Characterization of Nanoparticles Using DSPE-PEG2000 and Soluplus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fine Particles
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Particle Diameter, Polydispersity (PDI), and Zeta Potential
2.3.2. Stability Study
2.3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Observation
2.3.4. Acquisition of 31P-NMR Spectra
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Examination of Mixing Ratio for Preparation of Fine Particles
3.2. Particle Stability
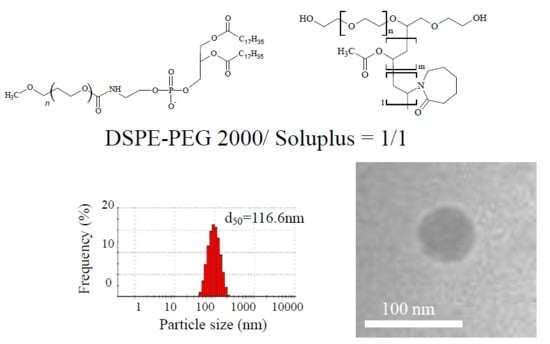
3.3. Shape Evaluation of DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus Particles
3.4. 31P-NMR Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maeda, H.; Konno, T. Metamorphosis of Neocarzinostatin to SMANCS; Springer-Verlag GmbH: Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 227–268. [Google Scholar]
- Daryl, C.; Charles, O.; Mark, E.; John, W.; Dmitri, B. Pharmacokinetics and in vivo drug release rates in liposomal nanocarrier development. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 97, 4696–4740. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.; Patel, B.B.; Tiwari, S. Colloidal nanocarriers: A review on formulation technology, types and applications toward targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 6, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How, C.W.; Rasedee, A.; Manickam, S.; Rosli, R. Tamoxifen-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier as a drug delivery system: Characterization, stability assessment and cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Pang, B.; Hyun, D.C.; Yang, M.; Xia, Y. Engineered Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12320–12364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Kuwata, Y.; Mutoh, M.; Ishiguro, N.; Utoguchi, N.; Shinohara, A.; Eriguchi, M.; Yanagie, H.; Maruyama, K. Effective anti-tumor activity of oxaliplatin encapsulated in transferrin–PEG-liposome. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 346, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoue, S.; Yamada, S.; Chan, H.K. Nanodrugs: Pharmacokinetics and safety. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moritz, M.G.; Moritz, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles as attractive drug vehicles: Composition, properties and therapeutic strategies. Mater Sci. Eng. C. 2016, 68, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Maruyama, K. Effective gene delivery with novel liposomal bubbles and ultrasonic destruction technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.M. Poly(ethylene glycol) Chemistry: Biotechnical and Biomedical Applications; Springer-Verlag GmbH: Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, N.; Matsumura, Y.; Kataoka, K. Development of polymeric micelles for targeting intractable cancers. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaki, Y.; Okada, T.; Scholz, C.; Iijima, M.; Kato, M.; Kataoka, K. The Reactive Polymeric Micelle Based on An Aldehyde-Ended Poly(ethylene glycol)/Poly(lactide) Block Copolymer. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Naito, M.; Kataoka, K. Analysis of Micelle Formation of an Adriamycin-Conjugated Poly(Ethylene Glycol)–Poly(Aspartic Acid) Block Copolymer by Gel Permeation Chromatography. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yasugi, K.; Harada, A.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Temperature-Related change in the properties relevant to drug delivery of poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(d,l-lactide) block copolymer micelles in aqueous milieu. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, B.; Arleth, L.; Hjelm, R.P.; Rubinstein, I.; Onyuksel, H. In vitro characterization of PEGylated phospholipid micelles for improved drug solubilization: Effects of PEG chain length and PC incorporation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 2476–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ogawa, N.; Kurimoto, I.; Yamamoto, H.; Furuno, T.; Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, M. Improvement of the Antitumor Activity of Poorly Soluble Sapacitabine (CS-682) by Using Soluplus® as a Surfactant. Boil. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, C.; Saito, S.; Suda, A.; Ogawa, N.; Kawashima, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Antibacterial activities of polymeric poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles and Soluplus® micelles against Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm and their characterization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71709–71717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, U.M.; Cui, Z. Long-circulating gadolinium-encapsulated liposomes for potential application in tumor neutron capture therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 312, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Yuda, T.; Okamoto, A.; Kojima, S.; Suginaka, A.; Iwatsuru, M. Prolonged circulation time in vivo of large unilamellar liposomes composed of distearoyl phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol containing amphipathic poly(ethylene glycol). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1128, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M. Prolonging the circulation time and modifying the body distribution of intravenously injected polystyrene nanospheres by prior intravenous administration of poloxamine-908. A ‘hepatic-blockade’ event or manipulation of nanosphere surface in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997, 1336, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: Mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, K.; Harada, A.; Nagasaki, Y. Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: Design, characterization and biological significance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-C.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Gong, T.; Sun, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.-R. Soluplus micelles for improving the oral bioavailability of scopoletin and their hypouricemic effect in vivo. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dian, L.; Yu, E.; Chen, X.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Wu, C. Enhancing oral bioavailability of quercetin using novel soluplus polymeric micelles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, P.C.; Hughes, R.; Rafter, J.J.; Bruce, W.R. Polyethylene glycol reduces inflammation and aberrant crypt foci in carcinogen-initiated rats. Cancer Lett. 2005, 223, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moribe, K.; Maruyama, S.; Inoue, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Fukami, T.; Tomono, K.; Higashi, K.; Tozuka, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Ascorbyl dipalmitate/PEG-lipid nanoparticles as a novel carrier for hydrophobic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanida, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Sato, H.; Kadota, K.; Tozuka, Y. Evaluation of the Micellization Mechanism of an Amphipathic Graft Copolymer with Enhanced Solubility of Ipriflavone. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, P.R.; Al Shaal, L.; Müller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Production and characterization of Hesperetin nanosuspensions for dermal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarmentocde, B.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F.; Ferreira, D. Development and characterization of new insulin containing polysaccharide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2006, 53, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terayama, H.; Hirota, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Esumi, K. Effect of dilution on aqueous dispersion of drug particles. Colloids Surf. B 2003, 27, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandstrom, M.C.; Johansson, E.; Edwards, K. Influence of preparation path on the formation of discs and threadlike micelles in DSPE-PEG 2000/lipid systems. Biol Chem. 2008, 132, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, M.; Hansson, P.; Edwards, K. Spherical Micelles and Other Self-Assembled Structures in Dilute Aqueous Mixtures of Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Lipids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 8420–8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokudome, Y.; Uchida, R.; Yokote, T.; Todo, H.; Hada, N.; Kon, T.; Yasuda, J.; Hayashi, H.; Hashimoto, F.; Sugibayashi, K. Effect of topically applied sphingomyelin-Based liposomes on the ceramide level in a three-Dimensional cultured human skin model. J. Liposome Res. 2010, 20, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inoue, Y.; Hibino, M.; Murata, I.; Kanamoto, I. A Nanocarrier Skin-Targeted Drug Delivery System using an Ascorbic Acid Derivative. Pharm. Res. 2017, 35, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | ZP (mV) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSPE-PEG2000 int | 52.0 ± 0.3 | −38.0 ± 1.3 | 0.952 |
| Soluplus int | 61.8 ± 0.4 | −11.1 ± 0.1 | 0.095 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 10/1 | 36.5 ± 1.1 | −28.5 ± 1.5 | 0.900 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 5/1 | 80.8 ± 0.9 | −29.2 ± 0.4 | 0.644 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 4/1 | 128.1 ± 1.8 | −28.1 ± 0.0 | 0.295 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 3/1 | 128.1 ± 1.1 | −27.1 ± 2.7 | 0.294 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 2/1 | 135.1 ± 0.4 | −26.3 ± 2.6 | 0.247 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 1/1 | 116.6 ± 0.0 | −13.7 ± 0.6 | 0.112 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 1/2 | 107.9 ± 2.2 | −9.6 ± 1.4 | 0.163 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 1/3 | 68.9 ± 0.8 | −9.9 ± 0.7 | 0.109 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 1/4 | 72.0 ± 0.4 | −11.3 ± 0.3 | 0.103 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 1/5 | 54.5 ± 0.1 | −6.0 ± 0.2 | 0.057 |
| DSPE-PEG2000/Soluplus = 1/10 | 56.1 ± 0.1 | −7.7 ± 1.0 | 0.101 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takayama, R.; Inoue, Y.; Murata, I.; Kanamoto, I. Characterization of Nanoparticles Using DSPE-PEG2000 and Soluplus. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4030028
Takayama R, Inoue Y, Murata I, Kanamoto I. Characterization of Nanoparticles Using DSPE-PEG2000 and Soluplus. Colloids and Interfaces. 2020; 4(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakayama, Rina, Yutaka Inoue, Isamu Murata, and Ikuo Kanamoto. 2020. "Characterization of Nanoparticles Using DSPE-PEG2000 and Soluplus" Colloids and Interfaces 4, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4030028
APA StyleTakayama, R., Inoue, Y., Murata, I., & Kanamoto, I. (2020). Characterization of Nanoparticles Using DSPE-PEG2000 and Soluplus. Colloids and Interfaces, 4(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4030028