Salt Content of Dairy Farm Effluents as an Indicator of Salinization Risk to Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
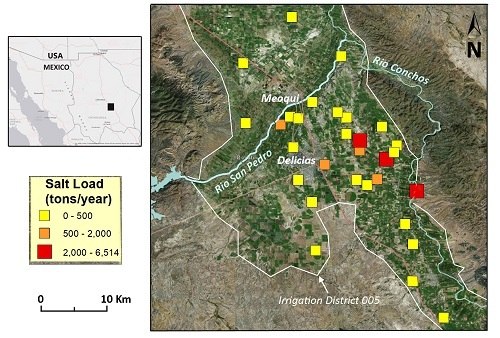
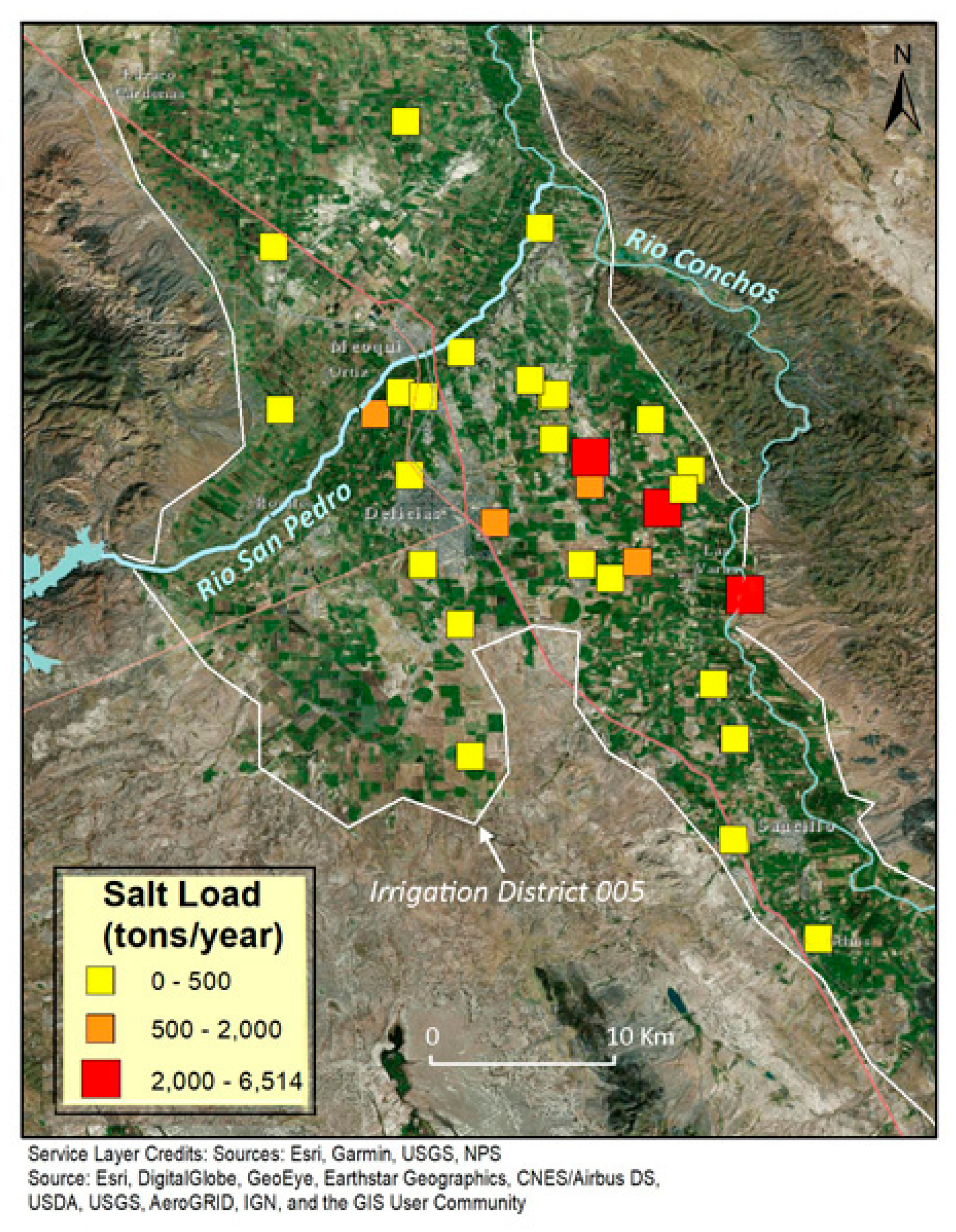
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Salinity, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), and EC
2.4. Waste and Salt Loads
3. Results
3.1. Waste Generation
3.2. Risk of Salinization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barkle, G.F.; Stenger, R.; Singleton, P.L.; Painter, D.J. Effect of regular irrigation with dairy farm effluent on soil organic matter and soil microbial mass. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Agricultural Waste Characteristics. In Agricultural Waste Management Field Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resource Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 4.1–4.14. [Google Scholar]
- Veltman, K.; Rotz, C.A.; Chase, L.; Cooper, J.; Ingraham, P.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Jones, C.D.; Gaillard, R.; Larson, R.A.; Ruark, M.; et al. A quantitative assessment of beneficial Management Practices to reduce carbon and reactive nitrogen footprints and phosphorous losses on dairy farms in the US Greal Lakes region. Agric. Syst. 2018, 166, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Turral, H. Water pollution from agriculture. In More People, More Food, Worse Water? Mateo-Sagasta, J., Marjani Zadeh, S., Turral, H., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and International Water Management Institute: Rome, Italy, 2018; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, J.C. Water Conservation and Use on Dairy and Livestock Farms. New Hampshire Extension. 2008, pp. 1–3. Available online: https://extension.unh.edu/resources/files/Resource000005_Rep4.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- Rengasamy, P. Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilbrook, J.; Roy, S. Salinity tolerance. In Plant Abiotic Stress, 2nd ed.; Jenks, M.A., Hasegawa, P.M., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 133–161. ISBN 978-1-118-41217-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Morin, S.; Barrington, S.; Whalen, J.; Bonnell, R.; Martinez, J. Surface irrigation of dairy farm effluent, Part I: Nutrient and bacterial load. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 95, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nennich, T.D.; Harrison, J.H.; VanWleringen, L.M.; Meyer, D.; Heinrichs, A.J.; Weiss, W.P.; St-Pierre, N.R.; Kincaid, R.L.; Davidson, D.L.; Block, E. Prediction of manure and nutrient excretion from dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Raza Ahmad, H. Spatio-temporal impacts of dairy lagoon water reuse on soil: Heavy metals and salinity. Environ. Sci.-Proc. Impacts 2015, 17, 1731–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawke, R.M.; Summers, S.A. Effects of land application of farm dairy effluent on soil properties: A literature review. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 49, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravva, S.; Sarreal, C. Survival of Salmonella enterica in aerated and nonaerated wastewaters from dairy lagoons. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 11249–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungan, R.S.; McKinney, C.W.; Leytem, A.B. Tracking antibiotic resistance genes in soil irrigated with dairy wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukias, J.; Tanner, C. Ponds for livestock wastes. In Pond Treatment Technology; Shilton, A., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK; International Water Association: London, UK, 2006; pp. 408–429. ISBN 9781843390206. [Google Scholar]
- Wichelns, D.; Quadir, M. Achieving sustainable irrigation requires effective management of salts, soil salinity, and shallow groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 157, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Haynes, R. Origin, nature, and treatment of effluents from dairy and meat processing factories and the effects of their irrigation on the quality of agricultural soils. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 1531–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoda, M.F.; Al-Awadi, S.M. Wastewater management in a dairy farm. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Biagioni, R.N.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Rivas-Lucero, B.A. An overview of nitrate sources and operating processes in arid and semiarid aquifer systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hairston, J.E. Animal Waste Management to Protect Water Quality: Land Application of Animal Wastes. Alabama Cooperative Extension System, ANR-790-4.6.4. 1995, pp. 1–5. Available online: www.aces.edi/pubs/docs/A/ANR-0790/WQ4.6.4.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Albers, J. Salts. In More People, More Food, Worse Water? Mateo-Sagasta, J., Marjani Zadeh, S., Turral, H., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and International Water Management Institute: Rome, Italy, 2018; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Irrigation and Drainage Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1985; pp. 2.1–2.4.7. ISBN 92-5-102263-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, K.C.; Di, H.J.; Anwar, M.R. The “critical” ESP value: Does it change with land application of dairy Factory effluent? N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 46, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Borrego, P. Water quality assessment of the Rio Conchos, Chihuahua, Mexico. Environ. Int. 1999, 25, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Villela, R.; Montero Martínez, M.J.; Santana Sepúlveda, J.S. La Cuenca del río Conchos: Una Mirada Desde las Ciencias Ante el Cambio Climático; Montero, M.J., Ibáñez, O.F., Eds.; Instituto Mexicano de Tecnología del Agua: Jiutepec, Mexico, 2017; pp. 109–156. ISBN 78-607-9368-90-0.
- Rivas-Lucero, B.A.; Segovia-Lerma, A.; Morales-Morales, H.A.; Hermosillo-Nieto, J.G.; Magaña-Magaña, J.E. Plan de Gestión Para el Desarrollo Sostenible de Explotaciones Lecheras de la Cuenca de Delicias; Tecnociencia Chihuahua: Chihuahua, Mexico, 2008; pp. 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Causapé, J.; Quílez, D.; Aragués, R. Assessment of irrigation and environmental quality at the hydrological basin level II. Salt and nitrate loads in irrigation return flows. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 70, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Fenn, L.B.; Swietlik, D. Flow, Salts, and Trace Elements in the Rio Grande: A Review; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Texas Water Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 1995; pp. 1–30.
- Grismer, M.E. Leaching fraction, soil salinity, and drainage efficiency. Calif. Agric. 1990, 44, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kort, W. Climate Change Impacts on Agriculture in the Rio Grande River Basin. Center for Water Policy, University of Wisconsin-Madison. 2013, pp. 1–5. Available online: uwm.edu/centerforwaterpolicy/wp-content/uploads/sites/170/2013/10Rio-Grande_Agriculture_Final.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2018).


| Farm | No. Cows | Wastewater 1000 m3 year−1 | Salt Load, tons year−1 | Ha. Irrigated | Crops | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onsite | Away | |||||
| 1 | 795 | 140.3 | 288.4 | 114 | 80 | Corn, alfalfa, soy beans |
| 2 | 2776 | 489.7 | 584.1 | 8 | 500 | Alfalfa, corn, triticale |
| 3 | 1223 | 215.8 | 199.1 | 9 | 750 | oats, corn |
| 4 | 2067 | 364.7 | 189.8 | 25 | 117 | n/a |
| 5 | 280 | 49.4 | 52.1 | 2 | 13 | Alfalfa, corn |
| 6 | 241 | 42.5 | 31.7 | 10 | 80 | Corn |
| 7 | 239 | 42.2 | 345.1 | 2 | 11 | Alfalfa, corn |
| 8 | 946 | 166.9 | 985.4 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 9 | 705 | 124.4 | 250.0 | 4 | 36 | Corn, pecan |
| 10 | 620 | 109.4 | 201.8 | 5 | 15 | Alfalfa, corn |
| 11 | 20,230 | 3568.9 | 6514.8 | 150 | 350 | Pecan |
| 12 | 2047 | 361.1 | 2691.6 | 2.5 | 350 | Alfalfa, corn, triticale, oats |
| 13 | 907 | 160 | 499.8 | 2.5 | 400 | Alfalfa, corn, triticale, oats |
| 14 | 2513 | 443.3 | 1519.2 | 14 | 181 | Oats, alfalfa, barley |
| 15 | 4162 | 734.2 | 2032.2 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 16 | 620 | 109.4 | 114.6 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 17 | 1265 | 223.2 | 179.4 | 8 | 360 | Wheat, oats, corn, alfalfa |
| 18 | 585 | 103.2 | 93.9 | n/a | 360 | Alfalfa |
| 19 | 330 | 58.2 | 58.7 | 3 | 40 | Alfalfa |
| 20 | 1023 | 180.5 | 272.4 | 8 | 192 | Corn, alfalfa, pecan |
| 21 | 750 | 132.3 | 353.1 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 22 | 106 | 18.7 | 53.1 | n/a | n/a | Alfalfa, corn |
| 23 | 2260 | 398.7 | 580.7 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 24 | 2061 | 363.6 | 898.5 | 8 | n/a | Pecan |
| 25 | 688 | 121.4 | 140.8 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 26 | 720 | 127.0 | 113.0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 27 | 836 | 147.5 | 313.9 | 2 | n/a | n/a |
| 28 | 250 | 44.1 | 50.3 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 29 | 286 | 50.5 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 30 | 267 | 47.1 | n/a | 1 | 4 | n/a |
| 31 | 220 | 38.8 | n/a | 2 | 30 | Alfalfa, corn |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivas Lucero, B.A.; Gutiérrez, M.; Magaña Magaña, J.E.; Márquez Salcido, F.; Márquez Fierro, W. Salt Content of Dairy Farm Effluents as an Indicator of Salinization Risk to Soils. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2040061
Rivas Lucero BA, Gutiérrez M, Magaña Magaña JE, Márquez Salcido F, Márquez Fierro W. Salt Content of Dairy Farm Effluents as an Indicator of Salinization Risk to Soils. Soil Systems. 2018; 2(4):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2040061
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivas Lucero, Bertha A., Mélida Gutiérrez, J. Eduardo Magaña Magaña, Francisco Márquez Salcido, and Walter Márquez Fierro. 2018. "Salt Content of Dairy Farm Effluents as an Indicator of Salinization Risk to Soils" Soil Systems 2, no. 4: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2040061
APA StyleRivas Lucero, B. A., Gutiérrez, M., Magaña Magaña, J. E., Márquez Salcido, F., & Márquez Fierro, W. (2018). Salt Content of Dairy Farm Effluents as an Indicator of Salinization Risk to Soils. Soil Systems, 2(4), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2040061