RFID Technology Serving Honey Bee Research: A Comprehensive Description of a 32-Antenna System to Study Honey Bee and Queen Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
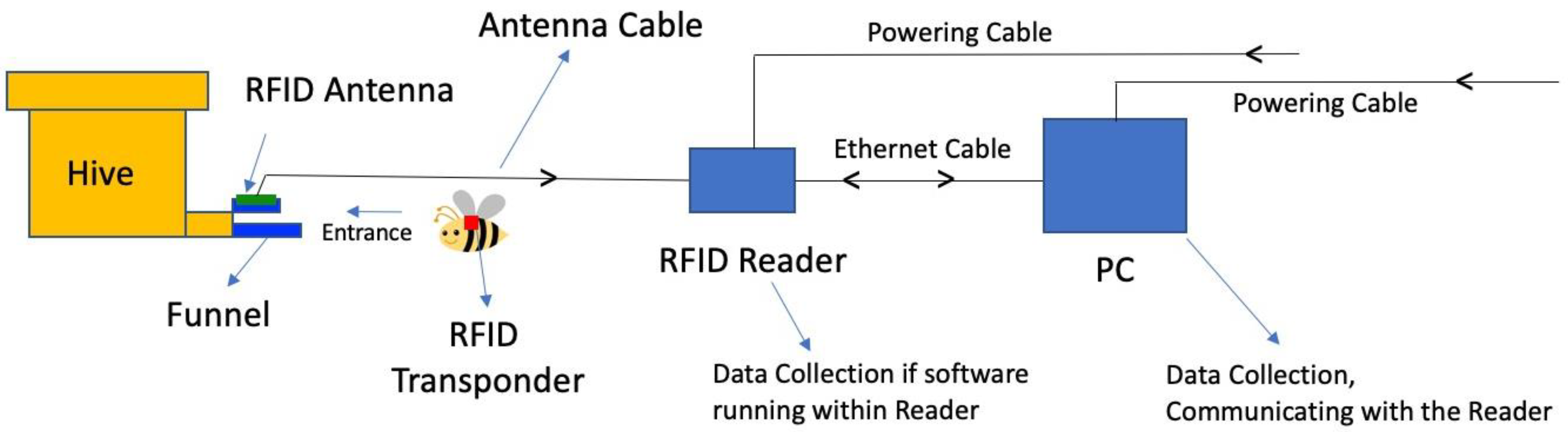
2.1. Electronic Hardware
2.2. Cables and Antennas
2.3. Transponders or Tags
2.4. Modification of Hive’s Entrance
2.5. Power Source and Solar Panel
2.6. Software and Computer
2.7. Data Collection
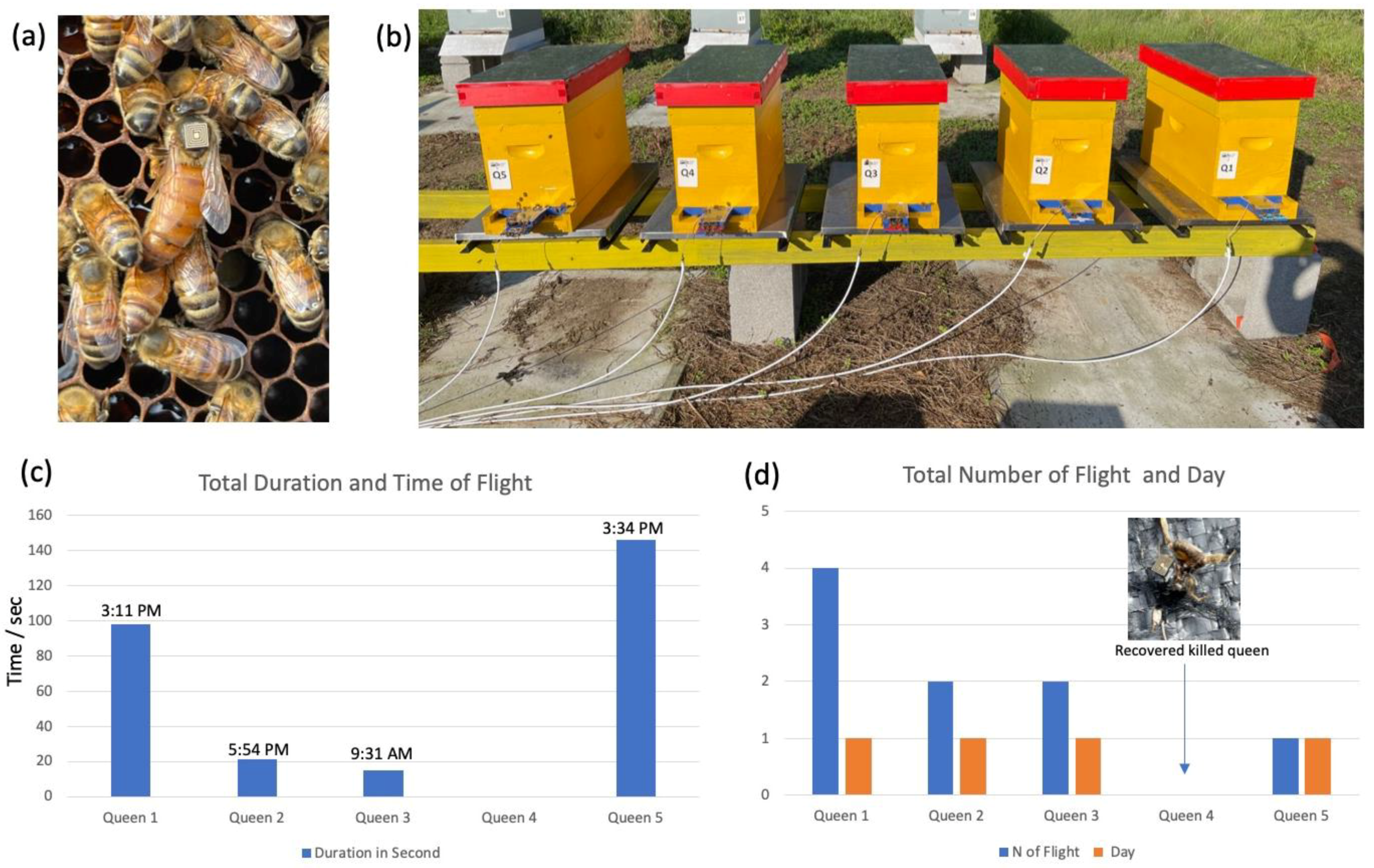
2.8. Queen Nuptial Flight Monitored by RFID
3. Results
3.1. Unit Activation
3.2. Transponder and Antenna
3.3. Transponder Renaming
3.4. Data Collection and Treatment
3.4.1. Using ItemTest Software
3.4.2. Using Speedway Connect Software
3.5. Power Source
3.5.1. Generator Capacity
3.5.2. V Battery with Invertor (600 W)
3.6. Preliminary Data: Queen Nuptial Flight
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, W. Ants can Carry Cheese: Secure and Private RFID-Enabled Third-Party Distribution. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.J.H.; Smith, F.D.; Sullivan, K.M.E.; Franks, N.R. Do ants make direct comparisons? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreau, M.; Arrufat, P.; Latil, G.; Jeanson, R. Use of radio-tagging to map spatial organization and social interactions in insects. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Souza, P.; Marendy, P.; Barbosa, K.; Budi, S.; Hirsch, P.; Nikolic, N.; Gunthorpe, T.; Pessin, G.; Davie, A. Low-Cost Electronic Tagging System for Bee Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Wang, W.; Qin, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Barron, A.B. Assessment of flight activity and homing ability in Asian and European honey bee species, Apis cerana and Apis mellifera, measured with radio frequency tags. Apidologie 2013, 44, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alburaki, M.; Steckel, S.J.; Williams, M.T.; Skinner, J.A.; Tarpy, D.R.; Meikle, W.G.; Adamczyk, J.; Stewart, S.D. Agricultural Landscape and Pesticide Effects on Honey Bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Biological Traits. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikle, W.G.; Corby-Harris, V.; Carroll, M.J.; Weiss, M.; Snyder, L.A.; Meador, C.A.D.; Beren, E.; Brown, N. Exposure to sublethal concentrations of methoxyfenozide disrupts honey bee colony activity and thermoregulation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0204635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meikle, W.G.; Adamczyk, J.J.; Weiss, M.; Gregorc, A.; Johnson, D.R.; Stewart, S.D.; Zawislak, J.; Carroll, M.J.; Lorenz, G.M. Sublethal Effects of Imidacloprid on Honey Bee Colony Growth and Activity at Three Sites in the U.S. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerge, K.; Frigaard, C.E.; Mikkelsen, P.H.; Nielsen, T.H.; Misbih, M.; Kryger, P. A computer vision system to monitor the infestation level of Varroa destructor in a honeybee colony. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 164, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; Cook, S.C.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Posada-Florez, F.; Noble, N.I.I.; Mowery, J.; Gulbronson, C.J.; Bauchan, G.R. Insights into the feeding behaviors and biomechanics of Varroa destructor mites on honey bee pupae using electropenetrography and histology. J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 119, 103950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanesio, D.; Saccani, M.; Maggiora, R.; Laurino, D.; Porporato, M. Design of an harmonic radar for the tracking of the Asian yellow-legged hornet. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2170–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanesio, D.; Saccani, M.; Maggiora, R.; Laurino, D.; Porporato, M. Recent upgrades of the harmonic radar for the tracking of the Asian yellow-legged hornet. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4599–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, S.; McMahon, D.P.; Lim, K.S.; Pull, C.D.; Clark, S.J.; Paxton, R.J.; Osborne, J.L. So near and yet so far: Harmonic radar reveals reduced homing ability of nosema infected honeybees. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riley, J.R.; Smith, A.D.; Reynolds, D.R.; Edwards, A.S.; Osborne, J.L.; Williams, I.H.; Carreck, N.L.; Poppy, G.M. Tracking bees with harmonic radar. Nature 1996, 379, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley-Rogers, G.; Yeates, D.K.; Croft, J.; Cawsey, E.M.; Suter, P.; Webb, J.; Morris, R.G.; Qian, Z.; Rodriguez, E.; Mandecki, W. Ultra-small RFID p-Chips on the heads of entomological pins provide an automatic and durable means to track and label insect specimens. Zootaxa 2012, 3359, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, S.; Bock, F.; Pirk, C.W.; Tautz, J. Automatic life-long monitoring of individual insect behaviour now possible. Zoology 2003, 106, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayup, M.M.; Gartner, P.; Agosto-Rivera, J.L.; Marendy, P.; de Souza, P.; Galindo-Cardona, A. Analysis of Honeybee Drone Activity during the Mating Season in Northwestern Argentina. Insects 2021, 12, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Silva, P.; Hrncir, M.; Guimaraes, J.T.F.; Arruda, H.; Costa, L.; Pessin, G.; Siqueira, P.; de Souza, P.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, L.V. Applications of RFID technology on the study of bees. Insects Sociaux 2010, 66, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Silva, P.; Costa, L.; Campbell, A.J.; Arruda, H.; Contrera, F.A.L.; Teixeira, J.S.G.; Gomes, R.L.C.; Pessin, G.; Pereira, D.S.; de Souza, P.; et al. Radiofrequency identification (RFID) reveals long-distance flight and homing abilities of the stingless bee Melipona fasciculata. Apidologie 2020, 51, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, L.; Nunes-Silva, P.; Galaschi-Teixeira, J.S.; Arruda, H.; Veiga, J.C.; Pessin, G.; de Souza, P.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.L. RFID-tagged amazonian stingless bees confirm that landscape configuration and nest re-establishment time affect homing ability. Insectes Sociaux 2021, 68, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfi, R.L.; Walter, J.A.; Roulston, T.H.; Stuligross, C.; McIntosh, S.; Bauer, L. The influence of conopid flies on bumble bee colony productivity under different food resource conditions. Ecol. Monogr. 2018, 88, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, T.; Meikle, W.G.; Wu, X.; Barron, A.B. Traces of a Neonicotinoid Induce Precocious Foraging and Reduce Foraging Performance in Honey Bees. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8252–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heidinger, I.M.M.; Meixner, M.D.; Berg, S.; Büchler, R. Observation of the mating behavior of honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) queens using radio-frequency identification (RFID): Factors influencing the duration and frequency of nuptial flights. Insects 2014, 5, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Requier, F.; Henry, M.; Decourtye, A. RFID microchips are flying to help the honeybees. Biofutur 2014, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, S.; Yoshiyama, M.; Nikkeshi, A.; Morimoto, N.; Kimura, K. Effect of cold narcosis on foraging behavior of European honey bees (Apis mellifera ligustica) tracked using a radio-frequency identification (RFID) system. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkkä, S.; Viikari, V.; Jaakkola, K. RFID-based butterfly location sensing system. In Proceedings of the 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 2045–2049. [Google Scholar]
- Decourtye, A.; Devillers, J.; Aupinel, P.; Brun, F.; Bagnis, C.; Fourrier, J.; Gauthier, M. Honeybee tracking with microchips: A new methodology to measure the effects of pesticides. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, F.; Gillard, T.; De Souza, P.; Vincent, B.; Budi, S.; Almeida, A.; Pessin, G.; Arruda, H.; Williams, R.N.; Engelke, U.; et al. Addressing RFID misreadings to better infer bee hive activity. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 31935–31949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, T.; Forster, C.C.; Westacott, J.; Wu, X.B.; Meikle, W.G.; Barron, A.B. Effects of late miticide treatments on foraging and colony productivity of European honey bees (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 2021, 52, 474–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.W.; Tautz, J.; Grünewald, B.; Fuchs, S. RFID tracking of sublethal effects of two neonicotinoid insecticides on the foraging behavior of Apis mellifera. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30023. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.J.; Tian, L.Q.; Wu, X.B.; Zeng, Z.J. RFID monitoring indicates honeybees work harder before a rainy day. Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemnitz, S.D. Wildlife Management Techniques Manual, 4th ed.; Wildlife Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 507–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kenward, R. A Manual for Wildlife Radio Tagging, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; London, UK, 2001; p. 311. [Google Scholar]
- Senadeera, P.M.; Dogan, N.S.; Xie, Z.; Savci, H.S.; Kateeb, I.; Ketel, M. Recent trends in RFID transponders. In Proceedings of the IEEE Southeastcon, Jacksonville, FL, USA, 4–7 April 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]



| Item Name | Description | Qt | Provider/Company | Cost/Unit (US $) | Total for the Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Source—Option 1 | |||||
| Solar Panel 150 W | Charge the generator | 1 | 4Patriots.com | 2500 | - |
| Generator 1800 W | Main power provider for use in remote setting | 1 | 4Patriots.com | ||
| Power Source—Option 2 | |||||
| 12 V 100 Ah battery | Rechargeable Sealed Lead Acid | 1 | Mighty Max Battery | 170 | 170 |
| Solar Panel 100 W | Charging the battery | 1 | Renogy | 100 | 100 |
| Power Invertor | 12 V DC Battery Power to AC (600 W) | 1 | Kinverch | 70 | 70 |
| Solar Charger Controller | 12 V/10 Amp | 1 | Renogy | 20 | 20 |
| Beekeeping Equipment | |||||
| Full deep hive with bottom screen board and super (Langstroth) | Protecting and housing all RFID electronics + a Laptop in the field | 1 | Any bee equipment vendors | 80 | 80 |
| Full deep hive with plain bottom board and super (Langstroth) | House and shelter the generator or battery in the field | 1 | Any bee equipment vendors | 80 | 80 |
| Electronics | |||||
| Speedway Reader | R420 UHF RFID Reader (4-Port) | 1 | Impinj | 1500 | 1500 |
| Small 5dBi antenna | Antenna for precision item location/(5 × 6) cm | 32 | Impinj | 25 | 800 |
| Antenna RF cable | Connect Hubs to bee colony (6 m) | 32 | echain Technology | 10 | 320 |
| Adapter Kit (4-Port) | Control up to 4 Antenna Hubs | 1 | echain Technology | 150 | 150 |
| Antenna Hub | Contains 8 ports each | 4 | echain Technology | 800 | 3200 |
| RFID transponder | Tags to fix on bees (2.5 × 2.5 × 0.4) mm | As needed | Hitachi | 1 | 30 |
| Portable Computer | With at least 4 GB of RAM (processing memory) | 1 | Any provider | - | - |
| Software | |||||
| ItemTest Software | Freely available, version: 2.3.0 | 1 | Impinj.com | Free | - |
| MultiReader Gen2 RFID | Freely available, version: 6.6.13 | 1 | Impinj.com | Free | - |
| Speedway Connect SW | Licensed software, version: 6.2.2.240 | 1 | Impinj.com | 350 | 350 |
| Total | 6870 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alburaki, M.; Madella, S.; Corona, M. RFID Technology Serving Honey Bee Research: A Comprehensive Description of a 32-Antenna System to Study Honey Bee and Queen Behavior. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi4040088
Alburaki M, Madella S, Corona M. RFID Technology Serving Honey Bee Research: A Comprehensive Description of a 32-Antenna System to Study Honey Bee and Queen Behavior. Applied System Innovation. 2021; 4(4):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi4040088
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlburaki, Mohamed, Shayne Madella, and Miguel Corona. 2021. "RFID Technology Serving Honey Bee Research: A Comprehensive Description of a 32-Antenna System to Study Honey Bee and Queen Behavior" Applied System Innovation 4, no. 4: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi4040088
APA StyleAlburaki, M., Madella, S., & Corona, M. (2021). RFID Technology Serving Honey Bee Research: A Comprehensive Description of a 32-Antenna System to Study Honey Bee and Queen Behavior. Applied System Innovation, 4(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi4040088







