Abstract
The microalgae-induced membrane system applied in wastewater treatment has attracted attention due to microalgae’s outstanding nutrient fixation capacity and biomass harvesting. However, the fundamental understanding of the interaction of microalgae and membrane surfaces is still limited. This study presents experimental and numerical methods to analyze the attachment of microalgae to the membrane. An atomic force microscope (AFM) analysis confirmed that a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sensor, as a simulated membrane surface, exhibited a rougher surface morphology than a polyurethane (PU) sensor did. The contact angle and adsorption analysis using a quartz crystal microbalance confirmed that the PDMS surface, representing the membrane surface, provided a better attachment affinity than the PU surface for microalgae because of the lower surface tension and stronger hydrophobicity of PDMS. The simulation studies of this work involved the construction of roughly circular-shaped particles to represent microalgae, rough flat surfaces to represent membrane surfaces, and the interaction energy between particles and surfaces based on XDLVO theory. The modeling results of the microalgae adsorption trend are consistent and verified with the experimental results. It was observed that the interfacial energy increased with increasing the size of particles and asperity width of the membrane surface. Contrarily, the predicted interaction energy dropped with elevating the number of asperities and asperity height of the microalgae and membrane. The most influential parameter for controlling interfacial interaction between the simulated microalgae and membrane surface was the asperity height of the membrane; changing the height from 50 nm to 250 nm led to alteration in the primary minimum from −18 kT to −3 kT. Overall, this study predicted that the microalgae attachment depends on the size of the asperities to a great extent and on the number of asperities to a lesser extent. These results provide an insight into the interaction of microalgae and membrane surface, which would provide information on how the performance of microalgae-based membrane systems can be improved.
1. Introduction
Wastewater is a global problem that a single technology cannot address due to the types of pollutant, the vastly different scales and regional conditions of municipalities [1]. Activated sludge is used in the wastewater treatment system [1]. Nevertheless, the traditional activated sludge wastewater treatment faces defects that may pollute the surface water and groundwater [2,3]. Therefore, the incentives for replacing the activated sludge system with another biological system are high. Due to their simple structure, microalgae can survive and proliferate rapidly under harsh environmental conditions, such as low pH [4], which will benefit microalgae cultivation in wastewater [5]. Microalgae can perform photosynthesis, i.e., an essential factor promoting life on Earth because it produces approximately half of the oxygen in the atmosphere and uses carbon dioxide to produce photos autotrophically [6,7]. Therefore, microalgae represent a promising biological system for treating various wastewater sources due to their metabolic flexibility to undergo photosynthetic autotrophic, polytrophic, or heterotrophic metabolism [8,9].
Membrane technologies are environmentally friendly processes used in wastewater treatment systems [10,11]. These techniques are simple in operation, easy to scale up, have a limited energy requirement, and need limited chemical treatment. Combining the membrane technology with the microalgae treatment technique can explore the advantages of efficient microalgae harvesting, cultivation, dehydration, processing, and excellent fractionation capabilities [10,11]. Despite these appealing uses, microalgae attachment is a significant obstacle to applying membrane technology in algal processes [12,13,14]. The attachment of algae to surfaces is influenced by the surface properties of the membrane and microalgae [15].
Nonetheless, few published papers [16,17] have studied the interfacial behaviors of microalgae in the membrane system. Although extensive studies made outstanding contributions to using microalgae in the membrane separation system for nutrient removal from wastewater [16,18], the information on cell adhesion to membrane surfaces and the interaction of microalgae and the membrane is minimal and inconclusive. However, such information is crucial for determining the method for controlling microalgae attachment, biofilm formation, and microalgae adhesion efficiency [19]. The objectives of this work were to experimentally assess the impact of membrane surface properties on microalgae cell attachment and to establish a numerical model to predict the interfacial interaction between microalgae and the membrane surface.
Generally, an overall comparison of the experimental results with the Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, Overbeek (DLVO) theoretical predictions shows the DLVO theory would overestimate the stability of some colloidal systems [20]. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the effect of surface morphology on interaction energy is neglected in the DLVO simulation process. Experiments have shown that the surfaces of colloidal particles have chemical heterogeneity and roughness [21,22,23,24,25]. Therefore, including particles’ surface properties would improve the simulation studies’ accuracy. Bendersky and coworkers applied the grid surface integration (GSI) approach to investigate the interaction energy between a smooth particle and a patterned surface and reported that the nano topography of the surface decreased the energy barrier developing between surfaces [26]. However, the past numerical work mainly assumed the spherical particle displayed a smooth texture and studied the surface morphology of the flat surface. Ozkan and coworkers concluded that the microalgae cell owned a rough surface [27]. Therefore, considering the impact of the surface morphology of microalgae on the interaction between the membrane surface and microalgae is essential. In this work, the surface characteristics of membrane and microalgae, as well as the deposition of algae on membrane materials, were experimentally investigated using advanced tools. This study also purposes to create one numerical model to explore the interaction energy between rough spherical particles representing microalgae and membrane surfaces.
The present work applied the rippled particle theory to construct a rough surface, where the surface roughness could be characterized by asperity number and asperity ratio [28]. It analyzed the effects of asperity number, asperity ratio, particle size, and membrane roughness parameters on the total interaction energy between the microalgae and membrane. As previous membrane studies made great efforts in investigating membrane filtration performance [29,30], the present work only aimed at studying the interaction between microalgae and membrane material rather than the performance of membrane filtration. Since microalgae contains hydroxyl groups, it can form hydrogen bonding in water (i.e., solvent). The counter ions present in water would neutralize the charged group of microalgae. If the surface charge was completely neutralized, the membrane performance would be deteriorated as the neutralized microalgae might cause fouling. Therefore, the acid–base interaction, which considered hydrophobic interaction and hydration interaction along with the classic DLVO theory, were selected as the fundamental theory for constructing the model. Our current work also applied the ripped particle theory and surface element integral (SEI) strategy combined with extended DLVO (XDLVO) theory [31] to construct the rough surface and quantify the total interaction energy, respectively. The applied rippled particle theory could help characterize the rough surface by asperity frequency and asperity amplitude [28]. Therefore, the ripped rough particle theory can help characterize the details of valleys and peaks of the ripples on the algae with similar structures. The predial sinusoidal function was used to generate the rough membrane surface [32]. The characteristics of rough surface morphology of microalgae and membranes can be simulated mathematically [33,34]. The rough surface of microalgae was constructed following Equations (1) and (2) [35]:
where is the radius of the element particle (i.e., microalgae), is the asperity amplitude, and n is the asperity frequency. Although previous work studied the interaction between sludge foulant and membrane [36], for the first time, we reported comprehensive simulation and experimental studies on the interaction of microalgae and membrane surface and explored the effects of surface morphology of microalgae and membrane on their interaction behavior.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A strain of microalgae, Chlorella Vulgaris (CPCC 90), was purchased from the Canadian Physiological Culture Centre (University of Waterloo, ON, Canada) and used as the microalgal inoculant in this work. Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (K2HPO4), copper sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O), ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), boric acid (H3BO3), calcium chloride, dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O), cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O), magnesium sulphate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O), zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O), manganese (II) chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), cobalt sulphate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), sodium molybdate dihydrate (Na2MoO4·2H2O), and ethylenediamine tetra-acetic (EDTA) were bought from Sigma-Aldrich. All chemicals were used without further purification.
2.2. Microalgae Cultivation
The algae samples of Chlorella Vulgaris were cultivated in the mineral salt medium (MSM) nutrient medium in the glass container (1 L) with continuous light illumination [37]. The medium’s mixed liquid suspended solids (MLSS) concentration was monitored every four days. The algae cultivation was conducted following the method established previously [38], and the microalgae concentration was 1.16 g/L.
2.3. Characterization of Microalgae
Algae cells’ surface area and size were characterized using an inverted microscope (Olympus IX51,Tokyo, Japan). In this work, the Image-pro plus 7.0 analysis software of the instrument was applied to determine the diameters of the cells, which helped determine the circularity of algae cells following Equation (3) [39]:
where Pcell and Acell represent the cell’s perimeter and the imaged area, respectively.
2.4. Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) Analysis
The surface roughness of QCM sensor was analyzed via AFM imaging (MFP-3D Origin+, OXFORD Instruments, Abingdon, UK). Three dimensional images were recorded in tapping mode with a silicon probe (AC160TS-R3, OXFORD Instruments, Abingdon, UK). The probe had silica lever coated with Al and 6 nm radius. Clean QCM sensors used for QCM analysis were removed from water and allowed to air dry before AFM scans were performed. The image model was performed as AC model with a 20 μm scan size and 1 Hz scan rate.
2.5. Contact Angle of the Algae-Coated Surface
In this investigation, a 0.45 μm filter paper was applied to filter 20 mL of algae solution. Then, the algae residue was saved on the filter papers and pressed between two glass slides for one week (Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials). After that, the contact angle of the droplets (5 µL) of solvents, i.e., water, diodomethane, and formamide was tested on the pressed filter papers using a tensiometer instrument (Biolin Scientific Finland, Espoo, Finland) [40,41]. In addition, the contact angles of these three solvents were investigated on (polyurethane) PU-coated and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sensors. The contact angle (θ) assessed the wettability of a solid surface with a liquid and was determined following the Young equation [42].
2.6. Adsorption of Algae on the Sensor Surface
The adsorption of microalgae on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and polyurethane (PU) sensors was studied by the quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D 401, E1, Q-Sense Inc., Gothenborg, Sweden). PDMS-coated sensors (Q-sense, BL-QSX 900) and PU-coated sensors (Q-sense, BL-QSX 999) were received from Q-sense manufacturer and used as substrates. The details of this analysis are available in the Supplementary Materials file.
2.7. Simulation of Circular Microalgae Interacted with Planar Membrane
It was stated that the surface of natural algae had rough morphology in the micrometer range [43]. Moreover, the membrane surface morphology significantly controls the attachment behavior of microalgae [44]. Therefore, it is essential to identify a reliable approach to construct the rough surface of the membrane and microalgae, which is the primary step in investigating the interfacial interaction between the microalgae and membrane.
In this study, the ripped rough particle theory was applied to construct the rough particle that can help characterize the details of valleys and peaks of the ripples on the algae with similar structures.
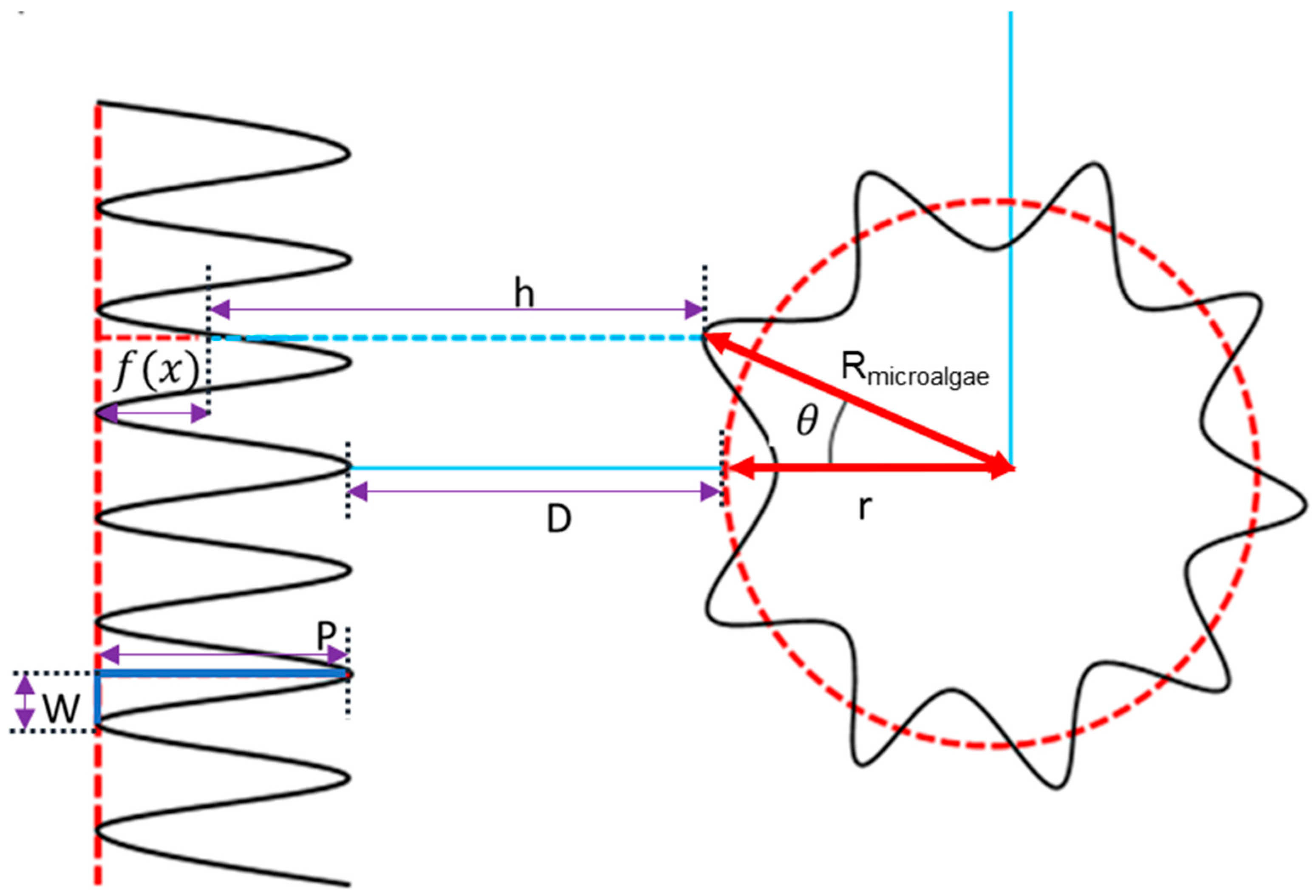
The interaction scenario of microalgae and membrane surface is shown in Figure 1. The separation distance (h) between membrane surface and microalgae can be expressed by Equation (4) [45]:
where D represents the closest distance between membrane and particle, and P is the height of asperities on the membrane with a rough surface. represents the surface roughness profile of the membrane, which is expressed by Equation (5):
where W is the width between uniform asperities on the membrane surface.
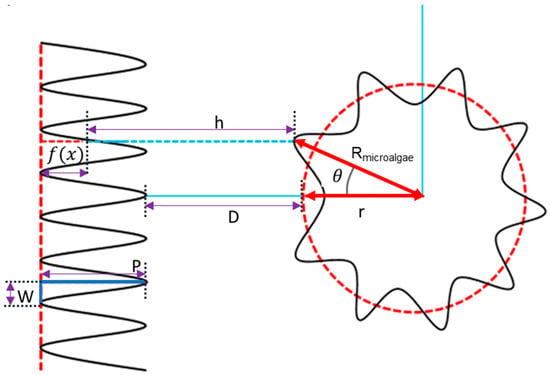
Figure 1.
Parameters involved in the interaction between membrane surface and microalgae.
2.8. Assessment of Interaction Energy
This section discusses the simulation of the interfacial energy developed between microalgae and membrane surfaces following the XDLVO theory. The total interaction energy between microalgae and membrane surface could be manufactured via the XDLVO theory, which included the electrostatic double layer (EL), Lifshitz–van der Waals (LW), and acid–base (AB) polar interaction energies [43,46,47].
The interfacial interaction energy could be described following Equations (6)–(9) [48]:
where represents the minimum equilibrium cut-off distance, which was assumed as 0.158 nm [48]. In addition, ζ represents the value of zeta potential, and κ−1 expresses the Debye length. λ represents the correlation length (0.6 nm) of molecules in a liquid medium [45]; ε represents the product of the permittivity of a vacuum (ε0 = 8.854 × 10−12 C2/J·m) and the relative permittivity (also called the dielectric constant) of the medium εr is 80 for water at 20 °C [49].
The process of the acid–base interaction is the electron acceptor–electron donor interaction. Additionally, the electron acceptor surface tension parameter and the electron donor surface tension parameter were applied to calculate the acid–base interaction, which were combined to count acid–base interaction interactions between polar condensed phase materials (microalgae and membranes). The interface tension of microalgae and membrane surface was described as the sum of a polar (acid–base) component () and an apolar (Lifshitz–van der Waals) component (). can be separated into an electron-accepting component () and an electron-donating component () [50,51]. According to the parameters of the interface tensions, the van der Waals attraction energy () and AB polar interaction energy () can be calculated following Equations (10) and (11):
where L represents liquid. If the values of surface tension for the solid were known, the and could be determined. Therefore, the surface tensions for liquid (, , and ) and contact angles of liquid droplets on solid surface () must be tested for at least three different liquids (formamide, water, and diiodomethane) to calculate the surface free energy of microalgae and membrane (, , and ) or (, , and ). In this modeling study, the above-mentioned parameters were collected from the results of the experiments in Section 3.2 and the previous literature (Table S1) [51].
Therefore, the individual AB, EL, and LW interaction energy between rough algae and rough membrane could be predicted by Equations (13)–(15) [52,53,54]:
2.9. Asperity Frequency
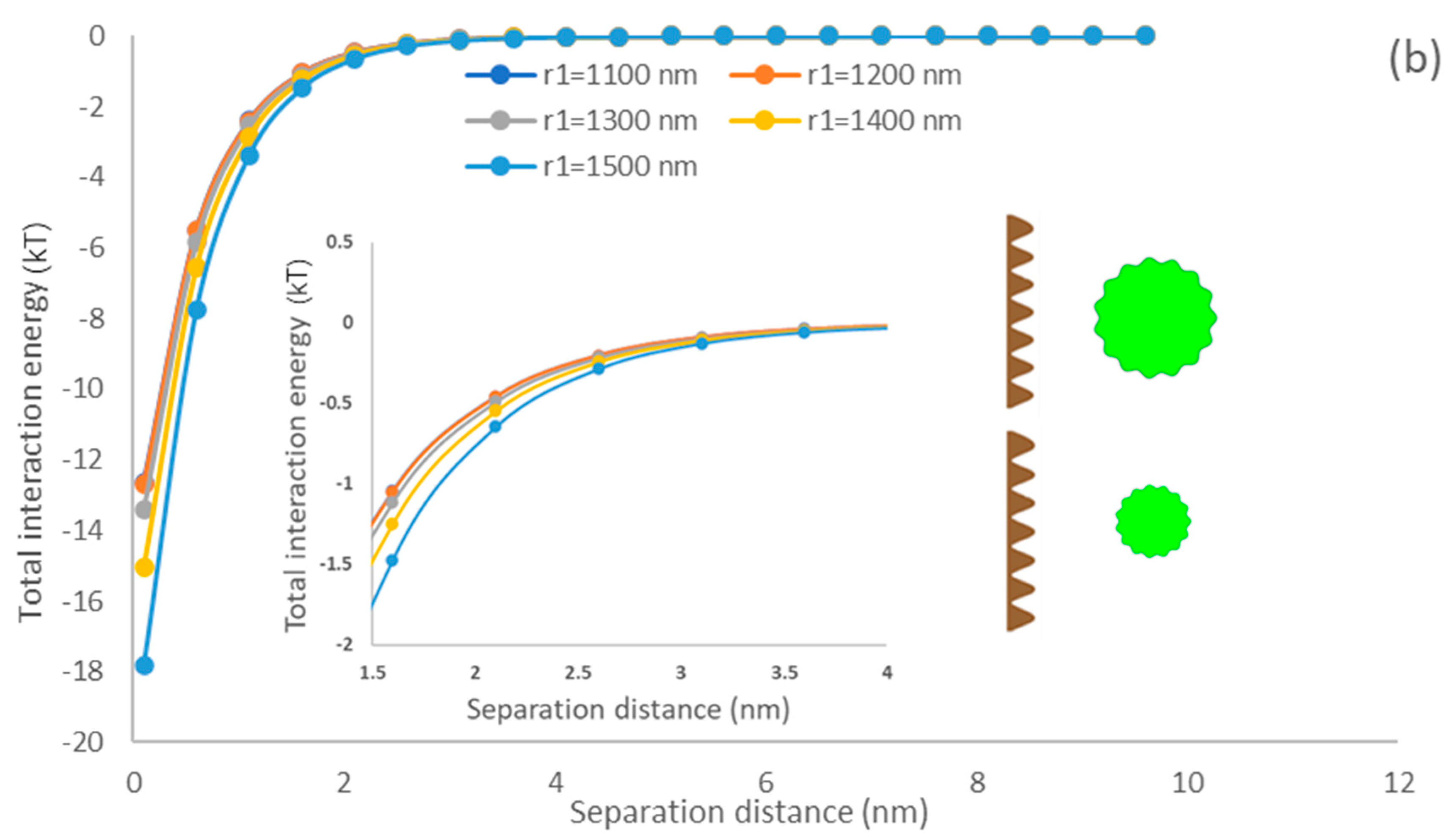
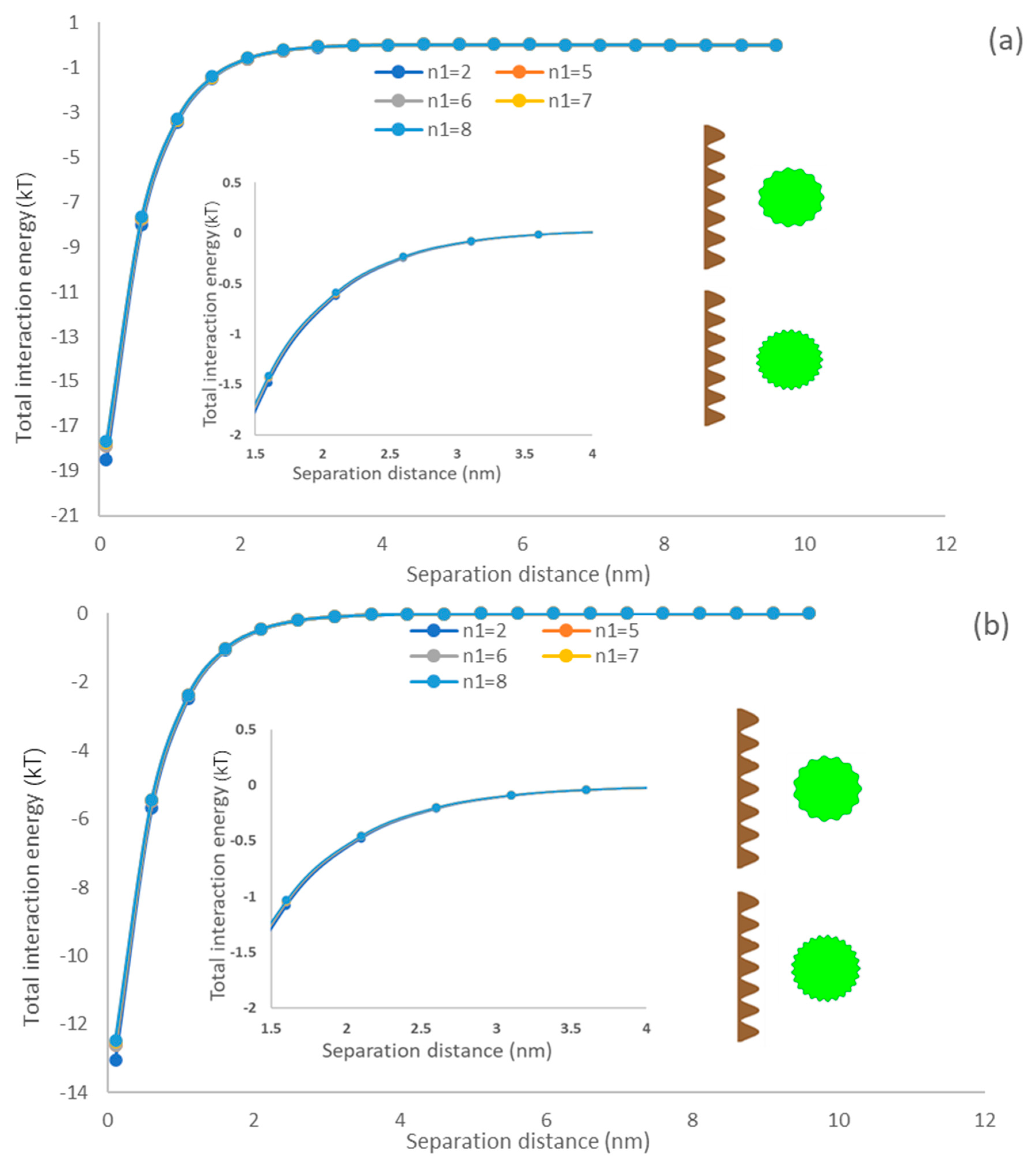
As shown in Equation (2), the asperity frequency, n, controls the density of asperities on the microalgae surface. The present work investigated the effects of asperity frequency on particle interactions, where n changed from 2 to 8 and other parameters were kept constant (r = 1100 nm, p = 50 nm, w = 50 nm, = 0.001).
2.10. Asperity Amplitude
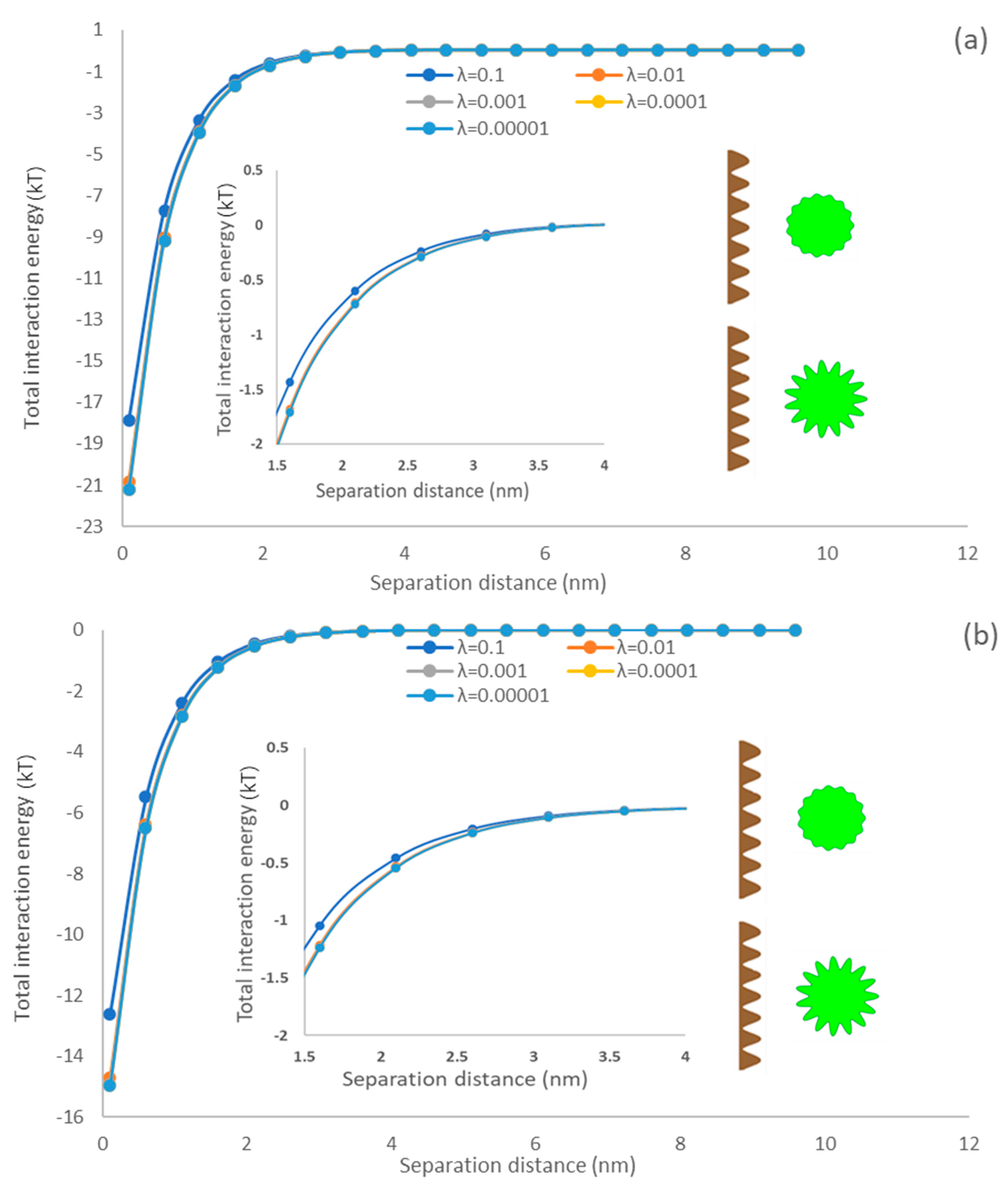
The size of asperities is controlled by the asperity amplitude and thus the surface morphology of microalgae. The present work analyzed the influence of the asperity amplitude on the particle interaction when changed from 0.00001 to 0.1, and other parameters were kept constant (r = 1100 nm, p = 50 nm, w = 50 nm, = 5).
2.11. Particle Radius
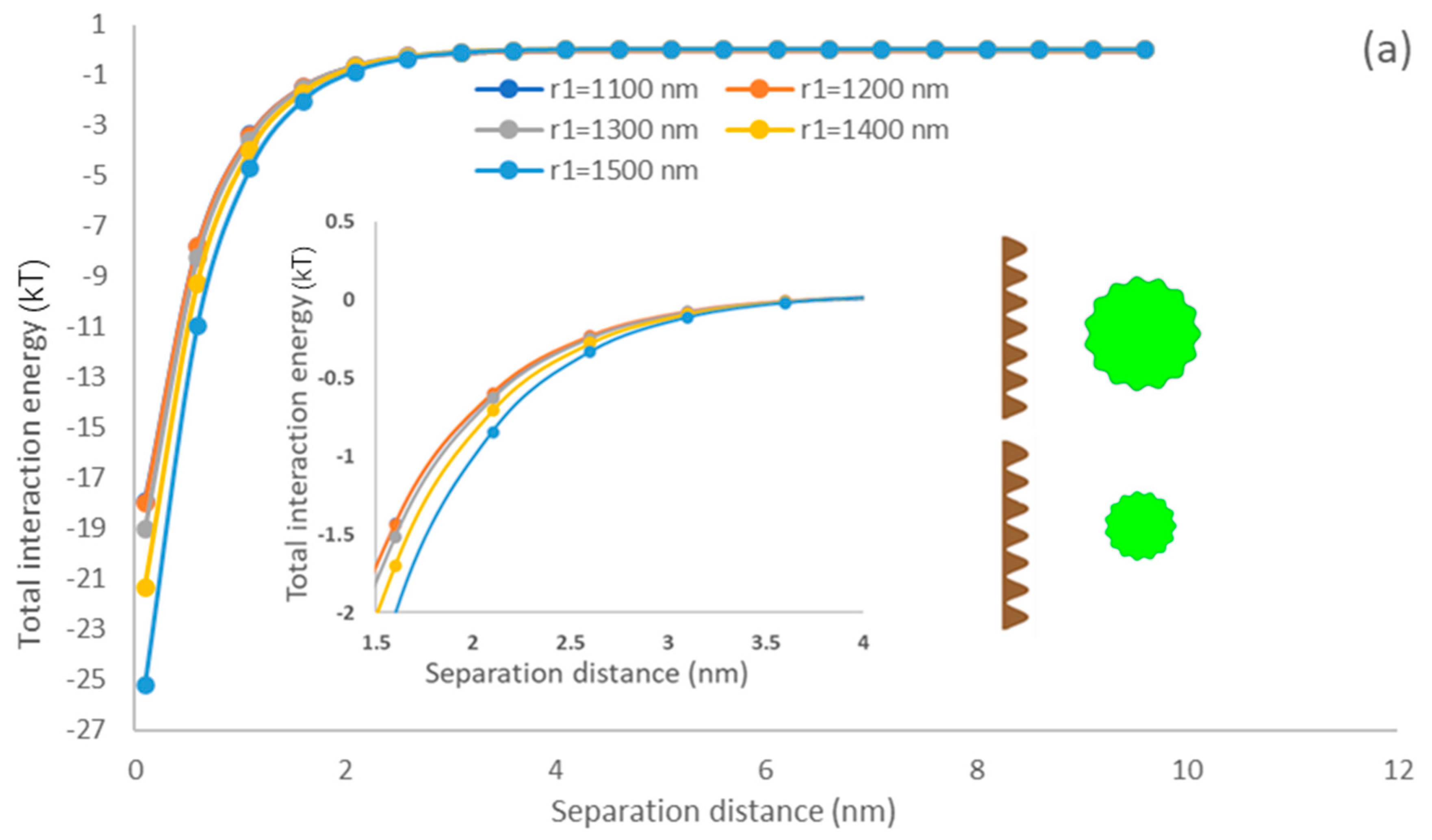
The effect of particle size (radius) on the interaction between microalgae and flat surface was investigated when r increased from 1100 nm to 1500 nm based on experimental results, and other parameters were kept constant (p = 50 nm, w = 50 nm, = 5, = 0.001).
2.12. Asperity Height
The morphology of the membrane surface affects the membrane’s interface behavior and interaction energy [49]. The effect of the asperity size of the membrane surface on the interfacial energy of the membrane and microalgae was investigated when P changed from 500 to 2500 nm and other parameters were kept constant (r = 1100 nm, = 0.001, w = 50 nm, = 5).
2.13. Asperity Width
The asperity width in Equation (5) represents the frequency of asperities and, thus, the number of asperities on the membrane surface [52]. The effect of the asperity width of the membrane surface on interaction energy was investigated when it was changed from 500 to 2500 nm, and other parameters were kept constant (r = 1100 nm, = 0.001, p = 50 nm, = 5).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microalgae Cell Characterization
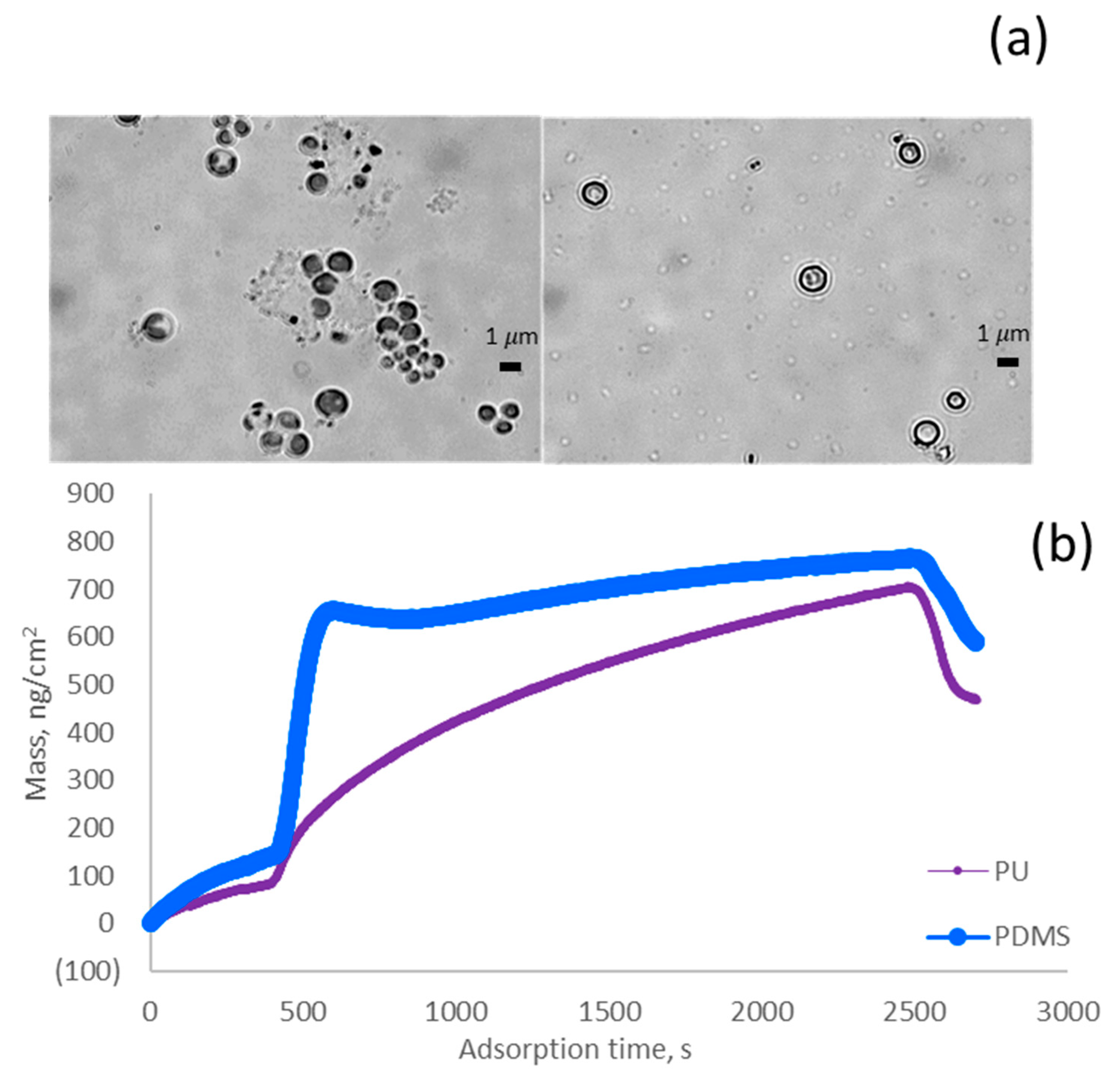
The surface morphologies of algae cells were observed (Figure 2a). It could be found that the cells mainly had spherical shapes with an average perimeter smaller than 1.8 µm. Based on Equation (3), they had a circularity of 0.96–0.99 with an average size of 1.1–1.5 µm. For this reason, the modeling studies considered a spherical shape for microalgae simulation.
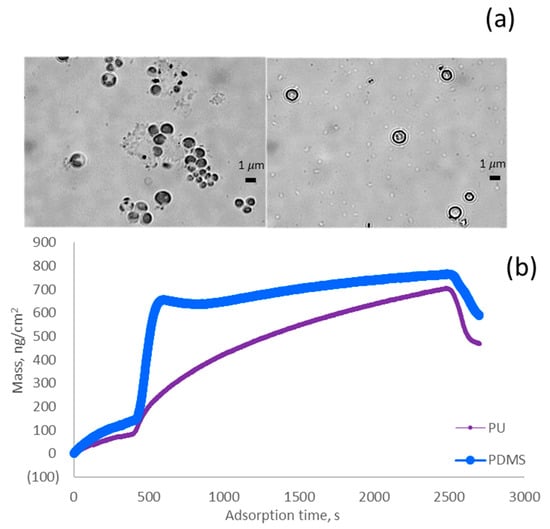
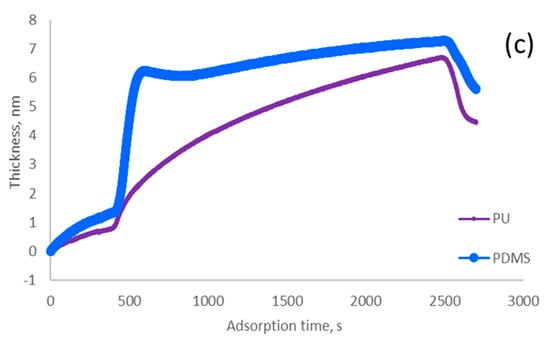
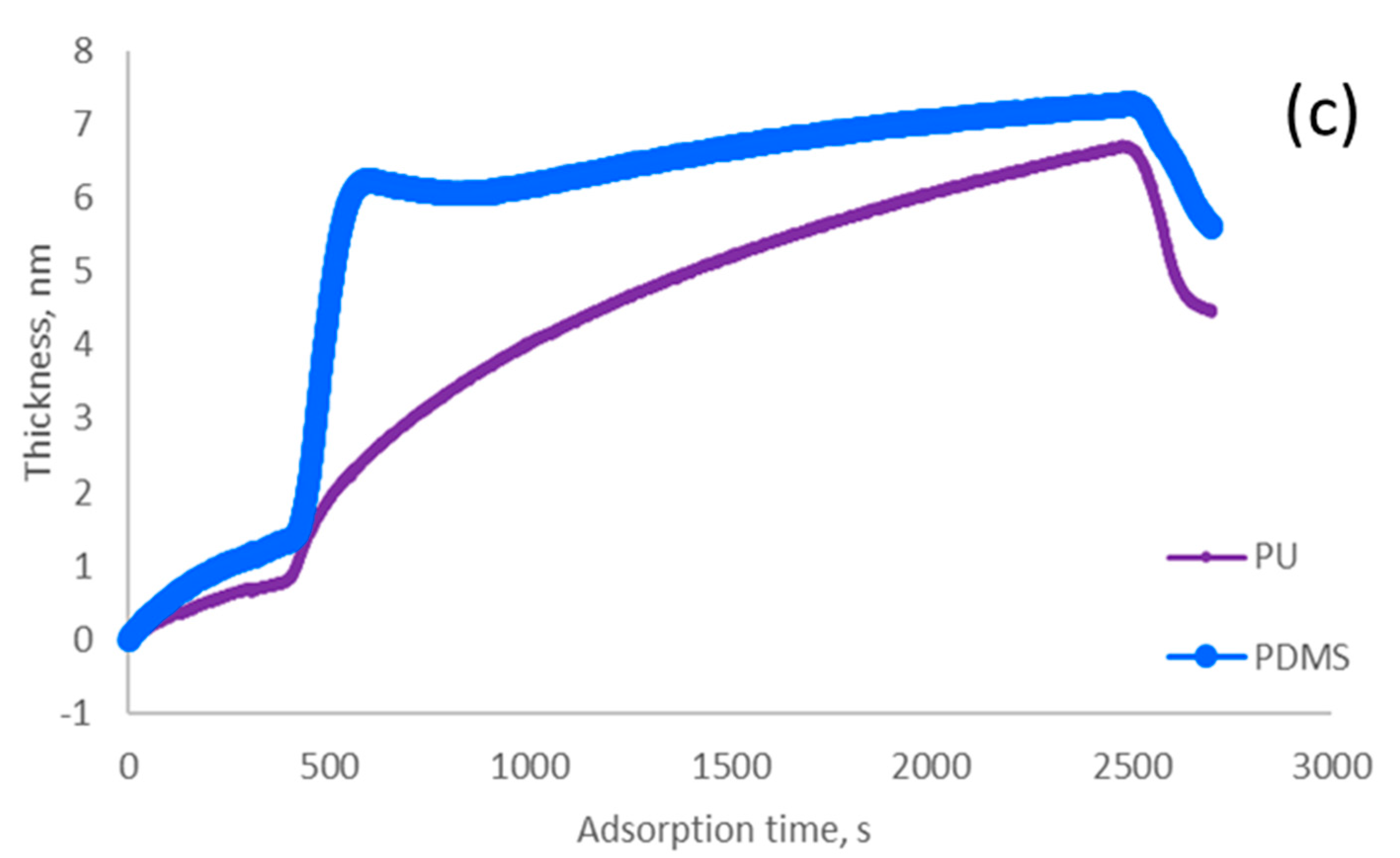
Figure 2.
Experimental results of microalgae (a) algae cells under an inverted microscope; (b) adsorbed mass of microalgae on the PU and PDMS surfaces; (c) adsorbed thickness of microalgae on the PU and PDMS surfaces.
3.2. Contact Angle and Surface Tension of Algae-Coated Surface
It can be seen in Table 1 that water made the largest contact angle on microalgae, PDMS, and PU coated surfaces (81.5, 89.6 and 55.7). The water solution provided the most extensive contact angle on the microalgae surface because the surface tension of water was larger than other solvents. In addition, the contact angle dropped as time elapsed on the microalgae surface, especially for that of water and formamide (Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials). The drop in the contact angle indicates the diffusion of the solvent, e.g., water, on the coated surface, e.g., algae. In this work, the surface tension of the membrane was different, and the surface of PU was more hydrophilic than the PDMS surface.

Table 1.
The input parameters of the Young equation (contact and surface tension).
3.3. Surface Roughness Characterization
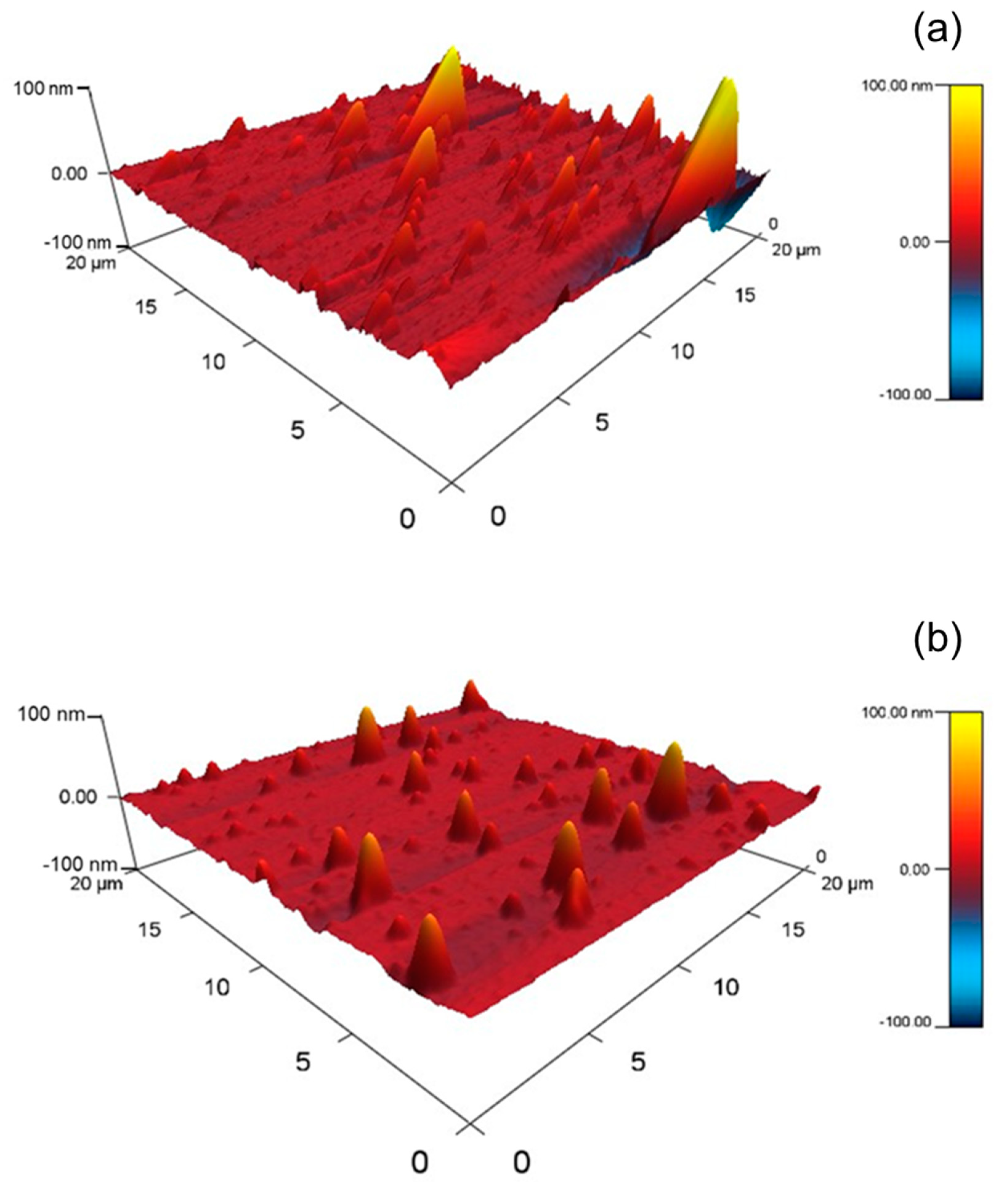
To observe the three-dimensional structure of the QCM sensors more intuitively, the AFM 3D-images of the surfaces of PDMS and PU sensors were analyzed and presented in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 3a, the PDMS membrane exhibits the ridge-and-valley characteristics. Although the PU surface showed ridge-and-valley patterns, its average surface roughness was much smaller than that of PDMS based on the magnitude of asperity height. Therefore, the PDMS sensor surface exhibited rougher surface morphologies (29.3 nm) than the PU sensor surface (2.9 nm). The exhibited images also support the results shown in Table 1, where the rougher surface obtained the larger value of contact angle.
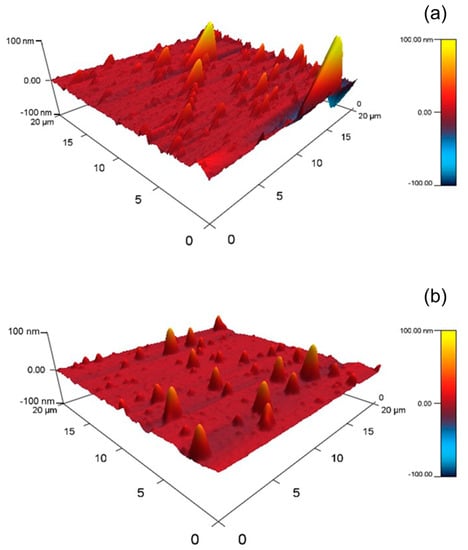
Figure 3.
The three-dimensional AFM images of sensor surface (a) PDMS sensor and (b) PU sensor.
3.4. Adsorption of Algae on Surface
Figure 2b,c show the amounts of adsorbed algae and the thickness of adsorbed microalgae on the surface of PU and PDMS. The analysis confirmed that the PDMS surface had the highest adsorption rate (i.e., mass/time) and thickness deposition rate (i.e., thickness increase/time), which originated from the stronger hydrophobicity of PDMS (Figure 2b,c). As the data in Table 1 reveals, the contact angles of algae and PDMS were close, and thus the hydrophobicity of these two materials is similar, promoting their interaction and higher adsorption of algae on the PDMS surface [55]. Moreover, the lower surface tension exhibited stronger hydrophobicity [56]. Therefore, the PDMS surface should have higher hydrophobicity than the PU surface, which is also associated with larger roughness of PDMS surface (Figure 3). In this case, the larger hydrophobic interaction might induce the larger replacement of algae for water molecules on the PDMS membrane surface [57]. The experiment results suggested that sensor surfaces were more hydrophobic, which might promote a faster and larger density of algae biofilm formation.
3.5. Modeling Analysis
3.5.1. Particle Size Effect
The effect of particle size of algae on the interfacial energy developed between the membrane and algae particles was simulated. As the actual average algae size (1.1–1.5 µm) was assessed, the simulation analysis was conducted in this range. Figure 4 shows that the total interaction energy increases with elevating the particle size as the interaction area increases between the microalgae and membrane where the green rough sphere represents the microalgae and brown flat surface represents the constructed membrane surface. In addition, it can be found that the interactions of the PDMS membrane surface are stronger than that of the PU surface, which would suggest that the PDMS membrane would provide more adsorption affinity to microalgae than the PU membrane. These results are supported by the higher adsorption rate shown in Figure 2b,c. They are attributed to the higher affinity of microalgae and PDMS surface to interact as they had similar hydrophobicity (Table 1) [58].
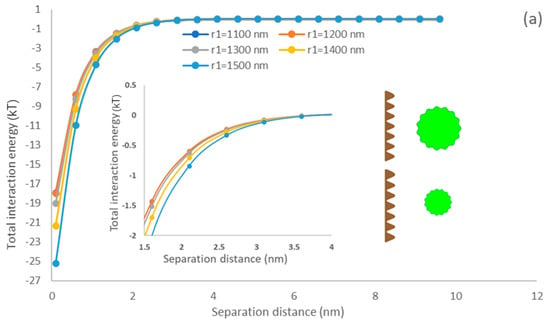
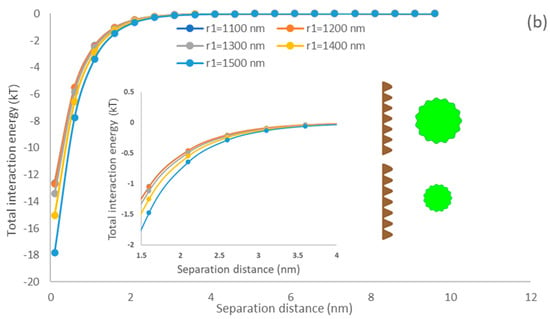
Figure 4.
The impacts of particle size on the interfacial interaction of membrane surface and spherical microalgae (a) PDMS (b) PU.
Yin and Wang investigated the impacts of scheelite particle size on particle interaction and reported that the interaction energy of particles elevated with enlarging the particles [59]. Mikelonis and coworkers investigated the attachment behavior of silver nanoparticles and concluded that the electric double layer repulsion energy and van der Waals attractive energy increased with enlarged particles [60]. The interaction of the surface and particle becomes more dominant as the size of the particle increases, which promotes the initial attachment affinity of particles on the surface. Interestingly, by considering surface roughness in our current modeling analysis, the predicted results showed a similar tendency to the previous study [59]. As our modeling results consider the AB polar interaction (Equation (13)) following the XDLVO theory, our results confirm the previously reported results and stress that AB polar interaction significantly promotes microalgae attachment affinity to the membrane surface.
3.5.2. Asperity Frequency Effects
The density of asperities on a spherical surface could be represented by the asperity frequency, which is a key parameter for characterizing the surface morphology of microalgae [61]. The impact of the asperity frequency representing the texture density of microalgae [62] on the interaction of the membrane and particle is shown in Figure 5. Regardless of the membrane type, it could be observed that particle asperity has a marginal impact on the interaction energy of the membrane surface and algae particle. As asperities are generated on the particle surface, the separation distance of the flat surface and particle would enlarge compared to a smooth particle, which would decrease interaction energy. The primary minimum decreases by increasing the asperity frequency suggesting a drop in the energy of attraction between membrane and algae (Figure 5). This phenomenon can be explained by the number of asperities as it did not enlarge the separation distance between microalgae and flat surfaces. Therefore, the asperity frequency had a limited effect on the interaction energy profile [63]. In other words, the microalgae have less attachment ability to the membrane if their asperity frequency increases at the short separation distance (0.158–2 nm). This behavior is attributed to the reduction in the surface roughness and thus adhesion of particles when the asperity frequency is increased [64,65,66]. This behavior was also reported by Drelich and Bowen, who generated a rough particle by covering hemispherical asperities on a smooth particle [67,68]. Our model simulated the rough surface by periodic sinusoidal shapes, i.e., a different approach from that taken by Drelich and Bower, but it predicted similar results (Figure 5). In addition, comparing Figure 4a,b), it can be observed that the depth of primary minimum generated on the PDMS surface is greater than that of the PU surface, which indicates that the PDMS surface had a higher adsorption affinity for microalgae.
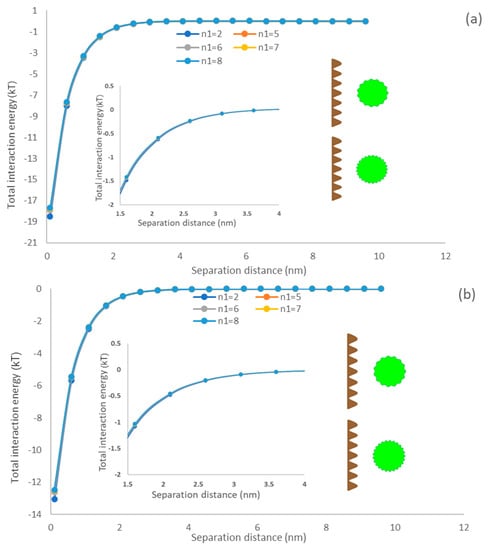
Figure 5.
The impacts of asperity frequency on the interfacial interaction of membrane surface and spherical microalgae (a) PDMS (b) PU.
3.5.3. Asperity Amplitude Effects
The ratio of asperities represents the shape and size of asperities on a spherical surface, which is another key factor in characterizing the surface morphology of microalgae [69]. Figure 6 exhibited the influences of the amplitude of asperities from rough surfaces on interaction energy between microalgae and membrane surfaces. It is observable that the total interaction energy dropped with diminishing the asperity ratio. These predictions follow expectations because the asperity ratio (λ) is elevated in Equation (4); the separation distance (h) would significantly extend, and thus the total interaction energy became weak. Raising the asperity ratio increased the asperity height, and the interaction area diminished with the shape size of asperities. Suresh and Walz simulated the interaction of a smooth flat surface and a rough sphere covered with hemispherical asperity and articulated that the interfacial interaction would be diminished by an enlarged radius of hemispherical asperity on the particle surface [70]. In this study, the rough surface morphology considers not only the protruding parts of the rough surface (hemispherical asperities [70]) but also the depression parts of asperities, which are closer to the naturally rough surface [68].
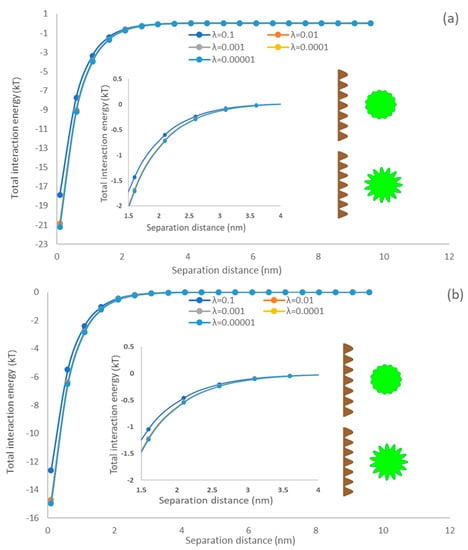
Figure 6.
The impacts of asperity amplitude on the interfacial interaction of membrane surface and spherical microalgae (a) PDMS (b) PU.
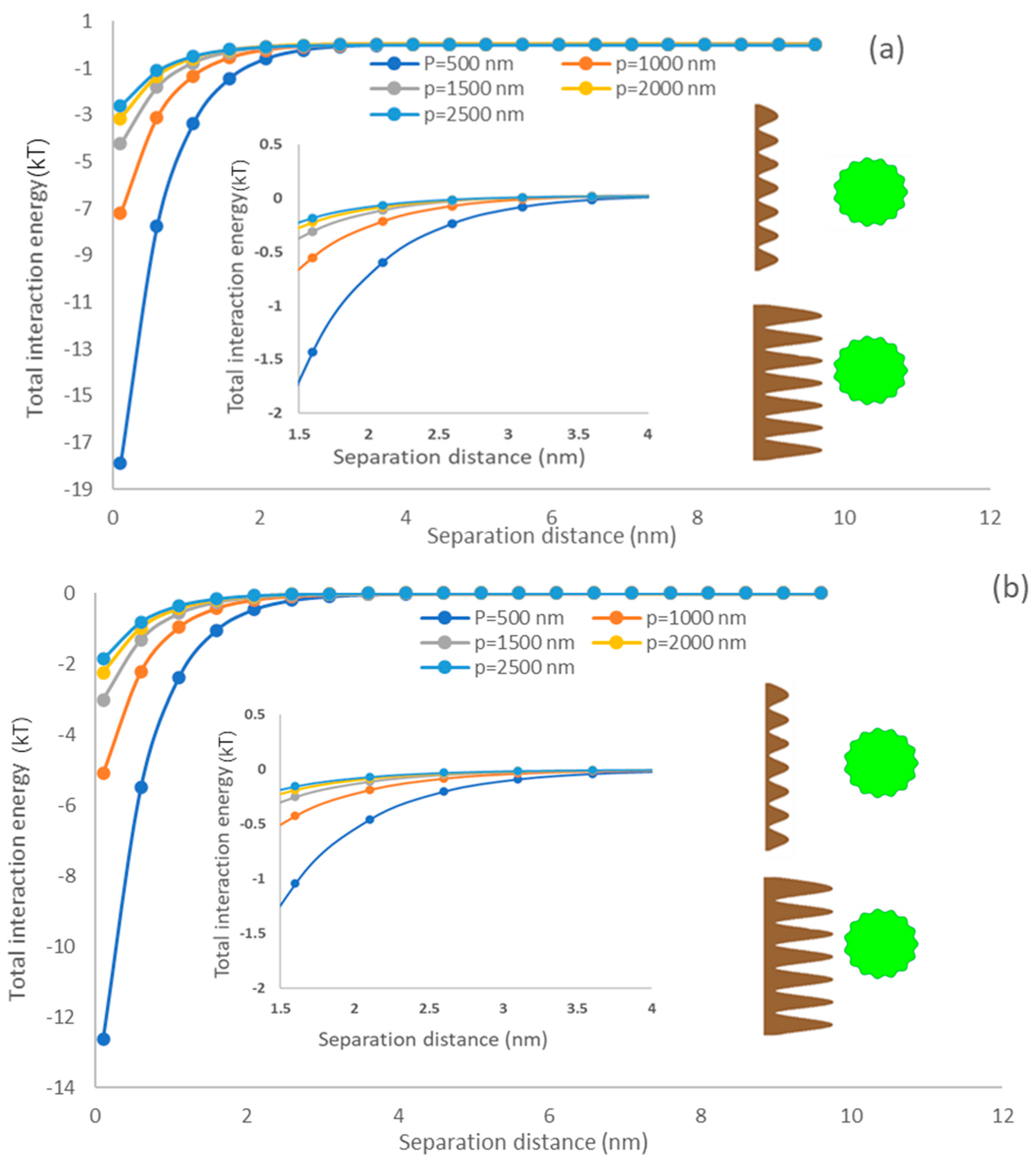
3.5.4. Asperity Height of the Membrane
Figure 7 exhibited the interfacial energy of the simulated membrane surface and algae particle as a function of the asperity height of the membrane. It could be observed that the total interaction energy decreased with an increase in the membrane asperity height. In this case, with enlarging the height of membrane asperity (p), the separation distance (h) between rough surfaces would increase, reducing the total interaction energy [71,72,73]. Compared with PU surfaces, PDMS displayed a stronger interfacial interaction under various asperity heights. Bendersky and coworkers applied an array of cylindrical pillars with varying diameters and heights and investigated the impacts of rough surfaces on the colloid–membrane interaction [67]. They articulated that raising surface roughness height would drop the energy barrier developed between smooth colloids and membrane surfaces [26]. Different from the previous study [26], the present model considered two rough surfaces with the consideration of depression parts of asperities of a spherical particle and flat membrane rather than a rough flat surface with asperities shaped as cylindrical pillars and a smooth particle. Our results also indicated that the surface roughness of the flat surface promotes the adhesion of microalgae to the membrane surface. Chen and coworkers also demonstrated that the rough surface promotes sludge foulant deposition [61]. In addition, the weakened attraction interaction energy (i.e., primary minimum) (Figure 7) indicates that the rough spherical microalgae promotes adhesion [74,75].
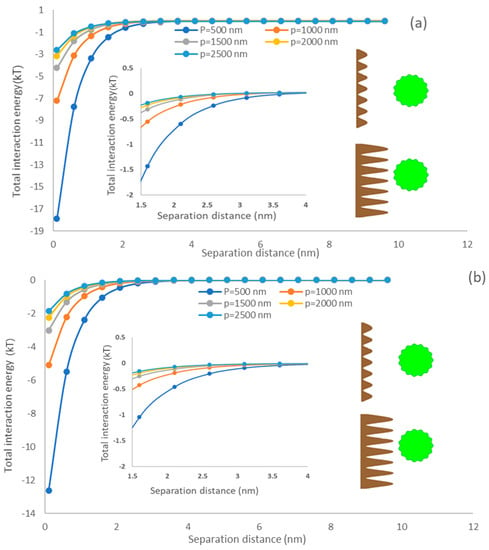
Figure 7.
The impacts of membrane asperity height on the interfacial interaction of membrane surface and spherical microalgae (a) PDMS (b) PU.
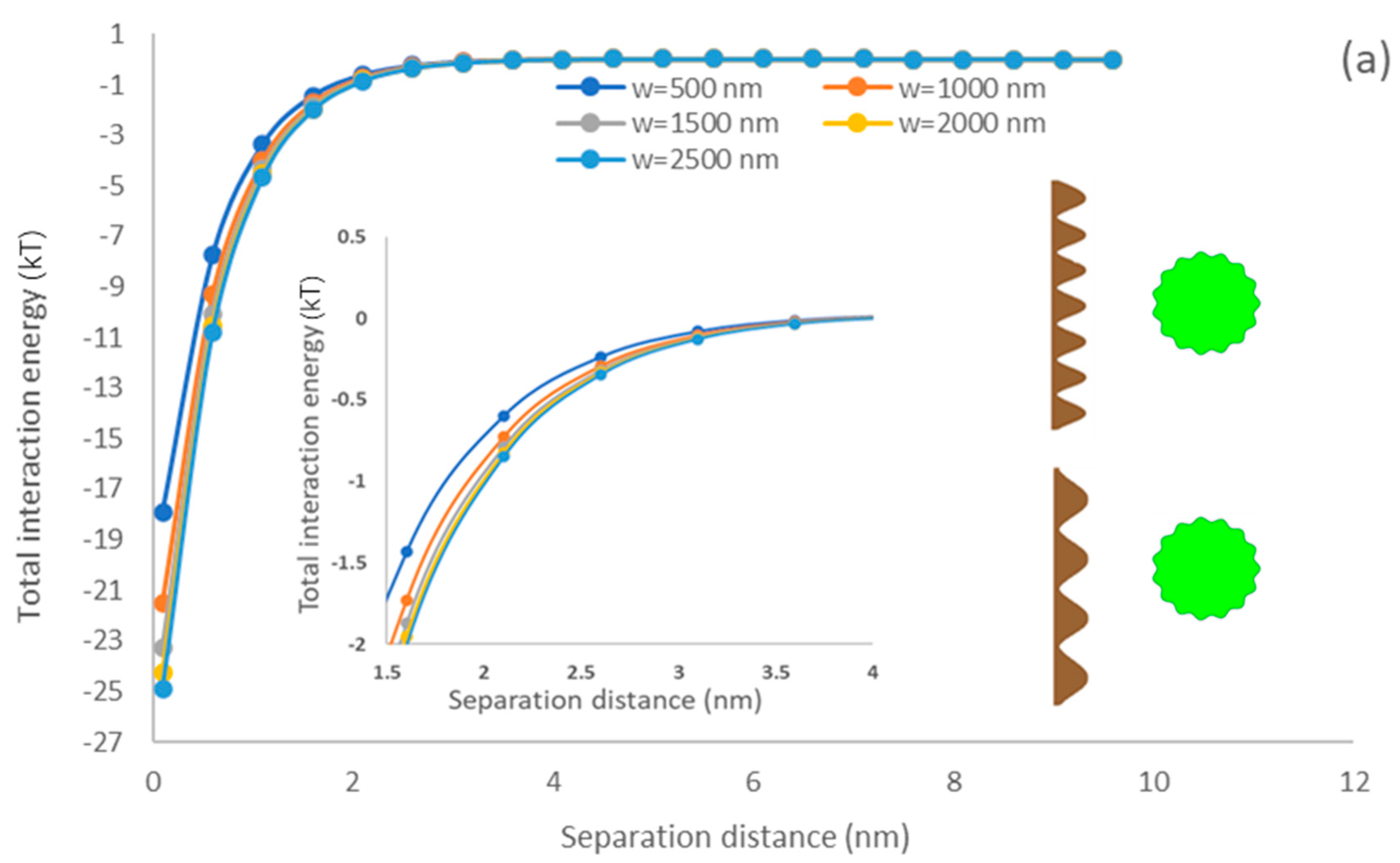
3.5.5. Membrane Asperity Width
Figure 8 demonstrates the impacts of the width of membrane asperity on the interfacial interaction of simulated membrane surface and microalgae. The primary minimum increased with elevating the membrane asperity width [76]. It also shows that the PDMS surface exhibited a better adhesion affinity than the PU surface for microalgae. When the width of membrane asperity width (w) was raised following Equation (4), the membrane roughness () reduced, and a smoother surface was generated. Lin and coworkers reported that the interfacial interaction strength between rough membranes and circular flocs would be weaker than smooth membrane surfaces and flocs [36]. The predicted results in our study also indicated that the rough surface morphology of the membrane surface could significantly reduce the interaction energy. Won and coworkers demonstrated that the formation of sludge cake was lower on the membrane surface with a rough surface morphology than that on the membrane surface with a smooth surface morphology [77]. Generally, the surface roughness would decrease the depth of the primary minimum, which would enhance the detachment ability of microalgae from the membrane surface.
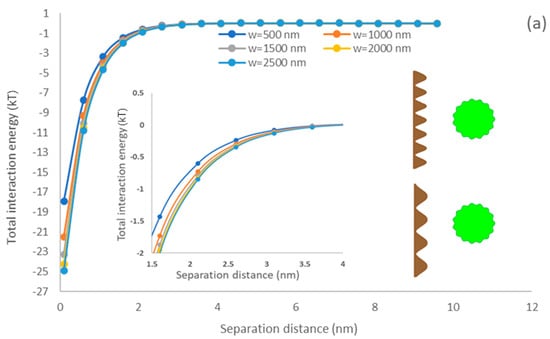
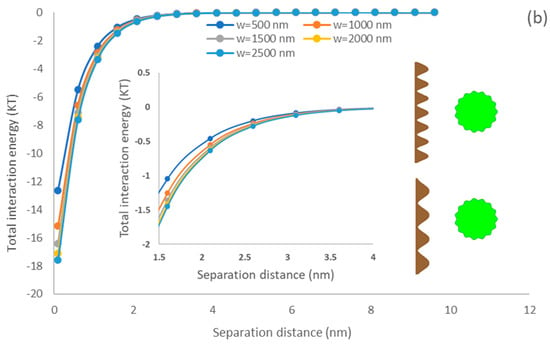
Figure 8.
The impacts of membrane asperity width on the interfacial interaction of membrane surface and spherical microalgae (a) PDMS (b) PU.
3.5.6. Identifying the Most Influential Parameter in Interfacial Interactions
This study applied a QCM experiment to analyze the adsorption rate of microalgae on the membrane surface and compared PDMS and PU membranes. As shown in Figure 2b,c, the PDMS surface obtained a better adsorption rate than the PU surface. The modeling results also supported the experiment because the interaction energy generated between PDMS surface and microalgae was more vital than that between the PU membrane and microalgae (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). Therefore, the results from the present work indicated that the membrane material had an obvious influence on the microalgae adsorption, and the PDMS surface facilitated the microalgae attachment more than the PU surface did. The main reason could be explained by the higher hydrophobicity of the PDMS membrane.
Moreover, it could be observed that the asperity height on the membrane was the most compelling characteristic of the total interaction energy generated by the simulated membrane surface and rough microalgae, regardless of the surface morphology of the microalgae. The predictions confirmed that raising the membrane asperity height from 500 to 2500 nm changed the primary minimum from −18 kT to −3 kT. However, the asperity frequency of microalgae had a minor effect on interfacial interaction. Therefore, our model may provide a new direction to control the microalgae adhesion or membrane fouling by modification methods, such as coating and poly grafting [78].
3.5.7. Modeling Validation
The modeling results predicted that the PDMS membrane obtained a better adhesion ability for microalgae than the PU membrane because the PDMS membrane exhibited a greater primary minimum in the above investigations (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). The predicted results indicated that the membrane material played an essential role in controlling particle interactions even though the surface morphology was under the same conditions. The adsorption analysis by QCM-D shown in Figure 2b,c also suggested that the PDMS surface provided a more significant adsorption rate than the PU surface. Therefore, the proposed model and simulated results could be supported and verified by the experimental results in Section 3.4.
4. Conclusions
This study presented experimental and simulation analyses of microalgae attached to a membrane surface. The AFM and contact angle analyses showed that the PDMS surface provided a rougher surface and higher hydrophobicity than the PU surface did, which can explain the reason for the larger value of contact angle of the PDMS surface than the PU surface. The QCM experimental results suggested the PDMS membrane exhibited better attachment affinity than the PU membrane for microalgae. The numerical predictions from the model in this study also indicated that the total interaction energy of the microalgae–PDMS surface was more potent than that of the microalgae–PU surface. Combined modeling and experimental results demonstrated that, compared to a hydrophilic membrane surface (i.e., PU), more hydrophobic membrane (i.e., PDMS) surfaces favored a faster biofilm formation. The modeling results also explored the effects of constructing parameters of microalgae and membranes on the interfacial interaction of the membrane surface and microalgae. The total interaction energy would increase with the enlarged particle and asperity width of the membrane surface. Conversely, the interfacial interaction would decrease with the increase in the asperity ratio, asperity number, and height of microalgae and membrane surface. In addition, the asperity height of the membrane provides the most effective factor in controlling the range of interfacial interaction and adhesion of algae on the surface. Therefore, the mathematical model in the present work could provide guidelines for membrane surface modification (coating or polygrafting) to improve the microalgae attachment or fouling control efficiency.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/colloids7010024/s1. Figure S1: Surface of filter paper covered with algae; Figure S2: Contact angle of diiodomethane, formamide and water on the surface of microalgae, PDMS, and PU sensor; Table S1: Surface tensions of three probe liquids. Reference [51] is cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
N.K.: microalgae cultivation, experiments, and data collection; D.L.: methodology, modeling, and original draft; Y.L.: experiments; B.L.: co-supervision, review, and editing; P.F.: supervision, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, NSERC, (Grant number #461256).
Data Availability Statement
Data can be available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Abbreviations
| AH | |
| D | the closest distance between the two-particle surface (nm) |
| the separation distance between two planar surfaces (nm) | |
| interaction energy per unit area (mJ/m2) | |
| the radius of element (smooth) ellipsoidal particle (nm) | |
| asperity ratio | |
| asperity number | |
| asperity height | |
| asperity width | |
| the radius of rough ellipsoidal particle (nm) | |
| the interaction energy between the membrane surface and particle (kT) | |
| surface tension parameter (mJ/m2) | |
| the permittivity of the suspending liquid (C/Vm) | |
| ζ | zeta potential (mV) |
| reciprocal Debye screening length (1/nm) | |
| angle coordinate in the spherical coordinate system | |
| decay length of AB interactions in water (0.6 nm) | |
| minimum equilibrium cut-off distance (0.158 nm) | |
| Superscripts | |
| AB | Lewis acid–base |
| EL | electrostatic double layer |
| LW | Lifshitz-van der Waals |
| Total | total |
| + | electron acceptor |
| − | electron donor |
| Subscripts | |
| liquid | |
| water | |
| microalgae surface | |
| membrane surface | |
| describing particle one and two (i = 1, 2) | |
References
- Wollmann, F.; Dietze, S.; Ackermann, J.U.; Bley, T.; Walther, T.; Steingroewer, J.; Krujatz, F. Microalgae wastewater treatment: Biological and technological approaches. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Gómez-Ramos, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Chemical evaluation of contaminants in wastewater effluents and the environmental risk of reusing effluents in agriculture. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M. A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinandan, S.; Perera, I.A.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Cole, N.; Megharaj, M. Acid-adapted microalgae exhibit phenotypic changes for their survival in acid mine drainage samples. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E.; Isambert, A. Commercial applications of microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, B.; Gao, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Su, G. Impacts of surface wettability and roughness of styrene-acrylic resin films on adhesion behavior of microalgae Chlorella sp. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Nagarajan, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Heterotrophic cultivation of microalgae for pigment production: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R. Mixotrophic cyanobacteria and microalgae as distinctive biological agents for organic pollutant degradation. Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, S.D.; Salvadó, J.; Farriol, X.; Torras, C. Antifouling microfiltration strategies to harvest microalgae for biofuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Yin, J.; Deng, B.; Hu, Z. Application of nano TiO2 modified hollow fiber membranes in algal membrane bioreactors for high-density algae cultivation and wastewater polishing. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, I.L.; Yeh, D.H. Membrane applications for microalgae cultivation and harvesting: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2014, 13, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.; Arafat, H.A.; Vankelecom, I.F. Membrane technology in microalgae cultivation and harvesting: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1283–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, H.; Haifeng, L.; Shanshan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhidan, L.; Na, D. Progress in microalgae cultivation photobioreactors and applications in wastewater treatment: A review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, D.A.; Gargano, I.; Pinto, G.; De Natale, A.; Pollio, A. Evaluating microalgae attachment to surfaces: A first approach towards a laboratory integrated assessment. Chem. Eng. Trans 2017, 57, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Yang, Z.-H.; Li, C.; Zeng, G.-M.; Ma, D.-H.; Zhou, L. A novel algal biofilm membrane photobioreactor for attached microalgae growth and nutrients removal from secondary effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Muylaert, K.; Vankelecom, I.F. Synergy between membrane filtration and flocculation for harvesting microalgae. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Peng, Y.-Y.; Li, C.; Cui, W.; Yang, Z.-H.; Zeng, G.-M. Coupled nutrient removal from secondary effluent and algal biomass production in membrane photobioreactor (MPBR): Effect of HRT and long-term operation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Bokhary, A.; Maleki, E.; Liao, B. A review of membrane fouling and its control in algal-related membrane processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, A.; Tavassoli, S.; Sepehrnoori, K. Investigation of modified Water chemistry for improved oil recovery: Application of DLVO theory and surface complexation model. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 574, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffadar, R.; Kalasin, S.; Davis, J.M.; Santore, M.M. The impact of nanoscale chemical features on micron-scale adhesion: Crossover from heterogeneity-dominated to mean-field behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffadar, R.D.; Davis, J.M. Interaction of micrometer-scale particles with nanotextured surfaces in shear flow. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffadar, R.D.; Davis, J.M. Dynamic adhesion behavior of micrometer-scale particles flowing over patchy surfaces with nanoscale electrostatic heterogeneity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 326, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Ko, C.-H.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Elimelech, M. Role of spatial distribution of porous medium surface charge heterogeneity in colloid transport. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 191, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassas, B.V.; Caliskan, H.; Guven, O.; Karakas, F.; Cinar, M.; Celik, M.S. Effect of roughness and shape factor on flotation characteristics of glass beads. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 492, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendersky, M.; Davis, J. DLVO interaction of colloidal particles with topographically and chemically heterogeneous surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 353, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, A.; Berberoglu, H. Physico-chemical surface properties of microalgae. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Ko, C.-H.; Elimelech, M. DLVO interaction between rough surfaces. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3365–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Cao, H.; Ma, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Microalgae filtration using an electrochemically reactive ceramic membrane: Filtration performances, fouling kinetics, and foulant layer characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseus, A.; Putra, Z.; Bilad, M.; Nordin, N.; Wirzal, M.; Jaafar, J.; Khan, A.L. Energy minimization of a tilted panel filtration system for microalgae filtration: Performance modeling and optimization. Algal Res. 2018, 34, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salou, M.; Siffert, B.; Jada, A. Study of the stability of bitumen emulsions by application of DLVO theory. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 142, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Gutiérrez, R.; Ferrer, I.; García, J.; Bayona, J.M. Capability of microalgae-based wastewater treatment systems to remove emerging organic contaminants: A pilot-scale study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 288, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.; Discart, V.; Vandamme, D.; Foubert, I.; Muylaert, K.; Vankelecom, I.F. Coupled cultivation and pre-harvesting of microalgae in a membrane photobioreactor (MPBR). Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melin, T.; Jefferson, B.; Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Wilde, W.; De Koning, J.; van der Graaf, J.; Wintgens, T. Membrane bioreactor technology for wastewater treatment and reuse. Desalination 2006, 187, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbelia, L.; Bilad, M.R.; Passaris, I.; Discart, V.; Vandamme, D.; Beuckels, A.; Muylaert, K.; Vankelecom, I.F. Membrane photobioreactors for integrated microalgae cultivation and nutrient remediation of membrane bioreactors effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Mei, R.; Chen, J.; Hong, H. A novel approach for quantitative evaluation of the physicochemical interactions between rough membrane surface and sludge foulants in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Arroyo, T.; Wei, W.; Ruan, R.; Hu, B. Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris and its potential application for the oil accumulation from non-sugar materials. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Leung, K.-T.; Lin, H.; Liao, B. The biological performance of a novel microalgal-bacterial membrane photobioreactor: Effects of HRT and N/P ratio. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xiao, S.; Chu, H.; Zhao, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Intelligent mitigation of fouling by means of membrane vibration for algae separation: Dynamics model, comprehensive evaluation, and critical vibration frequency. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, A.; Berberoglu, H. Adhesion of algal cells to surfaces. Biofouling 2013, 29, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, H.J.; Weerkamp, A.H.; van der Mei, H.C.; Van Pelt, A.; de Jong, H.P.; Arends, J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.A.Q.; Ali, S.; Fei, H.; Roshan, H. Current understanding of shale wettability: A review on contact angle measurements. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 181, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, A.; Berberoglu, H. Cell to substratum and cell to cell interactions of microalgae. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Huang, R. Effect of surface roughness on adhesion of graphene membranes. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 452001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Shen, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Li, R.; Wu, X.; Liao, B.-Q. Quantitative evaluation of the interfacial interactions between a randomly rough sludge floc and membrane surface in a membrane bioreactor based on fractal geometry. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X. Analyzing the effect of pH on microalgae adhesion by identifying the dominant interaction between cell and surface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Chen, J.Y.; Elimelech, M. DLVO interaction energy between spheroidal particles and a flat surface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 165, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, R.; Kuritz, T.; Powell, L.; Adcock, D. Membrane-based energy efficient dewatering of microalgae in biofuels production and recovery of value added co-products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5599–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Lin, H. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor: An unified approach to construct topography and to evaluate interaction energy between two randomly rough surfaces. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shen, L.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Yu, G. Influences of fractal dimension of membrane surface on interfacial interactions related to membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 500, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Cai, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Li, R. A novel integrated method for quantification of interfacial interactions between two rough bioparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 516, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, M.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Liao, B.-Q.; Lin, H. A new method for modeling rough membrane surface and calculation of interfacial interactions. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, L.; Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Yu, H.; Liao, B.-Q.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, R. Modeling three-dimensional surface morphology of biocake layer in a membrane bioreactor based on fractal geometry. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Fatehi, P. Interfacial interactions of rough spherical surfaces with random topographies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, H.; Song, S. Cell surface characterization of some oleaginous green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Huang, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhong, H. A novel surfactant styryl phosphonate mono-iso-octyl ester with improved adsorption capacity and hydrophobicity for cassiterite flotation. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.-H.; Xu, H.-L.; Teo, K.-C. Molecular mechanism of granulation. I: H+ translocation-dehydration theory. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, Y.; Ikada, Y. Effect of preadsorbed proteins on cell adhesion to polymer surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 155, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.-z.; Wang, J.-z. Effects of particle size and particle interactions on scheelite flotation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 3682–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelonis, A.M.; Youn, S.; Lawler, D.F. DLVO approximation methods for predicting the attachment of silver nanoparticles to ceramic membranes. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Cao, C.-q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.-n. Interaction energy evaluation of soluble microbial products (SMP) on different membrane surfaces: Role of the reconstructed membrane topology. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjari, S.; Sarhadi, H.; Shahdadi, F. Investigating the effect of Spirulina platensis microalgae on textural and sensory properties of baguette bread. J. Nutr. Food Secur. 2018, 3, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, J.Y. The effect of surface heterogeneities on colloidal forces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 74, 119–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Li, B.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Y. Surface roughness effect on deposition of nano-and micro-sized colloids in saturated columns at different solution ionic strengths. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Yu, G.; Cai, X.; Eulade, M.; Lin, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Liao, B.-Q. Effects of fractal roughness of membrane surfaces on interfacial interactions associated with membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Cai, X.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Lin, H.J.B.t. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor: New method and its applications in interfacial interaction quantification. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W.; Bowen, P.K. Hydrophobic nano-asperities in control of energy barrier during particle–surface interactions. Surf. Innov. 2015, 3, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W. A simplified analysis of the effect of nano-asperities on particle-bubble interactions. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Promdaen, S.; Wattuya, P.; Sanevas, N. Automated microalgae image classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 29, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, L.; Walz, J.Y. Effect of surface roughness on the interaction energy between a colloidal sphere and a flat plate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 183, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erramilli, S.; Genzer, J. Influence of surface topography attributes on settlement and adhesion of natural and synthetic species. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 4045–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.; Agarwal, G.K. Extended DLVO interactions between spherical particles and rough surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, N.; Parsons, D.F.; Craig, V.S. Roughness in surface force measurements: Extension of DLVO theory to describe the forces between hafnia surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6442–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Zhang, M.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Fouling mechanisms of gel layer in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oss, C.J. Hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of biosurfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 2, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, L.-P.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Y. Role of surface roughness in chemical detachment of colloids deposited at primary energy minima. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11, vzj2011.0057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.-J.; Lee, J.; Choi, D.-C.; Chae, H.R.; Kim, I.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, I.-C. Preparation and application of patterned membranes for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11021–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Meng, J.; Ye, J.; Yang, B.; Tian, Q.; Deng, C. Surface modification of PES ultrafiltration membrane by polydopamine coating and poly (ethylene glycol) grafting: Morphology, stability, and anti-fouling. Desalination 2014, 344, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).