTGAAGGCGTTGACC |
| R: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGTGCCACCTTGAATCGTCTGA | |
| T7-dsMyD88 | F: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGGTGAGCGTCAAAGAGACG |
| R: TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGTTTTACTGGCTTGTCCGGCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Zheng, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y. Human Defensin 5 Inhibits Plasmodium yoelii Development in Anopheles stephensi by Promoting Innate Immune Response. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080169
Liu T, Wang J, Li X, Yu S, Zheng D, Liu Z, Yang X, Wang Y. Human Defensin 5 Inhibits Plasmodium yoelii Development in Anopheles stephensi by Promoting Innate Immune Response. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2024; 9(8):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080169
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tingting, Jing Wang, Xin Li, Shasha Yu, Dan Zheng, Zhilong Liu, Xuesen Yang, and Ying Wang. 2024. "Human Defensin 5 Inhibits Plasmodium yoelii Development in Anopheles stephensi by Promoting Innate Immune Response" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 9, no. 8: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080169
APA StyleLiu, T., Wang, J., Li, X., Yu, S., Zheng, D., Liu, Z., Yang, X., & Wang, Y. (2024). Human Defensin 5 Inhibits Plasmodium yoelii Development in Anopheles stephensi by Promoting Innate Immune Response. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 9(8), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080169





