Abstract
Recently, studies on the mechanism and clinical application of stem cell-derived exosomes have increased. Although the number of patients with hearing loss is increasing, there is no ideal therapy for the recovery of auditory cells of an independent organ in humans. In this review, we proposed the use of stem cell-derived exosomes for treating hearing loss and summarized the exosome research strategy platform for preclinical studies. It is necessary to select a research direction to assess direct or indirect effects on recipients based on the physiological mechanisms of exosomes that deliver useful molecules (called payloads) to recipient cells or tissues. To apply exosomes in the auditory field, researchers should select a model for assessing the toxicity to the auditory cells and analyzing their mechanisms in the recipient tissue. Such in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo models have been designed and reported in previous studies. The analytical strategies in various models can evaluate the mechanism of exosomes based on exosome surface markers or the payload, thus helping the researchers in finding evidence regarding the efficacy of exosomes. Here, we propose three strategies for exosome application research in the auditory field.
1. Background
1.1. The Cause of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is increasing significantly because of an aging population and industrial development. Damage to the hair cells in the auditory organs is a known cause of hearing loss because of the inability to recognize auditory signals [1,2]. Apoptosis due to mitochondrial dysfunction in auditory cells has been reported to be a major cause [3]. Changes in mitochondrial DNA caused by cellular aging can also have an effect on hearing, and genetic analysis data confirm that nuclear genes are often a major factor in determining phenotypic differences in auditory cells [3]. Inflammation of the auditory organs has also been reported to affect hearing loss [4]. If the auditory organs are damaged by excessive external stimulation of the inner ear, the nerves are damaged, and recovery is impossible [1].
1.2. Requirements for a Material for Treating Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is reported as a permanent hearing impairment because of its high prevalence and few known treatment and recovery methods [5,6]. The number of elderly people has been increasing at a rate of 4.8% per year on average, more than half of those in their 60s are among 53.6% of the total elderly population, and the rate of hearing-impaired individuals in their 10s and 30s has also reached up to 19.2% because of the increase in the number of smartphones, which has also led to severe social isolation [7,8,9]. It is necessary to develop a treatment strategy using a biostable preventive substance that can reduce cellular damage to the auditory organ. With the technology developed so far, it is difficult to treat hearing loss with drugs alone, and the best available treatment includes hearing aids and cochlear implants; thus, development of an early diagnosis technology and an effective treatment strategy is pertinent [10,11,12]. Therefore, in this review, we intend to envision a strategy that has not been explored in the field of hearing previously. Here, we explain the use of stem cell exosomes, which are microscopic biomaterials of size 50 to 100 nm, in reaching the micro auditory organs and aiding in preventing hearing loss.
2. Strategies for Exosome Treatment
2.1. Current Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Research in the Auditory Field
The maturation of the multivesicular body (MVB), which is involved in the biological development mechanism of stem cell exosomes has been reported [13,14]. To allow overexpression of useful candidate factors with usually low expression levels in exosomes, a transporter capable of transferring the factors to MVB is required; furthermore, a technology for developing differentiated exosomes, in which the expressed stem cell exosomes can directly target specific receptor cells is being developed [15,16]. Biocompatibility of these exosomes can be demonstrated by mimicking molecular biological signaling mechanisms [17], and through the discovery of additional biomarkers, stem cell-derived exosomes can be applied not only for differentiation, antioxidation, and immunity, but also to regenerative medicine [15,16]. There are reported types of hearing loss includes noise-induced, genetic, sudden, ototoxicity, and age-related hearing loss [1,2,3,4,5]. The application of exosomes for prevention or treatment can be classified according to the type of hearing loss, suggesting that they may help restore abnormalities in chemical and biological mechanism [18,19,20]. The fundamental recovery of inner hair cells by exosome is difficult, because both noise-induced and sudden hearing loss occur due to physical stimulation of hair cell death. In addition, the application of exosomes for prevention and treatment for hearing restoration is difficult because genetic hearing loss is caused by developmental disorders in the embryonic period. However, there is an applicability of exosomes to treat the involvement of exosomes in the imbalance of signaling systems due to aging and changes in electronic mechanisms caused by these toxic drugs. It can be substantiated based on previous studies and reports that exosome-specific proliferative and protective factors can recover damaged tissues or cells [18,21]. This approach has great potential because of its broad scope of application.
2.2. Direct Exosome Treatment Strategy
Numerous researchers have reported applied studies using exosomes extracted from cultured media [22,23,24]. From a biological point of view, most studies have attempted to repair damaged tissues by exosomes treatment, which can be obtained from cell cultures and biofluids (blood, urine, etc.) [25,26,27]. Exosomes can promote keratinocytes by recruiting macrophages and neutrophils at the injury site. In addition, the extracted exosomes can decrease inflammatory molecules in the infected cells, thereby increasing cell viability [4,28].
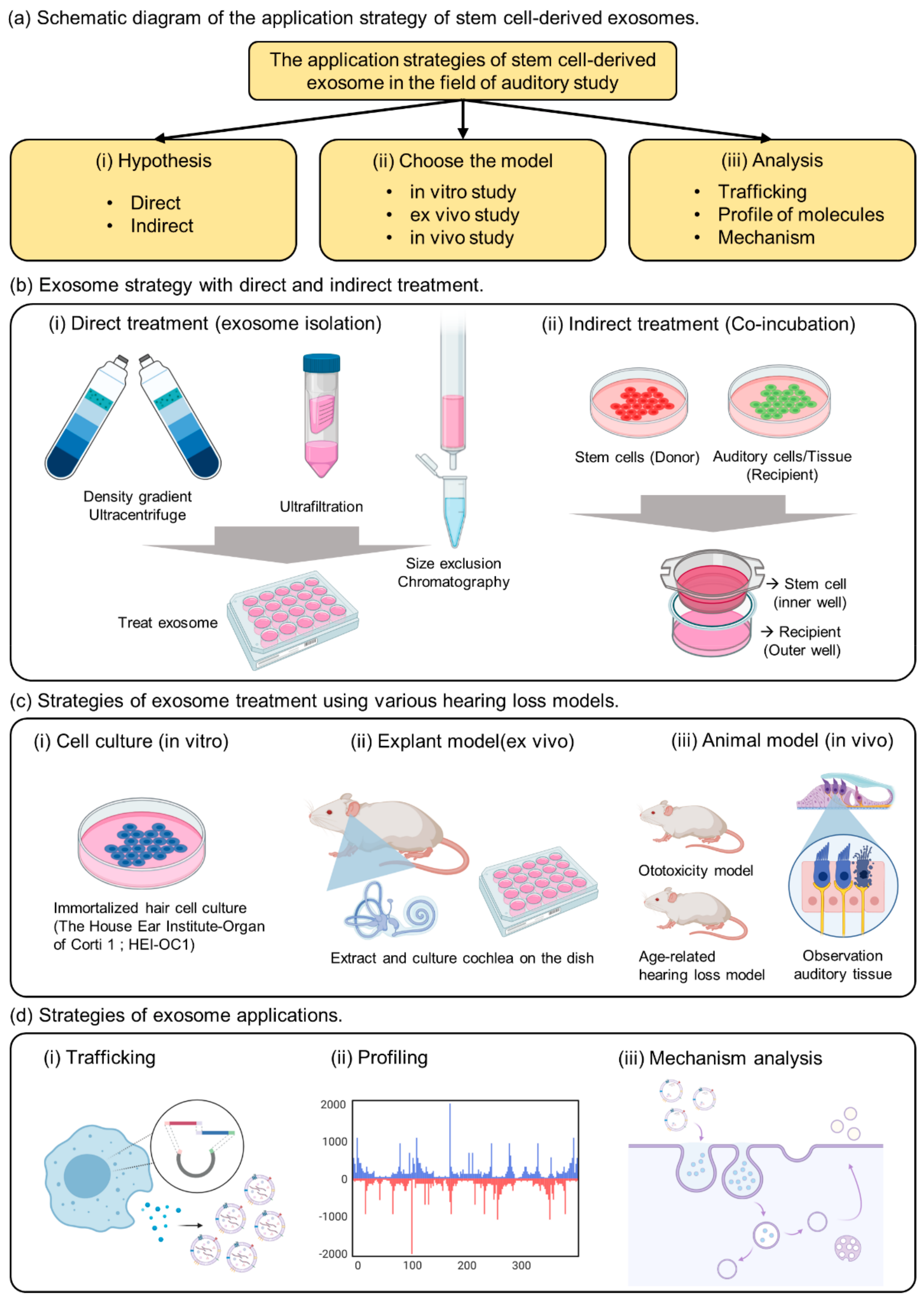
Various exosome isolation methods have been proposed to introduce exosomes directly into the cells or injured tissues (Figure 1b(i)).
Figure 1.
The summary of strategies for exosome application in the auditory field. (a) Schematic diagram of the application strategy of stem cell-derived exosomes. (b) Exosome strategy with direct and indirect treatment. (c) Strategies of exosome treatment using various hearing loss models. (d) Strategies of exosome applications.
The most common method includes fractionation of the sample with an ultracentrifuge and purification using a sucrose or iodixanol gradient [23,27,29]. Several studies have reported ultrafiltration methods to remove the impurities other than exosomes, to enrich the exosomes [22,25,28]. The size exclusion chromatography (SEC) method was proposed to remove unnecessary cytokines and obtain pure EV [24,26,30]. However, this method has a low yield and requires extraction after concentrating a large amount of sample. Therefore, to obtain exosomes that can be processed in the auditory organ, it is necessary to select a method that has the highest yield and purity [31,32]. In addition, to maintain the function of exosomes after isolation, the exosomes must be resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline for use in cell or animal experiments. Exosomes obtained from cell culture fluids or biological samples have low stability and must be stored frozen at -80 °C or used immediately.
2.3. Indirect Exosome Treatment Strategy
As previously reported, exosomes are vesicles composed of lipid membranes that are 100 to 200 nm in size; therefore, they have the property of being able to penetrate small-sized membranes [14,15,33]. Known to play an important role in cell-to-cell communication, useful factors can be divided into donor and recipient cells, and can be used to confirm delivery to the recipient cells [34,35,36]. As a strategy to confirm the effect of indirect exosomes, we propose a co-culture method (Figure 1b(ii)). Indirect culture methods have already been proven to deliver proliferative components [23,37]. This method can be used to determine the indirect effects of exosomes while delivering useful elements to the interior of the recipient cell.
The important point of this strategy is the composition of membranes and pore size when choosing the trans-well. If the pore size is 3 µm above the cell size, it would be impossible to move several cells at the same time; therefore, one should select a pore size below 0.4 µm [34,35]. Additionally, a polycarbonate membrane, which can deliver large amounts of EVs, is recommended. When donor cells are attached to the insertion well, the recipient cells are cultured in the outer well, and when the insertion well is cultured together after 24 h, communication between the cells through exosomes is activated in the medium. As a strategy for confirming accurate delivery, the delivery of fluorescent substances can be observed by genetic manipulation of EVs, and exosome markers expressed over time in the medium can be identified. If the two cell species are different, analysis through antibody reactions is also possible. Therefore, choosing co-culture as a method of confirming indirect effects without extracting exosomes from donor cells can be an important strategy to elucidate evidence for exosome transport.
3. Strategies of Exosome Therapy Using Various Hearing Loss Models
3.1. In Vitro Model
There are not many known auditory cells, but House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 (HEI-OC1) has been mainly reported in in vitro experiments (Figure 1c(i)) [9,37]. These cells have been proposed to be used for toxic drug screening (cisplatin, dexamethasone, gentamicin, penicillin, neomycin, streptomycin, tobramycin, etc.), apoptosis pathways, autophagy and senescence, cell differentiation, inflammatory responses, and hypoxic effects [38,39]. Although it is possible to analyze the properties of a specific drug according to the purpose of the experiment, caution must be exercised because the physiological properties of these cells are different from those of conventional primary cells or cancer cells. Although ion channels located on the surface of auditory cells can be analyzed, hearing cannot be determined [9,39]. Therefore, we suggest that HEI-OC1 may be a useful model for investigating biological responses related to auditory cells, including auditory sensory cells, but we believe that a careful approach is needed when evaluating drug effects.
3.2. Ex Vivo Model
Although many researchers have attempted to study hearing in vitro, analytical techniques have been developed only for short-term biological analysis [40,41]. Ex vivo models include extraction of the animal’s auditory organ, the cochlea, and culturing it in a medium similar to that of in vitro experiments.
By removing the bones of the cochlea, separating the organ of Corti, to which the hair cells are attached, and placing them on the dish, experiments can be conducted before cell division (Figure 1c(ii)). The human cochlea is difficult to obtain, but the use of mouse cochlea has been reported in previous studies [42]. This analysis can be used as a system that can shorten the reaction time and evaluate the effects of the drug, as well as the reaction to the drug in the tissue by controlling the medium conditions with growth factors. In a previous study, we conducted experiments to confirm the viability of cochlear hair cells and to evaluate the activity of the special markers Myo7a and phalloidin [20]. The technique of extracting explants can be observed with immunofluorescence, and changes in the surface morphology of the tissue can be observed with transmission electron microscopy. Therefore, cochlear explants are a good tool to quickly screen for toxicity rates based on drug concentration and can be used prior to in vivo testing.
3.3. In Vivo Model
The most important aspect of auditory clinical studies is that animal testing is indispensable, and it is necessary to confirm the phenotype by measuring auditory brainstem response (ABR) to reliably prove hearing loss [6,8]. The type of animal model can represent an age-related or ototoxic hearing loss model [4,7,8,43]. Physiological analysis of auditory cells is possible through in vitro experiments (Figure 1c(iii)), but it is difficult to find a treatment for hearing loss or clearly analyze the efficacy of the drug. Demonstrating the phenotype of toxic substances in vitro and in vivo, we can confirm that hearing loss is a systemic action of the drug in animals. We can evaluate whether the drug directly affects hearing, and measure the amount of change and survival rate by extracting the hair cells from the cochlea.
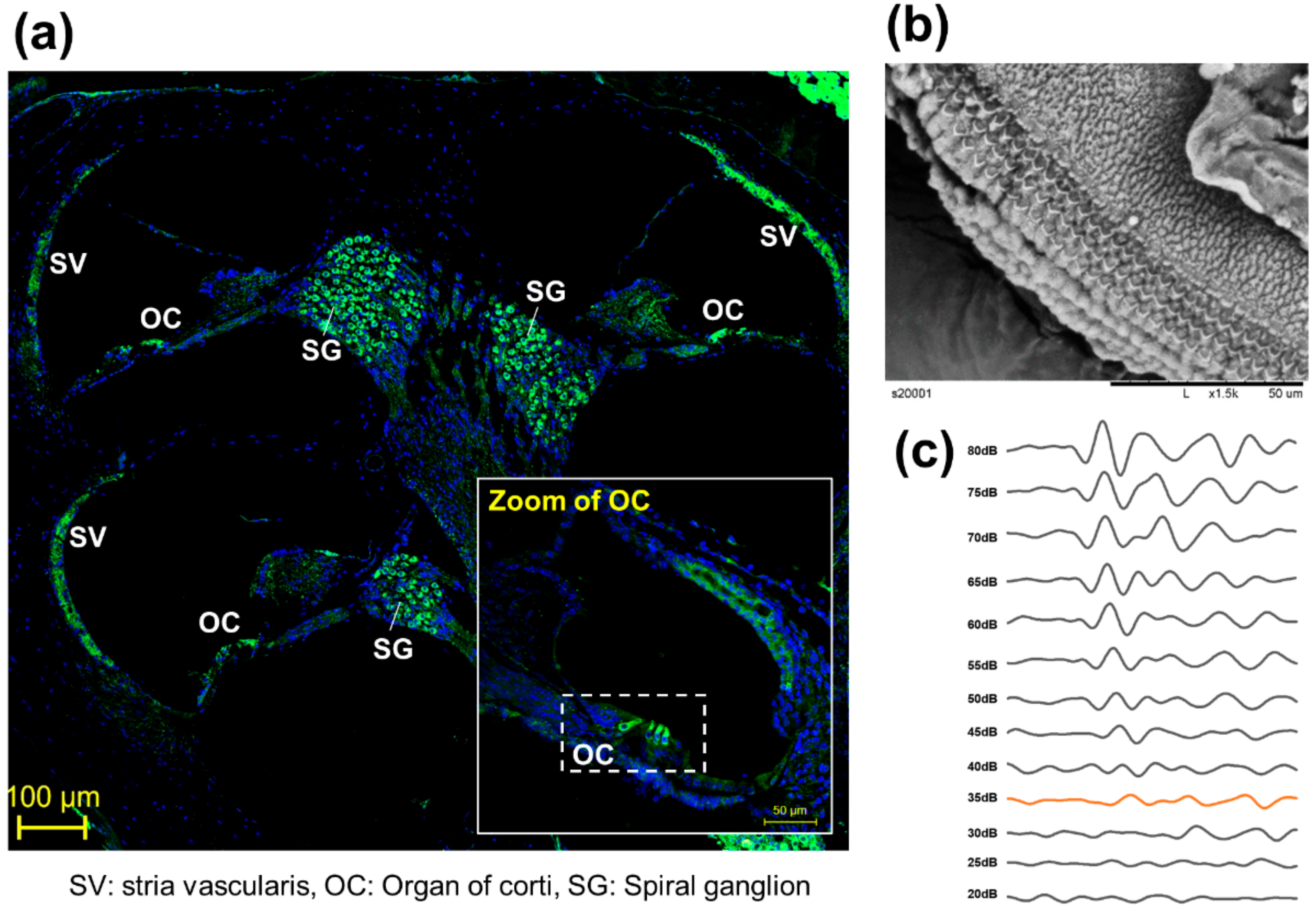
To observe the anatomical phenotype of hearing loss, the morphology can be observed either through immune fluorescence staining (Figure 2a) or electron microscopy (Figure 2b). The observation of changes in hair cells in the organ of Cotri is evidence of direct damage to the auditory organ, and the Myo7a staining, a representative hair cell marker, may prove a physical phenomenon of hearing abnormalities. In addition, in chemical hearing, it can be confirmed that there is an abnormality in electrochemical transmission by comparing the dB reduction trend through ABR measurement (Figure 2c).
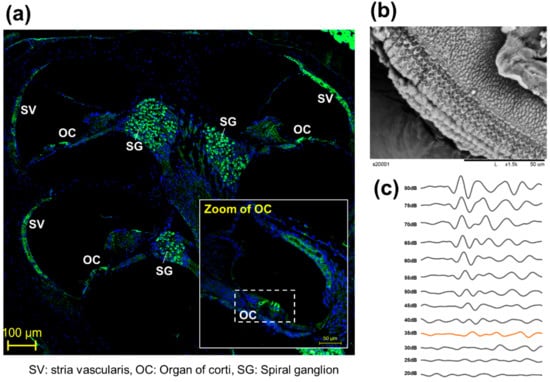
Figure 2.
Representative anatomical analysis strategy for in vivo experiments. (a) Analysis of whole auditory organ by immune fluorescence staining using Myosin 7a (Myo7a). (Myo7a: green, DAPI: blue), (b) Observation of organ of corti (OC) by transmission electron microscopy [8], (c) Comparison of hearing kinetics depending on 80 db to 20 dB on 8000 kHz.
4. Strategies of Exosome Applications
4.1. Development of Exosome Trafficking System
EV studies reported over the past decade have demonstrated that EVs retain their activity and carry several types of macromolecules as they are transferred from parent cells to recipient cells [14,44,45]. Representative hypotheses are related to the function and properties of EVs as mediators of intercellular communication and their ability to transport it to the target cells [46]. Previous studies have confirmed that stem cells with embedded nanoparticles can increase exosome production [47]. This demonstrates the possibility of using tube particles to transport specialized proteins to nanoparticles that could influence exosome development. In addition, a previous study reported direct engineering of a fluorescent substance into exosomes to confirm trafficking in human cells (Figure 1d(i)) [48,49].
Therefore, understanding the pathways leading to exosome development and internalization within target cells is an important goal in the current field of EV research. In addition, studies that uncover the unique biomolecules of exosomes are related to disease states and treatments; therefore, the discovery of new EV biomarkers is also a potential research topic.
4.2. Profiling of Payload in Exosomes
Next, the presence of DNA molecules in EVs has been widely reported [50,51]. Mitochondria and genomic DNA were found in EVs derived from double-stranded DNA, and those isolated from cell culture media and biological fluids (human and mouse) were found inside EVs (Figure 1d(ii)).
Thus, it was hypothesized that the EV DNA payload could be fluidly packaged by cell-type specific mechanisms [15,23,52]. However, EVs have been reported to have a random distribution rather than a constant amount of DNA distribution owing to certain mechanisms [23]. Finally, there is increasing interest in miRNA studies, which are known to be the main causes of gene and protein expression, and there are reports that the miRNA profile of the released exosomes cannot be randomly generated under certain immune response conditions. Proteins inherent in EVs include a complex set of proteins derived from parent cells (cytoplasmic, nuclear, mitochondrial, and membrane-bound proteins). Several proteomic studies have determined EV activity by defining unique EV properties associated with parent cells. Vesicle-specific proteins are often used as markers for specific heat shock proteins, tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, and CD81), major histocompatibility complex molecules, and proteins in the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) complex (Alix and TSG101) [15]. The biggest feature of EV protein classification is that it is mediated by members of the ESCRT family [16,52]. It is reported that ESCRT-dependent and independent pathways are classified by the association of ALIX and Rab 5 and Vps4 factors involved in exosome development.
4.3. Mechanism Analysis of Exosomes
Exosome viability is regulated by the MVB, which redirects endocytosis proteins to their destinations (such as cells or organs) (Figure 1d(iii)). Substances are internalized by endocytosis on the cell surface and transported through early and late endosomes. Exosome secretion is important for intralumenal vesicle (ILV) formation in MVBs [13,14,16]. They are surrounded by lipids that form a plasma membrane, which protects the contents of the vesicle and promotes its migration to the target cells. Recently, the classification of substances using an ESCRT-dependent or independent mechanism has been reported. Briefly, ESCRT contains the cytoplasmic complex of ESCRT 0, I, II, III, and Vps4. During maturation, the ESCRT complex accumulates on the surface of the MVB membrane, and the MVB migrates through the microtubules to the plasma membrane, releasing EVs.
However, clinically, the study of exosome endocytosis is of great importance [21,53]. The response at the receptor carries a risk of toxicity or side effects of exosomes; however, to date, this has not been confirmed when using exosomes in auditory cells [18,19,54]. In the case of cancer cell-derived exosomes, a factor that promotes the proliferation of cancer cells can metastasize [36]. Therefore, we believe that when using exosomes to be inserted into the auditory organs, we should test for toxicity and analyze which substances in the surrounding cells are stimulated.
5. Future Prospects
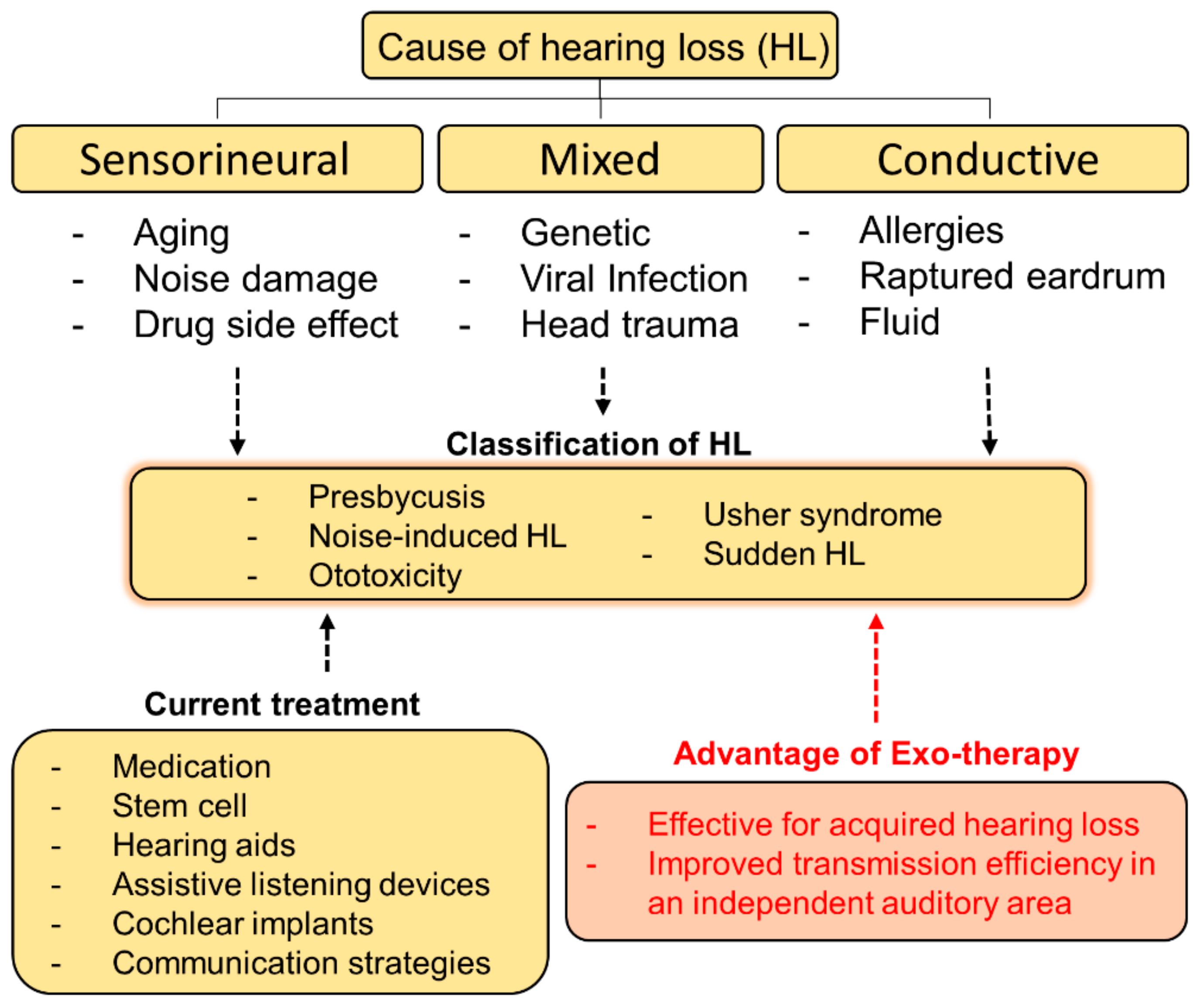
We tried to establish a method to treat hearing loss using exosomes in Figure 3. The schematic of this diagram is to present an approach direction of exosome-based therapy (exo-therapy) for application to hearing loss (Figure 3). Stem cell derived exosomes are used for communication between cell to cell, and it is known that the payload changed depending on the origin of the stem cells [55]. It has been reported that miRNAs and proteins generated in communication between donor cells and target cells are different. In other words, the author believe that it may be helpful to selectively deliver interest genes to cure tissue or cells in destination using exosome with different payload [55].
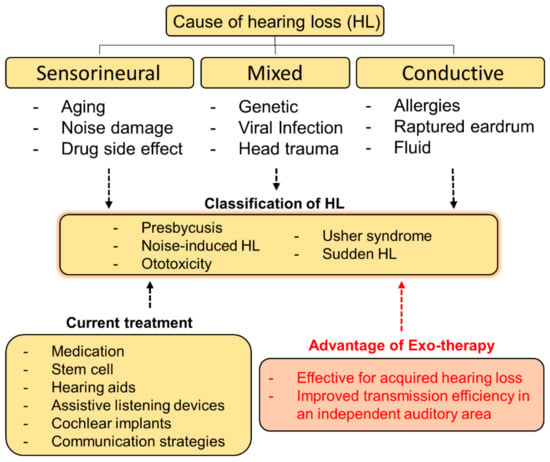
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram of causes, classification, and current treatments for hearing loss. The approach direction of exosome-based therapy (exo-therapy) for applying to hearing loss was described and its advantages were introduced.
We proposed three representative strategies for stem cell-derived exosome research in the auditory system as follows: (1) select the role of exosomes in direct and indirect reactions, (2) select a model that can be used in the study, (3) confirm the delivery of exosomes, and analyze the mechanisms for preventing hearing loss. The most important aspect of auditory research is that the prevention or regeneration of hearing loss in vivo must be confirmed through the ABR test. Injection of exosomes directly into the mammalian ear or via various routes through blood vessels should be considered. We suggest local injection of exosomes directly into the injured cochlea. This is because exosomes are systematically circulated in the body and then filtered by the kidneys or liver to show the direct effects of exosomes. Therefore, according to our proposal, the application of the auditory organs using exosomes is future-oriented.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Health Technology R&D project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) under Grant HI19C1334.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Health Technology R&D project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) under Grant HI19C1334. This work supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant: 2021R1I1A1A01040273).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Nash, S.D.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Nieto, F.J.; Huang, G.H.; Pankow, J.S.; Tweed, T.S. The Prevalence of Hearing Impairment and Associated Risk Factors. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurabi, A.; Keithley, E.M.; Housley, G.D.; Ryan, A.F.; Wong, A.C.-Y. Cellular mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.R.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Bykhovskaya, Y.; Spirina, O.; Fischel-Ghodsian, N. A nuclear-mitochondrial DNA interaction affecting hearing impairment in mice. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciello, F.; Di Pino, A.; Rolesi, R.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G.; Grassi, C.; Fetoni, A.R. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid: In vivo evidences in a model of noise-induced hearing loss. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Zuo, J. Cochlear hair cell regeneration after noise-induced hearing loss: Does regeneration follow development? Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.J.; Ju, H.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kwak, S.H.; Kang, M.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Cho, H.-J. Damage of Inner Ear Sensory Hair Cells via Mitochondrial Loss in a Murine Model of Sleep Apnea with Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Park, S.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, M.Y.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 722, 134838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Ha, S.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.-E.; Seo, Y.J. Induced Short-Term Hearing Loss due to Stimulation of Age-Related Factors by Intermittent Hypoxia, High-Fat Diet, and Galactose Injection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Bai, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Forskolin protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis and ROS production. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.S.; Emmett, S.D.; Robler, S.K.; Tucci, D.L. Global Hearing Loss Prevention. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 51, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Olson, E.N.; Bassel-Duby, R. Therapeutic approaches for cardiac regeneration and repair. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Sage, C.; Indzhykulian, A.A.; Scheffer, D.I.; Brisson, A.R.; Tan, S.; Wu, X.; Volak, A.; Mu, D.; Tamvakologos, P.I.; et al. Rescue of Hearing by Gene Delivery to Inner-Ear Hair Cells Using Exosome-Associated AAV. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide Triggers Budding of Exosome Vesicles into Multivesicular Endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, S.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chu, L.; Han, X.; Galons, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomes from different cells: Characteristics, modifications, and therapeutic applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 207, 112784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.; Fenix, A.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.F.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Théry, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Seo, Y.J. Engineering of Extracellular Vesicles Based on Payload Changes for Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U. Exosome-mediated protection of auditory hair cells from ototoxic insults. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2206–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breglio, A.M.; May, L.A.; Barzik, M.; Welsh, N.C.; Francis, S.P.; Costain, T.Q.; Wang, L.; Anderson, D.E.; Petralia, R.S.; Wang, Y.-X.; et al. Exosomes mediate sensory hair cell protection in the inner ear. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2657–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Park, J.-E.; Lee, S.H.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.K.; Seo, Y.J. Protective Effect of Msc-Derived Exosomes Against Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis via Heat Shock Protein 70 in Auditory Explant Model. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3790407 (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Garcia-Romero, N.; Esteban-Rubio, S.; Rackov, G.; Carrión-Navarro, J.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; Ayuso-Sacido, A. Extracellular vesicles compartment in liquid biopsies: Clinical application. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Li, H.-Y.; Yang, K.; Wu, J.-L.; Cai, X.-W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.-Q. Exosomes as potential alternatives to stem cell therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration: In-vitro study on exosomes in interaction of nucleus pulposus cells and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, E.; Johansson, H.J.; Mäger, I.; Lee, Y.; Blomberg, K.E.M.; Sadik, M.; Alaarg, A.; Smith, C.I.E.; Lehtiö, J.; El Andaloussi, S.; et al. Cells release subpopulations of exosomes with distinct molecular and biological properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Yu, H.; Yan, G.; Gao, M.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X. Characterization of Urinary Exosomes Purified with Size Exclusion Chromatography and Ultracentrifugation. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. A highly efficient method for isolating urinary exosomes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.F.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Möller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palviainen, M.; Saari, H.; Kärkkäinen, O.; Pekkinen, J.; Auriola, S.; Yliperttula, M.; Puhka, M.; Hanhineva, K.; Siljander, P.R.-M. Metabolic signature of extracellular vesicles depends on the cell culture conditions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1596669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Cho, W.L.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.D.; Park, H.-A.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Jo, D.-G.; Cho, Y.W. Functional recovery in photo-damaged human dermal fibroblasts by human adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1565885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Gálvez-Montón, C.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Roura, S.; Borràs, F.E. Extracellular vesicle isolation methods: Rising impact of size-exclusion chromatography. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2369–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, E.M.; Vestad, B.; Steffensen, L.A.; Aass, H.C.D.; Saeed, M.; Øvstebø, R.; Costea, D.-E.; Galtung, H.K.; Søland, T.M. Efficient extracellular vesicle isolation by combining cell media modifications, ultrafiltration, and size-exclusion chromatography. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, G.K.; Khan, M.A.; Zubair, H.; Srivastava, S.K.; Khushman, M.; Singh, S.; Singh, A. Comparative analysis of exosome isolation methods using culture supernatant for optimum yield, purity and downstream applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratta, S.; Tancini, B.; Sagini, K.; Delo, F.; Chiaradia, E.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C. Lysosomal Exocytosis, Exosome Release and Secretory Autophagy: The Autophagic- and Endo-Lysosomal Systems Go Extracellular. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzer, K.M.; Kranich, L.R.; Ruf, W.P.; Cagsal-Getkin, O.; Winslow, A.R.; Zhu, L.; Vanderburg, C.R.; McLean, P.J. Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Brown, B.A.; Siegel, A.P.; El Masry, M.S.; Zeng, X.; Song, W.; Das, A.; Khandelwal, P.; Clark, A.; Singh, K.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Crosstalk between Keratinocytes and Macrophages in Cutaneous Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12732–12748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, B.; Gondaliya, P.; Kirave, P.; Rawal, R.; Jain, A.; Garg, R.; Kalia, K. Exosome-mediated delivery of miR-30a sensitize cisplatin-resistant variant of oral squamous carcinoma cells via modulating Beclin1 and Bcl2. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1832–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, G.P.; Kaushal, V.; Hong, X.; Shah, S.V. Role and regulation of activation of caspases in cisplatin-induced injury to renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Liu, W.; Fan, Z.; Qian, F.; Zhang, D.; Han, Y.; Xu, L.; Sun, G.; Qi, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. c-Myb knockdown increases the neomycin-induced damage to hair-cell-like HEI-OC1 cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinec, G.; Thein, P.; Park, C.; Kalinec, F. HEI-OC1 cells as a model for investigating drug cytotoxicity. Hear. Res. 2016, 335, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landegger, L.D.; Dilwali, S.; Stankovic, K.M. Neonatal Murine Cochlear Explant Technique as an In Vitro Screening Tool in Hearing Research. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 124, e55704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogier, J.M.; Burt, R.A.; Drury, H.R.; Lim, R.; Nayagam, B.A. Organotypic Culture of Neonatal Murine Inner Ear Explants. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Lee, S.H.; Park, D.J.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, S.K. In vitro Time-lapse Live-Cell Imaging to Explore Cell Migration toward the Organ of Corti. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 166, e61947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowl, M.; Dawson, S.J. The Mouse as a Model for Age-Related Hearing Loss—A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2014, 61, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.S.; De Beer, M.A.; Giepmans, B.N.G.; Zuhorn, I.S. Endocytosis of Extracellular Vesicles and Release of Their Cargo from Endosomes. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4444–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Cheng, Q.; Hou, T.; Han, M.; Smbatyan, G.; Lang, J.; Epstein, A.L.; Lenz, H.-J.; Zhang, Y. Genetically Engineered Cell-Derived Nanoparticles for Targeted Breast Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Kim, S.; Zhang, E.; Tang, Y.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Markert, J.M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X. (Margaret) Targeted Exosomes for Drug Delivery: Biomanufacturing, Surface Tagging, and Validation. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e1900163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Yun, W.S.; Kim, W.C.; Park, J.-E.; Lee, S.H.; Ha, S.; Choi, J.S.; Key, J.; Seo, Y.J. Improvement of stem cell-derived exosome release efficiency by surface-modified nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Le, Q.-V.; Wu, Y.; Park, J.; Oh, Y.-K. Nanovesicle-Mediated Delivery Systems for CRISPR/Cas Genome Editing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böker, K.O.; Lemus-Diaz, N.; Ferreira, R.R.; Schiller, L.; Schneider, S.; Gruber, J. The Impact of the CD9 Tetraspanin on Lentivirus Infectivity and Exosome Secretion. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savina, A.; Furlán, M.; Vidal, M.; Colombo, M.I.; Gamel-Didelon, K.; Kunz, L.; Föhr, K.J.; Gratzl, M.; Mayerhofer, A. Exosome Release Is Regulated by a Calcium-dependent Mechanism in K562 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20083–20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Anderson, J.D.; Rahnama, L.M.A.; Gu, S.V.; Knowlton, A.A. Exosomes in disease and regeneration: Biological functions, diagnostics, and beneficial effects. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H1162–H1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.E.; Scruggs, B.S.; Schaffer, J.E.; Hanson, P.I. Effects of Inhibiting VPS4 Support a General Role for ESCRTs in Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Su, C. Design strategies and application progress of therapeutic exosomes. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, C.; Gao, S.; Tang, M.; Lu, L.; Yang, G.; Chai, R. The Roles of Exosomes in Visual and Auditory Systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Park, J.-E.; Kong, T.H.; Seo, Y.J. Alteration of payload in extracellular vesicles by crosstalk with mesenchymal stem cells from different origin. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).