Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) incidence has been increasing in recent years, and it now represents the sixth most common cancer diagnosis in men and the tenth in women. Although this is partly due to increased detection of incidental small renal masses on unrelated imaging, advanced RCC continues to be diagnosed in a significant portion of patients, with more than 15% presenting with distant metastases. Biomarkers can be a cost-effective tool to identify high-risk patients and institute appropriate individualised therapies. While the literature in this field is nascent, this paper focuses on several biomarkers that have been extensively investigated in the diagnosis and prognosis of RCC, as well as in predicting its response to treatments, particularly the newer immuno-oncology drugs.
Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a heterogeneous disease with a relatively unpredictable natural history. There are few reliable markers to distinguish between indolent and aggressive lesions at the time of diagnosis, predict relapse, and guide treatment decisions in the management of RCC.
Biomarkers have long been anticipated to deliver on the promise of precision medicine, and thus lead to better patient care and lower health care costs [1]. They are defined as “objectively measurable indicators of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes or pharmacologic responses to therapeutic intervention” [2]. Diagnostic biomarkers can allow for an early detection and classification of cancer. Prognostic biomarkers can inform clinicians about the natural course of an individual cancer and guide their decision of whom to treat, and how aggressively to treat. Predictive biomarkers assess the probability of a patient benefiting from a particular treatment.
Despite significant advances in our knowledge of RCC at a molecular level, there are no validated biomarkers for this disease. An array of serum, urine, and tissue-based biomarkers have been described, but each has its own practical limitations. Profiling complex fluids, such as serum and urine, requires awareness of the effect of other circulating proteases and nucleases on marker signals, as well as pre-fractionation strategies, given the vast difference in orders of magnitude in protein concentrations [3]. On the other hand, tumour heterogeneity may limit the utility of tissue-based markers [4].
This paper summarises the current status of the most widely studied molecular and genetic biomarkers in RCC. It is only a broad overview, and detailed description of individual markers should be sought in the referenced literature. While the recent advances in proteomics and metabolomics are likely to provide a more nuanced understanding of this disease in the future, their discussion is outside the scope of this paper.
Diagnostic Biomarkers
Improved characterisation of small renal masses is required to avoid surgical intervention in those with benign or indolent lesions and treat those with high metastatic potential in a timely manner. Given the high level of discordance in pathological subtyping as seen in non-clear cell RCC cases [5,6] or biopsy specimens [7], a diagnostic biomarker would be particularly useful.
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX)
CAIX is a downstream effector of HIF-1a and is thought to play a role in regulating intracellular and extracellular pH in tumour cells. It is highly expressed in 95% of clear cell RCC (ccRCC), compared with minimal expression in oncocytomas, chromophobe, and papillary RCC [8,9,10]. CAIX is also expressed in other tumours, including carcinomas of lung, breast, uterus, oesophagus, and brain, as well as in normal gastric mucosa [11]. While this somewhat limits the use of CAIX as a diagnostic marker for metastatic disease, there is ongoing enthusiasm for its utility in characterisation of the small renal mass. Several clinical trials have demonstrated the possibility of improving the performance of positron emission tomography/ computed tomography (PET/CT) by using radio-labelled girentuximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody against CAIX. REDECT, a phase III open-label multi-centre trial, assessed the diagnostic accuracy of 124I-girentuximab PET/CT in 195 patients undergoing nephrectomy and reported a sensitivity of 86.2% and specificity of 85.9% in non-invasively identifying ccRCC. Sensitivity was higher in tumours >2cm, and the overall positive predictive value was 94.4%, obviating the need for an invasive biopsy in these cases [12].
Gene expression profiling
Gene expression arrays have been created to differentiate between RCC subtypes and identify the aggressiveness and metastatic potential of tumours. Multiple studies have correlated the genetic expression profile of different types and grades of RCC with their morphological classification [13,14,15]. Analysis of these signatures from early stage ccRCC have also informed us of additional pathways in tumourigenesis, including the down- regulation of transcription factors required for normal renal development, such as GATA3, TFCP2L1, TFAP2B, and DMRT2. Other studies have identified a panel of up to 34 genes that is predictive of tumour aggression, and may function as a biomarker in the future [16].
Urinary biomarkers
Urine is an easily accessed source for biomarkers. Profiling studies have identified 2 promising proteins originating from the proximal tubule, aquaporin 1 and adipophilin, that may be shed in urine and have diagnostic potential. Initial results indicate that both proteins are significantly elevated in urine from patients with RCC compared with healthy controls, declining to control levels following nephrectomy [17,18]. Nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22), an accepted urothelial cancer marker, was found to also be significantly elevated in urine samples from patients with RCC in a few studies conducted more than 15 years ago; however, there have been no further reports since [19,20,21]. Other markers, eg, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinise-associated lipocalin (NGAL), and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have been inadequate in differentiating renal malignancy [22,23].
Tissue biomarkers
There is a wide panel of antibodies that are currently used for diagnostic purposes, including CK7, CD10, Pax 2, Pax 8, vimentin, and alpha-methylacyl-CoA (AMACR) [24]. Because of the particular difficulty in differentiating between benign and malignant eosinophilic tumours, a number of additional biomarkers have been studied to better characterise chromophobe RCC and oncocytoma such as Hale’s colloidal iron, several cadherins, and BCA2 [25]. Additional analysis of distinct chromosomal aberrations, such as TFE3 and TFEB, is now established for translocation-associated RCCs.
Composite biomarkers
The optimal future biomarker will likely be a panel of biomarkers utilising the strengths of those mentioned above. One such biomarker is the composite 3-marker panel of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), L-plastin (LCP1), and non-metastatic cell 1 protein (NM23A) that was evaluated in a cohort study of 189 patients, and further validated in 100 patients. Plasma levels of NNMT, LCP1, and NM23A were significantly elevated in patients with kidney cancer. This composite assay had a positive predictive value of 87.2%, and a negative predictive value of 97% for diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma [26]. A recent validation of this assay was conducted in 9 centres with 1042 individuals, resulting in similar findings: the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity were 0.871 and 0.894, respectively, and the resulting area under curve of receiver operating characteristic was 0.917 [27].
Prognostic Biomarkers
Accurate prognostic markers are the cornerstone of cancer management, and are indispensable in patient counselling, determining need for adjuvant therapies, and developing appropriate surveillance strategies. Currently, at least 8 prognostic nomograms are frequently utilised for predicting the risk of relapse and survival in RCC [28,29,30,31,32]. However, recent prospective validation of these models, using data from the ASSURE trial, showed a more substantial decrease in each of their prognostic abilities than previously reported in retrospective external validation studies [33]. Most models only marginally outperformed standard staging, and all had a C-index below 0.7 [34]. The search for more precise prognostic markers therefore continues.
Routine blood markers
Serum LDH, calcium, and haemoglobin have been widely reported to have independent prognostic significance in metastatic disease and are included in several nomograms [35,36].
Several studies have reported that C-reactive protein (CRP) is a strong predictor of metastasis and overall mortality after nephrectomy for localised RCC [37,38,39,40,41]. Immunohistochemical studies have also demonstrated significant intratumoural production of CRP which can be correlated with survival outcomes [42,43]. Interestingly, after adjusting for tumour staining, preoperative serum CRP was not a significant predictor of overall survival (OS) (P = 0.741) in one of these studies [43].
Thrombocytosis, another marker of the inflammatory milieu, is also an adverse prognostic factor in many cancers, including RCC [44,45,46]. However, in a predictive model comprising TNM stage, age, Fuhrman grade, histological subtype, and preoperative haemoglobin, thrombocytosis did not add any meaningful value, with a predictive accuracy gain of 0.3% only [47].
Increased peripheral blood or intratumoural neutrophils is also associated with poor survival [48,49,50,51,52]. Furthermore, a number of studies have demonstrated that a higher blood neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) portends a poorer prognosis [53,54,55]. NLR is emerging as a prognostic factor in several other cancers, and is thought to represent an impaired cell-mediated immune response due to systemic inflammation [56].
Changes in coagulation pathways are also well- recognised in malignancy. Cohort studies have reported significantly higher concentrations of plasma fibrinogen and D-dimer in patients with metastatic disease, and identified independent association with reduced cancer-specific survival (CSS) and OS [57,58,59].
The VHL, HIF, and VEGF axis
Mutation of the VHL gene has been associated with a longer progression-free survival (PFS) and CSS in ccRCC in some studies [60,61]; however, this was not reproduced in other analyses [62,63,64]. Similarly, analyses of elevated HIF-1a levels and survival have varied, with some studies demonstrating favourable prognosis, and others associating it with worse outcomes [65,66].
Increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) concentration has consistently been associated with worse tumour stage and grade, necrosis, microvessel invasion, and CSS [67,68]. However, given that VEGF is contained within platelets and released on clotting, falsely elevated results due to contamination of plasma with platelets or coagulation due to delays in processing the sample can occur, compromising its clinical applicability [69].
CAIX is one of the HIF target genes, and is associated with tumour growth, aggressive phenotype, and poor prognosis in most cancers [70,71,72]. In contrast, high CAIX expression is associated with a better prognosis in RCC in several studies [73,74,75,76]. In a larger study, however, CAIX expression was not an independent prognostic factor, after adjusting for the effect of nuclear grade, sarcomatoid differentiation, and tumour necrosis [11]. These findings were further validated at the 5-year follow-up of this study [77].
Immunologic markers
The B7 family of immune regulatory ligands produce co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory T-cell signals, and therefore have been identified as promising prognostic biomarkers. B7-H1 functions as a negative regulator of immunity, and its over-expression is independently associated with significantly increased progression to metastatic disease (RR 3.46; P < 0.001) and cancer-specific mortality (RR 3.92; P < 0.001) [78,79]. B7-H4 and, less strongly, B7-H3 have also been implicated as adverse prognostic factors [80,81]. Non-invasive immunoassays for the soluble forms of the B7 family are being developed with promising early results [82].
Given the immunogenic nature of RCC, pathologic specimens harbour a high number of tumour- infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Their prognostic significance is not established because of inconsistent findings on various multivariate analyses to date [83,84,85].
Markers of cell proliferation and apoptosis
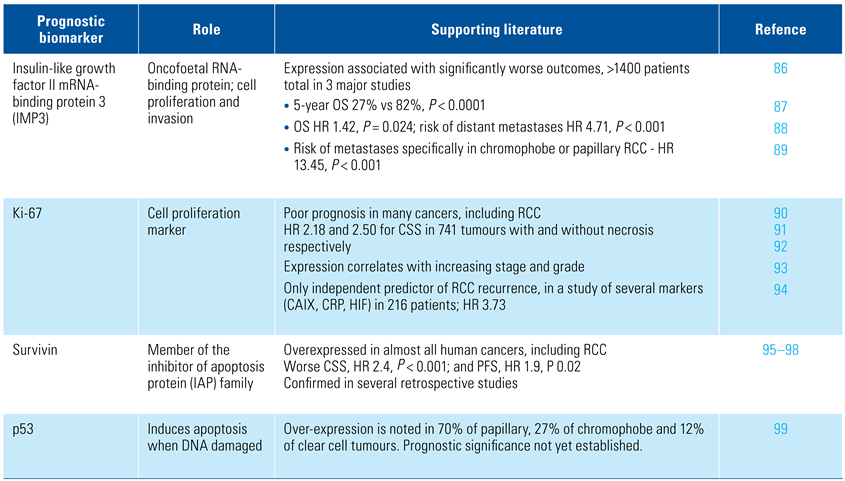
Various nuclear proteins that regulate cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis are established as prognostic markers in other cancers. Some of these are also very promising in RCC, as summarised in Table 1 [86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99].

Table 1.
Markers of cell proliferation and apoptosis as prognostic biomarkers.
The cell cycle progression (CCP) score is an RNA expression assay that measures the activity of 31 genes involved in cellular proliferation, which has been widely validated for use in prostate cancer. Most recently, its prognostic utility has also been demonstrated in predicting recurrence and mortality in a cohort of 565 RCC patients undergoing nephrectomy [100]. In another study from the same authors, a higher CCP score on renal mass biopsy was correlated with adverse pathology on surgery, suggesting its clinical value in risk-stratifying patients being considered for active surveillance of small renal masses [101].
Utility of biomarkers in prognostic models
Incorporation of molecular markers into existing prognostic models, as well as combining markers to create molecular signatures of the disease, will certainly be of greater utility than any single marker. A prognostic model using p53, CAIX, gelsolin, and vimentin, combined with metastatic status, T-stage and ECOG (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group) performance status was 79% accurate in a cohort of 318 patients [102]. In another study of 634 patients, the integration of BioScore, which is based on expression of Ki-67, survivin and B7-H1, with the UISS and SSIGN models improved the prognostic accuracy of the models by 4.5% and 1.6% respectively. Furthermore, patients with high BioScores were noted to be 5 times more likely to die from RCC (HR 5.03; P <0.001) [103].
Lastly, the prognostic value of multi-gene assays, such as ClearCode-34 and 16-gene signature, has been reported to be greater than the established predictive models, and has now been validated in at least one prospective cohort. There are certainly caveats around tumour heterogeneity and misclassification due to sample bias; however, the results so far have been encouraging [104,105,106,107].
Predictive Biomarkers
The therapeutic landscape in metastatic RCC has transformed in the past decade with the introduction of targeted and immuno-oncology treatments. Identifying markers that can reliably predict the response to specific treatments is essential to optimise patient management. This section focuses on predictive markers for these contemporary treatments.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Immunohistochemical expression of PD-L1 is the most studied marker in this realm. Studies to date have not established its independent predictive value. In all prospective trials, PD-L1 expression has been associated with worse prognosis, but not with response to checkpoint inhibitors [108,109,110]. Biological and logistical challenges in using PD-L1 as a biomarker have been well described, including intratumoural heterogeneity, discordant expression in primary and secondary sites, dynamic expression, and variation in immunohistochemical assays [111].
Biomarker analysis from trial JAVELIN-101 was recently published, and included a 26-gene expression signature and mutations and polymorphisms based on whole exome sequencing, in addition to PD-L1 expression [112]. PD-L1 expression was not predictive of response to avelumab. As in previous studies, tumour mutational burden did not demonstrate any significant predictive value [113]. Several genetic mutations and the 26-gene signature were implicated in predicting treatment response; however, these findings need to be further validated.
Likewise, the phase II IMmotion-150 trial demonstrated the utility of gene expression signatures, reflecting angiogenesis and effector T-cell response, in predicting response to atezolizumab. A high angiogenic signature was associated with improved response rate and PFS in patients treated with sunitinib, and patients with high effector T-cell signature had better responses to ICB. These findings were subsequently confirmed by the phase III IMmotion-151 trial [114].
Other predictive markers under investigation include tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes, mutation signatures and microsatellite instability, HLA classification, TGF-b expression, PD-L2, CTLA-4, mutational or neoantigen burden, and commensal gut microbiome [115,116].
Limitations
A major barrier to translating research findings to clinically applicable tools has been a lack of stand-ardisation in study methodologies and small sample sizes lacking statistical power to demonstrate any meaningful correlation. A shift to collaborative efforts of large research networks involving industry and scientific experts in prospective trials, instead of the traditional model of small laboratory-based retrospective studies, is hoped to yield higher quality data and provide us with an exciting and unprecedented opportunity for the discovery and large-scale validation of reliable, precise and cost-effective RCC biomarkers.
Conclusion
Volumes of literature have been published on numerous promising diagnostic, prognostic and predictive RCC biomarkers. None of these have yet been established for routine clinical use in management of this hetero- geneous disease.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Abbreviations
| CAIX | carbonic anhydrase IX |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Davis, J.C.; Furstenthal, L.; Desai, A.A.; Norris, T.; Sutaria, S.; Fleming, E.; et al. The microeconomics of personalized medicine: Today’s challenge and tomorrow’s promise. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biomarkers Definitions Working G. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudev, N.S.; Banks, R.E. Biomarkers of Renal Cancer. In Biomarkers of Kidney Disease, 2nd ed.; Edelstein, C.L., Ed.; Elsevier Inc., 2017; pp. 421–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, T.C.; Wood, C.G.; Karam, J.A. Biomarkers of renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummerlin, I.; ten Kate, F.; Smedts, F.; Horn, T.; Algaba, F.; Trias, I.; et al. Diagnostic problems in the subtyping of renal tumors encountered by five pathologists. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2009, 205, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, V.A.; Merino, M.J. Misdiagnosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2011, 8, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barocas, D.A.; Rohan, S.M.; Kao, J.; Gurevich, R.D.; Del Pizzo, J.J.; Vaughan, E.D., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis of renal tumors on needle biopsy specimens by histological and molecular analysis. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Beasley, N.J.; Watson, P.H.; Turner, K.J.; Pastorek, J.; Sibtain, A.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible expression of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 7075–7083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Genega, E.M.; Ghebremichael, M.; Najarian, R.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Argani, P.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX expression in renal neoplasms: Correlation with tumor type and grade. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 134, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillebroer, A.B.; Mulders, P.F.; Boerman, O.C.; Oyen, W.J.; Oosterwijk, E. Carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma: Implications for prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovich, B.C.; Sheinin, Y.; Lohse, C.M.; Thompson, R.H.; Cheville, J.C.; Zavada, J.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is not an independent predictor of outcome for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divgi, C.R.; Uzzo, R.G.; Gatsonis, C.; Bartz, R.; Treutner, S.; Yu, J.Q.; et al. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Results from the REDECT trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Rhodes, D.R.; Furge, K.A.; Kanayama, H.; Kagawa, S.; Haab, B.B.; et al. Gene expression profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Gene identification and prognostic classification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9754–9759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosari, F.; Parker, A.S.; Kube, D.M.; Lohse, C.M.; Leibovich, B.C.; Blute, M.L.; et al. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Gene expression analyses identify a potential signature for tumor aggressiveness. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5128–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thibodeau, B.J.; Fulton, M.; Fortier, L.E.; Geddes, T.J.; Pruetz, B.L.; Ahmed, S.; et al. Characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Urol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 168 e1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.J.; Tun, H.W.; Roper, S.M.; Kim, Y.; Kislinger, T. Current Status of Biomarker Discovery in Human clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Mol. Biomark Diagn. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.J.; London, A.N.; Luo, J.; Kharasch, E.D. Urinary biomarkers for the early diagnosis of kidney cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, J.J.; Mobley, J.; Song, J.; Vetter, J.; Luo, J.; Bhayani, S.; et al. Urinary concentrations of aquaporin-1 and perilipin-2 in patients with renal cell carcinoma correlate with tumor size and stage but not grade. Urology 2014, 83, 256–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Rhee, E.; Patel, H.; Park, E.; Kaswick, J. Urinary NMP22 and renal cell carcinoma. Urology 2000, 55, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, G.; Altinel, M.; Kocak, B.; Yazicioglu, A.; Gonenc, F. Value of urinary NMP-22 in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urology 2002, 60, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, K.; Ayan, S.; Gokce, G.; Kilicarslan, H.; Yildiz, E.; Gultekin, E.Y. Urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 for diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2005, 39, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.J.; London, A.N.; Lambert, M.C.; Kharasch, E.D. Sensitivity and specificity of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury molecule-1 for the diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in the sera and in the urine of human oncocytoma and renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.H.; Cheng, L.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Merino, M.J.; Netto, G.; Reuter, V.E.; et al. Renal tumors: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.L.; Rajandram, R.; Morais, C.; Yap, N.Y.; Samaratunga, H.; Gobe, G.C.; et al. Differentiation of oncocytoma from chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (RCC): Can novel molecular biomarkers help solve an old problem? J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su Kim, D.; Choi, Y.D.; Moon, M.; Kang, S.; Lim, J.B.; Kim, K.M.; et al. Composite three-marker assay for early detection of kidney cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2013, 22, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Ham, W.S.; Jang, W.S.; Cho, K.S.; Choi, Y.D.; Kang, S.; et al. Scale-up evaluation of a composite tumor marker assay for the early detection of renal cell carcinoma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattan, M.W.; Reuter, V.; Motzer, R.J.; Katz, J.; Russo, P. A postoperative prognostic nomogram for renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisman, A.; Pantuck, A.J.; Dorey, F.; Said, J.W.; Shvarts, O.; Quintana, D.; et al. Improved prognostication of renal cell carcinoma using an integrated staging system. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, I.; Blute, M.L.; Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Weaver, A.L.; Zincke, H. An outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: The SSIGN score. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovich, B.C.; Blute, M.L.; Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Frank, I.; Kwon, E.D.; et al. Prediction of progression after radical nephrectomy for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A stratification tool for prospective clinical trials. Cancer 2003, 97, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakiewicz, P.I.; Briganti, A.; Chun, F.K.; Trinh, Q.D.; Perrotte, P.; Ficarra, V.; et al. Multi-institutional validation of a new renal cancer-specific survival nomogram. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Cheng, C.; Ficarra, V.; Murai, M.; Oudard, S.; et al. Prognostic factors and predictive models in renal cell carcinoma: A contemporary review. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.F.; Jegede, O.; Haas, N.B.; Flaherty, K.T.; Pins, M.R.; Messing, E.M.; et al. Predicting renal cancer recurrence: Defining limitations of existing prognostic models with prospective trial-based validation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakiewicz, P.I.; Hutterer, G.C.; Trinh, Q.D.; Jeldres, C.; Perrotte, P.; Gallina, A.; et al. C-reactive protein is an informative predictor of renal cell carcinoma-specific mortality: A European study of 313 patients. Cancer 2007, 110, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, S.; Lamb, G.W.; Aitchison, M.; McMillan, D.C. Prospective study of the relationship between the systemic inflammatory response, prognostic scoring systems and relapse-free and cancer-specific survival in patients undergoing potentially curative resection for renal cancer. BJU Int. 2008, 101, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iimura, Y.; Saito, K.; Fujii, Y.; Kumagai, J.; Kawakami, S.; Komai, Y.; et al. Development and external validation of a new outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with nephrectomy based on preoperative serum C-reactive protein and TNM classification: The TNM-C score. J Urol. 2009, 181, 1004–1012; discussion 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.V.; Abbasi, A.; Owen-Smith, A.; Young, A.; Ogan, K.; Pattaras, J.; et al. Absolute preoperative C-reactive protein predicts metastasis and mortality in the first year following potentially curative nephrectomy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedke, J.; Chun, F.K.; Merseburger, A.; Scharpf, M.; Kasprzyk, K.; Schilling, D.; et al. Inflammatory prognostic markers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma - preoperative C-reactive protein does not improve predictive accuracy. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E771–E777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabs, W.J.; Busse, M.; Kruger, S.; Jocham, D.; Steinhoff, J.; Doehn, C. Expression of C-reactive protein by renal cell carcinomas and unaffected surrounding renal tissue. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.V.; Ali, S.; Abbasi, A.; Kucuk, O.; Harris, W.B.; Ogan, K.; et al. Intratumor C-reactive protein as a biomarker of prognosis in localized renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symbas, N.P.; Townsend, M.F.; El-Galley, R.; Keane, T.E.; Graham, S.D.; Petros, J.A. Poor prognosis associated with thrombocytosis in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2000, 86, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensalah, K.; Leray, E.; Fergelot, P.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Tostain, J.; Guille, F.; et al. Prognostic value of thrombocytosis in renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, R.; Shaheen, P.E.; Elson, P.; Misbah, S.A.; Wood, L.; Motzer, R.J.; et al. Thrombocytosis as a prognostic factor for survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2006, 107, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakiewicz, P.I.; Trinh, Q.D.; Lam, J.S.; Tostain, J.; Pantuck, A.J.; Belldegrun, A.S.; et al. Platelet count and preoperative haemoglobin do not significantly increase the performance of established predictors of renal cell carcinoma-specific mortality. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrier, S.; Escudier, B.; Gomez, F.; Douillard, J.Y.; Ravaud, A.; Chevreau, C.; et al. Prognostic factors of survival and rapid progression in 782 patients with metastatic renal carcinomas treated by cytokines: A report from the Groupe Francais d’Immunotherapie. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzpodien, J.; Royston, P.; Wandert, T.; Reitz, M.; Group DGCRCC-IT. Metastatic renal carcinoma comprehensive prognostic system. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskov, F.; Hokland, M.; Marcussen, N.; Torp Madsen, H.H.; von der Maase, H. Monocytes and neutrophils as ‘bad guys’ for the outcome of interleukin-2 with and without histamine in metastatic renal cell carcinoma--results from a randomised phase II trial. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.K.; Donskov, F.; Marcussen, N.; Nordsmark, M.; Lundbeck, F.; von der Maase, H. Presence of intratumoral neutrophils is an independent prognostic factor in localized renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4709–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskov, F. Immunomonitoring and prognostic relevance of neutrophils in clinical trials. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Nakashima, J.; Ohori, M.; Hatano, T.; Tachibana, M. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent predictor of recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Stoeckigt, C. Validation of the pre-treatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in a large European cohort of renal cell carcinoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Lou, L.; Ye, J.; Zhang, S. Prognostic role of the neutrophil- lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.S.; Fernandes, P.C., Jr.; Silva, M.J.; Lima, V.C.; Fontes, W.; Freitas-Junior, R.; et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: A narrative review. Ecancermedicalscience 2016, 10, 702. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Zheng, J.H.; Chen, X.S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, L.; et al. High preoperative plasma fibrinogen is an independent predictor of distant metastasis and poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 18, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Stojakovic, T.; Mannweiler, S.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R. High plasma fibrinogen level represents an independent negative prognostic factor regarding cancer-specific, metastasis-free, as well as overall survival in a European cohort of non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, S.; Amasyali, A.S.; Aytac, O.; Onem, K.; Issever, H.; Sanli, O. Increased preoperative levels of plasma fibrinogen and D dimer in patients with renal cell carcinoma is associated with poor survival and adverse tumor characteristics. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, H.P.; Bender, B.U.; Berger, D.P.; Laubenberger, J.; Schultze- Seemann, W.; Wetterauer, U.; et al. Prevalence, morphology and biology of renal cell carcinoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease compared to sporadic renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 1998, 160, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kishida, T.; Nakaigawa, N.; Baba, M.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. VHL tumor suppressor gene alterations associated with good prognosis in sporadic clear-cell renal carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraml, P.; Struckmann, K.; Hatz, F.; Sonnet, S.; Kully, C.; Gasser, T.; et al. VHL mutations and their correlation with tumour cell proliferation, microvessel density, and patient prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2002, 196, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, C.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Somatic VHL alteration and its impact on prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smits, K.M.; Schouten, L.J.; van Dijk, B.A.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.A.; Wouters, K.A.; Oosterwijk, E.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic alterations in the von hippel-lindau gene: The influence on renal cancer prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidgren, A.; Hedberg, Y.; Grankvist, K.; Rasmuson, T.; Bergh, A.; Ljungberg, B. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression in renal cell carcinoma analyzed by tissue microarray. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatte, T.; Seligson, D.B.; Riggs, S.B.; Leppert, J.T.; Berkman, M.K.; Kleid, M.D.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7388–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, J.; Grankvist, K.; Rasmuson, T.; Bergh, A.; Landberg, G.; Ljungberg, B. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor protein in human renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Fergelot, P.; Zerrouki, S.; Leray, E.; Jouan, F.; Bellaud, P.; et al. Plasma level and tissue expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in renal cell carcinoma: A prospective study of 50 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, R.E.; Forbes, M.A.; Kinsey, S.E.; Stanley, A.; Ingham, E.; Walters, C.; et al. Release of the angiogenic cytokine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from platelets: Significance for VEGF measurements and cancer biology. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinson, D.E.; Jones, J.L.; Richardson, D.; Wykoff, C.; Turley, H.; Pastorek, J.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX expression, a novel surrogate marker of tumor hypoxia, is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseide, K.; Kandel, R.A.; Bell, R.S.; Catton, C.N.; O’Sullivan, B.; Wunder, J.S.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX as a marker for poor prognosis in soft tissue sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4464–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, A.; Landuyt, W.; Pastorekova, S.; Moons, J.; Goethals, L.; Haustermans, K.; et al. Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX), a hypoxia-related protein, rather than vascular-endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a pro-angiogenic factor, correlates with an extremely poor prognosis in esophageal and gastric adenocarcinomas. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, M.H.; Seligson, D.; Han, K.R.; Pantuck, A.J.; Dorey, F.J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is an independent predictor of survival in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma: Implications for prognosis and therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandlund, J.; Oosterwijk, E.; Grankvist, K.; Oosterwijk-Wakka, J.; Ljungberg, B.; Rasmuson, T. Prognostic impact of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in human renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2007, 100, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patard, J.J.; Fergelot, P.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Klatte, T.; Trinh, Q.D.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; et al. Low CAIX expression and absence of VHL gene mutation are associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor survival of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuoc, N.B.; Ehara, H.; Gotoh, T.; Nakano, M.; Kamei, S.; Deguchi, T.; et al. Prognostic value of the co-expression of carbonic anhydrase IX and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Thompson, R.H.; Lohse, C.M.; Dronca, R.S.; Cheville, J.C.; Kwon, E.D.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is not an independent predictor of outcome in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) after long-term follow-up. BJU Int. 2013, 111, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.H.; Gillett, M.D.; Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Dong, H.; Webster, W.S.; et al. Costimulatory molecule B7-H1 in primary and metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 104, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.H.; Kuntz, S.M.; Leibovich, B.C.; Dong, H.; Lohse, C.M.; Webster, W.S.; et al. Tumor B7-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krambeck, A.E.; Thompson, R.H.; Dong, H.; Lohse, C.M.; Park, E.S.; Kuntz, S.M.; et al. B7-H4 expression in renal cell carcinoma and tumor vasculature: Associations with cancer progression and survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10391–10396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispen, P.L.; Sheinin, Y.; Roth, T.J.; Lohse, C.M.; Kuntz, S.M.; Frigola, X.; et al. Tumor cell and tumor vasculature expression of B7-H3 predict survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5150–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigola, X.; Inman, B.A.; Lohse, C.M.; Krco, C.J.; Cheville, J.C.; Thompson, R.H.; et al. Identification of a soluble form of B7-H1 that retains immunosuppressive activity and is associated with aggressive renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, T.; Murakami, S.; Takahashi, H.; Matsuzaki, O.; Shimazaki, J. Changes on distribution of CD4+/CD45RA- and CD8+/CD11- cells in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of renal cell carcinoma associated with tumor progression. Eur. Urol. 1992, 22, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolbeck, P.C.; Kaveggia, F.F.; Johansson, S.L.; Grune, M.T.; Taylor, R.J. The relationships among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, histopathologic findings, and long-term clinical follow-up in renal cell carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 1992, 5, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Skorupski, W.; Kwias, Z.; Nowak, J. Flow cytometric analysis of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Urol. 1997, 80, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdelski, C.; Jakani-Karimi, N.; Jacobsen, F.; Moller-Koop, C.; Minner, S.; Simon, R.; et al. IMP3 overexpression occurs in various important cancer types and is linked to aggressive tumor features: A tissue microarray study on 8,877 human cancers and normal tissues. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Chu, P.G.; Woda, B.A.; Rock, K.L.; Liu, Q.; Hsieh, C.C.; et al. Analysis of RNA-binding protein IMP3 to predict metastasis and prognosis of renal-cell carcinoma: A retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, N.E.; Sheinin, Y.; Lohse, C.M.; Parker, A.S.; Leibovich, B.C.; Jiang, Z.; et al. External validation of IMP3 expression as an independent prognostic marker for metastatic progression and death for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2008, 112, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lohse, C.M.; Chu, P.G.; Wu, C.L.; Woda, B.A.; Rock, K.L.; et al. Oncofetal protein IMP3: A novel molecular marker that predicts metastasis of papillary and chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. Cancer 2008, 112, 2676–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudderidge, T.J.; Stoeber, K.; Loddo, M.; Atkinson, G.; Fanshawe, T.; Griffiths, D.F.; et al. Mcm2, Geminin, and KI67 define proliferative state and are prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, M.K.; Thompson, R.H.; Sheinin, Y.; Lohse, C.M.; Cheville, J.C.; Leibovich, B.C.; et al. Ki-67 and coagulative tumor necrosis are independent predictors of poor outcome for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and not surrogates for each other. Cancer 2007, 110, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inwald, E.C.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Hofstadter, F.; Zeman, F.; Koller, M.; Gerstenhauer, M.; et al. Ki-67 is a prognostic parameter in breast cancer patients: Results of a large population-based cohort of a cancer registry. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013, 139, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, M.H.; Visapaa, H.; Seligson, D.; Kim, H.; Han, K.R.; Huang, Y.; et al. Prognostic value of carbonic anhydrase IX and KI67 as predictors of survival for renal clear cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, E.J.; Bauman, T.M.; Weiker, M.; Shi, F.; Downs, T.M.; Jarrard, D.F.; et al. Analysis and validation of tissue biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma using automated high-throughput evaluation of protein expression. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, D.C. Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8581–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.S.; Kosari, F.; Lohse, C.M.; Houston Thompson, R.; Kwon, E.D.; Murphy, L.; et al. High expression levels of survivin protein independently predict a poor outcome for patients who undergo surgery for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2006, 107, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.S.; Yeo, W.G.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, E. Expression of survivin in renal cell carcinomas: Association with pathologic features and clinical outcome. Urology 2007, 69, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krambeck, A.E.; Dong, H.; Thompson, R.H.; Kuntz, S.M.; Lohse, C.M.; Leibovich, B.C.; et al. Survivin and b7-h1 are collaborative predictors of survival and represent potential therapeutic targets for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigeuner, R.; Ratschek, M.; Rehak, P.; Schips, L.; Langner, C. Value of p53 as a prognostic marker in histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma: A systematic analysis of primary and metastatic tumor tissue. Urology 2004, 63, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.M.; Mehra, R.; Tiemeny, P.; Wolf, J.S.; Wu, S.; Sangale, Z.; et al. A multigene signature based on cell cycle proliferation improves prediction of mortality within 5 yr of radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosoian, J.J.; Feldman, A.S.; Abbott, M.R.; Mehra, R.; Tiemeny, P.; Wolf, J.S., Jr.; et al. Biopsy Cell Cycle Proliferation Score Predicts Adverse Surgical Pathology in Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Seligson, D.; Liu, X.; Janzen, N.; Bui, M.H.; Yu, H.; et al. Using protein expressions to predict survival in clear cell renal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5464–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.S.; Leibovich, B.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Sheinin, Y.; Kuntz, S.M.; Eckel-Passow, J.E.; et al. Development and evaluation of BioScore: A biomarker panel to enhance prognostic algorithms for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2009, 115, 2092–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.A.; Brannon, A.R.; Parker, J.S.; Fisher, J.C.; Sen, O.; Kattan, M.W.; et al. ClearCode34: A prognostic risk predictor for localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.; Goddard, A.; Knezevic, D.; Maddala, T.; Zhou, M.; Aydin, H.; et al. A 16-gene assay to predict recurrence after surgery in localised renal cell carcinoma: Development and validation studies. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghatalia, P.; Rathmell, W.K. Systematic review: ClearCode 34 - a validated prognostic signature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Kidney Cancer 2018, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Martini, J.F.; Magheli, A.; Svedman, C.; Lopatin, M.; et al. Validation of the 16-Gene Recurrence Score in patients with locoregional, high-risk renal cell carcinoma from a phase iii trial of adjuvant sunitinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4407–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal- Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal- Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Kurzrock, R. PD-L1 Expression as a Predictive Biomarker in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Albiges, L.; Haanen, J.B.A.G.; Larkin, J.M.G.; Uemura, M.; Pal, S.K.; et al. Biomarker analyses from JAVELIN Renal 101: Avelumab + axitinib (A+Ax) versus sunitinib (S) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.C.; Almeida, L.; Bergerot, P.G.; Dizman, N.; Pal, S.K. Relationship of tumor mutational burden (TMB) to immunotherapy response in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Huseni, M.; Atkins, M.B.; McDermott, D.F.; Powles, T.B.; Escudier, B.; et al. LBA31Molecular correlates differentiate response to atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) vs sunitinib (sun): Results from a phase III study (IMmotion151) in untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Gibney, G.T.; Weiner, L.M.; Atkins, M.B. Predictive biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e542–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, J.J.; Chowell, D.; Chan, T.A. The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2019, 19, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Vaziri, S.A.; Jaeger, E.; Elson, P.; Wood, L.; Bhalla, I.P.; et al. von Hippel-Lindau gene status and response to vascular endothelial growth factor targeted therapy for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 860–865; discussion 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Fay, A.P.; Gagnon, R.; Lin, Y.; Bahamon, B.; Brown, V.; et al. The role of aberrant VHL/HIF pathway elements in predicting clinical outcome to pazopanib therapy in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5218–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.T.; Liu, Y.; Zurita, A.J.; Lin, Y.; Baker-Neblett, K.L.; Martin, A.M.; et al. Prognostic or predictive plasma cytokines and angiogenic factors for patients treated with pazopanib for metastatic renal-cell cancer: A retrospective analysis of phase 2 and phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, A.B.; Halabi, S.; Shterev, I.; Starr, M.; Brady, J.C.; Dutcher, J.P.; et al. Identification of predictive biomarkers of overall survival (OS) in patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treated with interferon alpha (I) with or without bevacizumab (B): Results from CALGB 90206 (Alliance). J Clin Oncol. 2013, 31, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi, T.; Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, J.J. A systematic review of predictive and prognostic biomarkers for VEGF-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014, 40, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, A.G.; Motzer, R.J.; Hakimi, A.A. Prognostic biomarkers for response to vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 43, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Rini, B.I.; Donskov, F.; et al. Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Halabi, S.; Sanford, B.L.; Hahn, O.; Michaelson, M.D.; Walsh, M.K.; et al. Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of poor or intermediate risk: The Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2021 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.