Improved As-Synthesized Oleic Amido Propyl Betaine Surfactant Mixture for Stable Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension: Effect of Mixed Co-Solvents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Used
2.2. Improvement of As-Synthesized Amphoteric Surfactant for Better Solubility and Stability
2.3. Co-Solvent Ratio Study
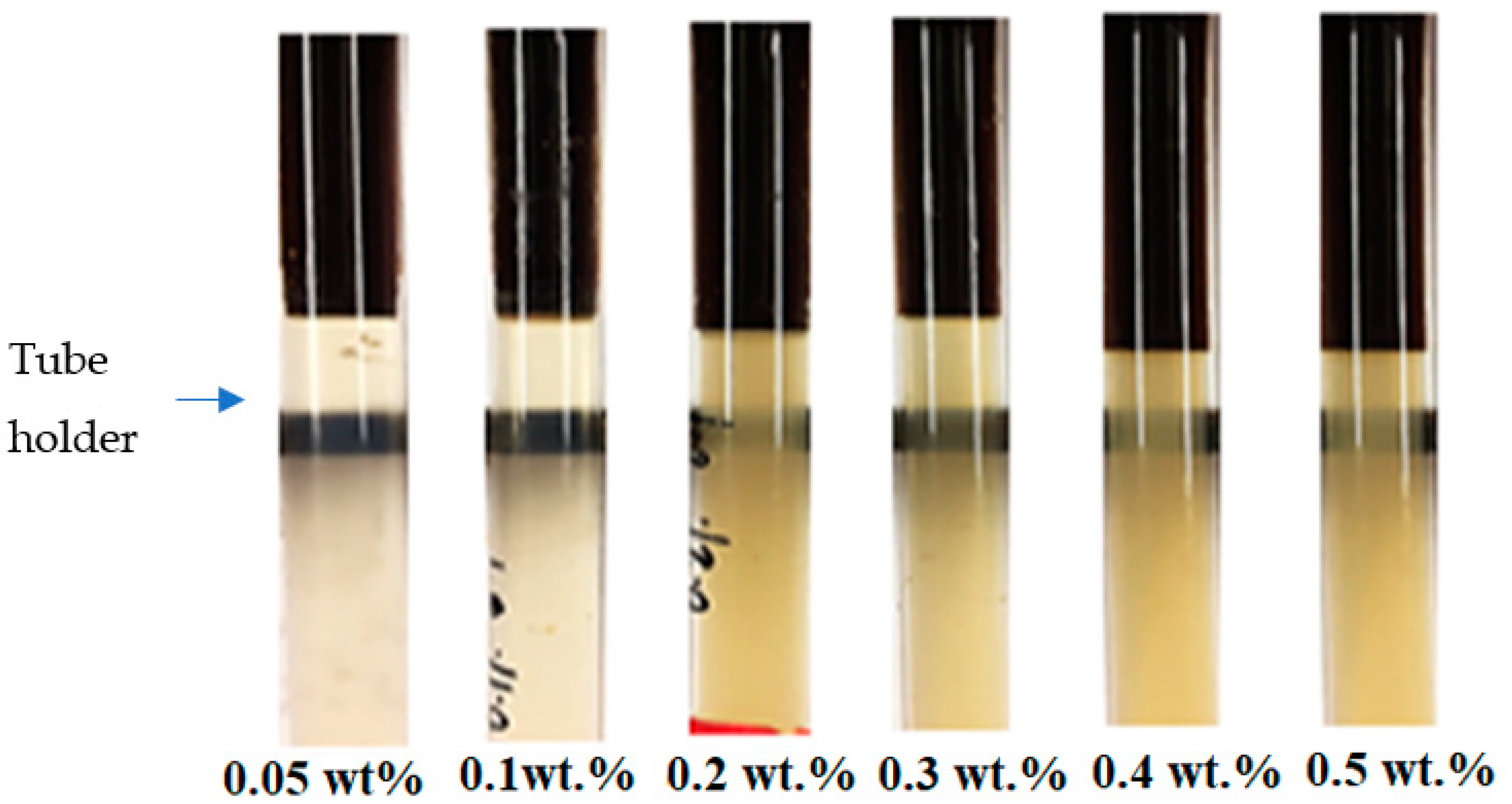
2.4. Turbidity Test
2.5. Oil–Water Interfacial Tension Test
2.6. Microemulsion Phase Behavior Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Solubility and Interfacial Tension of As-Synthesized Surfactants in Seawater
3.2. The Effect of Co-Solvent on Solubility and IFT
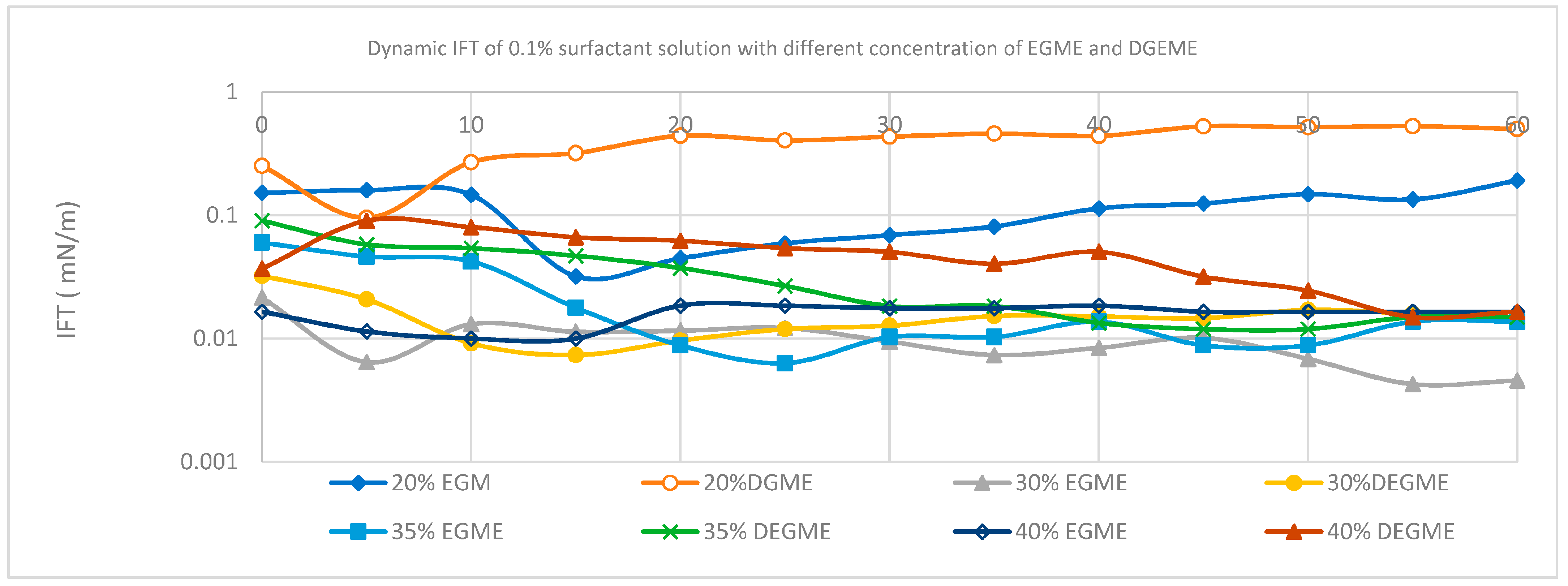
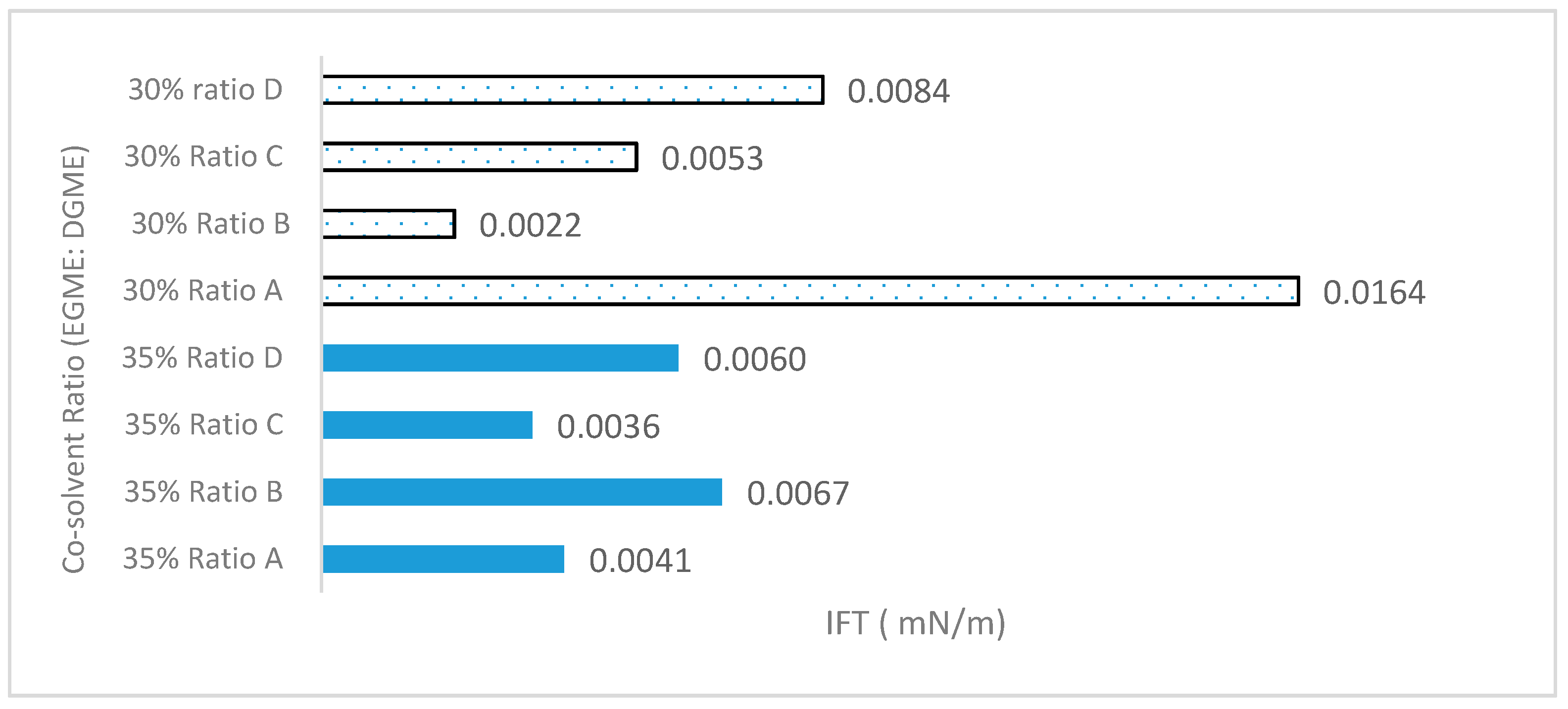
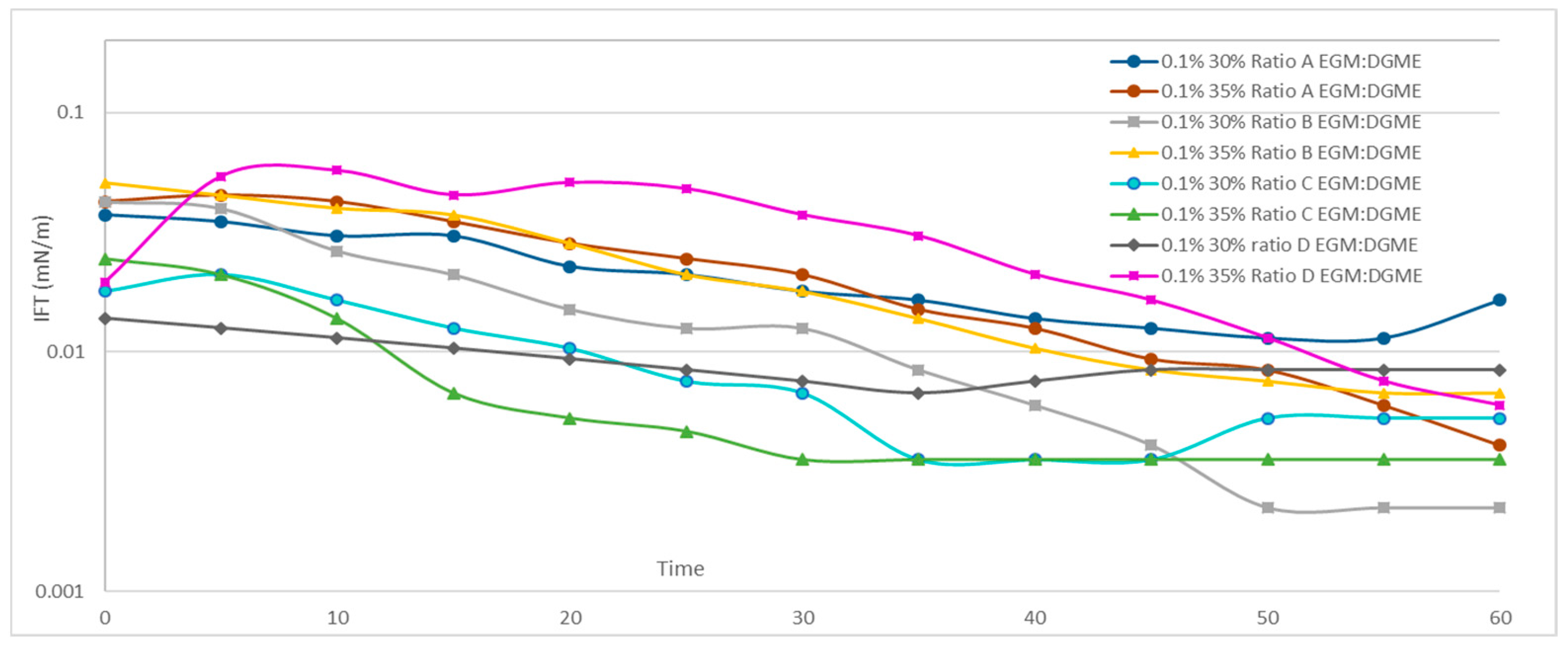
3.3. Effect of Mixed Solvents on the IFT of the Surfactant
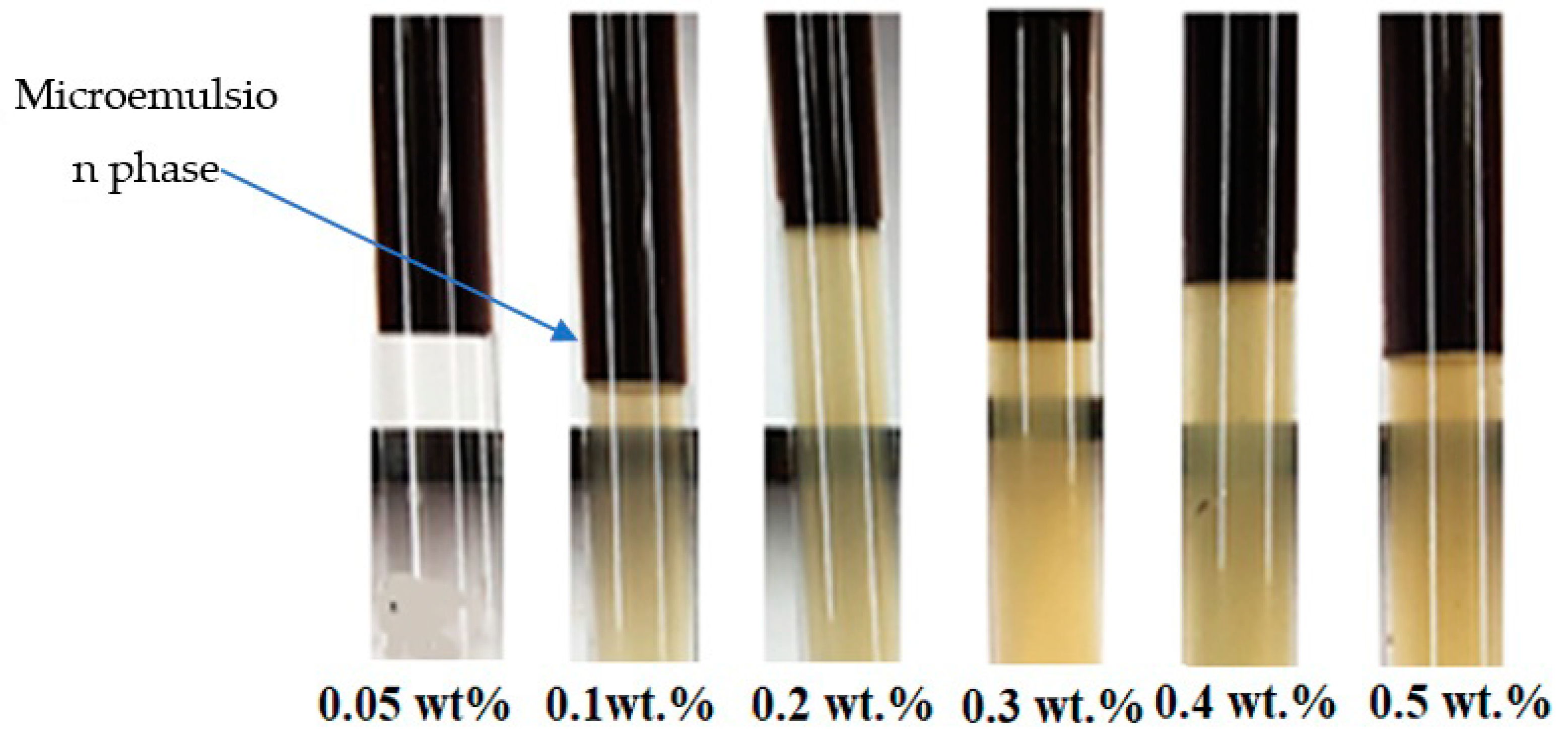
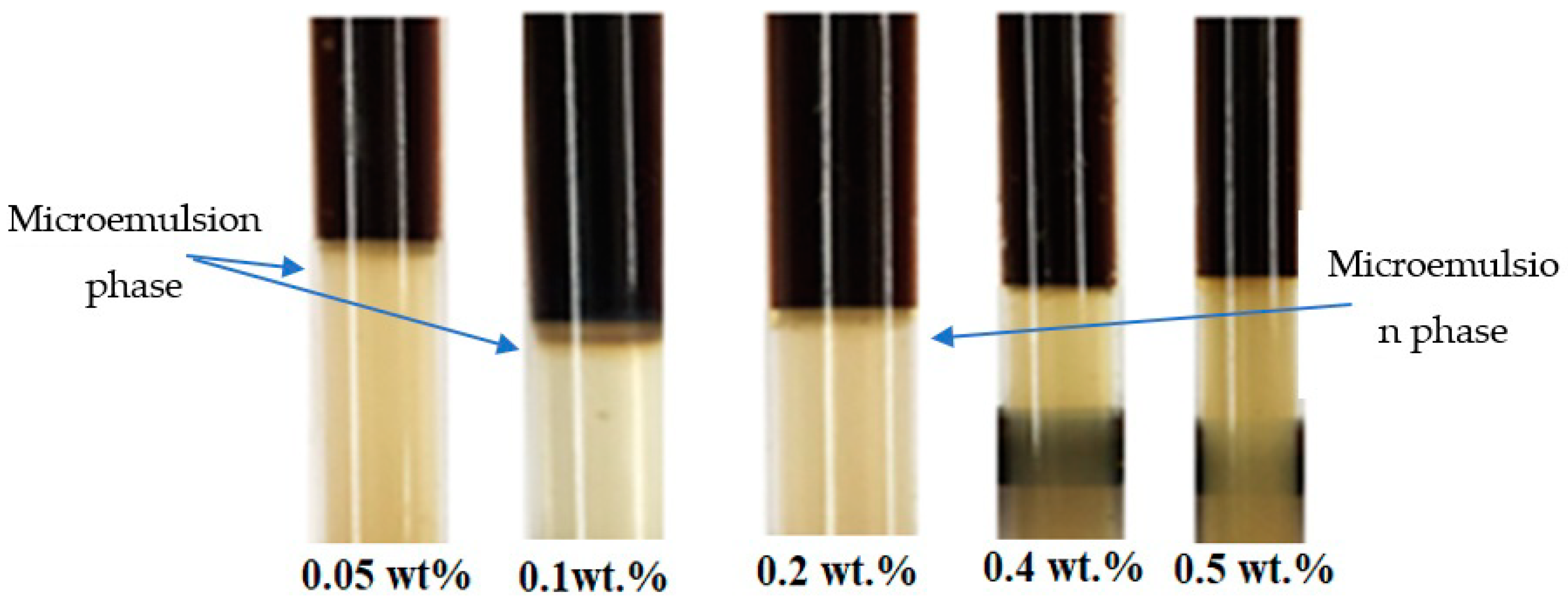
3.4. Microemulsion Phase Behavior Test on As-Synthesized Surfactant with a Co-Solvent Mixture
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.-Z.; Cai, H.-Y.; Zhang, F.; Tian, M.-Z.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Effect of Fatty Acids on Interfacial Tensions of Novel Sulfobetaines Solutions. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, R.; Sallai, R.; Bartha, L.; Vágó, Á. Selection Method of Surfactants for Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 5, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, H.; Yan, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. Synthesis and physiochemical performance evaluation of novel sulphobetaine zwitterionic surfactants from lignin for enhanced oil recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saki, M.; Reza, A. Influence of Surfactant Type, Surfactant Concentration, and Salinity on Interfacial Tension of a Brine/Live Oil/Surfactant Fluid System: A Case Study of Iranian Asmari Oil Reservoir. Iran. J. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, M.S.; Hussein, I.A.; Sultan, A.S. Review on Surfactant Flooding: Phase Behavior, Retention, IFT, and Field Applications. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7701–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Wu, W.; Wang, G. SPE 127452 Novel Surfactants that Attain Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension between Oil and High Salinity Formation Water without adding Alkali, Salts, Co-surfactants, Alcohol and Solvents Conditions for surfactants to attain ultra-low IFT at low concentrate. SPE Asia Pacific Enhanc. Oil Recover. Conf. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazir, N.A.; Ramli, A.; Yusof, N.M.; Saphanuchart, W.; Majanun, E.S. As-Synthesized Oleic Amido Propyl Betaine Surfactant Mixture and the Effect on the Crude Oil–Seawater Interfacial Tension. Processes 2020, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xiang, M.H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.H.; Shu, Z.R. The Laboratory Research on Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension Foam Flooding System with High-Temperature and High-Salinity. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 71, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Dean, R.M.; Britton, C.; Kim, D.H.; Weerasooriya, U.; Pope, G.A. The role of co-solvents and co-surfactants in making chemical floods robust. Proc. SPE Symp. Improv. Oil Recovery 2010, 2, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Dwarakanath, V.; Chaturvedi, T.; Jackson, A.; Malik, T.; Siregar, A.A.; Zhao, P. Using co-solvents to provide gradients and improve oil recovery during chemical flooding in a light oil reservoir. SPE Symp. Improv. Oil Recovery 2008, 3, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upamali, K.A.N.; Liyanage, P.J.; Cai, J.; Lu, J.; Jang, S.H.; Weerasooriya, U.P.; Pope, G.A. New Surfactants and Co-Solvents Increase Oil Recovery and Reduce Cost. SPE Improv. Oil Recovery Conf. 2016, 23, 2202–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J. Synthesis and physic-chemical properties of anion–nonionic surfactants under the influence of alkali/salt. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 419, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negin, C.; Ali, S.; Xie, Q. Most common surfactants employed in chemical enhanced oil recovery. Petroleum 2017, 3, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristantini, D.; Hakim, H.P.; Zuliardy, M.F. Addition of egbe and ethanol to enhance mes performance as chemical flooding material. J. Tek. Kim. Indones. 2018, 10, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.H.; Gan, L.M.; Koh, L.L.; Wong, M.K. Microemulsion systems with monobutyl ether of ethylene glycol or diethylene glycol as cosurfactant. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1988, 9, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novriansyah, A.; Bae, W.; Park, C.; Permadi, A.K.; Riswati, S.S. Optimal Design of Alkaline—Surfactant—Polymer Flooding under Low Salinity Environment. Polymers 2020, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czajka, A.; Hazell, G.; Eastoe, J. Surfactants at the Design Limit. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8205–8217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.A.D.L.; Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte; Neto, E.L.D.B.; Chiavone-Filho, O.; Foletto, E.L. Federal University of Santa Maria Influence of sodium chloride on the cloud point of polyethoxylate surfactants and estimation of Flory-Huggins model parameters. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioq. 2015, 1, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, C.; Ding, Q.; Du, M.; Feng, H.; Wei, Z.; Chen, A.; Zhao, M. The structure effect on the surface and interfacial properties of zwitterionic sulfobetaine surfactants for enhanced oil recovery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13993–14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, H.; Andelman, D. Kinetics of Surfactant Adsorption at Fluid-Fluid Interfaces. arXiv 1996, arXiv:cond-mat/9608140v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutin, A. Dynamic Adsorption of Surfactants at Air/Water Interface. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331327676 (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Chawla, R.; Doura, K.; McKay, D. Effect of alcohol cosolvents on the aqueous solubility of trichloroethylene. In Proceedings of the 2001 Conference on Environmental Research, Manhattan, KA, USA, 21–24 May 2001; pp. 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, P.S.; Lacks, D.J.; Gil, P.S.; Lacks, D.J. Effect of surfactant shape on solvophobicity and surface activity in alcohol-water systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 145, 204705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.J. Status of surfactant EOR technology. Petroleum 2015, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarveicy, H.; Haghtalab, A. Effect of amphoteric surfactant on phase behavior of hydrocarbon-electrolyte-water system-an application in enhanced oil recovery. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piispanen, P.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Surfactants Based on Natural Products. Diss. Kimi 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Beygi, M.R.; Varavei, A.; Lotfollahi, M.; Delshad, M. Low-Tension Gas Modeling in Surfactant Alternating Gas and Surfactant/Gas Coinjection Processes. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 11–13 August 2015; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Elmofty, O. Surfactant Enhanced Oil Recovery by Wettability Alteration in Sandstone Reservoirs. Master’s Thesis, Geosciences and Geological and Petroleum Engineering, Missouri S&T, Rolla, MO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, N.; Kumar, S.; Bera, A.; Mandal, A. Phase behaviour and characterization of microemulsion stabilized by a novel synthesized surfactant: Implications for enhanced oil recovery. Fuel 2019, 235, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.S.; Sultan, A.S.; Hussein, I.A. Screening of amphoteric and anionic surfactants for cEOR applications using a novel approach. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 476, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Hu, X.; Shui, X.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Z. A new type of renewable surfactants for enhanced oil recovery: Dialkylpolyoxyethylene ether methyl carboxyl betaines. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 489, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.N.; Deore, S.L. Emulsion Micro Emulsion and Nano Emulsion: A Review. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2016, 8, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

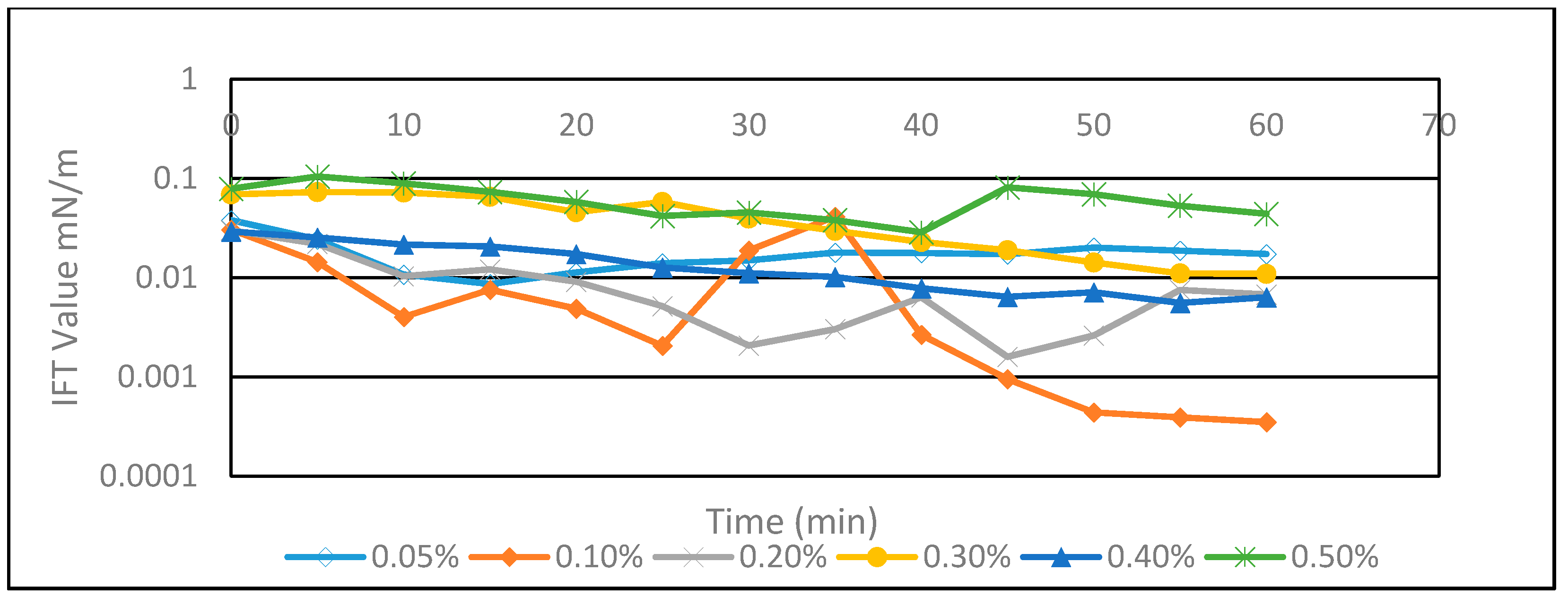
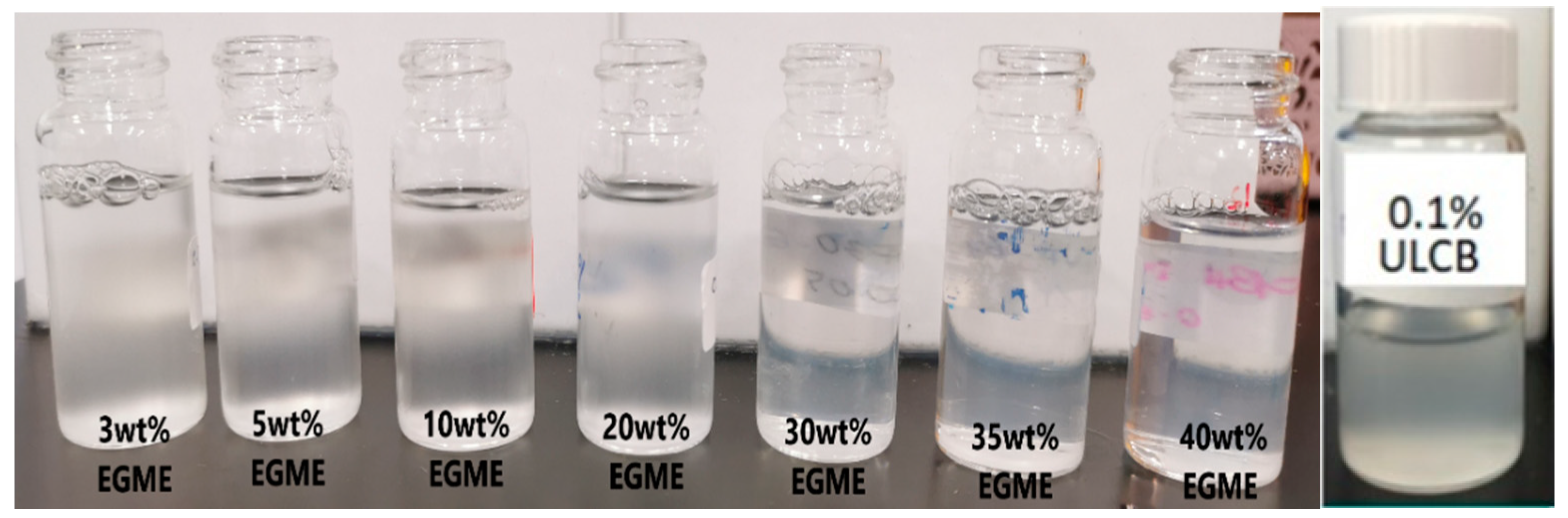
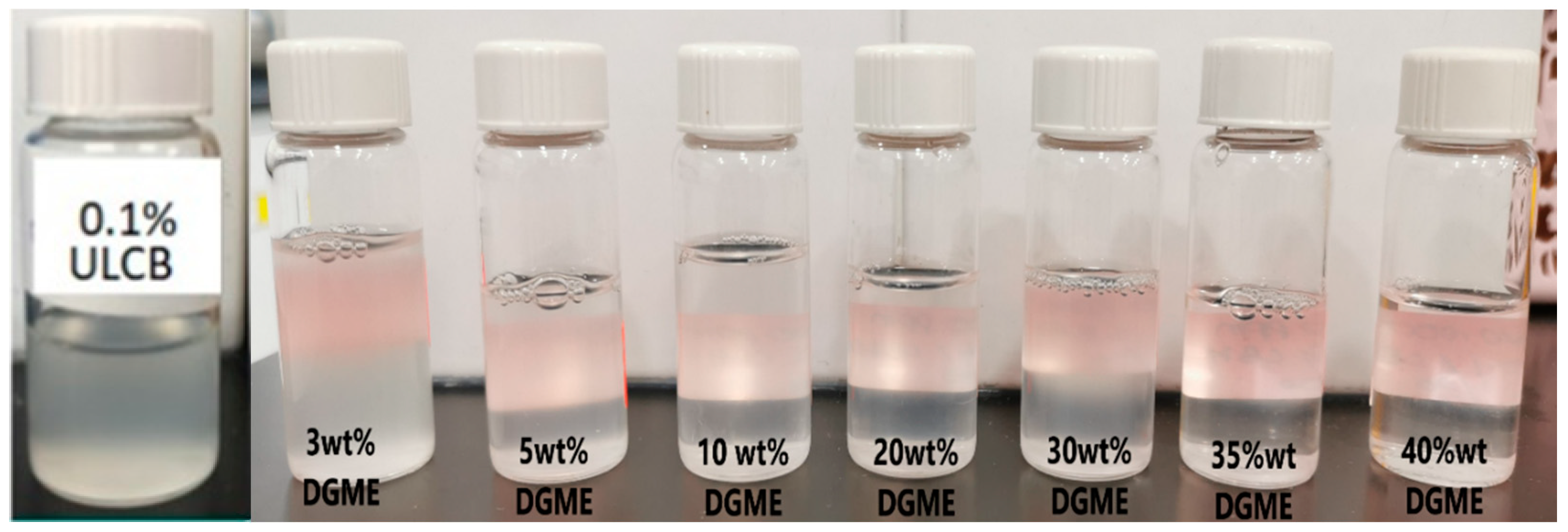
| Concentration (%) | Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|
| 0.05 | 79.5 |
| 0.1 | 149.4 |
| 0.2 | 189.9 |
| 0.3 | 234.2 |
| 0.4 | 308.8 |
| 0.5 | 316.2 |
| Concentration (%) | Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 69.5 |
| 5 | 64.1 |
| 10 | 59.2 |
| 20 | 48.2 |
| 30 | 44.5 |
| 35 | 33.5 |
| 40 | 34.4 |
| Concentration (%) | Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 40.8 |
| 5 | 40.2 |
| 10 | 38.1 |
| 20 | 34.1 |
| 30 | 28.5 |
| 35 | 23.7 |
| 40 | 23.4 |
| Concentration (wt.%) | Co-Solvent | IFT (m/N/m) at 60 min |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | EGME | 0.19126 |
| DGME | 0.49966 | |
| 30 | EGME | 0.00459 |
| DGME | 0.01487 | |
| 35 | EGME | 0.01371 |
| DGME | 0.01490 | |
| 40 | EGME | 0.01850 |
| DGME | 0.0166 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wazir, N.A.; Saphanuchart, W.; Ramli, A.; Yusof, N. Improved As-Synthesized Oleic Amido Propyl Betaine Surfactant Mixture for Stable Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension: Effect of Mixed Co-Solvents. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5010002
Wazir NA, Saphanuchart W, Ramli A, Yusof N. Improved As-Synthesized Oleic Amido Propyl Betaine Surfactant Mixture for Stable Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension: Effect of Mixed Co-Solvents. Colloids and Interfaces. 2021; 5(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleWazir, Norhidayah Ahmad, Wasan Saphanuchart, Anita Ramli, and Nurida Yusof. 2021. "Improved As-Synthesized Oleic Amido Propyl Betaine Surfactant Mixture for Stable Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension: Effect of Mixed Co-Solvents" Colloids and Interfaces 5, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5010002
APA StyleWazir, N. A., Saphanuchart, W., Ramli, A., & Yusof, N. (2021). Improved As-Synthesized Oleic Amido Propyl Betaine Surfactant Mixture for Stable Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension: Effect of Mixed Co-Solvents. Colloids and Interfaces, 5(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5010002





