Establishment of a Landscape Information Model (LIM) and AI Convergence Plan through the 3D Digital Transformation of Railway Surroundings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Site
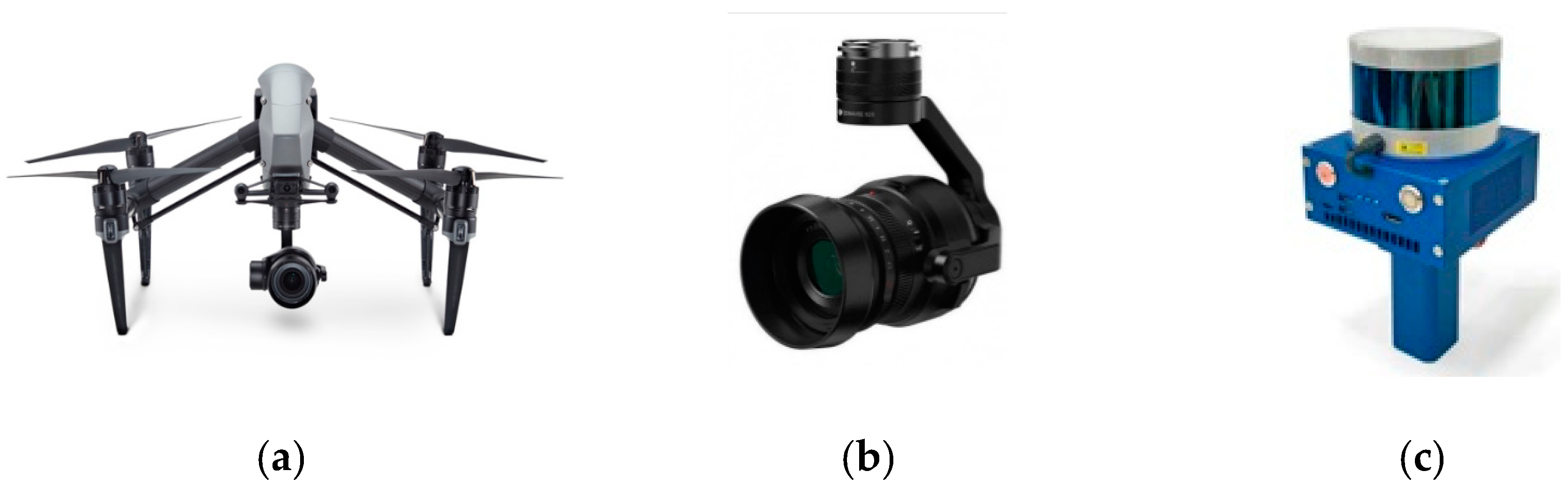
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.2.1. The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and Ground Control Point Settings
2.2.2. Acquiring Point Cloud Data
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Research Flowchart
2.3.2. Derivation of Components by Type
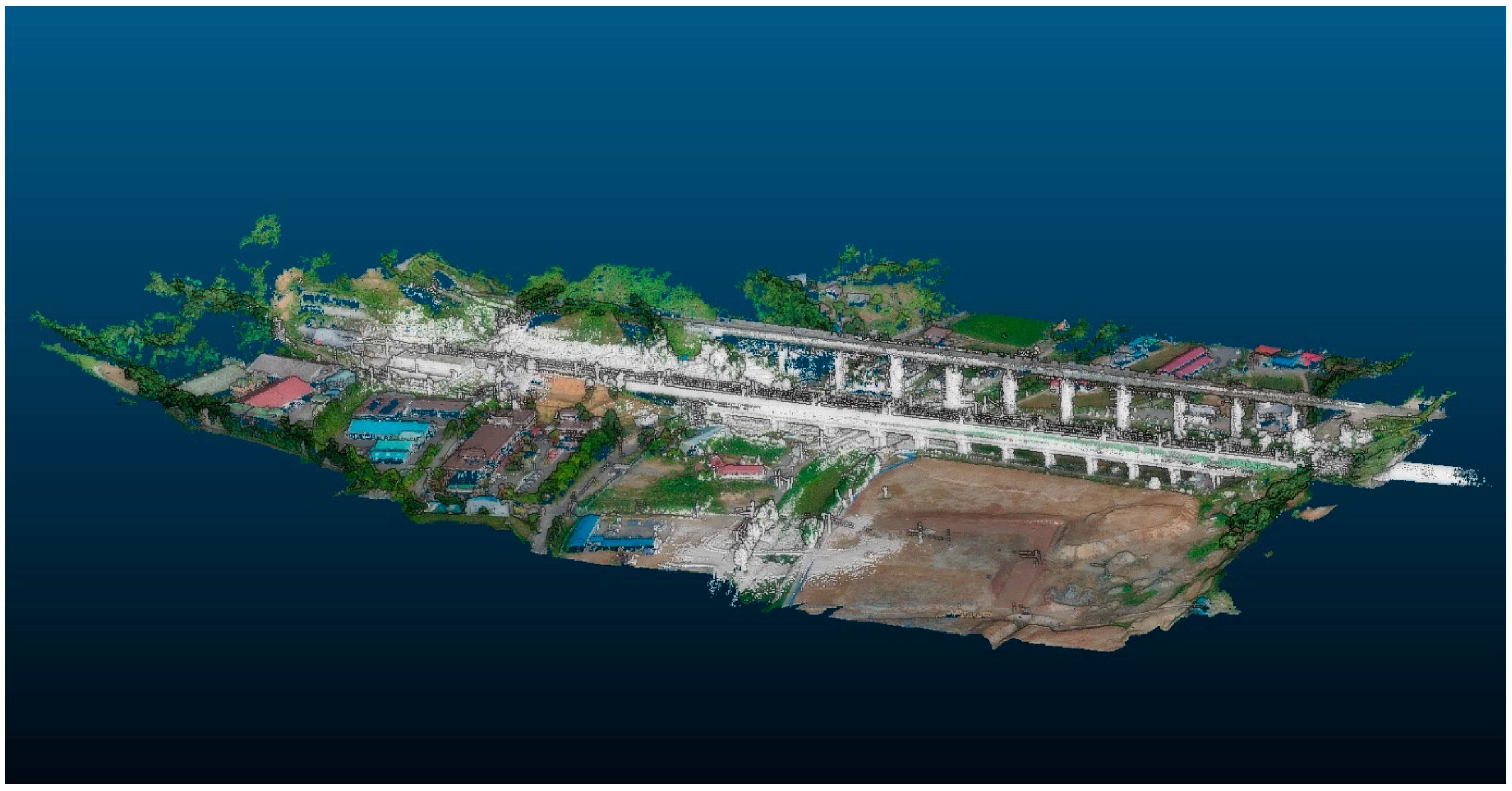
2.3.3. 3D Point Cloud Data Acquisition and Voxelization
2.3.4. LIM Construction and AI Convergence
3. Results and Discussion
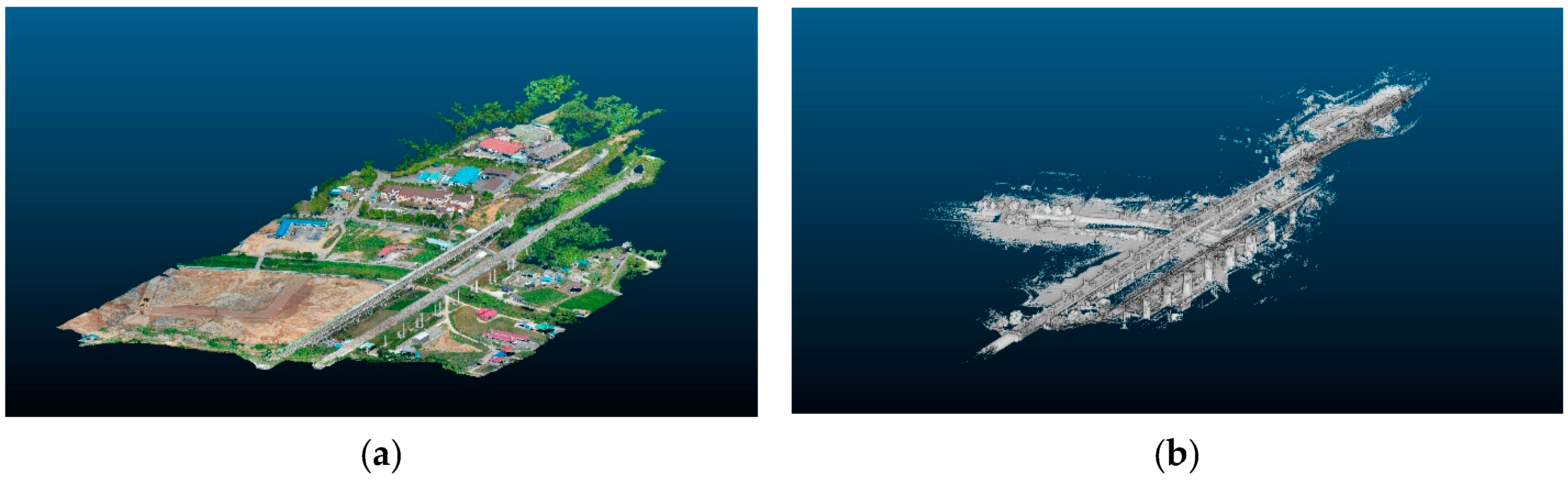
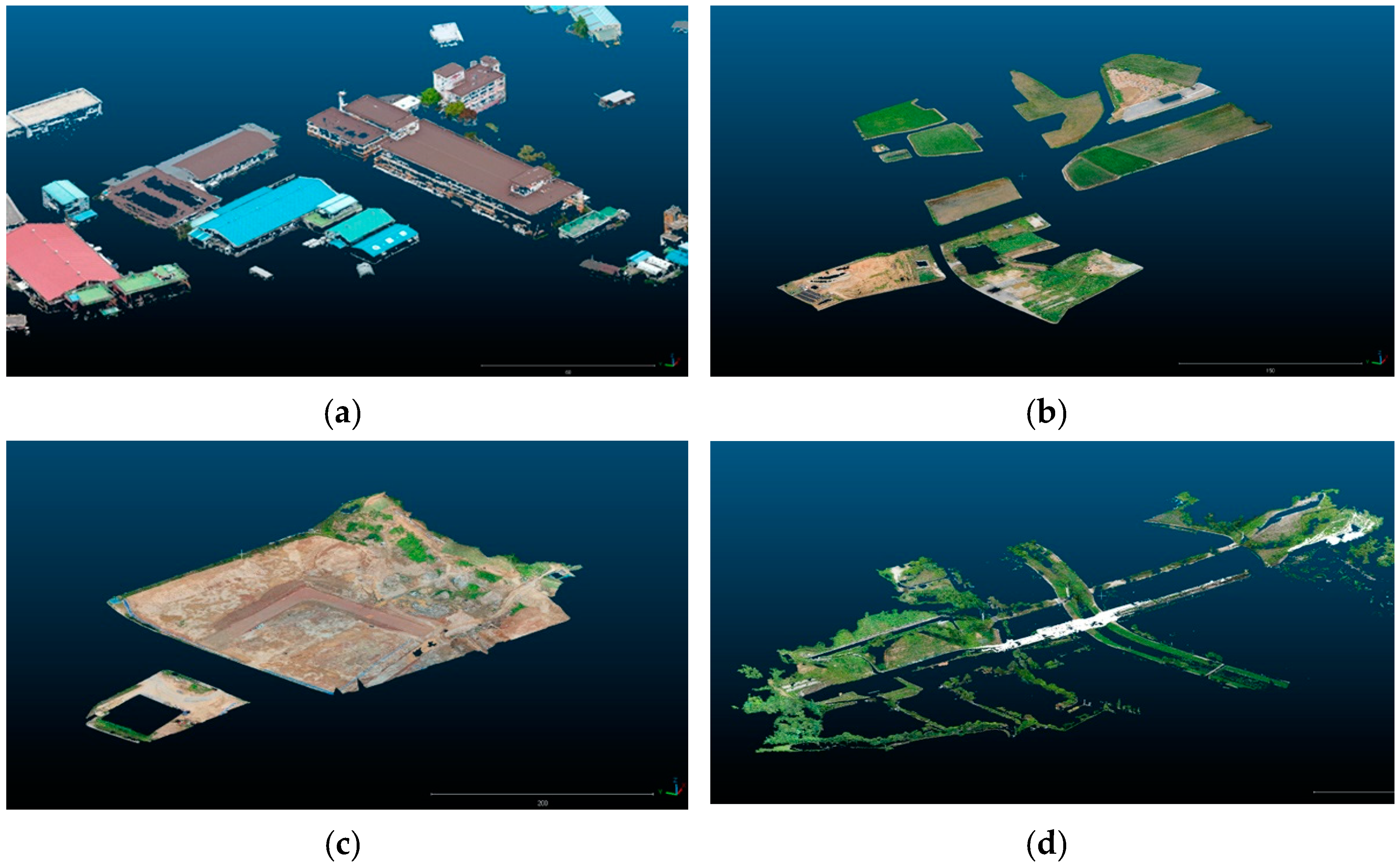
3.1. The 3D Digital Transformation
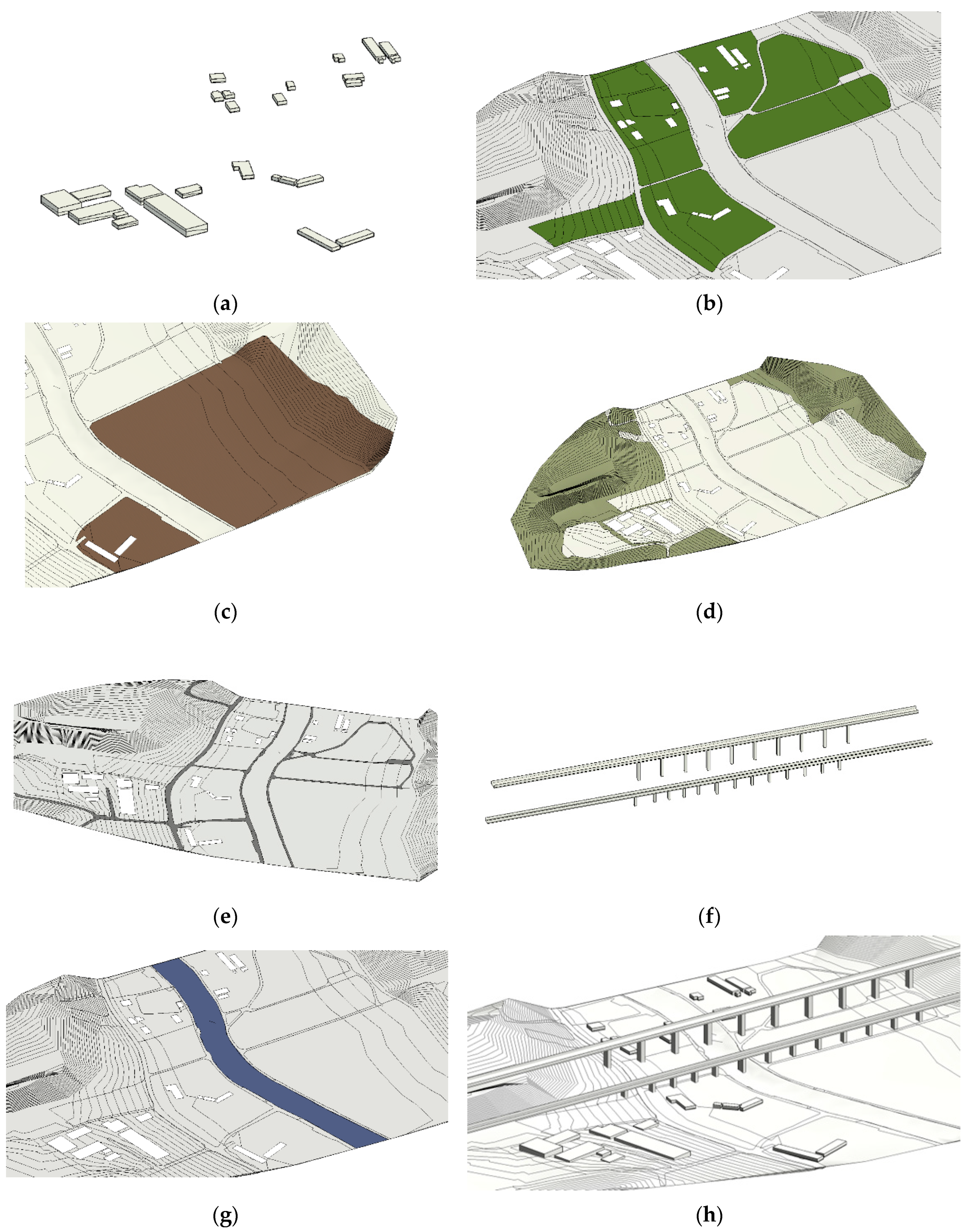
3.2. Voxelization of Landscape Infrastructure and Construction of the LIM
3.3. Interpolation of Point Cloud Data
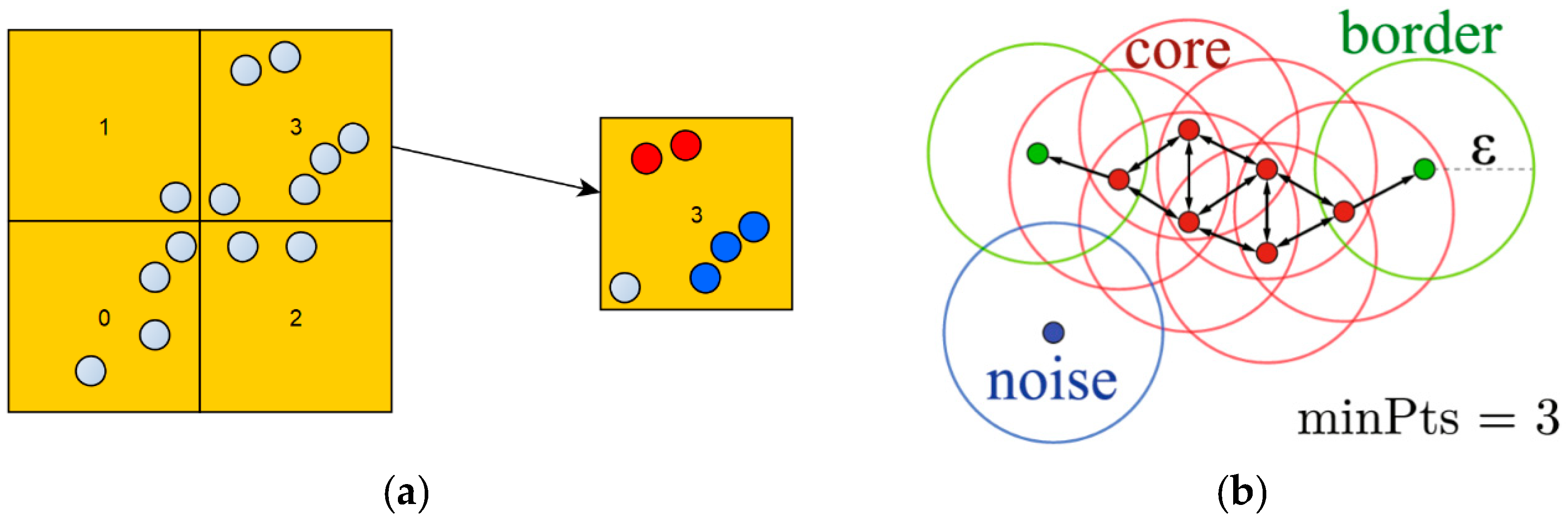
3.4. Clustering for AI Convergence
3.4.1. Grid Unit DBSCAN Application and Parameter Adjustment
3.4.2. The Clustering Follow-Up
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korea Railway Research Institute. Railway BIM 2030 Roadmap. 2018. Available online: http://big.yonsei.ac.kr/railbim/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Construction Industry BIM Basic Guidelines; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport: Sejong Special Self-Governing City, Republic of Korea, 2020. (In Korean)
- The Korean Version of the New Deal 2.0, the Core of the Hyper-Connected New Industry; Digital Twin Enablement Strategy; Information and Communication Strategy Committee: Sejong Special Self-Governing City, Republic of Korea, 2021. (In Korean)
- Government; Korean New Deal 2.0 Promotion Plan; Government: Sejong Special Self-Governing City, Republic of Korea, 2021. (In Korean)
- Kim, M.K. A study on the post-environmental impact assessment and derivation of optimal techniques for comprehensive railway test track using UAV. J. Korean Soc. Railway. 2021, 23, 625–636. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K. A basic study on the construction of railroad LIM and AI convergence using 3d digital transformation of comprehensive railway test track surrounding areas. 2022. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Mahdy, A.M.S. A numerical method for solving the nonlinear equations of Emden-Fowler models. J. Ocean. Eng. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.M.S.; Lotfy, K.; Lotfy, A.A. Use of optimal control in studying the dynamical behaviors of fractional financial awareness models. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 3401–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.M.S.; Higazy, M. Numerical different methods for solving the nonlinear biochemical reaction model. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2019, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner. Use the IoT Platform Reference Model to Plan Your IoT Business Solution. Gartner, Inc. in United States. 2016. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/3447218 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Gartner Glossary, Digital Twin. Available online: www.gartner.com (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Gartner. Top Strategic Technology Trends for 2021. Gartner, Inc. in United States. 2020. Available online: https://www.tom.travel/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/top-tech-trends-gartner-2021-1.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Kim, B.Y. Trends in landscaping field related to BIM and LIM vitalization plan. J. Korean Soc. Landsc. Archit. 2014, 42, 50–63. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.M.; Aliyu, A.A. The need for Landscape Information Modelling (LIM) in landscape architecture. Proc. DLA Conf. 2012, 531–540, ISBN 978-3-87907-519-5. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, B. Landscape and instruments. Landsc. J. 2013, 32, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipes, J.L. Building information modeling technology is the future for landscape architecture. Landsc. Archit. 2007, 97, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Landscape Institute. Available online: http://www.landscapeinstitute.org (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Norske Landskapsarkitekters Forening NLA. Available online: www.landskapsarkitektur.no (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Smart Construction Challenge 2022-BIM Contest for Designing SOC Fields such as Railways #13: Advancement of Design Quality through Application of BIM for High-Speed Railway Honam Scrap Rail Phase 2 Section 2 Construction BIM Design Case. Available online: http://smartconstchallenge.com/modules/board/bd_view.html?no=47&id=movie&ca=4&mc_code=3014&p=1&or=bd_order&al=asc (accessed on 25 January 2023). (In Korean).









| GCP ID | Easting | Northing | Elevation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 451,429.2324 | 224157.2707 | 50.4667 |
| 2 | 451,671.4710 | 224,371.6100 | 52.0550 |
| 3 | 451,577.9242 | 223,962.799 | 66.0829 |
| 4 | 451,539.4485 | 224,542.3181 | 50.2407 |
| 5 | 451,356.8614 | 224,325.9890 | 48.3972 |
| 6 | 451,274.3041 | 224,438.0376 | 47.7556 |
| GCP ID | Easting | Northing | Elevation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP1 | 451,657.8871 | 224,067.504 | 64.6463 |
| CP2 | 451,386.8250 | 224,517.566 | 49.1150 |
| BM1 | 451,537.2968 | 224,218.7368 | 50.1259 |
| BM2 | 451,533.3192 | 224,215.1106 | 50.0665 |
| BM3 | 451,430.9190 | 224,161.7759 | 50.4725 |
| Step | Research Goals and Contents | Research Method |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Literature review and test site selection | literature review |
| Level 2 | Classification of landscape infrastructure around railways by type and derivation of components by category | literature review, field investigation |
| Level 3 | Point cloud data generation and object recognition for landscape infrastructure around railroad | field investigation, analyze |
| Level 4 | Establishment of railway LIM dataset and review of artificial intelligence convergence possibility | analyze |
| Level 5 | Derivation of railway LIM construction plan that can be converged with railway BIM | analyze |
| Main Category | Middle Category | Subdivision | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patch | Natural greenery | Forest green belt, urban green belt, artificial green belt | Tree forests (coniferous, broad-leaved, mixed forests), shrub forests, grasslands, etc. |
| Farmland | Fields, paddy fields, orchards, livestock land, horticultural land | Subdivision according to tree species and cultivated species, ranch land, etc. | |
| Bare land | Unused land, construction sites, mineral springs, salted land | Subdivision according to land structure, subdivision according to construction purpose | |
| Corridor | Railway | Railways, tunnels, and railway facilities | Railways, tunnel facilities, railway auxiliary facilities |
| Road | Vehicle roadways, pedestrian paths | Expressways, national roads, cities and towns, archipelagos, old towns, hiking trails, etc. | |
| River | Embankments, high waterways, low waterways, load diagrams | The top of the embankment, access stairs, trails, sand bar deposits, etc. | |
| Object | Building | Residential areas, factories, schools, parking areas, warehouses, physical education | Detailed facilities within the building structure |
| Items | The Total Size of the Building Data | The Number of Points | The Volume | The Surface Area | The Voxel Ratio of Buildings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings | 395 MB | 15,557,253 | 1,628,847 m3 | 23,750 m2 | 9.75% |
| Farmland | 972 MB | 29,275,501 | 2,784,370 m3 | 50,284 m2 | 16.66% |
| Bare land | 1041 MB | 41,010,314 | 4,393,398 m3 | 83,764 m2 | 26.29% |
| Natural green land | 2099 MB | 63,236,852 | 5,815,540 m3 | 80,014 m2 | 34.81% |
| Roads | 216 MB | 8,516,645 | - | 15,527 m2 | - |
| Railway facilities | 1276 MB | 50,289,783 | 1,544,851 m3 | 20,685 m2 | 9.25% |
| Rivers | 94.4 MB | 3,718,117 | - | 6823 m2 | - |
| Step-by-Step Process | Details | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Merging and editing point clouds |
| The merging process and editing are performed in Cloud Compare. |
| 2 | Change settings (such as the location value of the point) |
| Location information is saved in the form of .las, .ply, etc. |
| 3 | Separation of the DTM and DSM |
| Adjustment of the setting values is required for high-quality results. |
| 4 | Noise removal |
| The SOR filter proceeds with the default settings. The upper part of the tree is excluded when applying the filter. |
| 5 | Segmentation |
| |
| 6 | File conversion |
| The Recap program is used. |
| 7 | File conversion |
| Processes such as family creation, terrain creation, and contour line creation are employed. |
| 8 | Visualization |
| |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-k.; Park, D.; Yun, S.; Park, W.-H.; Lee, D.; Chung, J.-D.; Chung, K.-J. Establishment of a Landscape Information Model (LIM) and AI Convergence Plan through the 3D Digital Transformation of Railway Surroundings. Drones 2023, 7, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030167
Kim M-k, Park D, Yun S, Park W-H, Lee D, Chung J-D, Chung K-J. Establishment of a Landscape Information Model (LIM) and AI Convergence Plan through the 3D Digital Transformation of Railway Surroundings. Drones. 2023; 7(3):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030167
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-kyeong, Duckshin Park, Suhwan Yun, Won-Hee Park, Duckhee Lee, Jeong-Duk Chung, and Kyung-Jin Chung. 2023. "Establishment of a Landscape Information Model (LIM) and AI Convergence Plan through the 3D Digital Transformation of Railway Surroundings" Drones 7, no. 3: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030167
APA StyleKim, M.-k., Park, D., Yun, S., Park, W.-H., Lee, D., Chung, J.-D., & Chung, K.-J. (2023). Establishment of a Landscape Information Model (LIM) and AI Convergence Plan through the 3D Digital Transformation of Railway Surroundings. Drones, 7(3), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7030167








