GANs and Artificial Facial Expressions in Synthetic Portraits
Abstract
:1. Generative Adversarial Networks
2. Artificial Creativity
3. Results
3.1. Prosopagnosia Project
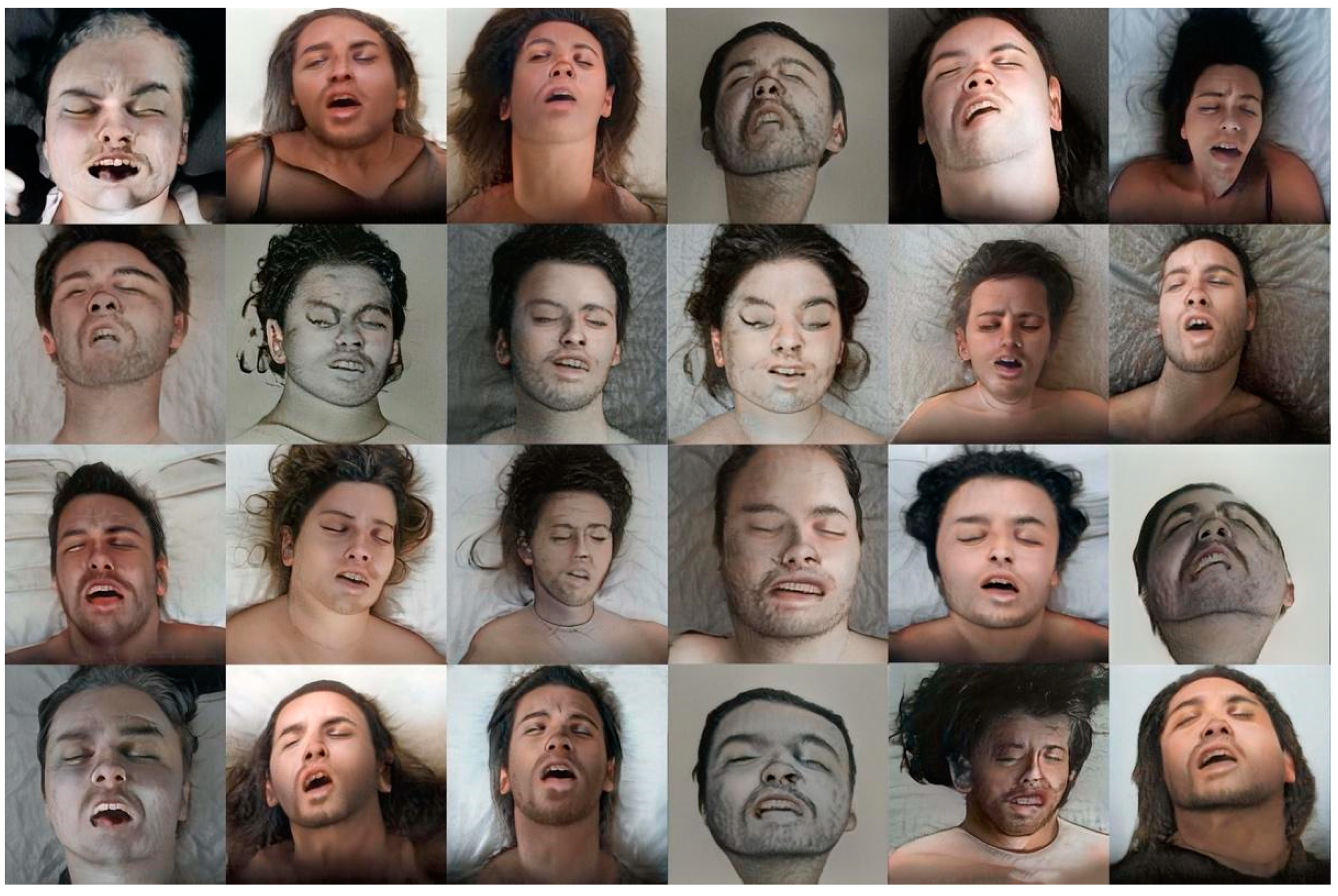
3.2. Beautiful Agony and La Petite Mort Projects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Generative Adversarial Networks


Appendix A.2. StyleGAN Training

Appendix A.3. Latent Space Representation of Our Data

References
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warder-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 2, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Wang, K.; Gou, C.; Duan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, F.Y. Generative adversarial networks: Introduction and outlook. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Hwang, U.; Yoo, J.; Yoon, S. How generative adversarial networks and their variants work: An overview. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; She, Q.; Ward, T.E. Generative Adversarial Networks: A Survey and Taxonomy. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.01529.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Gui, J.; Sun, Z.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Ye, J. A Review on Generative Adversarial Networks: Algorithms, Theory, and Applications. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2001.06937.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5967–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability and Variation. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.10196.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4396–4405. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and improving the image quality of StyleGAN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8107–8116. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Sun, X.; Li, K.; Guo, L.; Han, J. Perturbation-Seeking Generative Adversarial Networks: A Defense Framework for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, G.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Two-Stream Encoder GAN with Progressive Training for Co-Saliency Detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Laine, S.; Härkönen, E.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Alias-Free Generative Adversarial Networks. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.12423.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Härkönen, E.; Hertzmann, A.; Lehtinen, J.; Paris, S. Ganspace: Discovering Interpretable GAN Controls. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.02546.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, Z. Attribute-aware face aging with wavelet-based generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11869–11878. [Google Scholar]
- Broad, T.; Leymarie, F.F.; Grierson, M. Network bending: Expressive manipulation of deep generative models. In Artificial Intelligence in Music, Sound, Art and Design; Romero, J., Martins, T., Rodríguez-Fernández, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; p. 645. [Google Scholar]
- Manovich, L. Defining AI Arts: Three Proposals. Available online: http://manovich.net/content/04-projects/107-defining-ai-arts-three-proposals/manovich.defining-ai-arts.2019.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Boden, M.A. Inteligencia Artificial; Turner Noema: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Berns, S.; Colton, S. Bridging Generative Deep Learning and Computational Creativity. Available online: http://computationalcreativity.net/iccc20/papers/164-iccc20.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Fontcuberta, J.; Rosado, P. Prosopagnosia; RM Verlag: Barcelona, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Checa, A. Prensa y Partidos Políticos Durante la II República; Universidad de Salamanca: Salamanca, Spain, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.I. The Artist in the Machine: The World of AI-Powered Creativity; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiza, M.; Fernández, T.; Tamaro, E. Biografía de Alphonse Bertillon. Available online: https://www.biografiasyvidas.com/biografia/b/bertillon.htm (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Fontcuberta, J.; Rosado, P. Beautiful Agony. In Par le Rêve. Panorama 23; Kaeppelin, O., Ed.; Lefresnoy: Tourcoing, France, 2021; pp. 80–81. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado, P. La Petite Mort: Simulación artificial de la expresión de un orgasmo. In Cuerpos Conectados. Arte, Identidad y Autorrepresentación en la Sociedad Transmedia; Baigorri, L., Ortuño, P., Eds.; Dykinson: Madrid, Spain, 2021; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Fontcuberta, J.; Rosado, P. Prosopagnosia, Link to the Video on Vimeo. Available online: https://vimeo.com/495021778 (accessed on 27 July 2020).







| Nomenclature | Referred to |
|---|---|
| AdaIN | Adaptive Instance Normalization |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| CONV | Convolution Layer |
| DCGAN | Deep Convolutional GAN |
| FC | Full Connected Layer |
| FFHQ | Flickr-Faces-High Quality |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Networks |
| GPU | Graphical Processing Unit |
| NVlabs | NVIDIA Research Projects |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| ProGAN | Progressively Growing GAN |
| StyleGAN | Style-Based Generator Architecture for GAN |
| PSGAN | Perturbation-seeking GAN |
| TSE-GAN | Two Stream Encoder GAN |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosado, P.; Fernández, R.; Reverter, F. GANs and Artificial Facial Expressions in Synthetic Portraits. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2021, 5, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5040063
Rosado P, Fernández R, Reverter F. GANs and Artificial Facial Expressions in Synthetic Portraits. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2021; 5(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosado, Pilar, Rubén Fernández, and Ferran Reverter. 2021. "GANs and Artificial Facial Expressions in Synthetic Portraits" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 5, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5040063
APA StyleRosado, P., Fernández, R., & Reverter, F. (2021). GANs and Artificial Facial Expressions in Synthetic Portraits. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 5(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5040063







