Synthetic Nax Zeolite as a Very Efficient Heavy Metals Sorbent in Batch and Dynamic Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Fixed Bed Column Studies
Experimental Set-Up
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterizations
3.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Mass Effect
3.2.2. pH Effect
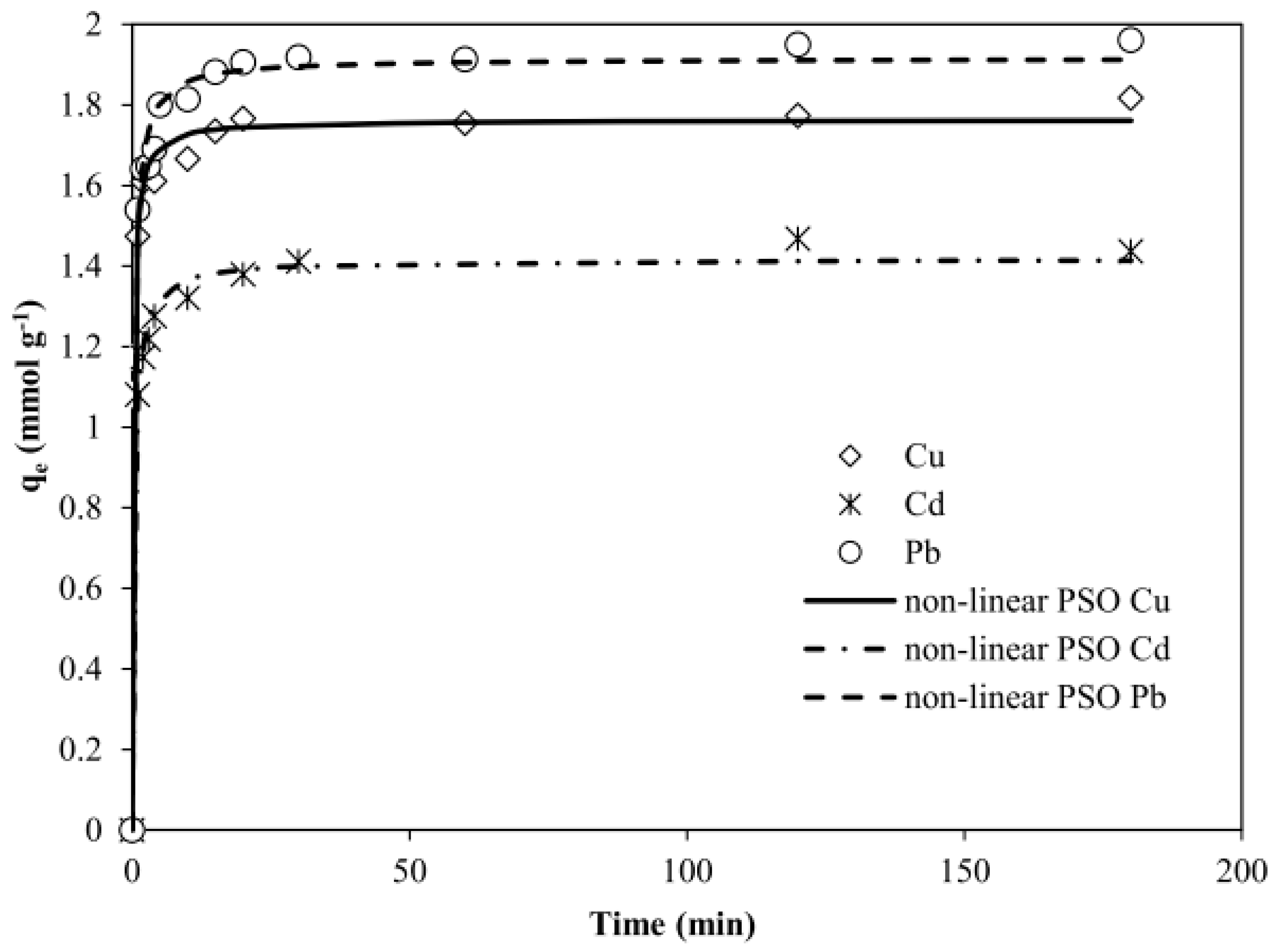
3.2.3. Kinetics Study
3.2.4. Intra-Particle Diffusion Model
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3.1. Langmuir Isotherm Model
3.3.2. Freundlich Isotherm Model
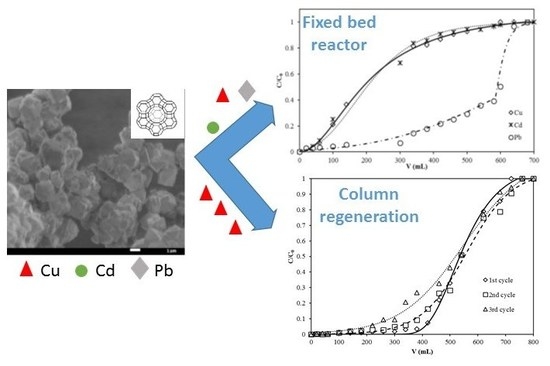
3.4. Breakthrough Curves
3.5. Column Regeneration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 166, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.M.; Adrian, D.D. A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, M.; Bandura, L. Sorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Glauconite. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesraoui-ouki, S.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Perry, R. Natural zeolite utilisation in pollution control: A review of applications to metals’ effluents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1994, 59, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadis, K.; Helmreich, B. Influence of chemical conditioning on the ion exchange capacity and on kinetic of zinc uptake by clinoptilolite. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, L.; Franus, M.; Panek, R.; Woszuk, A.; Franus, W. Characterization of zeolites and their use as adsorbents of petroleum substances. Przem. Chem. 2015, 3, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, O.; Akcay, H. Use of Natural Clinoptilolite to Improve Water Quality: Sorption and Selectivity Studies of Lead(II), Copper(II), Zinc(II), and Nickel(II). Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cincotti, A.; Mameli, A.; Locci, A.M.; Orru, R.; Cao, G. Heavy metals uptake by Sardinian natural zeolites: Experiment and modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, W. Characterization of X-type Zeolite Prepared from Coal Fly Ash. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Treacy, M.M.J.; Higgins, J.B. (Eds.) Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, Fourth Revised ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nibou, D.; Mekatel, H.; Amokranea, S.; Barkatb, M.; Trari, M. Adsorption of Zn2+ ions onto NaA and NaX zeolites: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, E.; Karapinar, N.; Donat, R. The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, K.S.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Kot, S.C. Removal of mixed heavy metal ions in wastewater by zeolite 4A and residual products from recycled coal fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe, Kungligasvenska vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanth Kumar, K. Linear and non-linear regression analysis for the sorption kinetics of methylene blue onto activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B137, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavandi, M.A.; Haddadian, Z.; Ismail, M.H.S.; Abdullah, N.; Abidin, Z.Z. Removal of Fe(III), Mn(II) and Zn(II) from palm oil mill effluent (POME) by natural zeolite. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, Z.; Batonneau-Gener, I.; Pouilloux, Y.; Hamad, H.; Saad, Z.; Kazpard, V. Divalent Heavy Metals Adsorption onto Different Types of EDTA-Modified Mesoporous Materials: Effectiveness and Complexation Rate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 212, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, C.; Tang, B.; Xu, J.; Lu, G.; Liu, P. Preparation of cellulose acetate/zeolite composite fiber and its adsorption behavior for heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M. Uber die adsorption in losungen. J. Phy. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohdee, K.; Asadullah, L.K. Enhancement of adsorption efficiency of heavy metal Cu(II) and Zn(II) onto cationic surfactant modified bentonite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElBastamy ElSayed, E. Natural diatomite as an effective adsorbent for heavy metals in water and wastewater treatment (a batch study). Water Sci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Chen, H.; Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Sun, J. Zeolite A synthesized from alkaline assisted pre-activated halloysite for efficient heavy metal removal in polluted river water and industrial wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 56, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| NaX Zeolite | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qeexp (mmol g−1) | First Order Kinetic Model | Second Order Kinetic Model | ||||||
| k1 (min−1) | qecal (mmol g−1) | R2 | k2 (g mmol−1 min−1) | qecal (mmol g−1) | h (mmol g−1min−1) | R2 | ||
| Cu2+ | 1.82 | 0.7 | 1.69 | 0.935 | 0.90 | 1.8 | 2.94 | 0.997 |
| Cd2+ | 1.54 | 1 | 1.35 | 0.978 | 1.19 | 1.45 | 2.52 | 0.996 |
| Pb2+ | 1.96 | 1 | 1.8 | 0.972 | 0.79 | 1.96 | 3.04 | 0.999 |
| kid1 (mmolg/g min1/2) | C1 | R2 | kid2 (mmol/g min1/2) | C2 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | 0.141 | 2.91 | 0.891 | 0.021 | 3.34 | 0.913 |
| Cd2+ | 0.209 | 2.04 | 0.844 | 0.014 | 2.73 | 0.64 |
| Pb2+ | 0.2 | 2.98 | 0.903 | 0.012 | 3.75 | 0.873 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | qmax (mmol g−1) | KL (L mmol−1) | R2 | n | Kf (L g−1) | R2 |
| Cu2+ | 4.0 | 57.7 | 0.991 | 5 | 4.5 | 0.738 |
| Cd2+ | 3.1 | 23.7 | 0.988 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 0.842 |
| Pb2+ | 3.2 | 52.0 | 0.991 | 5.3 | 3.4 | 0.860 |
| Metal Ion | Batch Capacity (mmol g−1) | Column Capacity (mmol g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | 1.02 | 0.960 |
| Cd2+ | 1 | 0.867 |
| Pb2+ | 2.21 | 2.23 |
| Capacity (mmol g−1) | Regeneration Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st cycle | 2.43 | - |
| 2nd cycle | 2.36 | 97.1 |
| 3rd cycle | 2.24 | 92.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ezzeddine, Z.; Batonneau-Gener, I.; Pouilloux, Y.; Hamad, H.; Saad, Z. Synthetic Nax Zeolite as a Very Efficient Heavy Metals Sorbent in Batch and Dynamic Conditions. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 2, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020022
Ezzeddine Z, Batonneau-Gener I, Pouilloux Y, Hamad H, Saad Z. Synthetic Nax Zeolite as a Very Efficient Heavy Metals Sorbent in Batch and Dynamic Conditions. Colloids and Interfaces. 2018; 2(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleEzzeddine, Zeinab, Isabelle Batonneau-Gener, Yannick Pouilloux, Hussein Hamad, and Zeinab Saad. 2018. "Synthetic Nax Zeolite as a Very Efficient Heavy Metals Sorbent in Batch and Dynamic Conditions" Colloids and Interfaces 2, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020022
APA StyleEzzeddine, Z., Batonneau-Gener, I., Pouilloux, Y., Hamad, H., & Saad, Z. (2018). Synthetic Nax Zeolite as a Very Efficient Heavy Metals Sorbent in Batch and Dynamic Conditions. Colloids and Interfaces, 2(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020022