Global Properties of Latent Virus Dynamics Models with Immune Impairment and Two Routes of Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Model
2.1. Nonnegativity and Boundedness
- (i)
- if then there exists a disease-free steady state ,
- (ii)
- if , then there exist two steady states and endemic steady state .
2.2. Global Stability
3. Model with Saturated Incidence Rate
3.1. Basic Properties
- (i)
- A disease-free steady state exists when
- (ii)
- An endemic steady state exists when .
3.2. Global Properties
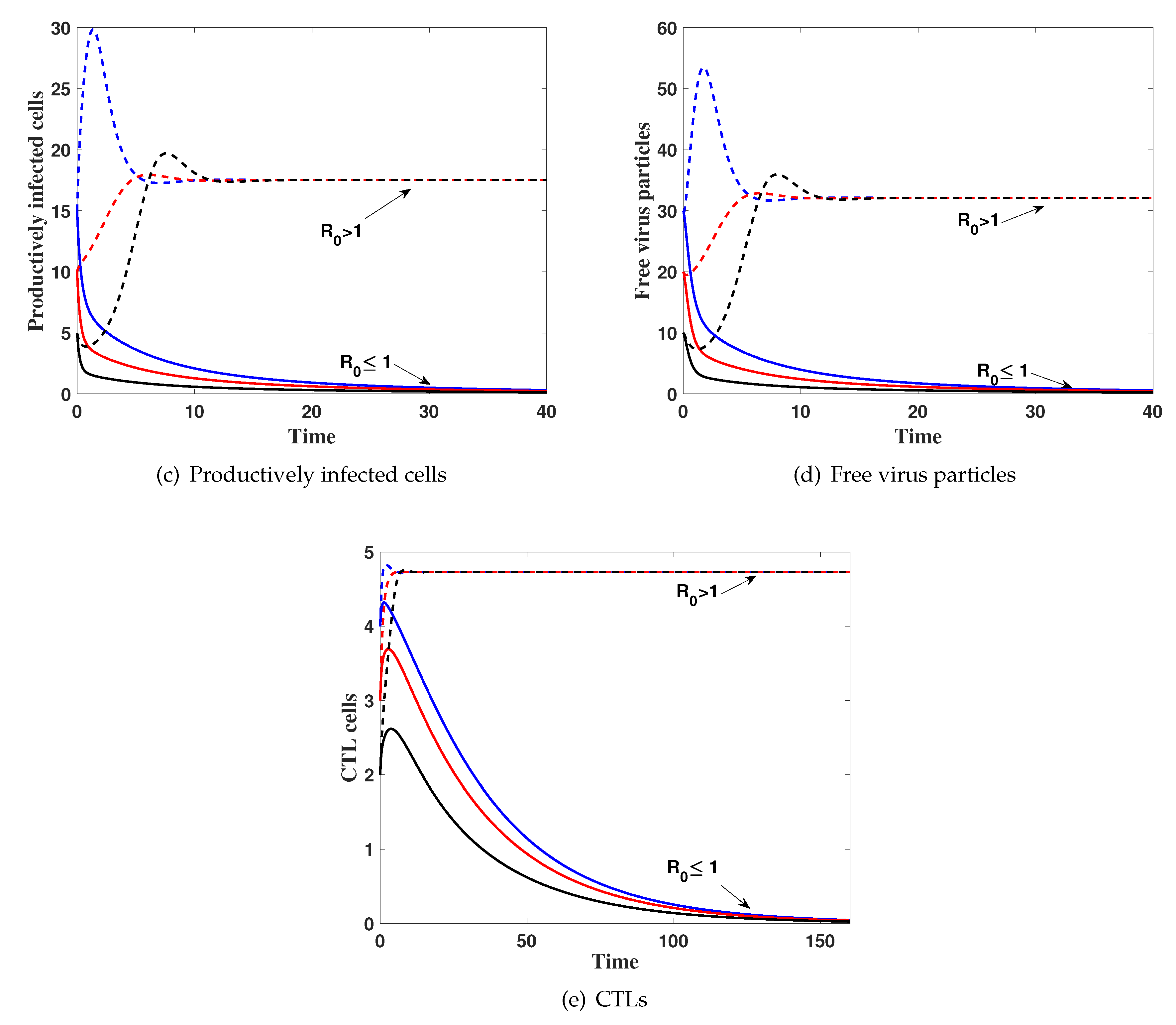
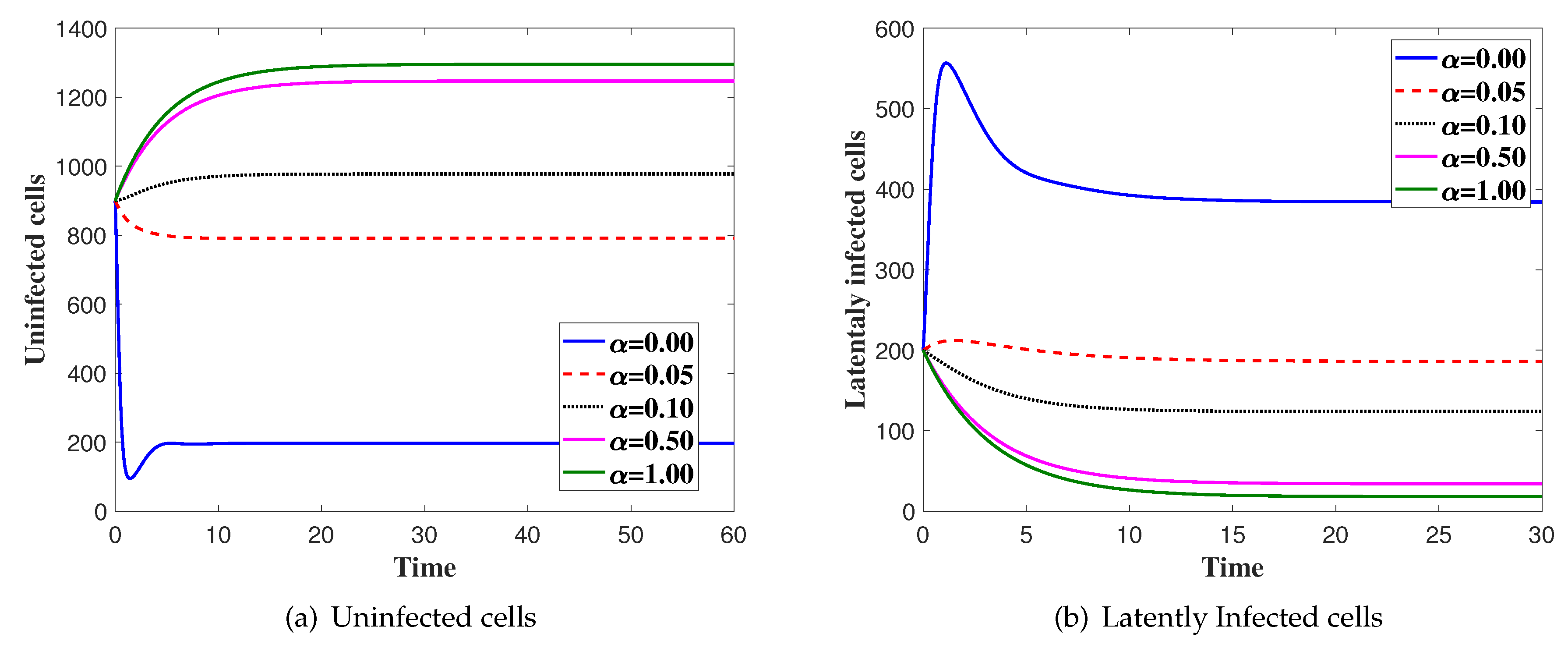
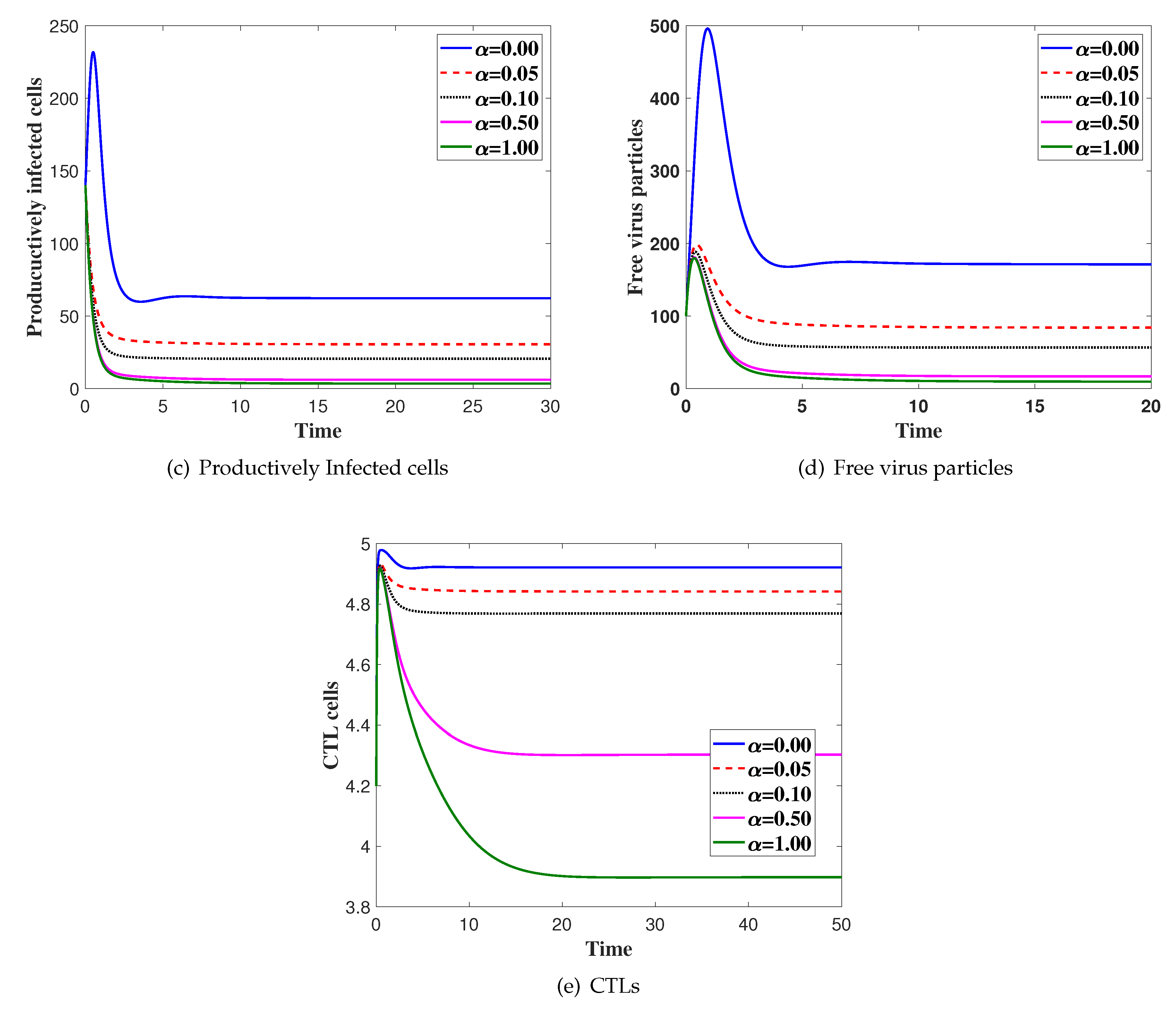
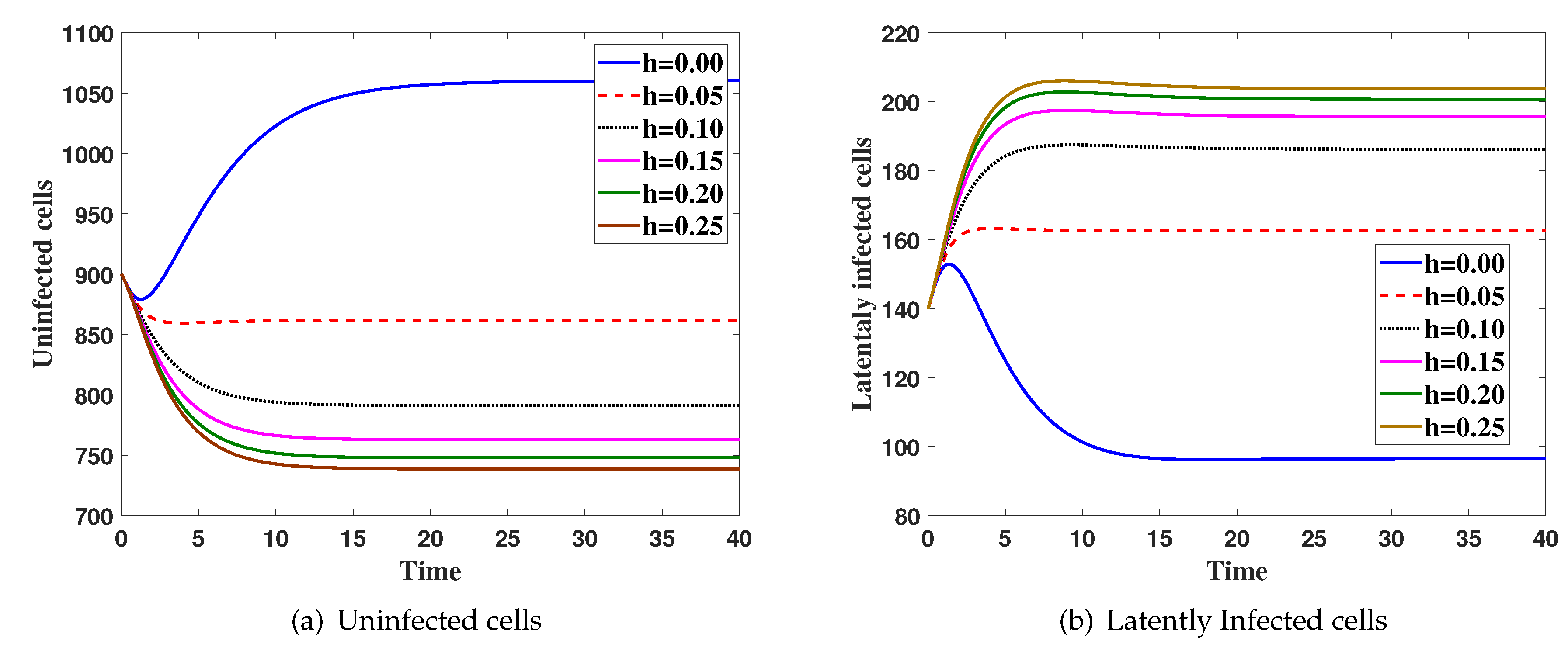
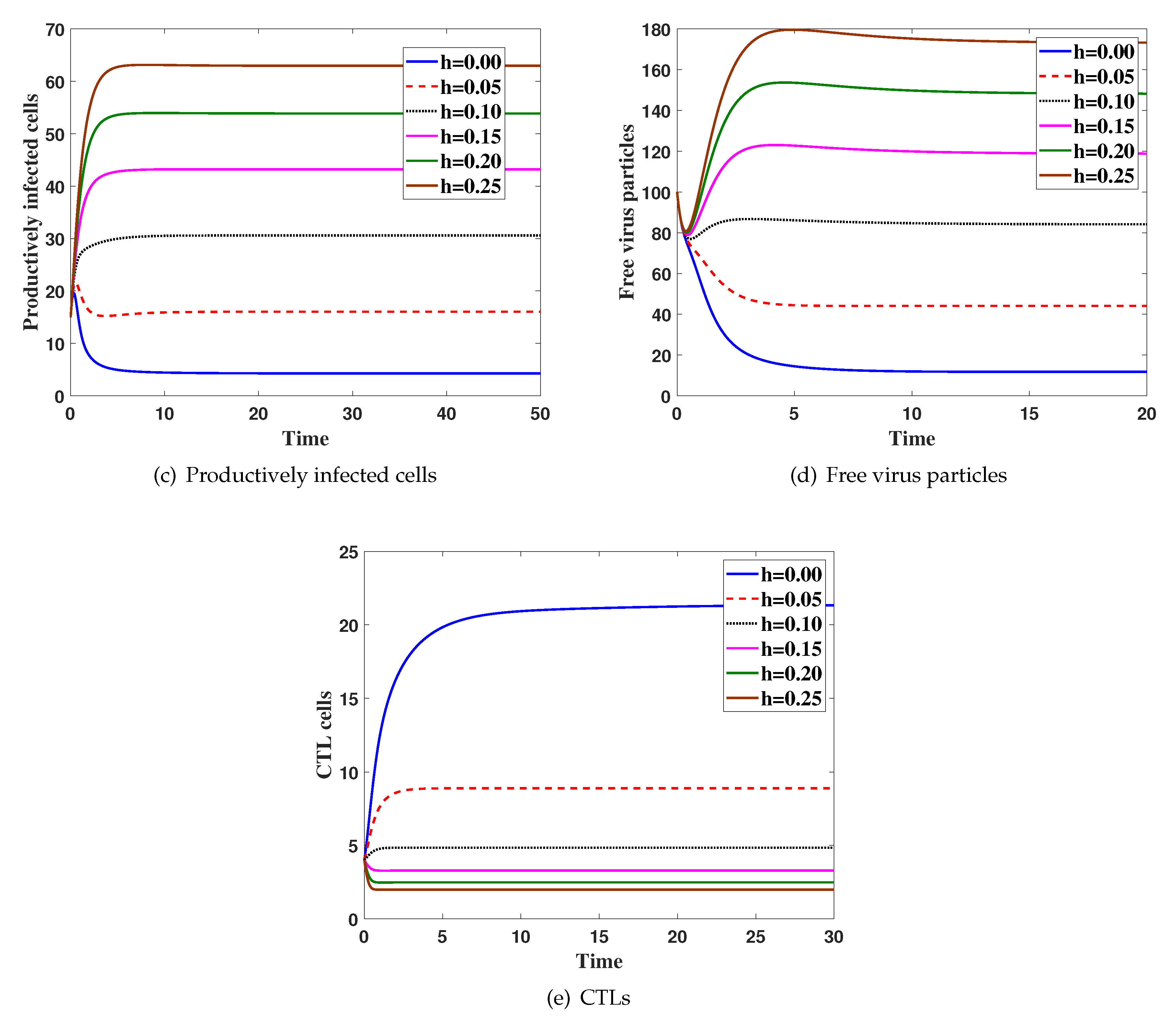
4. Numerical Simulations
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Effects of Latent Infection on the Virus Dynamics
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowak, M.A.; May, R.M. Virus Dynamics: Mathematical Principles of Immunology and Virology; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Perelson, A.S.; Nelson, P.W. Mathematical analysis of HIV-1 dynamics in vivo. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ma, W. Lyapunov functionals for delay differential equations model of viral infections. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2010, 70, 2693–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobeinikov, A. Global properties of basic virus dynamics models. Bull. Math. Biol. 2004, 66, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaiw, A.M. Global properties of a class of HIV models. Nonlinear Anal. 2010, 11, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiw, A.M. Global properties of a class of virus infection models with multitarget cells. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 69, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiw, A.M.; AlShamrani, N.H. Global stability of humoral immunity virus dynamics models with nonlinear infection rate and removal. Nonlinear Anal. 2015, 26, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, X. Dynamic analysis and optimal control for a model of hepatitis C with treatment. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2017, 46, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, H.G.; Li, M.Y. Backward bifurcation in a model for HTLV-I infection of CD4+ T cells. Bull. Math. Biol. 2005, 67, 101–114. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.A.; Bangham, C.R.M. Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses. Science 1996, 272, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Shu, H. Global dynamics of a mathematical model for HTLV-I infection of CD4+ T cells with delayed CTL response. Nonlinear Anal. 2012, 13, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Wang, L.; Watmough, J. Global stability of a nonlinear viral infection model with infinitely distributed intracellular delays and CTL imune responses. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2013, 73, 1280–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoes, R.; Wodarz, D.; Nowak, M.A. Virus dynamics: The effect to target cell limitation and immune responses on virus evolution. J. Theor. Biol. 1998, 191, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnapriya, P.; Pitchaimani, M. Modeling and bifurcation analysis of a viral infection with time delay and immune impairment. Jpn. J. Ind. Appl. Math. 2017, 34, 99–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Shi, X. Analysis of a viral infection model with immune impairment and cure rate. J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Impacts of the cell-free and cell-to-cell infection modes on viral dynamics. J. Dyn. Diff. Equat. 2018, 30, 1817–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, C.; Sattentau, Q. Retroviral spread by induction of virological synapses. Traffic 2004, 5, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, M.; Nikolic, D.S.; Piguet, V. How HIV-1 takes advantage of the cytoskeleton during replication and cell-to-cell transmission. Viruses 2011, 3, 1757–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.M. The role of cell-to-cell transmission in HIV infection. AIDS 1994, 8, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Orenstein, J.; Dimitrov, D.; Martin, M. Cell-to-cell spread of HIV-1 occurs within minutes and may not involve the participation of virus particles. Virology 1992, 186, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwami, S.; Takeuchi, J.S.; Nakaoka, S.; Mammano, F.; Clavel, F.; Inaba, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Misawa, N.; Aihara, K.; Koyanagi, Y.; et al. Cell-to-cell infection by HIV contributes over half of virus infection. Elife 2015, 4, e08150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, A.; Kim, J.T.; Balazs, A.B.; Dekel, E.; Mayo, A.; Milo, R.; Baltimore, D. Cell-to-cell spread of HIV permits ongoing replication despite antiretroviral therapy. Nature 2011, 47, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komarova, N.L.; Anghelina, D.; Voznesensky, I.; Trinite, B.; Levy, D.N.; Wodarz, D. Relative contribution of free-virus and synaptic transmission to the spread of HIV-1 through target cell populations. Biol. Lett. 2012, 9, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, N.L.; Wodarz, D. Virus dynamics in the presence of synaptic transmission. Math. Biosci. 2013, 242, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Culshaw, R.V.; Ruan, S.; Webb, G. A mathematical model of cell-to-cell spread of HIV-1 that includes a time delay. J. Math. Biol. 2003, 46, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lang, J.; Zou, X. Analysis of an age structured HIV infection model with virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmission. Nonlinear Anal. 2017, 34, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-S.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Takeuchi, Y. Stability analysis in delayed within-host viral dynamics with both viral and cellular infections. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2016, 442, 642–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zou, X. Modelling HIV-1 virus dynamics with both virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2014, 74, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Song, X.; Rong, L. Mathematical analysis of an HIV latent infection model including both virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmission. J. Biol. Dyn. 2017, 11, 455–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zou, L.; Ruan, S. Global dynamics of a delayed within-host viral infection model with both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions. Math. Biosci. 2015, 270, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiw, A.M.; Raezah, A.A.; Alofi, B.S. Dynamics of delayed pathogen infection models with pathogenic and cellular infections and immune impairment. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 025323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, T.-W.; Stuyver, L.; Mizell, S.B.; Ehler, L.A.; Mican, J.A.M.; Baseler, M.; Lloyd, A.L.; Nowak, M.A.; Fauci, A.S. Presence of an inducible HIV-1 latent reservoir during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13193–13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, J.K.; Hezareh, M.; Gunthard, H.F.; Havlir, D.V.; Ignacio, C.C.; Spina, C.A.; Richman, D.D. Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science 1997, 278, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.K.; Lunel, S.M.V. Introduction to Functional Differential Equations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Neumann, A. Global stability and periodic solution of the viral dynamics. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2007, 329, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, M.O.; Zubelli, J.P. Global stability for a class of virus models with Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte immune response and antigenic variation. Bull. Math. Biol. 2011, 73, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibelli, L.; Elaiw, A.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Althiabi, A.M. Heterogeneous population dynamics of active particles: Progression, mutations, and selection dynamics. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 2017, 27, 617–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raezah, A.A.; Elaiw, A.M.; Alofi, B.S. Global Properties of Latent Virus Dynamics Models with Immune Impairment and Two Routes of Infection. High-Throughput 2019, 8, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8020016
Raezah AA, Elaiw AM, Alofi BS. Global Properties of Latent Virus Dynamics Models with Immune Impairment and Two Routes of Infection. High-Throughput. 2019; 8(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaezah, Aeshah A., Ahmed M. Elaiw, and Badria S. Alofi. 2019. "Global Properties of Latent Virus Dynamics Models with Immune Impairment and Two Routes of Infection" High-Throughput 8, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8020016
APA StyleRaezah, A. A., Elaiw, A. M., & Alofi, B. S. (2019). Global Properties of Latent Virus Dynamics Models with Immune Impairment and Two Routes of Infection. High-Throughput, 8(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8020016




