Effects of UAS Rotor Wash on Air Quality Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
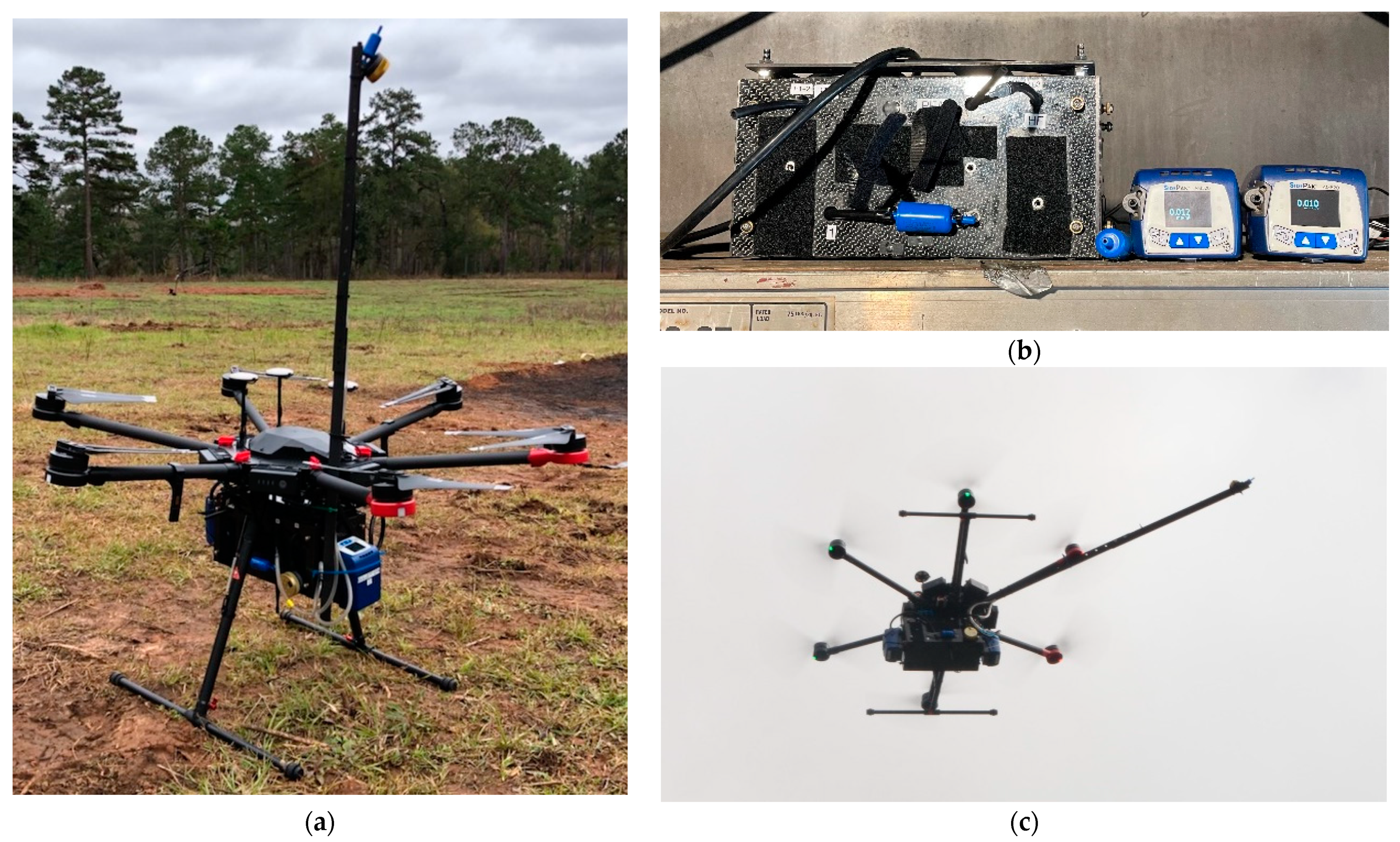
2.1. Emission Sampling
2.2. Emission Sampler
2.3. Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Indoor Laboratory Instrument Comparison
3.2. Open Burn Test Facility Testing
3.3. Field Tests of Rotor Wash Effects
3.3.1. CO2 and CO
3.3.2. PM2.5
3.3.3. Emission Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.-C.; Wang, J.-L.; Chang, C.-Y.; Liang, M.-C.; Lin, M.-R. Development of a multicopter-carried whole air sampling apparatus and its applications in environmental studies. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuyler, T.J.; Guzman, M.I. Unmanned Aerial Systems for Monitoring Trace Tropospheric Gases. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, T.F.; Salimi, F.; Morton, K.; Morawska, L.; Gonzalez, F. Development and Validation of a UAV Based System for Air Pollution Measurements. Sensors 2016, 16, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgues, J.; Marco, S. Environmental chemical sensing using small drones: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambey, V.; Prasad, A.D. A Review on Air Quality Measurement Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crazzolara, C.; Ebner, M.; Platis, A.; Miranda, T.; Bange, J.; Junginger, A. A new multicopter-based unmanned aerial system for pollen and spores collection in the atmospheric boundary layer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1581–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eu, K.S.; Yap, K.M. Chemical plume tracing: A three-dimensional technique for quadrotors by considering the altitude control of the robot in the casting stage. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eu, K.S.; Yap, K.M.; Tee, T.H. An Airflow Analysis Study of Quadrotor Based Flying Sniffer Robot. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Mechanics Engineering (ICAME), Hong Kong, China, 28–29 July 2014; pp. 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Koziar, Y.; Levchuk, V.; Koval, A. Quadrotor Design for Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE International Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology (ELNANO), Kyiv, Ukraine, 16–18 April 2019; pp. 736–739. [Google Scholar]
- Kuantama, E.; Tarca, R.; Dzitac, S.; Dzitac, I.; Vesselenyi, T.; Tarca, I. The Design and Experimental Development of Air Scanning Using a Sniffer Quadcopter. Sensors 2019, 19, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Meng, Q.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Ma, S.G. Simulate the aerodynamic olfactory effects of gas-sensitive UAVs: A numerical model and its parallel implementation. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 102, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, M.; Gonzalez, F.; Erskine, P.; Cliff, D.; Heuff, D. A Methodology to Monitor Airborne PM<sub>10</sub> Dust Particles Using a Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Sensors 2017, 17, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgués, J.; Esclapez, M.D.; Doñate, S.; Pastor, L.; Marco, S. Aerial Mapping of Odorous Gases in a Wastewater Treatment Plant Using a Small Drone. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.P.; Asadi, S.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Barholmai, M.; Schiller, J.H. Micro-Drone for Wind Vector Estimation and Gas Distribution Mapping. J. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Q.; Han, W.T.; Peng, M.M.; Zhang, M.F.; Yao, X.M.; Liu, W.S.; Wang, T.H. An Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Based Gas Sampling System for Analyzing CO2 and Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Laboratory. Sensors 2020, 20, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullett, B.; Aurell, J.; Mitchell, W.; Richardson, J. Use of an unmanned aircraft system to quantify NOx emissions from a natural gas boiler. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, P.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Herrero, J.L.; Lozano, J. Electrochemical gas sensing module combined with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for air quality monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, P.; Balistreri, C.; Pontelandolfo, P.; Triscone, G.; Pekoz, H.; Pignatiello, A. Development of an unmanned aerial vehicle UAV for air quality measurements in urban areas. In Proceedings of the 32nd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Samad, A.; Florez, D.A.; Chourdakis, I.; Vogt, U. Concept of Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for 3D Investigation of Air Quality in the Atmosphere-Example of Measurements Near a Roadside. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Han, W.T.; Zhang, M.F.; Yao, X.M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Peng, X.S.; Li, C.Q.; Dan, X.J. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Borne Sensor System for Atmosphere-Particulate-Matter Measurements: Design and Experiments. Sensors 2020, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán, J.J.; Joossen, G.; Sanz, D.; del Cerro, J.; Barrientos, A. Mini-UAV Based Sensory System for Measuring Environmental Variables in Greenhouses. Sensors 2015, 15, 3334–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, B.R.; Segales, A.R.; Waugh, S.; Duthoit, S.; Chilson, P.B. Considerations for temperature sensor placement on rotary-wing unmanned aircraft systems. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5519–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.K.; Tabor, D. Emissions from southeastern U.S. Grasslands and pine savannas: Comparison of aerial and ground field measurements with laboratory burns. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 111, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandesso, E.; Gullett, B.; Touati, A.; Tabor, D. Effect of Moisture, Charge Size, and Chlorine Concentration on PCDD/F Emissions from Simulated Open Burning of Forest Biomass. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.; Holder, A.; Kiros, F.; Mitchell, W.; Watts, A.; Ottmar, R. Wildland fire emission sampling at Fishlake National Forest, Utah using an unmanned aircraft system. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Aurell, J.; Mitchell, W.; Tabor, D.; Gullett, B. A small, lightweight multipollutant sensor system for ground-mobile and aerial emission sampling from open area sources. Atoms. Environ. 2017, 154, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. EPA OTM-48. Emission Factor Determination by the Carbon Balance Method. 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/emc/emc-other-test-methods (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Seltman, H.J. Experimental Design and Analysis. Carnegie Mellon University. 2015. Available online: http://www.stat.cmu.edu/~hseltman/309/Book/Book.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.; Grier, G.; Holder, A.; George, I. Seasonal emission factors from rangeland prescribed burns in the Kansas Flint Hills grasslands. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 304, 119769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.; Urbanski, S.P.; Dixit, P.; Qi, L.; Burling, I.; Yokelson, R.; Shrivastava, M.; Jung, H.; Weise, D.R.; Miller, W.; et al. Laboratory characterization of PM emissions from combustion of wildland biomass fuels. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9914–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Measured Parameter | Instrument/ Equipment | Method | Flow Rate/ Sampling Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CO2 Engine® K30 FR | NDIR | 1 L/min, 1 Hz |
| CO | EC4-500-CO | Electrochemical cell | 1 L/min, 1 Hz |
| PM2.5 Batch | SKC Personal Modular Impactor (PMI) | 37 mm Teflon filter/ gravimetric | 3 L/min |
| PM2.5 Time-Resolved | SidePak™ AM520 | 90° light-scattering | 1.7 L/min, 1 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.K. Effects of UAS Rotor Wash on Air Quality Measurements. Drones 2024, 8, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8030073
Aurell J, Gullett BK. Effects of UAS Rotor Wash on Air Quality Measurements. Drones. 2024; 8(3):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8030073
Chicago/Turabian StyleAurell, Johanna, and Brian K. Gullett. 2024. "Effects of UAS Rotor Wash on Air Quality Measurements" Drones 8, no. 3: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8030073
APA StyleAurell, J., & Gullett, B. K. (2024). Effects of UAS Rotor Wash on Air Quality Measurements. Drones, 8(3), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8030073






