A Survey of Methodologies for Assessing Mast Cell Density and Activation in Patients with Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Assessment
3. Summary of Methods for Mast Cell Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacy, B.E.; Pimentel, M.; Brenner, D.M.; Chey, W.D.; Keefer, L.A.; Long, M.D.; Moshiree, B. ACG clinical guidelines: Management of irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayyedi, P.M.; Lacy, B.E.; Andrews, C.N.; Enns, R.A.; Howden, C.W.; Vakil, N. ACG and CAG clinical guideline: Management of dyspepsia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 988–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert-Bayo, M.; Paracuellos, I.; González-Castro, A.M.; Rodríguez-Urrutia, A.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Alonso-Catoner, C.; Santos, J.; Vicario, M. Intestinal mucosal mast cells: Key modulators of barrier function and homeostasis. Cells 2019, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, L.; Chen, B.; Kim, J.J.; Chen, X.; Dai, N. Micro-inflammation in functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, A.; Ingles, D.P.; Myneedu, K.; Deoker, A.; Sarosiek, I.; Zuckerman, M.J.; Schmulson, M.J.; Bashashati, M. Mast cells are increased in the small intestinal mucosa of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashashati, M.; Moossavi, S.; Cremon, C.; Barbaro, M.R.; Moraveji, S.; Talmon, G.; Rezaei, N.; Hughes, P.A.; Bian, Z.X.; Choi, C.H.; et al. Colonic immune cells in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, G.; Carroll, G.; Mathe, A.; Horvat, J.; Foster, P.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Keely, S. Evidence for local and systemic immune activation in functional dyspepsia and the irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, L.; Sowa, A.S.; Lorentz, A. Mast cells in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2019, 28, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.M.; Balemans, D.; Van Wanrooy, S.; Dooley, J.; Cibert-Goton, V.; Alpizar, Y.A.; Valdez-Morales, E.E.; Nasser, Y.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Vanbrabant, W.; et al. Histamine receptor H1-mediated sensitization of TRPV1 mediates visceral hypersensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2015, 150, 875–887.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.H.; Joo, Y.E.; Choi, S.K.; Rew, J.S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, M.C. Activated mast cells infiltrate in close proximity to entric nerves in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2003, 18, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.R.; Xu, X.J.; Yao, S.K. Increased intestinal mucosal leptin levels in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, L.; Pan, L.; Yao, S.K. Increased expression of nerve growth factor correlates with visceral hypersensitivity and impaired gut barrier function in diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: A preliminary explorative study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.P.; Li, F.K.; Li, Y.Q. Anxiety and depression are associated with increased counts and degranulation of duodenal mast cells in functional dyspepsia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8010–8014. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.P.; Li, X.P.; Yang, W.R.; Li, F.K.; Li, Y.Q. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in the duodenal mucosa is associated with mast cell degranulation in patients with functional dyspepsia. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 45, 522–527. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Ge, W.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Cong, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Quantitative evaluation of duodenal eosinophils and mast cells in adult patients with functional dyspepsia. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.; Garsed, K.; Singh, G.; Duroudier, N.P.; Swan, C.; Hall, I.P.; Zaitoun, A.; Bennett, A.; Marsden, C.; Holmes, G.; et al. Impaired uptake of serotonin by platelets from patients with irritable bowel syndrome correlates with duodenal immune activation. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1434–1443.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; De Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Cottrell, G.S.; Santini, D.; Pasquinelli, G.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Grady, E.F.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, B.; Ramos, L.; Martínez, C.; Guilarte, M.; González-Castro, A.M.; Alonso-Cotoner, C.; Pigrau, M.; de Torres, I.; Rodiño-Janeiro, B.K.; Salvo-Romero, E.; et al. Downregulation of mucosal mast cell activation and immune response in diarrhoea-irritable bowel syndrome by oral disodium cromoglycate: A pilot study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Shen, J.; Kim, J.J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, L.; Dai, N. Increased duodenal eosinophil degranulation in patients with functional dyspepsia: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Lu, H.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y.; Ge, Z. The study on the role of inflammatory cells and mediators in post-infectious functional dyspepsia. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Lobo, B.; Pigrau, M.; Ramos, L.; González-Castro, A.M.; Alonso, C.; Guilarte, M.; Guilá, M.; de Torres, I.; Azpiroz, F.; et al. diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: An organic disorder with structural abnormalities in the jejunal epithelial barrier. Gut 2013, 62, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilarte, M.; Santos, J.; de Torres, I.; Alonso, C.; Vicario, M.; Ramos, L.; Martínez, C.; Casellas, F.; Saperas, E.; Malagelada, J.R. Diarrhoea-predominant IBS patients show mast cell activation and hyperplasia in the jejunum. Gut 2007, 56, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, C.; Vicario, N.; Ramos, L.; Lobo, B.; Mosquera, J.L.; Alonso, C.; Sánchez, A.; Guilarte, M.; Antolín, M.; de Torres, I.; et al. The jejunum of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome shows molecular alterations in the tight junction signaling pathway that are associated with mucosal pathobiology and clinical manifestations. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, J.H.; Park, D.I.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Sohn, C.I.; Jeon, W.K.; Kim, B.I.; Chae, S.W. Mucosal mast cell count is associated with intestinal permeability in patients with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balestra, B.; Vicini, R.; Cremon, C.; Zecchi, L.; Dothel, G.; Vasina, V.; De Giorgio, R.; Paccapelo, A.; Pastoris, O.; Stanghellini, V.; et al. Colonic mucosal mediators from patients with irritable bowel syndrome excite enteric cholinergic motor neurons. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 1118–e570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Guo, C. Protease activated receptor 4 status of mast cells in post infectious irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremon, C.; Stanghellini, V.; Barbaro, M.R.; Cogliandro, R.F.; Bellacosa, L.; Santos, J.; Vicario, M.; Pigrau, M.; Alonso Cotoner, C.; Lobo, B.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: The analgesic properties of dietary supplementation with palmitoyletholamide and polydatin in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, O.; Walter, S.A.; Casado-Bedmar, M.; Ström, M.; Salvo-Romero, E.; Vicario, M.; Mayer, E.A.; Keita, Å.V. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and mast cells regulate increased passage of colonic bacteria in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 948–960.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhner, S.; Li, Q.; Vignali, S.; Barbara, G.; De Giorgio, R.; Stanghellini, V.; Cremon, C.; Zeller, F.; Langer, R.; Daniel, H.; et al. Activation of human enteric neurons by supernatants of colonic biopsy specimens from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Wang, B.; Stanghellini, V.; de Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Di Nardo, G.; Trevisani, M.; Campi, B.; Geppetti, P.; Tonini, M.; et al. Mast cell-dependent excitation of visceral-nociceptive sensory neurons in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremon, C.; Carini, G.; Wang, B.; Vasina, V.; Cogliandro, R.F.; De Giorgio, R.; Stanghellini, V.; Grundy, D.; Tonini, M.; De Ponti, F.; et al. Intestinal serotonin release, sensory neuron activation, and abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klooker, T.K.; Braak, B.; Koopman, K.E.; Welting, O.; Wouters, M.M.; van der Heide, S.; Schemann, M.; Bischoff, S.C.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. The mast cell stabilizer ketotifen decreases visceral hypersensitivity and improves intestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2010, 59, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivinus-Nébot, M.; Dainese, R.; Anty, R.; Saint-Paul, M.C.; Nano, J.L.; Gonthier, N.; Marjoux, S.; Frin-Mathy, G.; Bernard, G.; Hébuterne, X.; et al. Combination of allergic factors can worsen diarrheic irritable bowel syndrome: Role of barrier defects and mast cells. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, J.S.; Choi, M.B.; Seo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Park, C.H.; Woo, H.O.; Youn, H.S.; Ko, G.H.; Baik, S.C.; et al. Relationship between headache and mucosal mast cells in pediatric Helicobaori-negative functional dyspepsia. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, W.A.; Shankar, R.; Taylor, T.J.; Del Valle-Pinero, A.Y.; Kleiner, D.E.; Kim, K.H.; Youssef, N.N. Inverse relationship of interleukin-6 and mast cells in children with inflammatory and non-inflammatory abdominal pain phenotypes. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2012, 3, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, G.; Barbara, G.; Cucchiara, S.; Cremon, C.; Shulman, R.J.; Isoldi, S.; Zecchi, L.; Drago, L.; Olivia, S.; Saulle, R.; et al. Neuroimmune interactions at different intestinal sites are related to abdominal pain symptoms in children with IBS. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, F.E.; Farahmand, F.; Pourpak, Z.; Asefi, H.; Amini, Z. Mast cell gastritis: Children complaining of chronic abdominal pain with histologically normal gastric mucosa biopsies except for increases in mast cells, proposing a new entity. Diagn. Pathol. 2009, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schurman, J.V.; Singh, M.; Singh, V.; Neilan, N.; Friesen, C.A. Symptoms and subtypes in pediatric functional dyspepsia: Relation to mucosal inflammation and psychological functioning. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, M.; Schurman, J.V.; Friesen, C.A. Histopathological changes in the gastroduodenal mucosa of children with functional dyspepsia. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäppi, M.G.; Borrelli, O.; Knafelz, D.; Williams, S.; Smith, V.V.; Milla, P.J. Mast cell-nerve interactions in children with functional dyspepsia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 47, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saad, A.G. Normal quantity and distribution of mast cells and eosinophils in the pediatric colon. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2011, 14, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, C.A.; Lin, Z.; Singh, M.; Singh, V.; Schurman, J.V.; Burchell, N.; Cocjin, J.T.; McCallum, R.W. Antral inflammatory cells, gastric emptying, and electrogastrography in pediatric functional dyspepsia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernetsova, E.; Sullivan, K.; de Nanassy, J.; Barkey, J.; Mack, D.; Nasr, A.; El Demellawy, D. Histologic analysis of eosinophils and mast cells of the gastrointestinal tract in healthy Canadian children. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 54, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, C.; Singh, M.; Singh, V.; Schurman, J.V. A cross-sectional study of nausea in functional abdominal pain: Relation to mucosal mast cells and psychological functioning. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goral, V.; Kucukoner, M.; Buyukbayram, H. Mast cells count and serum cytokine levels in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Hepatogastroenterology 2010, 57, 751–754. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, A.P.; Nandasiri, S.D.; Hewavisenthi, J.; Manamperi, A.; Ariyasinghe, M.P.; Dassanayake, A.S.; Jewell, D.P.; de Silva, H.J. Subclinical mucosal inflammationin diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in a tropical setting. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binesh, F.; Akhondei, M.; Pourmirafzali, H.; Rajabzadeh, Y. Determination of relative frequency of eosinophils and mast cells in gastric and duodenal mucosal biopsies in adults with non-ulcer dyspepsia. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2013, 23, 326–329. [Google Scholar]
- Tunc, B.; Filik, L.; Altintaş, E.; Turhan, N.; Ulker, A.; Dağli, U. Mucosal mast cells in irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 2005, 48, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, V.S.; Chen, W.; Shu, D.; Paulus, B.; Bethwaite, P.; Tie, A.; Wilson, I. Activation of the mucosal immune system in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Dong, L.; Luo, J.Y.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Lu, X.L.; Han, S.P. Decreased expression of serotonin in the jejunum and increased numbers of mast cells in the terminal ileum in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 6041–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fox, M.; Cong, Y.; Chu, H.; Zheng, X.; Long, Y.; Fried, M.; Dai, N. Lactose intolerance in irritable bowel syndrome patients with diarrhoea: The roles of anxiety, activation of the innate mucosal immune system and visceral sensitivity. Aliments Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Adeyemo, M.; Karagiannides, I.; Videlock, E.J.; Bowe, C.; Shih, W.; Presson, A.P.; Yuan, P.Q.; Cortina, G.; Gong, H.; et al. Serum and colonic mucosal immune markers in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, O.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, K.N.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S.; Sim, J.; Jang, K.S. Mast cell number, substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, G.Y.; Han, S.; Kim, S.E.; et al. Colonic mucosal immune activity in irritable bowel syndrome: Comparison with healthy controls and patients with ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, S.P.; Jenkins, D.; Spiller, R.C. Distinctive clinical, psychological, and histological features of postinfective irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Gundersen, D.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Hausken, T. Low-grade inflammation in the rectum of patients with sporadic irritable bowel syndrome. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cremon, C.; Gargano, L.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Santini, D.; Cogliandro, R.F.; De Giorgio, R.; Stanghellini, V.; Corinaldesi, R.; Barbara, G. Mucosal immune activation in irritable bowel syndrome: Gender-dependence and association with digestive symptoms. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, S.P.; Jenkins, D.; Neal, K.R.; Spiller, R.C. Relative importance of enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia, anxiety, and depression in postinfectious IBS. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z.X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.L.; Xu, H.X.; Sung, J.J.Y. Unbalanced expression of protease-activated receptors-1 and -2 in the colon of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, J.; Nordlander, S.; Eutamene, H.; Alquier-Bacquie, V.; Cartier, C.; Theodorou, V.; Le Nevé, B.; Törnblom, H.; Simrén, M.; Öhman, L. Colonic mast cell numbers, symptom profile, and mucosal expression of elements of the epithelial barrier in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M.; Clayton, N.; Breslin, N.P.; Harman, I.; Bountra, C.; McLaren, A.; O’Morain, C.A. Increased mast cells in the irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2000, 12, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Rhee, P.L.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.J.; Rhee, J.C. Mucosal mast cell counts correlate with visceral hypersensitivity in patients with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21 Pt 1, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Kim, D.K.; Cho, S.W. The alteration of enterochromaffin cell, mast cell, and lamina propria T lymphocyte numbers in irritable bowel syndrome and its relationship with psychological factors. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Lim, J.H.; Park, H.; Lee, S.I. Increased immunoendocrine cells in intestinal mucosa of postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome patients 3 years after acute Shigella infection- an observation in a small case control study. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giancola, F.; Volta, U.; Repossi, R.; Latorre, R.; Beeckmans, D.; Carbone, F.; Van den Houte, K.; Bianco, F.; Bonora, E.; Gori, A.; et al. Mast cell-nerve interactions correlate with bloating and abdominal pain severity in patients with non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.; Buckley, M.; Crotty, P.; O’Morain, C.A. Gastric mucosal mast cells are increased in Helicobacter pylori-negative functional dyspepsia. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 1, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheel, H.; Vicario, M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Martinez, C.; Keita, Å.V.; Pardon, N.; Santos, J.; Söderholm, J.D.; Tack, J.; et al. Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia. Gut 2014, 63, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, F.; Tominaga, K.; Fujikawa, Y.; Nagami, Y.; Kamata, N.; Yamagami, H.; Tanigawa, T.; Shiba, M.; Watanabe, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; et al. Concentration of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor positively correlates with symptoms in functional dyspepsia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 3478–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicario, M.; González-Castro, A.M.; Martínez, C.; Lobo, B.; Pigrau, M.; Guilarte, M.; de Torres, I.; Mosquera, J.L.; Fortea, M.; Sevillano-Aguilera, C.; et al. Increased humoral immunity in the jejunum of diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome associated with clinical manifestations. Gut 2015, 64, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, B.; Klooker, T.K.; Wouters, M.M.; Welting, O.; van der Loos, C.M.; Stanisor, O.I.; van Diest, S.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. Mucosal immune cell numbers and visceral hypersensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Is there any relationship. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 715–726. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, J.; Saint-Paul, M.C.; Dadone, B.; Patouraux, S.; Vivinus, M.H.; Ouvrier, D.; Michiels, J.F.; Piche, T.; Tulic, M.K. Inflammatory cell distribution in colon mucosa as a new tool for diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome: A promising pilot study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piche, T.; Saint-Paul, M.C.; Dainese, R.; Marine-Barjoan, E.; Iannelli, A.; Montoya, M.L.; Peyron, J.F.; Czerucka, D.; Cherikh, F.; Filippi, J.; et al. Mast cells and cellularity of the colonic mucosa correlated with fatigue and depression in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2008, 57, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.A.; Sepehr, G.J.; Hamilton, M.J.; Akin, C.; Castells, M.C.; Hornick, J.L. A clinicopathologic study of 24 cases of systemic mastocytosis involving the gastrointestinal tract and assessment of mucosal mast cell density in irritable bowel syndrome and asymptomatic patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coëffier, M.; Gloro, R.; Boukhettala, N.; Aziz, M.; Lecleire, S.; Vandaele, N.; Antonietti, M.; Savoye, G.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Déchelotte, P.; et al. Increased proteasome-mediated degradation of occluding in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Prabhakar, M.; Pennaneac’h, C.J.; Aro, P.; Ronkainen, J.; Storskrubb, T.; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Agreus, L. Duodenal mastocytosis, eosinophilia and intraepithelial lymphocytosis as possible disease markers in irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taki, M.; Oshima, T.; Li, M.; Sei, H.; Tozawa, K.; Tomita, T.; Fukui, H.; Watari, J.; Miwa, H. Duodenal low-grade inflammation and expression of tight junction proteins in functional dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, K.E.; Mun, Y.C.; Park, S. Degranulated eosinophils contain more fine nerve fibers in the duodenal mucosa of patients with functional dyspepsia. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wauters, L.; Ceulemanns, M.; Frings, D.; Lambaerts, M.; Accarie, A.; Toth, J.; Mols, R.; Augustijns, P.; De Hertogh, G.; Van Oudenhove, L.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors reduce duodenal eosinophilia, mast cells, and permeability in patients with functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1521–1531.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheel, H.; Vicario, M.; Boesmans, W.; Vanuytsel, T.; Salvo-Romero, E.; Tack, J.; Farré, R. Activation of eosinophils and mast cells in functional dyspepsia: An ultrastructural evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, M.J.; Desai, R.S.; Mamatha, G.S.; Kulkarni, M.; Khatri, J. Immunohistochemical expression of mast cells using c-Kit in various grades of oral submucous fibrosis. ISRN Pathol. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Samoilova, V.; Buchwalow, I.; Boecker, W.; Tiemann, M. Characterization of mast cell populations using different methods for their identification. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 147, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.C.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Moore, K.; Madigan, M.C.; Katsoulotos, G.; Krilis, S.A. An antibody raised against in vitro-derived human mast cells identifies mature mast cells and a population of cells that are Fc epsilon RI(+), tryptase (−), and chymase (−) in a variety of human tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribatti, D. The staining of mast cells: A historical overview. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, S.; Barki, N.; Jain, R.; Zulkhernain, N.S.; Buhner, S.; Schemann, M.; Weninger, W. Imaging of mast cells. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemann, M.; Michel, K.; Ceregrzyn, M.; Zeller, F.; Seidl, S.; Bischoff, S.C. Human mast cell mediator cocktail excites neurons in human and guinea-pig enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Gu, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Clinical efficacy and safety of ketotifen in treating irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioli, I.; Melzi, G.; Balsamo, V.; Castellucci, G.; Castro, M.; Catassi, C.; Rätsch, J.M.; Scotta, S. Food intolerance and irritable bowel of childhood: Clinical efficacy or oral sodium cromoglycate and elimination diet. Minerva Pediatr. 1993, 45, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lunardi, C.; Bambara, L.M.; Biasi, D.; Cortina, P.; Peroli, P.; Nicolis, F.; Favari, F.; Pacor, M.L. Double-blind cross-over trial of oral sodium cromoglycate in patients with irritable bowel syndrome due to food intolerance. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1991, 21, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, G.F.; Saggioro, A.; Alvisi, V.; Angelini, G.; Capurso, L.; di Lorenzo, G.; Dobrilla, G.; Dodero, M.; Galimberti, M.; Gasbarrini, G.; et al. Oral cromolyn sodium in comparison with elimination diet in the irritable bowel syndrome, diarrheic type. Multicenter study of 428 patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 30, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Peterson, K.A.; Murray, J.A.; Falk, G.W.; Gonsalves, N.; Chehade, M.; Genta, R.M.; Leung, J.; Khoury, P.; Klion, A.D.; et al. Anti-siglec-8 antibody for eosinophilic gastritis and duodenitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, C.A.; Kearns, G.L.; Andre, L.; Neustrom, M.; Roberts, C.C.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of montelukast in dyspeptic children with duodenal eosinophilia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
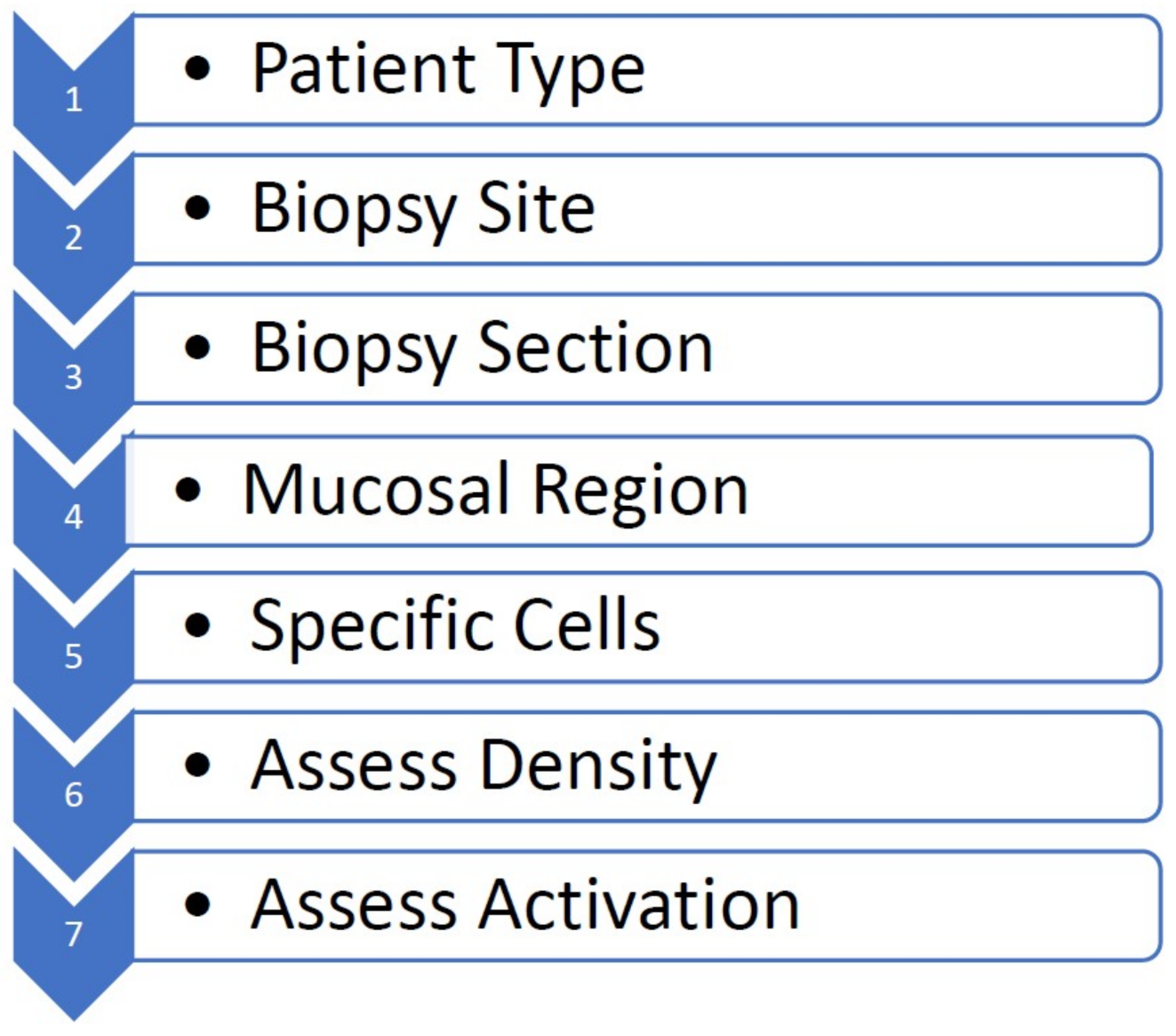
| Author | Country | Age Group | Population (N) | Mucosal Sites | Mast Cell ID Method | Number of Microscopic Fields Assessed | Field Selection | Cell Activation Assessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeom et al. [34] | Korea | 6–12 | FD (56) | Gastric antrum and body; duodenum | Anti-tryptase | 5 | Most involved area | No |
| Henderson et al. [35] | USA | 5–17 | AP-FGID (26) | Upper and lower | Toluidine Blue | 10 | Random | No |
| Di Nardo et al. [36] | Italy | 4–18 | IBS (21) | TI, Ascending and Descending Colon | Anti-tryptase | Not stated | Random | No |
| Mahjoub et al. [37] | Iran | 1–14 | Endoscopy patients (86) | Antrum | Giemsa | 10 | Not stated | No |
| Schurman et al. [38] | USA | 8–17 | FD (59) | Antrum and duodenum | Anti-tryptase | 5 | Most involved area | No |
| Singh et al. [39] | USA | 8–17 | FD (114) | Antrum and duodenum | Anti-tryptase | 5 | Most involved area | No |
| Schäppi et al. [40] | UK | 2–12 | FD (16) | Gastric | Anti-tryptase | 10 | Not stated | Yes |
| Saad et al. [41] | USA | 3.3–17.9 | Endoscopy patients: 92% for abdominal pain (41) | Cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and rectosigmoid colon | Anti-tryptase | 5 | Most involved area | No |
| Friesen et al. [42] | USA | 8–17 | FD (30) | Antrum | Anti-tryptase | 5–10 | Not stated | Yes |
| Chernetsova et al. [43] | Canada | 1–17 | Endoscopy patients designated as healthy (38) | Gastric body and antrum, duodenum, TI, cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon, and rectum | Hematoxylin-Phloxine-Saffron and Giemsa | Not stated | Most involved area | No |
| Friesen et al. [44] | USA | 8–17 | AP-FGID (208) | Antrum and duodenum | Anti-tryptase | 5 | Most involved area | No |
| Author | Country | Age Group | Population (N) | Mucosal Sites | Mast Cells ID Method | Number of Microscopic Fields Assessed | Field Selection | Density Different from Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goral et al. [45] | Turkey | Mean 35–36 years | IBS (72) | Cecum and rectum | Giemsa | 10 | Not stated | Yes |
| De Silva et al. [46] | Sri Lanka | 18–59 years | IBS-D (49) | Ileum, cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, and rectum | Giemsa | 10 | Not stated | Yes |
| Binesh et al. [47] | Iran | 15–76 years | FD (25) | Stomach and duodenum | Giemsa | ≥5 | Not stated | No |
| Tunc et al. [48] | Turkey | 27–64 years | IBS (11) | Cecum | Toluidine blue | 10 | Not stated | Yes |
| Chadwick et al. [49] | New Zealand | 19–79 years | IBS (77) | Ascending, transverse, descending, and rectum | Tryptase | 15 | Not stated | Yes |
| Wang et al. [50] | China | Mean 42–49 years | IBS-D (20) and IBS-C (18) | Duodenum, jejunum, and TI | Tryptase | 6 | Not stated | Yes |
| Yang et al. [51] | China | 16–75 years | IBS-D (55) | TI, ascending and sigmoid | Tryptase | Not stated | Not stated | Yes |
| Chang et al. [52] | USA | 18–55 years | IBS-PI (45) | Sigmoid | Tryptase | % of area | Not stated | No |
| Sohn et al. [53] | Korea | 18–72 years | IBS-D (22) | Rectum | Tryptase | Not stated | Most representative | Yes |
| Ahn et al. [54] | Korea | Median 32 years | IBS-D (83) | Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid, and rectum | Tryptase | 6 | Not stated | Yes |
| Dunlop et al. [55] | UK | Mean 38–40 years | IBS (75) | Rectum | Tryptase | 4 | Not stated | Yes |
| El-Sahly et al. [56] | Norway | 18–62 years | IBS (50) | Rectum | Tryptase | 10 | Random | No |
| Cremon et al. [57] | Italy | 22–75 years | IBS (48) | Descending colon | Tryptase | % of area | Random | Yes |
| Dunlop et al. [58] | England | Mean 42 years | IBS-PI (28) | Rectum | Tryptase | 4 | Not stated | No |
| Bian et al. [59] | China | 21–66 years | D-IBS (10) | Descending colon | Tryptase | ≥10 | Random | Yes |
| Sundin et al. [60] | Sweden | Mean 32 years | IBS (43) | Sigmoid colon | Tryptase | 3 | Not stated | No |
| O’Sullivan et al. [61] | Ireland | 28–65 years | IBS (14) | Cecum, ascending, descending, and rectum | Tryptase | 3 | Not stated | Yes |
| Park et al. [62] | Korea | 25–65 years | IBS-D (18) | TI, ascending, and rectum | Tryptase | 6 | Not stated | Yes |
| Lee et al. [63] | South Korea | Mean 48 years | IBS (42) | Rectum | Tryptase | 5 | Not stated | Yes |
| Kim et al. [64] | Korea | Mean 30–51 years | IBS (18) | Descending, sigmoid, and rectum | Tryptase | 5 | Not stated | Yes |
| Giancola et al. [65] | Belgium | 18–68 years | FD (13) | Duodenum | Tryptase | 4 | Random | Yes |
| Hall et al. [66] | Ireland | 18–79 years | FD (62) | Gastric body and antrum | Tryptase | 15 | Not stated | Yes |
| Vanheel et al. [67] | Belgium | 17–52 years | FD (15) | Duodenum | Tryptase | ≥7 | Representative | Yes |
| Tanaka et al. [68] | Japan | Mean 45 years | FD (9) | Duodenum | Tryptase | 5 | Not stated | No |
| Vicario et al. [69] | Spain | 18–63 years | IBS-D (49) | Jejunum | CD117 | 8 | Not stated | Yes |
| Braak et al. [70] | Amsterdam | 19–65 years | IBS (66) | Ascending and descending colon | CD117 | 18 | Not stated | Yes- decreased |
| Boyer et al. [71] | France | Mean 54–67 years | IBS (11) | Cecum, transverse, descending, and rectum | CD117 | 4 | Not stated | Not reported |
| Piche et al. [72] | France | Mean 54 years | IBS (50) | Cecum | CD117 | 5 | Not stated | Yes |
| Doyle et al. [73] | USA | 18–78 years | IBS (100) | Colon | Anti-kit | 5 | Area of highest density | Yes |
| Coeffier et al. [74] | France | Mean 44.6 years | IBS (25) | Descending colon | CD117 | 10 | Not stated | Yes |
| Walker et al. [75] | Sweden | Mean 53 years | FD (51) and IBS (41) | Duodenum | CD117 | 5 | Not stated | Yes |
| Taki et al. [76] | Japan | Mean 53 years | FD (35) | Duodenum | CD117 | ≥3 | Representative | Yes |
| Lee et al. [77] | Korea | Mean 36 years | FD (51) | Duodenum | c-KIT | 5 | Hot spots | No |
| Wauters et al. [78] | Belgium | 18–64 years | FD (45) | Duodenum | c-kit | 3 | Not stated | Yes |
| Author | Country | Age Group | Population (N) | Mucosal Sites | Mast Cells ID Method | Number of Microscopic Fields Assessed | Field Selection | Density Different from Controls | Activation Different from Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Park et al. [10] | Korea | Mean 48 years | IBS-D (14) | Cecum and rectum | Toluidine blue | Up to 20 | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Liu et al. [11] | China | 22–40 years | IBS-D (42) | Rectosigmoid junction | Toluidine blue | 5 | Random | No | Yes |
| Xu et al. [12] | China | 18–49 years | IBS-D (38) | Rectosigmoid junction | Toluidine blue | 5 | Random | Yes | No |
| Yuan et al. [13] | China | Mean 45–47 years | FD (48) | Duodenum | Toluidine blue | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Yuan et al. [14] | China | Mean 45–47 years | FD (48) | Duodenum | Toluidine blue | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Wang et al. [15] | China | Mean 46 years | FD (141) | Duodenum | Toluidine blue | 4-6 random sites, then 5 | Random | Yes | Yes |
| Foley et al. [16] | England | Mean 42 years | IBS-D (20) | Duodenum | Tryptase | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Lee et al. [24] | Korea | 24–66 years | IBS-D (16) | Rectum | Tryptase | 5 | Not stated | No | Yes |
| Barbara et al. [17] | Italy | 22–75 years | IBS (44) | Descending colon | Tryptase | Area occupied | Random | Yes | Yes |
| Balestra et al. [25] | Italy | 21–70 years | IBS (37) | Descending colon | Tryptase | % of LP occupied | Random | Yes | Yes |
| Han et al. [26] | China | 18–59 years | PI-IBS (23) | Left colon | Tryptase | ≥8 | Not stated | Yes-area; No- number | Yes |
| Cremon et al. [27] | Italy, Spain, France, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina | Mean 37–40 years | IBS (54) | Proximal descending colon | Tryptase | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Not reported |
| Bednarska et al. [28] | Sweden | 19–55 years | IBS (32) | 30-40 cm from anal verge | Tryptase | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Buhner et al. [29] | Italy | 27–68 years | IBS (11) | Proximal descending colon | Tryptase | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Barbara et al. [30] | Italy | 19–70 years | IBS (29) | Proximal descending colon | Tryptase | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Li et al. [20] | China | 17–65 years | FD (65) | Antrum | Tryptase | 10 | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Vanheel et al. [79] | Belgium | 23–43 years | FD (24) | Duodenum | Tryptase | ≥7 | Representative | Yes | No |
| Du et al. [19] | China | Mean 48 years | FD (96) | Duodenum | Tryptase | 5 | Random | Not reported | No |
| Cremon et al. [31] | Italy | 22–56 years | IBS (25) | Descending colon | Tryptase | Area occupied | Random | Yes | Yes |
| Klooker et al. [32] | The Netherlands | 19–65 years | IBS (29) | Descending and rectum | Tryptase or CD117 | 18 | Not stated | Yes- decreased | Yes- decreased |
| Martinez et al. [21] | Spain | 18–60 years | IBS-D (45) | Jejunum | CD117 | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Vivinus-Nébot et al. [33] | France | 42–58 years | IBS (34) | Cecum | CD117 | 3 | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Lobo et al. [18] | Spain | 18–65 years | IBS-D (43) | Jejunum | CD117 | 10 | Not stated | No | Yes |
| Guilarte et al. [22] | Spain | 21–56 years | D-IBS (20) | Jejunum | CD117 | 8 | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
| Martinez et al. [23] | Spain | 18–59 years | IBS-D (25) | Jejunum | CD117 | Not stated | Not stated | Yes | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friesen, H.; Singh, M.; Singh, V.; Schurman, J.V.; Friesen, C.A. A Survey of Methodologies for Assessing Mast Cell Density and Activation in Patients with Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders. Gastrointest. Disord. 2021, 3, 142-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040016
Friesen H, Singh M, Singh V, Schurman JV, Friesen CA. A Survey of Methodologies for Assessing Mast Cell Density and Activation in Patients with Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2021; 3(4):142-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040016
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriesen, Hunter, Meenal Singh, Vivekanand Singh, Jennifer V. Schurman, and Craig A. Friesen. 2021. "A Survey of Methodologies for Assessing Mast Cell Density and Activation in Patients with Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders" Gastrointestinal Disorders 3, no. 4: 142-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040016
APA StyleFriesen, H., Singh, M., Singh, V., Schurman, J. V., & Friesen, C. A. (2021). A Survey of Methodologies for Assessing Mast Cell Density and Activation in Patients with Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 3(4), 142-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040016






