Antioxidant Effect of Vitamins in Olive Oil Emulsion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
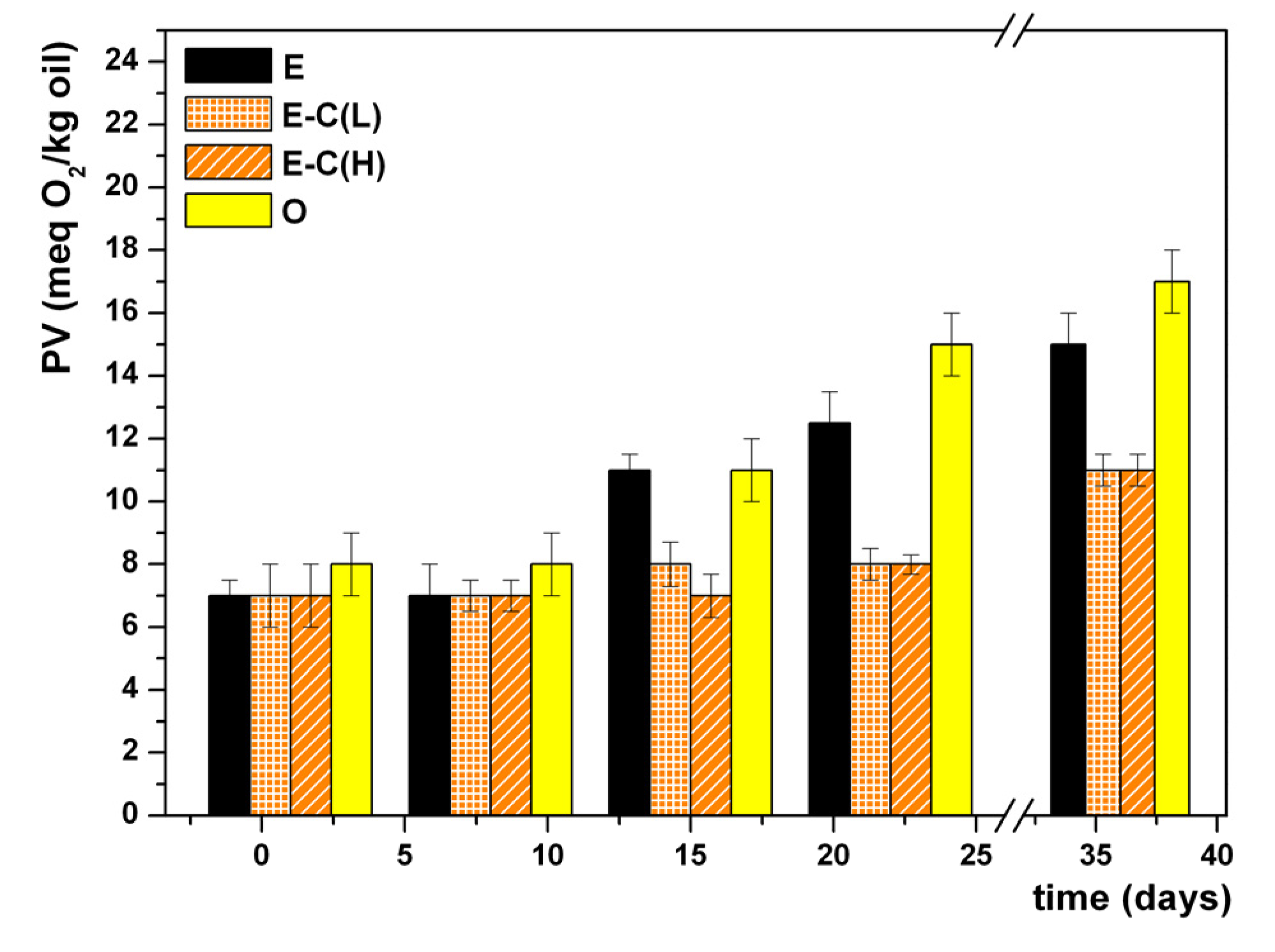
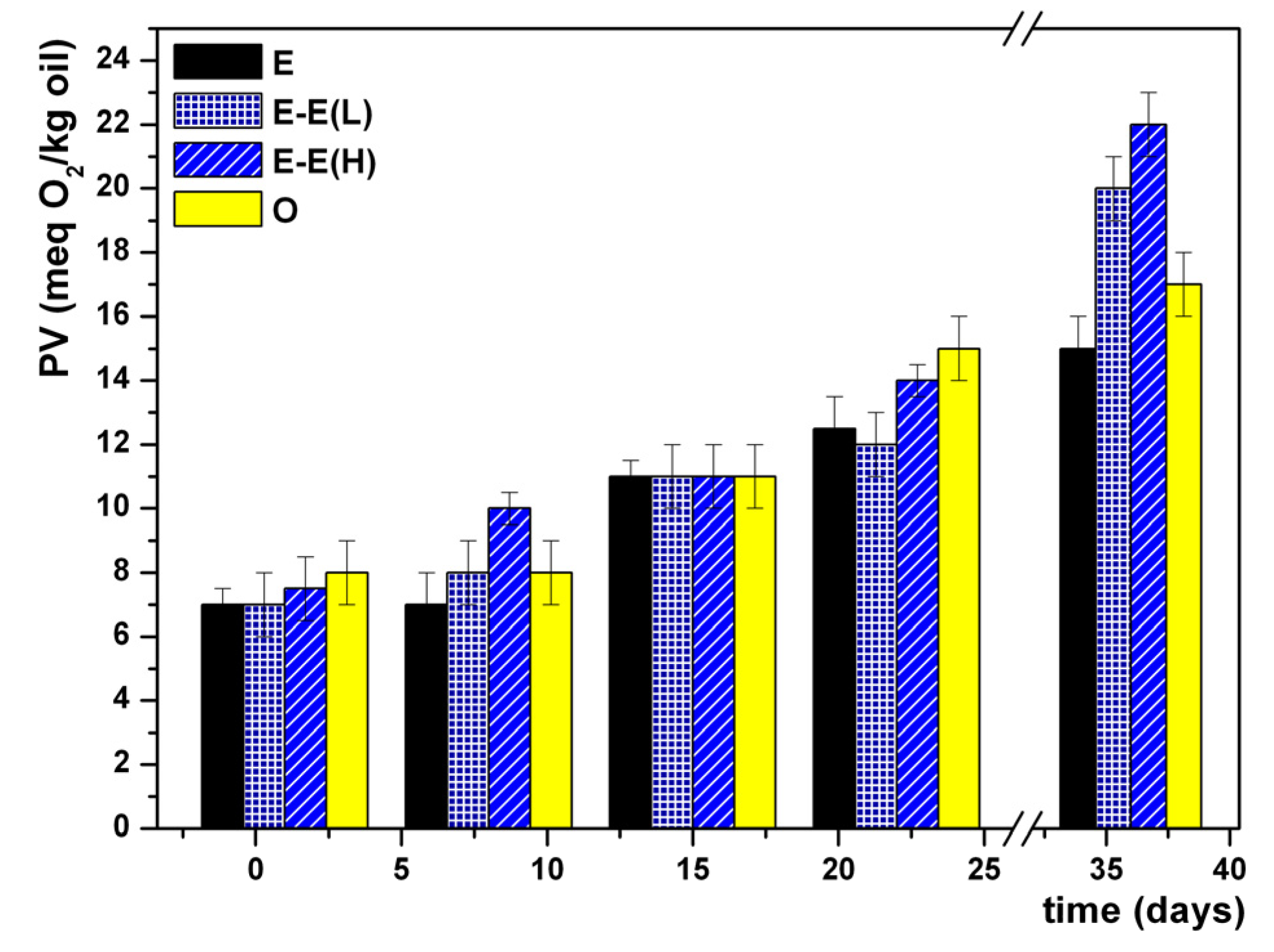
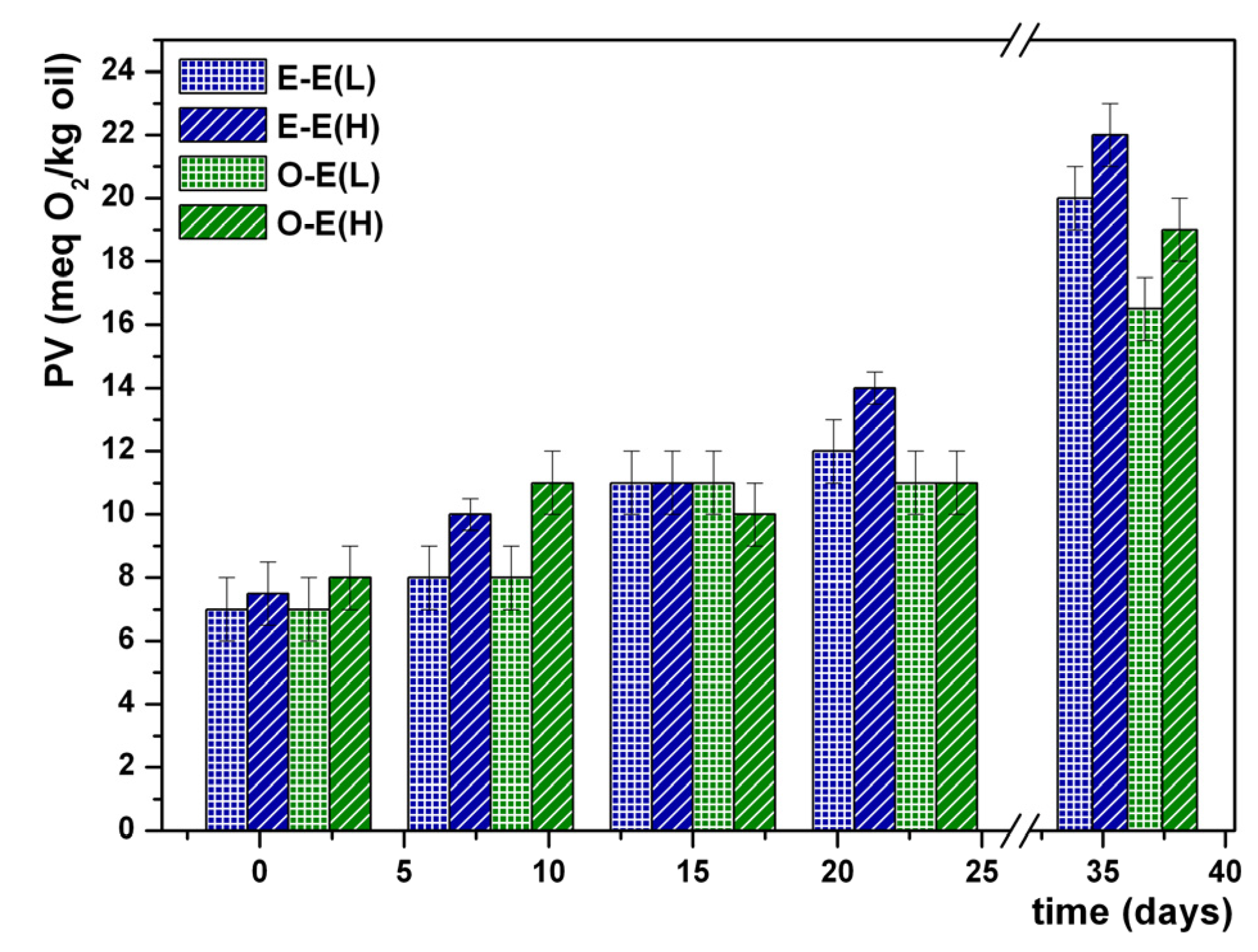
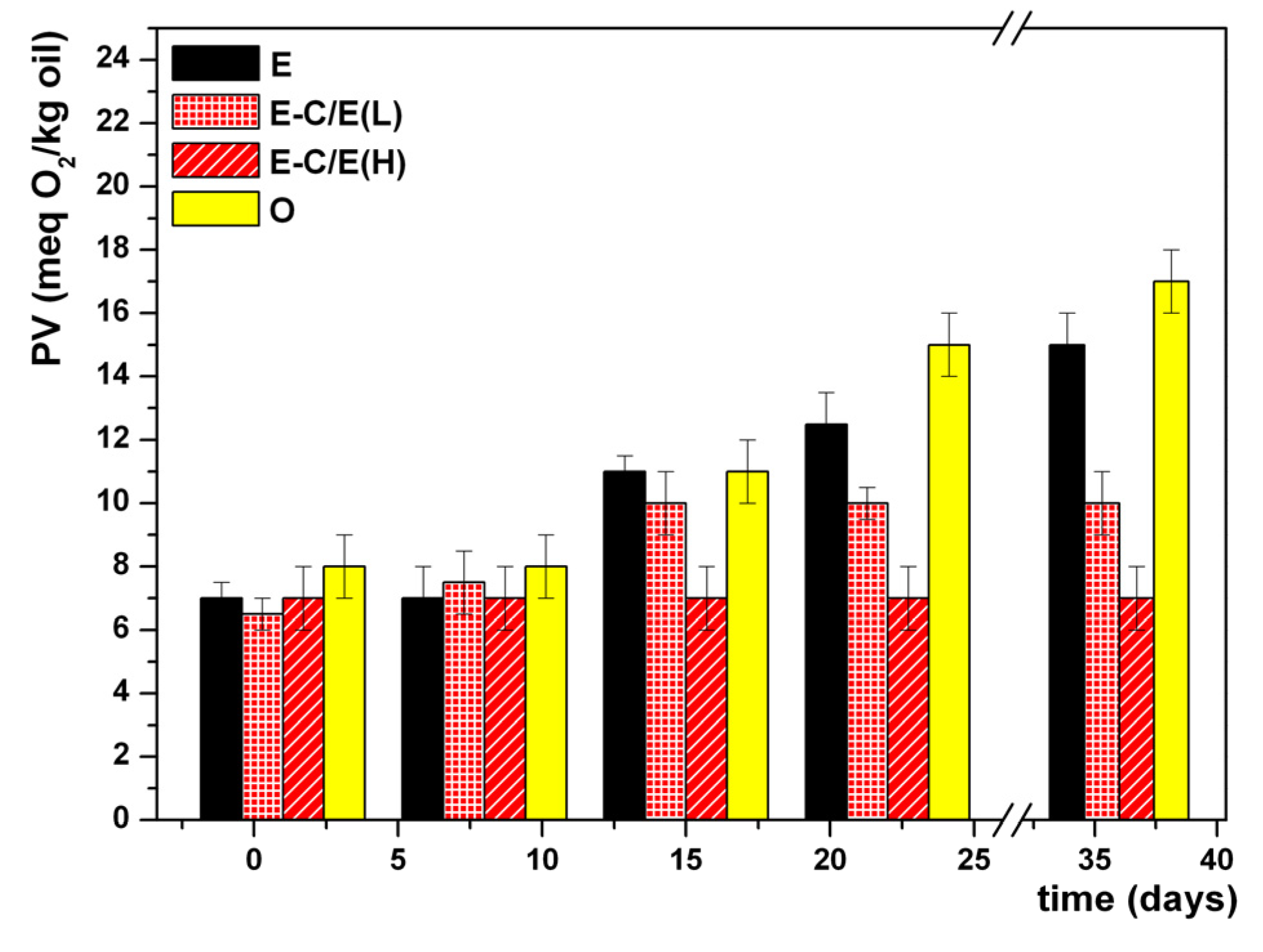
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of Food and Agricolture. FAO Agriculture Series; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1996; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Doley, J. Chapter 14—Vitamins and Minerals in Older Adults: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Deficiency. In Nutrition and Functional Foods for Healthy Aging; Watson, R.R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, J.; Epand, R.F.; Epand, R.M. Tocopherols and tocotrienols in membranes: A critical review. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 739–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Luo, S.-C.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lin, F.-J.; Cheng, C.-C.; Wein, Y.-S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-J. Isolation and Identification of α-CEHC Sulfate in Rat Urine and an Improved Method for the Determination of Conjugated α-CEHC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11105–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lešková, E.; Kubíková, J.; Kováčiková, E.; Košická, M.; Porubská, J.; Holčíková, K. Vitamin losses: Retention during heat treatment and continual changes expressed by mathematical models. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 252–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E.; Kawarami, A.; Yammamoto, Y.; Kamiya, Y. Oxidation of lipids VIII. Synergistic inhibition of oxidation of phosphatidylcholine liposomes in acqueous dispersions by Vitamin E and Vitamin C. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 58, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, G.; Cuomo, F.; Hochkoeppler, A.; Ceglie, A.; Lopez, F. Use of Rhodotorula minuta live cells hosted in water-in-oil macroemulsion for biotrasformation reaction. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, L.; Cinelli, G.; Cofelice, M.; Ceglie, A.; Lopez, F.; Cuomo, F. Effect of the coexistence of sodium caseinate and Tween 20 as stabilizers of food emulsions at acidic pH. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 168, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, F.; Perugini, L.; Marconi, E.; Messia, M.C.; Lopez, F. Enhanced Curcumin Bioavailability through Nonionic Surfactant/Caseinate Mixed Nanoemulsions. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Double Emulsions Stabilized by Food Biopolymers. Food Biophys. 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Food applications of emulsion-based edible films and coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, M.M.; Watson, A.D.; Wilde, P.J. Emulsions - Creaming and rheology. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Zhang, S.; Holmes, M.; Ettelaie, R. Colloidal aspects of digestion of Pickering emulsions: Experiments and theoretical models of lipid digestion kinetics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 263, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoen, R.; Jangchud, A.; Jangchud, K.; Harnsilawat, T.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of interfacial composition on oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by biopolymer emulsifiers. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 1–609. [Google Scholar]
- Cinelli, G.; Cuomo, F.; Ambrosone, L.; Venditti, F.; Lopez, F. Determination of bisphenol A in red wine using a double vortex–ultrasound-assisted microextraction assay: Role of the interfacial properties. Biotechnol. Prog. 2019, 35, e2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekkarinen, S.S.; Stöckmann, H.; Schwarz, K.; Heinonen, I.M.; Hopia, A.I. Antioxidant activity and partitioning of phenolic acids in bulk and emulsified methyl linoleate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3036–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenakis, A.; Papadimitriou, V.; Sotiroudis, T.G. Colloidal structures in natural oils. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, M.; Spyropoulos, F.; Norton, I. The effect of interfacial microstructure on the lipid oxidation stability of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosone, L.; Cinelli, G.; Mosca, M.; Ceglie, A. Susceptibility of water-emulsified extra virgin olive oils to oxidation. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, K.; Huang, S.W.; German, J.B.; Tiersch, B.; Hartmann, J.; Frankel, E.N. Activities of antioxidants are affected by colloidal properties of oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions and bulk oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4874–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Ropers, M.H.; Genot, C. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 945–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, G.; Sbrocchi, G.; Iacovino, S.; Ambrosone, L.; Ceglie, A.; Lopez, F.; Cuomo, F. Red Wine-Enriched Olive Oil Emulsions: Role of Wine Polyphenols in the Oxidative Stability. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraho, T.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Mechanisms of lipid oxidation in food dispersions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mosca, M.; Cuomo, F.; Lopez, F.; Ceglie, A. Role of emulsifier layer, antioxidants and radical initiators in the oxidation of olive oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhu, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Influence of aqueous phase emulsifiers on lipid oxidation in water-in-walnut oil emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikekar, R.V.; Nitin, N. Distribution of encapsulated materials in colloidal particles and its impact on oxidative stability of encapsulated materials. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9233–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, B. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant vitamins: Mechanisms of action. Am. J. Med. 1994, 97, S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shi, J.; Colina Ibarra, A.; Kakuda, Y.; Jun Xue, S. The scavenging capacity and synergistic effects of lycopene, vitamin E, vitamin C, and β-carotene mixtures on the DPPH free radical. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Chen, W.F.; Zhou, B. Antioxidant synergism of green tea polyphenols with α-tocopherol and l-ascorbic acid in SDS micelles. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates Barclay, L.R.; Locke, S.J.; Macneil, J.M. Autoxidation in micelles. Synergism of vitamin C with lipid-soluble vitamin E and water-soluble Trolox. Can. J. Chem. 1985, 63, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, E.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J.; Karbownik, M.; Manchester, L.C.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Fulia, F.; Barberi, I. Individual and synergistic antioxidative actions of melatonin: Studies with vitamin E, vitamin C, glutathione and desferrrioxamine (desferoxamine) in rat liver homogenates. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Ceglie, A.; Ambrosone, L. Biocompatible water-in-oil emulsion as a model to study ascorbic acid effect on lipid oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EEC) No. 2568/91 of 11 July 1991 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis Official Journal L 248, 5 September 1991. Off. J. L 1991, 248, 1–83.
- Csáki, K.F. Synthetic surfactant food additives can cause intestinal barrier dysfunction. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 76, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moonen, H.; Bas, H. Mono-and diglycerides. Emuls. Food Technol. 2004, 40–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyakov, P.M.; Mal’kov, V.D.; Sedova, T.P. The effect of fatty alcohols and valeric acid on the regions of existence of a three-phase system containing water, oil, and surfactant. Colloid J. 2002, 64, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, G.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmad, F.J. Theory and Practice of Physical Pharmacy-E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.-G.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-D. Novel evaluation method for the water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion stability by turbidity ratio measurements. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Ceglie, A.; Ambrosone, L. Antioxidant dispersions in emulsified olive oils. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, M.Z.; Shehab, S.K.; Darwish, N.; El-Zoheiry, E. A new titrimetric method for the determination of vitamin C. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 53, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, J.; Yanishlieva, N.; Gordon, M. Antioxidants in Food: Practical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, R. Vitamin E: Mechanism of its antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 1997, 3, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Boersma, M.G.; Haan, L.D.; Spenkelink, B.; Awad, H.M.; Cnubben, N.H.P.; Van Zanden, J.J.; Woude, H.V.D.; Alink, G.M.; Koeman, J.H. The pro-oxidant chemistry of the natural antioxidants vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenoids and flavonoids. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 11, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Oil (%) | Water (%) | E471 (%) | Span80 (%) | Tween80 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98.9 | 1 | 0.1 | – | – |
| 2 | 98.8 | 1 | 0.2 | – | – |
| 3 | 97.9 | 2 | 0.1 | – | – |
| 4 | 97.8 | 2 | 0.2 | – | – |
| 5 | 97.5 | 2 | 0.5 | – | – |
| 6 | 98.5 | 1 | – | 0.5 | – |
| 7 | 98.0 | 1 | – | 1.0 | – |
| 8 | 97.75 | 1 | – | 0.75 | 0.5 |
| Sample | Span 80 (%) | Water (%) | Vitamin C (mol) | Vitamin E (mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 1.0 | 1.0 | – | – |
| E-C(L) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 × 10−5 | – |
| E-C(H) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.05 × 10−4 | – |
| E-E(L) | 1.0 | 1.0 | – | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| E-E(H) | 1.0 | 1.0 | – | 1.05 × 10−4 |
| E-C/E(L) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 × 10−5 | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| E-C/E(H) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.05 × 10−4 | 1.05 × 10−4 |
| O-E(L) | – | – | – | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| O-E(H) | – | – | – | 1.05 × 10−4 |
| O | – | – | – | – |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuomo, F.; Cinelli, G.; Chirascu, C.; Marconi, E.; Lopez, F. Antioxidant Effect of Vitamins in Olive Oil Emulsion. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4020023
Cuomo F, Cinelli G, Chirascu C, Marconi E, Lopez F. Antioxidant Effect of Vitamins in Olive Oil Emulsion. Colloids and Interfaces. 2020; 4(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuomo, Francesca, Giuseppe Cinelli, Catalina Chirascu, Emanuele Marconi, and Francesco Lopez. 2020. "Antioxidant Effect of Vitamins in Olive Oil Emulsion" Colloids and Interfaces 4, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4020023
APA StyleCuomo, F., Cinelli, G., Chirascu, C., Marconi, E., & Lopez, F. (2020). Antioxidant Effect of Vitamins in Olive Oil Emulsion. Colloids and Interfaces, 4(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4020023






