In Situ Study of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-MoSx Nanohybrids as Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of GOQD-MoSx Nanohybrids
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. Operando X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) Measurements
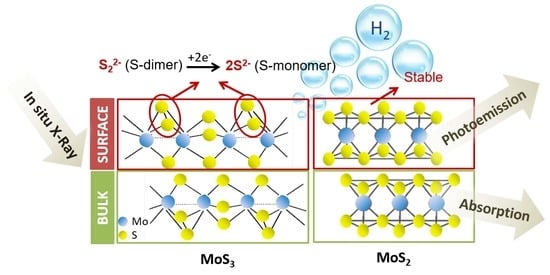
2.4. In Line Photoemission and Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helm, M.L.; Stewart, M.P.; Bullock, R.M.; DuBois, M.R.; DuBois, D.L. A Synthetic Nickel Electrocatalyst with a Turnover Frequency above 100,000 s−1 for H2 Production. Science 2011, 333, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walter, M.G.; Warren, E.L.; McKone, J.R.; Boettcher, S.W.; Mi, Q.X.; Santori, E.A.; Lewis, N.S. Solar Water Splitting Cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.D.; Le Goff, A.; Jousselme, H.J.B.; Guillet, N.; Palacin, S.; Dau, H.; Fontecave, M.; Artero, V. Noncovalent Modification of Carbon Nanotubes with Pyrene-Functionalized Nickel Complexes: Carbon Monoxide Tolerant Catalysts for Hydrogen Evolution and Uptake. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, T.F.; Jorgensen, K.P.; Bonde, J.; Nielsen, J.H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Identification of Active Edge Sites for Electrochemical H2 Evolution from MoS2 Nanocatalysts. Science 2007, 317, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merki, D.; Hu, X.L. Recent developments of molybdenum and tungsten sulfides as hydrogen evolution catalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3878–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Longo, A.; Dzade, N.Y.; Sharma, A.; Hendrix, M.M.R.M.; Bol, A.A.; de Leeuw, N.H.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Hofmann, J.P. The Origin of High Activity of Amorphous MoS2 in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 4383–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez Casalongue, H.G.; Benck, J.D.; Tsai, C.; Karlsson, R.K.B.; Kaya, S.; Ng, M.L.; Pettersson, L.G.M.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Nørskov, J.K.; Ogasawara, H.; et al. Operando characterization of an amorphous molybdenum sulphide nanoparticle catalyst during hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 29252–29259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle-Kaiser, B.; Merki, D.; Vrubel, H.; Gul, S.; Yachandra, V.K.; Hu, X.; Yano, J. Evidence from in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy for the involvement of terminal disulfide in the reduction of protons by an amorphous molybdenum sulfide electrocatalyt. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, P.D.; Tran, P.; Orio, T.; Torelli, M.S.; Truong, Q.D.; Nayuki, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Chiam, S.Y.; Yi, R.; Honma, I.; et al. Coordination polymer structure and revisited hydrogen evolution catalytic mechanism for amorphous molybdenum sulphide. Natur. Mater. 2016, 15, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Nielsen, R.J.; Goddard, W.A.; Soria, M.P. The Reaction Mechanism with Free Energy Barriers for Electrochemical Dihydrogen Evolution on MoS2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6692–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ting, L.R.L.; Deng, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Peterson, A.A.; Yeo, B.S. Catalytic Activities of Sulfur Atoms in Amorphous Molybdenum Sulfide for the Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xie, J.; Zhan, J.G.; Li, S.; Grote, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Lei, Y.; Pan, B.; et al. Controllable Disorder Engineering in Oxygen-Incorporated MoS2 Ultrathin Nanosheets for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17881–17888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, B.; Jung, G.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Baek, D.S.; Sa, Y.J.; Ban, H.W.; Son, J.S.; Park, K.; Kwak, S.K.; Joo, S.H. Monomeric MoS42–-Derived Polymeric Chains with Active Molecular Units for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, A.M.; Richardson, P.W.; Price, S.W.T.; Chouchelamane, G.; Cavillo, L.; Hendra, P.J.; Toney, M.F.; Russell, A.E. Inhibitive effect of Pt on Pd-hydride formation of Pd@Pt core-shell electrocatalysts: An in situ EXAFS and XRD study. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 262, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M.J. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. Synchrotron Rad. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newville, M. EXAFS analysis using FEFF and FEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2001, 8, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hibble, S.J.; Rice, D.A.; Pickup, D.M.; Beer, M.P. Mo K-edge EXAFS and S K-edge absorption studies of the amorphous molybdenum sulphides MoS4.7, MoS3, and MoS3·nH2O (n~2). Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 5109–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, R.I.; Dent, A.J.; Hibble, S.J. In situ investigation of the thermal decomposition of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate using combined time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikin, D.A.; Stankovich, S.; Zimney, E.J.; Piner, R.D.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Evmenenko, G.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper. Nature 2007, 448, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C.C.R.; Tay, B.K.; Edwin, T.H.T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From Bulk to Monolayer MoS2: Evolution of Raman Scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous Lattice Vibrations of Singleand Few-Layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Xiao, F.-X.; Yang, H.B.; Khoo, S.Y.; Chen, J.; Fan, Z.; Hsu, Y.-Y.; Chen, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B. Hierarchical Ni-Mo-S nanosheets on carbon fiber cloth: A flexible electrode for efficient hydrogen generation in neutral electrolyte. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Qiao, X.-F.; Shi, W.; Wu, J.-B.; Jiang, D.-S.; Tan, P.-H. Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2757–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.H.; Chan, S.S. Infrared and Raman studies of amorphous MoS3, and poorly crystalline MoS2. J. Catal. 1981, 72, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourisseau, C.; Gorochov, O.; Schleich, D.M. Comparative IR and Raman studies of various amorphous MoS3 and LixMoS3 phases. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1989, B3, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xia, B.; Ge, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wang, X. Ultrathin MoS2 nanoplates with rich active sites as highly efficient catalyst for hydrogen evolution. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12794–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Zhang, W.; Wei, K.-H.; Li, L.-J. Highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen production by MoSx grown on graphene-protected 3D Ni foams. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.Y.; Park, S.-K.; Chung, Y.-H.; Yu, S.-H.; Lim, D.-H.; Jung, N.; Ham, H.C.; Park, H.-Y.; Piao, Y.; Yoo, S.J.; et al. Edge-exposed MoS2 nano-assembled structures as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, G.; Yang, G.; Peng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, J.-J. Focusing on luminescent graphene quantum dots: Current status and future perspectives. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4015–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Liao, H.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Sun, L.; et al. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties. Natur. Commun. 2014, 5, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vrubel, H.; Merki, D.; Hu, X. Hydrogen evolution catalysed by MoS3 and MoS2 particles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, T.; Muijsers, J.C.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W. Structure of Amorphous MoS3. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 9194–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cramer, S.P.; Liang, K.S.; Jacobson, A.J.; Chang, C.H.; Chianelli, R.R. EXAFS studies of amorphous molybdenum and tungsten trisulfides and triselenides. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, M.V.; Jacobsen, K.W.; Norskov, J.K. Atomic and electronic structure of MoS2 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. 2003, B 67, 085410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raybaud, P.; Hafner, J.; Kresse, G.; Kasztelan, S.; Toulhoat, H. Structure, energetics, and electronic properties of the surface of a promoted MoS2 catalyst: An ab initio local density functional study. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Favaro, M.; Cattelan, M.; Price, S.W.T.; Russell, A.E.; Calvillo, L.; Agnoli, S.; Granozzi, G. In Situ Study of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-MoSx Nanohybrids as Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts. Surfaces 2020, 3, 225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3020017
Favaro M, Cattelan M, Price SWT, Russell AE, Calvillo L, Agnoli S, Granozzi G. In Situ Study of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-MoSx Nanohybrids as Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts. Surfaces. 2020; 3(2):225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleFavaro, Marco, Mattia Cattelan, Stephen W. T. Price, Andrea E. Russell, Laura Calvillo, Stefano Agnoli, and Gaetano Granozzi. 2020. "In Situ Study of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-MoSx Nanohybrids as Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts" Surfaces 3, no. 2: 225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3020017
APA StyleFavaro, M., Cattelan, M., Price, S. W. T., Russell, A. E., Calvillo, L., Agnoli, S., & Granozzi, G. (2020). In Situ Study of Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-MoSx Nanohybrids as Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts. Surfaces, 3(2), 225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3020017