Promoting Agritourism in Poland with Ready-Made Digital Components and Rustic Cyberfolklore
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Digital Artefacts and Digital Folklore
2.2. Digital Ready-Made Graphics
2.3. New Trends in Website Design
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Procedure and Sampling
3.2. Research Object
4. Results
4.1. Results of Digital Artefact Analysis
4.2. Investigation into the ccTLD Websites
5. Discussion
5.1. Digital Artefacts Bear Witness to the Evolution of the Web
5.2. The Digital Ecosystem Is Made from Ready-Made Components
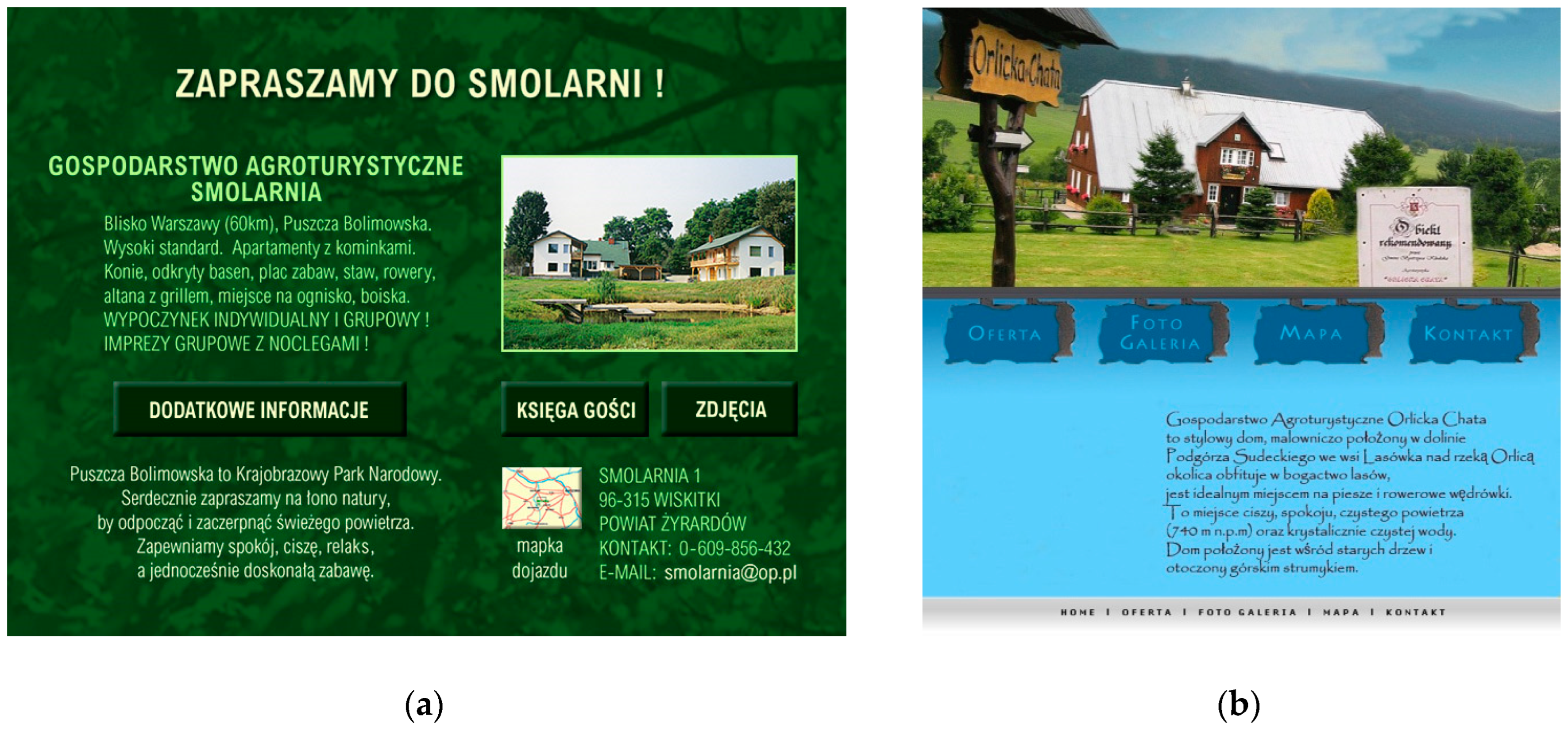
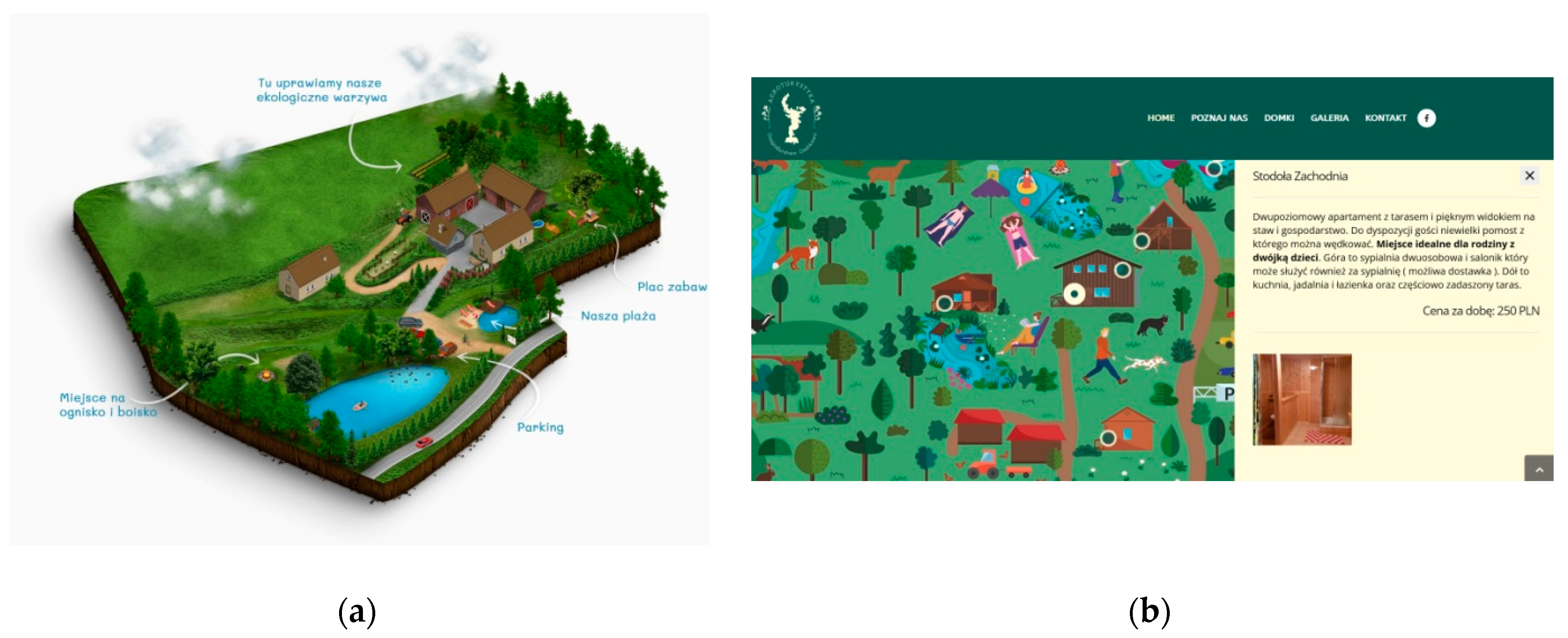
5.3. Evolution of Design—The Case Study
6. Conclusions
6.1. Practical Implications
6.2. Limitations and Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ante, L. The non-fungible token (NFT) market and its relationship with Bitcoin and Ethereum. Fintech 2022, 1, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, K. Forgotten agritourism: Abandoned websites in the promotion of rural tourism in Poland. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2019, 10, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnaby, P. Citizen-created content, digital equity and the preservation of community memory. In Proceedings of the 75th IFLA General Conference and Council: World Library and Information Congress, Milan, Italy, 23–27 August 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Huurdeman, H.C.; Kamps, J.; Samar, T.; de Vries, A.P.; Ben-David, A.; Rogers, R.A. Lost but not forgotten: Finding pages on the unarchived web. Int. J. Digit. Libr. 2015, 16, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thouvenin, F.; Hettich, P.; Burkert, H.; Gasser, U. 4 Web Archives. In Remembering and Forgetting in the Digital Age; Law, Governance and Technology Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Charter on the Preservation of Digital Heritage. 2003. Available online: https://bit.ly/unesco-digital (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Smith, L. Uses of Heritage; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Król, K. Digital cultural heritage of rural tourism facilities in Poland. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 11, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronner, S.J. Practice theory in folklore and folklife studies. Folklore 2012, 123, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshenblatt-Gimblett, B. Intangible heritage as metacultural production1. Mus. Int. 2004, 56, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błachowski, A. Polska Sztuka Ludowa Jako Kategoria Kultury. Kultura Ludowa.pl. 2016. Available online: https://kulturaludowa.pl/artykuly/polska-sztuka-ludowa-jako-kategoria-kultury/ (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Platania, M. Agritourism farms and the web. An exploratory evaluation of their websites. Agris-Line Pap. Econ. Inform. 2014, 6, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicha, K.; Rutecka, P. Quality Factors for Agro-touristic Websites—An Exploratory Study. In Marketing and Smart Technologies; Reis, J.L., López, E.P., Moutinho, L., Santos, J.P.M.d., Eds.; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streifeneder, T.; Hoffmann, C.; Corradini, P. The future of agritourism? A review of current trends of touristic commercialisation in rural areas. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, R.M.; Romagnoli, L. Customer Satisfaction with Farmhouse Facilities and Its Implications for the Promotion of Agritourism Resources in Italian Municipalities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gössling, S.; Lane, B. Rural tourism and the development of internet-based accommodation booking platforms: A study in the advantages, dangers and implications of innovation. J. Sustain. Tour. 2015, 23, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Nevarez, C.; Hyman, M.R. Common practices in destination website design. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2012, 1, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.J.; Wolfe, K.; Hodur, N.; Leistritz, F.L. Tourist word of mouth and revisit intentions to rural tourism destinations: A case of North Dakota, USA. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2013, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, L.; Kline, C.; Oliver, J.; Kariko, D. Exploring emotional response to images used in agritourism destination marketing. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 9, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, K.; Hernik, J. Digital Folklore of Rural Tourism in Poland. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, M.; Reunanen, M. Preserving Our Digital Heritage: Experiences from the Pelikonepeijoonit Project. In History of Nordic Computing 2. HiNC 2007. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Impagliazzo, J., Järvi, T., Paju, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 303, pp. 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Thoms, W. Folklor. Lit. Ludowa 1975, 6, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyk, U. Dzieje pojęcia „folklor” w polskim dyskursie humanistycznym. Ogrody Nauk. I Szt. 2014, 4, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Kajfosz, J. Elementy Magii w Folklorze Medialnym; Gańczarczyk, G., Grochowski, P., Eds.; Folklor w Dobie Internetu: Toruń, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lourdi, I.; Papatheodorou, C.; Nikolaidou, M. A multi-layer metadata schema for digital folklore collections. J. Inf. Sci. 2007, 33, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, R.; Yamamoto, K. A sightseeing support system using augmented reality and pictograms within urban tourist areas in Japan. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinzenz, F. The added value of rating pictograms for sustainable hotels in classified ads. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2019, 29, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, K. Trendy projektowe w prezentacji gospodarstw agroturystycznych w Internecie. Tur. I Rozw. Reg. 2017, 7, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormode, G.; Krishnamurthy, B. Key differences between Web 1.0 and Web 2.0. First Monday 2008, 13, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camilleri, M.A. E-commerce websites, consumer order fulfillment and after-sales service satisfaction: The customer is always right, even after the shopping cart check-out. J. Strat. Manag. 2021, 15, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, P.; Schlaich, P.; Sinner, D. Single-Page-Website. In Digitalmedien-Projekte. Bibliothek der Mediengestaltung; Springer Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villareal-Freire, Á.; Aguirre, A.F.A.; Ordoñez, C.A.C. Reverse engineering for the design patterns extraction of android mobile applications for attention deficit disorder. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2019, 61, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sundar, S.S. How does parallax scrolling influence user experience? A test of TIME (Theory of Interactive Media Effects). Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2018, 34, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.H.; Chang, J.W.; Lee, C.C. Designing attractive gamification features for collaborative storytelling websites. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinandito, A.; Az-zahra, H.M.; Fanani, L.; Putri, A.V. Analysis of web content delivery effectiveness and efficiency in responsive web design using material design guidelines and User Centered Design. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Sustainable Information Engineering and Technology (SIET), Malang, Indonesia, 24–25 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamasbi, S.; Siegel, M.; Tullis, T. Generation Y, web design, and eye tracking. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2010, 68, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Menezes, M.; Falco, M. The Relationship of the Studies of Ergonomic and Human Computer Interfaces—A Case Study of Graphical Interfaces in E-Commerce Websites. In Design, User Experience, and Usability. Practice and Case Studies. HCII 2019; Marcus, A., Wang, W., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, A.; Amram, A. The Internet Archive and the socio-technical construction of historical facts. Internet Hist. 2018, 2, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, I. Finding Community in the Ruins of GeoCities: Distantly Reading a Web Archive. UWSpace. 2015. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10012/11650 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Baker, J. GeoCities and diaries on the early web. In The Diary; Ben-Amos, B., Ben-Amos, D., Eds.; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Król, K.; Zdonek, D. Initiatives to Preserve the Content of Vanishing Web Hosting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, E.J.; Stem, D.E.; Sprott, D.E. Banner advertisement and Web site congruity effects on consumer Web site perceptions. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2004, 104, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Osorio, D.; Peris-Ortiz, M.; Armengot, C.R.; Colino, A. Web 5.0: The future of emotional competences in higher education. Glob. Bus. Perspect. 2013, 1, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhury, N. World wide web and its journey from web 1.0 to web 4.0. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2014, 5, 8096–8100. [Google Scholar]
- Hobsbawm, E.; Ranger, T. The Invention of Tradition; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzięglewski, M.; Juza, M. Cyfrowe Praktyki i Strategie Upowszechniania i Odbioru Dziedzictwa Kulturowego; Raport Metodologiczny; Wydawnictwo Małopolskiego Instytutu Kultury w Krakowie: Kraków, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, B. What It Was Like to Surf the Web in 1989. Motherboard Blog. 2014. Available online: http://bit.ly/2Wibwg1 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Leshed, G. Posters, Lurkers, and in between: A Multidimensional Model of Online Community Participation Patterns; HCI International: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.E.; Battles, K. Exchange and interconnection in US network radio: A reinterpretation of the 1938 War of the Worlds broadcast. Radio J. Int. Stud. Broadcast Audio Media 2011, 9, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, J.; Brooks, D.W. Broken links: The ephemeral nature of educational WWW hyperlinks. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2002, 11, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yossef, Z.; Kumar, R.; Broder, A.; Tomkins, A. Sic transit gloria telae: Towards an understanding of the web’s decay. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on World Wide Web, New York, NY, USA, 17–20 May 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Solihin, W.; Eastman, C.M. The Mechanism and Challenges of Validating a Building Information Model regarding data exchange standards. Autom. Constr. 2019, 100, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, T. Agent-Based Modeling (ABM). In Neue Trends in den Sozialwissenschaften; Jäckle, S., Ed.; Springer VS: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachner, F.; Fincke, F.; Butz, A. UX Metrics: Deriving Country-Specific Usage Patterns of a Website Plug-In from Web Analytics. In Human-Computer Interaction—INTERACT 2017. INTERACT 2017; Bernhaupt, R., Dalvi, G., Joshi, A., Balkrishan, D.K., O’Neill, J., Winckler, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat, I.; Adeli, P.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Karimi, M.A. User-centred web design, usability and user satisfaction: The case of online banking websites in Iran. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 81, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Lazard, A.J.; White, S.R. The influence of visual complexity on initial user impressions: Testing the persuasive model of web design. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2020, 39, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Ready-Made Component | Present/Absent | Layout | Menu/Buttons | Banner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of websites | 177 | 79 | 102 | 106 |
| Percentage (%) | 40.88 | 18.24 | 23.56 | 24.48 |
| Design Characteristic | Modern Layout | Carousel; Parallax Scrolling | Old Design | One-Page Design | Long-Page Design | Front Banner | Hero Image; Macro Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of websites | 285 | 308 | 148 | 32 | 8 | 92 | 168 |
| Percentage (%) | 65.82 | 71.13 | 34.18 | 7.39 | 1.85 | 21.25 | 38.80 |
| Ready-Made Component | Present/Absent (0,1) | Layout | Menu/Buttons | Banner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of websites | 147 | 125 | 88 | 88 |
| Percentage (%) | 33.95 | 28.87 | 20.32 | 20.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Król, K.; Zdonek, D. Promoting Agritourism in Poland with Ready-Made Digital Components and Rustic Cyberfolklore. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010023
Król K, Zdonek D. Promoting Agritourism in Poland with Ready-Made Digital Components and Rustic Cyberfolklore. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2023; 7(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKról, Karol, and Dariusz Zdonek. 2023. "Promoting Agritourism in Poland with Ready-Made Digital Components and Rustic Cyberfolklore" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 7, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010023
APA StyleKról, K., & Zdonek, D. (2023). Promoting Agritourism in Poland with Ready-Made Digital Components and Rustic Cyberfolklore. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 7(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010023










