Response of Organic Matter Decomposition to No-Tillage Adoption Evaluated by the Tea Bag Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sampling
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analyses
2.3. Tea Bag Experiment
2.4. Statistical Analyses
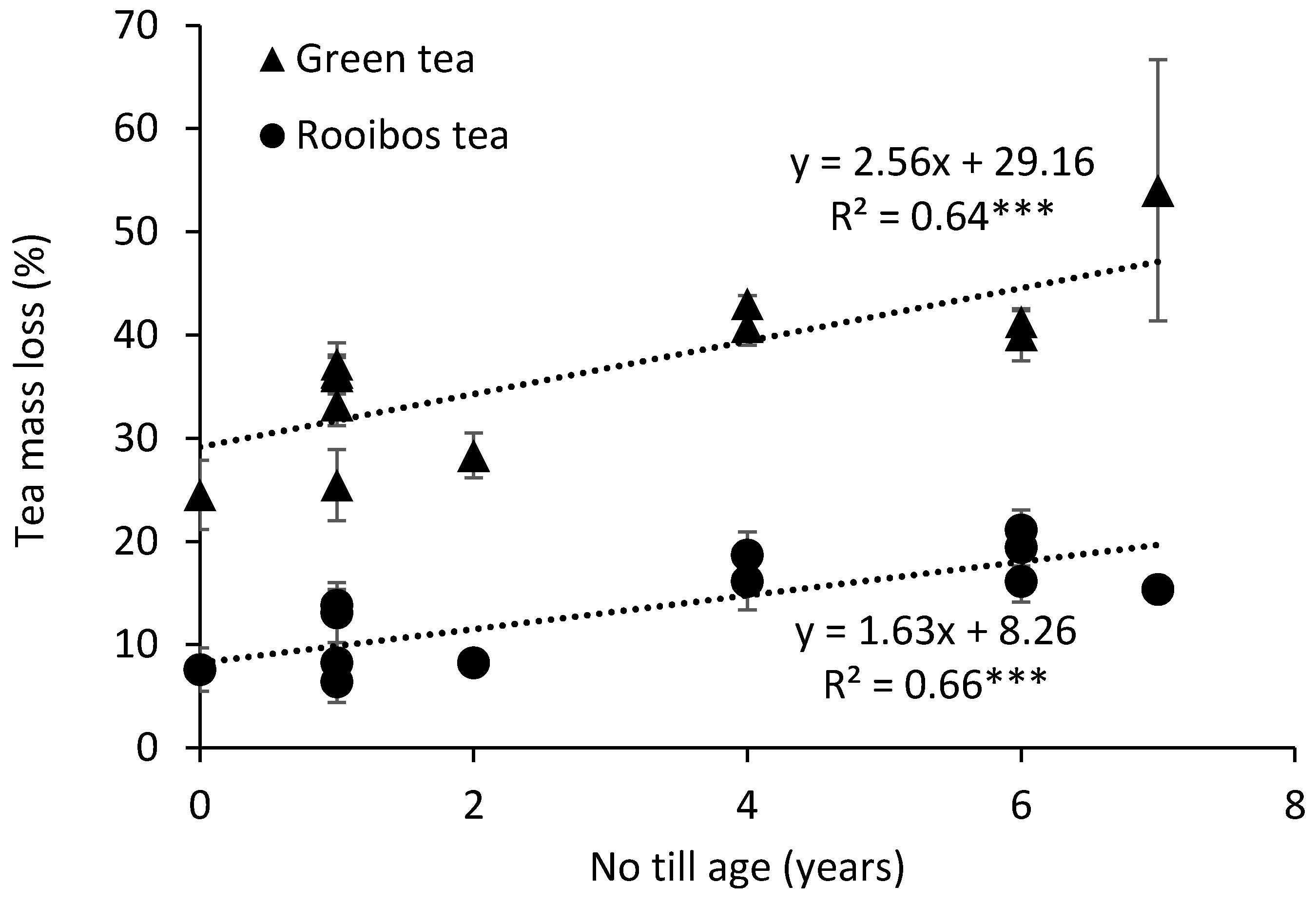
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kertész, Á.; Madarász, B. Conservation Agriculture in Europe. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soane, B.D.; Ball, B.C.; Arvidsson, J.; Basch, G.; Moreno, F.; Roger-Estrade, J. No-till in northern, western and south-western Europe: A review of problems and opportunities for crop production and the environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 118, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmar, R. Adoption of conservation agriculture in Europe: Lessons of the KASSA project. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autret, B.; Mary, B.; Chenu, C.; Balabane, M.; Girardin, C.; Bertrand, M.; Grandeau, G.; Beaudoin, N. Alternative arable cropping systems: A key to increase soil organic carbon storage? Results from a 16 year field experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimassi, B.; Cohan, J.-P.; Labreuche, J.; Mary, B. Changes in soil carbon and nitrogen following tillage conversion in a long-term experiment in Northern France. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 169, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; de Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of agricultural management practices on soil quality: A review of long-term experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Capelle, C.; Schrader, S.; Brunotte, J. Tillage-induced changes in the functional diversity of soil biota—A review with a focus on German data. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 50, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.M.; Mazza, G.; Muschitiello, C.; Castellini, M.; Stellaccia, A.M.; Navarro, A.; Lagomarsino, A.; Vitti, C.; Rossi, R.; Rana, G. Short-term effects of conversion to no-tillage on respiration and chemical-physical properties of the soil: A case study in a wheat cropping system in semi-dry environment. Ital. J. Agrometerol. 2017, 22, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zuber, S.M.; Behnke, G.D.; Nafziger, E.D.; Villamil, M.B. Multivariate assessment of soil quality indicators for crop rotation and tillage in Illinois. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paul Obade, V.; Lal, R. Towards a standard technique for soil quality assessment. Geoderma 2016, 265, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Zeiss, M.R. Soil health and sustainability: Managing the biotic component of soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettieri, M.; Knicker, H.; Murillo, J.M.; Madejón, E.; Hatcher, P.G. Soil organic matter degradation in an agricultural chronosequence under different tillage regimes evaluated by organic matter pools, enzymatic activities and CPMAS 13C NMR. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Mahmood, T.; Islam, K.R. Effect of long term no-till and conventional tillage practices on soil quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 131, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Zsolnay, A.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Past, present and future of soil quality indices: A biological perspective. Geoderma 2008, 147, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, R.; Ochoa, V.; Hinojosa, M.B.; Carreira, J.A. Suitability of enzyme activities for the monitoring of soil quality improvement in organic agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibblewhite, M.; Ritz, K.; Swift, M. Soil health in agricultural systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keuskamp, J.A.; Dingemans, B.J.J.; Lehtinen, T.; Sarneel, J.M.; Hefting, M.M. Tea Bag Index: A novel approach to collect uniform decomposition data across ecosystems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, I.; Kepfer-Rojas, S.; Schmidt, I.K.; Larsen, K.S.; Beier, C.; Berg, B.; Verheyen, K. Early stage litter decomposition across biomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1369–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Z.; Elisabeth, H.; Dombos, M. Tea Bag method: A new possibility to assess impacts of agri-environmental measures on soil functioning. Hung. Agric. Res. 2017, 26, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- International Union of Soil Science. World Reference Base for Soil Resources; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, H.D. Cation exchange capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1, Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 891–901. [Google Scholar]
- Houben, D.; Meunier, C.; Pereira, B.; Sonnet, P. Predicting the degree of phosphorus saturation using the ammonium acetate–EDTA soil test. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, T.; Gustot, Q.; Couder, E.; Houben, D.; Iserentant, A.; Lutts, S. Comparison of EDTA-enhanced phytoextraction and phytostabilisation strategies with Lolium perenne on a heavy metal contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, R. Climate, leaf litter chemistry and leaf litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: A triangular relationship. Oikos 1997, 79, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.M.; Aber, J.D.; Muratore, J.F. Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 1982, 63, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Amatangelo, K.; Dorrepaal, E.; Eviner, V.T.; Godoy, O.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hoorens, B.; Kurokawa, H.; Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; et al. Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, G. Rates of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: Global patterns and controlling factors. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascault, N.; Cécillon, L.; Mathieu, O.; Hénault, C.; Sarr, A.; Lévêque, J.; Farcy, P.; Ranjard, L.; Maron, P.-A. In situ dynamics of microbial communities during decomposition of wheat, rape, and alfalfa residues. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvadet, M.; Chauvat, M.; Fanin, N.; Coulibaly, S.; Bertrand, I. Comparing the effects of litter quantity and quality on soil biota structure and functioning: Application to a cultivated soil in Northern France. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaerts, B.; Mezzalama, M.; Unno, Y.; Sayre, K.D.; Luna-Guido, M.; Vanherck, K.; Dendooven, L.; Deckers, J. Influence of tillage, residue management, and crop rotation on soil microbial biomass and catabolic diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 37, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, S.; Parkinson, R.; Bol, R.; Dixon, L.; Russell, P.; Donovan, S.; Allen, D. Effect of tillage system and straw management on organic matter dynamics. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Minamiya, Y.; Tsuzura, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Yagioka, A.; Kaneko, N. Changes in water stable aggregate and soil carbon accumulation in a no-tillage with weed mulch management site after conversion from conventional management practices. Geoderma 2014, 221–222, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimassi, B.; Mary, B.; Fontaine, S.; Perveen, N.; Revaillot, S.; Cohan, J.-P. Effect of nutrients availability and long-term tillage on priming effect and soil C mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.Y.Y.; Scow, K.M.; Córdova-Kreylos, A.L.; Holmes, W.E.; Six, J. Microbial community composition and carbon cycling within soil microenvironments of conventional, low-input, and organic cropping systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cookson, W.R.; Murphy, D.V.; Roper, M.M. Characterizing the relationships between soil organic matter components and microbial function and composition along a tillage disturbance gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y.; Xu, S.; Deng, G. Changes in soil microbial properties with no-tillage in Chinese cropping systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.P.; Feng, Y.; Githinji, L.; Ankumah, R.; Balkcom, K.S. Impact of No-Tillage and Conventional Tillage Systems on Soil Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, e548620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Clayton, G.W.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Harker, K.N.; Turkington, T.K.; Rice, W.A. Decomposition of crop residues under conventional and zero tillage. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 84, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickings, K.; Grandy, A.S.; Reed, S.; Cleveland, C. Management intensity alters decomposition via biological pathways. Biogeochemistry 2010, 104, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.; Ludwig, B.; Schmidt, J.H.; Bergstermann, A.; Rauber, R.; Joergensen, R.G. Influence of tillage on degradation kinetics using the litterbag method. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainiemi, V.; Arvidsson, J.; Kätterer, T. Short-term organic matter mineralisation following different types of tillage on a Swedish clay soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingery, W.L.; Wood, C.W.; Williams, J.C. Tillage and amendment effects on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization and phosphorus release. Soil Tillage Res. 1996, 37, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oorts, K.; Merckx, R.; Gréhan, E.; Labreuche, J.; Nicolardot, B. Determinants of annual fluxes of CO2 and N2O in long-term no-tillage and conventional tillage systems in northern France. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 95, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucon, M.-P.; Houben, D.; Lambers, H. Plant functional traits: Soil and ecosystem services. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, C.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; DeClerck, F.; Gatere, L.; Grace, P. Conservation agriculture and ecosystem services: An overview. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 187, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | NT Age (Years) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | pH | CEC (cmolc kg−1) | Organic C (%) | Total N (%) | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 17.00 | 72.93 | 10.07 | 7.13 | 10.74 | 11.79 | 0.12 | 9.90 |
| 2 | 1 | 24.14 | 65.63 | 10.23 | 8.37 | 17.10 | 10.77 | 0.12 | 9.26 |
| 3 | 1 | 16.42 | 72.03 | 11.55 | 6.69 | 9.42 | 17.94 | 0.18 | 9.93 |
| 4 | 1 | 23.58 | 52.15 | 24.27 | 8.06 | 15.06 | 16.20 | 0.19 | 8.69 |
| 5 | 1 | 29.10 | 57.31 | 13.60 | 8.13 | 15.68 | 13.49 | 0.14 | 9.49 |
| 6 | 1 | 15.84 | 72.81 | 11.35 | 7.98 | 8.56 | 13.03 | 0.12 | 11.23 |
| 7 | 2 | 18.42 | 72.13 | 9.45 | 7.11 | 11.06 | 10.14 | 0.11 | 9.40 |
| 8 | 4 | 22.41 | 67.24 | 10.35 | 8.07 | 15.60 | 15.91 | 0.14 | 11.09 |
| 9 | 4 | 15.63 | 74.31 | 10.06 | 7.21 | 10.60 | 12.53 | 0.12 | 10.14 |
| 10 | 6 | 25.05 | 64.53 | 10.42 | 8.49 | 16.94 | 12.41 | 0.16 | 8.03 |
| 11 | 6 | 13.95 | 64.09 | 21.96 | 8.40 | 10.28 | 13.82 | 0.15 | 9.22 |
| 12 | 6 | 28.33 | 55.84 | 15.83 | 7.88 | 21.18 | 21.24 | 0.21 | 10.27 |
| 13 | 7 | 18.78 | 73.57 | 7.65 | 7.57 | 12.86 | 14.09 | 0.14 | 10.24 |
| Properties | Green Tea | Rooibos Tea |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrolysable fraction 1 (g g−1) | 0.842 | 0.552 |
| C 1 (%) | 49.055 | 50.511 |
| N 1 (%) | 4.019 | 1.185 |
| Al (mg kg−1) | 1461 ± 21 | 86 ± 1 |
| Ca (mg kg−1) | 5850 ± 64 | 1918 ± 132 |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | 107 ± 4 | 98 ± 3 |
| K (mg kg−1) | 15251 ± 88 | 2799 ± 113 |
| Mg (mg kg−1) | 2108 ± 4 | 1561 ± 48 |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 1030 ± 5 | 53 ± 2 |
| Na (mg kg−1) | 599 ± 51 | 2832 ± 10 |
| P (mg kg−1) | 2781 ± 15 | 425 ± 17 |
| S (mg kg−1) | 1489 ± 20 | 415 ± 14 |
| N | C:N | pH | CEC | Ca | K | Mg | P | GT Mass Loss | RT Mass Loss | NT Age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 0.90 *** | 0.25 | −0.05 | 0.39 | 0.27 | 0.75 ** | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.27 |
| N | −0.19 | 0.10 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.66 * | 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.29 | |
| C/N | −0.30 | −0.26 | −0.31 | 0.14 | −0.33 | −0.06 | 0.02 | −0.22 | −0.05 | ||
| pH | 0.53 | 0.37 | −0.26 | 0.28 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.57 * | 0.30 | |||
| CEC | 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.31 | ||||
| Ca | −0.02 | 0.98 *** | −0.37 | −0.04 | 0.17 | −0.22 | |||||
| K | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.28 | ||||||
| Mg | −0.40 | −0.06 | 0.13 | −0.23 | |||||||
| P | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.50 | ||||||||
| GT mass loss | 0.65 * | 0.80 *** | |||||||||
| RT mass loss | 0.81 *** |
| DF | Sum Sq | F Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green tea | 5 | 0.595 | 10.68 | <0.001 |
| Rooibos tea | 5 | 0.332 | 7.30 | <0.001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houben, D.; Faucon, M.-P.; Mercadal, A.-M. Response of Organic Matter Decomposition to No-Tillage Adoption Evaluated by the Tea Bag Technique. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2030042
Houben D, Faucon M-P, Mercadal A-M. Response of Organic Matter Decomposition to No-Tillage Adoption Evaluated by the Tea Bag Technique. Soil Systems. 2018; 2(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleHouben, David, Michel-Pierre Faucon, and Anne-Maïmiti Mercadal. 2018. "Response of Organic Matter Decomposition to No-Tillage Adoption Evaluated by the Tea Bag Technique" Soil Systems 2, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2030042
APA StyleHouben, D., Faucon, M.-P., & Mercadal, A.-M. (2018). Response of Organic Matter Decomposition to No-Tillage Adoption Evaluated by the Tea Bag Technique. Soil Systems, 2(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2030042







