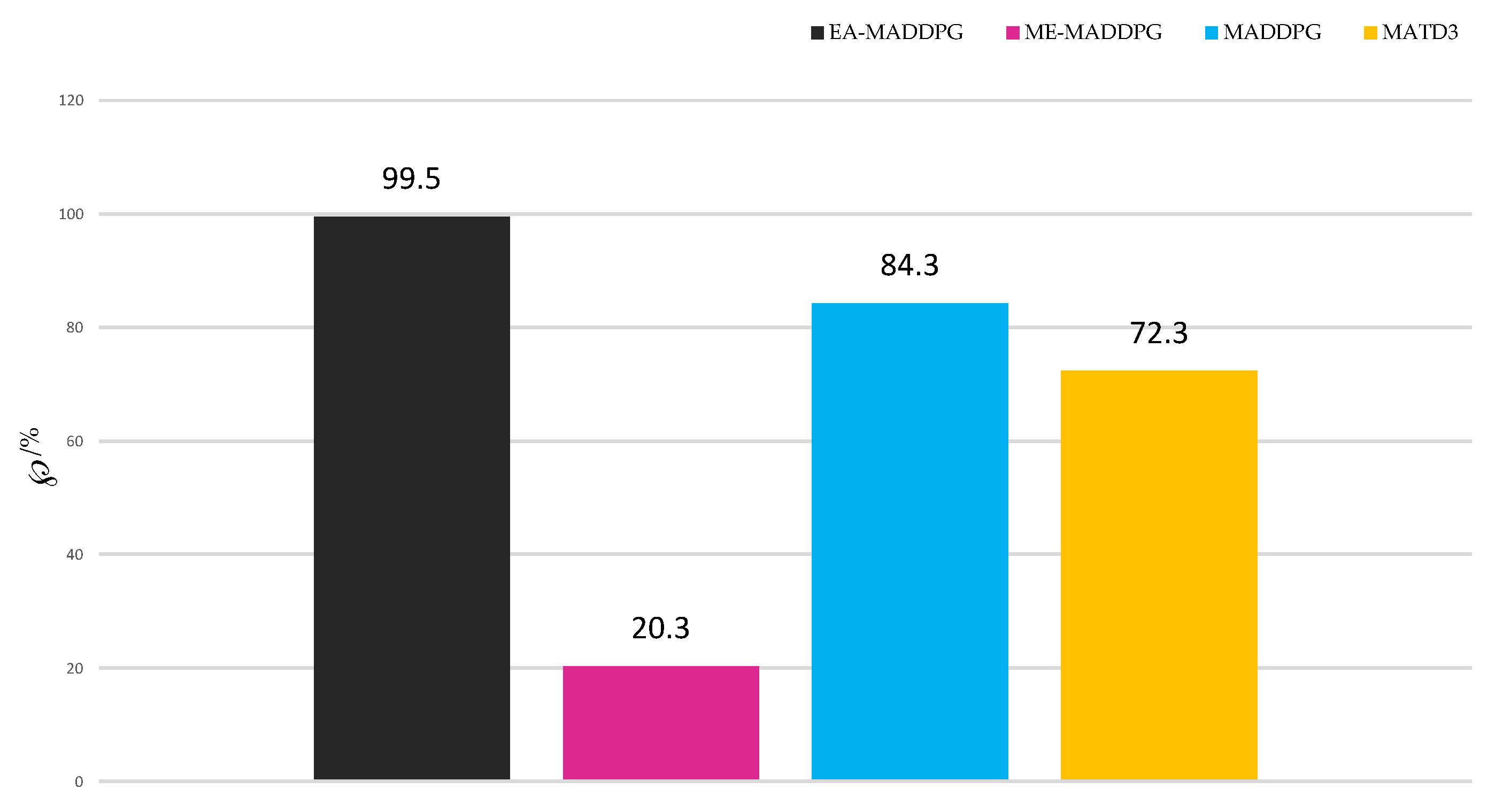Abstract
This paper proposes an improved multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm called the equal-reward and action-enhanced multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (EA-MADDPG) algorithm to solve the guidance problem of multiple missiles cooperating to intercept a single intruding UAV in three-dimensional space. The key innovations of EA-MADDPG include the implementation of the action filter with additional reward functions, optimal replay buffer, and equal reward setting. The additional reward functions and the action filter are set to enhance the exploration performance of the missiles during training. The optimal replay buffer and the equal reward setting are implemented to improve the utilization efficiency of exploration experiences obtained through the action filter. In order to prevent over-learning from certain experiences, a special storage mechanism is established, where experiences obtained through the action filter are stored only in the optimal replay buffer, while normal experiences are stored in both the optimal replay buffer and normal replay buffer. Meanwhile, we gradually reduce the selection probability of the action filter and the sampling ratio of the optimal replay buffer. Finally, comparative experiments show that the algorithm enhances the agents’ exploration capabilities, allowing them to learn policies more quickly and stably, which enables multiple missiles to complete the interception task more rapidly and with a higher success rate.
1. Introduction
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), especially drones, have been widely applied and played a key role in several local wars due to their low cost, flexible maneuverability, strong concealment, and ability to perform tasks in harsh environments. Although drone technology has shown great potential in areas such as reconnaissance, logistics, and environmental monitoring, its security issues have also raised widespread concern, especially how to effectively address the threat of hostile drones [1]. Therefore, the study of UAV interception is essential, especially in the context of the rapid development and widespread application of UAV technology today.
The algorithms are mainly divided into two major categories: rule-based approaches [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11] and learning-based approaches [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Within these categories, the methods can be further divided into single and multiple types. Single interception guidance methods: Command to line-of-sight guidance adjusts the interceptor’s path based on external commands, precisely controlling the interception process [4]. Optimal guidance designs guidance laws by minimizing a cost function to find the best path under given performance metrics [5]. Augmented proportional navigation adjusts the guidance gain to adapt to different interception conditions, enhancing efficiency against high-speed or highly maneuverable targets [6]. Predictive guidance adjusts the flight path of the interceptor based on predictions of the target’s movements, combating fast-maneuvering targets [7]. Multiple interception guidance methods: The leader–follower strategy involves one UAV acting as the leader, formulating the interception strategy, while the other UAVs follow and execute the plan, simplifying the decision-making process and ensuring team actions are synchronized [8]. The coordinated attack strategy requires high coordination among UAVs to determine the best angles and timings for the attack, effectively utilizing the team’s collective strength to increase the success rate of interceptions [9]. The sequential or alternating attack strategy allows UAVs to attack in a predetermined order or timing, maintaining continuous pressure on the target and extending the duration of combat [10]. The distributed guidance strategy enables each UAV to make independent decisions based on overall team information, enhancing the team’s adaptability and robustness, suitable for dynamic battlefield environments [11].
In recent decades, the rapid development and success of reinforcement learning have made it an ideal tool for solving complex problems, particularly in the field of UAV interception applications. The development of single-agent reinforcement learning algorithms began in the early 1980s, with initial explorations focusing on simple learning control problems [12]. Into the 21st century, with enhancements in computational power and data processing capabilities, deep learning techniques began to be integrated into reinforcement learning. Mnih et al. pioneered the deep q-network, achieving control levels in visually rich Atari games that matched or exceeded human performance for the first time [13]. Additionally, the deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithm [14], proposed by Lillicrap et al., and the proximal policy optimization algorithm [15] by Schulman et al., further expanded the application of reinforcement learning in continuous action spaces. Haarnoja et al. introduced the soft actor–critic algorithm, which optimized policies within a maximum entropy framework, demonstrating its superiority in handling tasks involving high dimensions and complex environments [16]. However, single-agent algorithms face challenges such as the exponential explosion in state-action space and local optima when dealing with multi-agent systems. To overcome these challenges, researchers have extended single-agent algorithms to multi-agent algorithms, such as multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (MADDPG), multi-agent actor–critic, multi-agent proximal policy optimization (MAPPO), and multi-agent twin-delayed deep deterministic policy gradient (MATD3) [17,18,19,20]. In the realms of single UAV and multiple UAV interception, reinforcement learning has emerged as a significant research focus. For a single UAV, as studied by Koch et al., deep reinforcement learning is employed to train the UAV for autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance in environments with obstacles [21]. In the context of multiple UAVs, Qie et al. proposed an artificial intelligence method named simultaneous target assignment and path planning based on MADDPG to train the system to solve target assignment and path planning simultaneously according to a corresponding reward structure [22].
1.1. Related Works
In the field of UAV interception, various studies have explored effective interception strategies for both single UAV and multiple UAV environments to tackle challenging missions. Garcia et al. focused on designing minimal-time trajectories to intercept malicious drones in constrained environments, breaking through the limitations of traditional path planning in complex settings [23]. Tan et al. introduced a proportional-navigation-based switching strategy for quadrotors to track maneuvering ground targets, addressing the limitations of traditional proportional derivative control. By dynamically switching between proportional navigation and proportional derivative controls, the proposed method reduced tracking errors and oscillations, demonstrating improved performance and robustness against measurement noise. The optimal switching points, derived analytically, ensured minimal positional errors between the UAV and the target [24]. Cetin et al. addressed the visual quadrotor interception problem in urban anti-drone systems by employing a model predictive control (MPC) method with terminal constraints to ensure engagement at a desired impact angle. The modified MPC objective function reduced the interceptor’s maneuvering requirements at the trajectory’s end, enhancing efficiency. The proposed guidance methodology was successfully tested in various scenarios, demonstrating effective interception of both maneuvering and non-maneuvering targets with minimal maneuvering at the interception’s conclusion [25]. Xue et al. introduced a fuzzy control method for UAV formation trajectory tracking, simplifying control logic and improving stability. Simulations confirm the method’s effectiveness in achieving rapid and stable formation docking [26]. Li et al. developed an enhanced real proportional navigation guidance method for gun-launched UAVs to intercept maneuvering targets, addressing limitations such as saturation overload and capture region constraints. By integrating an extended Kalman filter for data fusion and trajectory prediction, the method improved guidance accuracy and overcame system delay issues, resulting in more effective interception of “Low–slow–small” targets [27]. Liu et al. explored a cooperative UAV countermeasure strategy based on an interception triangle, using a geometric formation formed by three UAVs to enhance interception efficiency [28]. Tong et al., inspired by the cooperative hunting behavior of Harris’s hawks, proposed a multi-UAV cooperative hunting strategy, optimizing the interception process by mimicking natural cooperative behaviors [29]. In addition to drones, research on the interception of other moving objects also offers valuable insights. Shaferman et al. focused on developing and optimizing guidance strategies that enable multiple interceptors to coordinate their operations to achieve a predetermined relative intercept angle. By employing advanced optimization algorithms, this research significantly enhanced mission efficiency, particularly in scenarios where the intercept angle was crucial for successful interception [30]. Chen et al. explored and developed methods for enhancing the accuracy of target recognition and matching in missile guidance systems that used television-based seekers [31].
While rule-based methods have laid a solid foundation for UAV interception, the dynamic and unpredictable nature of modern aerial environments necessitates more adaptable and intelligent approaches. This is where reinforcement learning comes into play, offering significant advantages in UAV interception tasks. Reinforcement learning allows UAVs to learn from interactions with the environment, enabling them to make decisions in real time and adapt to changes dynamically.
In the single-agent domain, to address the issue of using drones to intercept hostile drones, Ting et al. explored the use of a deep q-network (DQN) with a graph neural network (GNN) model for drone-to-drone interception path planning, leveraging the flexibility of GNNs to handle variable input sizes and configurations. The proposed DQN-GNN method effectively trained a chaser drone to intercept a moving target drone, demonstrating the feasibility of integrating GNNs with deep reinforcement learning for this purpose. Results showed that the chaser drone could intercept the target in a reasonable time, suggesting that this approach enhanced the efficiency of drone interception tasks [32]. Furthermore, to counter the threat of small unmanned aerial systems to airspace systems and critical infrastructure, Pierre et al. applied deep reinforcement learning to intercept rogue UAVs in urban airspace. Using the proximal policy optimization method, they verified its effectiveness in improving interception success rates and reducing collision rates [33]. In addition, research on unmanned surface vessels (USVs) and missile interception is also of important reference significance. Du et al. introduced a multi-agent reinforcement learning control method using safe proximal policy optimization (SPPO) for USVs to perform cooperative interception missions. The SPPO method incorporated a joint state–value function to enhance cooperation between defender vessels and introduced safety constraints to reduce risky actions, improving the stability of the learning process. Simulation results demonstrated the effectiveness of the SPPO method, showing high performance in reward and successful cooperative interception of moving targets by the USVs [34]. Liu et al. introduced a combined proximal policy optimization and proportional–derivative control method for USV interception, enhancing interception efficiency. Simulation results showed that the proposed method significantly reduced the interception time compared to traditional approaches [35]. Hu et al. presented the twin-delayed deep deterministic policy gradient (TD3) algorithm to develop a guidance law for intercepting maneuvering targets with UAVs. The proposed method improved upon traditional proportional navigation guidance by directly mapping the line-of-sight rate to the normal acceleration command through a neural network, resulting in enhanced accuracy and convergence of the guidance system [36]. Li et al. proposed a covertness-aware trajectory design method for UAVs based on an enhanced TD3 algorithm. By integrating multi-step learning and prioritizing experience replay techniques, the method enabled UAVs to adaptively select flight velocities from a continuous action space to maximize transmission throughput to legitimate nodes while maintaining covertness. Considering the impact of building distribution and the uncertainty of the warden’s location, this approach effectively addressed issues that were challenging for standard optimization methods and demonstrated significant performance advantages over existing deep reinforcement learning baselines and non-learning strategies in numerical simulations [37]. Li et al. employed a quantum-inspired reinforcement learning (QiRL) approach to optimize the trajectory planning in UAV-assisted wireless networks without relying on prior environmental knowledge. QiRL introduced a novel probabilistic action selection policy inspired by quantum mechanics’ collapse and amplitude amplification, achieving a natural balance between exploration and exploitation without the need for tuning exploration parameters typical in conventional reinforcement learning methods. Simulation results validated the effectiveness of QiRL in addressing the UAV trajectory optimization problem, demonstrating faster convergence and superior learning performance compared to traditional q-learning methods [38]. Li et al. introduced TD3 and quantum-inspired experience replay (QiER) to optimize the trajectory planning for UAVs in cellular networks, enhancing performance in reducing flight time and communication outages and improving learning efficiency by effectively balancing exploration and exploitation [39].
For multi-agent systems, Wan et al. presented an enhanced algorithm based on MADDPG called mixed-experience MADDPG (ME-MADDPG), which enhanced sample efficiency and training stability by introducing artificial potential fields and a mixed-experience strategy. Experiments demonstrated that ME-MADDPG achieved faster convergence and better adaptability in complex dynamic environments compared to MADDPG, showing superior performance in multi-agent motion planning [40]. In order to enhance navigation and obstacle avoidance in multi-agent systems, Zhao et al. proposed the MADDPG-LSTM actor algorithm, which combined long short-term memory (LSTM) networks with the MADDPG algorithm, and the simplified MADDPG algorithm to improve efficiency in scenarios with a large number of agents. Experimental results showed that these algorithms outperformed existing networks in the OpenAI multi-agent particle environment, and the LSTM model demonstrated a favorable balance in handling data of varying sequence lengths compared to transformer and self-attention models [41]. Huang et al. proposed and validated the MADDPG for its effectiveness and superior performance in multi-agent defense and attack scenarios [42]. For collaborative drone tasks, a cooperative encirclement strategy based on multi-agent reinforcement learning was proposed, using the attention-mechanism MADDPG algorithm, which addressed the problem of surrounding airborne escape targets in a collaborative drone attack scenario [43]. Using the all-domain simulation 3D war game engine from China Aerospace System Simulation Technology, Wei et al. conducted simulations of confrontations between UAVs and radar stations. By designing rewards and integrating LSTM networks into multi-agent reinforcement learning, the recurrent deterministic policy gradient (RDPG) method was improved, and a combination of MADDPG and RDPG algorithm was developed, significantly enhancing the algorithm’s effectiveness and accuracy [44]. Jeon et al. introduced a fusion–multiactor–attention–critic model for energy-efficient navigation control of UAVs. The model incorporated a sensor fusion layer and a dissimilarity layer to optimize information processing, resulting in improved energy efficiency and 38% more deliveries within the same time steps compared to the original multiactor–attention–critic model [45]. Yue et al. proposed a method for multi-object tracking by a swarm of drones using a multi-agent soft actor–critic approach [46]. For the pursuit–evasion game of multi-rotor drones in obstacle-laden environments, Zhang et al. proposed the CBC-TP Net, a multi-agent bidirectional coordination target prediction network, which incorporated a vectorized extension of the MADDPG method to ensure effective task execution even if the “swarm” system was compromised [47]. The priority-experience replay-based multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm (PER-MADDPG) has shown excellent performance in increasing the success rate of pursuits and reducing response times, featuring faster convergence and reduced oscillations compared to the MADDPG algorithm [48]. Zhu et al. applied deep reinforcement learning to the cluster control problems of multi-robot systems in complex environments, proposing the PER-MADDPG algorithm, which significantly enhanced learning efficiency and convergence speed. Experimental results validated the effectiveness of this algorithm in completing cluster tasks in obstacle-laden environments [49]. Jiang et al. integrated self-attention into the MADDPG algorithm to enhance the stability of learned policies by adapting to the dynamic changes in the number of adversaries and allies during confrontations. They presented a simplified 2D simulation environment and conducted experiments in three different collaborative and confrontational scenarios, demonstrating improved performance over baseline methods [50]. Zhang et al. tested the distributed decision-making and collaboration tasks of heterogeneous drones in a Unity3D cooperative combat environment, proposing an improved MAPPO algorithm and enhancing the algorithm’s generalizability through the course learning [51]. Huang et al. developed a collaborative path planning method for multiple drones based on the MATD3 algorithm with dual experience pools and a particle swarm optimization algorithm, significantly reducing the age of information [52]. Some typical methods are summarized in Table 1.
1.2. Contributions
This paper investigates the guidance of multiple missiles in three-dimensional space for intercepting a single UAV with random initial positions and uncertain trajectories. We use an improved algorithm called equal-reward and action-enhanced multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (EA-MADDPG) based on the MADDPG algorithm for training the control policy of the missiles to enhance their ability to complete interception tasks. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- In multi-agent collision avoidance tasks, MADDPG-LSTM outperforms standard MADDPG due to the LSTM’s capability to handle sequential data. This advantage arises from the LSTM’s underlying principle of maintaining long-term dependencies and capturing temporal patterns through its specialized memory cells and gating mechanisms. Compared to LSTM, the EA-MADDPG in this paper, based on an equal reward setting and an optimal replay buffer with a special storage mechanism, enhances the utilization of important experiences during learning, thereby improving the collision avoidance training effectiveness in multi-missile interception tasks.
- Prioritized experience replay techniques can enhance exploration performance by prioritizing and sampling experiences based on their significance within the replay buffer. In contrast, this paper introduces a new method to enhance exploration performance by incorporating an action filter. During training, agents use the action filter for action selection with a certain probability, executing these actions to enhance exploration and acquire unique experiences for storage.
- ME-MADDPG [40] generates special experiences using an artificial potential field with a certain probability and incorporates them into the buffer for sampling and training. In this paper, the EA-MADDPG uses an action filter for action selection to generate unique experiences for storage and learning. All actions are derived from the output of the agents’ actor networks.

Table 1.
Typical Methods.
Table 1.
Typical Methods.
| Article | Method |
|---|---|
| [41,44] | MADDPG with long short-term memory networks |
| [37,48,49] | Prioritized experience replay techniques |
| [40] | Artificial potential field and mixed-experience mechanism |
The remaining parts of this paper are structured as follows. Section 2 introduces the basic notations. Section 3 presents the kinematic models of missiles and the UAV, as well as the description of the problem. Section 4 details the adopted EA-MADDPG algorithm. Section 5 conducts simulations and discusses the results, and Section 6 summarizes the conclusions of the paper.
2. Notation
N represents the number of agents within the environment. The set of states represents the possible configurations of all agents. The set denotes the possible action space of all agents, and denotes the action space of agent i. The set denotes the observation space of all agents, and denotes the observation space of agent i. denotes the state of all agents at a certain moment. denotes the information observed by agent i at a certain moment. , where represents the joint action vector of all agents at a certain moment, and denotes the action executed exclusively by agent i within the environment at a certain moment. (abbreviated as ) denotes the policy generated by the actor network of the ith agent, with representing the actor network’s parameters. It takes observations as input and produces actions as output. (abbreviated as ) denotes the policy generated by the target actor network of the ith agent, with representing the target network’s parameters. , it is the action value function generated by the critic network of the ith agent, with representing the critic network’s parameters and representing the set . is the action value function generated by the target critic network of the ith agent, with representing the target critic network’s parameters and representing the set . denotes the subsequent state reached by agents after executing their current actions. , where , denotes the joint reward vector of all agents, and represents the immediate reward obtained by agent i within the environment. denotes the total expected return of agent i, where denotes the max step in an episode. represents the noise added to actions during reinforcement learning training to enhance exploration. denotes the replay buffer used to store the past experience tuples collected. denotes the discount rate used in calculating cumulative rewards. denotes the parameters used for updating the target network. denotes the number of experience tuples used for training at one time. denotes the derivative of y with respect to x.
3. Modeling and Problem Description
This paper considers the problem of a group of N missiles intercepting a single intruding UAV which aims to attack some ground target. In this section, the models of the missiles and the UAV are introduced first, which is then followed by the detailed description of the intercepting problem in rigorous mathematics.
3.1. Modeling of Missiles and the UAV
Define . For , the kinematic model of the ith missile is given by
where denote the position and velocity of the ith missile at the kth step, respectively. denotes the duration of each step. Furthermore, the velocity is given by
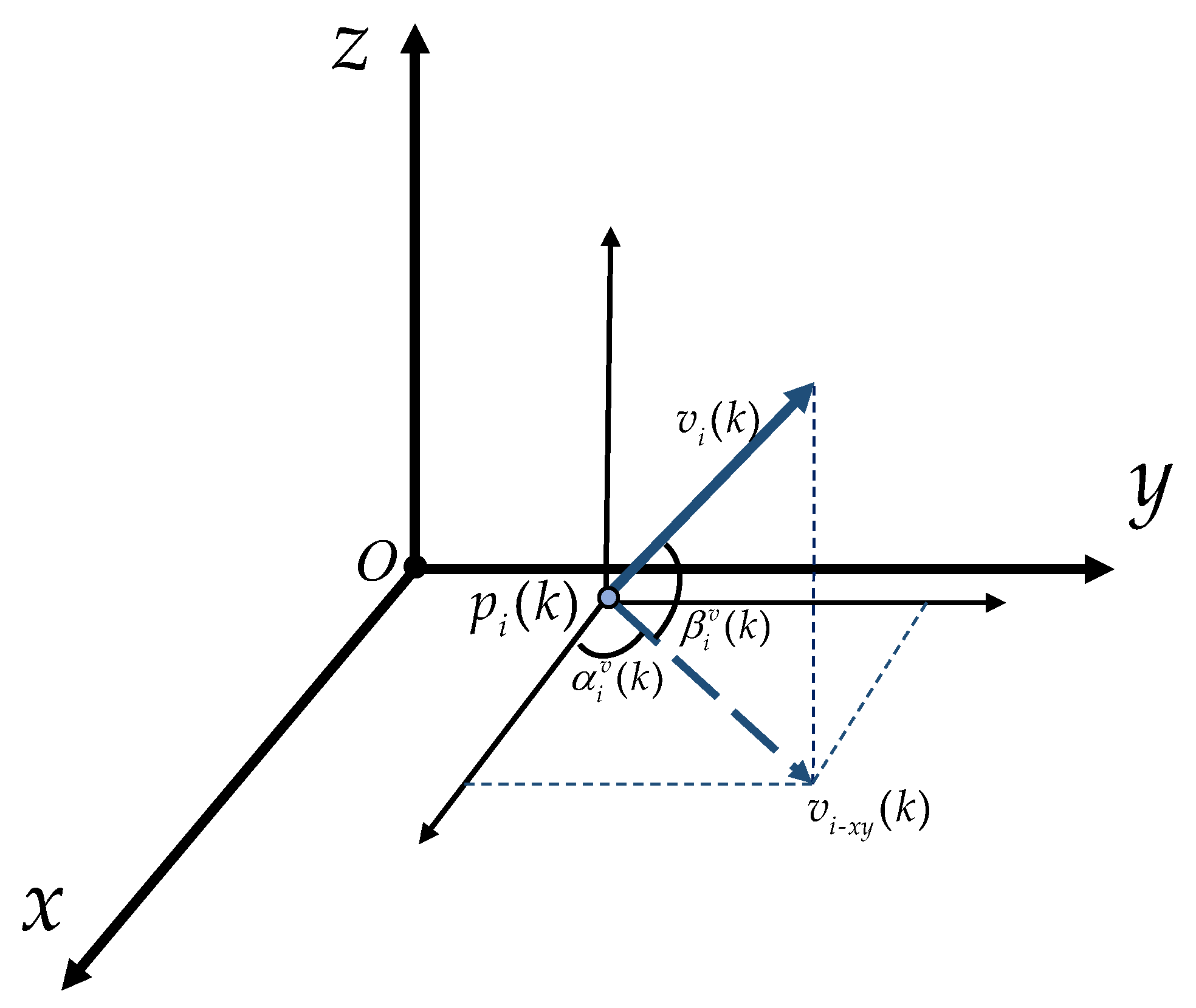
Here, the speed satisfies , where denotes the maximum linear velocity. Moreover, as shown in Figure 1, denotes the projection of onto the plane parallel to O–. denotes the angle of with respect to the positive semi-axis of x, with counterclockwise being positive and clockwise being negative, and this rule of sign for angles is adopted throughout this paper. denotes the angle of with respect to . The angles of and are governed by
where the corresponding angular velocities are considered as the control inputs of the missiles. To make the control practical, it is assumed that and for some control input saturation threshold .
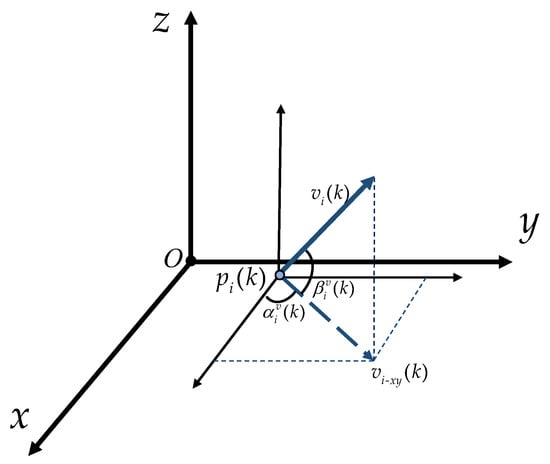
Figure 1.
The heading parameters of the ith missile.
The kinematic model of the UAV is given by
where denote the position and velocity of the UAV at the kth step, respectively. The velocity is given by
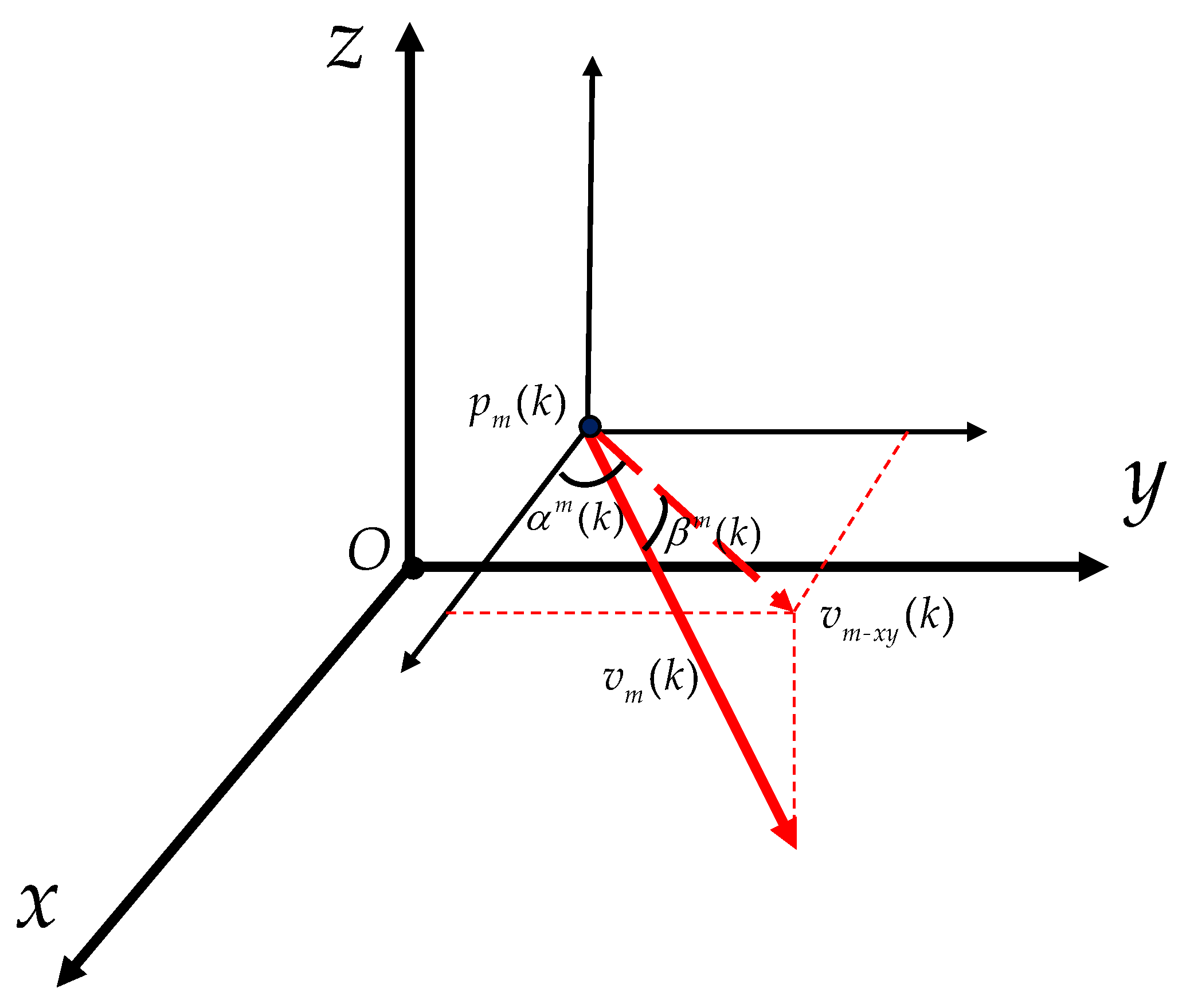
As shown in Figure 2, denotes the projection of onto the plane parallel to O–. denotes the angle of with respect to the positive semi-axis of x. denotes the angle of with respect to . represent the noise subject to a uniform distribution. Note that the speed of the UAV is the same as the maximal speed of the missiles.
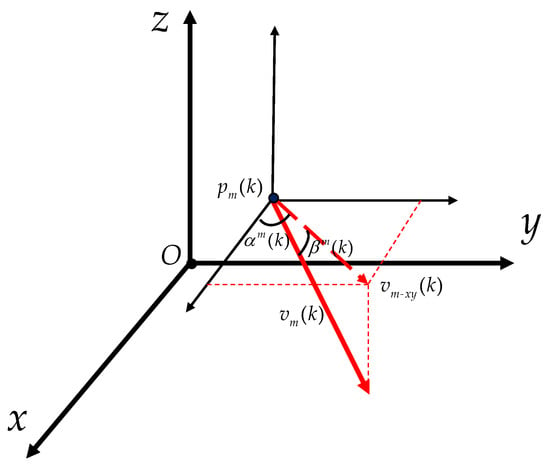
Figure 2.
The heading parameters of the UAV.
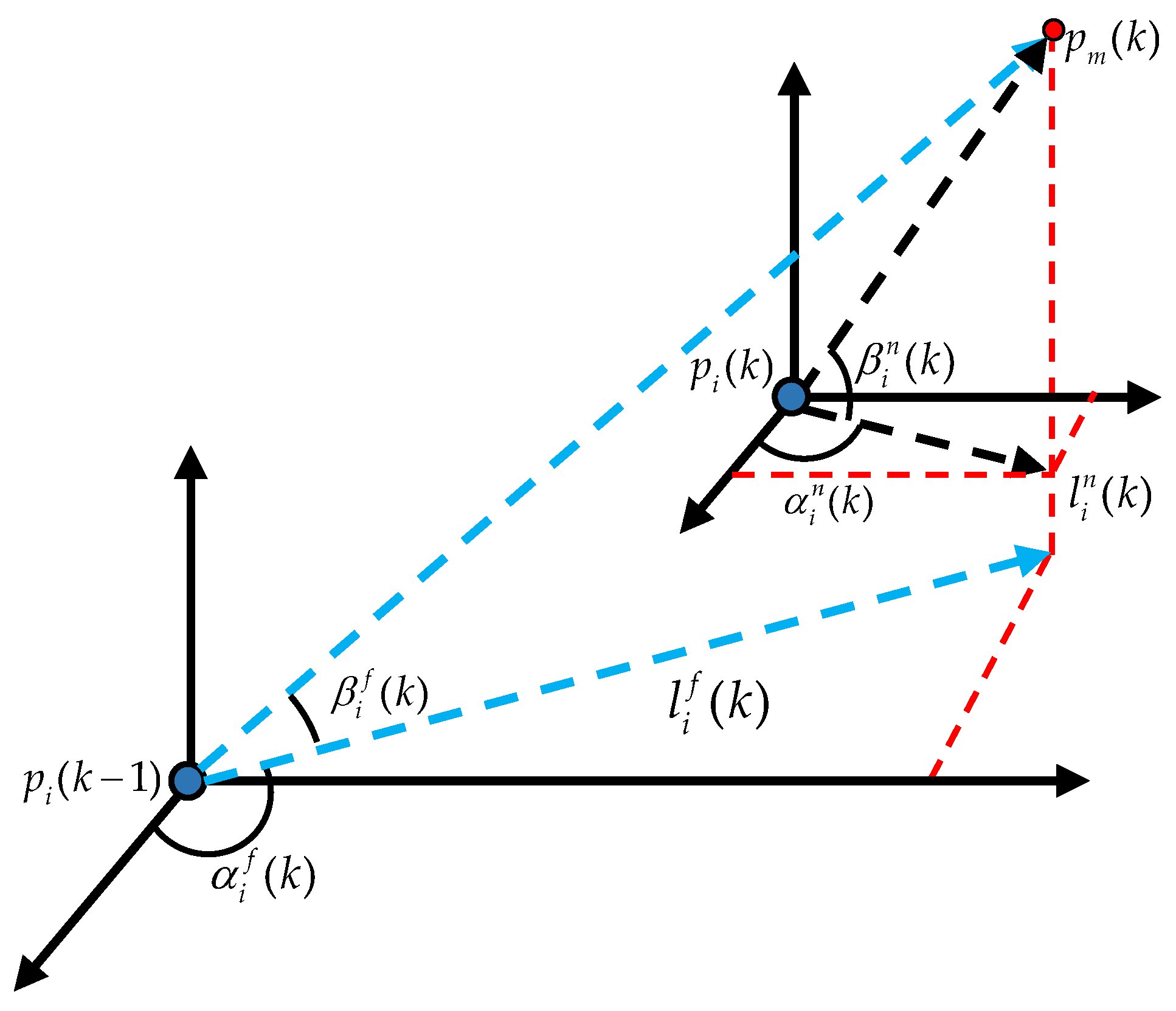
As shown in Figure 3, denotes the projection of onto the plane parallel to O–, and denotes the projection of onto the plane parallel to O–. Note that represents the current relative position between the ith missile and the UAV, whereas represents the semi-historical relative position. denotes the angle of related to the positive semi-axis of x. denotes the angle of related to . denotes the angle of related to the positive semi-axis of x. denotes the angle of related to . Based on these angles, we define
where denotes the angle of with respect to . denotes the angle of with respect to after they are both rotated around the z-axis to align within the same vertical plane. Moreover, for ,
where denotes the angle of with respect to . denotes the angle of with respect to after they are both rotated around the z-axis to align within the same vertical plane. In addition, we simply set and .
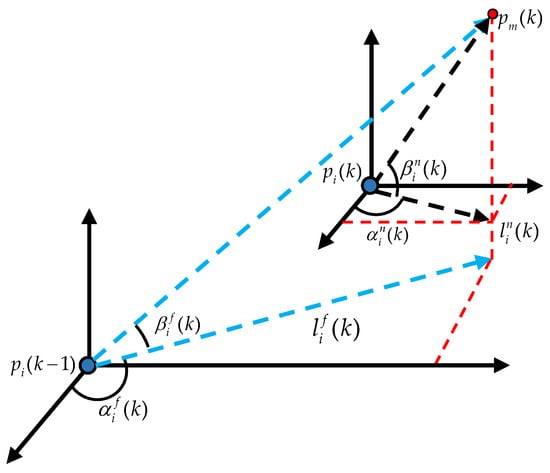
Figure 3.
The current and semi-historical heading parameters between the ith missile and the UAV.
3.2. Problem Description
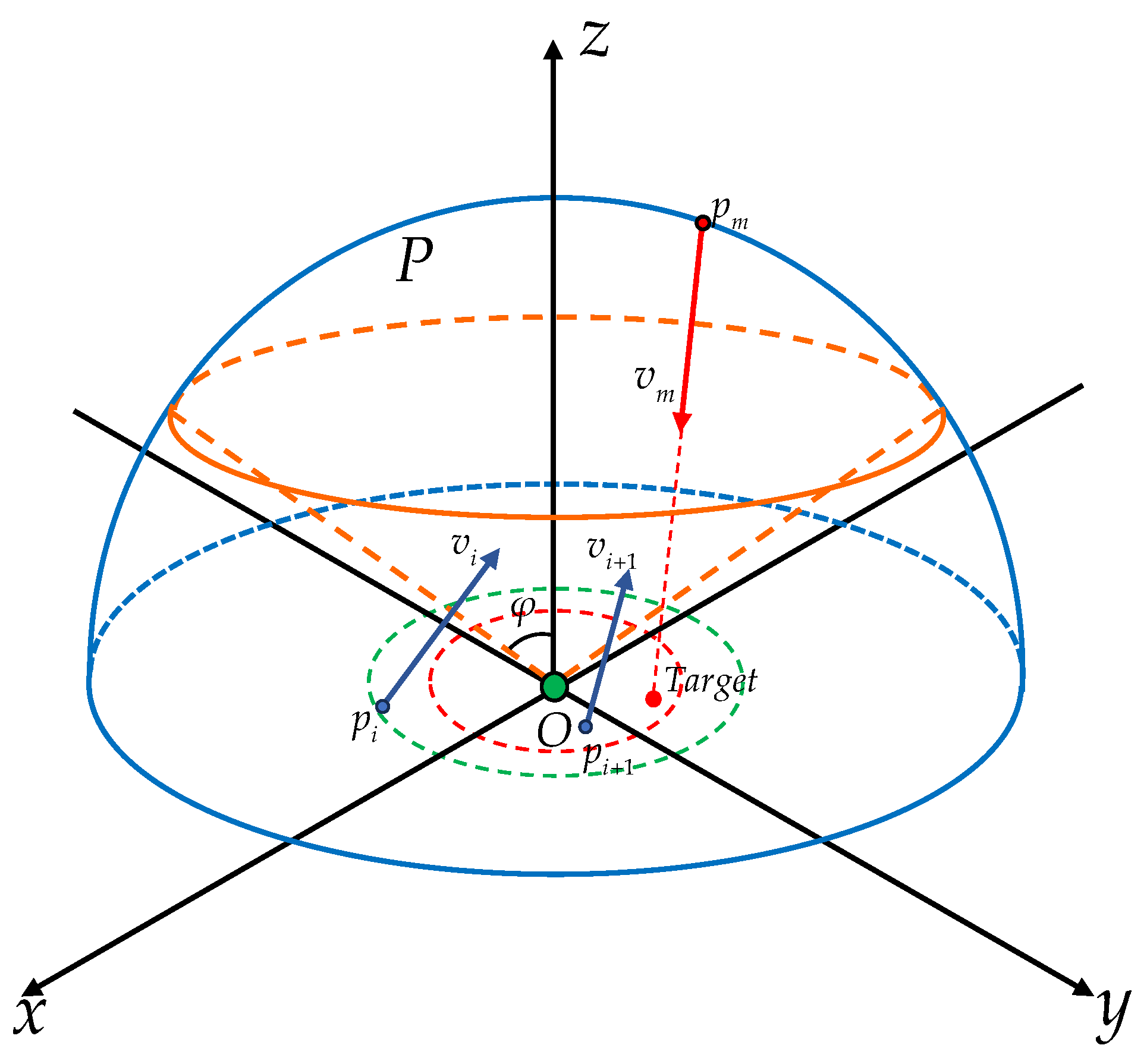
In Figure 4, the blue curves represent a hemisphere with center O and radius . The orange curves represent a cone with apex O and inner angle . The cone intersects with , and let the upper hemisphere be denoted by . In this paper, it is assumed that , i.e., the UAV will appear randomly on the upper hemisphere. Let denote the position of the target, satisfying
for some . For all k, the angles of of and are set to be such that the vector has the same direction as the vector . For , let . Suppose
for some . Moreover, for , and are set to be such that the vector has the same direction as the vector . The control objective is to design the control inputs of the missiles, i.e., such that there exist and satisfying the following two conditions simultaneously,
and for , at least one of these two conditions does not hold. Here, denotes the intercepting distance of the UAV. and denotes the safety distance of the target. At the same time, we define:
which represents the distance between the UAV and the target at the time when the UAV is successfully intercepted.
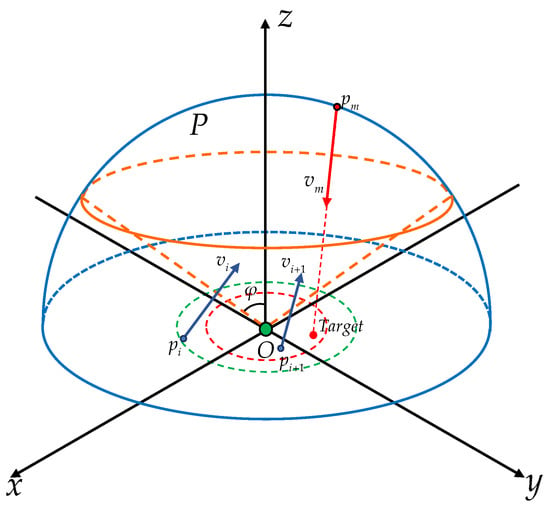
Figure 4.
Environment description.
For the multi-missile guidance and interception problem described above, we chose the MADDPG algorithm as the fundamental method. Here were the reasons for this choice: First, in multi-agent systems, missiles need to work together to achieve a common goal. Each missile must optimize its own behavior while considering the actions of other missiles to avoid mutual interference. MADDPG is designed to handle such coordination by using shared global information during training. This allows each missile to consider the actions of other missiles and learn how to coordinate effectively to approach the UAV faster while avoiding collisions. Second, the action space of missiles is continuous because the missiles are controlled by flight angular velocities. This requires the algorithm to handle continuous action parameters rather than discrete choices. MADDPG can effectively handle continuous action spaces and is very suitable for multi-agent systems that require precise control. Third, MADDPG allows for centralized training where all missiles can access global information, which helps in learning effective coordination strategies. During execution, each missile makes decisions based only on local information, which reduces the computational burden and improves real-time decision-making. Finally, for the MATD3 algorithm that uses twin critics, as the number of missiles increases, the complexity of training and maintaining more network parameters rises. Therefore, in situations with a larger number of agents, the simplicity and efficiency of MADDPG make it a better choice, as it can reduce the computational cost associated with training and maintaining critic networks.
We used the EA-MADDPG algorithm to train actor networks for each missile, with , , and as inputs for each actor and and as the continuous action outputs. The goal was for the missiles to move toward the UAV more quickly while avoiding collisions with each other and with the ground, thereby completing the interception task. Each missile was assigned a separate critic network, which used the inputs and outputs of the corresponding actor network as inputs and output q-value.
4. EA-MADDPG
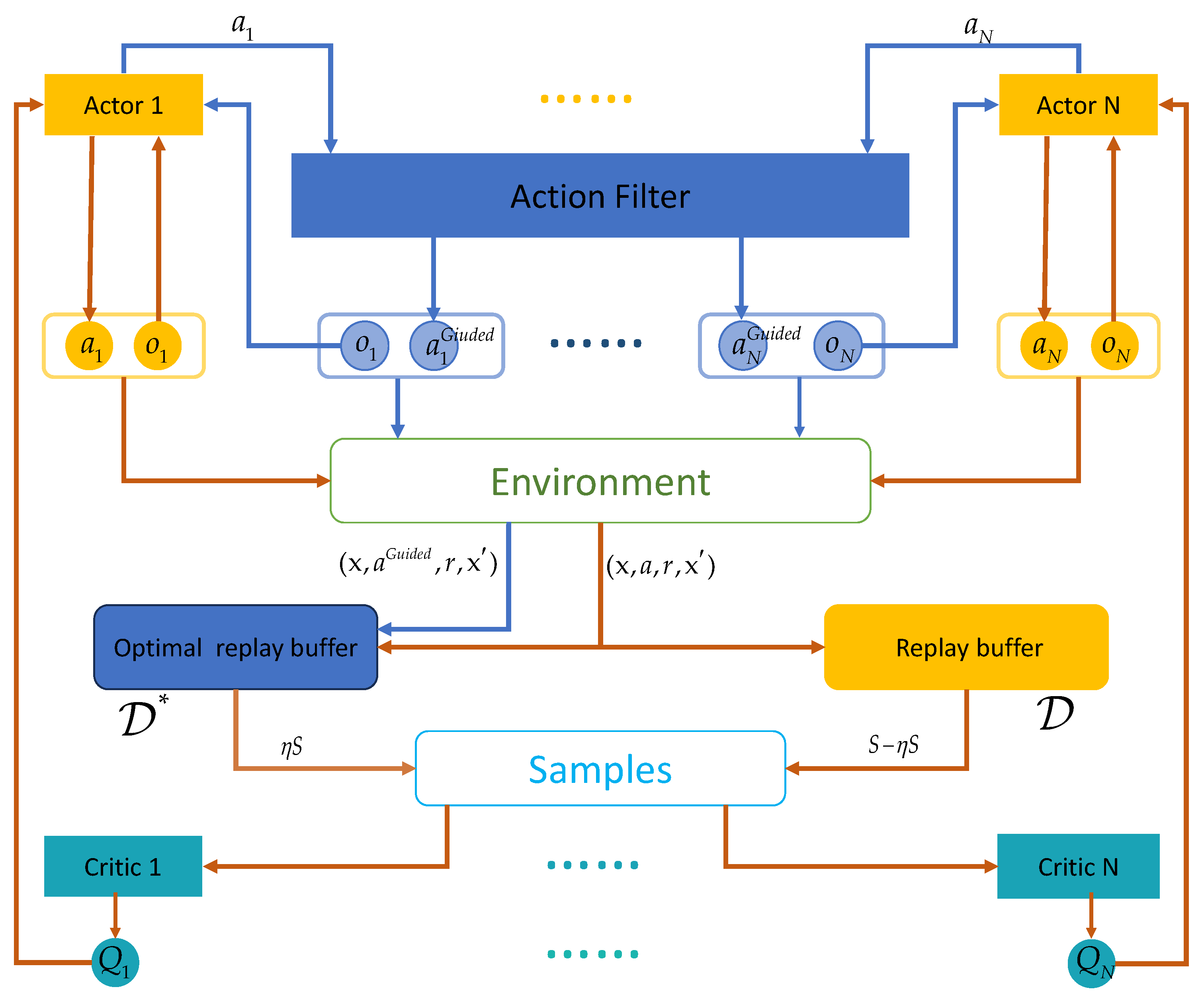
Figure 5 shows the framework of EA-MADDPG. Compared to MADDPG, EA-MADDPG has two additional components: the action filter and the optimal replay buffer . During the experience collection phase, we introduce the guided mode, as indicated by the blue arrows in the figure. After the policy network of agent i outputs the action based on the observation , is input into the action filter which outputs filtered action where and . Once agents have completed the filtered actions, we obtain an experience tuple that is stored in optimal replay buffer where . The steps indicated by the brown arrows in the figure are essentially the same as those in the MADDPG algorithm, with two differences: first, experience tuples were stored simultaneously in both buffers, and second, sampling was conducted from the two buffers in proportion . Next, we provide a detailed introduction to the EA-MADDPG algorithm.
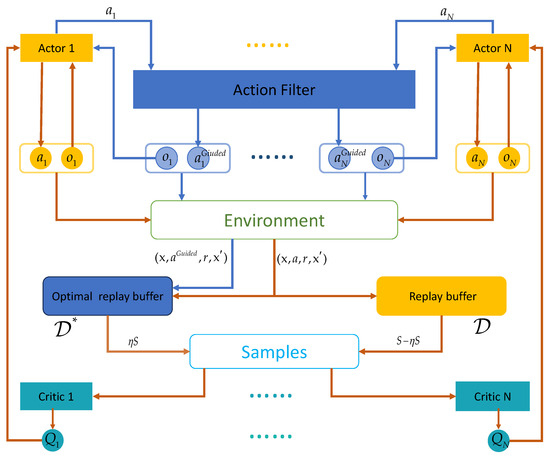
Figure 5.
The structure of the EA-MADDPG algorithm.
4.1. Equal Reward Setting
In the training of the MADDPG algorithm, a set of reward functions is established, enabling agents to receive rewards through these functions each time they complete actions within the environment. In EA-MADDPG, we introduce an additional set of reward functions and a reward setting called the equal reward setting to further enhance the training capabilities.
The key characteristic of the equal reward setting is that every state has the same maximum reward:
where is a constant value. For any given state , the maximum reward value that can be obtained is equal.
Next, we propose two specific reward functions that meet the above setting. For each agent i:
where
denotes the maximum angular velocity that can change the agent’s direction from both vertical and horizontal perspectives in one step. . denotes the penalty for agent i after agent i collides with other agents, and denotes the penalty for agent i after agent i hits the ground:
Next, let us take in as an example to explain why and satisfy equal reward setting.
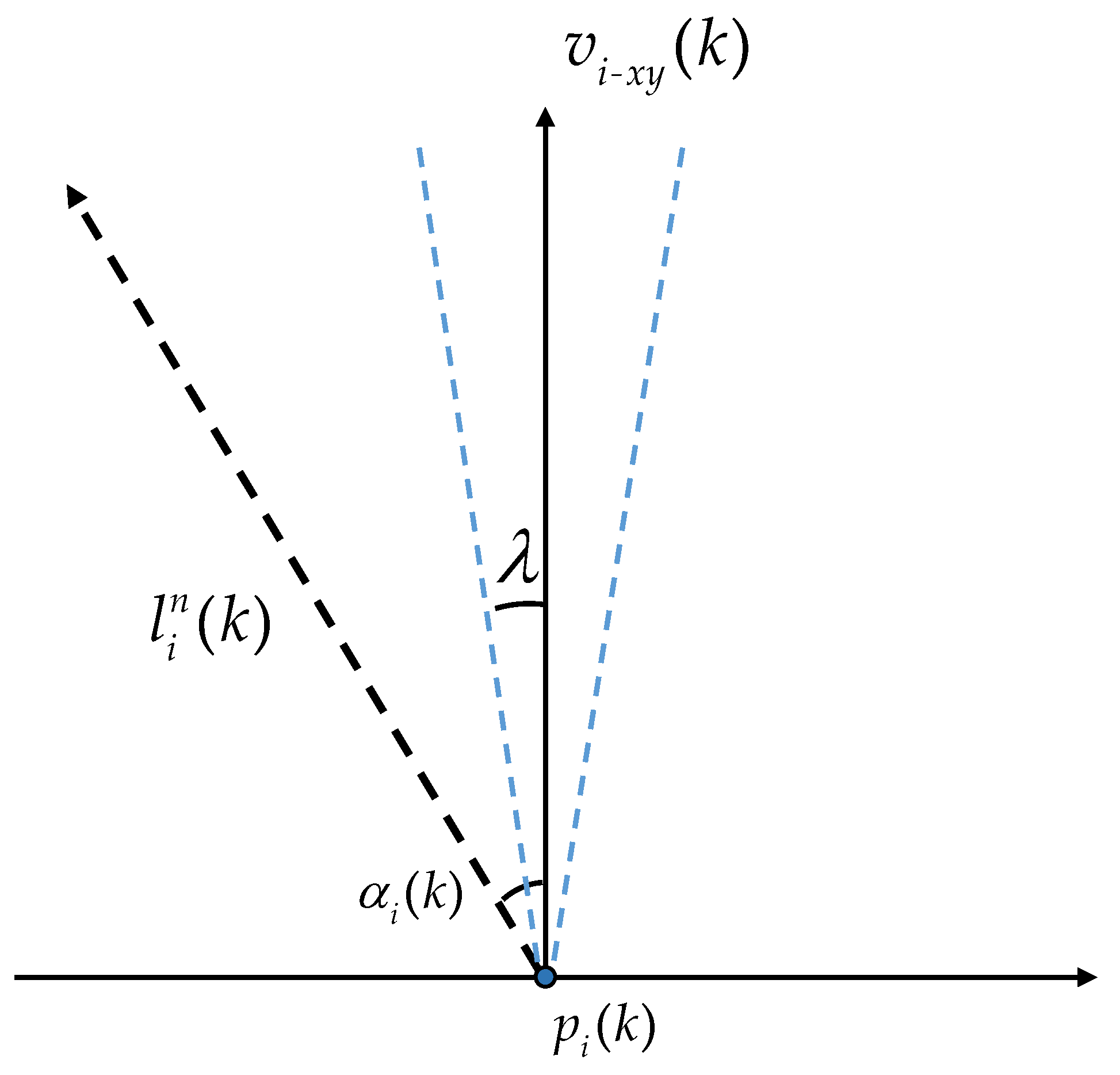
As shown in Figure 6, it is the plane parallel to O– and the angle between the two blue dashed lines in the figure represents the range within which the missile can change its velocity direction in one step from horizontal perspectives. The blue dashed lines about are symmetric. When is greater than , the reward is maximized at 2 when and decreases as decreases. Similarly, if is less than , the reward is also maximized at 2 when action and decreases as increases. If the angle is within , the reward is maximized at 2 when action and decreases as changes to both sides. The above is the general logic of the function and ensures that the maximum reward obtained from it is 2. Therefore, extending to each term of , they all meet the equal reward setting, meaning that satisfies the equal reward setting. has a similar composition to ; therefore, also possesses this property.
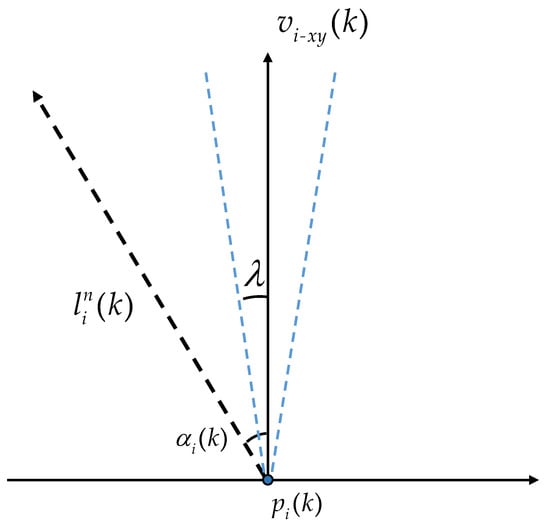
Figure 6.
Schematic of .
4.2. Optimal Replay Buffer
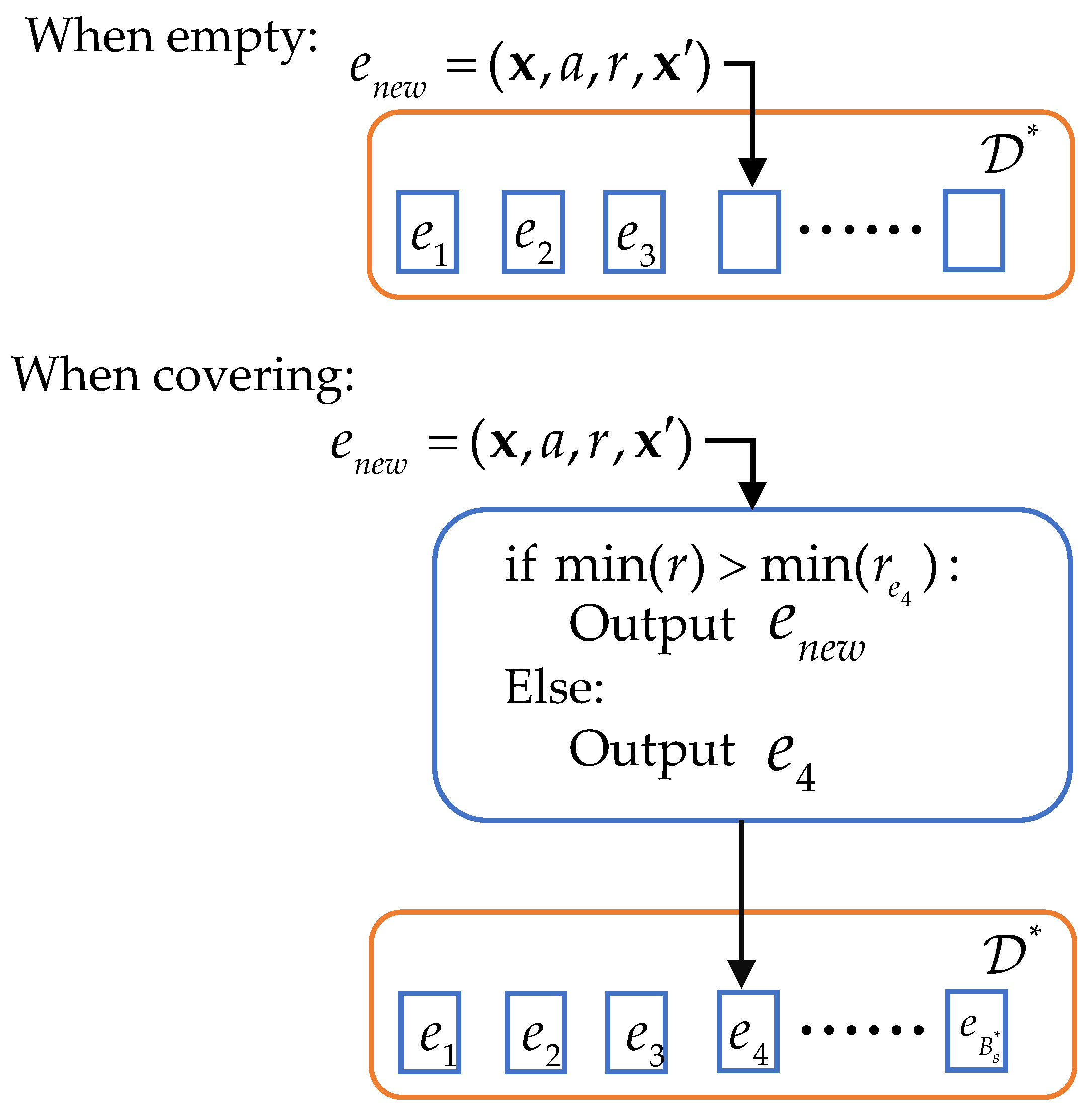
MADDPG uses a single experience replay buffer . In ME-MADDPG, we introduce an additional replay buffer called optimal replay buffer. Figure 7 shows that is a tuple containing the experience saved in the current step. are all experience tuples stored in the buffer , and denotes the maximum storage size of . When storing experiences, the method of storing experience tuples in empty slots is the same as . When experience tuples in are being overwritten, requires an additional step of judgment. For example, as shown in the figure, when is about to cover since r contains the rewards of all agents at this step, we select the minimum reward value in and compare it with the corresponding minimum reward value in . The experience tuple corresponding to the larger of the two compared reward values is then stored.
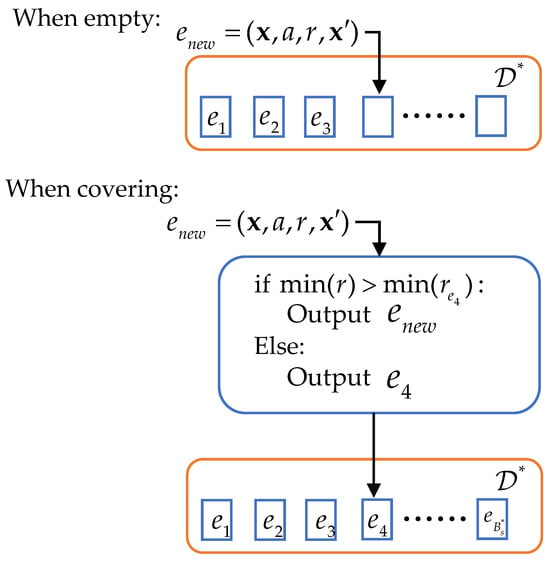
Figure 7.
Optimal replay buffer .
During training, samples can be extracted from and in proportion and then mixed for learning:
denotes the number of experience tuples collected from . denotes the number of experience tuples collected from . denotes the current episode value. denotes the decay rate of . denotes the initial proportion we set.
4.3. Action Filter
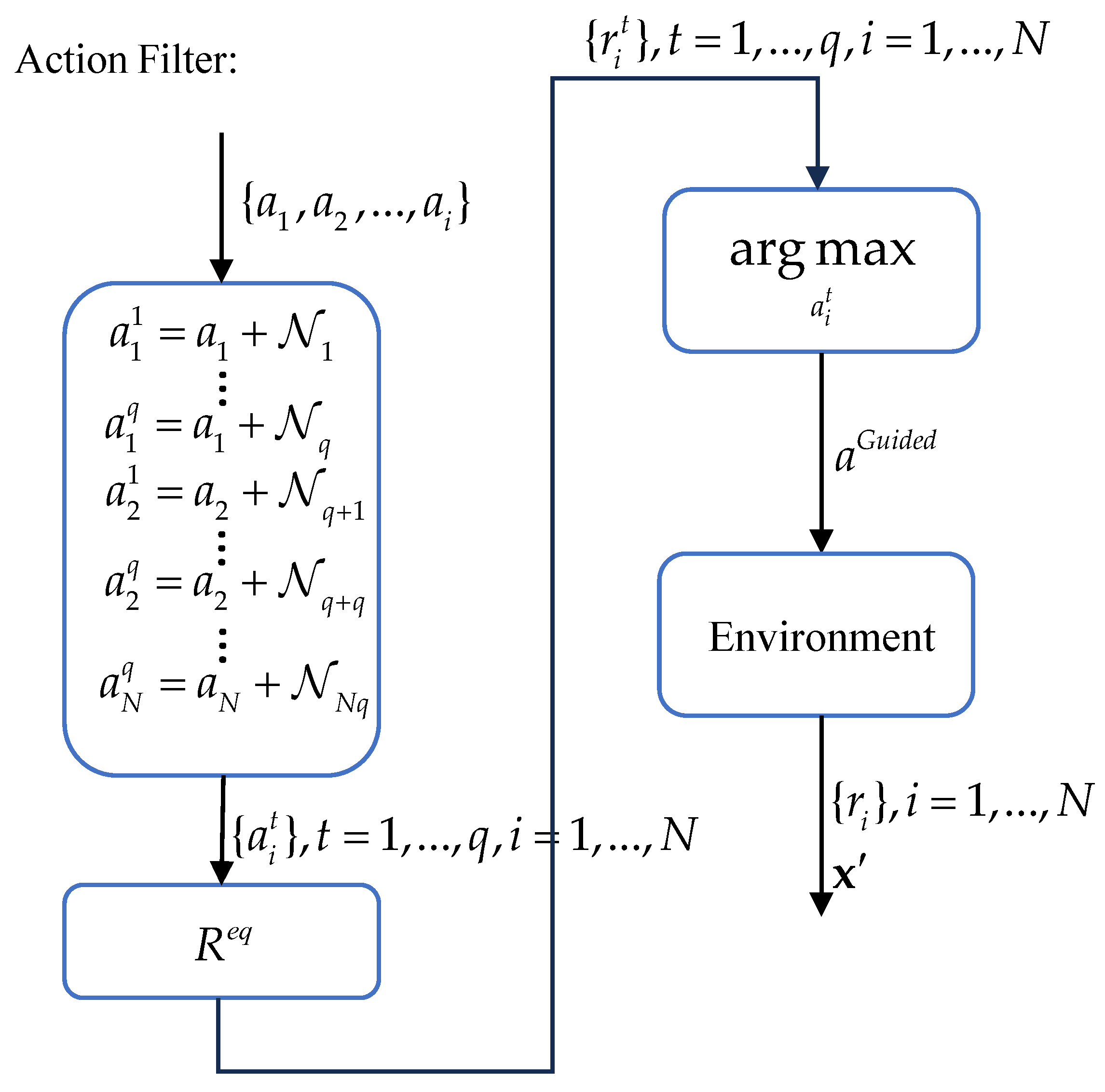
In the training of reinforcement learning, the exploration performance of agents is critical to the speed and effectiveness of learning. Therefore, we introduce an action filter. In the introduction above, we introduced the guided mode, using the action filter. As shown in Figure 8, after agents derive the action set and input it into the action filter, we generate a batch of random noise from , where denotes the repeated exploration coefficient, and integrate it with the action set to create a collection of exploratory actions . The observations , the actions , and these exploratory actions are then fed into the set of reward functions mentioned above to generate a set of exploratory rewards , ,. We input them into the filter:
Subsequently, agents execute , obtain rewards , and move to the next state .
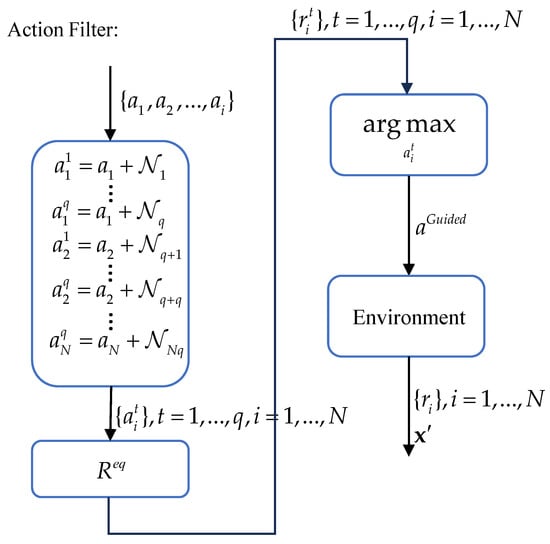
Figure 8.
Action filter under guided mode.
The noise is generated by:
where and the values in K follow a standard normal distribution. denotes the amplitude of noise. denotes the noise decay rate.
During training, we have a certain probability of choosing the guided mode. As the training progresses, the probability gradually approaches zero:
where denotes the probability decay rate we set. denotes the initial probability. Algorithm 1 presents the pseudocode for EA-MADDPG.
| Algorithm 1 EA-MADDPG |
|
5. Simulation and Discussion
Comprehensive simulation results are given in this section to examine the performance of the EA-MADDPG algorithm. Two scales were considered, namely and .
5.1. Simulation Setting
Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 below list the values of relevant parameters for two training environments. Table 5 lists the values of parameters related to training.

Table 2.
Initial missile positions when .

Table 3.
Initial missile positions when .

Table 4.
Common parameters for both environments.

Table 5.
Training’s parameters.
Table 6 and Table 7 list the dimensionality parameters of each layer in the actor networks and critic networks, respectively. For each agent, both the actor and critic networks (including the target networks for actor and critic) employed a classic feedforward neural network structure, a multi-layer perceptron (MLP). Each network comprised an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer.

Table 6.
The (target) actor network’s parameters.

Table 7.
The (target) critic network’s parameters.
In the actor network, the input layer was fully connected and used a rectified linear unit (ReLU) as the activation function, with a normalization function applied to the batch input data. In the critic network, the input layer was also fully connected and used a rectified linear unit (ReLU) as the activation function, but it passed the input data directly using an identity function. The hidden layers in both networks were fully connected, with ReLU as the activation function. The output layer in both networks was fully connected; in the actor network, the hyperbolic tangent activation function was used.
For reference, we used the MADDPG [17], ME-MADDPG [40], MADDPG-L [41], MAPPO [19] and MATD3 [20] algorithms in the same environment. At the same time, we replaced the multiple critics in the EA-MADDPG framework with a single universal critic to evaluate the performance of all agents. This framework was called EA-MADDPG-S. The training was conducted on a computer equipped with an AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 3975WX 32-core CPU, 128 GB of RAM, and an NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU.
5.2. Simulation Results and Discussion
5.2.1. Training Result
Through training, we obtained the following results:
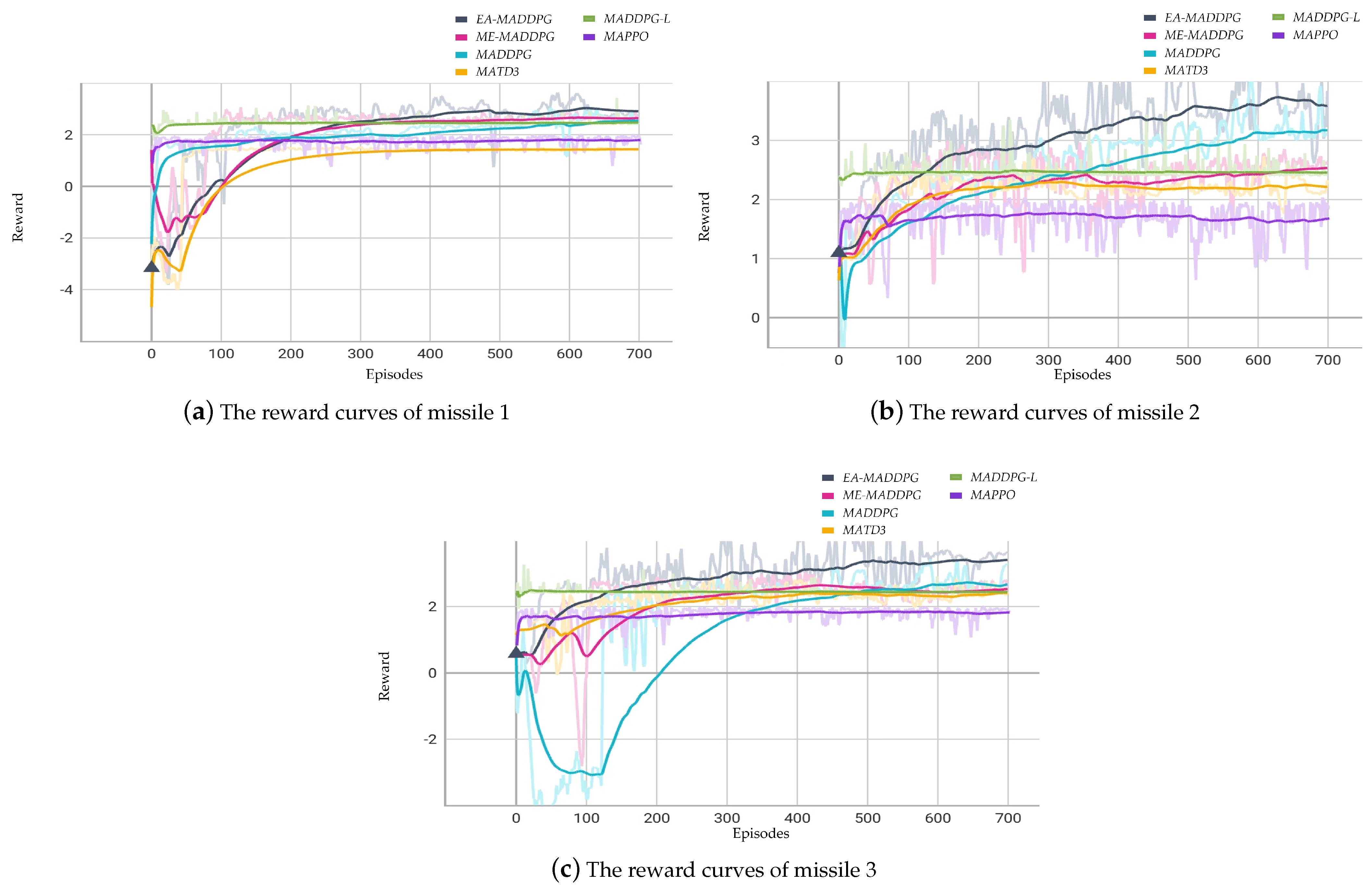
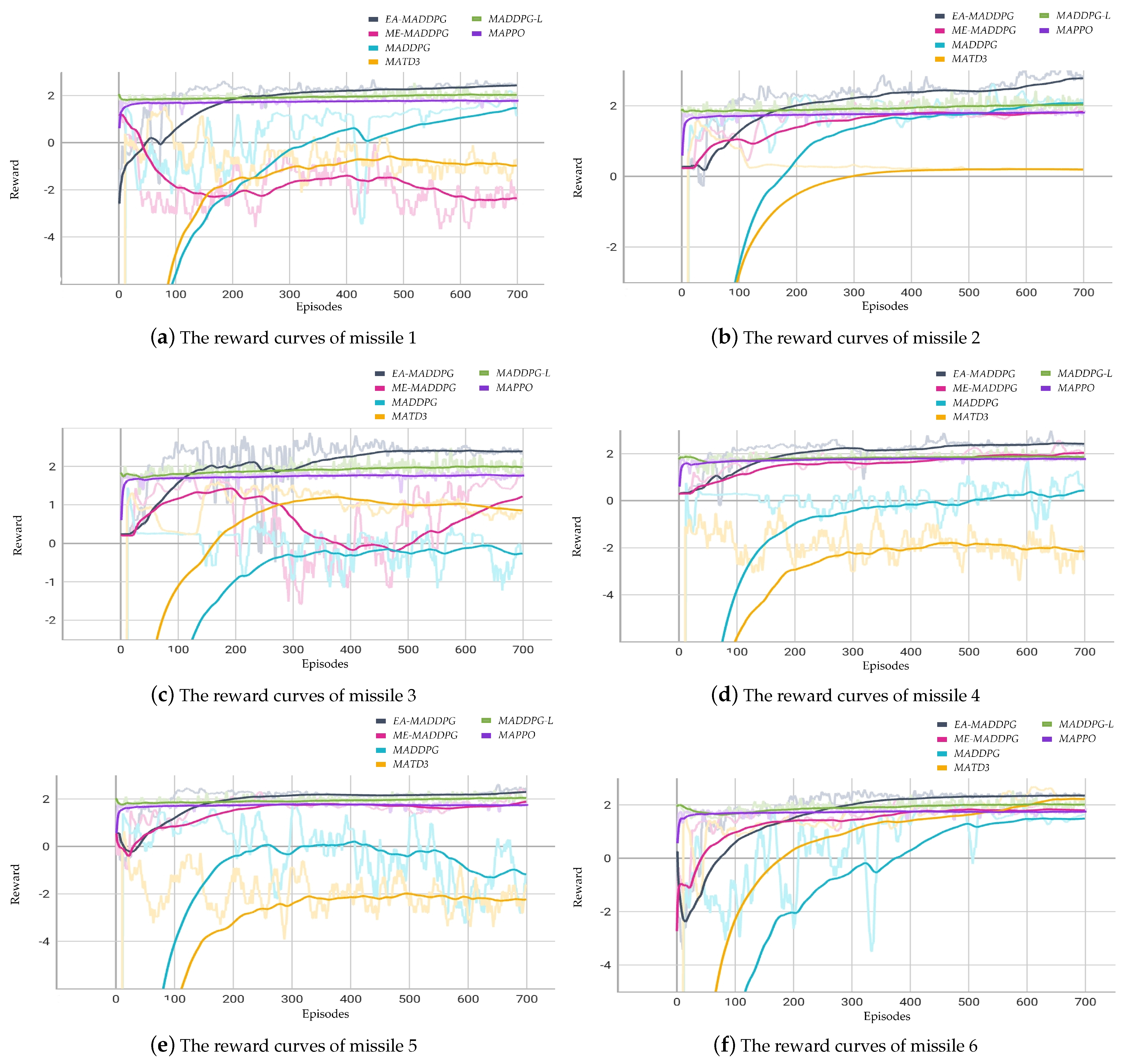
Figure 9 illustrates the curves of the average reward of three missiles throughout the training episodes for . Figure 10 illustrates the curves of the average reward of six missiles throughout the training episodes for .
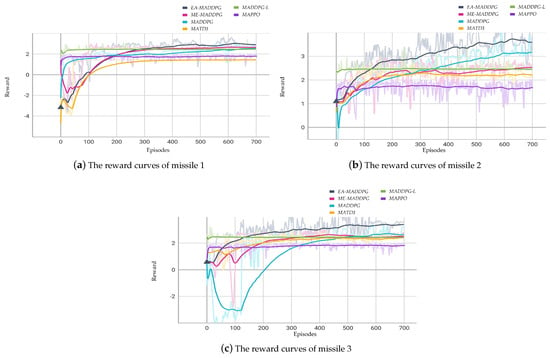
Figure 9.
The courses of reward for missiles for .
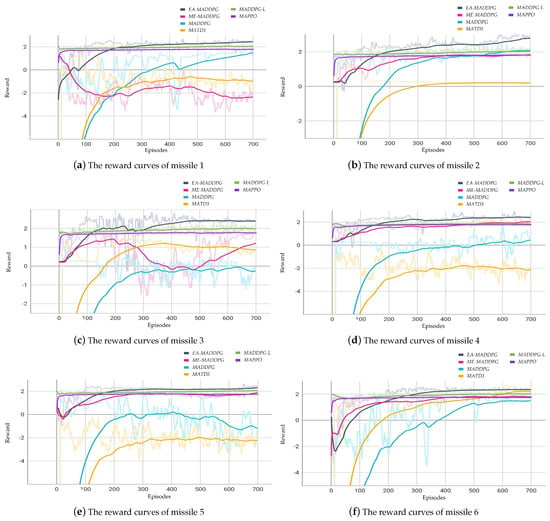
Figure 10.
The courses of reward for missiles .
The reward functions (18) for missiles reflected our expectation of a joint optimal strategy for multiple missiles, where all missiles approached the UAV more quickly while avoiding collisions with each other. If one missile performed poorly during training, resulting in a lower individual reward, it also affected the rewards of the other missiles, causing the overall rewards of all missiles to decrease.
From Figure 9 and Figure 10, we can see that the training performance of the MADDPG-L and MAPPO algorithms was not very effective in the current environment, as the reward curves showed little change from the beginning to the end of training. Therefore, in the following convergence analysis of the reward curves we do not include these two algorithms.
In the three vs. one environment, as shown in Figure 9, missile collisions and crashes into the ground occurred at the beginning of the training, leading to low and even negative reward values. Through continuous training, the missiles learned to fly toward the UAV while avoiding collisions, leading to an increase in reward values. In the subsequent training process, the convergence values of the reward curves under the EA-MADDPG algorithm were higher than those of other algorithms. This indicated that under this algorithm, the three missiles could approach the UAV more quickly while avoiding collisions with each other.
In the six vs. one environment, as shown in Figure 10, the reward curves under the EA-MADDPG algorithm converged, and both the convergence speed and convergence values were greater than those of the reward curves under other algorithms. As the number of missiles increased, the difficulty of training began to rise. Within the same episodes, the reward curve of missile 1 was negative under ME-MADDPG. The reward curves of missiles 3, 4, and 5 were negative under MADDPG. The reward curves of missiles 1, 4, and 5 were negative under MATD3. This indicated that the corresponding missiles were still experiencing collisions with each other or crashing into the ground, which also affected the training and reward values of the other missiles. Under EA-MADDPG, the missiles could actively explore and collect good experiences through the action filter, quickly learning new strategies to overcome the aforementioned issues. To prevent excessive learning for this portion of experiences and stabilize subsequent learning effects and reward curves, EA-MADDPG mixed these experiences with normally obtained experiences in optimal replay buffer . At the same time, it reduced the probability and the sampling ratio according to certain decay rates.
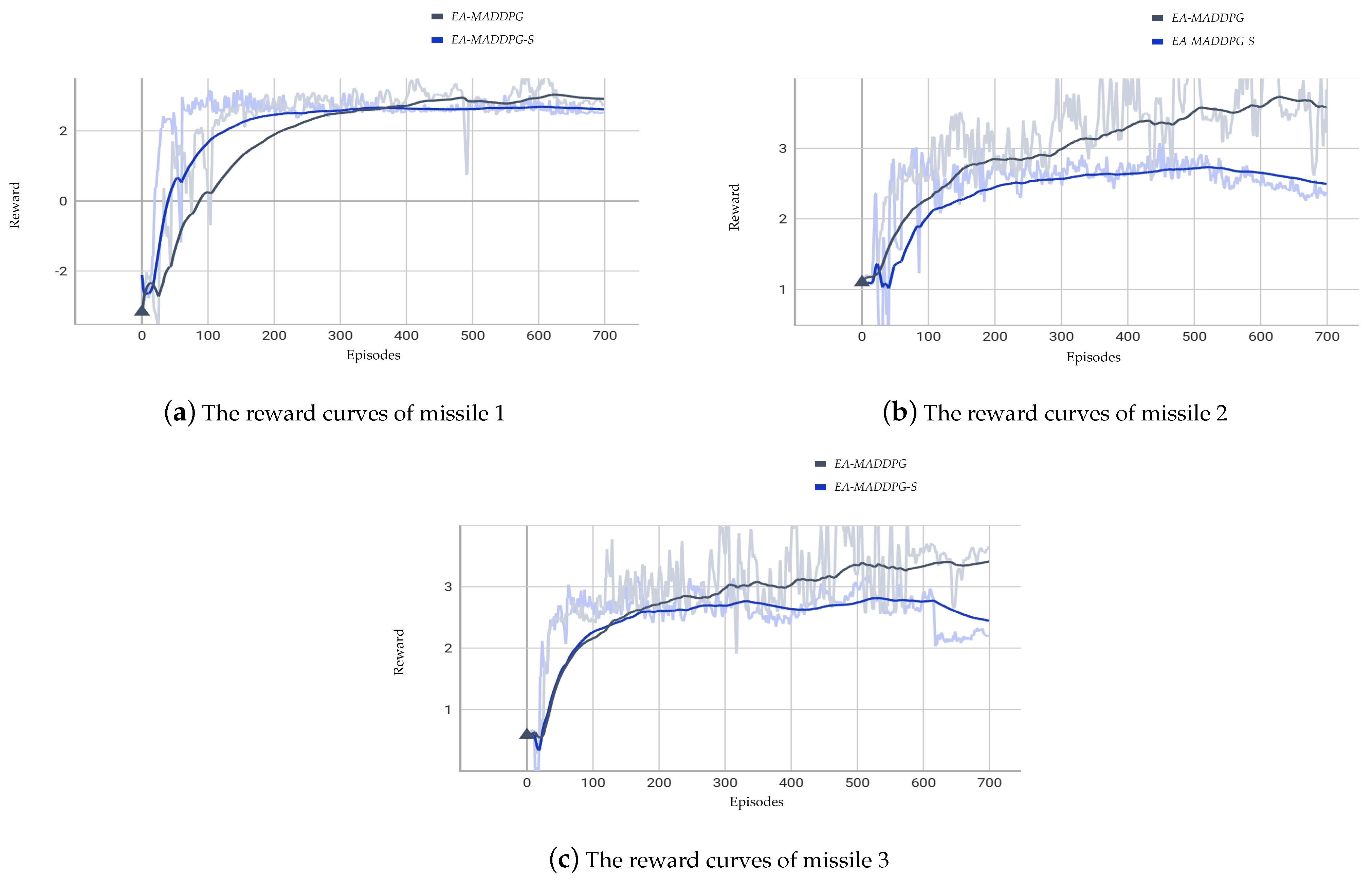
We compared the reward curves of EA-MADDPG and EA-MADDPG-S in the three vs. one environment. As shown in Figure 11, the reward curve of missile 1 under EA-MADDPG-S converged faster than that under EA-MADDPG. However, the convergence speed of missile 2 was slower under EA-MADDPG-S compared to EA-MADDPG. For missile 3, the convergence speeds of both algorithms were roughly the same. Nonetheless, the final convergence values for all missiles under EA-MADDPG were higher than those under EA-MADDPG-S. From the comparison of the reward curves above, we conclude that training with a single critic was less effective than having a separate critic for each agent.
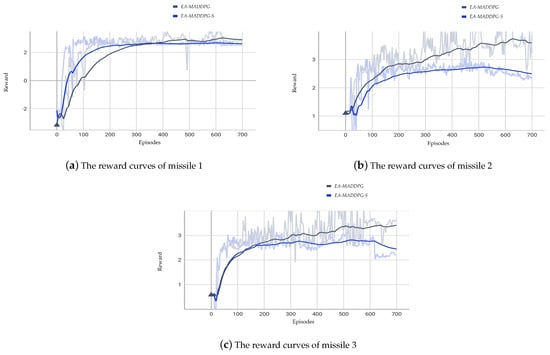
Figure 11.
Comparison of reward curves under the EA-MADDPG and EA-MADDPG-S algorithms.
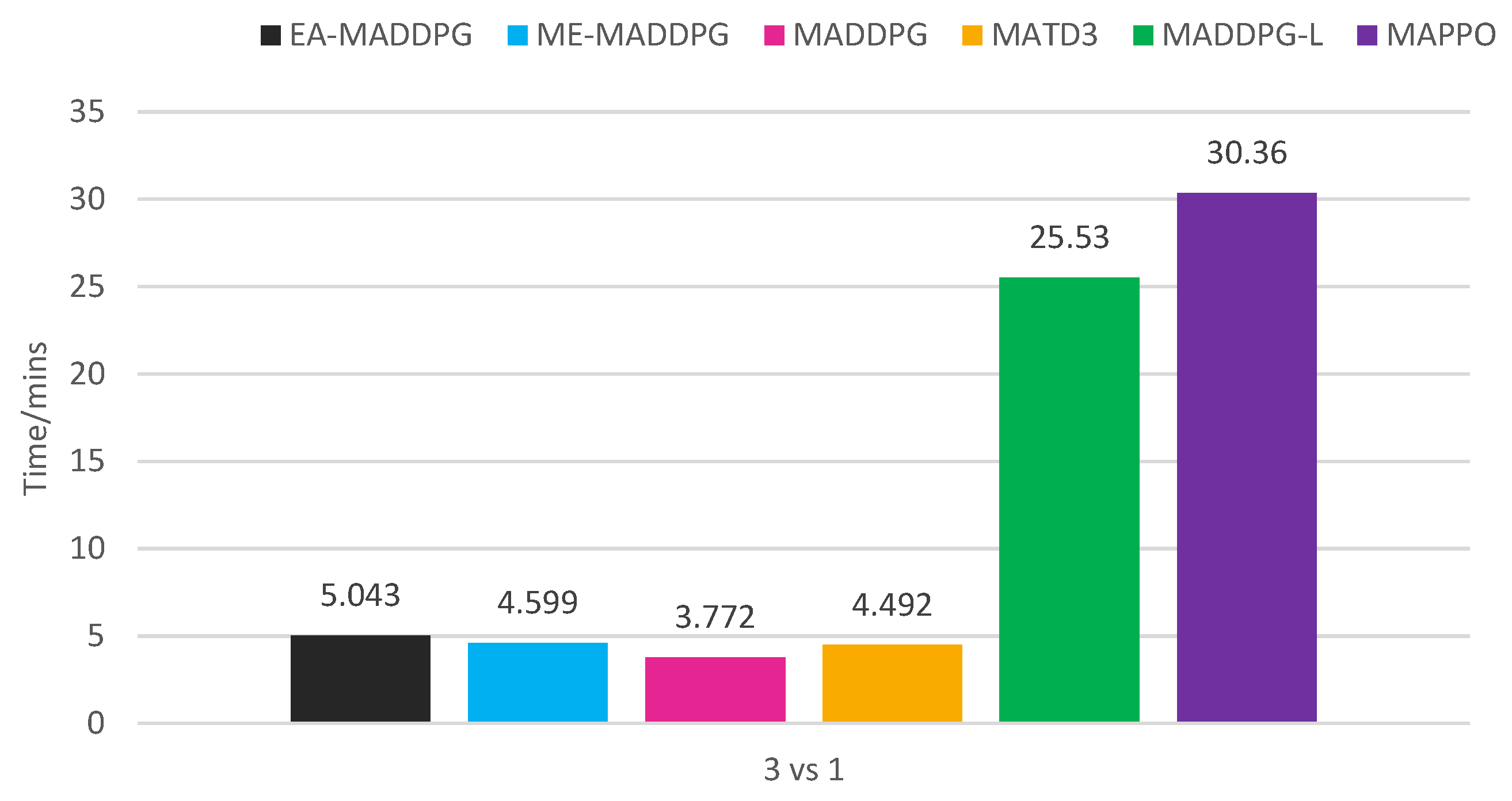
As shown in Figure 12, EA-MADDPG required additional time consumption compared to MADDPG. Analyzing EA-MADDPG’s training process, in the action filter, we needed to introduce a batch of noise to generate exploratory actions, calculate the , and select based on . All these steps required additional time consumption. Additionally, storing and sampling from also incurred extra time costs. When and the sampling ratio are set improperly, the extra time consumption increases. The algorithm analysis and experiments demonstrated that both the action filter and the optimal replay buffer design introduced additional time complexity.
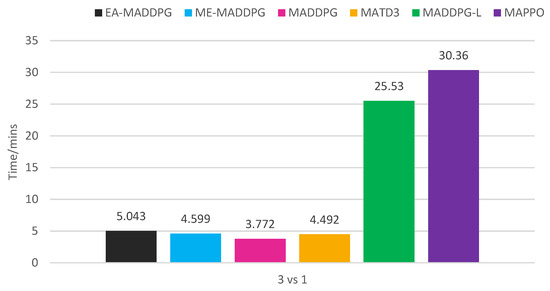
Figure 12.
Training time consumption of algorithms in 3 vs. 1 environment.
5.2.2. Policy Networks Testing
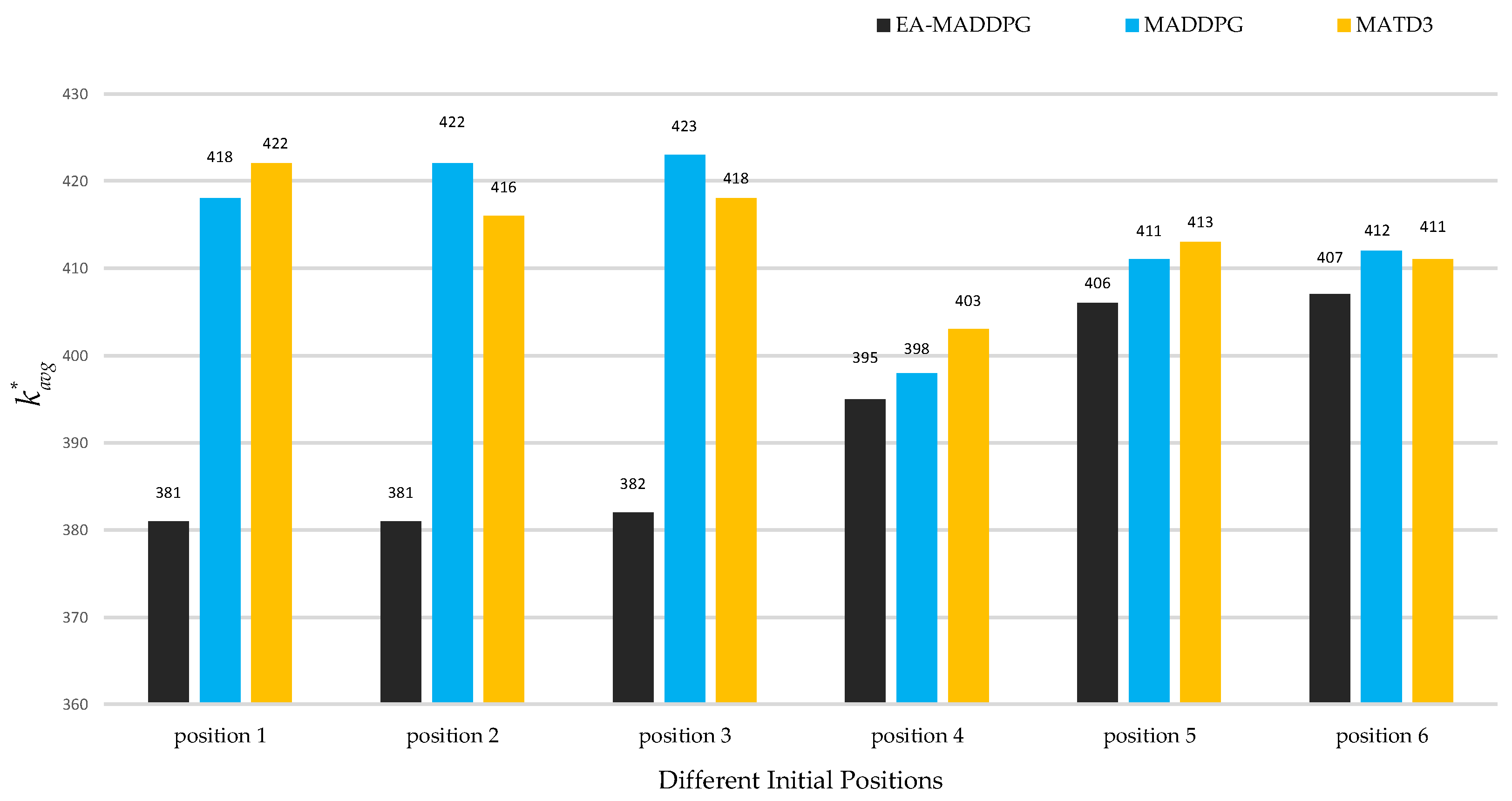
Next, we evaluated the trained policy networks in the three vs. one environment. The testing procedure was as follows: First, we selected several initial positions and strike coordinates for the UAV, observed the interception trajectories of three missiles and the UAV, conducted 100 tests for each position, and compared and under different algorithms for each position, where denote the average values of and d, respectively. Second, 1000 tests were conducted with randomly generated initial positions and strike coordinates. We compared the percentage ℘ of successful interceptions under different algorithms across these 1000 trials.
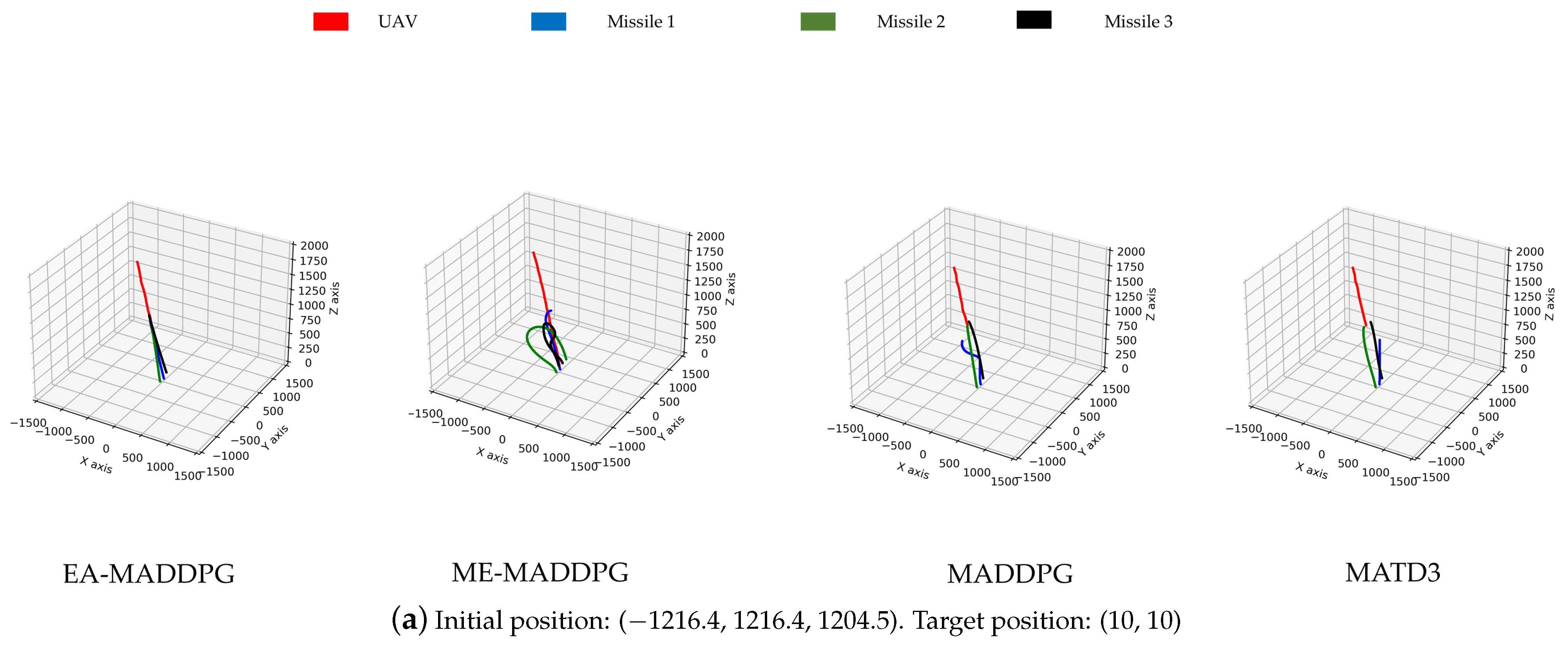
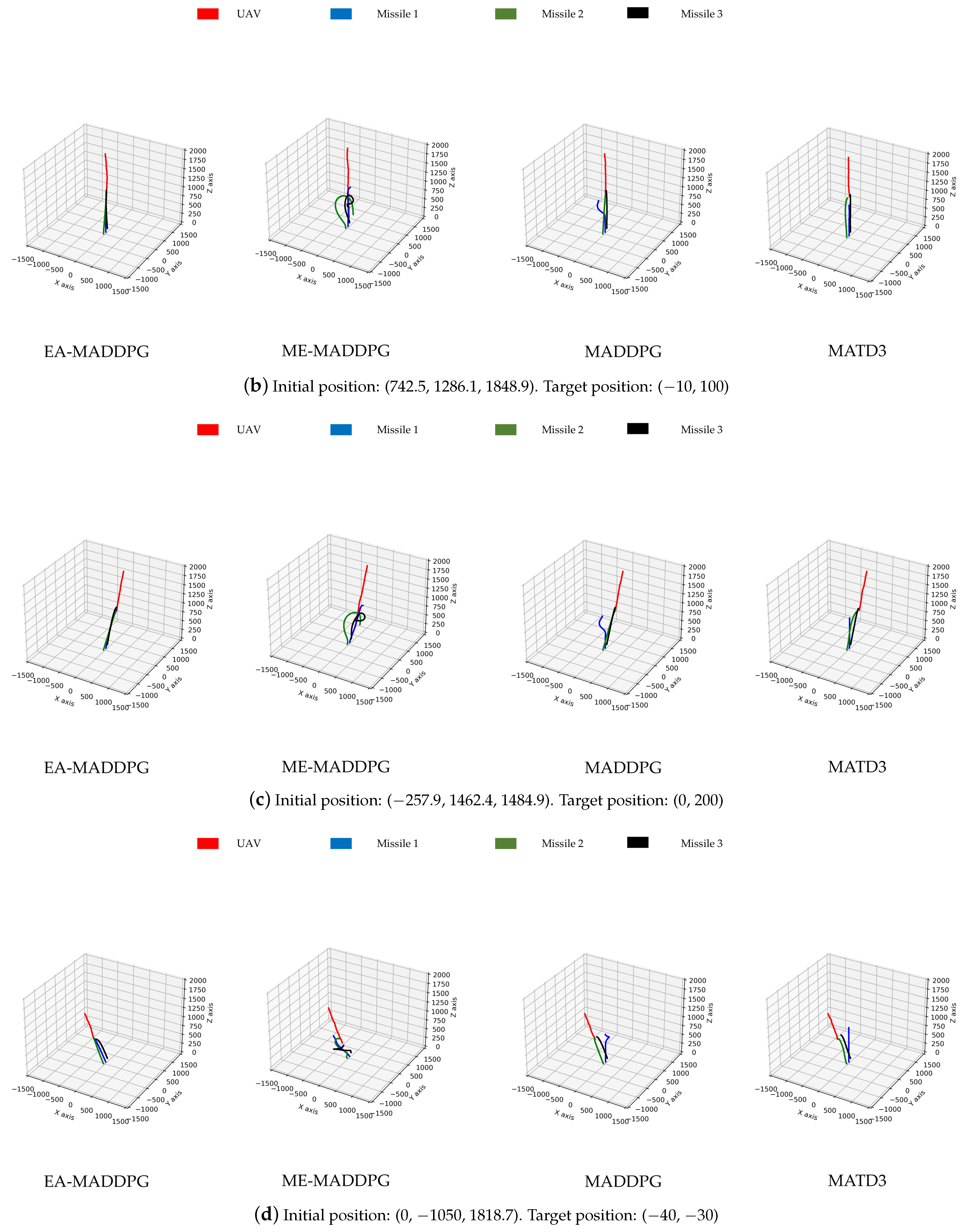
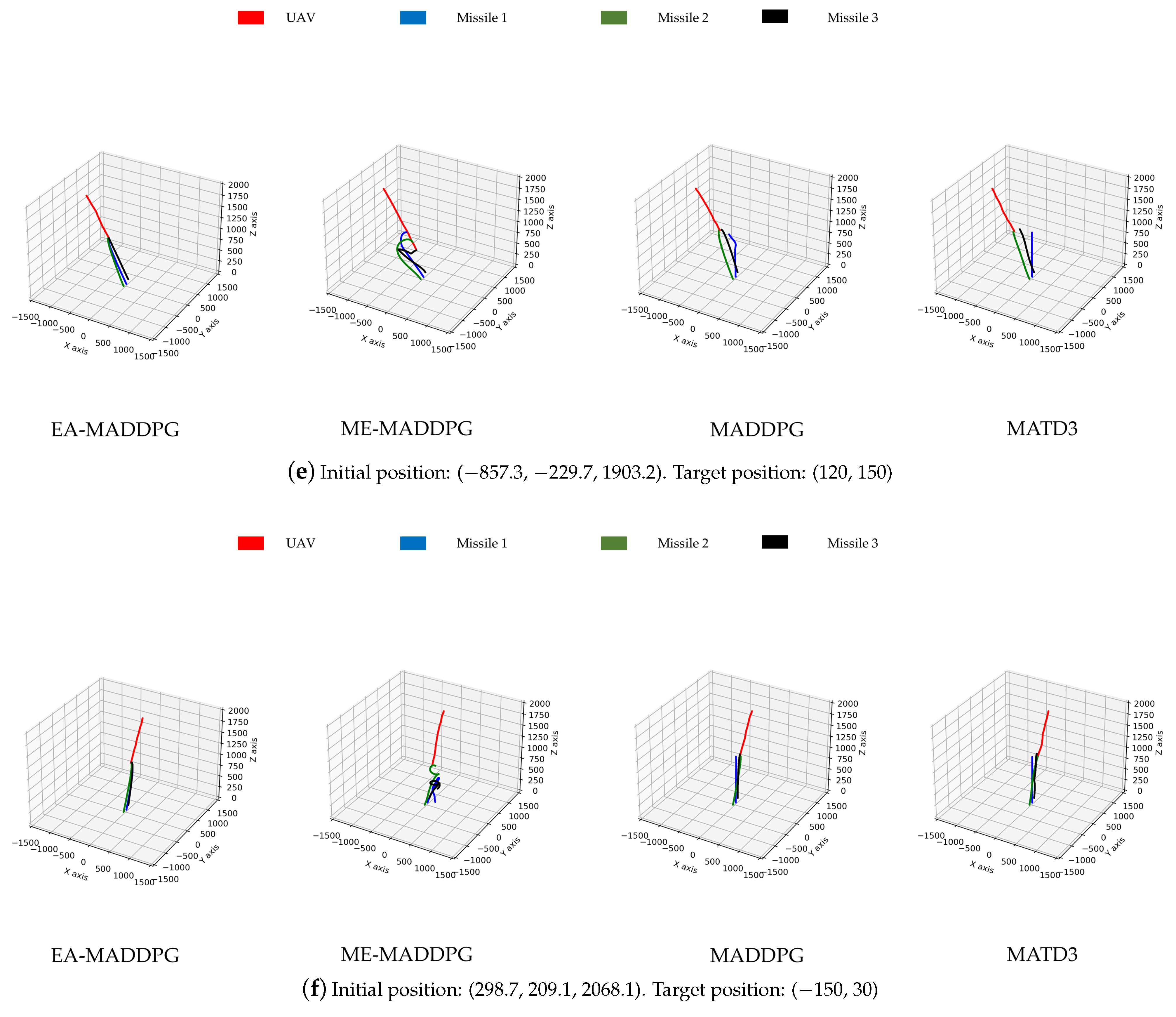
As shown in Figure 13, the missile trajectories under the EA-MADDPG algorithm most closely matched the trajectories we expected: three missiles were all able to quickly move towards the UAV that was performing small-amplitude irregular movements. From the trajectories under the ME-MADDPG, it can be seen that although the three missiles no longer crashed into the ground or collided with each other, they were still unable to approach the target UAV quickly. This explained the reason for the lower convergence values of the curves of ME-MADDPG mentioned above. The trajectories under MADDPG showed that missile 2 and missile 3 achieved better training results because they could move towards the UAV, while missile 1 did not perform well. Similar to MADDPG, the missile trajectories under the MATD3 exhibited the same performance. Missile 2 and missile 3 could move towards the UAV, while missile 1 did not perform well and only flew straight up. From the trajectory plots, we can explain why the convergence values of the reward curves for the other algorithms were lower than those of the EA-MADDPG algorithm.
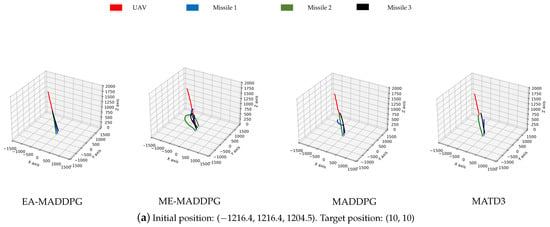
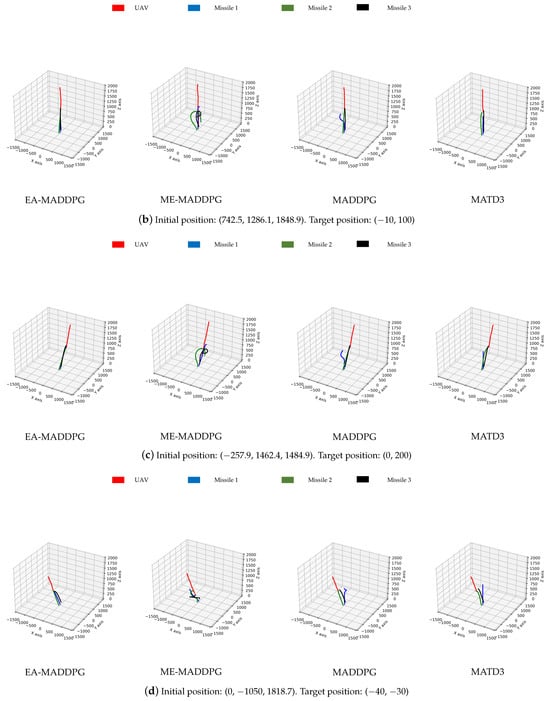
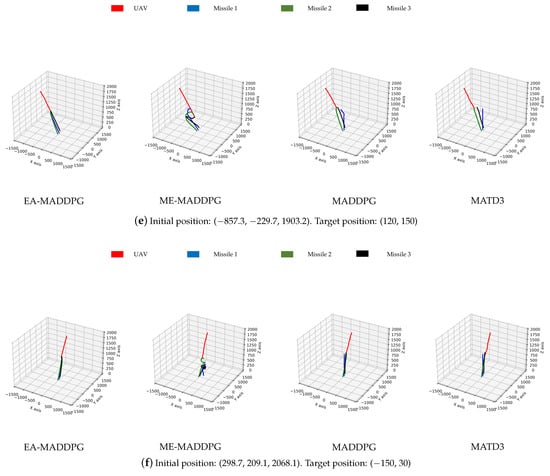
Figure 13.
The trajectories of missiles under four different algorithms with varying initial and target positions.
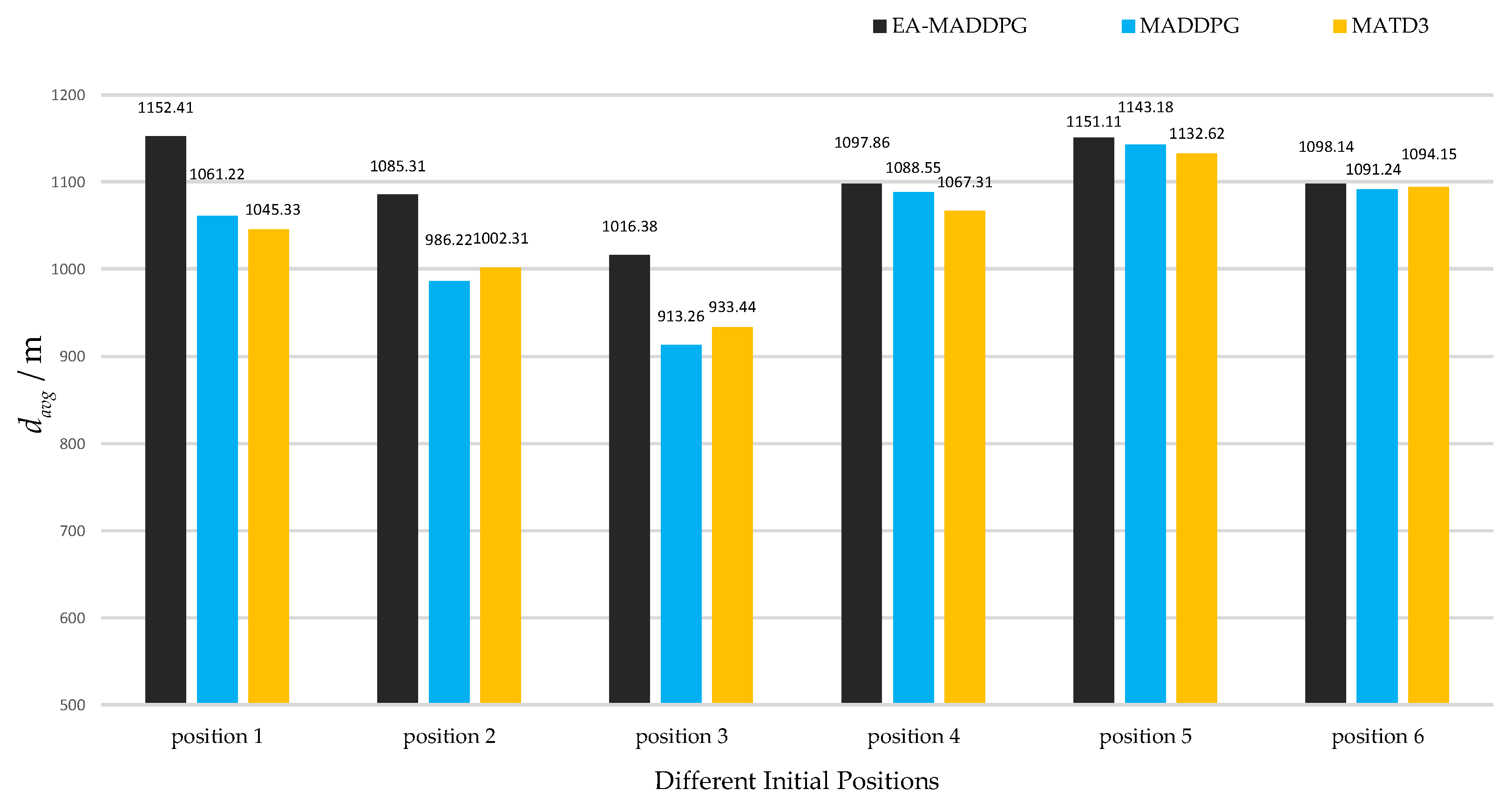
As shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15, the two graphs intuitively demonstrated the speed of UAV interception under three algorithms and did not show data under ME-MADDPG because its interception success rate was too low (the interception success percentage is shown below), making the interception data not referential. Under the EA-MADDPG algorithm, positions 1 to 6 required significantly fewer steps for interception, and the UAV was intercepted at a longer distance, thus showing a greater advantage. Combining the analyses mentioned above, we conclude that EA-MADDPG outperformed other algorithms both in terms of the combined training effect of multiple missiles (i.e., all missiles were ideally trained) and the speed of interception.
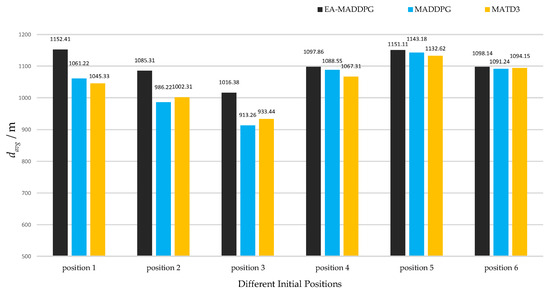
Figure 14.
under different positions. Positions 1 to 6 correspond to initial positions and target positions in Figure 13a–f.
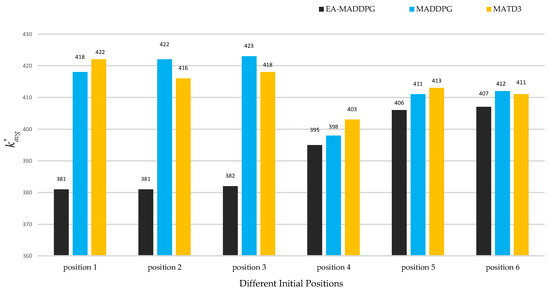
Figure 15.
under different positions. Positions 1 to 6 correspond to initial positions and target positions in Figure 13a–f.
Next, we conducted 1000 sets of tests to compare the percentage ℘ of successful interceptions under different algorithms.
As shown in Figure 16, EA-MADDPG, with an interception success rate of 99.5%, exceeded MADDPG at 84.3% and MATD3 at 72.3%, while the percentage for ME-MADDPG was only 20.3%. This demonstrated that EA-MADDPG’s training effect in terms of interception success rate surpassed the other three algorithms.
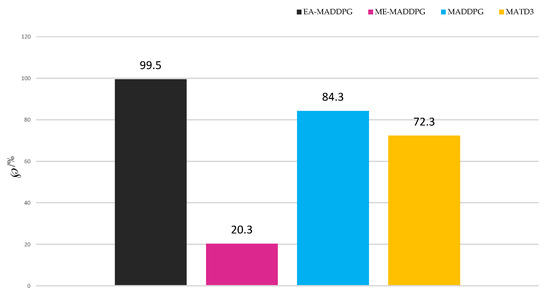
Figure 16.
The interception success percentage ℘ among 1000 tests.
6. Conclusions
This paper stemmed from the reality of the progressively increasing threat of drones and the ongoing development of multi-agent reinforcement learning. In response to the growing threat of UAVs, this paper combined multi-agent reinforcement learning technology with the use of missiles to explore the issue of using missiles for UAV defense in three-dimensional space, applying missiles in defense against UAVs.
This paper proposed an improved variant of the MADDPG algorithm called EA-MADDPG. Compared to the original algorithm, the EA-MADDPG algorithm had two distinct advantages: first, it enhanced the exploration of multiple agents through the action filter, allowing the agents to be more “proactive” in exploring and updating their strategies when they were experiencing poor training outcomes; second, through the design of the equal-reward setting and the optimal replay buffer, the agents were able to more efficiently utilize the experiences gained from “proactive” exploration, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the training.
This study explored a scenario with a single UAV. However, in reality, UAVs often operate in groups to perform tasks. Therefore, in the future, we will further investigate multi-UAV scenarios and multi-agent reinforcement learning strategies for multi-target interception tasks. Additionally, balancing exploration and exploitation during agent training has always been a crucial aspect of reinforcement learning research. In the EA-MADDPG framework presented in this paper, the series of exploratory actions were generated by adding multiple simple random noises. This design still has considerable room for improvement. Future work will consider incorporating Ornstein–Uhlenbeck noise for research and will also refer to the action selection principles based on relevant quantum theory from the QiRL framework and the prioritization principles for experiences in the replay pool from the QiER framework for more in-depth research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G. and H.C.; methodology, X.L. and H.C.; software, X.L. and Y.Z.; validation, X.L.; formal analysis, X.L. and H.C.; investigation, X.L. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, X.L. and H.C.; visualization, X.L.; supervision, H.G. and H.C.; funding acquisition, H.G. and H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant numbers 62173149, 62276104, and U22A2062, in part by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation under grant numbers 2021A1515012584, 2022A1515011262, and in part by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
DURC Statement
Current research is limited to guidance and control, which is beneficial and does not pose a threat to public health or national security. Authors acknowledge the dual-use potential of research involving guidance and control and confirm that all necessary precautions have been taken to prevent potential misuse. As an ethical responsibility, authors strictly adhere to relevant national and international laws about DURC. Authors advocate for responsible deployment, ethical considerations, regulatory compliance, and transparent reporting to mitigate misuse risks and foster beneficial outcomes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the DURC Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
| DDPG | Deep deterministic policy gradient |
| TD3 | Twin-delayed deep deterministic policy gradient |
| MADDPG | Multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient |
| EA-MADDPG | Equal-reward and action-enhanced multi-agent deep deterministic |
| policy gradient | |
| EA-MADDPG-S | Equal-reward and action-enhanced multi-agent deep deterministic policy |
| gradient with single critic | |
| ME-MADDPG | Mixed experience multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient |
| MATD3 | Multi-agent twin-delayed deep deterministic policy gradient |
| MADDPG-L | Multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient with long short-term memory |
| MAPPO | Multi-agent proximal policy optimization |
| MLP | Multi-layer perceptron |
| ReLU | Rectified linear unit |
References
- Kang, H.; Joung, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.; Cho, Y.S. Protect your sky: A survey of counter unmanned aerial vehicle systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168671–168710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Jing, W.X. Geometric approach to capture analysis of PN guidance law. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2008, 12, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.; Takano, H.; Baba, Y. Robust path-following for UAV using pure pursuit guidance. In Aerial Vehicles; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.T.; Lee, J.G. Improved command to line-of-sight for homing guidance. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Bryson, A.E. Applied Optimal Control: Optimization, Estimation and Control; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, S. On Proportional Navigation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1983, AES-19, 497–510. [Google Scholar]
- Shima, T.; Rasmussen, S. UAV Cooperative Decision and Control: Challenges and Practical Approaches; SIAM: University City, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Michael, N. Opportunities and challenges with autonomous micro aerial vehicles. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.L.; Bruni, S. Collaborative Human-UAV Decision Making: Applications in Civilian UAVs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhuang, J. A study on a sequential one-defender-N-attacker game. Risk Anal. 2019, 39, 1414–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.W.; McLain, T.W. Small Unmanned Aircraft: Theory and Practice; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barto, A.G.; Sutton, R.S.; Anderson, C.W. Neuronlike adaptive elements that can solve difficult learning control problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1983, SMC-13, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillicrap, T.P.; Hunt, J.J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1861–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.I.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Pieter Abbeel, O.; Mordatch, I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Neural information processing systems foundation: Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Sha, F. Actor-attention-critic for multi-agent reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 2961–2970. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Velu, A.; Vinitsky, E.; Wang, Y.; Bayen, A.M.; Wu, Y. The Surprising Effectiveness of MAPPO in Cooperative, Multi-Agent Games. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.01955. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, J.; Gabler, V.; Osa, T.; Sugiyama, M. Reducing overestimation bias in multi-agent domains using double centralized critics. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01465. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, W.; Mancuso, R.; West, R.; Bestavros, A. Deep reinforcement learning for UAV navigation and obstacle avoidance. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 3, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Qie, H.; Shi, D.; Shen, T.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Joint optimization of multi-UAV target assignment and path planning based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. IEEE access 2019, 7, 146264–146272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; Viguria, A.; Heredia, G.; Ollero, A. Minimal-time trajectories for interception of malicious drones in constrained environments. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision Systems: 12th International Conference, ICVS 2019, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–25 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 734–743. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.; Kumar, M. Tracking of ground mobile targets by quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles. Unmanned Syst. 2014, 2, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, A.T.; Koyuncu, E. Model Predictive Control-Based Guidance with Impact Angle Constraints for Visual Quadrotor Interception. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Rome, Italy, 3–6 July 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M. Trajectory tracking control method of UAV formation based on fuzzy control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cryptography, Network Security, and Communication Technology (CNSCT 2023), Changsha, China, 6–8 January 2023; Volume 12641, pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xie, M.; Dong, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, X.; Qu, G.; Wang, Z.; Yan, P. RTPN method for cooperative interception of maneuvering target by gun-launched UAV. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 5190–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, T.; Zhao, T.; Liu, S.; Ma, C. Research on cooperative UAV countermeasure strategy based on interception triangle. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computer Application, Hangzhou, China, 27–29 October 2023; pp. 1015–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, B.; Liu, J.; Duan, H. Multi-UAV interception inspired by Harris’ Hawks cooperative hunting behavior. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Sanya, China, 27–31 December 2021; pp. 1656–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Shaferman, V.; Shima, T. Cooperative optimal guidance laws for imposing a relative intercept angle. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2015, 38, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Fancheng, K.; ZHANG, D.; Zhenzhou, B. Research on Target Matching of Television Guided Missile Seeker. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electronic Industry and Automation (EIA 2017), Suzhou, China, 23–25 June 2017; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 319–321. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, J.A.S.; Srigrarom, S. Drone-to-drone interception path planning by Deep Q-network with Graph Neural Network based (DQN-GNN) model. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), Penang, Malaysia, 9–12 June 2023; pp. 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, J.E.; Sun, X.; Novick, D.; Fierro, R. Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Countering Uncrewed Aerial Systems. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems, Montbéliard, France, 28–30 November 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 394–407. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Liu, G.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W. Safe multi-agent learning control for unmanned surface vessels cooperative interception mission. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Guilin, China, 9–11 July 2022; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L. USV Target Interception Control With Reinforcement Learning and Motion Prediction Method. In Proceedings of the 2022 37th Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), Beijing, China, 19–20 November 2022; pp. 1050–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Xiao, L.; Guan, J.; Yi, W.; Yin, H. Intercept Guidance of Maneuvering Targets with Deep Reinforcement Learning. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2023, 2023, 7924190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Aghvami, A.H. Covertness-aware trajectory design for UAV: A multi-step TD3-PER solution. In Proceedings of the ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–20 May 2022; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Aghvami, A.H.; Dong, D. Intelligent trajectory planning in UAV-mounted wireless networks: A quantum-inspired reinforcement learning perspective. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Aghvami, A.H.; Dong, D. Path planning for cellular-connected UAV: A DRL solution with quantum-inspired experience replay. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 7897–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Wu, D.; Li, B.; Gao, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, D. ME-MADDPG: An efficient learning-based motion planning method for multiple agents in complex environments. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 2393–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Zhou, N.; Liu, C.; Su, H.; Liu, Y.; Cong, J. Time-aware MADDPG with LSTM for multi-agent obstacle avoidance: A comparative study. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 4141–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fu, M.; Qu, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, S. A deep reinforcement learning-based method applied for solving multi-agent defense and attack problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 176, 114896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Duan, Y. Cooperative Encirclement Strategy for Multiple Drones Based on ATT-MADDPG. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 6th International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Qingdao, China, 21–24 July 2023; pp. 1035–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Yang, L.; Cao, G.; Lu, T.; Wang, B. Recurrent MADDPG for object detection and assignment in combat tasks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 163334–163343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Lee, H.; Kaliappan, V.K.; Nguyen, T.A.; Jo, H.; Cho, H.; Min, D. Multiagent reinforcement learning based on fusion-multiactor-attention-critic for multiple-unmanned-aerial-vehicle navigation control. Energies 2022, 15, 7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Lv, M.; Yan, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, A.; Li, L.; Zuo, J. Improving Cooperative Multi-Target Tracking Control for UAV Swarm Using Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR), Beijing, China, 21–23 April 2023; pp. 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Dou, L.; Tian, B. Game of drones: Multi-UAV pursuit-evasion game with online motion planning by deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 7900–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, G.; Li, Y.; Sheng, A.; Xu, L. A Many-to-Many UAV Pursuit and Interception Strategy Based on PERMADDPG. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Conference on Robotics and Computer Vision (ICRCV), Nanjing, China, 15–17 September 2023; pp. 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Dai, W.; Yao, W.; Ma, J.; Zeng, Z.; Lu, H. Multi-robot flocking control based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 150397–150406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhuang, D.; Xie, H. Anti-drone policy learning based on self-attention multi-agent deterministic policy gradient. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems, Changsha, China, 24–26 September 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 2277–2289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhou, D.; Yang, Z. Multiple-uav reinforcement learning algorithm based on improved ppo in ray framework. Drones 2022, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Song, G.; Gai, W. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Driven UAV Data Collection Path Planning: A Study on Minimizing AoI. Electronics 2024, 13, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).