Influence of Casein and Milk Phospholipid Emulsifiers on the Digestion and Self-Assembled Structures of Milk Lipids
Abstract
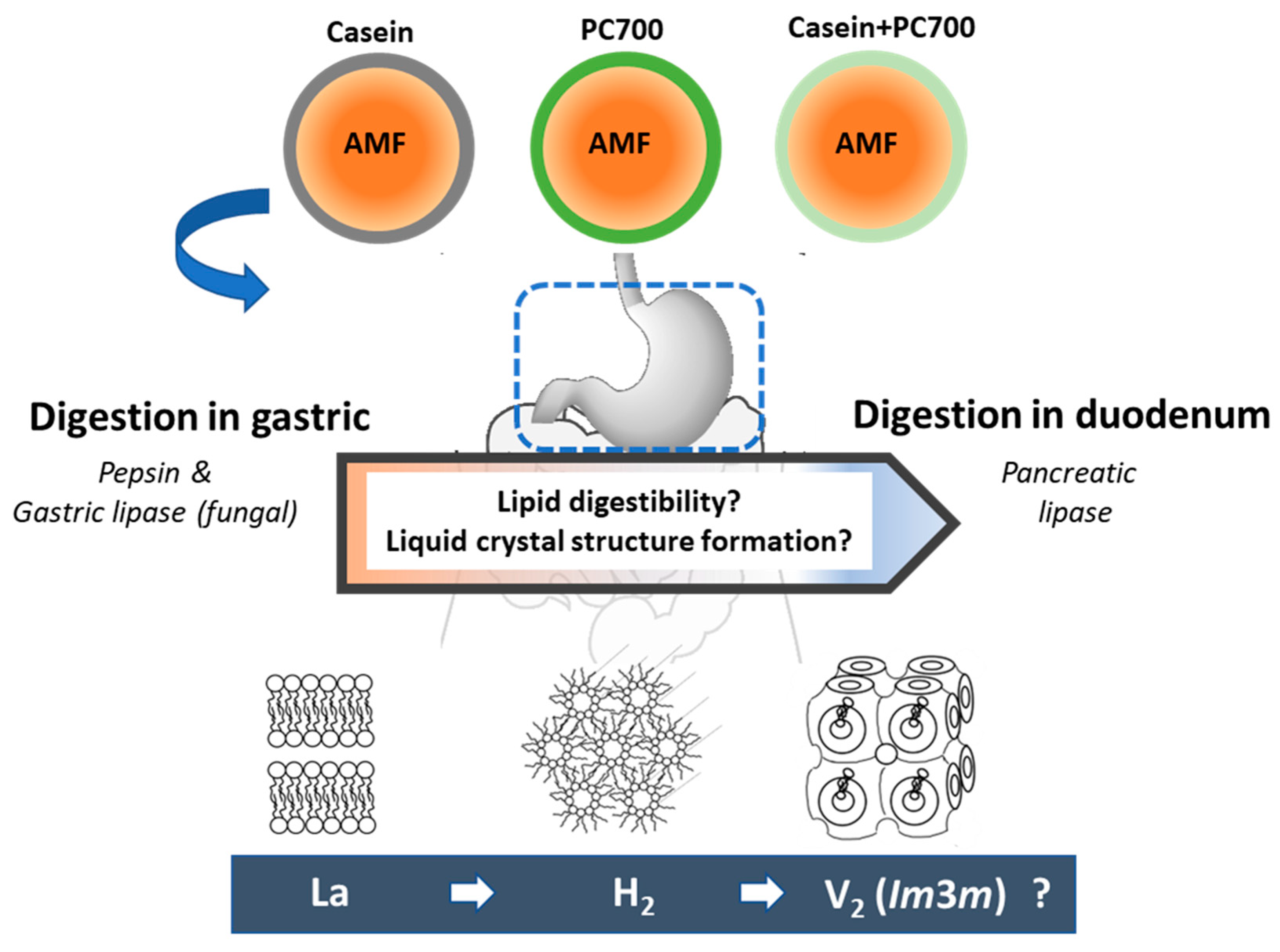
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
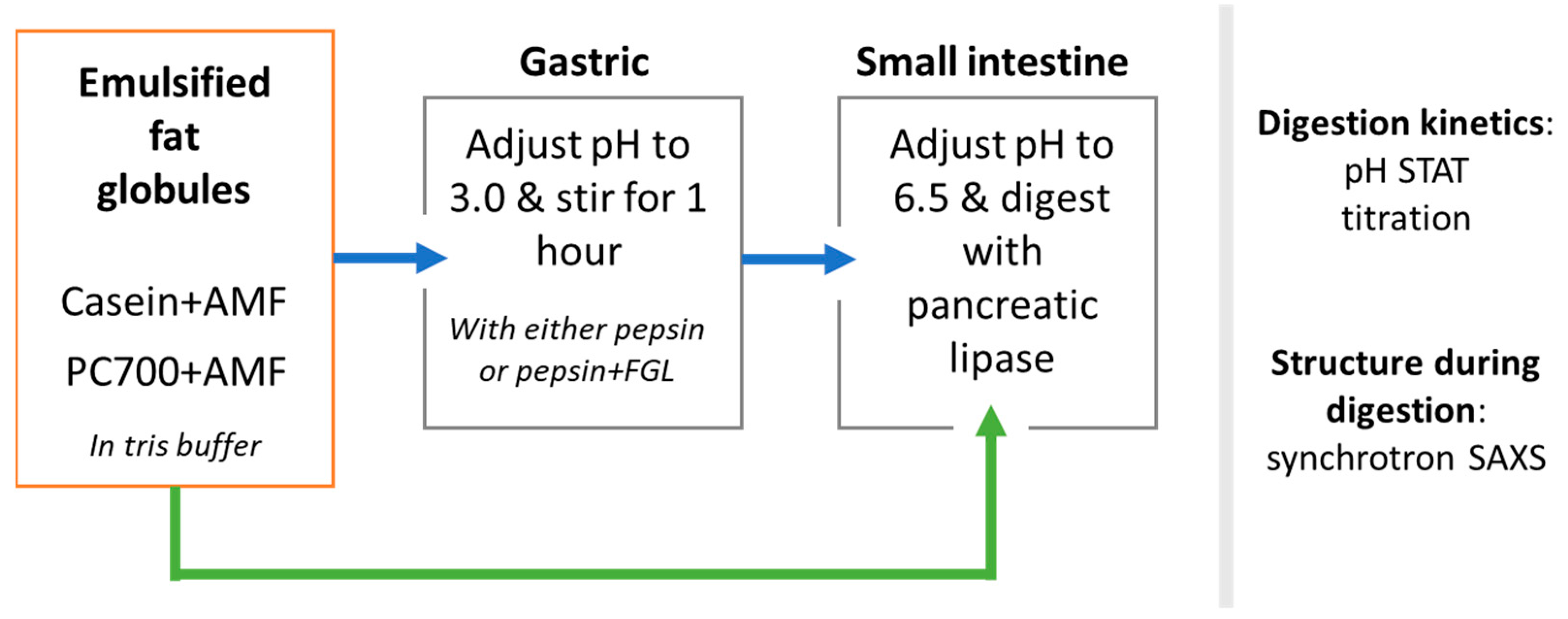
2.2.1. Preparation of Milk Fat Emulsions
2.2.2. In Vitro Digestion of Milk Fat Emulsions
2.2.3. Self-Assembled Structures Formed during Digestion of Fat Globules: Synchrotron SAXS Measurements
2.2.4. Particle Size Distributions of Fat Globules: Laser Light Scattering
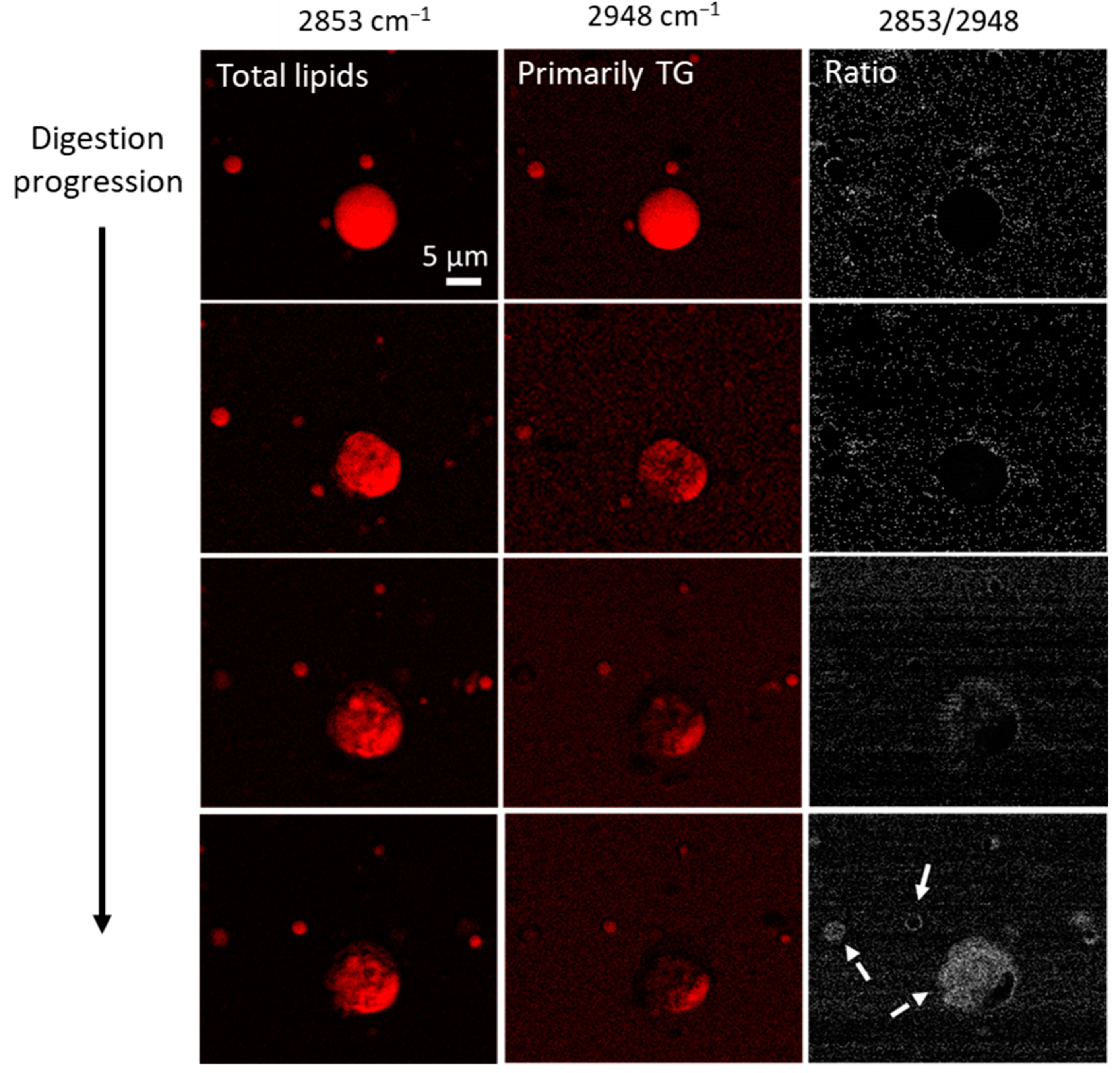
2.2.5. Imaging of Fat Globules: CARS Microscopy
3. Results
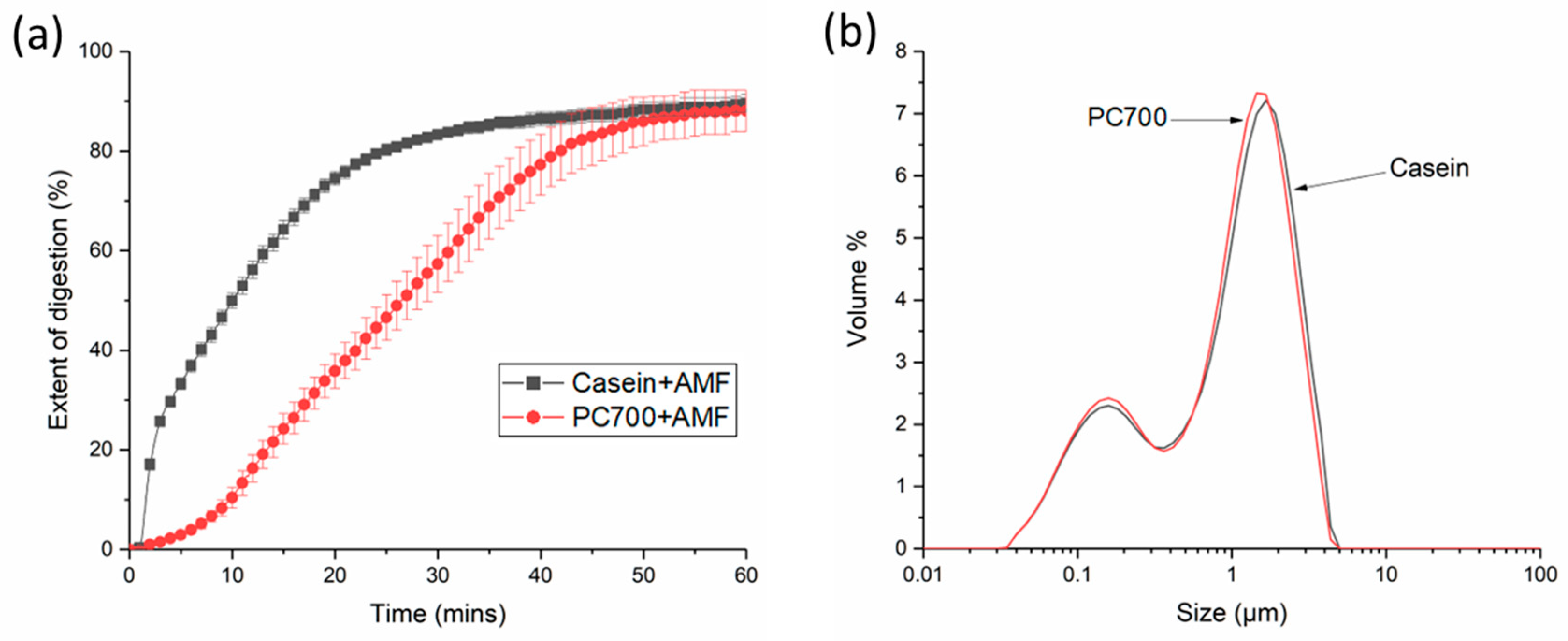
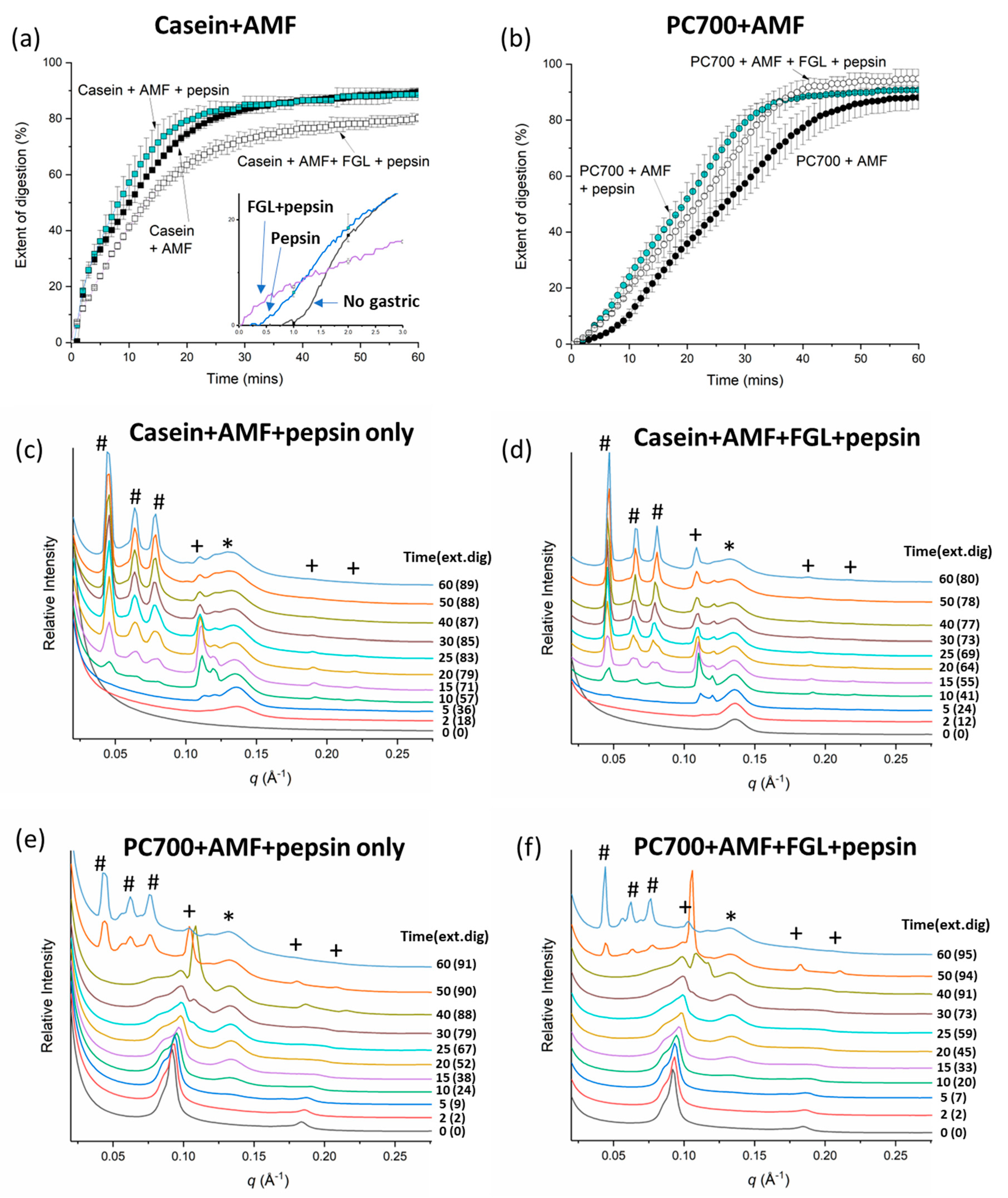
3.1. Digestion and Structure Formation of Casein- and PC700-Emulsified Fat Globules under Small Intestinal Conditions
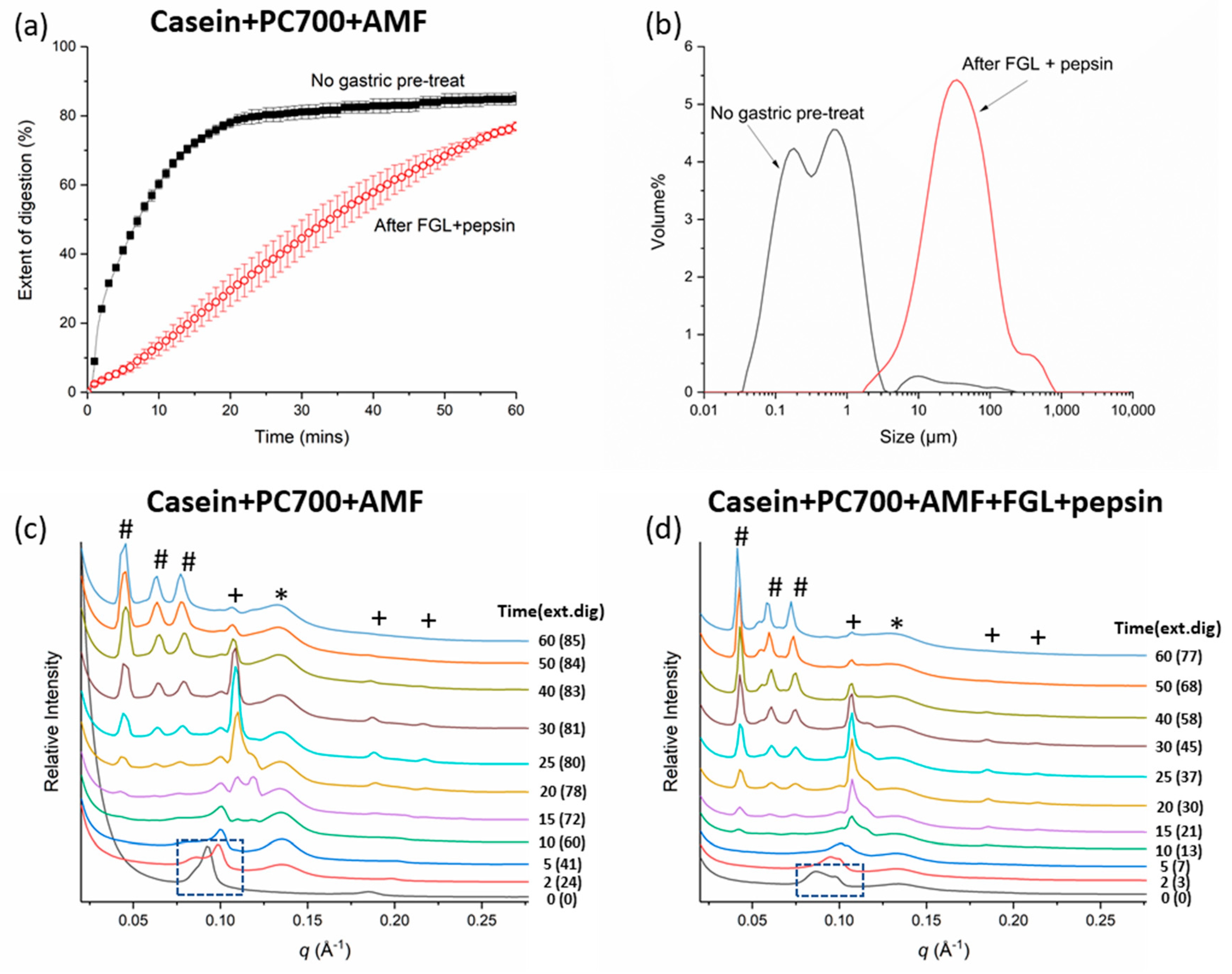
3.2. Effects of Gastric pre-Digestion on the Digestion of Casein- and PC700-Emulsified Fat Globules under Small Intestinal Conditions
3.2.1. Individual Emulsifiers
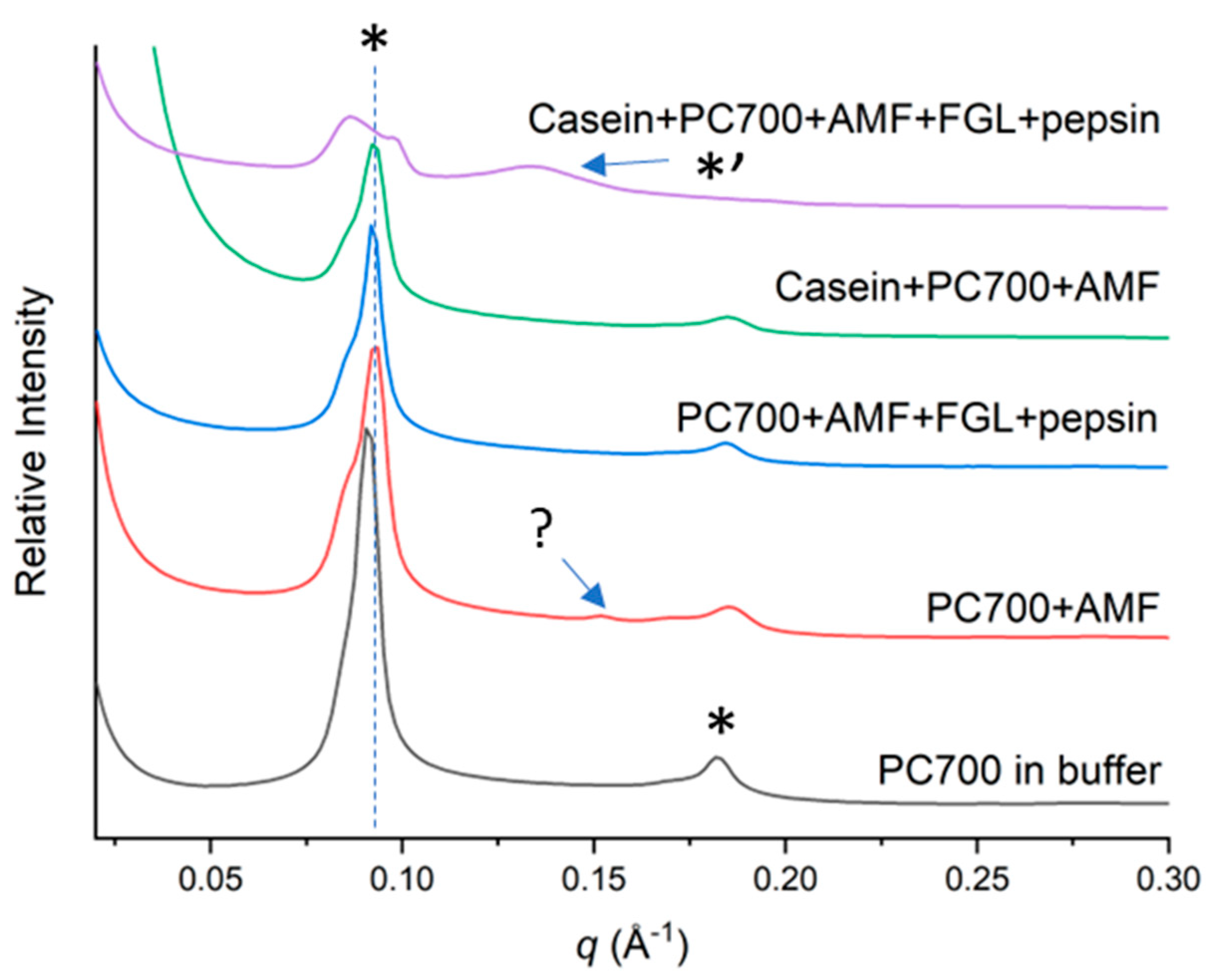
3.2.2. Mixed Emulsifiers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. World Health Organization: 10 Facts on Breastfeeding. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/features/factfiles/breastfeeding/en/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.D.; França, G.V.A.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, A.; Kenney-Muir, N.; Whitford, H.; Renfrew, M.J. Breastfeeding: Policy Matters. Identifying Strategies to Effectively Influence Political Commitment to Breastfeeding: A Review of Six Country Case Studies. 2015, Save the Children London, UK. Available online: https://www.childlinesa.org.za/wp-content/uploads/breastfeeding_policy_matters.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Council of Australian Governments Health Council. Australian National Breastfeeding Strategy: 2019 and Beyond; The Department of Health, Australian Government: Canberra, NSW, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyasoglu, H.; Gültekin-Özgüven, M.; Ozcelik, B. Production of human milk fat substitute with medium-chain fatty acids by lipase-catalyzed acidolysis: Optimization by response surface methodology. Lebensm. Wiss. Und-Technol. 2011, 44, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erp, H.; Bryant, F.M.; Martin-Moreno, J.; Michaelson, L.V.; Bhutada, G.; Eastmond, P.J. Engineering the stereoisomeric structure of seed oil to mimic human milk fat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallier, S.; Vocking, K.; Post, J.A.; Van De Heijning, B.; Acton, D.; Van Der Beek, E.M.; Van Baalen, T. A novel infant milk formula concept: Mimicking the human milk fat globule structure. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, E.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Domellöf, M. Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-protein formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claumarchirant, L.; Cilla, A.; Matencio, E.; Sanchez-Siles, L.M.; Castro-Gomez, P.; Fontecha, J.; Alegría, A.; Lagarda, M.J. Addition of milk fat globule membrane as an ingredient of infant formulas for resembling the polar lipids of human milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Moro, G.E.; Boehm, G. Early supplementation of prebiotic oligosaccharides protects formula-fed infants against infections during the first 6 months of life. Nutr. J. 2007, 137, 2420–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knol, J.; Scholtens, P.; Kafka, C.; Steenbakkers, J.; Gro, S.; Helm, K.; Klarczyk, M.; Schöpfer, H.; Böckler, H.-M.; Wells, J. Colon microflora in infants fed formula with galacto-and fructo-oligosaccharides: More like breast-fed infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 40, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J.M.; Abi-Hanna, A.; Moore, N.; Yolken, R.H. Long-term consumption of infant formulas containing live probiotic bacteria: Tolerance and safety. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker-Zierikzee, A.M.; Alles, M.S.; Knol, J.; Kok, F.J.; Tolboom, J.J.; Bindels, J.G. Effects of infant formula containing a mixture of galacto- and fructo-oligosaccharides or viable Bifidobacterium animalis on the intestinal microflora during the first 4 months of life. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.C.; Peng, K.-Y.; Salim, M.; Ramirez, G.; Hawley, A.; Clulow, A.J.; Boyd, B.J. Correlating Digestion-Driven Self-Assembly in Milk and Infant Formulas with Changes in Lipid Composition. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 3087–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, M.; Ramirez, G.; Peng, K.-Y.; Clulow, A.J.; Hawley, A.; Ramachandruni, H.; Beilles, S.; Boyd, B.J. Lipid Compositions in Infant Formulas Affect the Solubilization of Antimalarial Drugs Artefenomel (OZ439) and Ferroquine during Digestion. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2749–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, M.; Khan, J.; Ramirez, G.; Clulow, A.J.; Hawley, A.; Ramachandruni, H.; Boyd, B.J. Interactions of artefenomel (OZ439) with milk during digestion: Insights into digestion-driven solubilization and polymorphic transformations. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3535–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, M.; Khan, J.; Ramirez, G.; Murshed, M.; Clulow, A.J.; Hawley, A.; Ramachandruni, H.; Beilles, S.; Boyd, B.J. Impact of ferroquine on the solubilization of artefenomel (OZ439) during in vitro lipolysis in milk and implications for oral combination therapy for malaria. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, B.J.; Salim, M.; Clulow, A.J.; Ramirez, G.; Pham, A.C.; Hawley, A. The impact of digestion is essential to the understanding of milk as a drug delivery system for poorly water soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.C.; Gavin, P.; Libinaki, R.; Ramirez, G.; Boyd, B.J. A new lipid excipient, phosphorylated tocopherol mixture, TPM enhances the solubilisation and oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble CoQ10 in a lipid formulation. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.F.; Yao, T.T.; Zhang, X.X.; Gan, L.; Zhu, C.; Yu, H.Z.; Gan, Y. Lipid-based formulations to enhance oral bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug anethol trithione: Effects of lipid composition and formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, E.A.; Stepniewska, K.; Lindegårdh, N.; Annerberg, A.; Kham, A.; Brockman, A.; Singhasivanon, P.; White, N.J.; Nosten, F. How much fat is necessary to optimize lumefantrine oral bioavailability? Trop. Med. Int. Health 2007, 12, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salentinig, S.; Phan, S.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J. Self-assembly structure formation during the digestion of human breast milk. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clulow, A.J.; Salim, M.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J. A closer look at the behaviour of milk lipids during digestion. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 211, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentinig, S.; Phan, S.; Khan, J.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J. Formation of highly organized nanostructures during the digestion of milk. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10904–10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.; Antona, C.; Robert, B.; Lopez, C.; Armand, M. The size and interfacial composition of milk fat globules are key factors controlling triglycerides bioavailability in simulated human gastro-duodenal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, M.; Wooster, T.J.; Day, L.; Xu, M.; Lundin, L.; Keogh, J.; Clifton, P. Impact of gastric structuring on the lipolysis of emulsified lipids. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Cui, J.; Singh, H. Effect of the fat globule membrane on in vitro digestion of milk fat globules with pancreatic lipase. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeekin, T.L.; Polis, B.D. Milk Proteins. In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Anson, M.L., Edsau, J.T., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1949; pp. 201–228. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, R.; Clark, R.; Ferris, A. Composition of the lipids in human milk: A review. Lipids 1980, 15, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C. Milk fat globules enveloped by their biological membrane: Unique colloidal assemblies with a specific composition and structure. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Fong, B.Y.; MacGibbon, A.K.H.; Norris, G. Qualitative and Quantitative Study of Glycosphingolipids in Human Milk and Bovine Milk Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Data-Dependent Acquisition-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; MacGibbon, A.K.H.; Haggarty, N.; Armstrong, K.M.; Roy, N.C. Bovine dairy complex lipids improve in vitro measures of small intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhinder, G.; Allaire, J.M.; Garcia, C.; Lau, J.T.; Chan, J.M.; Ryz, N.R.; Bosman, E.S.; Graef, F.A.; Crowley, S.M.; Celiberto, L.S.; et al. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Supplementation in Formula Modulates the Neonatal Gut Microbiome and Normalizes Intestinal Development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Flores, R.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Pouliot, Y. Beverages based on milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) and other novel concepts for dairy-based functional beverages. In Functional and Speciality Beverage Technology; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Palmano, K.P.; MacGibbon, A.K.H.; Gunn, C.A.; Schollum, L.M. In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-inflammatory Activity of Bovine Milkfat Globule (MFGM)-derived Complex Lipid Fractions. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Caggioni, M.; Squires, T.M.; Gilchrist, J.F.; Prescott, S.W.; Spicer, P.T. Heterogeneity, suspension, and yielding in sparse microfibrous cellulose gels 1. Bubble rheometer studies. Rheol. Acta 2019, 58, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Singh, H.; Munro, P.A. Sodium Caseinate-Stabilized Emulsions: Factors Affecting Coverage and Composition of Surface Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3807–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clulow, A.J.; Salim, M.; Hawley, A.; Boyd, B.J. Milk mimicry—Triglyceride mixtures that mimic lipid structuring during the digestion of bovine and human milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillhart, C.; Imanidis, G.; Kuentz, M. Insights into drug precipitation kinetics during in vitro digestion of a lipid-based drug delivery system using in-line raman spectroscopy and mathematical modeling. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 3114–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, F.; Doreau, M.; Ferlay, A.; Chilliard, Y. Technical Note: Estimation of Milk Fatty Acid Yield from Milk Fat Data. J. Dairy. Sci. 2007, 90, 2302–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, A.I.I.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M. X-ray Diffraction of Lipid Model Membranes. In Methods in Membrane Lipids; Owen, D.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 199–225. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, S.T. Identification of lyotropic liquid crystalline mesophases. Handb. Appl. Surf. Colloid Chem. 2001, 2, 299–332. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.P.R.; Rago, G.; Domke, K.F.; Velikov, K.P.; Bonn, M. Label-Free Imaging of Lipophilic Bioactive Molecules during Lipid Digestion by Multiplex Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microspectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8433–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Kelly, A.L. Physical Chemistry of Milk Fat Globules. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry Volume 2 Lipids; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 173–212. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, M.; Wan Iskandar, W.F.N.; Patrick, M.; Zahid, N.I.; Hashim, R. Swelling of Bicontinuous Cubic Phases in Guerbet Glycolipid: Effects of Additives. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5552–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, S.; Gragson, D.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; Everett, D. Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy to Probe the Milk Fat Globule Membrane and Associated Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4250–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Cauty, C.; Guyomarc’h, F. Organization of lipids in milks, infant milk formulas and various dairy products: Role of technological processes and potential impacts. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitman, J.; Wood, D.L. Changes in Milk Fat Phospholipids During Lactation. J. Dairy. Sci. 1990, 73, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Du, M.; Mao, X. Change in interfacial properties of milk fat globules by homogenization and thermal processing plays a key role in their in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, S.C.; Bellanger, A.; Ménard, O.; Pladys, P.; Le Gouar, Y.; Dirson, E.; Kroell, F.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A.; Bourlieu, C. Impact of human milk pasteurization on gastric digestion in preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Van de Wiele, T.; Do, T.N.H.; Debyser, G.; Struijs, K.; Devreese, B.; Dewettinck, K.; Van Camp, J. Stability of milk fat globule membrane proteins toward human enzymatic gastrointestinal digestion. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.S.; Kamili, A.; Wat, E.; Chung, R.W.; Tandy, S. Dietary phospholipids and intestinal cholesterol absorption. Nutrients 2010, 2, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiassen, J.H.; Nejrup, R.G.; Frøkiær, H.; Nilsson, Å.; Ohlsson, L.; Hellgren, L.I. Emulsifying triglycerides with dairy phospholipids instead of soy lecithin modulates gut lipase activity. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1522–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, F.; Barrowman, J.A.; Verger, R.; Laugier, R. Secretion and contribution to lipolysis of gastric and pancreatic lipases during a test meal in humans. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengsfeld, H.; Beaumier-Gallon, G.; Chahinian, H.; Caro, A.D.; Verger, R.; Laugier, R.; Carrière, F. Physiology of Gastrointestinal Lipolysis and Therapeutical Use of Lipases and Digestive Lipase Inhibitors. In Lipases and Phospholipases in Drug Development; Müller, G., Petry, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 195–229. [Google Scholar]
- Fredrikzon, B.; Hernell, O. Role of feeding on lipase activity in gastric contents. Acta Paediatr. 1977, 66, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salim, M.; MacGibbon, A.K.H.; Nowell, C.J.; Clulow, A.J.; Boyd, B.J. Influence of Casein and Milk Phospholipid Emulsifiers on the Digestion and Self-Assembled Structures of Milk Lipids. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7030056
Salim M, MacGibbon AKH, Nowell CJ, Clulow AJ, Boyd BJ. Influence of Casein and Milk Phospholipid Emulsifiers on the Digestion and Self-Assembled Structures of Milk Lipids. Colloids and Interfaces. 2023; 7(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalim, Malinda, Alastair K. H. MacGibbon, Cameron J. Nowell, Andrew J. Clulow, and Ben J. Boyd. 2023. "Influence of Casein and Milk Phospholipid Emulsifiers on the Digestion and Self-Assembled Structures of Milk Lipids" Colloids and Interfaces 7, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7030056
APA StyleSalim, M., MacGibbon, A. K. H., Nowell, C. J., Clulow, A. J., & Boyd, B. J. (2023). Influence of Casein and Milk Phospholipid Emulsifiers on the Digestion and Self-Assembled Structures of Milk Lipids. Colloids and Interfaces, 7(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7030056






