An Integrated Approach to Remediate Saline Soils and Mining Waste Using Technosols and Pasture Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
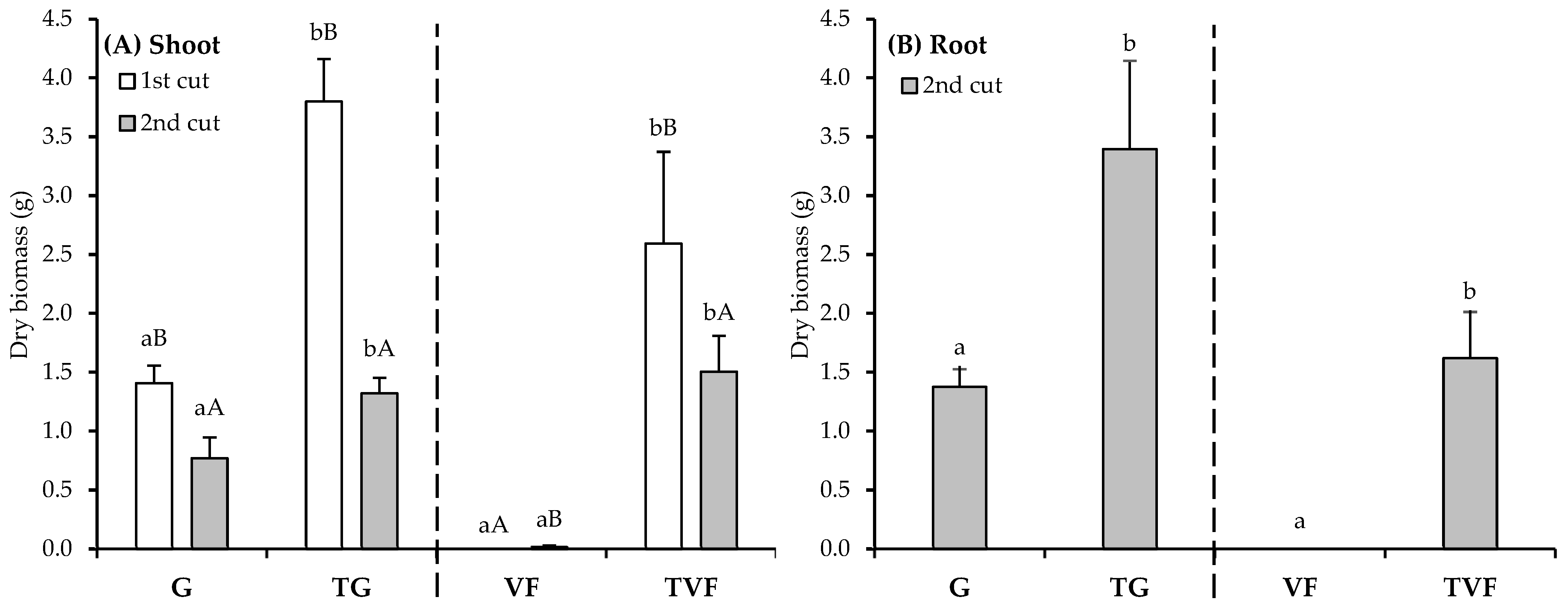
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterisations of Gossan Waste, Salt-Affected Fluvisol, and Technosols
3.2. Biological Characterisations of Gossan Waste, Satl-Affected Fluvisol, and Technosols
3.3. Ecotoxicological Characterisations of Gossan Waste, Salt-Affected Fluvisol, and Technosols
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Elements (mg kg−1) | G | VF |
|---|---|---|
| As | 9126.67 ± 238.77 | 15.6 ± 0.01 |
| Cd | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| Cu | 218.67 ± 5.81 | 27.33 ± 0.69 |
| Hg | 26.67 ± 6.67 | 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Mn | 27.67 ± 1.76 | 598.32 ± 12.27 |
| Ni | 2.77 ± 0.43 | 27.50 ± 0.67 |
| Pb | 29,633.33 ± 554.78 | 37.73 ± 2.19 |
| Zn | 83.33 ± 6.62 | 103.67 ± 1.89 |
References
- Environment & Resources Authority. Soil Degradation Threats. Available online: https://era.org.mt/topic/soil-degradation-threats/ (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Montanarella, L. Trends in Land Degradation in Europe. In Climate and Land Degradation. Environmental Science and Engineering; Sivakumar, M.V.K., Ndiang’ui, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Lima, E.C.; Zhang, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Global Soil Pollution by Toxic Elements: Current Status and Future Perspectives on the Risk Assessment and Remediation Strategies—A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Chu, L.; Lu, H.; Qi, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Kuang, S.; Tang, B.; Wong, V. Towards Sustainable Agriculture for the Salt-Affected Soil. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Hartman, S.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Rulli, M.C.; D’Odorico, P. The Tradeoff between Water Savings and Salinization Prevention in Dryland Irrigation. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 183, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N. Reclamation of Saline and Sodic Soil Through Phytoremediation. In Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Development; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, B.; Fernando, A.L. Aided Phytostabilization of Mine Waste. Bio-Geotechnol. Mine Site Rehabil. 2018, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matanzas, N.; Afif, E.; Díaz, T.E.; Gallego, J.R. Phytoremediation Potential of Native Herbaceous Plant Species Growing on a Paradigmatic Brownfield Site. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; van Zyl, D. Identification of Grass Species Candidates for Phytostabilization and Enhanced Metal(Loid)s Immobilisation Using Cost-Effective Amendments on Sulfidic Mine Tailings. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2023, 37, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.S.; Arán, D.; Abreu, M.M.; de Varennes, A. Engineered Soils Using Amendments for in Situ Rehabilitation of Mine Lands. In Bio-Geotechnologies for Mine Site Rehabilitation; Prasad, M.N.V., Favas, P.J.d.C., Maiti, S.K., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 131–146. ISBN 9780128129876. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Vila, A.; Covelo, E.F.; Forján, R.; Asensio, V. Phytoremediating a Copper Mine Soil with Brassica Juncea L., Compost and Biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11293–11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, T.L.; Sikirica, N.; Mondini, C.; López, G.; Kuikman, P.J.; Holden, N.M. Biochar, Compost and Biochar-Compost Blend as Options to Recover Nutrients and Sequester Carbon. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, F. Recuperación de Suelos Degradados, Reutilización de Residuos y Secuestro de Carbono. Una Alternativa Integral de Mejora de La Calidad Ambiental. Recur. Rurais 2004, 1, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Macías, F.; Macías-García, F.; Nieto, C.; Verde, J.R.; Pérez, C.; Bao, M.; Camps-Arbestain, M. Gestión de Residuos y Cambio Climático. In Gestión de Residuos Orgánicos de uso Agrícola; Mosquera, M.E.L., Osés, M.J.S., Eds.; Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico de la Universidade de Santiago de Compostela: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2011; pp. 11–24. ISBN 9788498878226. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-De-Mora, A.; Madejón, P.; Burgos, P.; Cabrera, F.; Lepp, N.W.; Madejón, E. Phytostabilization of Semiarid Soils Residually Contaminated with Trace Elements Using By-Products: Sustainability and Risks. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3018–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022; ISBN 9798986245119. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, E.S.; Abreu, M.M.; Macías, F. Rehabilitation of Mining Areas through Integrated Biotechnological Approach: Technosols Derived from Organic/Inorganic Wastes and Autochthonous Plant Development. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macías, F.; Bao, M.; Macías-García, F.; Camps Arbestain, M. Valorización Biogeoquímica de Residuos Por Medio de La Elaboración de Tecnosoles Con Diferentes Aplicaciones Ambientales. Agua Residuos 2007, 5, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, E.S.; Abreu, M.M.; Macías, F.; de Varennes, A. Chemical Quality of Leachates and Enzymatic Activities in Technosols with Gossan and Sulfide Wastes from the São Domingos Mine. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1366–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, V.; Flórido, F.G.; Ruiz, F.; Perlatti, F.; Otero, X.L.; Oliveira, D.P.; Ferreira, T.O. The Potential of a Technosol and Tropical Native Trees for Reclamation of Copper-Polluted Soils. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Vila, A.; Asensio, V.; Forján, R.; Covelo, E.F. Assessing the Influence of Technosol and Biochar Amendments Combined with Brassica Juncea L. on the Fractionation of Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a Polluted Mine Soil. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemaninejad, A.; Arteaga, J.; Spiers, G.; Beckett, P.; McGarry, S.; Mykytczuk, N.; Basiliko, N. Blended Pulp Mill, Forest Humus and Mine Residual Material Technosols for Mine Reclamation: A Growth-Chamber Study to Explore the Role of Physiochemical Properties of Substrates and Microbial Inoculation on Plant Growth. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordán, M.M.; García-Sánchez, E.; Almendro-Candel, M.B.; Pardo, F.; Vicente, A.B.; Sanfeliu, T.; Bech, J. Technosols Designed for Rehabilitation of Mining Activities Using Mine Spoils and Biosolids. Ion Mobility and Correlations Using Percolation Columns. Catena 2017, 148, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinhas, A.; Caperta, A.D.; Teixeira, G.; Carvalho, L.; Abreu, M.M. Harnessing Sediments of Coastal Aquaculture Ponds through Technosols Construction for Halophyte Cultivation Using Saline Water Irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinhas, A.; Ferreira, T.C.; Abreu, M.M.; Caperta, A.D. Conservation of a Critically Endangered Endemic Halophyte of West Portugal: A Microcosm Assay to Assess the Potential of Soil Technology for Species Reintroduction. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 604509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinhas, A.; Ferreira, T.C.; Abreu, M.M.; Caperta, A.D. Germination and Sustainable Cultivation of Succulent Halophytes Using Resources from a Degraded Estuarine Area through Soil Technologies Approaches and Saline Irrigation Water. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5029–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Clothier, B.; Bishop, P.; Vázquez, F.M. Reclamation of Salt-Affected Soils Using Pumice and Algal Amendments: Impact on Soil Salinity and the Growth of Lucerne. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Clothier, B.; Bishop, P.; Vázquez, F.M. Use of Either Pumice or Willow-Based Biochar Amendments to Decrease Soil Salinity under Arid Conditions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, V.; Vega, F.A.; Andrade, M.L.; Covelo, E.F. Technosols Made of Wastes to Improve Physico-Chemical Characteristics of a Copper Mine Soil. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Perlatti, F.; Oliveira, D.P.; Ferreira, T.O. Revealing Tropical Technosols as an Alternative for Mine Reclamation and Waste Management. Minerals 2020, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, H.M.; Ferreira, A.D.; Ruiz, F.; Bovi, R.C.; Deng, Y.; de Souza Júnior, V.S.; Otero, X.L.; Bernardino, A.F.; Cooper, M.; Ferreira, T.O. Early Pedogenesis of Anthropogenic Soils Produced by the World’s Largest Mining Disaster, the “Fundão” Dam Collapse, in Southeast Brazil. Catena 2022, 219, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, A.; Mundodi, L.; Sederkenny, A.; Anderson, N.; Missen, J.; Yellishetty, M. From Spoil to Soil: Utilising Waste Materials to Create Soils for Mine Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mine Closure, Brisbane, Australia, 4–6 October 2022; Tibbett, M., Fourie, A.B., Boggs, G., Eds.; Mine Earth: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 1237–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Arán, D.; Santos, E.S.; Abreu, M.M.; Antelo, J.; Macías, F. Use of Combined Tools for Effectiveness Evaluation of Tailings Rehabilitated with Designed Technosol. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1857–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Valero, A.M.; Pérez-López, R.; Matos, J.; Capitán, M.A.; Nieto, J.M.; Sáez, R.; Delgado, J.; Caraballo, M. Potential Environmental Impact at São Domingos Mining District (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Iberian Peninsula): Evidence from a Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quental, L.; Bourguignon, A.; Sousa, A.J.; Batista, M.J.; Brito, M.G.; Tavares, T.; Abreu, M.M.; Vairinho, M.M.; Cottard, F. MINEO Southern Europe Environment Test Site: Contamination Impact Mapping and Modelling: Final Report; MINEO Project-Assessing and Monitoring the Environmental Impact of Mining in Europe Using Advanced Earth Observation Techniques; Information Society Technologies, EU: Luxembourg, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-López, R.; Álvarez-Valero, A.M.; Nieto, J.M.; Sáez, R.; Matos, J.X. Use of Sequential Extraction Procedure for Assessing the Environmental Impact at Regional Scale of the São Domingos Mine (Iberian Pyrite Belt). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3452–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoas, I.; Barral, M.F. Métodos de Análise de Solos. Comunicações Do Instituto de Investigação Científica Tropical. In Série de Ciências Agrárias N.o 10; Instituto de Investigação Científica Tropical: Lisbon, Portugal, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lakanen, E.; Erviö, R. A Comparison of Eight Extractants for the Determination of Plant Available Micronutrients in Soils. Acta Agric. Fenn. 1971, 123, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Activation Laboratories Ltd. Code 6—Total Recoverable Natural Waters with Low TDS (<0.05%), Analysed by ICP-MS. Available online: https://actlabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Actlabs-Schedule-of-Services-Euro-2021.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Activation Laboratories Ltd. Code 6—Overrange Elements in Code 6 MB Reanalyzed by ICP-MS If Required. Available online: https://actlabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Actlabs-Schedule-of-Services-Euro-2021.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Feng, M.H.; Shan, X.Q.; Zhang, S.; Wen, B. A Comparison of the Rhizosphere-Based Method with DTPA, EDTA, CaCl2, and NaNO3 Extraction Methods for Prediction of Bioavailability of Metals in Soil to Barley. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 137, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.Y. Analyse Des Mécanismes de Désagrégation et de La Mobilisation Des Particules de Terre Sous l’action Des Pluies. Ph.D. Thesis, Université d’Orléans, Orléans, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil Enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Mickelson, S.H., Bigham, J.M., Eds.; SSSA Book Series; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. ISBN 9780891188650. [Google Scholar]
- Dotaniya, M.L.; Aparna, K.; Dotaniya, C.K.; Singh, M.; Regar, K.L. Role of Soil Enzymes in Sustainable Crop Production. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology: Production, Applications, and Future Prospects; Kuddus, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 569–589. ISBN 9780128132807. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Maiti, S.K. Soil Dehydrogenase Enzyme Activity in Natural and Mine Soil—A Review. Middle-East. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 13, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Glucosidases and Galactosidases in Soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Phosphatases in Soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1977, 9, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-Term Assay of Soil Urease Activity Using Colorimetric Determination of Ammonium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Irfan, M.; Han, M.; Huang, Y.; Han, X.; Yang, Q. Production, Purification and Characterization of Novel Beta Glucosidase from Newly Isolated Penicillium Simplicissimum h-11 in Submerged Fermentation. EXCLI J. 2013, 12, 528–540. [Google Scholar]
- Krämer, S.; Green, D.M. Acid and Alkaline Phosphatase Dynamics and Their Relationship to Soil Microclimate in a Semiarid Woodland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yang, L. Soil Enzymatic Activity and Growth of Rice and Barley as Influenced by Organic Manure in an Anthropogenic Soil. Geoderma 2003, 115, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jecu, L. Solid State Fermentation of Agricultural Wastes for Endoglucanase Production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2000, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, C.F.A.; Burns, R.G. Activity, Origins and Location of Cellulases in a Silt Loam Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1987, 5, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J.N.; Butler, J.H.A. Short-Term Assays of Soil Proteolytic Enzyme Activities Using Proteins and Dipeptide Derivatives as Substrates. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The Biological Activities of β-Glucosidase, Phosphatase and Urease as Soil Quality Indicators: A Review. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC 17025; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Veloso, A.; Sempiterno, C.; Calouro, F.; Rebelo, F.; Pedra, F.; Castro, I.V.; da Conceição Gonçalves, M.; da Encarnação Marcelo, M.; Pereira, P.; Fareleira, P.; et al. Manual de Fertilização Das Culturas, 3rd ed.; Calouro, F., Ed.; INIAV (Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, I.P.): Lisbon, Portugal, 2022; ISBN 978-972-579-063-2. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Garrido, A.; Reyes-Martín, M.P.; Vidigal, P.; Abreu, M.M. A Green Solution for the Rehabilitation of Marginal Lands: The Case of Lablab Purpureus (L.) Sweet Grown in Technosols. Plants 2023, 12, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APA (Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente). Solos Contaminados—Guia Técnico—Valores de Referência Para Solo. Revisão 3—Setembro de 2022; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Lisbon, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- CCME (Canada Council of Ministers of the Environment). Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health: Summary Tables (Updated September, 2007); Canada Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran; Bharti, R.; Sharma, R. Effect of Heavy Metals: An Overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Assessment of Heavy Metal Release into the Soil after Mine Clearing in Halgurd-Sakran National Park, Kurdistan, Iraq. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madejón, P.; Caro-Moreno, D.; Navarro-Fernández, C.M.; Rossini-Oliva, S.; Marañón, T. Rehabilitation of Waste Rock Piles: Impact of Acid Drainage on Potential Toxicity by Trace Elements in Plants and Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780133254488. [Google Scholar]
- Oster, J.D. Sodic Soil Reclamation. In Towards the Rational Use of High Salinity Tolerant Plants. Tasks for Vegetation Science; Lieth, H., Al Masoom, A.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 27, pp. 485–490. ISBN 978-94-011-1858-3. [Google Scholar]
- Macía, P.; Fernández-Costas, C.; Rodríguez, E.; Sieiro, P.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.A. Technosols as a Novel Valorization Strategy for an Ecological Management of Dredged Marine Sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Torre, S.; Garcia-Caparrós, P.; Nogales, A.; Abreu, M.M.; Santos, E.; Cortinhas, A.L.; Caperta, A.D. Sustainable Agricultural Management of Saline Soils in Arid and Semi-Arid Mediterranean Regions through Halophytes, Microbial and Soil-Based Technologies. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 212, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781420093704. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils. Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9789400744691. [Google Scholar]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Gomez-Eyles, J.L. Effects of Biochar and Greenwaste Compost Amendments on Mobility, Bioavailability and Toxicity of Inorganic and Organic Contaminants in a Multi-Element Polluted Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradelo, R.; Villada, A.; Barral, M.T. Reduction of the Short-Term Availability of Copper, Lead and Zinc in a Contaminated Soil Amended with Municipal Solid Waste Compost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. Occurrence of Arsenic Contamination in Canada: Sources, Behavior and Distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-López, M.; Vela-Cano, M.; Correa-Galeote, D.; Martín-Peinado, F.; Marínez Garzón, F.J.; Pozo, C.; González-López, J.; Sierra Aragón, M. Soil Remediation Approach and Bacterial Community Structure in a Long-Term Contaminated Soil by a Mining Spill (Aznalcóllar, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Garrido, A.; Romero-Freire, A.; García-Carmona, M.; Martín Peinado, F.J.; Sierra Aragón, M.; Martínez Garzón, F.J. Arsenic Fixation in Polluted Soils by Peat Applications. Minerals 2020, 10, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Kumpiene, J.; Park, J.; Makino, T.; Kirkham, M.B.; Scheckel, K. Remediation of Heavy Metal(Loid)s Contaminated Soils—To Mobilize or to Immobilize? J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Salgado, M.M.; Gutiérrez-Romero, V.; Jannsens, M.; Ortega-Blu, R. Biological Soil Quality Indicators: A Review. In Current Research, Technology and Education Topics in Applied Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Spain, 2010; pp. 319–328. ISBN 9788461461950. [Google Scholar]
- Kandeler, E.; Kampichler, C.; Horak, O. Influence of Heavy Metals on the Functional Diversity of Soil Microbial Communities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1996, 23, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, H.; Meli, P.; Butler, B.; Paolini, J.; Matus, F.; Merino, C.; Cornejo, P.; Kuzyakov, Y. Meta-Analysis of Heavy Metal Effects on Soil Enzyme Activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Garrido, A.; Romero-Freire, A.; Paniagua-López, M.; Martínez-Garzón, F.J.; Martín-Peinado, F.J.; Sierra-Aragón, M. Technosols Derived from Mining, Urban, and Agro-Industrial Waste for the Remediation of Metal(Loid)-Polluted Soils: A Microcosm Assay. Toxics 2023, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Mineral Tolerance of Animals: Second Revised Edition, 2005; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 0309096545. [Google Scholar]
- de Varennes, A. Produtividade Dos Solos e Ambiente; Escolar Editora: Lisbon, Portugal, 2003; ISBN 978-972-592-156-2. [Google Scholar]
- Balat, M.; Ayar, G. Biomass Energy in the World, Use of Biomass and Potential Trends. Energy Sources 2005, 27, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physicochemical Characteristics | G | TG | VF | TVF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |
| pH (H2O) | 3.80 ± 0.04 aA | 4.08 ± 0.09 aB | 6.53 ± 0.23 b | 6.70 ± 0.13 b | 8.26 ± 0.07 A | 8.52 ± 0.05 B | 8.46 ± 0.13 A | 8.89 ± 0.11 B |
| EC (dS m−1) | 0.70 ± 0.17 aB | 0.12 ± 0.02 aA | 1.33 ± 0.30 bB | 0.32 ± 0.14 bA | 11.20 ± 1.52 bB | 0.83 ± 0.11 A | 3.96 ± 1.20 aB | 0.64 ± 0.45 A |
| Corg (g kg−1) | 4.22 ± 0.74 a | 5.41 ± 1.77 a | 9.23 ± 1.24 bA | 14.18 ± 2.50 bB | 18.87 ± 1.36 a | 19.43 ± 0.72 a | 28.15 ± 0.67 b | 28.13 ± 1.30 b |
| NT (g kg−1) | 0.16 ± 0.01 aA | 0.27 ± 0.02 aB | 1.18 ± 0.20 bB | 0.70 ± 0.22 bA | 1.65 ± 0.05 aA | 1.81 ± 0.10 aB | 2.73 ± 0.17 b | 2.48 ± 0.13 b |
| PExt (mg kg−1) | 0.56 ± 0.68 a | bdl a | 55.97 ± 8.02 b | 46.72 ± 9.94 b | 92.69 ± 2.19 a | 98.04 ± 2.77 a | 424.29 ± 27.35 b | 425.33 ± 43.02 b |
| KExt (mg kg−1) | 37.49 ± 17.30 a | 22.95 ± 6.21 | 153.81 ± 25.13 bB | 23.63 ± 2.50 A | 799.29 ± 29.89 a | 811.77 ± 24.34 | 942.85 ± 38.58 bB | 844.44 ± 54.21 A |
| Elements (g kg−1) | G | TG | VF | TVF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |
| Ca | 0.38 ± 0.05 aB | 0.06 ± 0.02 aA | 2.25 ± 0.69 bB | 1.04 ± 0.54 bA | 4.04 ± 0.29 a | 3.23 ± 0.55 a | 8.61 ± 0.84 b | 7.85 ± 2.90 b |
| Mg | 0.03 ± 0.01 aB | 0.01 ± 0.01 aA | 0.07 ± 0.01 bB | 0.02 ± 0.01 bA | 2.25 ± 0.28 bB | 1.57 ± 0.07 A | 1.66 ± 0.09 aB | 1.49 ± 0.06 A |
| Na | 0.11 ± 0.04 B | 0.05 ± 0.01 A | 0.24 ± 0.17 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 11.15 ± 2.64 bB | 5.36 ± 1.15 bA | 4.44 ± 2.08 aB | 2.25 ± 0.42 aA |
| K | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.02 bB | 0.02 ± 0.00 A | 0.78 ± 0.03 a | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 0.99 ± 0.07 bB | 0.82 ± 0.05 A |
| Cu | 0.002 ± 0.001 aA | 0.006 ± 0.001 aB | 0.006 ± 0.001 bA | 0.009 ± 0.001 bB | 0.007 ± 0.000 aA | 0.011 ± 0.001 aB | 0.010 ± 0.000 bA | 0.014 ± 0.001 bB |
| Fe | 0.029 ± 0.002 aA | 0.044 ± 0.006 aB | 0.145 ± 0.015 bB | 0.125 ± 0.006 bA | 0.148 ± 0.003 aA | 0.175 ± 0.022 aB | 0.566 ± 0.025 bB | 0.495 ± 0.034 bA |
| Mn | 0.001 ± 0.001 a | 0.000 ± 0.000 a | 0.003 ± 0.001 bB | 0.001 ± 0.001 bA | 0.288 ± 0.009 b | 0.282 ± 0.017 b | 0.242 ± 0.006 aB | 0.221 ± 0.009 aA |
| Zn | 0.003 ± 0.001 a | 0.003 ± 0.001 a | 0.006 ± 0.001 b | 0.006 ± 0.001 b | 0.011 ± 0.001 aA | 0.014 ± 0.002 aB | 0.018 ± 0.001 bA | 0.020 ± 0.001 bB |
| Elements (mg kg−1) | G | TG | VF | TVF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |
| As | 0.15 ± 0.17 a | bdl | 3.89 ± 0.16 b | 4.10 ± 0.24 | 0.15 ± 0.17 aA | 0.45 ± 0.06 B | 0.48 ± 0.05 b | 0.45 ± 0.13 |
| Cu | 1.05 ± 0.13 | 0.90 ± 0.07 b | 0.76 ± 0.29 | 0.71 ± 0.02 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
| Ni | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.04 bB | 0.11 ± 0.02 A | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| Pb | 5.48 ± 1.27 b | 6.01 ± 0.59 b | 0.95 ± 0.95 a | 0.88 ± 0.29 a | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| Sb | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.12 | 0.18 ± 0.13 | bdl | bdl |
| S | 647.56 ± 13.26 B | 162.08 ± 19.18 A | 907.58 ± 214.50 B | 197.21 ± 69.89 A | 792.24 ± 322.77 B | 239.53 ± 53.58 bA | 428.45 ± 191.97 B | 132.11 ± 35.52 aA |
| Zn | 3.05 ± 0.52 B | 1.94 ± 0.21 aA | 3.70 ± 1.07 | 3.80 ± 0.23 b | 0.49 ± 0.08 b | 0.56 ± 0.04 b | 0.36 ± 0.06 a | 0.35 ± 0.05 a |
| Aggregates’ Distribution (%) | G | TG | VF | TVF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >2 mm | 34.53 ± 5.44 a | 67.98 ± 3.50 b | 73.76 ± 10.43 a | 93.56 ± 0.50 b |
| 1–2 mm | 15.05 ± 2.91 b | 7.69 ± 1.35 a | 10.01 ± 4.61 b | 1.04 ± 0.29 a |
| 0.5–1 mm | 15.19 ± 1.20 b | 7.78 ± 0.93 a | 6.81 ± 3.41 b | 0.68 ± 0.23 a |
| 0.2–0.5 mm | 13.32 ± 1.84 b | 6.56 ± 1.68 a | 3.94 ± 2.01 b | 0.41 ± 0.12 a |
| 0.1–0.2 mm | 10.79 ± 1.25 b | 5.15 ± 1.15 a | 1.84 ± 0.87 b | 0.20 ± 0.04 a |
| 0.05–0.1 mm | 5.78 ± 0.62 b | 2.56 ± 0.19 a | 0.50 ± 0.23 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| <0.05 mm | 5.34 ± 1.09 b | 2.29 ± 0.55 a | 3.15 ± 0.83 | 4.07 ± 0.19 |
| Elements | G | TG | VF | TVF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Cut | 2nd Cut | 1st Cut | 2nd Cut | 1st Cut | 2nd Cut | 1st Cut | 2nd Cut | |
| As (mg kg−1) | 62.55 ± 27.74 b | 78.33 ± 26.22 b | 16.07 ± 4.12 a | 17.65 ± 3.92 a | - | - | bdl | bdl |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 25.12 ± 7.57 bA | 57.09 ± 8.02 B | 15.79 ± 2.55 aA | 55.04 ± 1.32 B | - | - | 46.74 ± 16.56 | 49.51 ± 6.31 |
| Ni (mg kg−1) | 10.63 ± 4.45 bB | 6.20 ± 0.32 bA | 4.15 ± 0.58 a | 4.44 ± 0.39 a | - | - | 5.00 ± 1.37 | 3.80 ± 0.67 |
| Pb (mg kg−1) | 160.39 ± 67.66 b | 216.52 ± 71.06 b | 27.99 ± 9.17 a | 40.50 ± 10.90 a | - | - | 0.98 ± 1.13 | 1.93 ± 2.23 |
| Sb (mg kg−1) | 2.78 ± 0.98 | 1.89 ± 1.52 | bdl | bdl | - | - | bdl | bdl |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 46.75 ± 6.15 A | 65.00 ± 4.39 aB | 72.72 ± 27.08 | 85.82 ± 1.35 b | - | - | 56.00 ± 7.59 | 59.37 ± 3.48 |
| Ca (g kg−1) | 5.95 ± 0.74 aB | 4.43 ± 1.01 aA | 14.43 ± 1.70 b | 12.84 ± 0.94 b | - | - | 3.59 ± 0.50 | 3.99 ± 0.72 |
| Co (mg kg−1) | 0.55 ± 0.22 b | 0.48 ± 0.10 | 0.09 ± 0.18 a | bdl | - | - | bdl | bdl |
| Fe (g kg−1) | 1.31 ± 0.46 | 1.25 ± 0.34 b | 1.34 ± 1.86 | 0.49 ± 0.24 a | - | - | 0.37 ± 0.41 | 0.50 ± 0.34 |
| K (g kg−1) | 15.29 ± 2.98 a | 12.67 ± 2.08 a | 26.51 ± 2.29 bB | 21.47 ± 2.10 bA | - | - | 33.29 ± 2.94 B | 24.97 ± 4.76 A |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 57.29 ± 4.96 a | 58.78 ± 14.24 a | 100.48 ± 22.03 bA | 207.89 ± 77.50 bB | - | - | 25.50 ± 5.15 | 35.97 ± 5.83 |
| Mg (g kg−1) | 1.95 ± 0.13 aB | 1.48 ± 0.38 aA | 3.65 ± 0.52 b | 3.47 ± 0.23 a | - | - | 3.06 ± 0.21 | 3.20 ± 0.28 |
| Mo (mg kg−1) | 4.56 ± 6.56 | bdl | 3.30 ± 1.43 A | 6.66 ± 1.38 B | - | - | 3.54 ± 0.79 | 3.31 ± 0.11 |
| Na (g kg−1) | 6.16 ± 1.03 A | 9.78 ± 0.48 B | 9.19 ± 3.62 | 7.31 ± 2.84 | - | - | 26.86 ± 2.91 | 24.54 ± 3.44 |
| P (g kg−1) | 3.12 ± 0.47 a | 2.74 ± 0.14 a | 5.29 ± 0.64 b | 5.76 ± 0.17 b | - | - | 6.76 ± 0.83 | 7.26 ± 0.55 |
| S (g kg−1) | 9.61 ± 1.34 b | 8.26 ± 1.03 | 7.90 ± 0.95 a | 8.29 ± 2.16 | - | - | 3.39 ± 0.05 | 3.76 ± 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilar-Garrido, A.; Vidigal, P.; Caperta, A.D.; Abreu, M.M. An Integrated Approach to Remediate Saline Soils and Mining Waste Using Technosols and Pasture Development. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040103
Aguilar-Garrido A, Vidigal P, Caperta AD, Abreu MM. An Integrated Approach to Remediate Saline Soils and Mining Waste Using Technosols and Pasture Development. Soil Systems. 2024; 8(4):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040103
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilar-Garrido, Antonio, Patrícia Vidigal, Ana Delaunay Caperta, and Maria Manuela Abreu. 2024. "An Integrated Approach to Remediate Saline Soils and Mining Waste Using Technosols and Pasture Development" Soil Systems 8, no. 4: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040103
APA StyleAguilar-Garrido, A., Vidigal, P., Caperta, A. D., & Abreu, M. M. (2024). An Integrated Approach to Remediate Saline Soils and Mining Waste Using Technosols and Pasture Development. Soil Systems, 8(4), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040103








